biol454 receptor signaling
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
protein phosphorylation is a common mode of … in cells
regulation
.. messengers are key components of signaling
second
(t/f) in response to a signal, a cell may regulate activities in the initial cytosolic phase or nuclear phase
true
how does phosphatase stop signaling?
removal of phosphate groups
what degradation of signaling component can stop or activate signaling pathway?
ubiquitin-degradation
this domain recognizes p-Tyr peptides
SH2
this domain mediates protein-protein interactions by binding to proline rich regions
SH3
this domain binds to p-lipid PIP3 and PIP2 or inositol
PH (pleckstrin homology)
what links multiple kinases/enzymes together to promote assembly of larger signaling ocmplexes?
adaptor proteins
extracellular domains of surface proteins do what to initiate signaling?
recognize soluble secreted ligands or molecules on neighboring cell surface
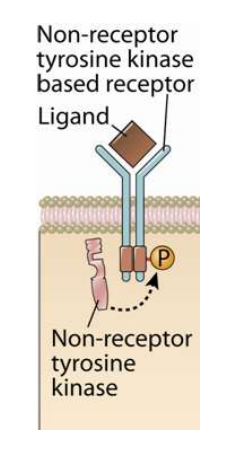
how do non-receptor tyrosine kinases work?
separate intracellular tyrosine kinase interacts with receptor to phosphorylate the receptor or other interacting proteins
what differentiates tyrosine kinases from non-receptor tyrosine kinases?
membrane receptor has no intrinsic catalytic activity in non-receptor
antigen receptors (BCR, TCR), cytokine receptors, and integrin receptors use what type of immune receptor signaling?
non-receptor tyrosine kinases
non-receptor TK (1)
binding of the ligand initiates Tyrosine kinase doing what?
phosphorylation of Y a.a residue
non-receptor TK (2)
after Y is phosphorylated, what occurs?
recognized by second protein
initiates next step in protein cascade
what is associated with the cytoplasmic tail of the cytokine receptor?
JAKs
when the cytokine receptor is bound to a cytokine, what conformation change occurs?
dimerization
in the JAK-STAT pathway…
what recognizes the phosphorylated receptor tail?
STATs
in the JAK-STAT pathway…
what phosphorylates the STAT?
JAKs
in the JAK-STAT pathway…
the pSTAT forms a dimer and does what?
dissociates from the receptor tail
in the JAK-STAT pathway…
what are active transcription factors that induce gene expression? where do they translocate to?
pSTAT, nucleus
(t/f) common gamma chain (yc) is used as a receptor subunit for certain cytokine receptors
true
severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) is due to mutations in the common gamma gene, which leads to
defects in IL-signaling
how are BCR and TCR signaling similar to antigen receptor signaling?
receptor clustering
Src family are initial non-receptor TKs
activate through ITAM
what is fine tuned by
progressive ITAM use
co-receptor modulated signals
inhibitory receptors
antigen receptor signaling
what do these signals induce?
weak → ?
strong → ?
weak → positive selection
strong → negative selection (cell death)
the interaction of TCR with Ag:MHC is associated with what complex?
CD3
which complex consists of:
heterodimers of gamma or delta chains
zeta chains
CD3
CD3 signaling molecules have ITAM/ITIM motifs
ITAM
what receptors are crucial in the first step of TCR complex ITAM phosphorylation
CD4 and CD8 co-receptors
when does CD3-zeta open up their ITAMs?
when TCR binds to pMHC
when CD3 zeta chains are brought together by pMHC binding, it causes Src kinases to…
be able to phosphorylate ITAMS
how does TCR pMHC binding change the conformation of CD3 zeta chains?
CD3 zeta opens up their itams
zeta chains close together
Src kinases phosphorylate ITAMs
clustering inside lipid rafts is due to what binding to TCR?
MHC:Ag complex
when MHC:Ag binds to TCR, what type of co-receptors cluster in lipid raft?
CD4 or CD8 co-receptors
Which Src family kinase is associated with the cytoplasmic domain of coreceptors CD4 or CD8
LCK
What is the significance of supramolecular activation cluster? (SMAC)
region of contact between T cell and APC
TCR complex recognizes MHC:peptide in the middle of what?
synapse or c-SMAC
(t/f) p-SMAC has integrins on the outside
true
why is clustering important with low amounts of pMHCs?
better trigger multiple TCRs
(t/f) in the resting T cell, ITAMs are phosphorylated
false, they are not phosphorylated
when a TCR complex activates, what phosphorylates Tyr on CD3 complex ITAMs?
LCK
P-Tyr on CD3 serves as a docking site for
ZAP-70
what kinase is this?
Syk family
SH2 domains
bind to p-Y on ITAM
ZAP-70
what:
binds phosphotyrosines
phosphorylates adaptor proteins like LAT
ZAP-70
when ZAP-70 phosphorylates major adaptor protein LAT, what occurs?
multiple signal molecules coming together
what major adaptor protein is responsible for starting cascades that activate…
NFAT
AP-1
NfKb
LAT
when PLCy1 is recruited, it is added to what two domains?
pLAT (SH2)
membrane PIP-3 (PH)
PLCy1 hydrolyzes membrane PIP2 to make… (2)
free IP3 and membrane-DAG (diacylglycerol)
a receptor on the ER recognizes cytosolic IP3 and does what?
depletes ER Ca++ levels
how does PLCy1 initiate Ca++ through PIP2 hydrolysis?
PLCy1 recruited and binds to pLAT and membrane PIP3
hydrolyzes PIP2
frees IP3 and membrane-DAG
receptor recognizes cytosolic IP3
what happens when STIM in the ER membrane senses low Ca++ levels in the lumen?
it opens up CRAC on the plasma membrane
(t/f) Ca++ flux happens within 15 minutes of TCR:pMHC binding
true
phosphatase Calcineurin is activated by what Ca++-dependent protein?
Calmodulin
NFAT goes into the nucleus when dephosphorylated by?
calcineurin
PLCy1 hydrolysis of PIP2 frees what 2 molecules?
IP3 and membrane DAG
how are membrane DAG and NF-kB associated?
membrane DAG recognized by and activates PKC0
PKC0 activates NF-kB
(t/f) LAT is only necessary for:
PLCy1 → NFAT
Grb2-SOS → AP-1
false, missing PLCy1 → NFkB
LAT bound Grb2-SOS exchanges GDP
puts in a GTP in RAS → RAS-GTP
what pathway is activated?
MAP kinase pathway
how is membrane DAG associated in activation of the MAP kinase pathway?
mDAG bound by RasGRP1
exchanges RAS-GDP to RAS-GTP
what are the two ways to activate RAS-GTP?
LAT- GrbSOS
DAG - RasGRP
PI3 kinase phosphorylates PIP2 → PIP3
PIP3 is recognized by ? and phosphorylates AKT
PDK1
what kinase inactivates pro-apoptosis factors leading to proliferation?
AKT