Markets and regulation 1.2 | Quizlet
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What are the three main types of imperfect competition?
Monopoly, Oligopoly, and Monopolistic Competition.
What is consumer surplus?
The difference between what consumers are willing to pay and the market price.
What is producer surplus?
The difference between the market price and the minimum price producers are willing to accept.
What is total surplus?
The sum of consumer and producer surplus; represents total welfare from trade.
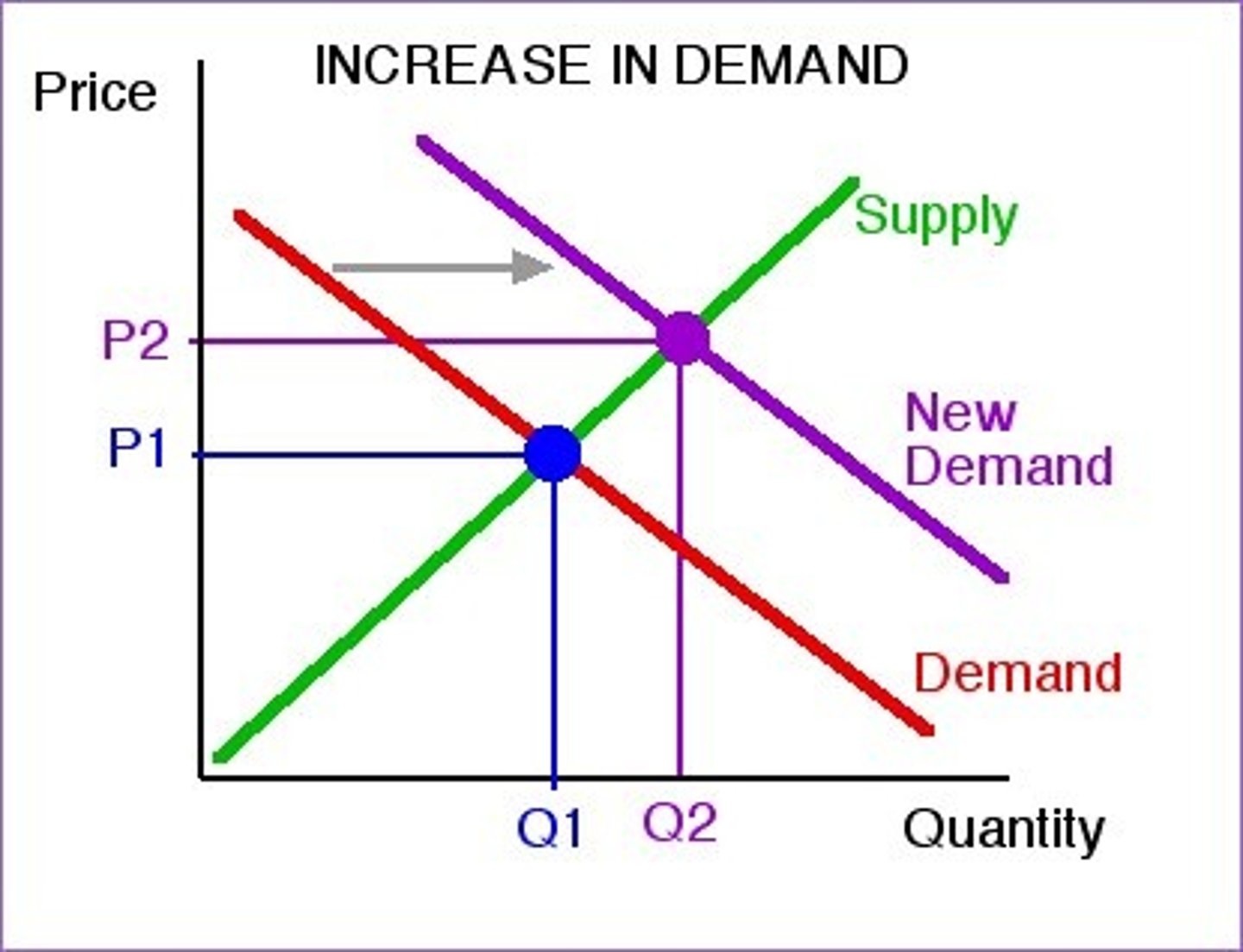
What happens when demand increases?
The demand curve shifts right, increasing price and quantity.
