INTRA OPERATIVE NURSING
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Fourth Year Duty - OMMC
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Intraoperative Stage
Begins with the client’s arrival in the operating room and ends with client’s transfer to the recovery room.
Teaching continues during the initial intraoperative phase.
Explaining all preparation, answering last-minute questions, and explaining delays to the client and family.
Admission to OR > Anesthesia > Recovery Room/ PACU
Intraoperative Phase
Asepsis and Infection Control
Homeostasis and Hemostasis
Safe administration of Anesthetic Agents
Nursing Goals in Intraoperative Phase
Surgeon
Assistant to the surgeon
Scrub Nurse
Scrubbed Team
Anesthesiologist/Anesthetist
Circulating Nurse
Pathologist
Others
Unscrubbed Team
Surgeon
Primary responsible for the preoperative medical history and physical assessment.
Performance of the operative procedure according to the needs of the patients.
The primary decision maker regarding surgical technique to use during the procedure.
Assistant Surgeon
May be a physician ( surgeon, resident, intern or clerk), physician assistant, certified registered nurse first assistant (CRNFA) or Surgical technologist.
Assists the surgeon during the surgery in any way the surgeon requests
Holds retractors in the wound to expose the operative site.
Places clamps on blood vessels
Assists in suturing & ligating bleeders
Anesthesiologist
Or a certified registered nurse anesthetist (CRNA)
Gives and controls the anesthetic for the client
Must see to it that all the equipment & supplies necessary for the induction of anesthesia are available
Determine when the surgeon or circulating nurse may proceed with positioning & preparing the operative site
Monitors the client’s vital signs, intake & output during operation
Keeps the surgeon aware of the client’s condition
Determine when the client may be moved to the post-anesthesia recovery stretcher after the operation has been completed
Sets up sterile supplies and instruments
Assists in gowning & gloving of the surgical team
Assists in draping the client and the field
Assists the surgeon as needed throughout the surgery
Hands instrument, sutures, sponges, etc. as needed in efficient manner
Keep operative field tidy during the case
Wipes blood from instruments
Keeps close watch on needles, instruments & sponges so that none will be misplaced or lost in the operative field
Keeps accurate needle/instrument count
Supplies sterile dressing materials
Cares for all instruments & supplies left after case
Scrub Nurse (SGDAHKKK)
Send for the patient at the appropriate time
Receives, greets, identifies the patient
Checks the chart for completeness
Assists the client in moving safely to operating table
Ties the scrubbed member’s gowns
Functions as the coordinator & overseer of the room during the procedure to maintain sterility
Check operating room lights for good condition
Positions the client
Performs urinary catheterization if required & connects the catheter to the drainage bag
Does the counting (instrument, sponge, and needles) with the scrub nurse
Supplies foot stools if needed by the surgical team
Watches foreheads of surgical team for perspiration
Fills out required operative records completely & legally
Remains in the room as much as possible to be constantly available
Watches progress of surgery anticipates needs, reacts quickly to emergency
Sees that the surgical team is supplied with every necessary item to perform the operation efficiently
Uses equipment & supplies economically & conservatively
Directs cleaning of room & preparation for next operation
Circulating Nurse (SICATOCPU)
Located out of the mainstream of the hospital
Near PACU, pathology and laboratory department, blood bank and radiology department
Surgical suite should be large enough to allow for correct technique but small enough to minimize movement of patients, personnel and supplies
Surgical Environment (Location)
Unrestricted
Street clothes are permitted
Serves as an outside to inside access area
Example: dressing room
Semi-restricted
Limited only to properly attired, authorized personnel
Scrub suits and head coverings – required attire
Patient’s hair also covered
Restricted
Masks required to supplement OR attire
OR theater
3 Zones of Surgical Area
20 x 20 x 10 with a minimum floor space of 360 square feet
Size of procedure room
68 F - 75 F ( 20 - 24 degrees C)
The temperature in the procedure room should maintained between _____________________
Humidity level between 30 - 60 % at all times
15 air exchanges per hour
Air exchange in each procedure room should be at least ________, and at least 3 of that should be fresh air.

Medical Asepsis vs. Surgical Asepsis
Close-fitting cotton dresses, pantsuits, jumpsuits, and gowns.
Shirts and waist drawstrings should be tucked inside the pants to prevent accidental contact with sterile areas and to contain skin shedding.
Wet or soiled garments should be changed
Headgear should completely cover the hair (head and neckline, including beard) so that single strands of hair pins, clips, and particles of dandruff or dust do not fall on the sterile field.
Shoes should be comfortable and supportive. Shoes worn in from the outside must be covered with disposable shoe covers for protection from soiling.
Shoe covers are worn one time only and are removed upon leaving the restricted area.
Masks are worn at all times in the restricted zone of the OR.
High-filtration masks decrease the risk for postoperative wound infection by containing and filtering microorganisms from the oropharynx and nasopharynx.
Masks should fit tightly, should cover the nose and mouth completely, and should not interfere with breathing, speech, or vision.
