Grade 10 Review
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
3 Types of radioactive emissions
Alpha particles, beta particle and gamma radiations
Atomic #
Element identify depending on the # of protons present
Average atomic mass
Weighted avg of all isopoes of a particular element in existence.
How will the quantity of an isotope have an effect on the avg atomic mass
More of an isotope, it will have a greater effect on the avg atomic mass
Charge, relative mass, location and symbol of Electron
-
1/2000
Around the nucleus in ring
e-
Charge, relative mass, location and symbol of Neutron
0
1
Inside nucleus
n0
Charge, relative mass, location and symbol of Protons
+
1
inside nucleus
p+
Electronegativity
The pull an atom has on electrons
Not a direct measure - the results of ranking atoms against each other using other measures
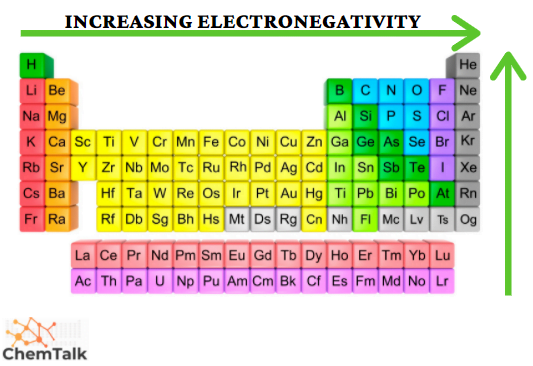
What makes the electronegativity decrease in a group
Down a group, electronegativity decreases as electrons are held in higher orbits with more electrons overall
What makes the electronegativity decrease in a period
Across a period electronegativity decreases as valence shells approach an octet.
Losing electrons becomes less desirable as gaining electrons becomes more desirable
Atomic radius
The distance from the centre of the nucleus to the valence electrons
Atomic radius for molecular elements
Half the distance between nuclei is the atomic radius
What makes the atomic radius decrease in a group
Due to additional atomic orbits
What makes the atomic radius decrease in a period
Due to stronger attraction between the nucleus and electron cloud
How does the atomic radius vary between atomic radii, ionic radii for cations and anions
Ionic radii for cations are half the length between the nuclei atomic radius compared to atomic radii, while Ionic radii for anions are double the length between the nuclei atomic radius.
anion radii > cation radii
How are the # of n,e and p in an atom
p+ = #e-
n0 = mass# - #p+
Different elements have different # of protons
How many electrons in each orbit
1st -- 2e-
2nd -- 8e-
3rd -- 8e-
How radioisotypes are diff from other isotypes
they are unstable, meaning their nuclei have excess energy and will undergo radioactive decay, emitting radiation (particles and energy) to achieve stability, whereas other isotopes are stable and do not decay, remaining unchanged over time
How was Mendeleev's periodic table arranged
Based on atomic mass and included gaps for elements with predicted properties that had not yet been found
How was Meyer's periodic table arranged
Based on molar volume (atomic mass / solid density)
Isotopes
Atoms of same elem type, but diff mass. (Diff # of neutrons)
Represented using a nuclear symbol/standard atomic notation or by adding a mass # to an element name or symbol with a hyphen
E.g. Carbob - 12, carbon-13 or C-12
How to radioisotopes affect careers
Many careers use radioisotopes and have special safety protocols as a result.
Radioisotopes decay into what?
Stable atoms
Radioistopes
Isotopes w unstable nuclei.
Capable of undergoing radioactive decay in order to become more stable
Standard atomic notation
Mass # (A = P+N)
Atomic # = # of protons
Chemical symbol for elem.
Valence electrons
Outermost electrons
What do bohr-rutherford diagrams show
Complete arrangement of subatomic particles in an atom or ion: protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons arranged in orbits
What do valence electrons determine
Chemistr: ionic charge, molecular bonding, etc.
