Zoology ppw 1
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
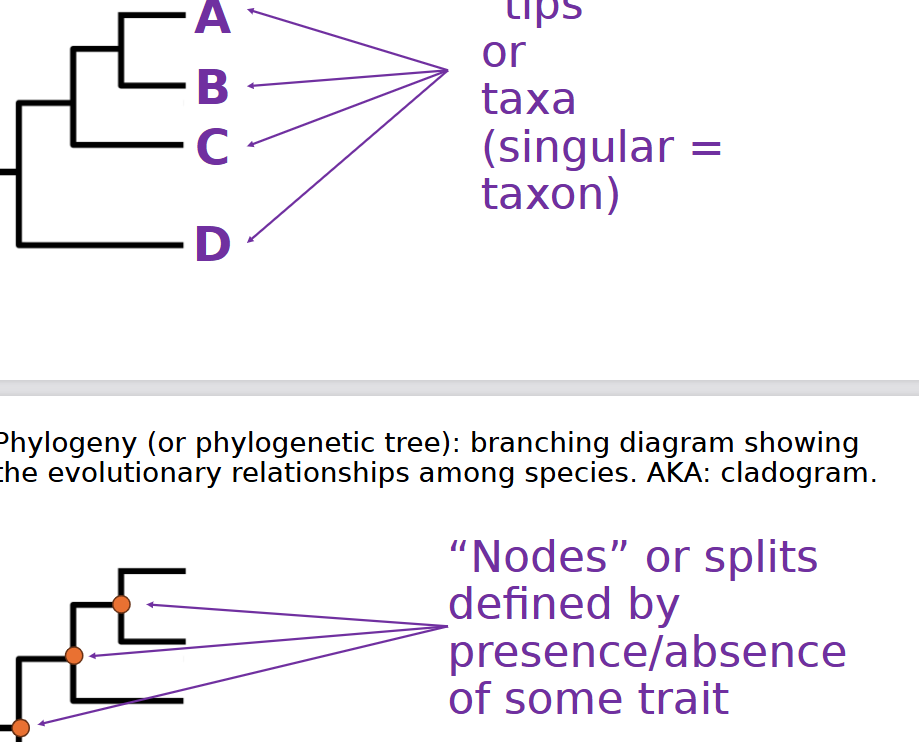
phylogeny/phylogenetic tree
branching diagram showing the evolutionary relationships among species (cladogram?)
tips/taxa vs. nodes
singular taxon vs splits defined by presence or absence of some trait
phylogenies can be rotated on any
node
phylogenetic systematics
classifying organisms based on evolutionary relationships
Linnean taxonomy
