4N051 Module 7. Nursing Fundamentals
1/205
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
206 Terms
terminal cleaning
This type of cleaning is directed primarily toward objects the patient has actually been in contact with
private room
You have a pediatric patient diagnosed with a highly infectious disease needing contact precautions. What is the most effective type of isolation unit you should place them in?
Surgical equipment
Vascular Probes
Heart catheters
Equipment that is categorized as critical have a high risk of transmitting diseases or infections and must be completely sterile. What items considerably high risk?
intended use of the medical equipment.
The proper level of cleaning or sterilization for medical equipment depends on?
Terminal cleaning
What type of cleaning is directed primarily towards objects the patients have been in contact with?
Gently pull the ear down and back
When performing an ear irrigation for a pediatric patient, how do you straighten the ear canal?
Daily or per provider's orders
For diabetic patients, how often should their feet be cleaned?
3 seconds
When a patient is performing incentive spirometry and they have inhaled, how long should you instruct them to hold their breath for?
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
The solution you use is selected by your local infection control committee according to ___________ _________ ___________ standards.
Regular.
What type of cleaning would you use for handrails, bedrails, call lights, and light switches??
3
A Pap smear is recommended every ___ year(s) for average-risk persons who are 21-65 years of age.
Bleeding, Inflammation, Polyps
A proctoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, and a colonoscopy are examinations that are used to identify all of the following. What are those?
Once q24h.
How often should the bladder irrigation solution container be changed?
Expiratory reserve
Tidal reserve
Residual volumes
The respiratory (or lung) volumes include all of the following
Type of specimen, date and time, patient's name, sponsor's social security number (or DoD ID number), patient registration number (for inpatients) and physician's name.
All specimens should be labeled with which of the following information?
Relieve pain from muscle spasms and to correct mild deformities
What are the main purposes for skin tractions?
lithotomy position
What is the common position for a patient who is having a pap exam?
Paracentesis
___________ is the withdrawal of excess fluid from the abdominal or peritoneal cavity
thoracentesis
___________ is the surgical "puncture or tapping" of the chest wall to remove fluid or air from the pleural space.
pneumothorax (air in the pleural space),
hemothorax (i.e., blood in the pleural space), or
emphysema (i.e., pus in the pleural space).
The physician may perform thoracentesis procedure as part of the treatment for what kinds of conditions?
third and fourth
The lumbar puncture (LP) is the insertion of a needle into the subarachnoid space, usually between the _____ and the _______ of lumbar vertebrae, to aspirate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
spinal tap
A __________ _____is normally performed for analysis of CSF or to measure CSF pressure to aid in the evaluation of some underlying condition.
True. bacterial and viral infections,
True or False. The spinal tap provides important information about intracranial pressure and the composition of the CSF. It is widely used in the diagnosis of _________ and _____________ such as spinal meningitis, along with the evaluation of seizure disorders.
Percutaneous Biopsy
Tissue is obtained by simply "inserting a needle" through the skin. What kind of Biopsy is it?
punch biopsy
What kind of biopsy when the Tissue is obtained by a punch, such as in a bone marrow biopsy.
needle biopsy
Tissue is obtained by puncture of a tumor, the tissue within the lumen of the needle being detached by rotation, and the needle withdrawn. What kind of biopsy is it?
insicional biopsy
A kind of biopsy in which a "selected portion of a lesion."
