A&P 1 Exam 2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/118
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
1
New cards
4 primary tissues
epithelial, connective, nervous, and muscular
2
New cards
3 primary germ layers
ectoderm
endoderm
mesoderm
endoderm
mesoderm
3
New cards
ectoderm
outer
gives rise to the epidermis and nervous system
gives rise to the epidermis and nervous system
4
New cards
endoderm
inner
gives rise to mucous membrane lining digestive and respiratory tracts, digestive glands, among other things
gives rise to mucous membrane lining digestive and respiratory tracts, digestive glands, among other things
5
New cards
mesoderm
middle
becomes gelatinous tissue called mesenchyme
gives rise to cartilage, bone, blood, muscle
wispy collagen fibers and fibroblasts in gel matrix
becomes gelatinous tissue called mesenchyme
gives rise to cartilage, bone, blood, muscle
wispy collagen fibers and fibroblasts in gel matrix
6
New cards
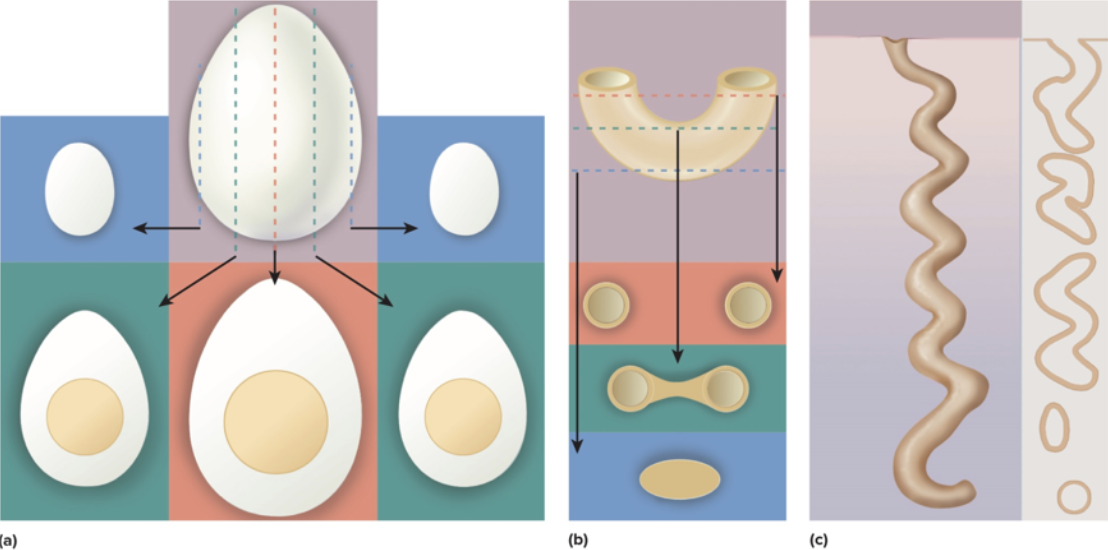
tissue sections
Longitudinal- cut on long axis
Cross- cut perpendicular to long axis
Oblique- cut at angle between longitudinal and cross
Cross- cut perpendicular to long axis
Oblique- cut at angle between longitudinal and cross
7
New cards
properties of epithelium
* cover body surfaces and line cavities
* makes up most glands
* avascular
* cells very close together
* basement membrane, basal surface, apical surface
* simple or stratified
* makes up most glands
* avascular
* cells very close together
* basement membrane, basal surface, apical surface
* simple or stratified
8
New cards
simple squamous
* rapid diffusion and transport
* location: alveoli, glomeruli, endothelium, serosa
* location: alveoli, glomeruli, endothelium, serosa
9
New cards
simple cuboidal
* resists abrasion, retards water loss through skin, resists penetration by pathogens
* location: epidermis, palms and soles
* location: epidermis, palms and soles
10
New cards
non-keratinized stratified squamous
* resists abrasion (not as strongly as keratinized) and penetration of pathogens
* location: tongue, oral mucosa, esophagus, and vagina
* location: tongue, oral mucosa, esophagus, and vagina
11
New cards
stratified cuboidal
* secretes sweat, produces sperm, produces ovarian hormones
* location: sweat gland ducts, ovarian follicles and seminiferous tubules
* location: sweat gland ducts, ovarian follicles and seminiferous tubules
12
New cards
transitional
* allows for filling of urinary tract (stretching)
* location: ureter and bladder
* location: ureter and bladder
13
New cards
simple vs stratified epithelia
simple: touches the basement membrane
stratified: some cells rest on top of each other (not touching basement membrane)
stratified: some cells rest on top of each other (not touching basement membrane)
14
New cards
7 types of cells found in fibrous connective tissue.
