Human Parasitology Exam II (Lectures 9-17)
1/145
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
146 Terms
Nematode classification
*classification based on morphology
*2 classes
adenophorea
cellular hypodermis (tissue that contains individual cells)
no phasmids (specialized sensory structure).
secernenta
syncytial hypodermis (no cell boundaries)
have phasmids
Nematode habitats
free-living (most)
they don’t need a host
ecosystem processes
decomposition
nutrient cycling
aquatic
soil
parasitic
plants
ag importance
destruction of ~10% of all crops
vertebrates
major medical importance
> 3 billion humans
Nematode general morphology
roundworm
elongate, cylindrical, both ends tapered.
“tube within tube”
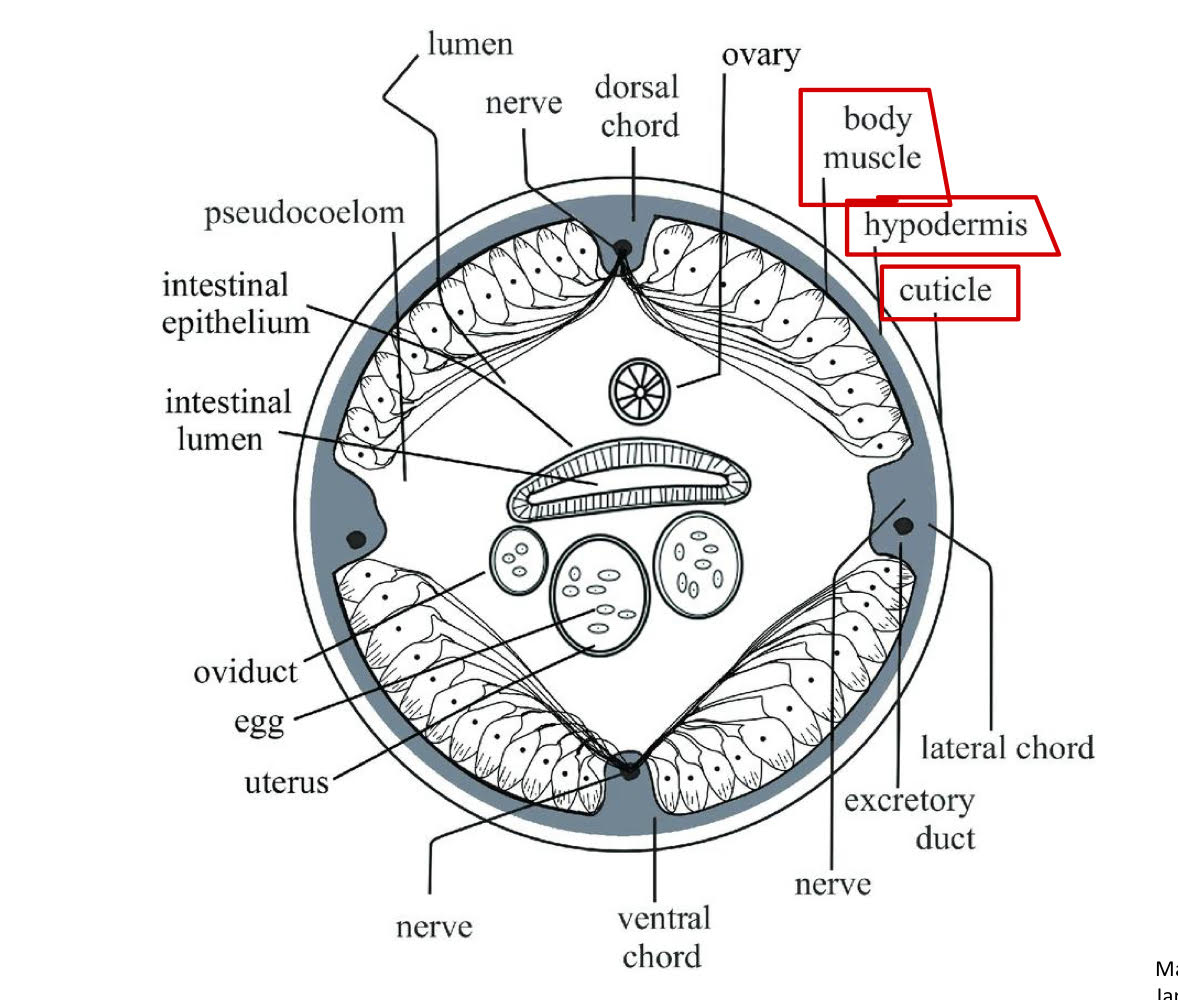
body wall
digestive tract
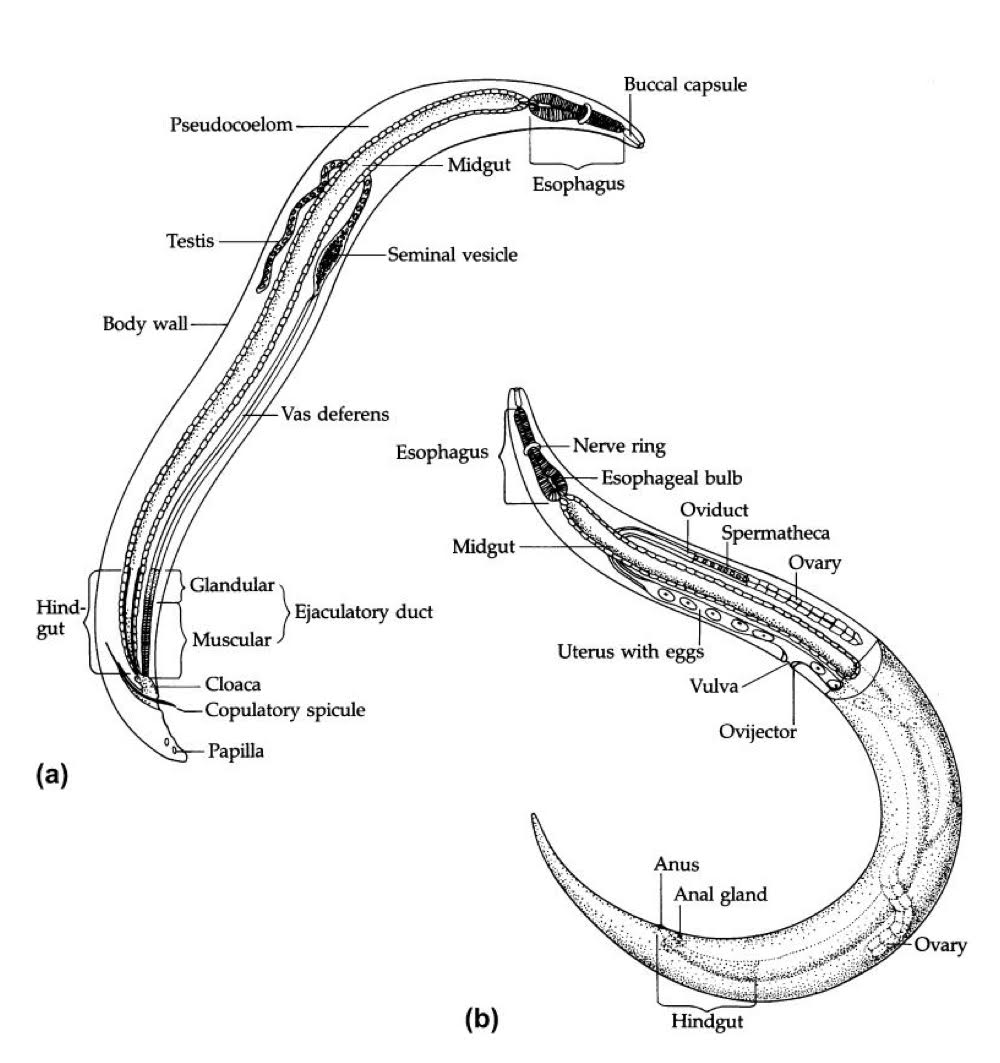
nematode adult morphology (the body wall)
body wall
collagen
covers entire body surface + lines openings.
hypodermis
formation of cuticle during molting
morphology used in classification
cellular→ class adenophorea
syncytial→ class secernentea
muslce layer beneath hypodermis
nematode adult morphology (digestive tract)
complete digestive tract
mouth→ gut→ anus
3 major regions
foregut: lined with cuticle
mouth
circular opening
may have lips (# varies among spp.)
buccal cavity
between mouth + esophagus
useful for ID
not present in all spp.
size + shape vary
may have teeth or cutting plates (thickening of cuticles)
esophagus
esophageal glands: digestive enzymes
muscular: forces food through, esophago-intestinal, and valve into midgut.
Midgut
no cuticle
single layer of cells: microvilli which helps with absorption
Hindgut
lined with cuticle
anus
pseudocoelom
fluid filled with cavity between body wall + digestive tract.
hemolymph: transport solutes and structural
hydrastatic skeleton: support and locomotion
Nematode reproductive system for males
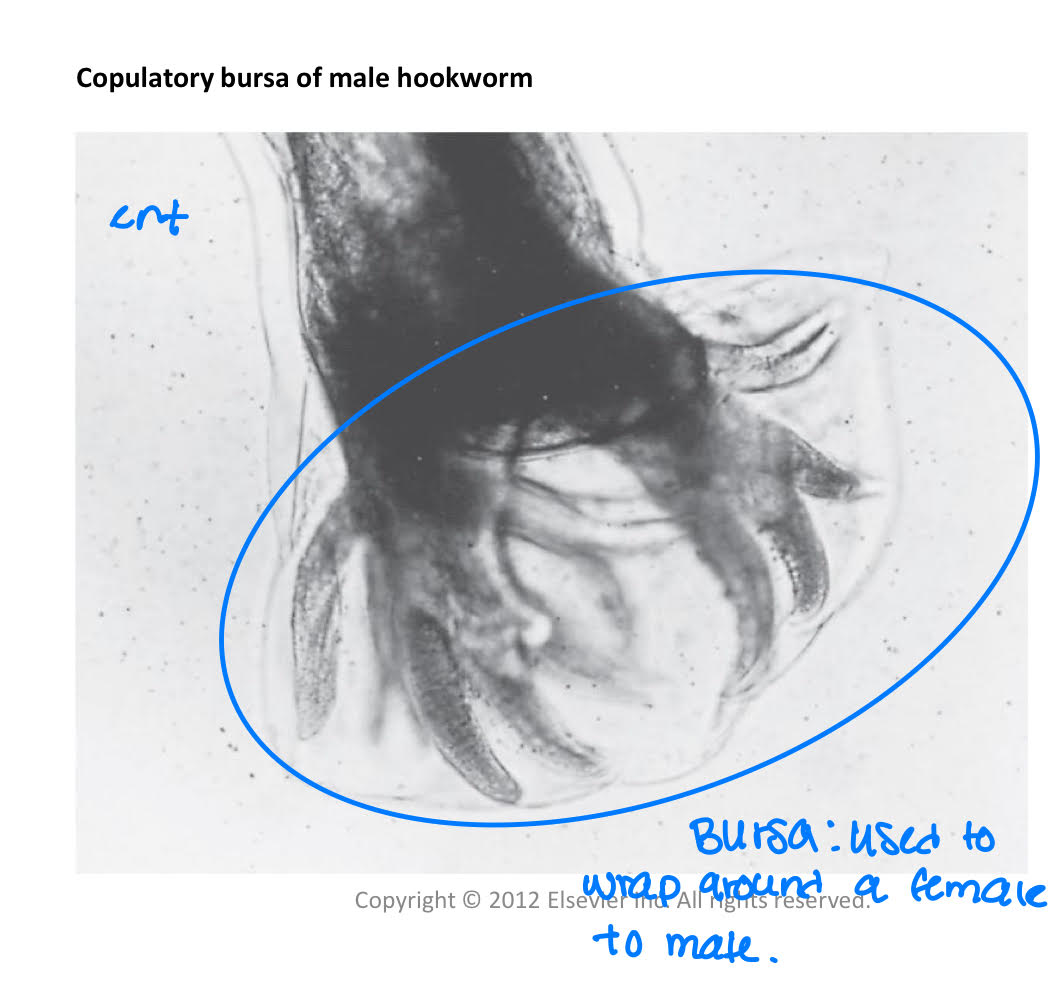
*dioecious + sexually dimorphic (male and female look different)
testes
sperm (pseudopodia)
bursa (used to wrap around a female to mate)
Nematode reproductive system for females
ovary→ produces oocytes
sperm penetrates oocyte which initiates the process of eggshell formation.
eggshell
chitinous layer
lipid layer
resistance to desiccation (drying out) and penetration by H2O → solutuble substances
proteinaceous layer
uterine secretions
some spp.
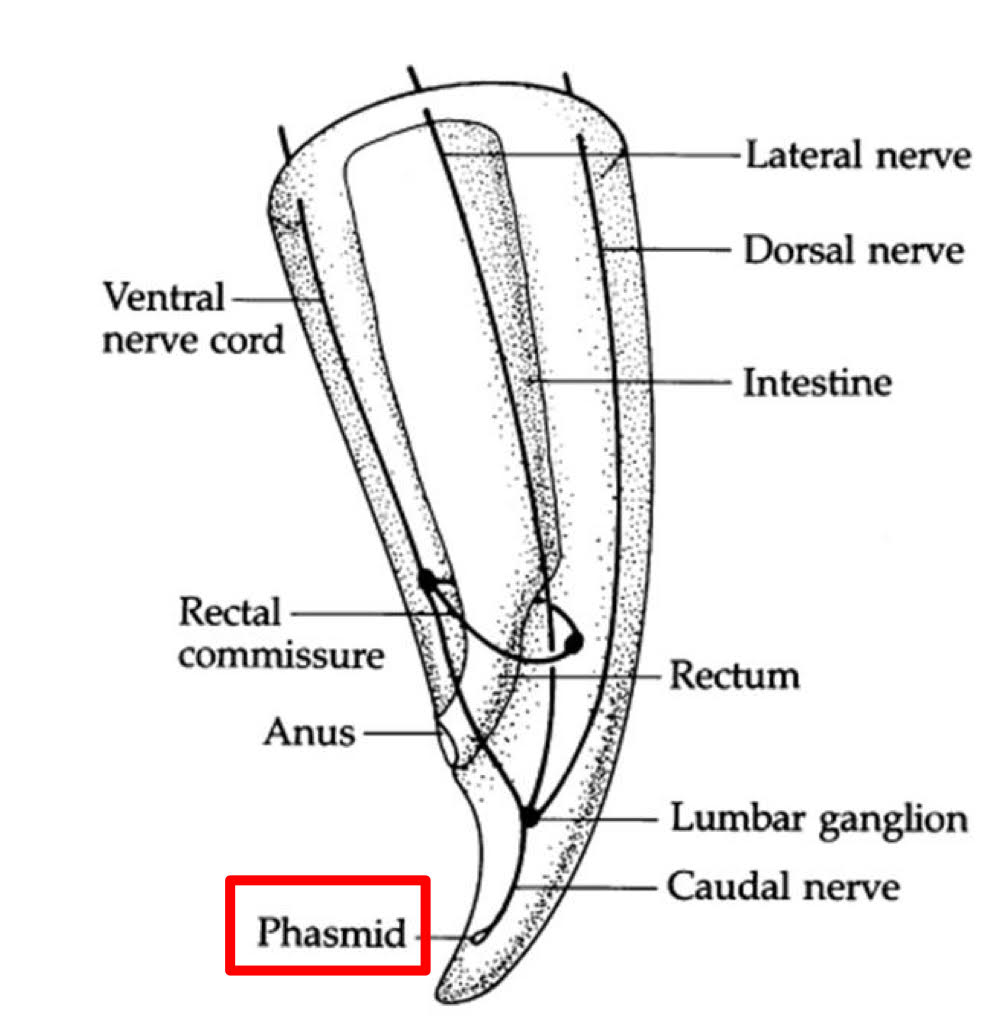
Nematode Nervous System
commissures
circumesophageal (around the esophagus)
rectal
ventral nerve cord
sense organs
labial papillae
mechanoreceptors
ex.pressure
cephalic papillae
mechanoreceptors
amphids
chemoreceptors
phasmids
chemoreceptors
characters used in taxonomic classification
absent→ class adenophorea
present→ class secernentea
Neurotransmission (2 types of nerve fibers) of nematodes
excitatory nerve fibers
release Ach at neuromuscular junctions
depolarize muscle membranes
increase in AP
increase in Ach→ depolarization→ increase in AP
inhibitory nerve fibers
release gammaaminobutyric acid (GABA)
binds to receptors on muscle + is inhibitory
hyperpolarizes muscle membranes
decrease in AP.