Surgical Attire
Surgical Scrub
Process of minimizing (as far as possible) microorganisms and retarding their re-growth from the sterile/scrub team members hands and arms through both mechanical (brushing) and chemical (antiseptics) means prior to participating in a operation or surgical procedure
Chlorhexidine Gluconate
Povidone iodine
Triclosan
Common Antimicrobial Skin Agents Used for the Surgical Scrub
Timed Scrub
A surgical scrub where each anatomic area is brushed for a specific length of time (1 ½ min for hand and 1 min for each arm)
Brush Stroke Scrub
A surgical scrub where each anatomic area is brushed for a specific number of strokes (30 for fingers and 20 for arm)
Surgical handrub
Hand rubbing technique for surgical preparation must be performed on perfectly clean, dry hands. On arrival in the Operating room and after having donned (cap and mask), hands must be washed with soap and water.
After the operation when removing gloves, hands must be rubbed with an alcohol-based formulation or washed with soap and water if any residue talc or biological fluids are present. (e.g. the glove is punctured).
Surgical procedure may be carried out after the other without the need for handwashing, provided that the hand rubbing technique for surgical hand preparation is followed.
Only sterile items are used within the sterile field
Sterile personnel are gowned and gloved
Tables are sterile only at table level
Sterile personnel touch only sterile items or areas; unsterile personnel touch only unsterile items or areas
Unsterile personnel avoid reaching over the sterile field; sterile personnel avoid leaning over an unsterile area
The edges of anything that encloses sterile contents are considered unsterile
The sterile field is created as close as possible to the time of use.
Sterile areas are continuously kept in view
Sterile personnel keep well within the sterile area
Sterile personnel keep contact with sterile areas to a minimum
Unsterile personnel avoid sterile areas
Destruction of the integrity of microbial barriers results in contamination
Microorganisms must be kept to an irreducible minimum
Principles of Surgical Asepsis
specific procedure, h/w & age, anesthesia administration, and any limitations specific to the client (arthritis, emphysema, and deformities)
Factors that influence position during surgery are:
Dorsal Recumbent Position
Abdominal, extremity, vascular, chest, neck, facial, ear, breast surgeries
Position technique:
Client lies flat on bed with arms either extended on arm boards or placed along side of the body
Small padding placed under client’s head, neck and under knees
Vulnerable pressure points should be padded.
Safety strap applied 2 inch above knees
Eyes should be protected by using eye patch or ointment.
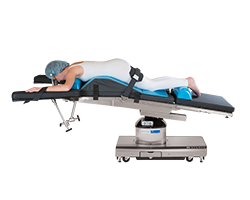
Prone Position
Surgeries involving posterior surface of the body ( spine, neck, buttocks and lower extremities )
Positioning Techniques:
Chest rolls or bolster are placed on operating table prior to positioning
Foam head rest, head turned to side or facing downward
Patient’s arms are rotated to the padded arm boards that face head, bringing them through their normal range of motion.
Padding for knees and pillow for lower extremities to prevent toes from touching mattress.
Safety strap applied 2 in. above the knees
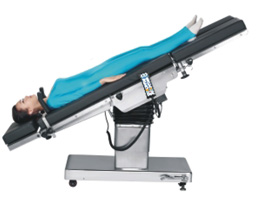
Trendelenburg Position
Surgeries involving lower abdomen, pelvic organ when there is a need to tilt abdominal viscera away from the pelvic area.
Positioning Techniques:
Patient is supine with head lower than feet.
Shoulder braces should not be used as they may cause damage brachial plexus.
When patient is returned to supine position, care must be taken move leg section slowly, then the entire table to level position.
Modification of this position can be used for hypovolemic shock.
Extremity position and safety strap are the same as for supine
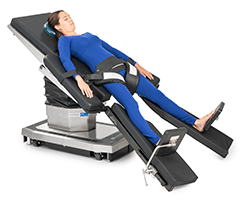
Reverse Trendelenburg Position
Upper abdominal, head, neck and facial surgery
Positioning Technique:
Patient is supine with head higher than feet.
Small pillow under neck and knees.
Well - padded footboard should be used to prevent slippage to foot of the table.
Anti embolic hose should be used if position is to be maintained for an extended period of time.
Patient should be returned slowly to supine position.
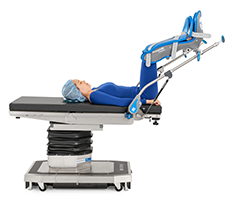
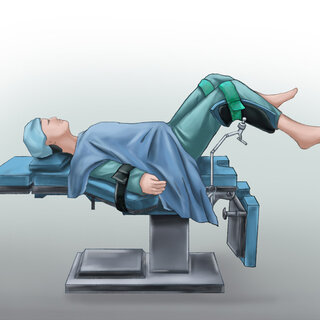
Lithotomy Position
Perineal, vaginal, rectal surgeries; combined abdominal vaginal procedure
Positioning Techniques:
Patient is placed in supine position with buttocks near lower break in the table ( sacrum are should be well padded )
Feet are placed in stirrups, stirrups height should not be excessively high or low, but even on both sides.
