ASU anatomy 202 exam 2
1/173
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Respiratory and Lymphatic systems
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
174 Terms
what is lymph?
recovered fluid
What is clonal deletion?
the process of destroying T and B cells that react to self antigens; macrophages phagocytize them
What is the lineage of antibody and memory cell production?
b cells > plasma cells > antibodies > memory cells
What is active immunity?
producing antibodies to protect yourself
What is passive immunity?
someone gave you the antibodies, produced somewhere else
What is natural immunity?
aquired through personal exposure
What is naturally aquired immunity?
immunity aquired during fetal and breast feeding periods
What is artifically passive aquired immunity?
in addition to current exposure, they give a booster shot to increase the antibody production
What is artificially passive aquired active immunity?
only during artifical interventions (vaccines)
What are T helper cells?
necessary for clonal selection; activates T cytotoxic cells & release of antibodies
What is the IGD antigen associated with?
allergies
What is the IGM antigen associated with?
acute allergy attacks
Why is the structure of an antibody important?
Antibodies have a very small region of amino acid sequence which helps them to match the antigen (the binding site) and the variable reagion (the only part of the molecule that changes)
How many lobes are in each lung?
right-3
left-2
What is the anatomical sequence of the respiratory system?
nasal cavity > larynx > glottis (epiglottis) > trachea > R/L primary bronchi > secondary bronchi > tertiary bronchi > terminal bronchioles > respiratory bronchioles > alveoli
How many lobar bronchiole are there?
5
3 -right
2 -left
Where do most objects that are aspirated go?
right main bronchus
Where does gas exchange occur?
alveoli, at the end of each terminal bronchiole
What is the bronchus lined with inside the lung?
mucosa
What is asthma?
a smooth muscle contricted spasm; resistance to air flow
How does oxygen move within the lungs? What cells are used & for what?
oxygen moves into the alveoli via the gradient'
squamous: easy profusion
simple cubodial: secretes sirfactin & protects epithelium and reduces friction
What is the residual volume? What is its purpose?
the volume of air left in lung no matter what; the residual volume prevents the lungs to collapse during voluntary respiration
What is the percent of oxygen in the air we breathe in?
22%
What is the assumed partial pressure for the atmosphere?
760 mmHg
What is the partial pressure for oxygen?
760 x .21 = 160mmmHg
What happens with altitude with partial pressure of oxygen?
in higher elevations, the ratio of oxygen in the air is still 21%, there is just less total air. This lowers the partial pressure of oxygen
How does ventilation occur?
it is done by changing the volume and the pressure in the lungs
How does exhalation occur?
When the thorax contracts, the pressure increases (becomes greater), and air will flow out
How does inhalation occur?
When the thorax relaxes, the pressure is greater in the atmosphere, and air will flow in
What is the intrinsic relationship in the pulmonary system?
partial pressure is the fraction of oxygen multiplied by atmospheric pressure
What happens when you give someone supplemental oxygen?
supplemental oxygen increases the amount of O2 in the blood (both the hemoglobin (98% of where oxygen is in blood) and the plasma). this will keep ischemic tissues from dying
What is the relationship between pH and Co2?
Inverse relationship.
The increase of Co2 in the blood makes the blood decrease in acidity. When this happens respiration will increase to help get rid of excess Co2 in the blood to raise the pH back to a normal level.
define pathogenic
disease-causing
what is the immune system?
not an organ system but cell population that inhabits all organs and defends the body from agents of disease
what is the lymphatic system?
network of organs and vein-like vessels
what are the functions of the lymphatic system?
fluid recovery, Immunity, and lipid absorption
what is edema
fluid in tissue
what is lymphedema
fluid in tissues caused by the lymphatic system
what is elephantiasis
limb or other part of the body becomes very enlarged due to obstruction of the lymphatic vessels
what are lymphatic vessels
transport the lymph
what are lymphatic tissues
aggregations of lymphocytes in mucous membranes and various organs
how are lymphatic organs separated from surrounding organs?
separated from surrounding organs by connective tissue capsules
what is the route of lymph flow
lymphatic capillaries → collecting trunks → collecting ducts → subclavian vein
what are the 6 lymphatic trunks
jugular, subclavian, bronchomediastinal, intercostal, intestinal, and lumbar
what are the 2 collecting ducts
right lymphatic duct and thoracic duct, these both drain into the subclavian veins
what are the mechanisms of lymph flow
flows at low pressure and speed bc no heart to pump
valves to prevent backflow
move by rhythmic contractions of vessels
aides by skeletal muscle pump
thoracic pump aids flow from abnormal to the thoracic cavity
rapidly flowing bloodstream in subclavian veins draws lymph into it
how does exercise affect lymphatic return
increases it
diffuse lymphatic tissue
the simplest form, lymphocytes are scattered, not densely clustered, prevalent in body passages open to the exterior, MALT
what is MALT?