increase in GABA→ hyperpolarization → decrease in AP
Drug treatments for nematodes
some interfere with neuromuscular transmission.
paralysis → flaccid (limp) or spastic (tense)
piperazine
blocks Ach
hyperpolarizes muscle membranes
flaccid paralysis (loses mortality)
worm expelled by host
ivermectin
stimulates release of GABA
hyperpolarizes muscle membranes
flaccid paralysis
worm expelled by host
pyrantel
inhibits cholinesterase (normally inactivared Ach)
spastic paralysis
albendazole + mebendazole
inhibit polymerization of tubulin into microtubules
impaired glucose uptake
unable to maintain E production
immobilization → death
nematode cuticle process of molting
larva grows
secretes exsheathing fluid
cuticle detaches from hypodermis (secrete a new cuticle).
hypoderis secretes new cuticle
old cuticle broken down by enzymes and ruptures
larva exits
nematodes routes of infection
oral
skin penetration
vector
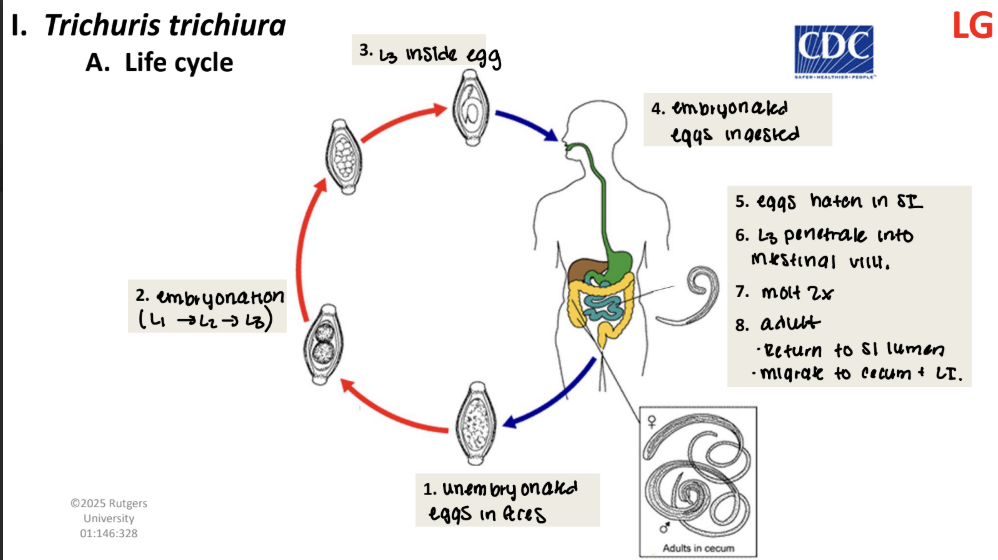
trichuris trichiura life cycle
unembryonated eggs in feces
embryonation (L1→ L2→ L3)
L3 inside egg
embryonated eggs ingested
eggs hatch in SI
L3 penetrate into intestinal wall
molt 2x
adult
return to SI lumen
migrate to cecum + LI.
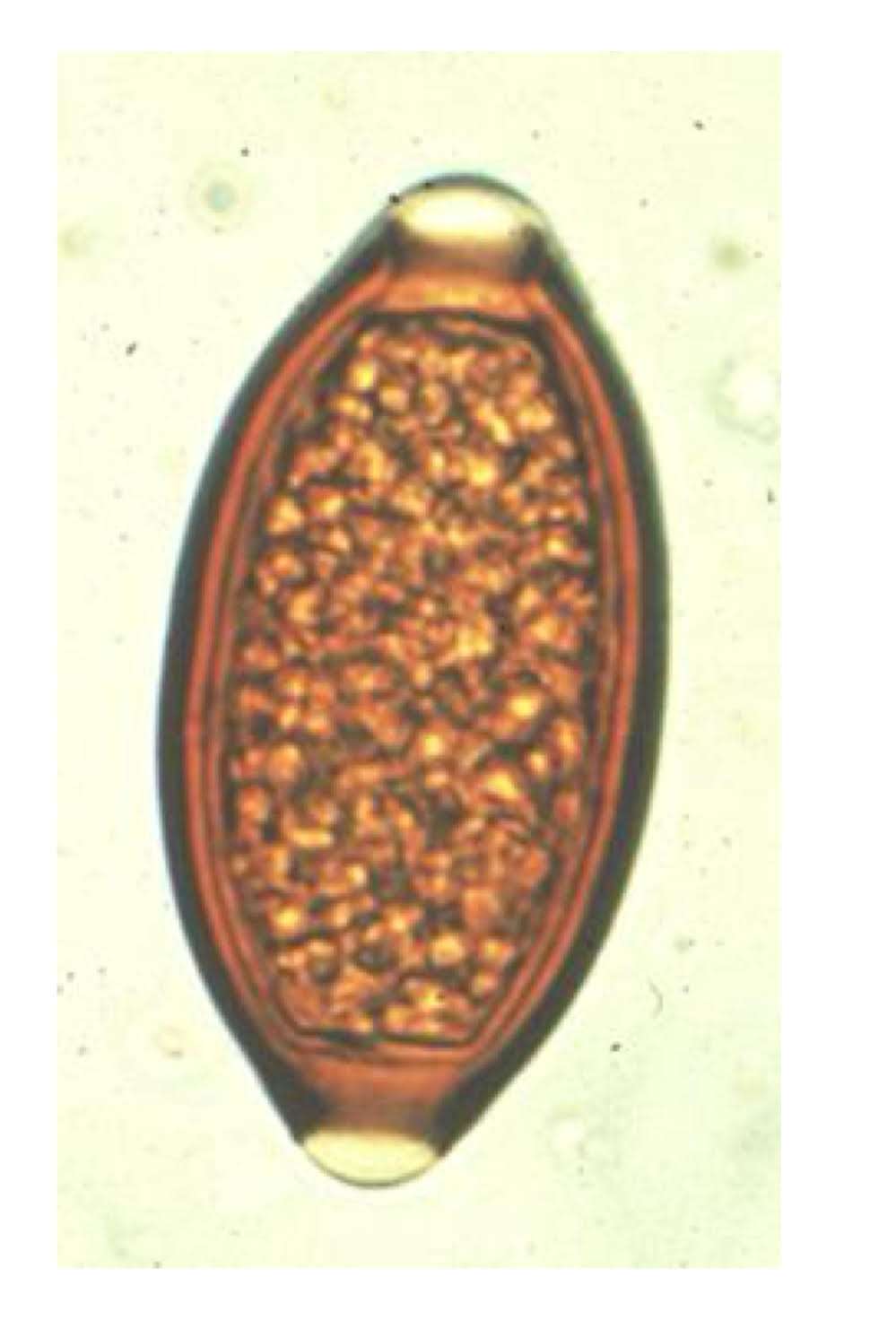
trichuris trichiura egg morphology
very thick wall
opercular knobs
trichuris trichiura adult morphology
ant end: slender
post end: thicker
commonly called “whipworm”
male: coiled post end
trichuris trichiura pathology
adults burrow into mucosa + feed
trauma to intestinal lining
this trauma is called “colitis”
chronic hemorrhage + anemia: ~0.005 ml blood/worm/day lost in stools.
increased peristalsis in LI: rectal prolapse (to come out)
trichuris dysentery syndrome (TDS)
children
ex. 200 worms in a child and the child would needs an increase does of Fe 4.25 mg/day.
systemic effects
stunted growth
impaired cognitive function
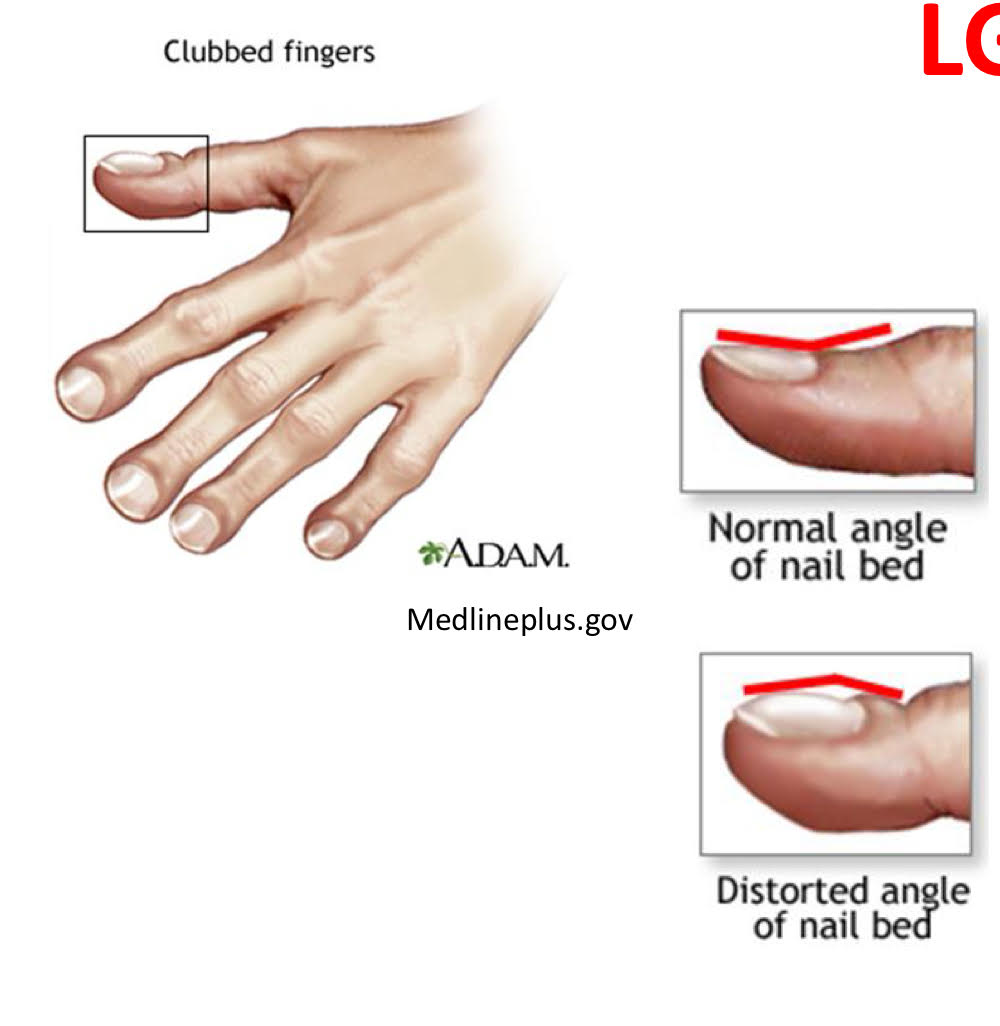
finger + toe clubbing
children → heavy infections (children love to play in the dirt and trichuris trichiura live in the soil)
trichuris trichiura diagnosis
eggs in feces
trichuris trichiura treatment
mebendazole
albendazole
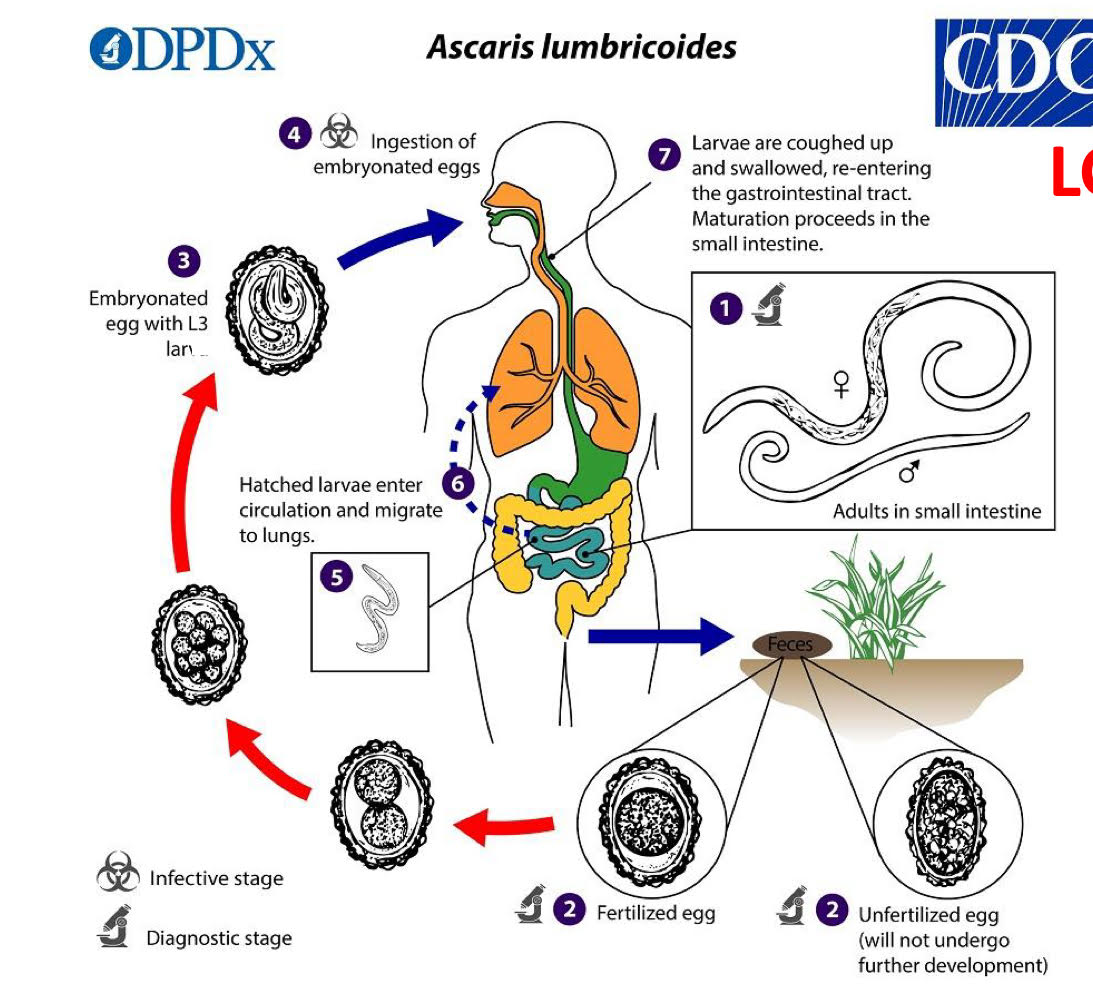
ascaris lumbricoides life cycle
unembryonated eggs in feces
embryonation
L2 inside egg
egg ingested
hatch in SI
molt 2x (=L4)
enter circulation
migrate to lungs
L4 coughed up and swallowed
molt to adult in SI.