classifying organisms based on shared characteristics
clade
set of all taxa descended from common ancestor

clades are monophyletic which means
they include ancestor and all of its descendants
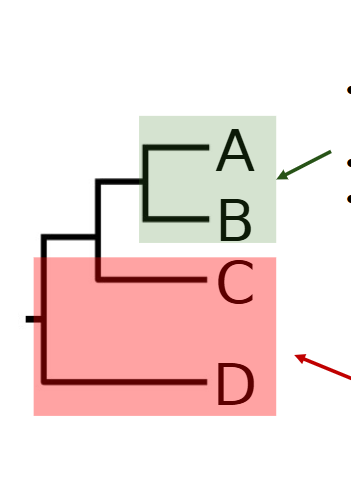
why is the red not a clade
it does not include all of the descendants of the common ancestor; so it is paraphyletic
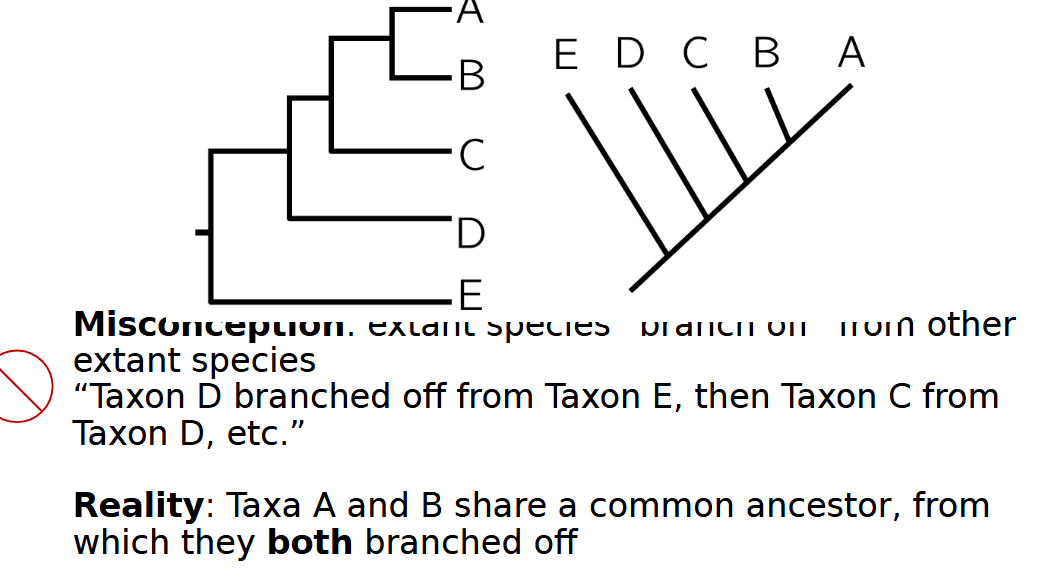
common misconception about phylogenies
