B- Lactams Antibiotics
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
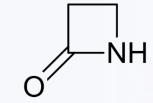
The β-lactam ring
What structural feature defines β-lactam antibiotics?
- Antibiotic Activity
Penicillin G (benzylpenicillin)
What was the first antibiotic used in therapy?
Penicillin V (phenoxymethyl penicillin)
What is the biosynthetic relative of penicillin G?
Gram-positive bacteria
What type of bacteria are penicillin G and V most effective against?
Cephalosporins
What is the second major group of β-lactam antibiotics?
Penicillinase-producing staphylococci and Gram-negative bacilli.
Which bacteria are semisynthetic β-lactam antibiotics (cephalosporins) particularly effective against?
Potent and rapid bactericidal action and low toxicity in the host.
What are the two properties that contribute to the importance of β-lactam antibiotics in chemotherapy?
Selective inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis.
What makes β-lactam antibiotics lethal to bacteria?
Transpeptidase enzyme
Which enzyme do β-lactam antibiotics inhibit?
It catalyzes the biosynthesis of dipeptidoglycan, providing strength and rigidity to the bacterial cell wall.
What does the transpeptidase enzyme do?
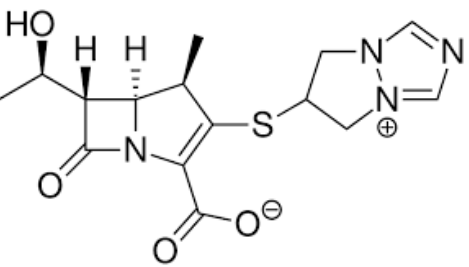
β-lactam thiazolidine structure.
The structure of the penicillin molecule shows a fused ring system of unusual design, the? (Parent Structure)
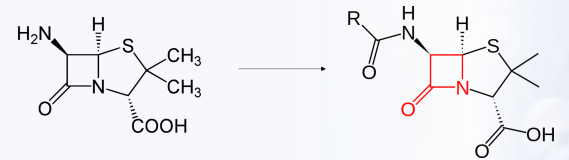
6-aminopenicillanic acid (6-APA)
What is the core compound/structure in penicillin?
Cysteine
Valine
Precursor of 6-aminopenicillanic acid (6-APA)
By acylating the 6-amino group with various side chains.
How is 6-aminopenicillanic acid (6-APA) converted into penicillins?
- Hydrolysis of the B-lactam ring in acid
- Hydrolysis of the B-lactam ring via B-lactamase
- Limited spectrum of activity
The structure of penicillins can be modified by attaching various moieties to the R-group to address at least one of three problems:
It stabilizes the penicillin to acid-catalyzed hydrolysis.
What effect does adding an electron-withdrawing group (addition of oxygen) at the α-position of benzylpenicillin have?
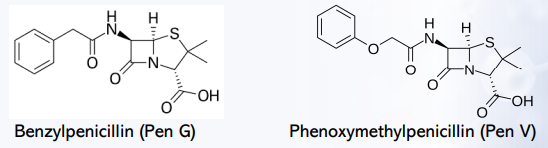
Benzylpenicillin (Pen G) to Phenoxymethylpenicillin (Pen V)
Example of Electron- Withdrawing Groups
Streptococcus pyogenes
Pen V is important to prevent what type of bacteria?
- The M protein is structurally similar to cardiac muscle tissue.
-Because of this similarity, the immune system may mistakenly attack the heart during a Strep A infection, leading to rheumatic fever and subsequent rheumatic heart disease.
Strep Throat
Streptococcus pyogenes is the causative agent of?
It confers resistance to β-lactamase (penicillinase).
What effect does adding bulky R-groups to the penicillin structure have?
β-lactamase (penicillinase) produced by Staphylococcus aureus.
Which bacterial enzyme do bulky R-groups on penicillin protect against?
Bulky
Staphylococcus aureus is a problem to what groups?
Methicillin
The first ever bulky group drug that is used for Staphylococcus aureus.
Vancomycin
Drug of choice for MRSA
Linezolid
Drug of choice for Vancomycin Resistance
Less active than either penicillin G or penicillin V
Disadvantage of the addition of Bulky Groups
Methicillin
Nafcillin
Oxacillin
Example of Bulky Groups
Introducing an Ionized or Polar Group
What modification of Penicillin G increases its activity against Gram-negative bacilli (broader spectrum of activity)?