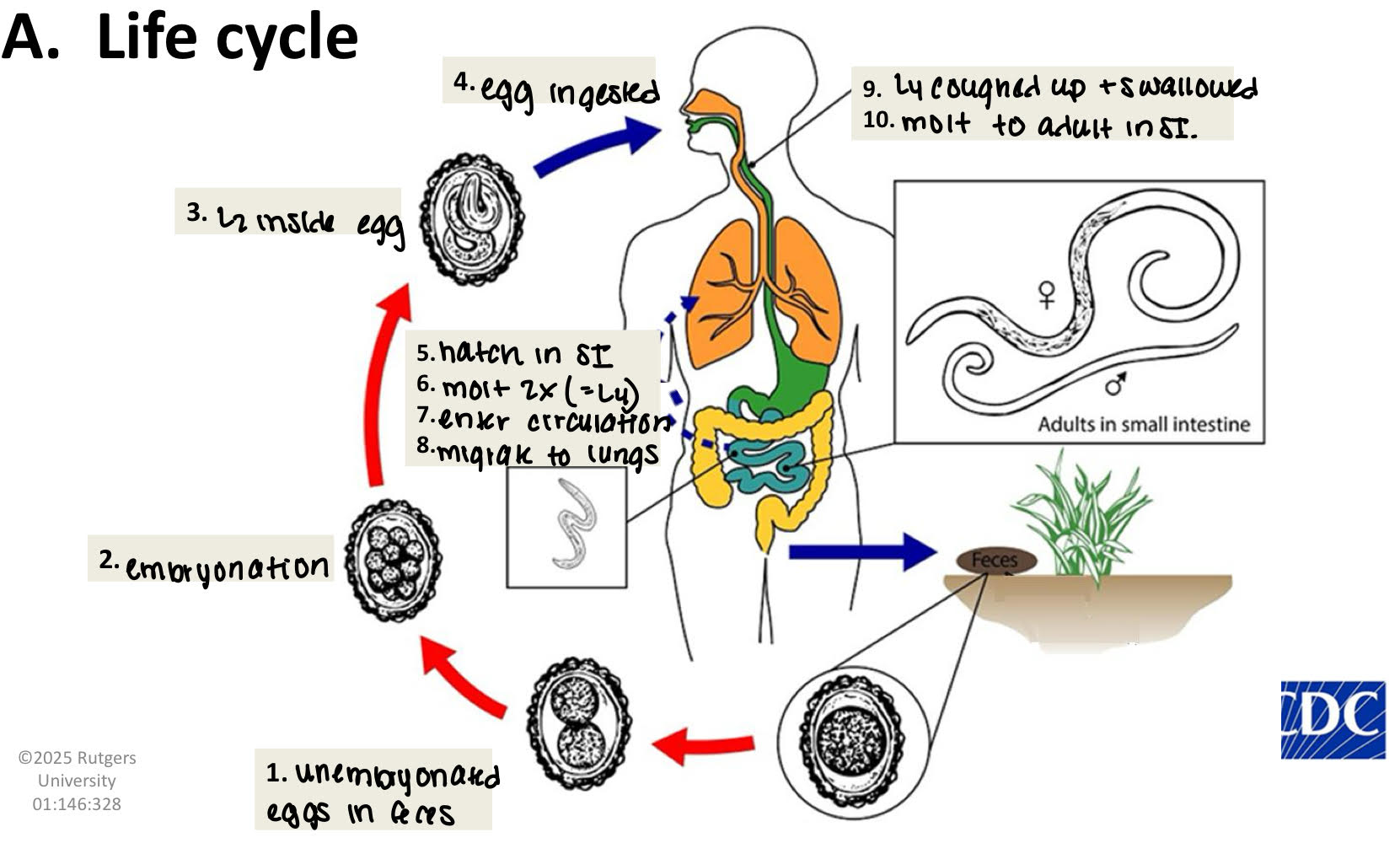
ascaris lumbricoides eggs morphology
mammilated
proteinaceous layer (outermost)
thick, bumpy
absorbs bils → golden brown
VERY RESISTANT
lipid layer (innermost)
ascarosides
unique to ascaris
eggshell impermeable to H2O soluble substance
ascaris lumbricoides adult morphology
large
males: 30 cm x 3mm
females: 35 cm x 5mm
mouth surrounded by 3 lips
female
27 million eggs in uterus.
releases 200,000 eggs per day.
massive contamination
ascaris lumbricoides pathology
migration
L2 get lost + die
ex. spleen, liver, brain
inflammation
granuloma (contains the threat from spreading)
pulmonary
L2 damage lung capillaries
blood pools + tissue damage
lung congestion
secondary bacterial infection
Intestinal
pain
allergic response to waste (rashes and asthma)
obstruction
pierce intestine→ peritonitis → death
wander
ascaris lumbricoides diagnosis
eggs in feces
ascaris lumbricoides treatment
albendazole, mebendazole
ivermectin
surgery
hookworms life cycle
unembryonated eggs in feces
embryonation
L1 hatch
feed on feces + molt 2x
L3 (penetrates your foot)
L3 enters circulation
migrate to lungs
molt to L4
L4 coughed up + swallowed
molt → adult → live in SI
2 species:
ancylostoma duodenale
necator americanus
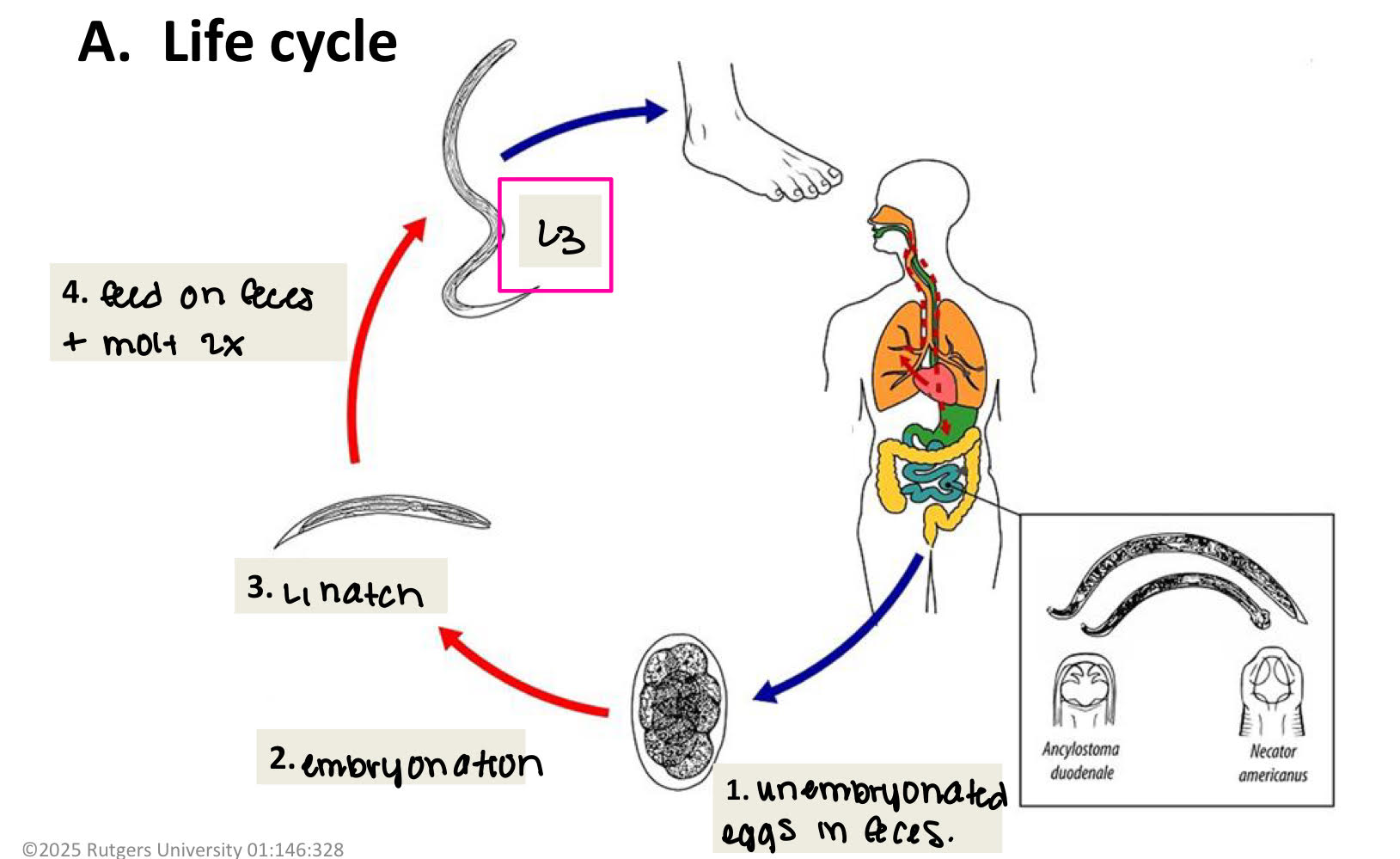
hookworm egg morphology
oval, thin shell
difficult to identify spp.
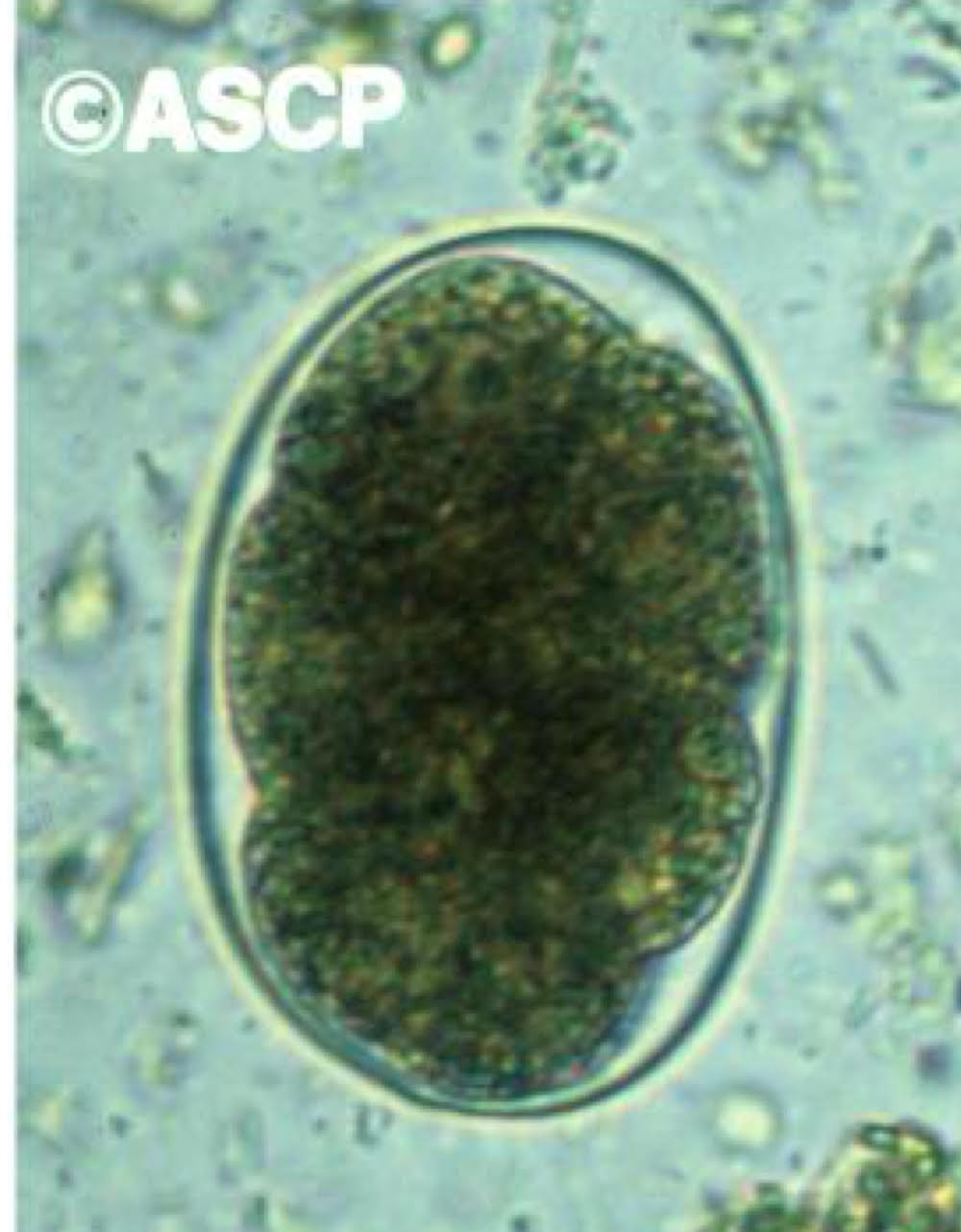
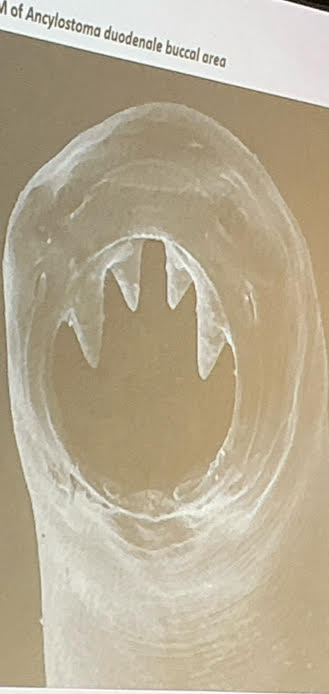
hookworm adult morphology
ant end curved dorsally
large buccal cavity
teeth or cutting plates
males