the top or most right taxons are the most evolved; in reality no currently living organism is more evolved than another
common misconceptions about outgroups
another misconception is no change in primitive taxa after divergence

common misconception of extant species
they branch off from other extant species, instead they share a common ancestor
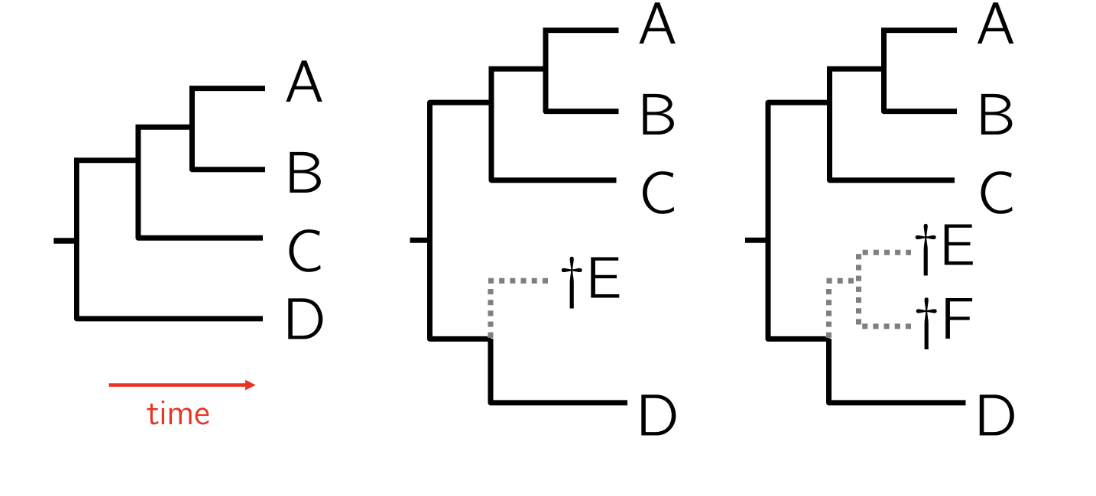
representation of extinct organisms on phylogenetic tree
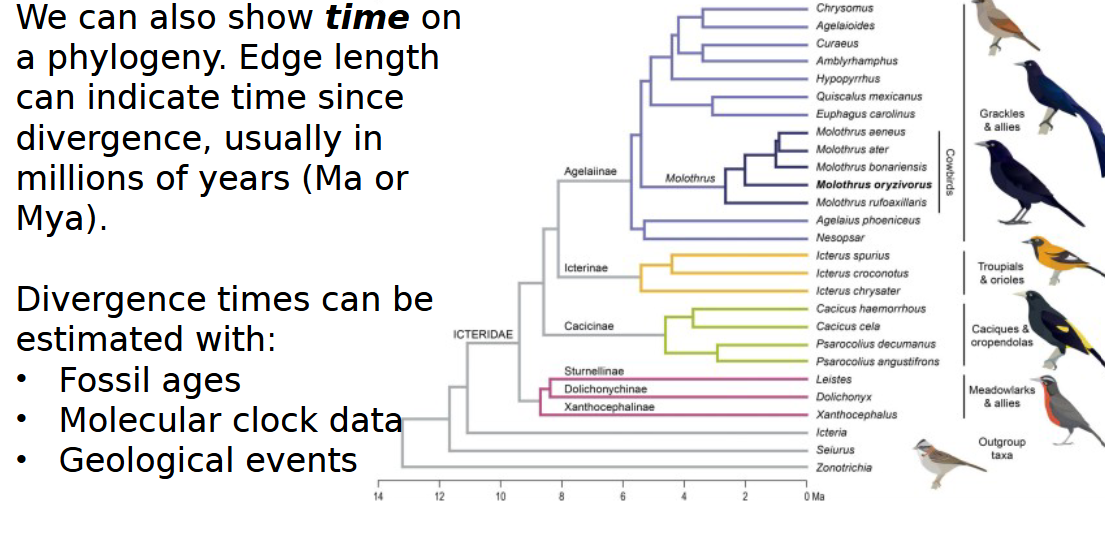
divergence times can be estimated with (FMG)