* fibroblasts
* macrophages
* leukocytes
* plasma cells
* mast cells
* adipocytes
* macrophages
* leukocytes
* plasma cells
* mast cells
* adipocytes
15
New cards
macrophages function
phagocytize foreign material and activate immune system
16
New cards
function of leukocytes
neutrophils attack bacteria, lymphocytes react against bacteria, toxins and other foreign antigens
17
New cards
function of plasma cells
synthesize antibodies (proteins)
18
New cards
function of mast cells
secrete heparin to inhibit clotting and histamine to dilate blood vessels
19
New cards
function of adipocytes
store triglycerides (fat)
20
New cards
what is the matrix of connective tissue
ground substance (interstitial fluid) + collagen/elastic/reticular fibers
21
New cards
functions of collagen fibers
* most abundant protein in body
* tough, flexible, and stretch-resistant
* tendons, ligaments and deep layer of the skin
* tough, flexible, and stretch-resistant
* tendons, ligaments and deep layer of the skin
22
New cards
functions of reticular fibers
* thin collagen fibers coated with glycoprotein
* form framework of spleen and lymph nodes
* form framework of spleen and lymph nodes
23
New cards
functions of elastic fibers
* thinner than collagenous fibers
* branch and rejoin each other
* made of elastin
* allows stretch and recoil
* branch and rejoin each other
* made of elastin
* allows stretch and recoil
24
New cards
areolar connective tissue
* loose connective tissue, highly vascularized
* location: underlies epithelia, in serous membranes, between muscles, passageways for nerves and blood vessels
* location: underlies epithelia, in serous membranes, between muscles, passageways for nerves and blood vessels
25
New cards
dense irregular connective tissue
* densely packed, randomly arranged collagen fibers, withstands unpredictable stress
* location: deeper layer of skin, capsules around organs
* location: deeper layer of skin, capsules around organs
26
New cards
adipose connective tissue
* space between adipocytes occupied by areolar/reticular tissue and blood capillaries, brown and white fat, energy storage, insulation, cushioning
* location: subcutaneous fat, around organs
* location: subcutaneous fat, around organs
27
New cards
hyaline cartilage
* “fish eye soup”, eases joint movement, holds airway open, moves vocal chords, growth of juvenile long bones
* location: articular and costal cartilage, trachea, larynx, fetal skeleton
* location: articular and costal cartilage, trachea, larynx, fetal skeleton
28
New cards
elastic cartilage
* provides flexible elastic support
* location: external ear, epiglottis
* location: external ear, epiglottis
29
New cards
fibrocartilage
* large coarse bundles of collagen fibers, resists compression and absorbs shock
* location: pubic symphysis, menisci, intervertebral discs
* location: pubic symphysis, menisci, intervertebral discs
30
New cards
blood
* fluid, transports cells and dissolved matter, plasma, Erythrocytes (RBC), Leukocytes (WBC), thrombocytes
* location: veins and arteries
* location: veins and arteries
31
New cards
what distinguishes excitable tissues from other tissues
only muscular tissue contracts (via electrical signals) and only nervous tissue can initiate an electrical signal
32
New cards
Nervous tissue cells
* neurons
* neuroglia
* neuroglia
33
New cards
junctions that hold cells and tissues together
tight junction, desmosome, gap junction
