Lecture 7-12: Adaptive Immunity/B cell/T cell/Lymphoid organs
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
what is the function of primary lymphoid tissue?
development and education of lymphocytes
what are the primary lymphoid organs?
thymus, bone marrow, Peyer’s patches (ruminants/horses), bursa (birds)
where is the thymus located?
in the cranial mediastinum over the heart
how is the thymus structured?
Dark area, light area
what does the dark area of the thymus contain?
lymphocyte rich cortex
what does the light area of the thymus contain?
thymic medullary epithelium
which cell migrate to the thymus?
lymphoid progenitor cells from the bone marrow migrate to the thymus
what type of lymphocytes do the lymphoid progenitors become in the thymus?
T cells
what is the structure of the bone marrow?
large amount of hematopoietic cells supported by reticular connective tissue, adipocytes, and sinusoidal cappilaries
how is the bursa structured in the bird?
round sac located above cloaca, contains folds of epithelium containing lymphoid follicles
what type of lymphocytes develop in the bone marrow?
B cells
what does education indicate relative to lymphocytes?
training in which B cells and T cells undergo to distinguish self from non-self antigens
what is the importance of the education of lymphocytes?
to avoid hypersensitivity and autoimmunity
what are naive lymphocytes?
lymphocytes that have not encountered specific antigens and been activated
where do naive lymphocytes migrate after development in the primary lymphoid organs?
travel to secondary lymphoid organs
what occurs to lymphocytes when they enter the secondary lymphoid organs?
circulate to encounter antigens and to develop into effector lymphocytes
what is the structure of the BCR?
contains 2 heavy chains, 2 light chains, bond by disulfide bonds
what forms the heavy chains of the BCR?
Fc region
what is the structure of the light chains?
Fab region
what is the function of the Fab region?
antigen binding regions - contain variable regions
what does the Fc region contain?
constant region that determines isotype and primary function of immunoglobulin
how is the TCR structured?
heterodimer of 2 chains with a variable and constant region
what are the possible constant regions?
alpha and beta; gamma and delta
which species contains a large quantity of gamma and delta T cells?
ruminants
what is the driving factor of the formation of diverse and unique BCR and TCR to create the specificity of the immune response?
gene rearrangement
what occurs during gene rearrangment?
random selection of gene segments resulting in genetic diversity of BCR and TCR
where does gene rearrangement occur?
primary lymphoid organs
how are B cells educated?
undergo central tolerance
what are the two fates of self-reactive B cells?
apoptosis and negative selection
receptor editing of variable region genes, followed by apoptosis if edit fails
what genes make up the variable region of the T cell?
V - variable gene segment
D - diversity gene segment
J - joining gene segment
what are the genes that are only found in lymphocytes and are involved with cleaving DNA and protecting the dsDNA breaks from repair mechanisms?
RAG1 and RAG2
what are the 3 major steps in T cell development?
rearrangement of TCR genes, positive selection, negative selection
what occurs when TCR genes rearrange?
Αβ and γδ TCRs compete for expression
what occurs if Αβ TCR win?
surface molecules are expressed on developing thymocytes
what occur if γδ TCRs win?
cell leaves thymus
what are the surface receptors on Αβ T cells?
CD3, CD4 and/or CD8
what is the process of positive selection?
cells become class restricted by recognizing antigens presented on MHC1 or MHC2 molecules of thymic epithelial cells
cells with TCR that can bind to MHC molecules and antigen are positively selected for; cells lacking undergo apoptosis
what does class restriction lead to?
upregulation of CD8 or CD4 receptors
what happens if a TCR binds to MHC 1 molecule?
upregulation of CD8
what happens if a TCR binds to a MHC 2 receptor?
upregulation of CD4
what occurs during negative selection of T cells?
T cells are tested against self-antigenswh
what happens if a TCR binds to MHC and a self-antigen?
undergo apoptosis
what are the T cells called if they pass positive selection and negative selection?
self-tolerant
what is the gene that is critical for T cell education and self-tolerance?
autoimmune regulator gene (AIRE)
where is the AIRE gene expressed?
thymic medullary epithelial cells with MHC molecules
what happens if this gene is lacking?
autoimmune diseases
how does a bursectomy affect the ability to produce antibodies?
total circulating lymphocytes decreased, humoral immunity (antibody concentration) markedly decreased
how does a thymectomy affect the ability to produce antibodies?
No T cells in secondary lymphoid tissue or circulation, cause defective T cell mediated immunity
how do defects in gene rearrangement alter the ability to produce antibodies?
severe combine immunodeficiency, cannot develop B or T cells
what are the functions of the secondary lymphoid tissue?
antigen trapping, clonal expansion, develop immunological memory
how is immunological memory beneficial to the host?
long term immunity; more potent immune response upon re-encounter with the same antigen; lasts a lifetime; generated in secondary lymphoid organs
when is the immunological memory formed?
during the primary immune response
what is an effector lymphocyte?
lymphocytes that have come in contact with an antigen and are “activated”
where are T cells located in the lymph nodes generally?
paracortex
where are B cells found within a lymph node?
follicles
where are T cells found within the spleen?
PALS - periarteriolar sheath
where are B cells found in the spleen?
white pulp, follicles
what is the process of chemotaxis?
movement of the cell in a response to a chemical stimulus
what is a chemokine?
cytokines that direct chemotaxis; tells cells WHERE to go
what are integrins?
transmembrane cell adhesion proteins and signaling receptors
What is the HEV?
high endothelial venules
what is the function of HEV?
specialized blood vessels that mediate lymphocyte trafficking to lymph nodes; “sticky” for naive lymph nodes
which chemokine receptors are on dendritic cells that home the cell to the paracortex?
CXCR4
CCR7
what ligand does CXCR4 on DC bind to on the paracortex?
