Sports Unit 1 (section A)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is the purpose of the skeletal system
To provide structure, protection and movement.
They can also be used to store minerals.
What are the 4 bone types and each of their functions?
Long-Movement
Short-Shock absorption
Flat-Protection
Irregular-Support
What is an example of each bone type ?
Long-Femur
Short-Carpals
Flat-Skull
Irregular-Vertebrae
what are the 5 Joint types and examples of each?
Fixed-Skull
Hinge-Knee ,elbow
Ball and socket-Shoulder ,hip
Pivot-Neck
Gliding-Wrist
Name the two major parts of the skeleton and give one example bone from each
Axial skeleton (e.g., vertebrae) and Appendicular skeleton (e.g., femur).
What is a synovial joint and name two movements that occur at it.
A freely-moveable joint with a synovial cavity, fluid
Movements: flexion/extension, abduction/adduction.
what are 2 examples of synovial joints?
ball and socket and hinge
What are the 3 main types of joint classification?
Fibrous (fixed)
Cartilaginous (slightly moveable)
Synovial (freely moveable).
What are 3 bone examples of cartilaginous joints?
Vertebrae,sacrum or ribs
what are 2 characteristics of a fibrous joint?
They are fixed with no movement
The bones interlock with each other
What are 2 characteristics of cartilaginous joints?
They only allow limited movement
The bones are joined together by cartilage
What are 2 characteristics of synovial joints?
They allow free movement of the bone in any direction
They have a synovial cavity filled with synovial fluid which reduces friction
What are 3 examples of synovial joints?
shoulder,hip and knee
What is the difference between the axial and appendicular skeleton in terms of function?
The axial skeleton supports and protects the central nervous system and vital organs whereas the appendicular skeleton enables movement and supports limbs.
what does leverage mean in the skeletal system?
Bones act as levers and joints act as fulcrums and the muscles apply force to move the bones, enabling movement of the body or limbs.
How does a hinge joint differ from a ball-and-socket joint?
A hinge joint allows movement in one plane like flexion/extension in the knee whereas a ball-and-socket joint allows a wide range of movement in many planes (e.g., shoulder/hip)
What are bones made from when you’re born?
mostly soft cartilage that slowly turns into hard bone.
What is the process called when cartilage turns into bone?
ossification
Where does bone growth in length happen?
At the growth plates (epiphyseal plates) near the ends of long bones.
what do osteoblasts do?
they build new bone tissue by secreting collagen
what do osteoclasts do?
they dissolve bone minerals
how does exercises affect bone growth
Weight-bearing exercise (like running, makes bones denser and stronger.
what do weight bearing activities do in terms of exercise?
They bear the weight of the body and they absorb shock which reduces the risk of injuries.
what is the function of ligaments?
Ligaments connect bones to other bones which gives strength to stop unwanted movement
what is the name of the top of the vertebrae and how many bones does it have?
cervical - 7 bones
what is the name of the middle of the vertebrae and how many bones does it have?
thorarcic - 12 bones
what is the name of the lower middle of the vertebrae and how many bones does it have?
lumbar - 5 bones
what is the name of the bottom of the vertebrae and how many bones does it have?
sacrum - 5 bones
what is the name of the very end of the vertebrae and how many bones does it have?
coccyx - 4 bones
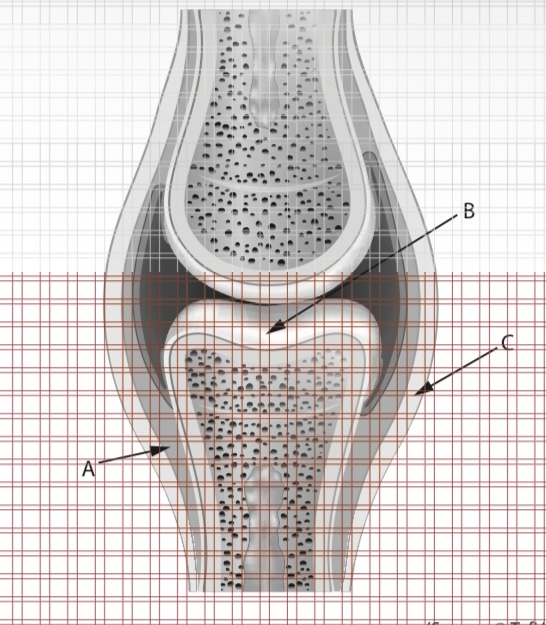
a- bone
b-cartilage
c-synovial membrane
2 types of posterior deviations
scoliosis - lateral curve of the spine to the right/left
kyphosis - outwards curve of the thoracic part of the spine.
what does cartilage do?
reducing friction and absorb shock
what is the function of the synovial membrane?
To secrete synovial fluid
What’s the function of the bursa and where is it found?
To reduce friction and found in synovial joint
What is arthritis?
Disease of a skeleton that is mainly developed by people over 40 and usually in women
What is Osteoarthritis?
Causes articular cartilage to thin and it causes pain and lack of mobility.
What is Osteoporosis?
The reduction in bone density caused by a lack of calcium which makes the bones brittle.