34
New cards
tight junction
linkage between two adjacent cells by transmembrane cell-adhesion proteins
35
New cards
desmosome
hook-like, j shaped proteins that arise from the cytoskeleton to hold cells together (like a clothing snap)
36
New cards
gap junction
formed by ring-like connexons, located in cardiac and smooth muscle, embryonic tissue, lens and cornea
37
New cards
different types of glands
endocrine, exocrine, unicellular
38
New cards
endocrine
no ducts, secrete hormones directly into blood
39
New cards
exocrine
maintain contact with epithelia surface via ducts, external or internal
40
New cards
unicellular
can be endocrine or exocrine, found in nonsecretory epithelia
41
New cards
classification of duct shape
simple (unbranched)
compound (branched)
compound (branched)
42
New cards
classification of gland shape
tubular (narrow)
acinar (dilated sac)
tubuloacinar (both)
acinar (dilated sac)
tubuloacinar (both)
43
New cards
modes of glandular secretion
protein secretion
merocrine secretion
holocrine secretion
merocrine secretion
holocrine secretion
44
New cards
protein secretion
lipid droplet covered by membrane, used by mammary glands
45
New cards
merocrine secretion
uses vesicles that release via exocytosis, used by eccrine sweat glands (tear glands, pancreas, gastric glands)
46
New cards
holocrine secretion
cells accumulate a product until they disintegrate, done by oil glands of scalp and skin
47
New cards
types of body’s membranes
cutaneous membrane
mucous membrane
serous membrane
mucous membrane
serous membrane
48
New cards
cutaneous membrane
* the skin
* largest membrane in the body
* contains stratified squamous epithelium (epidermis) resting on connective tissue (dermis)
* largest membrane in the body
* contains stratified squamous epithelium (epidermis) resting on connective tissue (dermis)
49
New cards
mucous membrane
* lines passageways that open to external environment
* consist of epithelial, areolar and smooth muscle tissue
* absorption, secretion and protection
* consist of epithelial, areolar and smooth muscle tissue
* absorption, secretion and protection
50
New cards
serous membrane
* internal membranes
* contain simple squamous epithelium and areolar tissue
* covers organs and lines walls of body cavities
* contain simple squamous epithelium and areolar tissue
* covers organs and lines walls of body cavities
51
New cards
modes of tissue growth
hyperplasia
hypertrophy
neoplasia
hypertrophy
neoplasia
52
New cards
hyperplasia
cell multiplication
53
New cards
hypertrophy
enlargement of preexisting cells
54
New cards
neoplasia
development of a tumor
55
New cards
ways tissue can change from one type to another
differentiation
metaplasia
metaplasia
56
New cards
differentiation
development of more specialized form from unspecialized tissue
57
New cards
metaplasia
changing from one type of mature tissue to another
58
New cards
ways the body repairs damaged tissues
regeneration
fibrosis
fibrosis
59
New cards
regeneration
replacement with same cell type
60
New cards
fibrosis
replacement with scar tissue
61
New cards
histological structure of the epidermis
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
* stem cells
* keratinocytes (majority)
* melanocytes
* tactile
* dendritic
* strata
* stem cells
* keratinocytes (majority)
* melanocytes
* tactile
* dendritic
* strata
62
New cards
histological structure of the dermis.