What is the Law of Periodicity
When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, certain sets of properties recur periodically
E.g. Down a column, elements react in similar ways or atoms have similar sizes across a row
Who made the Periodic Table
Dmitri Mendeleev and Lothar Meyer
Why do ions form
Atoms are most stable with full valence shells
They will gain electrons (nonmetals) or lose electrons (metals) in order to have a stable outer orbit
Ions have diff. # of elec from atoms
What is the reason for atomic radius decrease
The decrease in atomic radius across a period is due to a phenomenon known as shielding
Shielding
Reduction of the nuclear charge experienced by an electron
Decrease in atomic radius across a period.
Coulomb’s Law
Larger charges result in greater attraction or repulsion
A greater distance between charges results in less attraction or repulsion
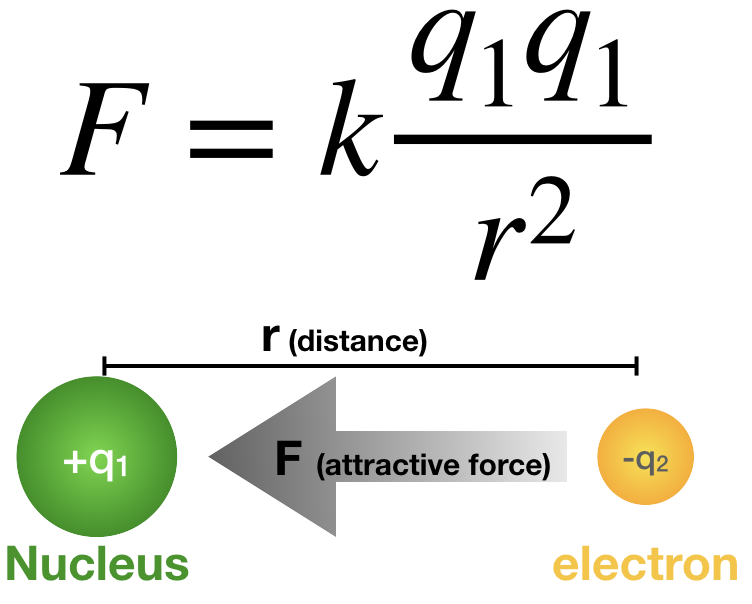
Z
Atomic # Z
Zeff
Effective nuclear charge experienced by a valence electron
What do inner electrons do
Inner electrons fully shield the nucleus for valence electrons
What do other valence electrons do
Other valence electrons partially shield the nucleus for valence electrons
What happens if you increase Z
Increasing Z increases # of electrons. If electrons are added to valence shell, Zeff also increases, leading to a stronger attraction between the valence and nucleus
Higher Zeff means stronger attraction between e- and nucleus
Ionization energy
The energy required to remove the highest energy electron
The first ionization energy targets a valence electron in a neutral atom
Higher IE —> harder to remove
*always requires energy input
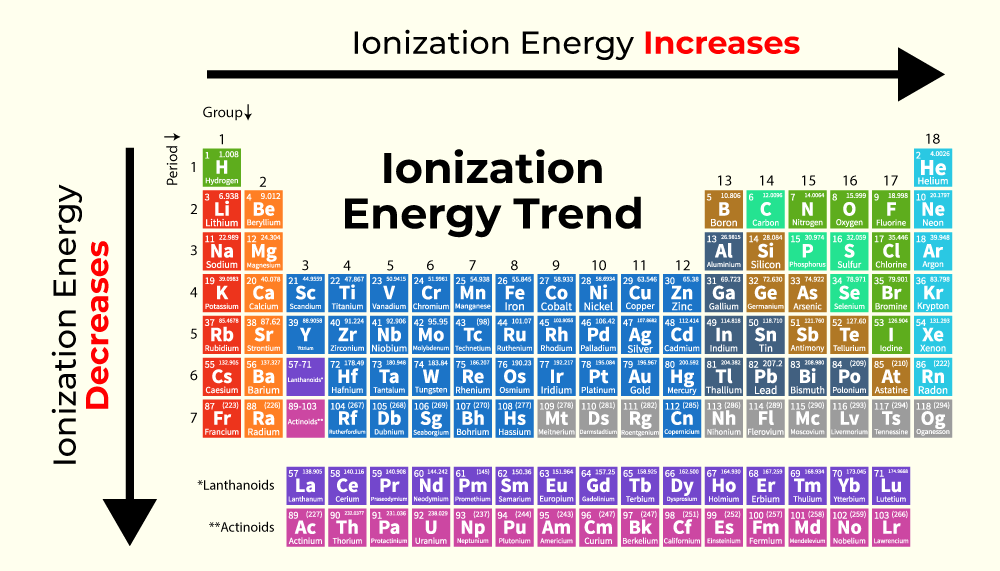
What happens when you go down a group relating to ionization
Down a group, first ionization energy decreases as electrons are further away from the nucleus and are less tightly held.