fossils, molecular clocks, geological events
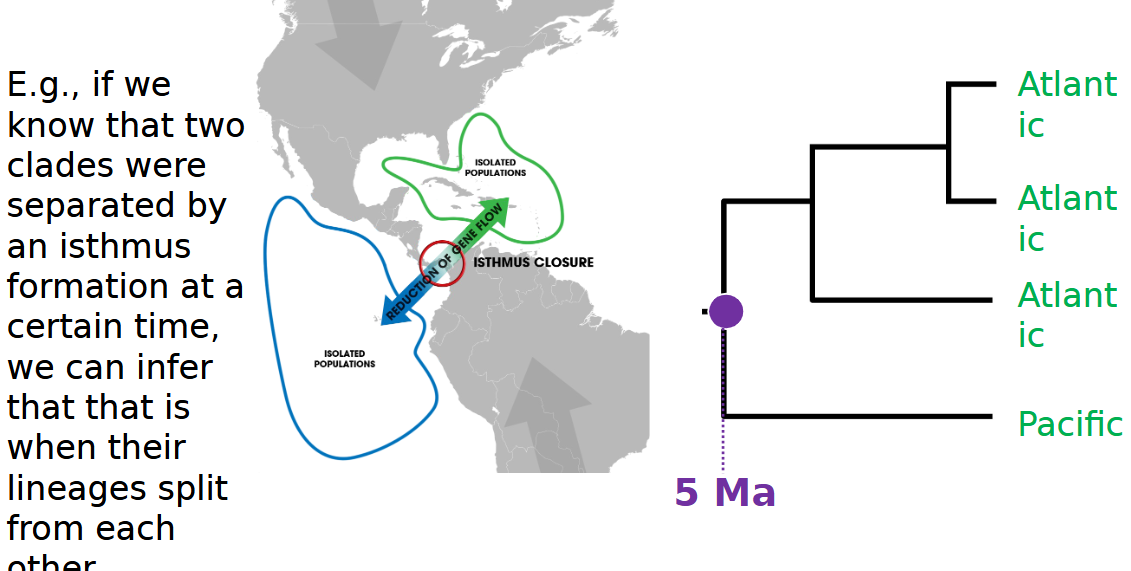
geological divergence time example
isthmus formation
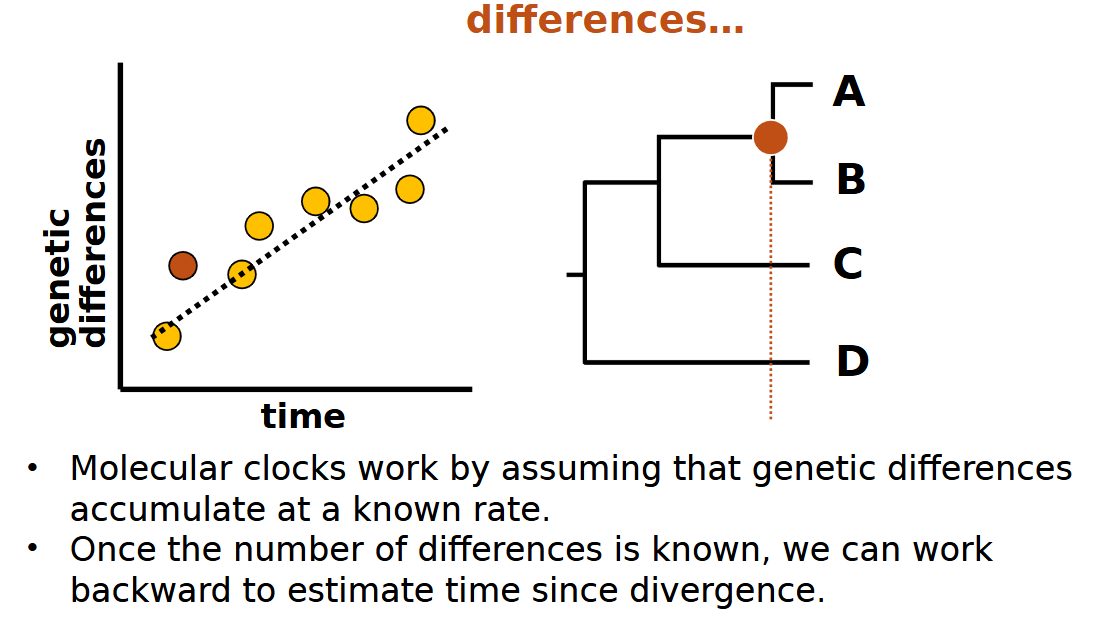
how do molecular clocks work
on the assumption that genetic differences accumulate at a specific rate and once all those differences are known you can calculate it
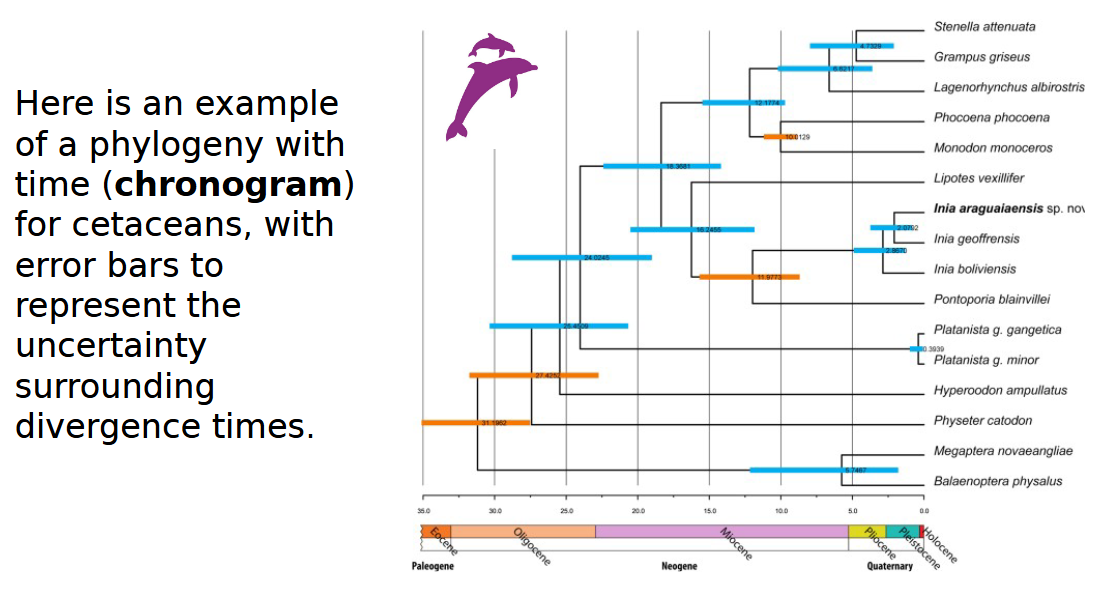
chronogram
phylogenetic tree where branch lengths are scaled to represent time