copulatory bursa
hookworm pathology
invasion
L3 enter sin
ground itch
local rash + irritation → inflammatory reaction to bacteria
migration
lungs
L3 break out of capillaries + into alveoli
pneumoia + coughing
intestinal
most serious stage
burrow into intestinal mucosa → feed on blood (anticoagulants)
blood loss
Na ~ 0.03 ml blood/worm/day
Ad ~0.2 ml blood/worm/day
worms survive 2-14 years
anemia
stunted growth + cognitive function
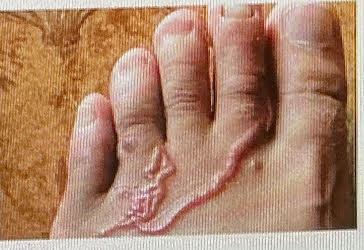
hookworm diagnosis
eggs in feces
hookworm treatment
albendazole + mebendazole
iron therapy
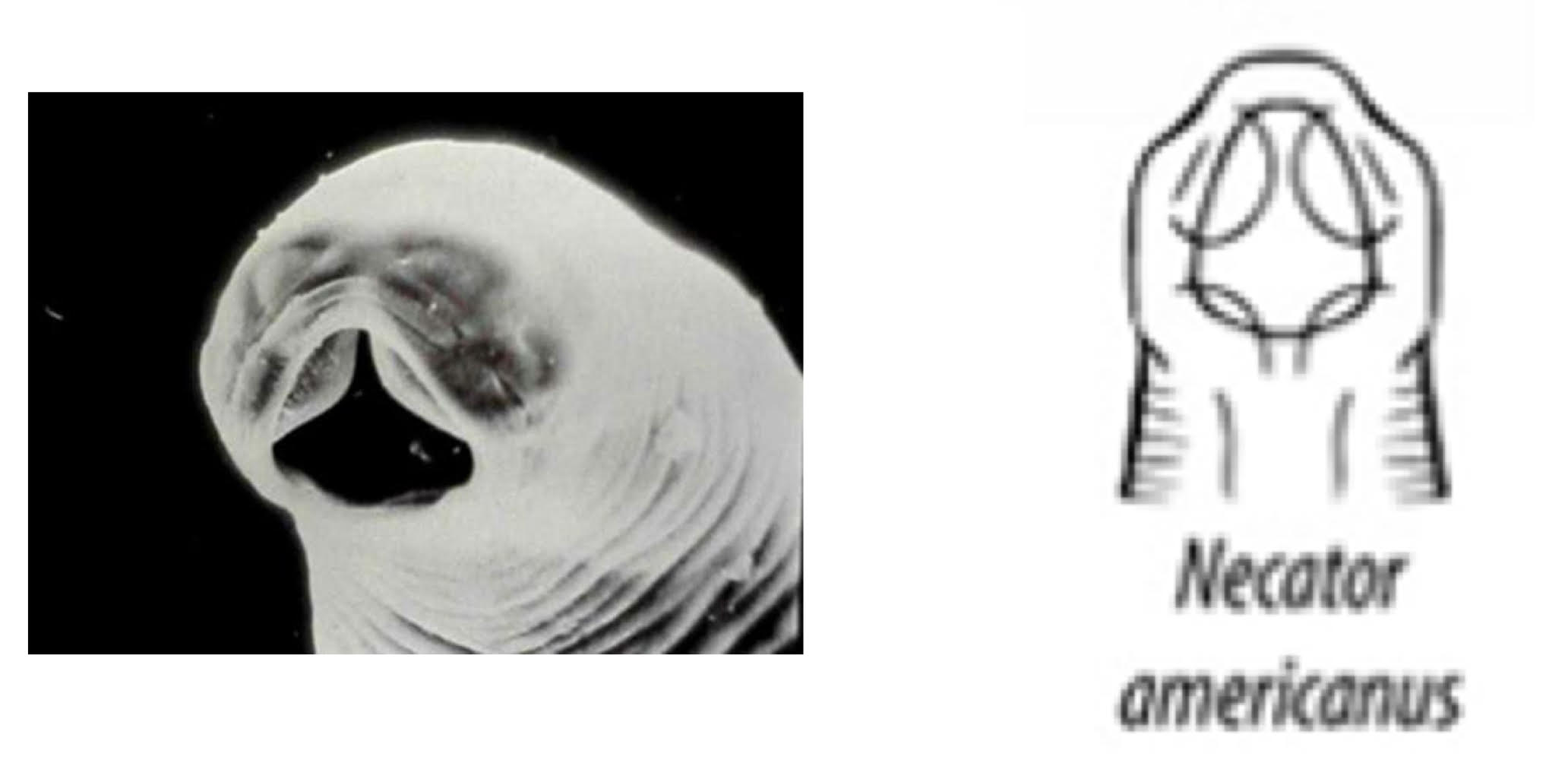
Necator americanus (hookworm)
from SE US + South America '
Buccal cavity
anterior: 4 cutting plates
posterior: 4 teeth
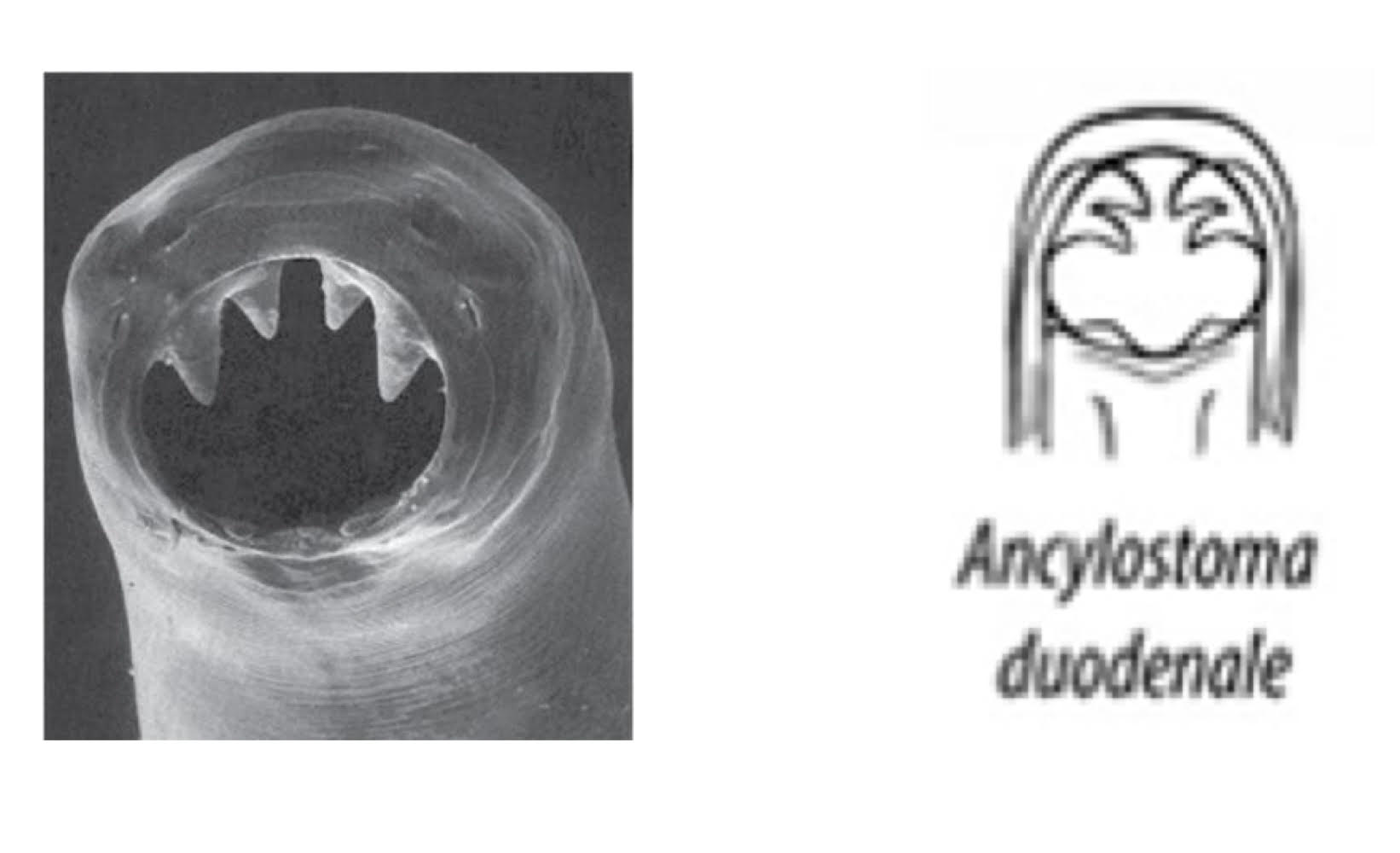
ancylostoma duodenale (hookworm)
from Europe, Asia, Africa
buccal cavity
anterior: 2 cutting plates (each with 2 teeth)
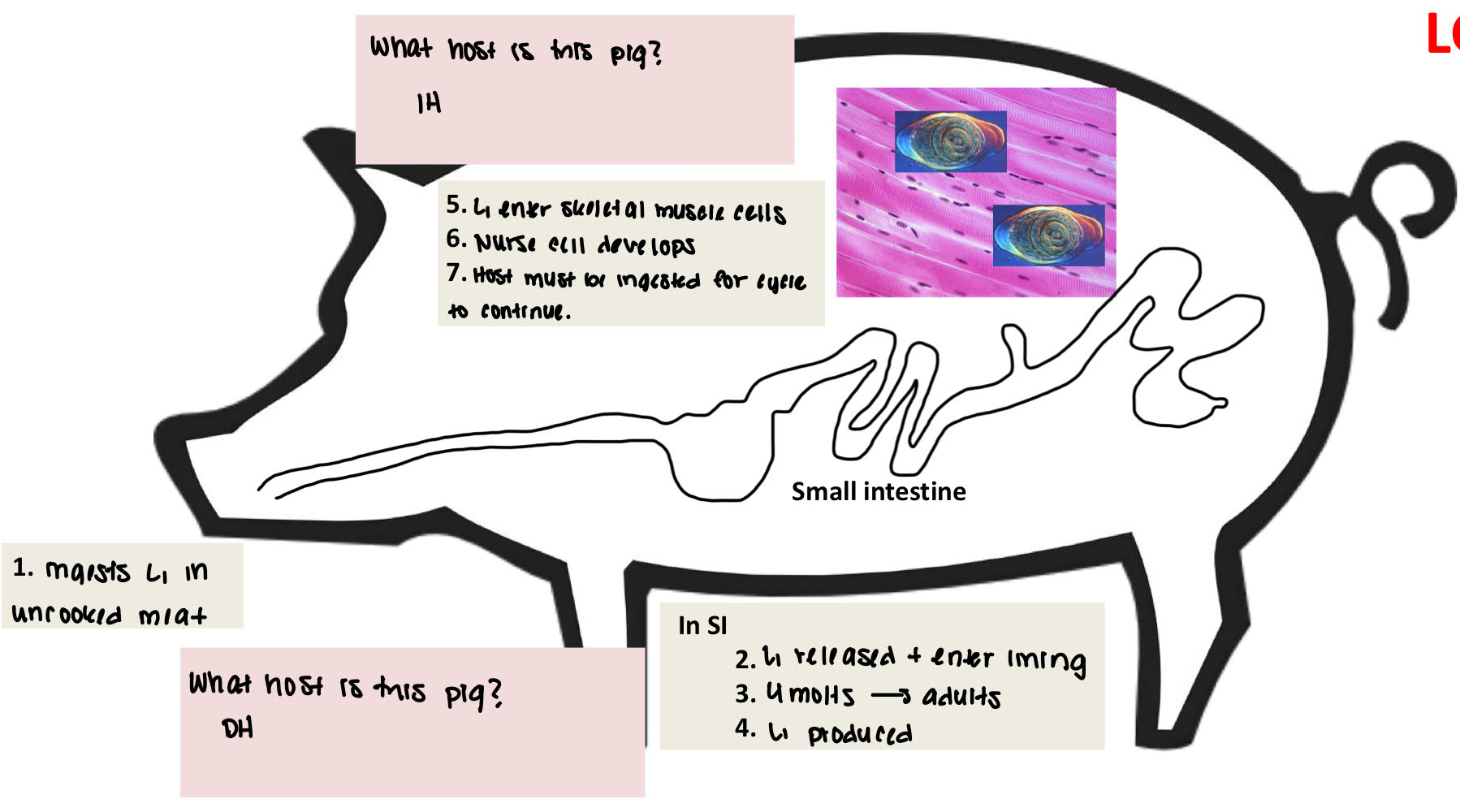
Trichinella spiralis life cycle
ingests L1 in uncooked meat (pig is DH)
(in SI) L1 released + enter lining
4 molts→ adults
L1 produced
(pig becomes IH) L1 enter skeletal muscle cells
nurse cell develops
host must be ingested for cycle to continue
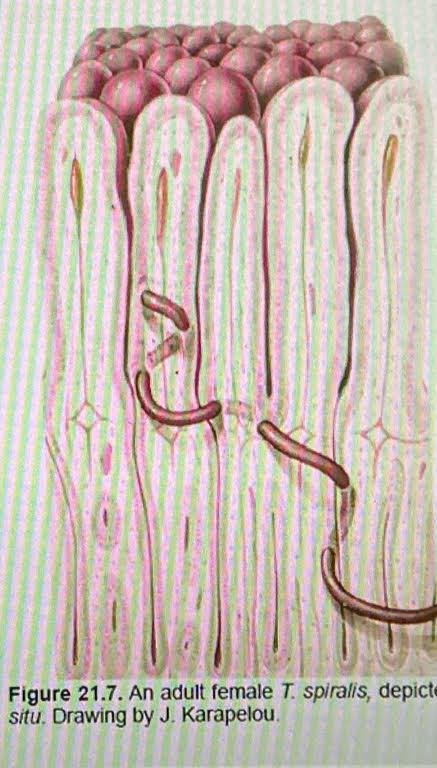
Trichinella spiralis morphology
very small
females: ~ 3mm
males: ~ 1.5 mm
stichocytes
glandular cells in esophagus
excretory-secretory antigen (ESA)
live in SI
intramulticellular in epithlial cells (within many cells)
female
ovoviviparous → L1
they do produce eggs but do not release the eggs. Instead, they hatch inside the uterus.