What happens when you go across a period relating to ionization
Across a period, the first ionization energy increases as a full valence shell is approached.
Electron Affinity
The energy absorbed (+) or released (-) when an electron is added to an atom
Least stable and most stable where?
Most stable = highest EA
Least stable = lower EA
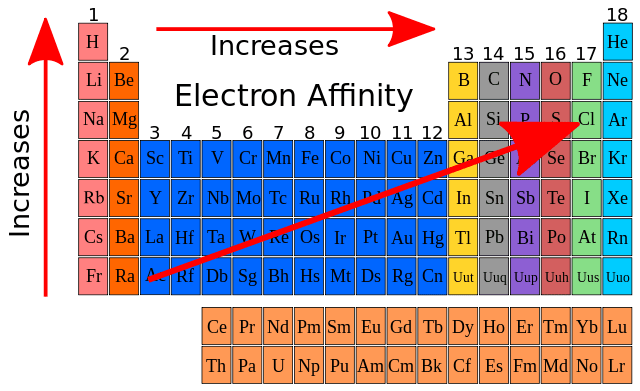
What does negative electron affinity mean
Negative electron affinities mean a stable anion is formed
What does positive electron affinity mean
positive electron affinities mean an unstable anion results
What happens when you go down a group relating to electron affinity
Down a group, electron affinity decreases as atoms have more electron.
What happens when you go across a period relating to electron affinity
Across a period, electron affinity increases as a full valence shell is approached.
Difference between Ionic and Covalent bonding
Ionic:
The result of a transfer of electrons
Usually forms between a metal and a nonmetal
Electrostatic in nature (+ and — attracted to eachother_
Covalent:
The result of sharing of electrons
Usually forms between 2 nonmetals
The result of overlapping valence shells
What is electronegativity
EN
Measure of the pull an atom has on electrons
Indirect measure, not an actual energy change like electron affinity
Most useful as a comparision measurement
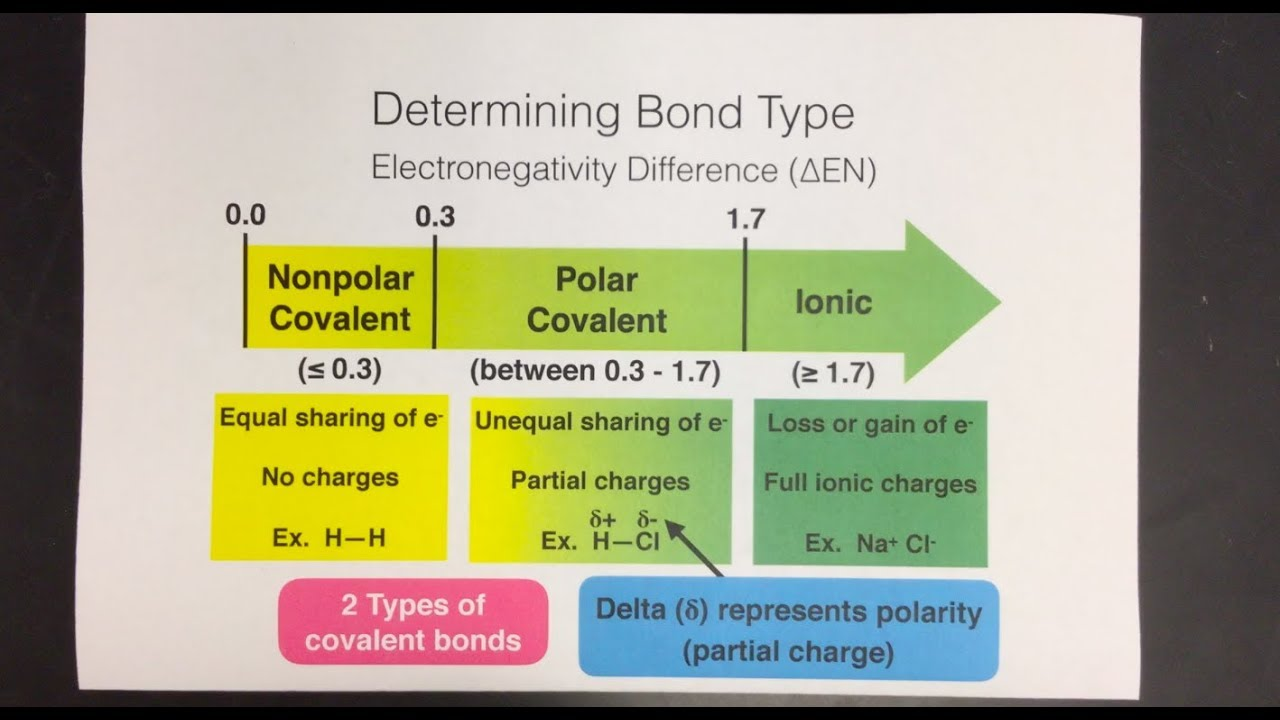
How to calculate ΔEN
Meaning difference in electronegativity
Calculated per bond
Always positive
Larger ΔEN - smaller ΔEN
What is ΔEN useful for?
A very good predictor of the nature of chemical bonds
Draw the guidelines that are used to classify bonds based on ΔEN
What do lewis dot diagrams visualize
Show valence electrons arranged around the chemical symbol.
What is another name for noble gases
Inert gases
Characteristic of noble gases
Do not react with other substances because they are already stable
Why are noble gases stable
Full valence shell
Octet rule
Elements are most stable with a valence like a noble gas with 8 electrons.