CXCL12
what ligand does CCR7 on DC, T cell, and B cell bind to on the paracortex?
CCL19 and CCL21
which specific molecules interact to attract the T cell and B cell to the HEV?
CD62L on the T/B cell interacts with CD34/GlyCAM-1 on HEV
What occurs to the CCR7 and CD62L when the T cell is activated?
CCR7 and CD62L are shed to allow the T cell to leave the paracortex and go towards inflammation sites
what receptor and ligand homes B cells to LN follicles?
CXCR5 on B cells bind to CXCL13 in follicles
what are the 3 signals for T cell activation
antigen-specific
co-stimulation
Cytokines
what is the function of signal 1 (antigen specific) in T cell activation?
engagement of the TCR to MHC:peptide complex (antigen)
What are the specific receptors and ligands involved in signal 1 in T cell activation?
TCR, CD3, CD4, CD8
what are TCR?
t cell receptor
what does CD3 assist in?
assists in signal transduction
what is the purpose of CD4 on T cells?
specify MHC class 2; bind to MHC class 2 on APC and involves extracellular antigens
what is the purpose of CD8 on T cells?
specify MHC Class 1; interact with MHC 1 on all nucleated cells and involves intracellular antigens
What is the purpose of signal 2 (co-stimulation) in T cell activation?
acts as a 2 factor authentication
what are the ligands that are involved with co-stimulation during T cell activation?
CD154 on T cell binds to CD40 on APC
CD28 on T cell binds to B7 on APC
what effect does the binding of CD154 on T cells to CD40 on APC during co-stimulation cause?
DC releases cytokines; upregulates CD28 on T cell
what effect does the binding of CD28 on T cells binding to B7(CD80/CD86) on APC cause?
enhances cytokine expression and survival genes in T cell; upregulates CTLA-4 expression
what does the binding of CTLA-4 to CD80/CD86 2-3 days later cause?
STOPs activation
what is the purpose of the signal 3 in T cell activation?
Stimulate proliferation of T cells
what cytokines are involved in the proliferation of T cells during activation?
IL-2
how is T cell activation regulated?
peripheral tolerance outside of primary lymphoid tissue to prevent autoimmunity
what occurs if APC only has specific peptide:MHC complex and no co-stimulatory molecule?
the T cell becomes anergic
what occurs if the T cell only binds to the co-stimulatory molecule?
nothing will occur
what type of cell do naive B cells have to encounter to receive survival signals to continue circulation in order to find their antigen?
follicular dendritic cell
what happens to the B cell if it binds to its antigen?
waits in T cell zone until a matching T cell binds to form a pair
how are pig lymph nodes different from dogs?
considered “inside out” - cortex on the inside and medulla on the outside
do not contain lymphocytes in lymph
circulation = bloodstream → HEV → lymph node paracortex → efferent vein
what is the circulation through the dog lymph node?
bloodstream → HEV → lymph node paracortex → efferent lymphatics → thoracic duct
what special secondary lymphoid structures do ruminants and cervids have?
hemal nodes; contian B cells in cortex and T cells at the center
what are the two functions of splenic red pulp?
removes aged blood cells and immune complex coated cells
salvage iron and bilirubin from red cells
what structures does white pulp contain?
contain marginal zone, follicles, PALS; does NOT contain HEV
what are MALT tissues?
tonsils, GI (GALT), bronchial (BALT), Nasal (NALT), urogenital
how can bone marrow act as a secondary lymphoid organ?
memory cells and plasma cells colonize; second does of antigen causes bone marrow to release large quantities of antibodies in studies
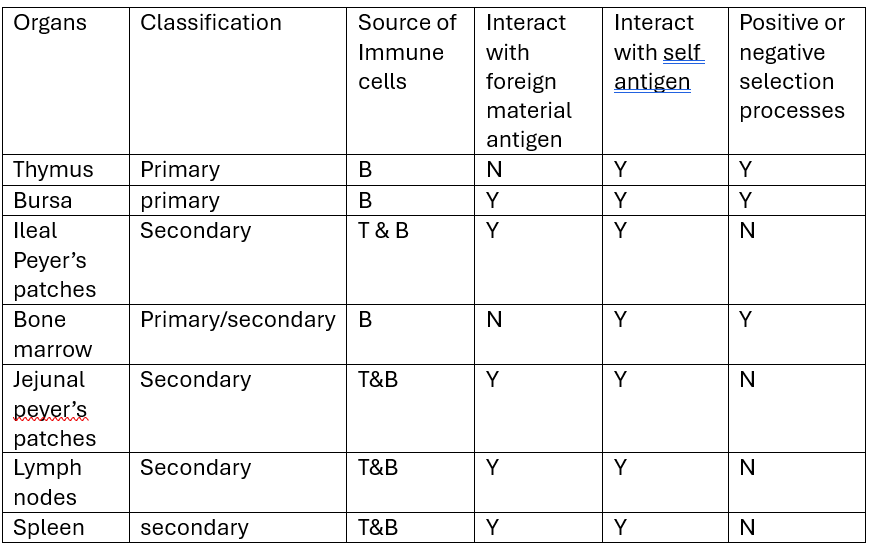
compare and contrast primary and secondary lymphoid organs:
source of immune cells
interaction with foreign material/antigen
interaction with self antigen
negative or positive selection
what are the T cell subtypes?
Th1, Th2, Th17, Tfh, Treg
what are polarizing cytokines?
cytokines that direct the cytokines to differentiate into their subtypes
what are effector cytokines?
cytokines that are secreted by effector cells to perform a function
what is the t cell preceptor for Th1, Th2, Th17, Tfh, Treg?
CD4+ T cells
what cytokines polarize T cells into Th1 cells
IL-12, IFN-gamma