Trichinella spiralis pathology
intestinal phase (mild)
worms penetrate intestinal mucosa.
lesions + inflammation
nausea, diarrhea, fever, abdominal pain
migration phase (severe)
L1 migrating through body → muscle pain
tongue, diaphragm, jaw→ difficulty breathing, chewing, swallowing
inflammatory phase (moderate)
strong immune rxn to larvae
heart damage, nerve disorders
disease called trichinosis
Trichinella spiralis diagnosis
ELISA
detects antibody against ESA
muscle biopsy
clinical symptoms
Trichinella spiralis treatment
mebendazole + albendazole
relieve symptoms
bed rest
corticosteroids
O2
Anisakis simplex life cycle
marine mammals= DH
crustaceans= 1st IH
fish= 2nd IH
humans ingests raw/insufficiently cooked fish → ingests L3 = accidental host
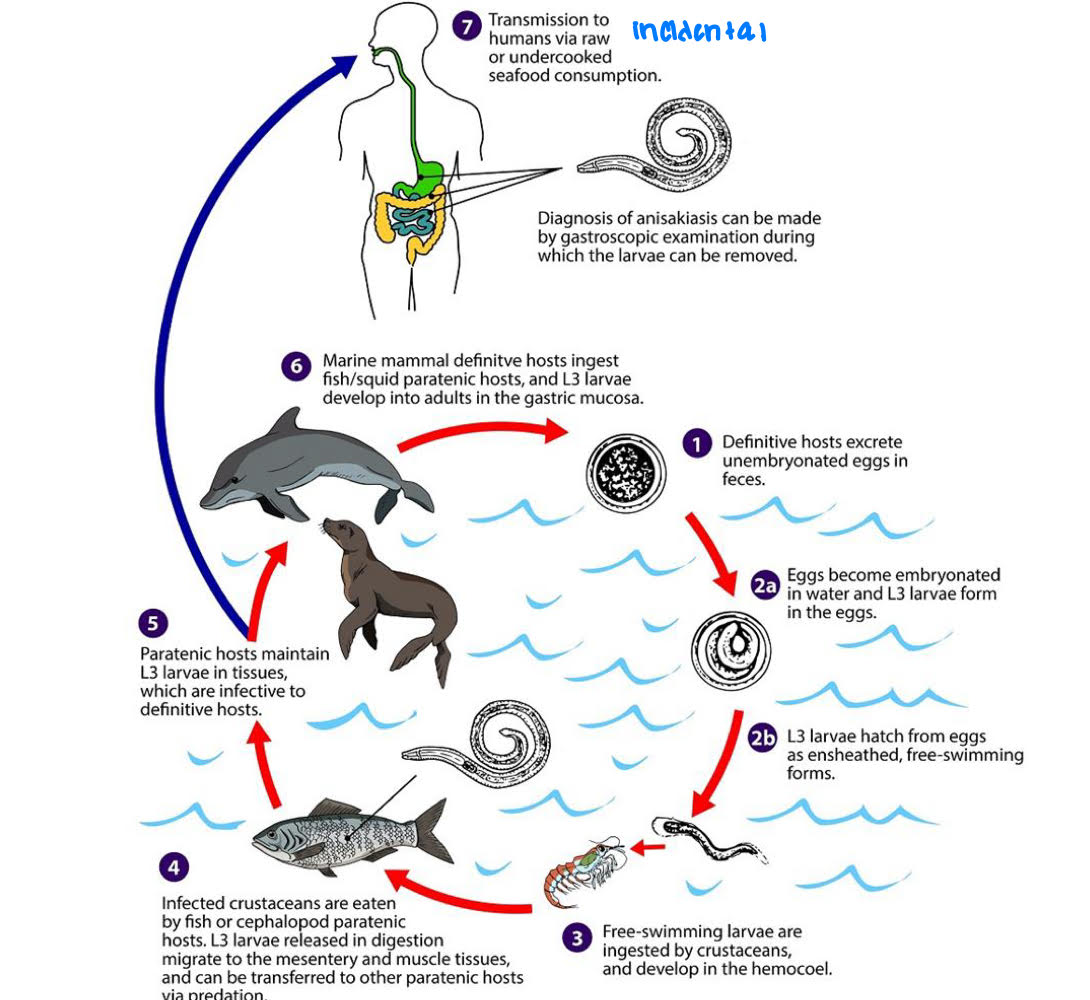
Anisakis simplex pathology
L3 invade stomach wall or intestinal wall
Acute
intense abdominal pain
nausea + vomitting
Chronic
Abscesses (pocket of pus)
granulomas
Anisakis simplex diagnosis
gastrointestinal symptoms
endoscopy or x-ray
Anisakis simplex treatment
removal
albendazole
Dracunculus medinensis life cycle
human ingests H2O containing copecods with L3
L3 penetrate stomach/intestinal wall → enters sub-q tissue → molts to adult + mates
male dies → female migrates to skin surface (legs) → blisters
female emerges from blister → ovoviviparous → L1 into H2O.
L1 eaten by copecod (IH) → into hemocoel → molts to L3.
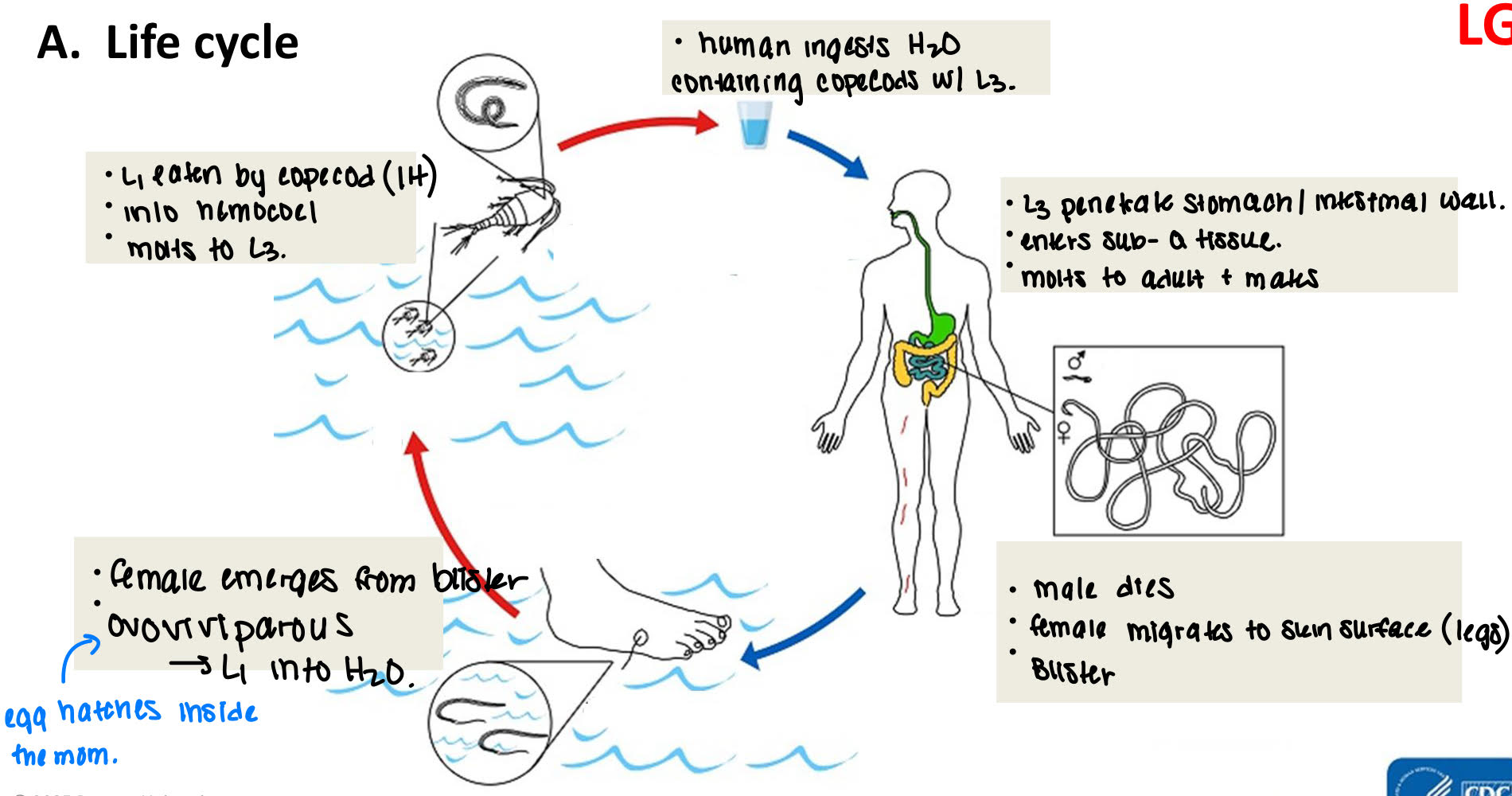
dracunculus medinensis pathology
blister
abscessed → pain
2o bacterial infection
non-emergent worms
do not reach skin surface
die → calcified
arthritis
inflammation of one or more joints
dracunculus medinensis diagnosis
itchy, red blister with worm
dracunculus medinensis treatment
windworm on stick
pouring cold water can help stimulate the worm to come out faster
parasitologist’s dilemma
eradication may lead to lower death rate
if birth rate stays same, then pop size will increase
problem: if pop cannot be supported by available resources → decline in quality of life
general characteristics of filarial nematodes
live in blood or tissues
transmitted by vector
ovoviviparous
eggs hatch in uterus + microfilariae (mf) released
mf
advanced embryos
ingested by vector during blood meal
periodicity
in peripheral (hands, arms, legs…) blood only @ certain time
Wolbachia sp
intracellular gram negative bacterium
~75% of all insects
reprofunctions + sex determination
endosymbiont of many filarial spp
all stages
hypodermis (part of body wall) + repro tissue
LPS (lipopolysaccharide) → inflammatory response → pathology
doxycycline (antibiotic)
kills wolbachia (a bacterium)
adult filarial worms stunted + less mf develop
Wulchereria bancrofti life cycle
when mosquito takes a blood meal, saliva lumbricants and anticoagulants goes into the blood along with the L3.
L3 molts twice and becomes an adult
adults prodice sheathed microfilariae that migrate into lymphatic and peripheral blood circulation.
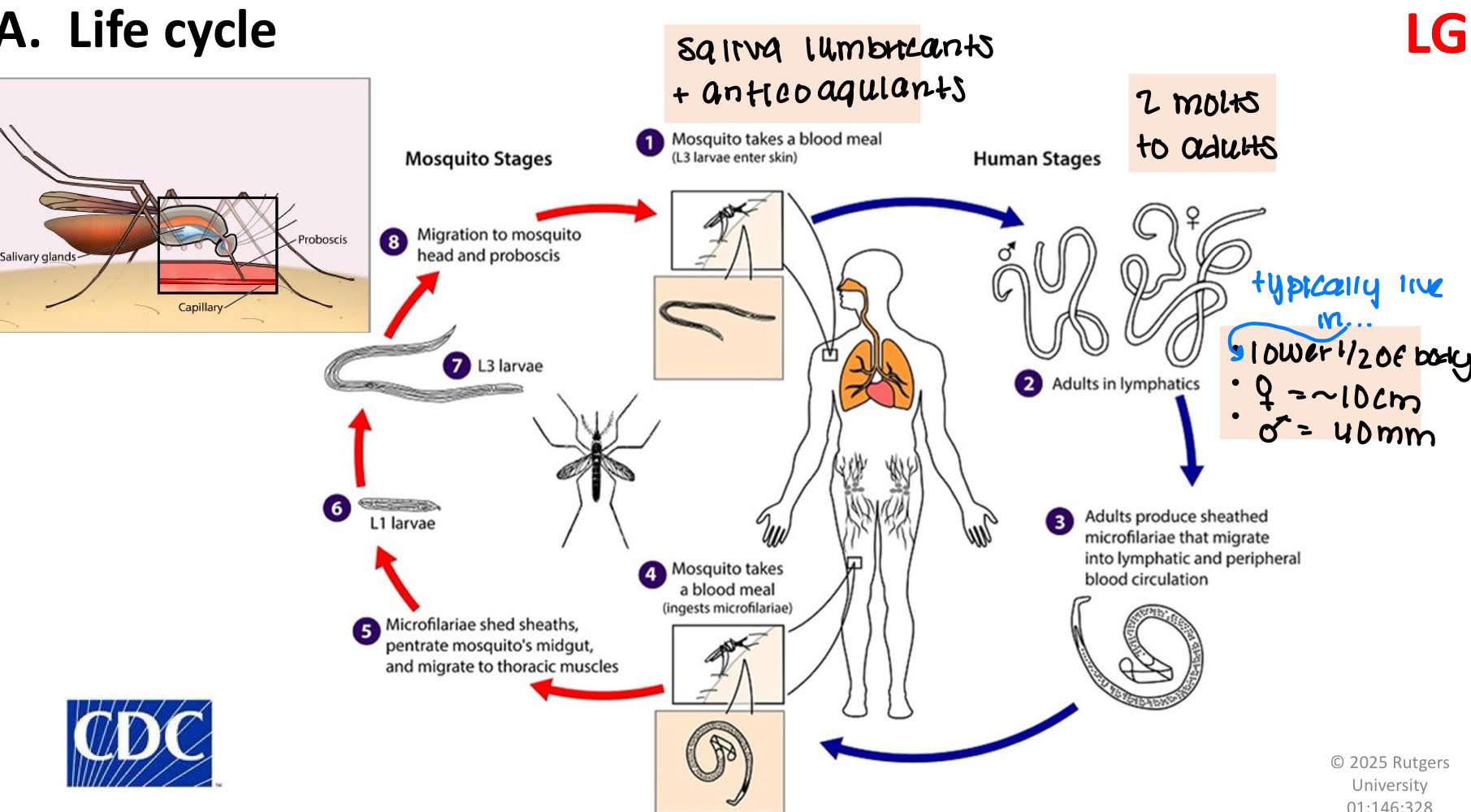
Wulchereria bancrofti pathology
incubation phase
asymptomatic
no detectable microfilaremia (not developed yet)
inflammatory phase (acute)
response to antigen from dying/degenerating adults
episodic adenolymphangitis (ADL)
attacks of fever, chills, and edema
Obstructive phase (chronic)
10-20 yr after 1st exposure
lymph tissue blocked
worms, granulomas, fibrous tissue, fat.
lymphoedema
legs, genitlas, arms, breats
hydrocele → swelling in scrotum
Wulchereria bancrofti diagnosis
mf in blood @ peak periodicity
Ciruclating Filarial Antigen (CFA) test
ELISA
droplet any time
ultrasound
worms in lymhatics
Wulchereria bancrofti treatment
exercise limb
chemotherapy → combination of
DEC= diethylcarbamazine → damages cuticle → immune response goes up
albendazole
ivermectin (=mectizan)
Hygiene
wash
shoes
antibiotic creams
Wulchereria bancrofti control
WHO
eradication
elimination
Why possible?
no animal reservoir
simple, accurate diagnostic tests
treatment
effective + inexpensive
large scale once/yr
variety of options/combos (resistance goes down)
collateral health benefits
plans of action
drug companies
Brugia malayi (Lymphatic filariasis)
adults
female= 55 mm
male= 25 mm
mf
periodicity= night
vector= mosquito
same as W.bancrofti in
life cycle
pathology
diagnosis
treatment
*only difference is the size. It’s a bit smaller than bancrofti
Onchocerca volvulus life cycle
blackfly (genus simulium) takes a blood meal (L3 larvae enter the bite wound)
subcutaneous tissues
adults in subcutaneuous nodule
adults produce unsheathed microfilariae that typically are found in skin and in lymphatics of connective tissues, but also occasionally in peripheral blood, urine, and sputum.
blackfly takes a blood meal (ingests microfilariae)
microfilariae penetrate blackfly’s midgut and migrate to thoracic muslces.