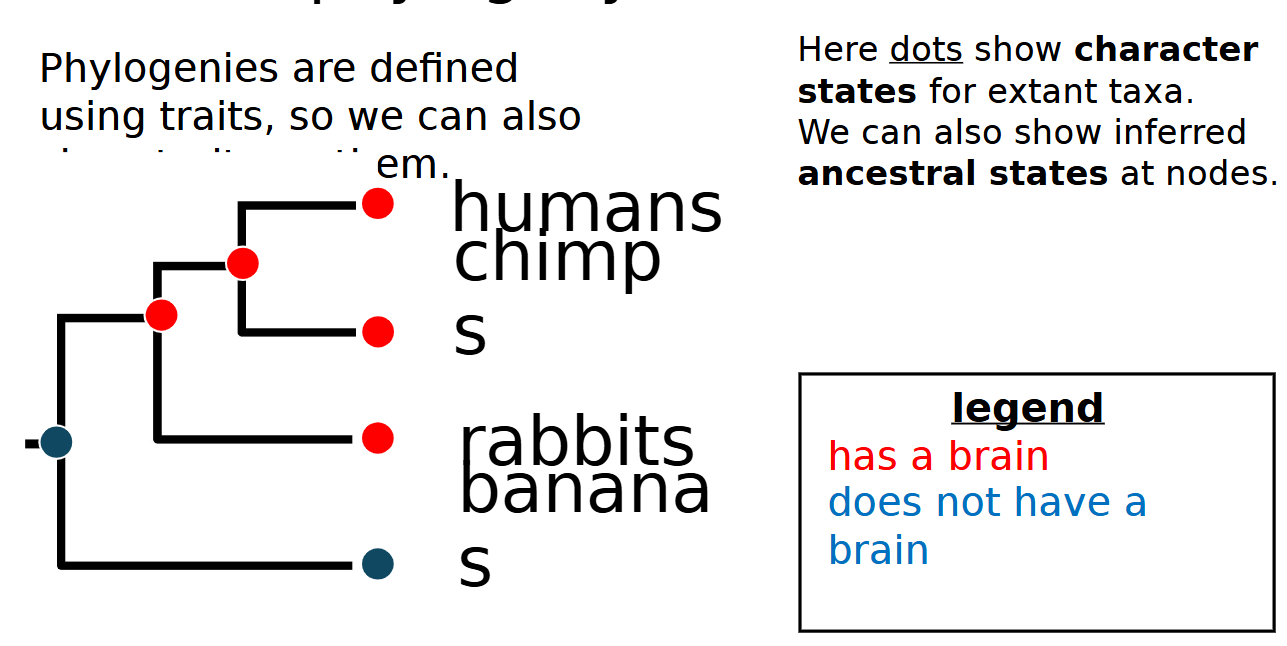
phylogenies are defined using
traits
dots on phylogenies show character states for
character states/inferred ancestral traits are at nodes
how to show changes in character states
tick marks
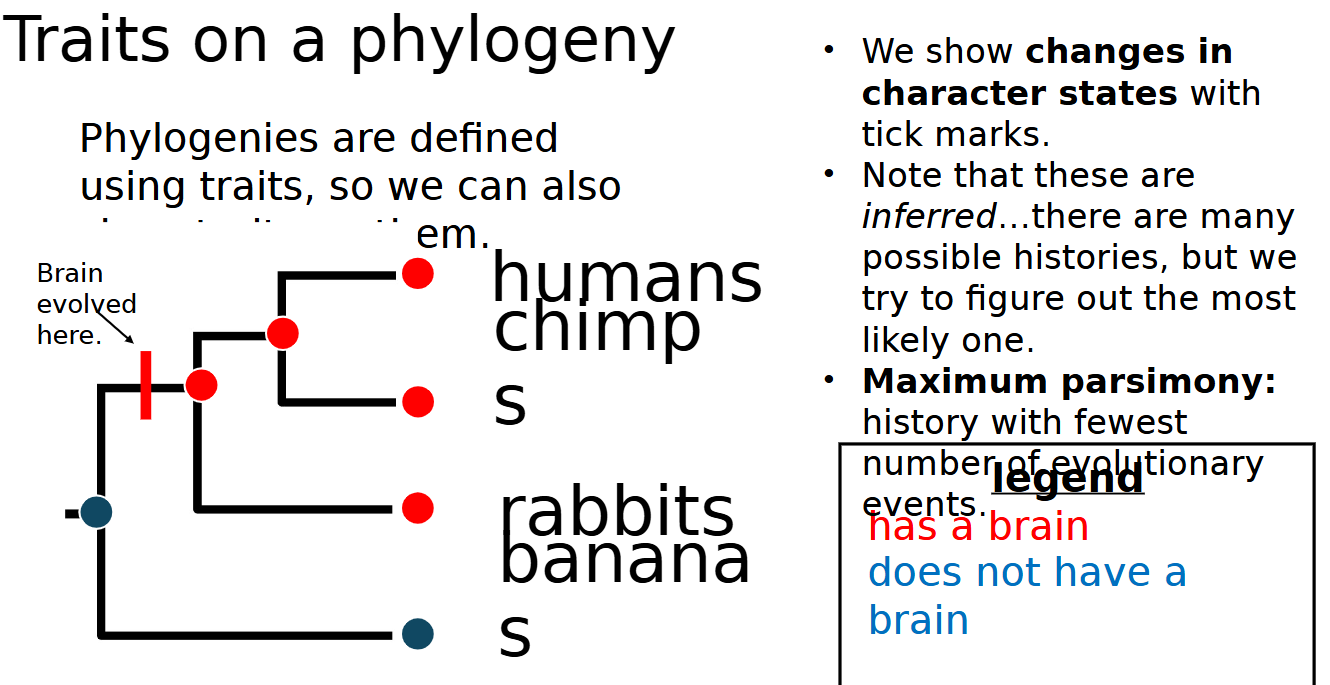
maximum parsimony
history with fewest number of evolutionary events/most accurate or simplest tree
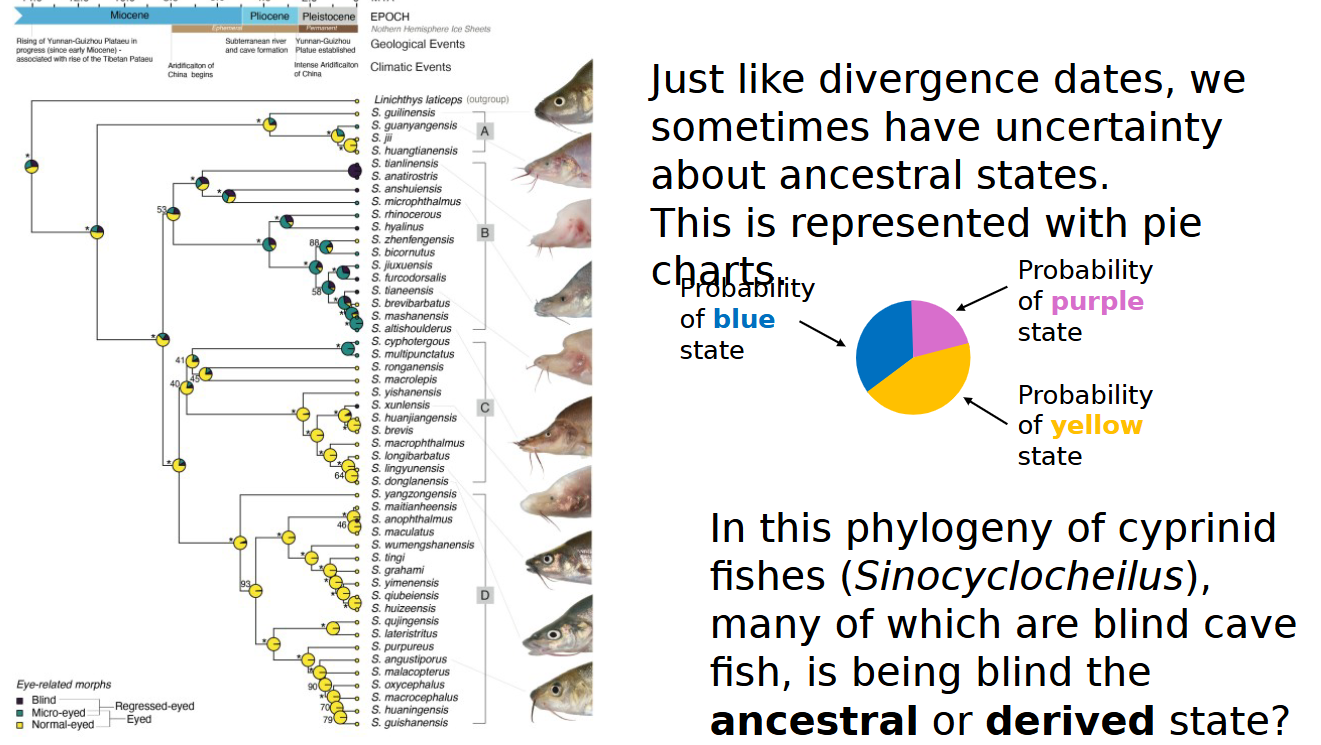
uncertainty about ancestral traits are also represented with
pie charts (blind is derived)
homology vs homoplasy
when similarity of trait is due to shared ancestry (divergent evolution) vs not due to shared ancestry (convergent evolution=homoplasy)
apomorphy
a trait that has changed from its ancestral form
pleisomorphy
an ancestral trait
synapomorphy
apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and hypothesized to occur in their most recent common ancestor but not any other taxa (hair and mammary glands for humans)