Amino
Carboxyl
Urea
Examples of Polar Groups
Carbenicillin
Ticarcillin
Example of the Addition of Polar Groups
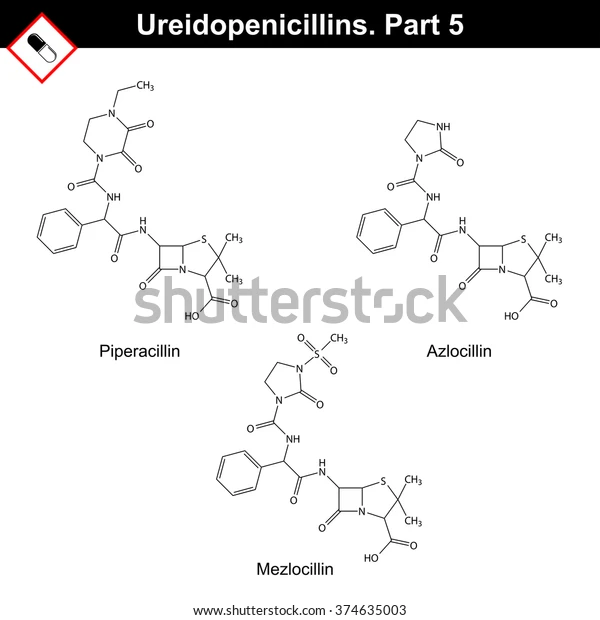
a-acylureido–substituted penicillins
Penicillins: Polar Groups
- Exhibit greater activity against certain Gram-negative bacilli than carbenicillin.
- Although these are acylated derivatives of ampicillin, the antibacterial spectrum of activity of the group is more like that of carbenicillin.
Klebsiella spp
Enterobacter spp.
P. aeruginosa
The acylureidopenicillins are, however, superior to carbenicillin against?
Azlocillin
Mezlocillin
Piperacillin
Examples of a-acylureido–substituted Penicillins:
Isoxazoyl Penicillins
Aminopenicillins
Examples of Penicillins that contain more than one modification:
Electron- Withdrawing Group
Bulky Group
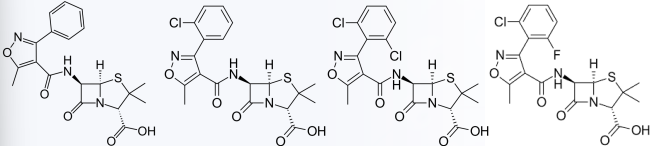
Isoxazoyl Penicillins Modification
Oxacillin
Cloxacillin
Dicloxacillin
Flucloxacillin
Examples of Isoxazoyl Penicillins Modification
Electron- Withdrawing Group
Polar Group
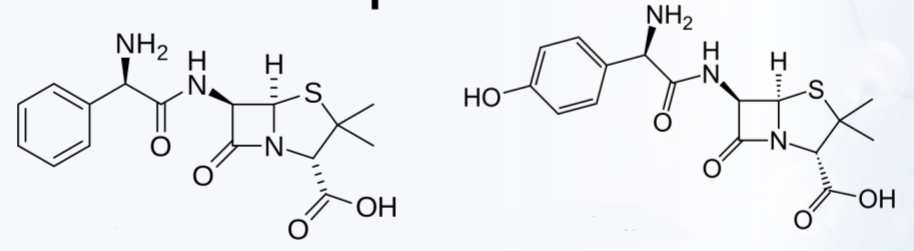
Aminopenicillins Modification
Ampicillin
Amoxicillin
Examples of Aminopenicillins Modification
β-Lactamase Inhibitors
Prevent the inactivation of β-lactam antibiotics by β-lactamase enzymes.
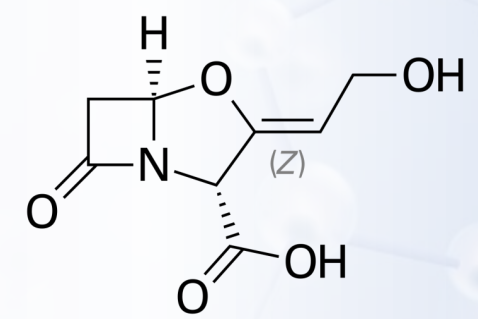
Clavulanic Acid
What was the first naturally occurring β-lactamase inhibitor discovered?