L1 larvae
L3 larvae
migrate to head and blackfly’s proboscis
mf
no periodicity
stay in skin + phototaxis
vector
blackfly (simulian spp.)
scarifies skin → pool of blood
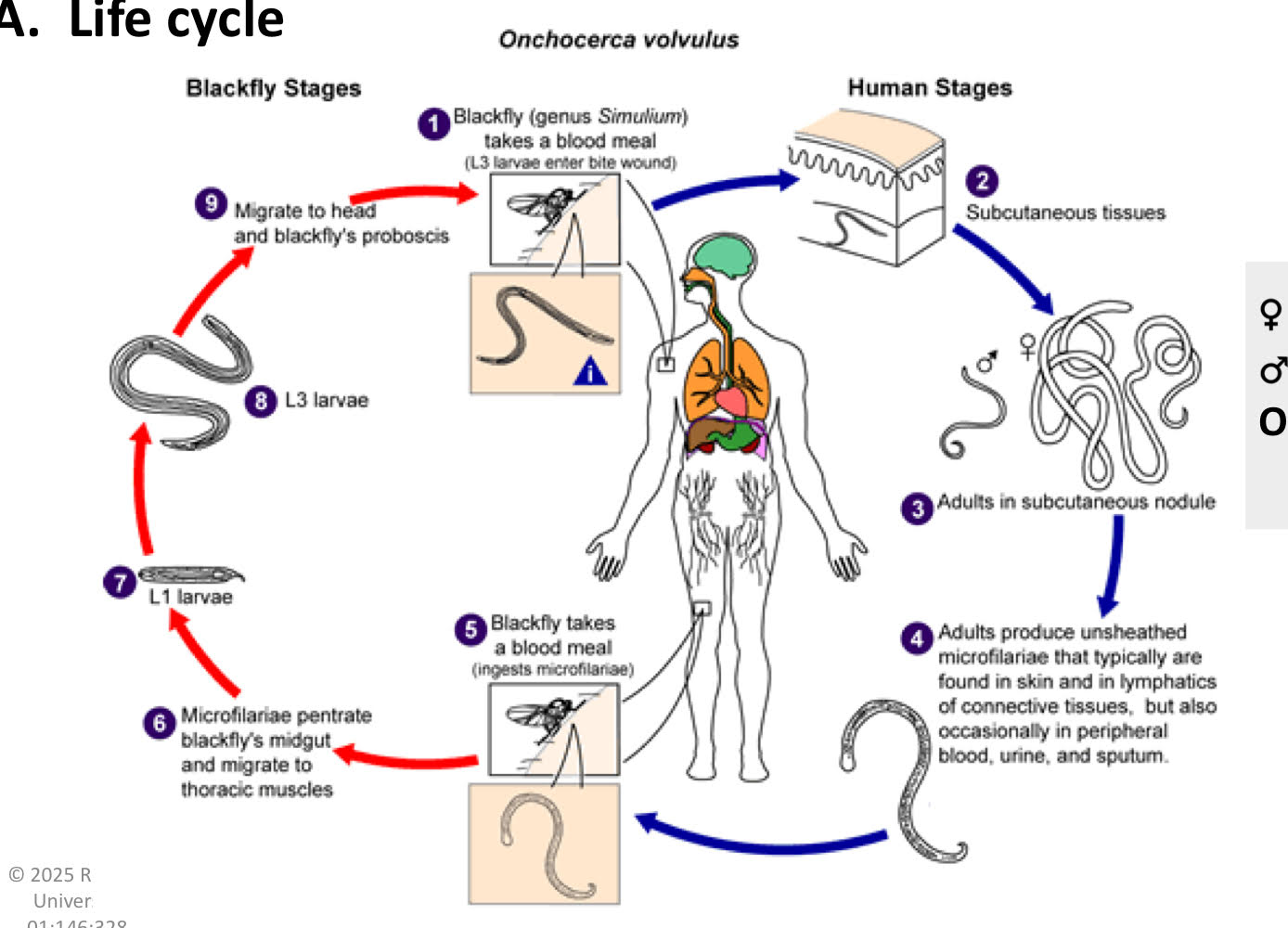
Onchocerca volvulus pathology
onchocercomas
benign
may cause disfigurement but does not cause too much problem.
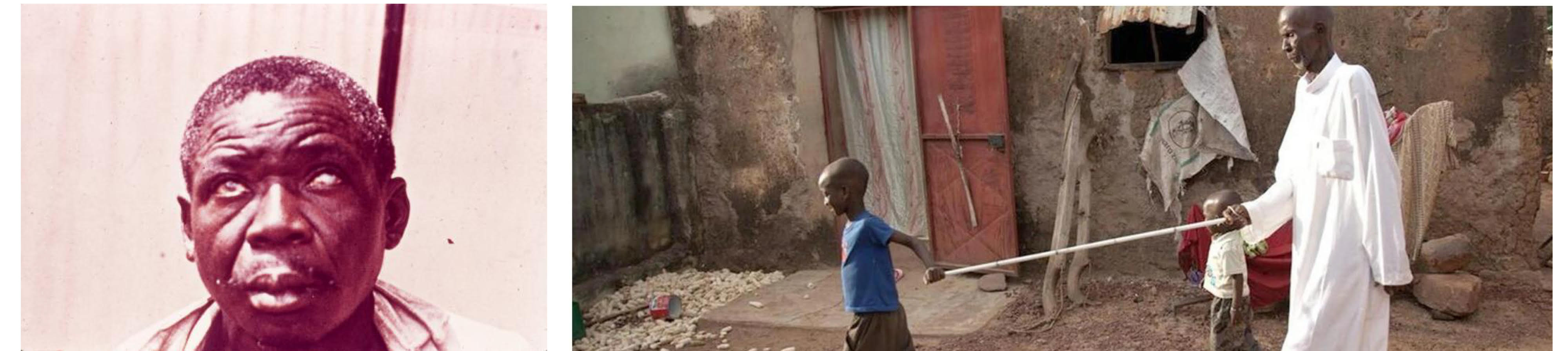
onchocerciasis
disease of skin + eyes
mf
alive= little pathology
dead/degenerating: host immune reponse
acute skin lesions: mf in skin
persistant, itchy rash
2o infections
skin thickens + local nymph enlarge
chronic skin lesions
skin thickened + discolored → “lizard”
loss of skin elasticity
hanging groins
femoral + inguinal lymph nodes enlarge + hand in loose skin
ocular lesion
mf invade eye + die
inflammatory rxn → blindness

Onchocerca volvulus diagnosis
skin raised + thin slice with razor
in saline on slide → microscope → mf
do NOT draw blood
Onchocerca volvulus treatment
ivermectin → kills mf
Doxycycline → kills adult worm
surgery
Onchocerca volvulus control
carter center river blindness program
since 1996 in 11 countries in Americas + Africa
mectizan (merce)
eliminated in
Columbia (2013)
Ecuador (2014)
Mexico (2015)
Guatemala (2016)

Loa Loa life cycle
fly (genus chrysops) takes a blood meal (L3 larvae enter bite wound)
adults in subcutaneous tissue
adults produce sheathed microfilariae that are found in spinal fluid, urine, sputum, peripheral blood and in the lungs.
fly takes a blood meal (ingests microfilariae)
microfilariae shed sheaths, penetrate fly’s midgut, and migrate to thoracic muscles
L1 larvae
L3 larvae
migrate to head and fly’s sproboscis
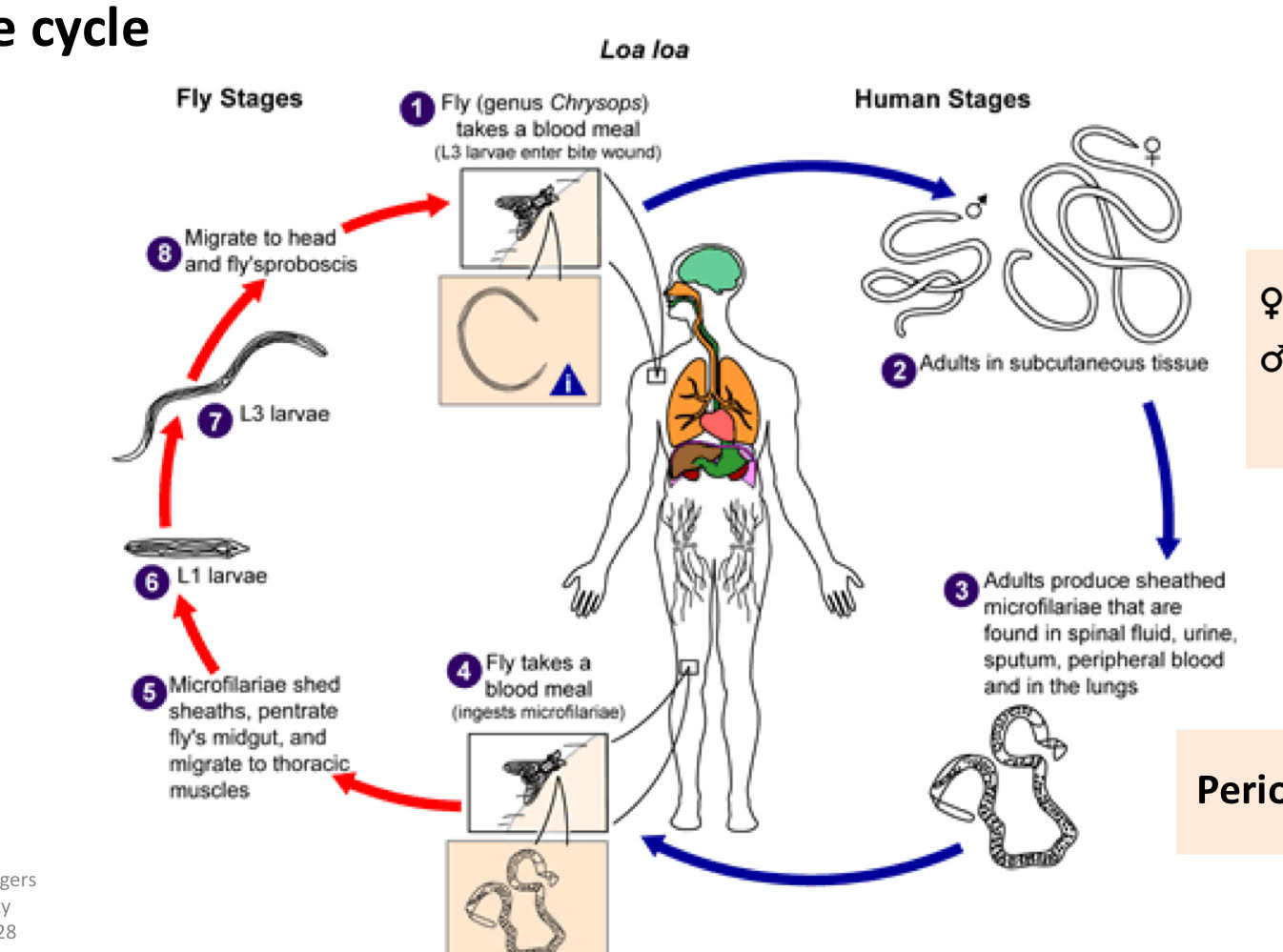
loa loa pathology
mild
adults wander in sub-Q tissue
calabar swelling
inflammatory rxn
localized, painful temporary
migration across eye
loa loa diagnosis
mf in blood
loa loa treatment
surgery
ivermectin + DEC
dirofilaria immitis (heartworm) life cycle
mosquito takes a blood meal (L3 larvae enter the bite wound)
adults in pulmonary arteries, and heart
adults produce microfilariae that typically are found in peripheral blood
mosquito takes a blood meal (ingests microfilariae)
microfilariae penetrate mosquito’s midgut and migrate to Malpighian tubules
L1 larvae
L3 larvae
migrate to head + mosquito’s proboscis
lesions in pulmonary vessels
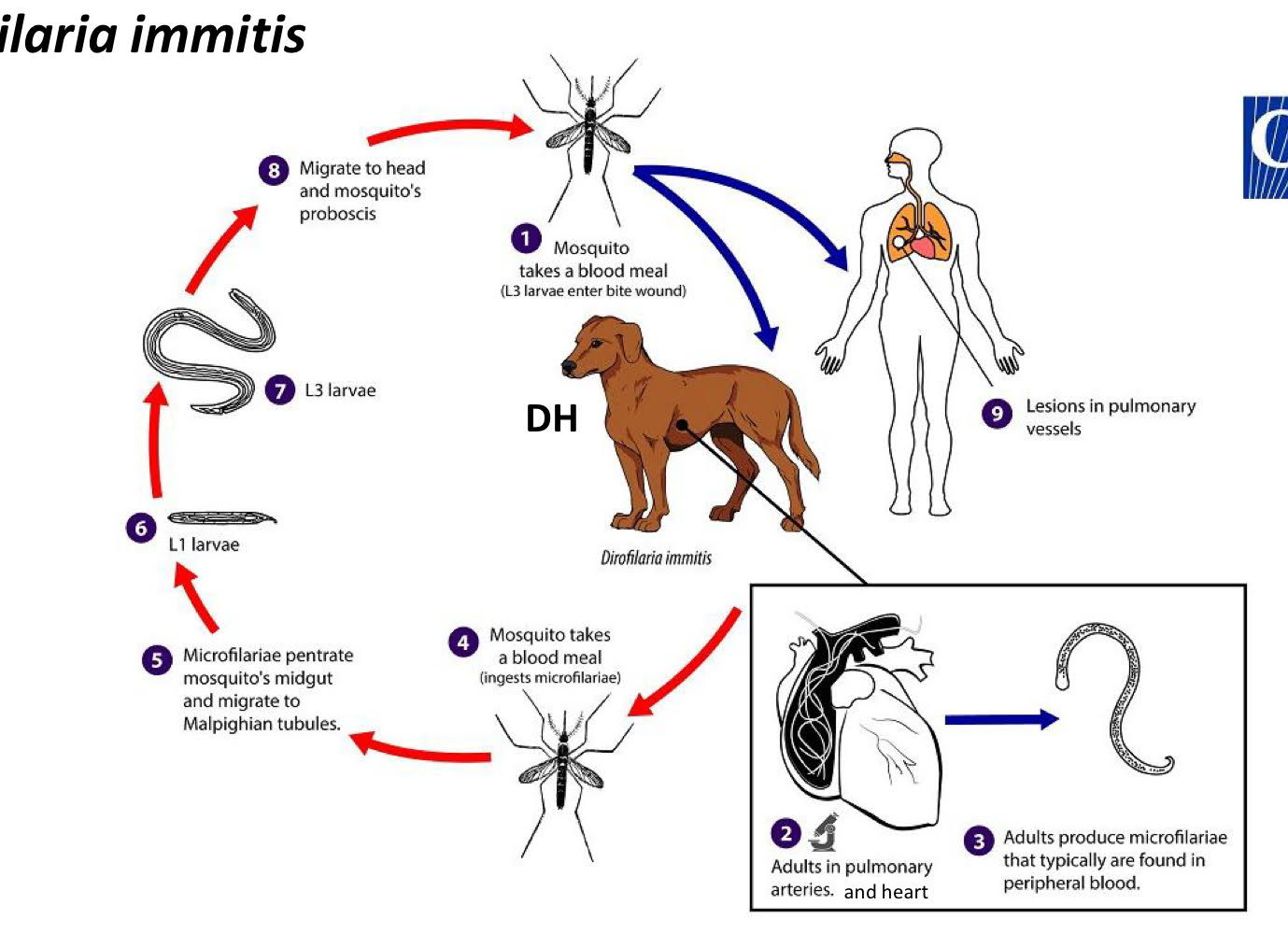
dirofilaria immitis pathology
heart function impaired
fatigue + loss of condition
cough + respiratory problems
dirofilaria immitis diagnosis
mf in blood
dirofilaria immitis treatment
immiticide
contains arsenic
toxicity → low margin of safety
kills adult worms (they live in the heart)
contraindicated in caval syndrome
worms in venae cava + rt atrium → block blood vessels
surgery
risky + expensive
human health