Knee brace must not compress vascular structures or nerves in the popliteal space.
Pressure from metal stirrups against upper inner aspect of thigh and calf should be avoided
Legs should be raised and lowered slowly and simultaneously ( may require two people )
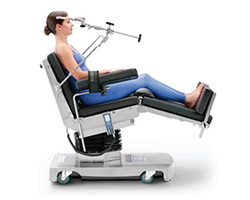
Fowler’s Position
A sitting position often used to facilitate breathing and comfort during examinations or procedures.
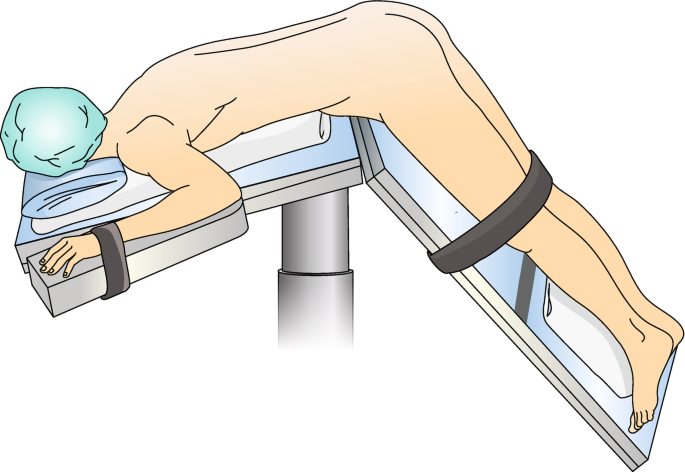
Jack Knife Position (Kraske)
Rectal procedures, sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy
Positioning Techniques:
Table is flexed at center break
All precautions taken with prone position are taken with Jack knife position.
Table strap applied over thighs
Laparotomy (abdominal incision), Trendelenburg, Lithotomy, and Side Lying
Positions for Kidney Surgery
Narcosis
It is the state of profound unconsciousness produced by a drug
Hypnosis
It is artificially induced sleep
Induction
It is the period from the beginning of administration of anesthetic until the client losses consciousness
Anesthesia
The state of “narcosis“
Anesthetics
________ can produce muscle relaxation, block transmission of pain nerve impulses and suppress reflexes. It can also temporary decrease memory retrieval and recall.
Respiration, O2 saturation, CO2 levels, HR and BP, and Urine output
The effects of anesthesia are monitored by considering the following parameters:
General Anesthesia
reversible state consisting of complete loss of consciousness and sensation
protective reflexes such as cough and gag are lost
provides analgesia, muscle relaxation and sedation
produces amnesia and hypnosis
Beginning or Induction
What is this current Stage of Anesthesia?
(Analgesia, Sedation and Relaxation)
Begins with induction and ends with loss of consciousness
Patient feels drowsy and dizzy, has a reduced sensation to pain, and is amnesic
Hearing is exaggerated
Excitement or Delirium
What is this current Stage of Anesthesia?
Begins with loss of consciousness and ends with relaxation, regular breathing, and loss of eyelid reflex
Patient may have irregular breathing, increased muscle tone, and involuntary movement of the extremities
Laryngospasm or vomiting may occur
Patient is susceptible to external stimuli
Surgical/Operative Anesthesia
What is this current Stage of Anesthesia?
Begins with generalized muscle relaxation and ends with loss of reflexes and depression of vital functions
The jaw is relaxed, and breathing is quiet and regular
The patient cannot hear
Sensation (i.e. pain) are lost
Medulla Paralysis/ Danger
What is this current Stage of Anesthesia?
Medullary Depression
Begins with depression of vital functions and ends with respiratory failure, cardiac arrest, and possible death
Respiratory muscles are paralyzed; apnea occurs
Pupils are fixed and dilated
Inhalation
Intravenous
Regional/Local
Methods of Administration of General Anesthesia
Mask Inhalation
Anesthetic gas or vapor of a volatile liquid is inhaled through a face mask attached to an anesthesia machine by breathing tubes. The mask should fit tightly to minimize escape of gases into room air
General Endotracheal Tube Anesthesia (GETA)
Anesthetic vapor or gas is inhaled directly into trachea through a nasal or oral tube inserted between the vocal cords by direct or blind laryngoscopy. The tube must be securely fixed in place to minimize tissue trauma. The patient is given oxygen before and after suctioning.
Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA)
A device for maintaining a patient airway without tracheal intubation, consisting of a tube connected to an oval inflatable cuff that has seals the larynx. It was the 1st effective product to offer significant advantages over traditional methods of airway support during surgical procedures and life-saving interventions
Intravenous Anesthesia
The circulation, usually via the peripheral vein. A drug that produces hypnosis, sedation, amnesia and or analgesia that is injected directly into the vein
Regional/Local Anesthesia
Briefly disrupts sensory nerve impulse transmission from a specific body area or region, with or without affecting the motor function and not impairing consciousness