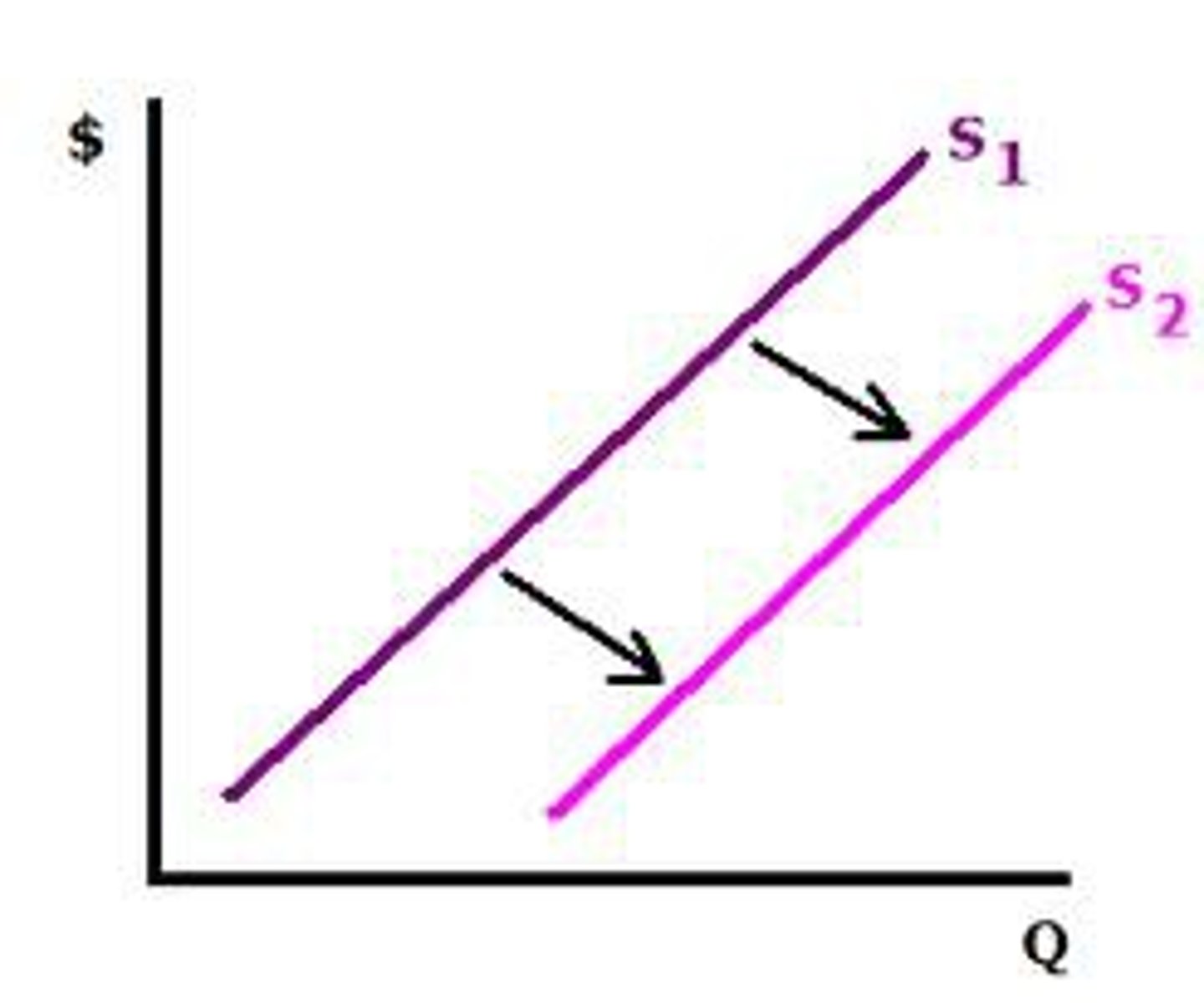
What causes the supply curve to shift right?
More suppliers, better technology, or lower production costs.
What is economic efficiency in terms of allocation?
When production matches consumer desires (Pareto efficiency).
What is a monopoly?
A market with one supplier who sets the price.
What causes monopolies?
Technical, natural, or legal reasons (e.g. patents, infrastructure).
What is a natural monopoly?
A firm with high fixed costs and scale advantages—efficient but has pricing power.
Why is price not equal to marginal revenue in a monopoly?
Because lowering the price to sell more units affects all units sold, reducing MR.
Where does a monopolist maximize profit?
Where marginal revenue (MR) = marginal cost (MC).
What is deadweight loss in a monopoly?
The loss of total welfare because output is lower and price is higher than in perfect competition.
What are other efficiency losses in monopoly?
Rent-seeking, X-inefficiency, and reduced innovation (dynamic inefficiency).
What is the economic basis of competition law?
Less competition increases deadweight loss, so law aims to preserve competition.
What are key EU legal tools for competition?
Article 101 (ban on cartels), Article 102 (abuse of dominance), and merger control (Reg. 139/2004).
What is an oligopoly?
A market with a few large suppliers, possibly selling homogeneous or differentiated goods.
Why is oligopoly hard to model?
Because firms interact strategically (e.g. price retaliation, marketing, product differences).
What is a cartel?
A group of firms acting together like a monopoly, often illegally.
Why are cartels unstable?
Free-riding, enforcement issues, and new entrants threaten their cooperation.
What is monopolistic competition?
Many firms selling differentiated products with some pricing power.
What happens in the short term under monopolistic competition?
Firms earn profit where MR = MC; profits attract new firms.
What happens in the long term under monopolistic competition?
New firms reduce demand per firm; economic profit becomes zero.
What is the welfare effect of monopolistic competition?
Prices above MC and output below optimal level create deadweight loss, but differentiation adds value.
What are disadvantages of imperfect competition?
Higher prices, lower output, inefficiencies, and coordination (e.g. cartels).
What are potential advantages of imperfect competition?
Consumer choice and incentives for innovation (especially in monopolistic competition).