state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being, and not merely the absence of diease of infirmity (WHO)
public health
“the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life, and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private communities, and individuals.” ~CEA Winslow
epidemiology
basic science of public health
branch of medical science that studies facts which determine presence + absence of diseases + disorders
ascaris model life cycle
direct
no IH
no amplification
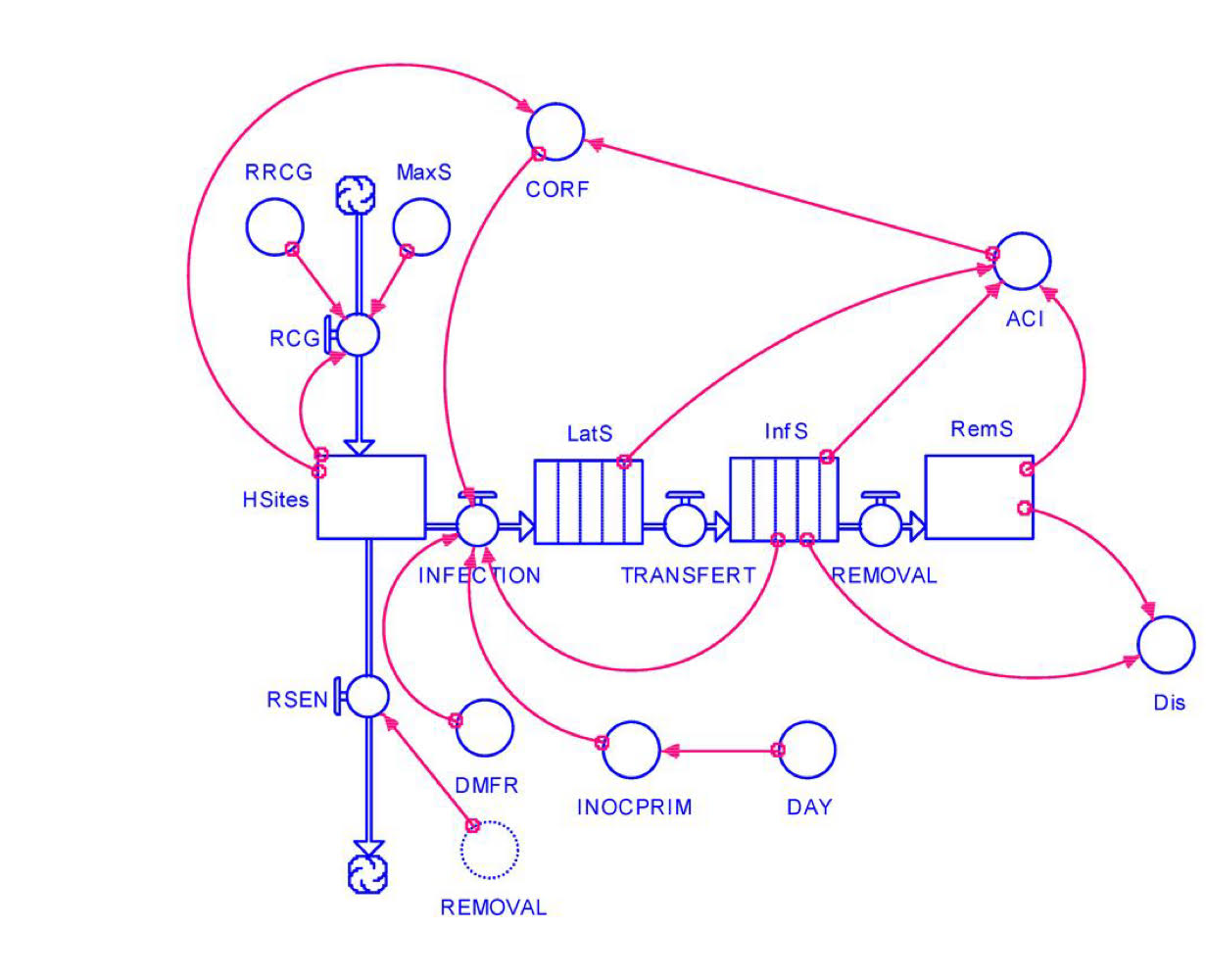
buidling ascaris model
r= per capita reproductive rate
rA= net reproductive rate
β= per capita transmission rate
chances the egg will actually get ingested + develop into an adult
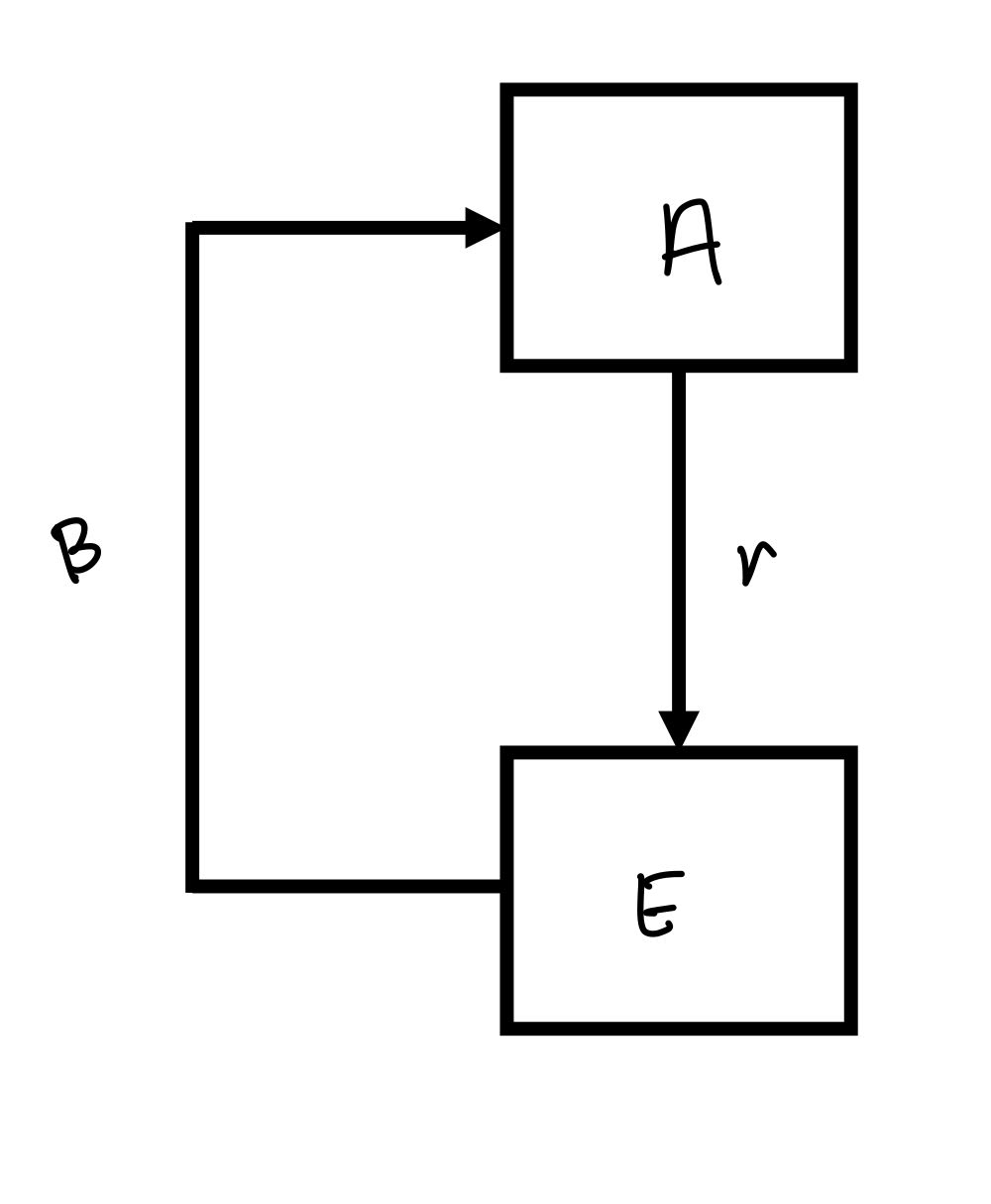
using model to control Ascaris infections
increase parasite elimination
Aμ1: increase μ1 by treating host
chemotherapy
Eμ2: increase μ2 by killing eggs in ext env. (ascaris eggs are very resistant to the ext env so this methoid would be difficult).
decrease parasite transmission (β)
↓ contact (ex. washing your hands)
↓ # of eggs (killing adult worms to prevent laying eggs)
↓ # hosts
↓ rA ( decreasing the rate of eggs being produced)
*best way to control is chemotherapy + education
eradication
no longer exists anywhere in the world
seldom (rare) realistic
elimination
localized eradication
no longer exists in a specfic geographical region
smallpox eradication - 1980
Ro= 2
natural exposure → long-lasting immunity
vax
long-lasting protective immunity
1 dose
easy to adminster
effective delivery + education campaign
fear of disease → public acceptance
no animal reservoir
govt cooperation
$$$
however most important? → vax
why parasite elimination + eradication are difficult
no vax available for any
Dracunculus
only parasite sp that may soon be eradicated
not bc of vax
because of education + other control measures
living standards are bad
poor sanitation
poor hygiene
poor meat insepction
lack of education
enterobius vermicularis life cycle
eggs on perianal folds
embryonated eggs ingested by human
larvae hatch in small intestine
adults in lumen of cecum
gravid female migrates to perianal region at night to lay eggs
retroinfection
eggs hatch in perianal area
L1 migrate back
autoinfection
hosts ingests eggs produced by worms in body
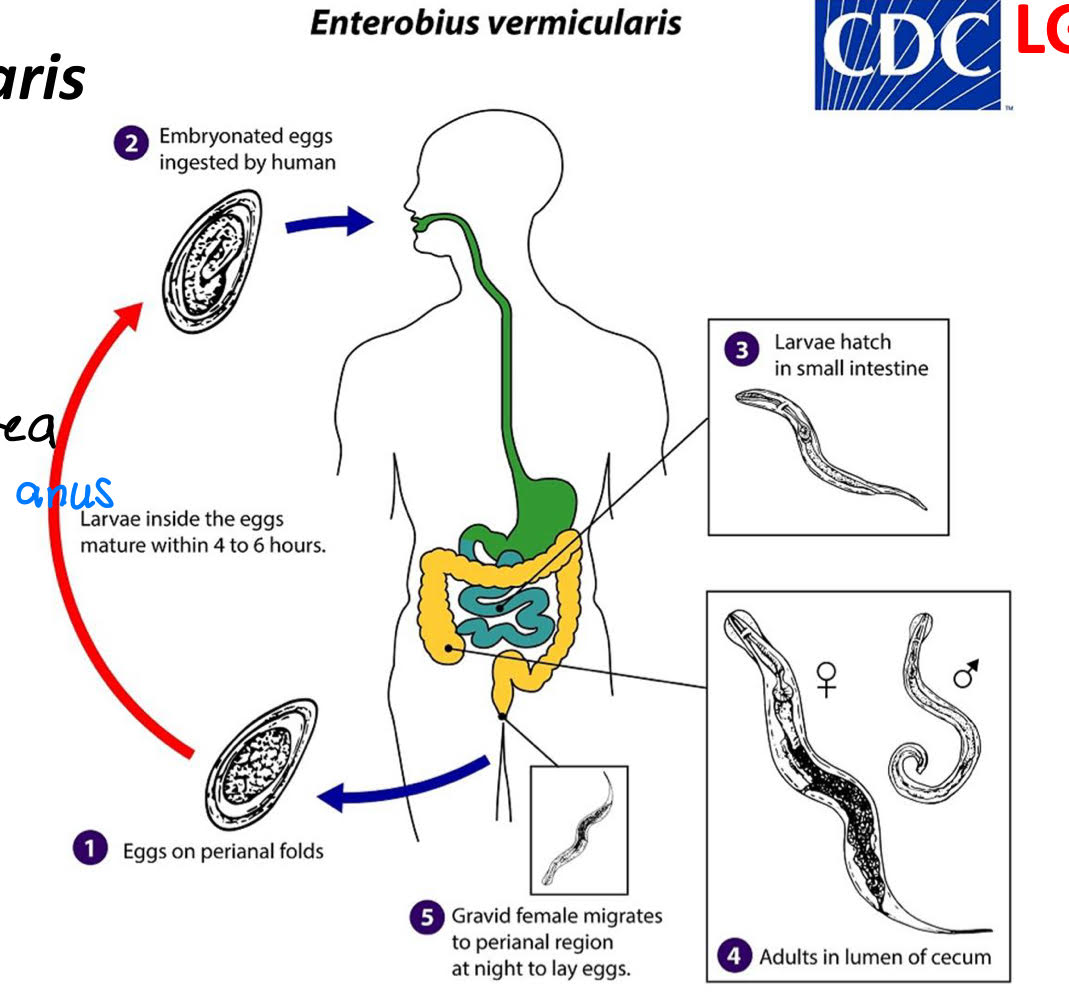
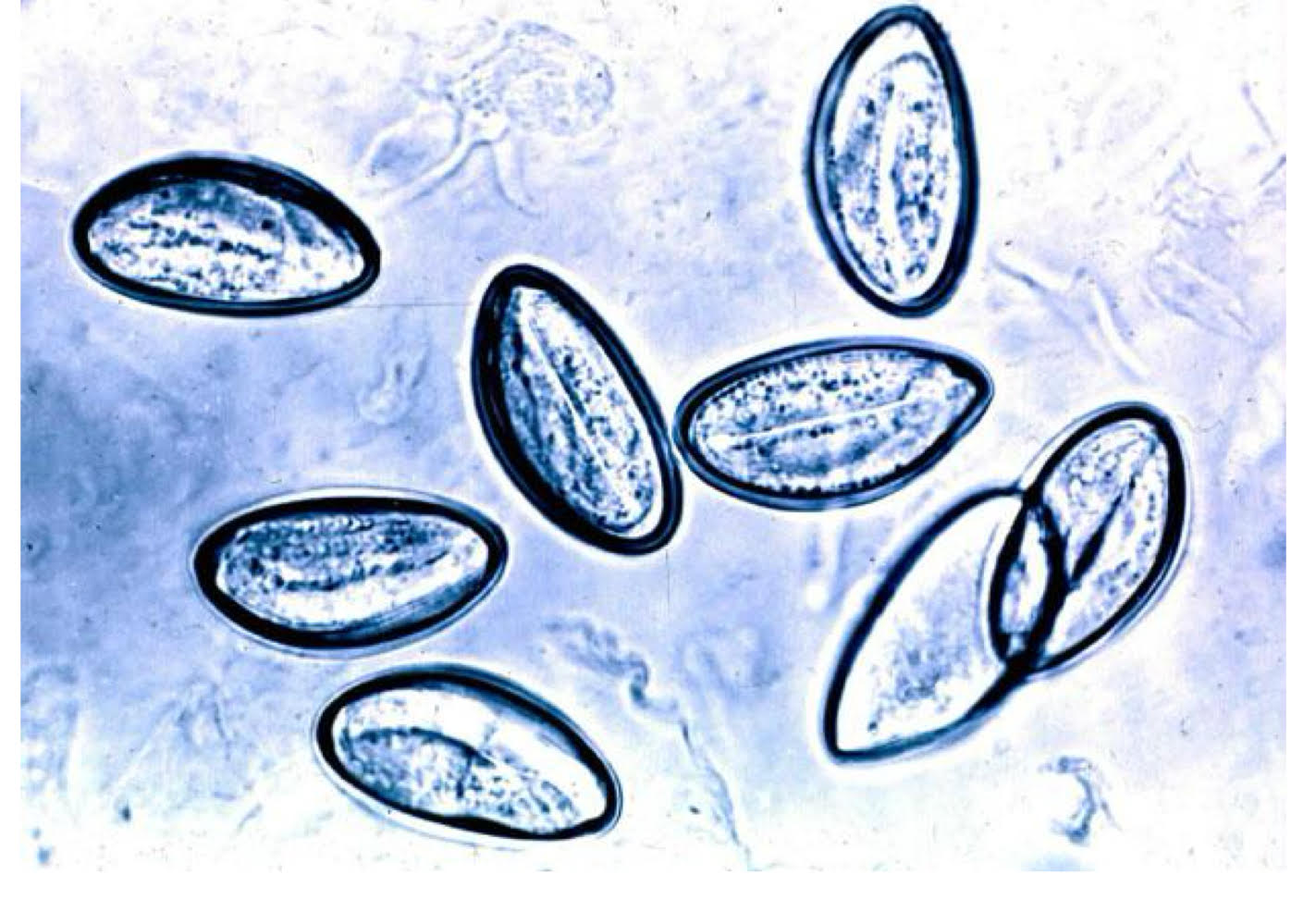
enterobius vermicularis morphology
eggs
flattened side
adults
alae
female → pinworm
male → curved posterior
enterobius vermicularis pathology
most asymptomatic
damage within intestine + around anus → inflammation + bacterial invasion
sleeplessness + irritiability
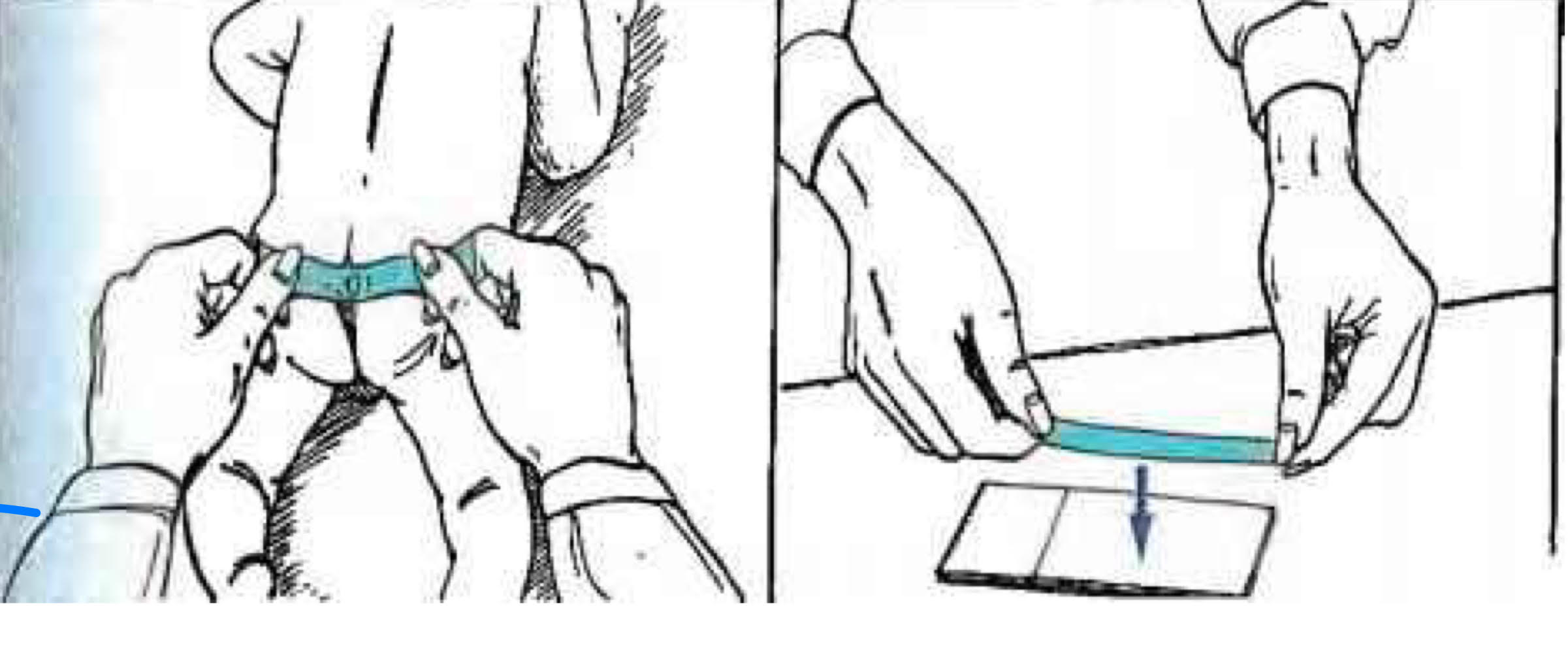
enterobius vermicularis diagnosis
scotch tape test
enterobius vermicularis treatment
pyrantel
albendazole
mebendazole
Protozoa
unicellular eukaryotes
heterotrophs
~ 45,000 spp.