Steps to draw lewis structures of simple ionic compounds
Cations are shown as the chemical symbol with an empty valence
Anions are shown as the chemical symbol with a full valence
Both ion types must be in square brakets with the charge as the superscript
All ions must be represented, either with repeated ions or coefficients
Steps to drawing lewis structure of simple molecles
Chemical symbols represent the atom centres
A single dot represents a lone electron (unstable).unbonding e
A pair of dots represents a lone pair of electrons. unbonding e
Bonding pairs of electrons are represented with a single line between bonded atoms. bonding e
Why do covalent bonds form
Atoms want a full octet
Equalish sharing of e
Steps to drawing lewis structure of simple covalent compounds
Calculate the number of valence electrons that must be represented (add up the valence electrons of all atoms).
Identify the central atom (least electronegative, usually listed first). Draw it in the middle of the space.
Arrange all other atoms around the central atom. Draw a single bond from each to the central atom.
Determine how many electrons are currently represented. If all valence electrons are represented by the single bonds, the structure is done.
If additional electrons need to be drawn in, add them to outer atoms first to give full valences/octets.
If every outer atom has an octet but there are still valence electrons that need to be allocated, add them to the central atom.
If there are not enough electrons to give the central atom a full valence (octet), convert a lone pair into a multiple bond with the central atom.
Advanced Lewis Structures: Electron Deficient Atoms
Exception: Group 13 elements only need 6 valence electrons.
Polyatomic ions
Groups of covalently bound atoms may overall gain or lose electrons, gaining an overall positive or negative charge.
Advanced Lewis Structures: Polyatomic Ions
For ions, subtract the charge from the electron count (account for electrons lost or gained).