mucosa associated lymphatic tissue
what are lymphatic nodules (follicles)
dense masses of lymphocytes and macrophages that congregate in response to pathogens
in lymph nodes, tonsils, and appendix
what is peyer patches
dense clusters in the ileum, type of lymphatic nodules
what are primary lymphatic organs
RBM and thymus, site where T and B cells become immunocompetent
what are secondary lymphatic organs
nodes, tonsils, and spleen, immunocompetent cells populate these tissues
describe RBM
involved in hematopoiesis (blood formation), and immunity (WBCs)
describe thymus in fetus vs adult
very large in fetus bc it develops T-cells, shrinks when adult
what does the thymus do
secrete hormones that regulate T-cell development, mature T cells
compare afferent and efferent in lymph nodes and why
lots of afferent, few efferent, creates a bottleneck to slow the fluid
function of lymph nodes
organs that filter lymph and act as a site for T and B cell activation
450 in adults
reticular cells and macrophages phagocytize foreign matter
lymphocytes respond to antigens
common site for metastatic cancer
name the 5 tonsils and where they are
palatine - pair in oral cavity, most often infected
lingual - pair at root of tongue
pharyngeal - 1 on back wall of the nasopharynx
what is tonsillitis
inflammation of the tonsils
tonsils
help filter out germs that enter through your nose or mouth to protect the rest of your body from infection
function of spleen
blood production in fetus
blood reservoir
RBC disposal
immune reaction: filters blood and can quickly detect antigens
first line of defense
external barriers; skin and mucous membranes
second line of defense
non-specific defense; leukocytes, macrophages, antimicrobial proteins, immune surveillance, inflammation, and fever
effective against a broad range of pathogens
third line of defense
the immune system; defeats pathogen and leaves the body with a memory of it so it can defeat it faster in the future
what are your non-specific defenses
broadly effective, no prior exposure, external barriers; inflammation and fever
what are your specific defenses
results from prior exposure, protects against only a particular pathogen, immune system
what are your external barriers
skin - dry and nutrient-poor
mucous membranes - stickiness of mucus, include lysosomes
subepithelial areolar tissue - tissue gel is a viscous barrier of hyaluronic acid
what are lysosomes
enzyme that destroys bacterial cell walls
what is hyaluronidase
enzyme used by pathogens to circumvent the hyaluronic acid defense
what is lactic acid
a component of sweat, many microbes cannot survive in an acidic environment
what is keratin
toughness
define phagocyte
a cell like a WBC that engulfs and absorbs waste material, microorganisms or other foreign bodies in the bloodstream and tissues
what are neutrophils
wander in tissues and phagocytize bacteria
create a killing zone and degranulation
eosinophils
found especially in mucous membranes
phagocytize antigen-antibody complexes, allergens and inflammatory chemicals
antiparasitic effects: aggregate and release enzymes onto parasites
basophils and mast cells