connective tissue
* mostly collagen
* papillary layer (areolar tissue)
* reticular layer (dense irregular tissue)
* mostly collagen
* papillary layer (areolar tissue)
* reticular layer (dense irregular tissue)
63
New cards
cyanosis
blueness due to oxygen deficiency
64
New cards
erythema
redness due to increased blood flow
65
New cards
pallor
paleness due to decreased blood flow
66
New cards
albinism
milky white skin and blue-gray eyes due to genetic lack of melanin synthesizing enzyme
67
New cards
jaundice
yellowing due to bilirubin in blood
68
New cards
hematoma
bruising (clotted blood under skin)
69
New cards
bronzing
excessively tan/brown. Symptom of Addison’s Disease
70
New cards
common markings of the skin
friction ridges
flexion lines
freckles and moles
hemangiomas
flexion lines
freckles and moles
hemangiomas
71
New cards
friction ridges
markings on the fingertips that leave oily fingerprints on surfaces we touch
72
New cards
flexion lines
creases on digits, palms, wrists, elbows
73
New cards
freckles and moles
aggregations of melanocytes
74
New cards
hemangiomas
birthmarks, caused by benign tumors of dermal capillaries
75
New cards
structure and function of nails
* nail plate, free edge, nail body, nail root
* function for grooming, picking apart food, counterforce to enhance sensitivity, etc
* function for grooming, picking apart food, counterforce to enhance sensitivity, etc
76
New cards
two types of sweat glands
apocrine and merocrine (eccrine)
77
New cards
apocrine sweat gland
* groin, anal region, axillam areola, beard area
* inactive until puberty
* responds to stress and sexual stimulation
* ducts lead to hair follicles
* bromhidrosis
* inactive until puberty
* responds to stress and sexual stimulation
* ducts lead to hair follicles
* bromhidrosis
78
New cards
merocrine (eccrine) sweat gland
* most numerous
* palms, soles, forehead
* simple tubular glad
* cools body
* palms, soles, forehead
* simple tubular glad
* cools body
79
New cards
sebaceous glands
* flask-shaped, short ducts
* sebum- oily secretion
* keep skin and hair from becoming brittle and dry
* sebum- oily secretion
* keep skin and hair from becoming brittle and dry
80
New cards
ceruminous glands
* coiled, simple tubes
* external ear canal
* earwax (cerumen)
* waterproofs and protects ears
* external ear canal
* earwax (cerumen)
* waterproofs and protects ears
81
New cards
mammary glands
milk producing glands that develop only during pregnancy
modified apocrine sweat glands
rich secretion released through ducts opening at nipple
modified apocrine sweat glands
rich secretion released through ducts opening at nipple
82
New cards
three most common forms of skin cancer
* basal cell carcinoma
* squamous cell carcinoma
* malignant melanoma
* squamous cell carcinoma
* malignant melanoma
83
New cards
basal cell carcinoma
most common
least dangerous
forms from cells in stratum basale
least dangerous
forms from cells in stratum basale
84
New cards
squamous cell carcinoma
arises from keratinocytes of stratum spinosum
85
New cards
malignant melanoma
most dangerous
arises from melancytes
arises from melancytes
86
New cards
three classes of burns
first degree
second degree
third degree
second degree
third degree
87
New cards
first degree burn
epidermis only
heals in days
heals in days
88
New cards
second degree burns
part of the dermis
2 weeks-several months to heal, may leave scars
2 weeks-several months to heal, may leave scars
89
New cards
third degree burns
all of epidermis/dermis + deeper tissue
needs fluid replacement
infection control
supplemental nutrition
needs fluid replacement
infection control
supplemental nutrition
90
New cards
tissues and organs that compose the skeletal system
* cartilage
* ligaments
* tendons
* ligaments
* tendons
91
New cards
functions of the skeletal system
* support
* protection
* movement
* electrolyte balance
* acid-base balance
* blood formation
* protection
* movement
* electrolyte balance
* acid-base balance
* blood formation
92
New cards
bones as a tissue vs as an organ.
tissue: osseous tissue (connective tissue with the matrix hardened by calcium phosphate and other minerals)
organ: consists of multiple tissues
organ: consists of multiple tissues
93
New cards
osteogenic cell
stem cells found in endosteum and inner layer of periosteum
94
New cards
osteoblast
bone forming cells
95
New cards
osteocytes
strain sensors, regulate bone remodeling
96
New cards
osteoclast
bone-dissolving cells
97
New cards
importance of each constituent of bone tissue
* mineral portion gives stiffness
* protein/polymer portion gives flexibility
* protein/polymer portion gives flexibility
98
New cards
histology of the 2 types of bone tissue
compact bone tissue:
* concentric lamellae around central canal
* perforating (perpendicular) canals
\
spongy bone tissue:
* trabeculae (thin plates of bone)
* spaces filled with red bone marrow
* few osteons
* no central canals
* concentric lamellae around central canal
* perforating (perpendicular) canals
\
spongy bone tissue:
* trabeculae (thin plates of bone)
* spaces filled with red bone marrow
* few osteons
* no central canals
99
New cards
red bone marrow
(myeloid tissue)
makes blood
makes blood
100
New cards
yellow bone marrow
stores energy(fatty tissue)