It causes potent and progressive inactivation of β-lactamases.
What is the mechanism of action of clavulanic acid?
- Sulbactam
- Tazobactam
What are two additional mechanism-based β-lactamase inhibitors synthesized after clavulanic acid?
Suicide Substrates
β-Lactamase inhibitors are sometimes called? (they are also substrates for the enzymes they inactivate)
Clavulanic acid
B-Lactamase Inhibitors
- Isolated from Streptomyces clavuligeris
- A potent inhibitor of S. aureus B-lactamase and plasmid-mediated B-lactamases elaborated by Gram-negative bacilli
- effective against B-lactamase–producing strains of S. aureus, E. coli, K. pneumoniae, Enterobacter, H. influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, and Haemophilus ducreyi, which are resistant to amoxicillin alone
Co-amoxiclav (Augmentin®)
What is the combination of clavulanic acid + amoxicillin called?
- Clavulanic (Protect Amoxicillin)
- Amoxicillin (Antibiotic)
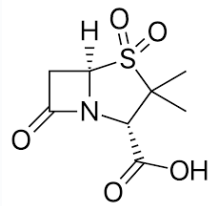
Sulbactam
B-Lactamase Inhibitors
- Has weak intrinsic antibacterial activity but potentiates the activity of ampicillin and carbenicillin against B-lactamase–producing S. aureus and members of the Enterobacteriaceae family
- Combined with ampicillin as sterile powder for injection (Unasyn®)
Unasyn® (sterile powder for injection)
B- Lactamase Inhibitors
What is the combination of sulbactam + ampicillin called?
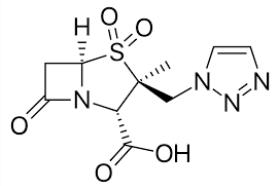
Tazobactam
B-Lactamase Inhibitors
Available in fixed-dose, injectable combinations with piperacillin consisting of an 8:1 ratio of piperacillin to tazobactam by weight (Zosyn® , Piptaz®)
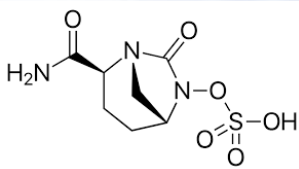
Avibactam
B-Lactamase Inhibitors
Available in combination with ceftazidime (Avycaz®)
Thienamycin
Imipenem–Cilastatin
Carbapenems: 1st Generation
B- Lactamase
Carbapenems are resistant to?
Dihydropeptidase
Carbapenems are metabolized by what enzyme?
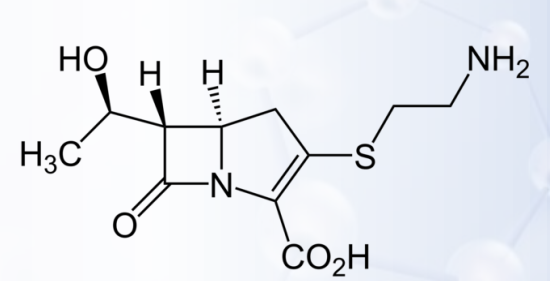
Thienamycin
CARBAPENEMS
- First carbapenem antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces cattleya.
- Highly active against most aerobic and anaerobic Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, including S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, and B. fragilis.
- Resistant to inactivation by most β-lactamases, making it effective against many strains resistant to penicillins and cephalosporins.
Imipenem- Cilastatin (Primaxin®)
CARBAPENEMS
- The combination provides a chemically and enzymatically stable form of thienamycin that has clinically useful pharmacokinetic properties
Cilastatin
Dihydropeptidase-I inhibitor that prevents the renal degradation of imipenem.
Meropenem
Biapenem
Carbapenems: 2nd Generation
Meropenem
CARBAPENEMS
- Approved for the treatment of infections caused by multiply resistant bacteria and for empirical therapy for serious infections, such as bacterial meningitis, septicemia, pneumonia, and peritonitis
- Exhibits greater potency against Gram-negative and anaerobic bacteria than does imipenem, but it is slightly less active against most Gram-positive species

Biapenem
CARBAPENEMS
- Has broad-spectrum antibacterial activity that includes most aerobic Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria and anaerobes
- Stable to DHP-I and resistant to most B-lactamase