aid in mobility and action of WBC;s by the release of Histamine and heparin
lymphocytes
T-cells and B-cells are apart of this
NK cells are non-specific
most abundant lymphocyte in the blood
80% T-cells, 15% B-cells, 5% NK cells
what are NK cells
natural killer cells, large lymphocytes that attack and destroy bacteria, transplanted tissue, host cells infected with viruses or have turned cancerous
monocytes
move from blood into connective tissue and transform into macrophages
macrophages
phagocytic cells, 2 types; wandering and fixed
very large, process foreign matter and display antigenic fragments to certain T cells alerting the immune system to the presence of the enemy
wandering macrophages
actively seek pathogens
fixed macrophages
only phagocytize pathogens that come to them
ex: microglia, dust cells, hepatic macrophages
what are antimicrobial proteins
inhibit microbial reproduction and provide short-term, nonspecific resistance to pathogenic bacteria and viruses; interferons and complement system
what are interferons
polypeptides secreted by cells invaded by viruses
what are interferon antiviral effects
don’t benefit the cell that secretes them
diffuse to neighboring cells and stimulate them to produce antiviral proteins
activate NK cells and macrophages to destroy infected host cells
what are interferon anticancer effects
activated NK cells can destroy cancer cells
what is the complement system
group of proteins that contribute to nonspecific and specific immunity
what are the 4 methods of pathogen destruction used by the complement system
inflammation
immune clearance
phagocytosis
cytolysis
what are the 3 routes of complement activation
classical, alternative, and lectin pathways
inflammation of complement action
mast cells and basophils secrete histamine and other inflammatory chemicals
immune clearance
principal means of clearing foreign antigens from the bloodstream
phagocytosis
neutrophils and macrophages can’t phagocytize “naked” bacteria, viruses, or other pathogens
cytolysis
bind to enemy cell and attracts more complement proteins
membrane attack complex (MAC) forms and creates a hole in target cell which ruptures it
what is immune surveillance
NK cells continually patrol the body on the lookout for pathogens and diseased host cells
NK cell releases perforins, which polymerase and form a hole in the enemy cell membrane
granzymes from NK cells enter perforin hole and degrade enemy cell enzymes
enemy cell dies by apoptosis
macrophage engulf and digests dying cell
how is a fever beneficial
promotes interferon activity, accelerating metabolic rate and tissue repair
inhibiting pathogen reproduction
over 104 it is dangerous because enzymes can stop working
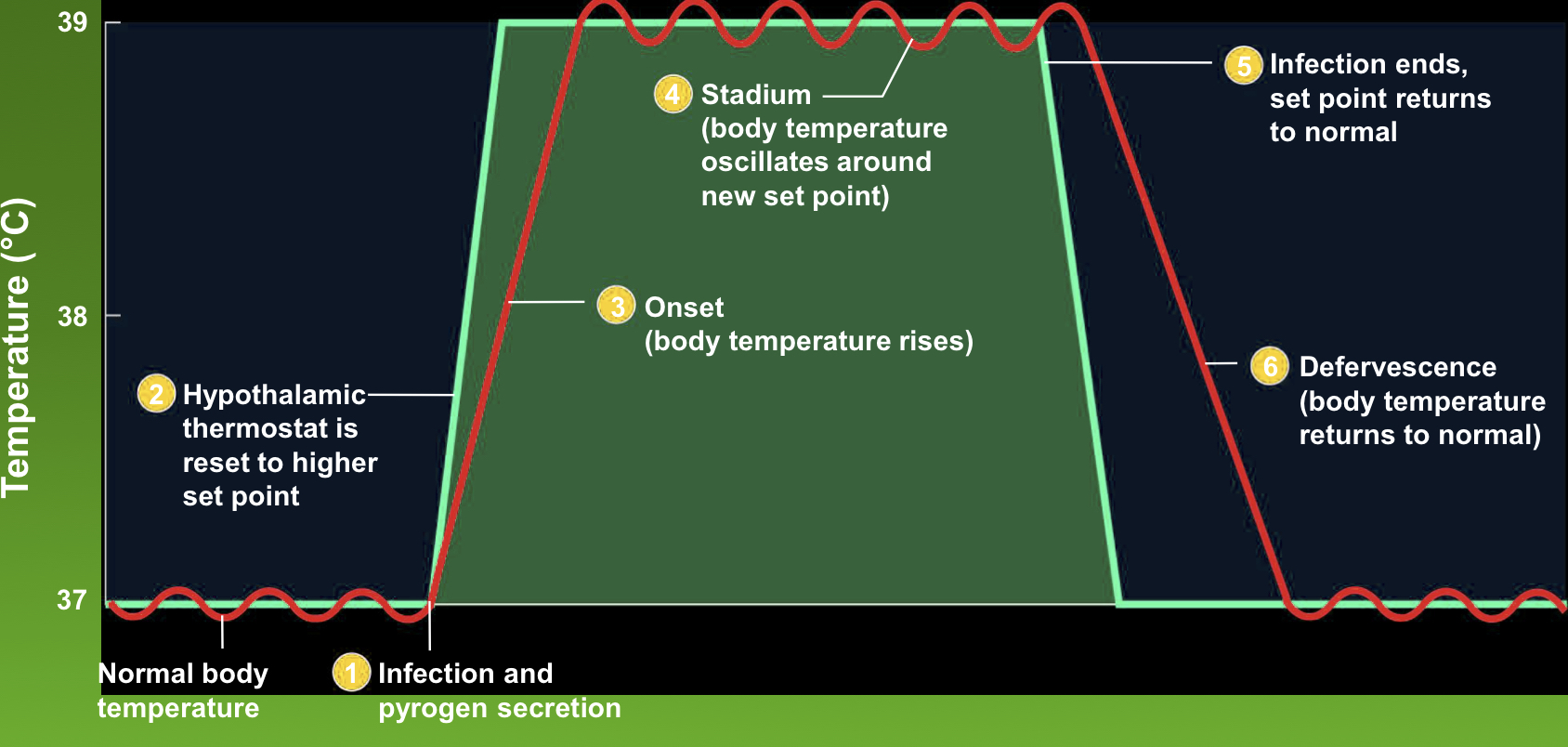
what produces a fever
pyrogens
stages of fever
onset, stadium, and defervescence
Reye syndrome
serious disorder in children younger than 15 following an acute viral infection like chickenpox or the flu
swelling of brain neurons, pressure of swelling brain
can be triggered by the use of aspirin
what are the cardinal signs of inflammation
redness (erythema)
swelling (edema)
heat caused by hyperemia
pain