Excisional Biopsy
________ Biopsy when Tissue is removed by "surgical cutting."
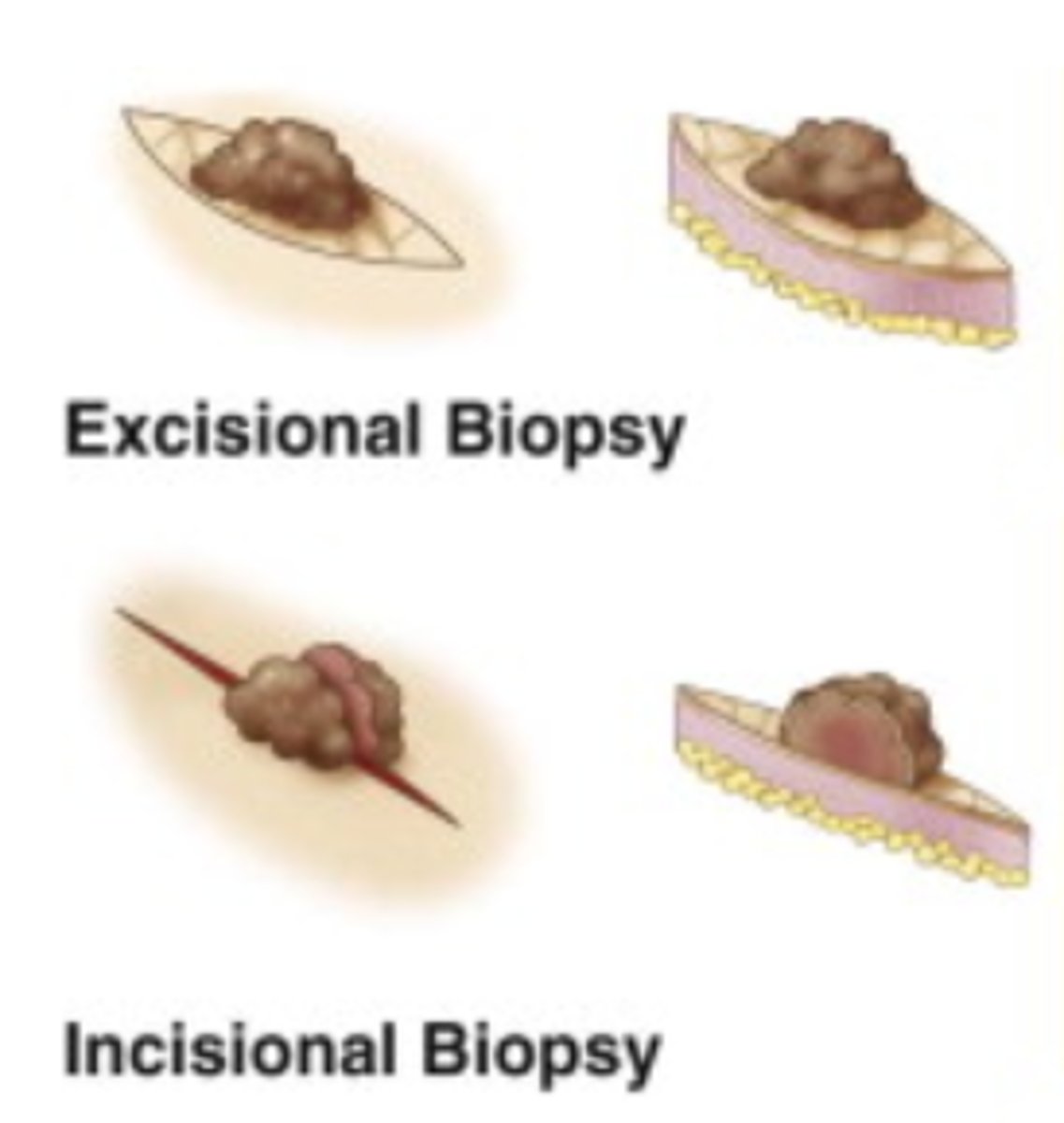
cone biopsy
Inverted cone of tissue is excised, as from the uterine cervix. What kind of Biospy is it?
Tympanometry
___________ is a test used to assess the mobility of the tympanic membrane in a quick and simple method. It can detect "disorders of the middle ear such as fluid."
tympanogram
A ___________ (the graph the results are recorded on) "measures the response to sound" and different pressures within the ear as the "eardrum moves back and forth."
zero
A normal tympanogram will peak at _______ on the "Air Pressure," displaying a low level reading with a flat graph or one without a peak; the third type may show a distinct peak, but it will be shifted to a negative pressure, thus signaling an estuation tube dysfunction.
Vasectomy
Cyst
________ is a male sterilization that consists of bilateral removal of a part of the vas deferens.
________removal is a removal of an inflamed closed sac in or under the skin lined with epithelium and containing fluid or semisolid material.
Laceration
_____________ repair is a surgical repair of jagged or smooth skin tissue by sutures, surgical staples, or medical glue. Lacerations can occur either by surgical means or traumatic injury.
Biopsy
is a removal and examination, usually microscopic, of tissue or fluid from the living body to establish a precise diagnosis.
cutting or dissecting,
grasping or holding,
clamping or occluding, and
exposing or retracting instruments.