Order Amoebida (Phylum Rhizopoda) habitat
most free-living
some in intestinal tract

Order Amoebida (Phylum Rhizopoda) symbioses w/ human
most commensals +/0
a few parasite +/-
Order Amoebida (Phylum Rhizopoda) 3 genera in humans
entamoeba
endolimax
iodamoeba
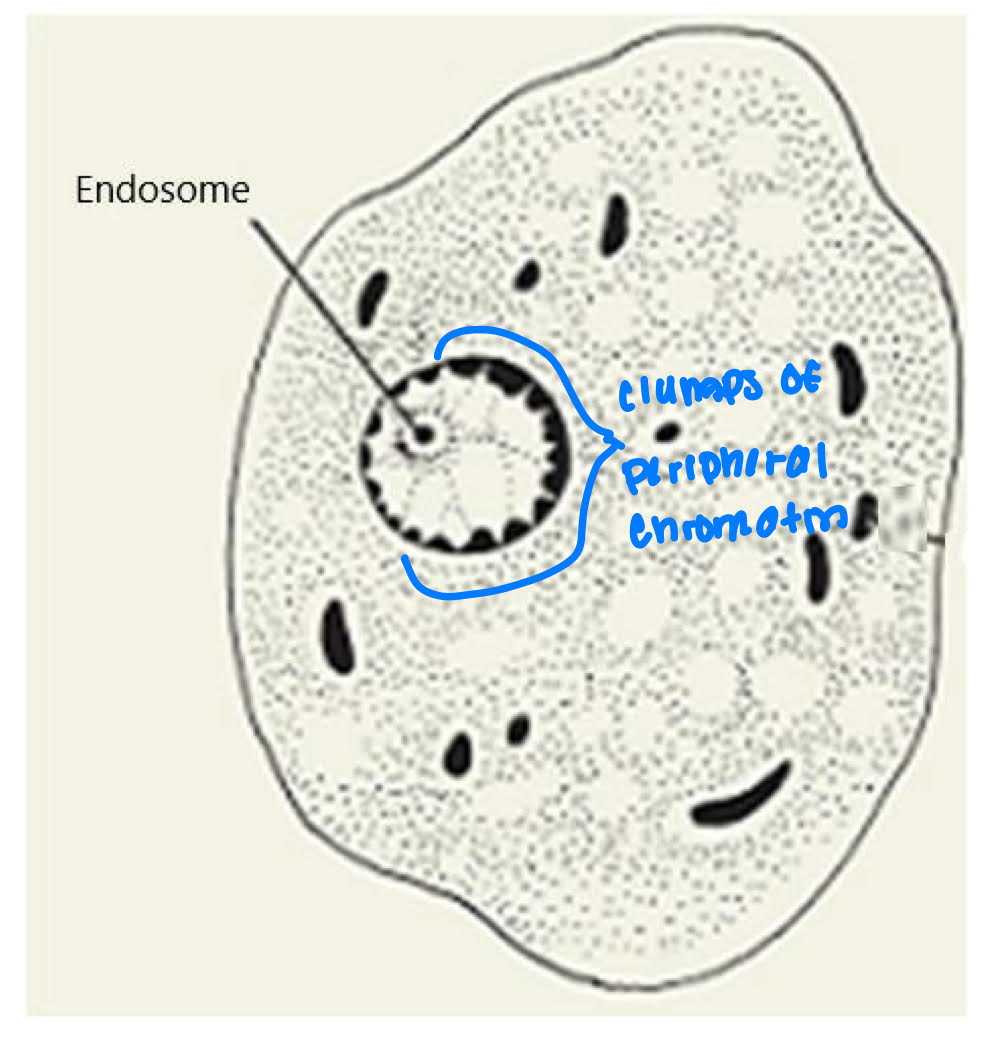
Genus entamoeba nucleus
distribution of peripheral chromatin (PC)
size + position of endosome
chromatin mass
small or large
centric or eccentric
Genus entamoeba life cycle
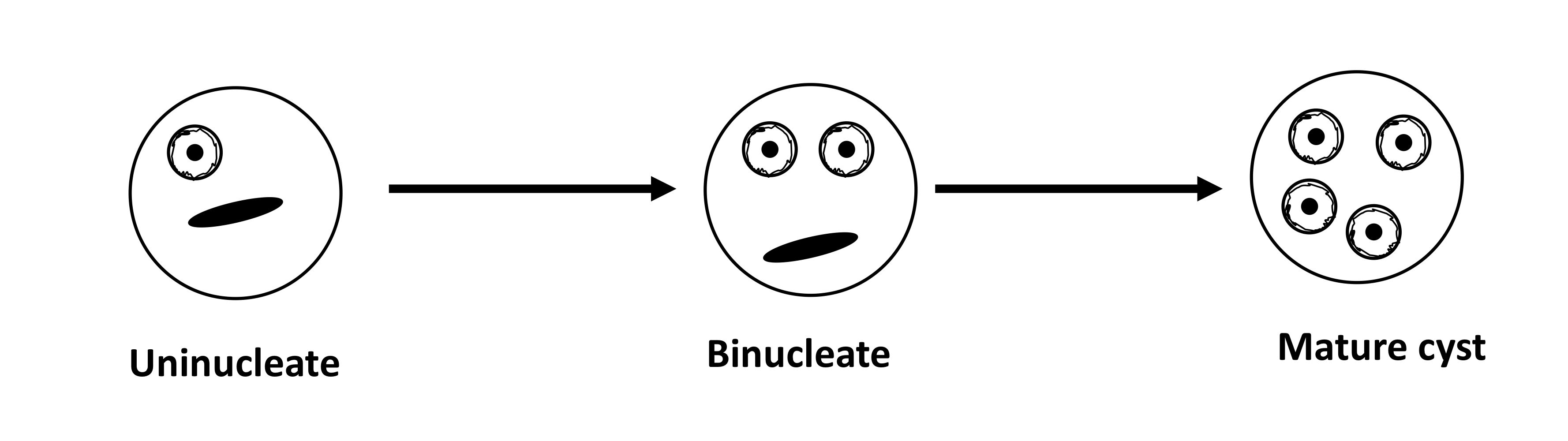
trophozoite
feeding stage
lives in host
cyst
exists host
resistant
transmission stage
chromatoidal bars
deposits of nucleic acids
morphology differs between spp
young cysts vs. old cysts
Entamoeba trophozoites morphology
~25 μm diameter
crypts of LI
starch + mucus
Nucleus
endosome= small + centric
PC= fine, evenly distributed
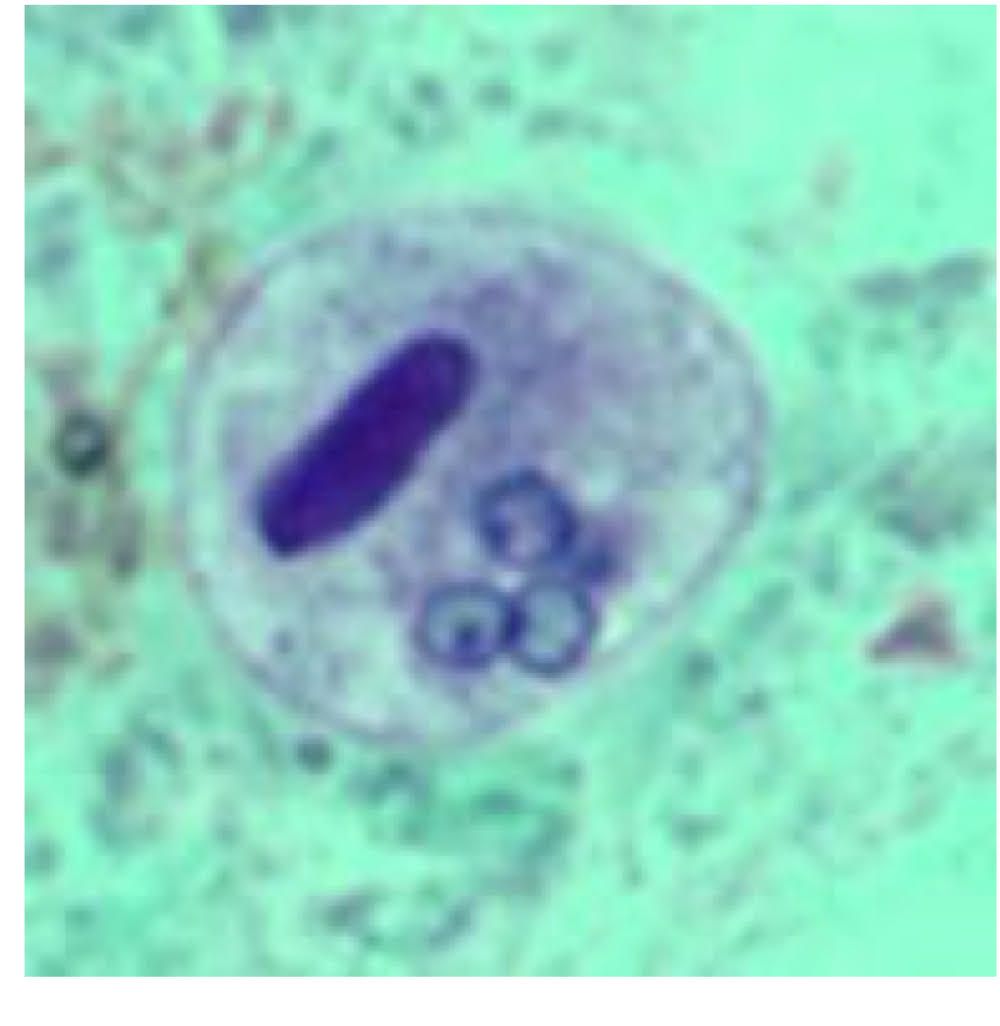
Entamoeba cyst morphology
10-20 μm diameter
young cyst
chromatoidal bar with rounded ends
entamoeba noninvasive pathology
noninvasive intestinal disease (luminal)
minor abdominal pain, cramps, diarrhea
asymptomatic
most self-resolve in a few months
pass cyst → carrier
entamoeba invasive Amoebic Colitis pathology
amoebic colits (infection at the colon)
trophozoites release secretagogue
substance that stimulates secretion of another substance → mucus secretion increase → depletion
gal/galNAc lectin
protein with high binding specificity for particular carbohydrate
on surface of trophozoite, binds galactose with high affinity
cytoadherence binds to surface of host cell
host cells that lack Gal residue on surface glycoportins → resistant
Amebapores → host cell lyses
cysteine proteases → tissue destruction
leads to flask-shaped ulcers, bleeding, electrolyte loss
amoebic colitis symptoms
symptoms take 2-4 weeks to develop
diarrhea, fever, nausea, vomiting
10-20 stools per day → dehydration
acute necrotizing colitis - tissue death
rare, but exteremely severe
most of mucosa is involved
severe bloody diarrhea
mortality exceeds 50%
Extraintestinal amoebiasis pathology (not in the intestine)
perforate intestial wall → peritonitis
enter circulatory system → ectopic sites → abscesses
amoebic liver abscesses
months to years after intial infection
fever, hepatomegaly, pain
pulmonary amoebiasis
direct extension of liver abscesses through diaphragm
cough, chest pain, dyspea + fever
no cycts formed → dead end
Entamoeba histolytica diagnosis
cysts in feces (luminal amoebiasis)
ELISA: detect antibody