What are the four basic classifications of instruments you will use for a minor surgery?
endoscopic,
endoscopic instruments
_____________examination is the inspection of a body cavity or hollow organ by means of a lighted instrument. The stomach, esophagus, colon, and rectum can all be examined by using _______________ ______________
fiber optic scope
______ ________ _________enables the provider to see the inside of the colon on a display screen by moving the head of this around.
clear liquid
Patient scheduled for a sigmoidoscopy will normally have a diet restricted to _______ ______ the day before the test.
24 hours
Bowel cleansing with laxatives, cathartics, and enemas should be performed within how many hours before the test
sigmoidoscope.
This is an inspection of the sigmoid colon by means of an endoscope called a _________
ensure patient empties his or her bladder prior to the procedure.
with sigmoidoscope, what do you need to ensure that the patient do prior to procedure?
procedure will take anywhere from 30-90 minutes and the scope is inserted much farther
The same steps of colonoscopy are performed as with the sigmoidoscopy, except the what?
The procedure provides:
-view of the airways of the lung
- collect lung secretions and
-to biopsy for tissue specimens.
A bronchoscopy is a diagnostic procedure in which a fiber optic tube is inserted through the nose or mouth into the lungs. What is this procedure provides?
anesthetic jelly
If the bronchoscopy is performed through the nose, what will first be inserted into one nostril?
incentive spirometer
atelectasis
The _______ __________is used to promote voluntary deep breathing. This expands the lungs capacity, allowing them to fill fully with air. This exercise is used to prevent or treat _______ in postoperative patients.
-increase the amount of air inhaled
-expelled to improve profusion.
What is the goal of incentive spirometer?
neuropathy, and poor circulation
Nerve damage, known as _________ and ______ ____________are the most common causes of diabetic foot problems.
Monofilament testing
_________ testing is an inexpensive, easy-to-use, and portable test for assessing the loss of protective sensation,
endotracheal tube
This acts as an artificial airway and inserted through the mouth or the nose into trachea. These are often used for trauma patients, medical emergencies and at times short term for complex patients.
you need to determine whether the patient is wearing contact lenses and if so, which type. If present, remove immediately.
What is the first step you need to do as a technician if the patient got splashed with chemical in his/her eyes?
It may cause dizziness or nausea
In ear irrigation, why you cannot use cold water?
How comfortably a patient can see
Visual efficiency refers to what?
It contains epithelial cells, which can interfere with the test results.
Why should the first drop of blood from a capillary stick be wiped off prior to collection?
Possible tympanic membrane perforation
When should an ear irrigation NOT be performed?
10-30 minutes
In eye irrigation how many minutes do you need to flush the eyes with sterile saline or water?
ecchymosis.
The damage usually includes cell damage and torn blood vessels in the dermis, and leakage of tissue fluid and blood into the damaged tissues. This leakage causes edema and pain and produces a characteristic "black and blue" discoloration called ?
Hematoma
This is a pool of blood that forms beneath the skin when large amounts of tissue are damaged and large blood vessels are ruptured. This also occur with fractures or when organs are damaged.
subungual hematoma
Another common type of hematoma is the ___________hematoma. After a blow or crushing injury to the fingernail, the patient experiences severe and sometimes excruciating pain that persists for hours and may even be associated with a vaso-vagal (sudden loss of consciousness) response.
False, the abrasion usually does NOT penetrate completely through the dermis.
Abrasion is the loss of a portion of the epidermis as the result of the skin being rubbed or scraped across a rough surface.
True or False-There may be some bleeding from the capillary vessels in the dermis; the abrasion usually does penetrate completely through the dermis.
pain sensors
Abrasions are usually extremely painful because multiple _________ _________ are normally found in the damaged area.
Evulsion
This is an injury in which a piece of skin is either torn completely loose from all attachments or left hanging as a flap.
laceration
This is a cut produced by a sharp object. The cutting object may leave a torn or jagged wound through the skin and may penetrate into the subcutaneous tissue, underlying muscles, and associated nerves and blood vessels.
incition
This is a smooth cut produced by a sharp object. The sharp object in most cases is a knife or surgical scalpel.
Puncture wound.
This is an injury caused by a stab with a knife, ice pick, splinter, or any other pointed object, including a bullet.
hemostasis
During inflammation phase, blood vessels constrict, platelet aggregation occurs (clumping together) and the formation of fibrin from the action of thrombin on fibrinogen as well as epithelial migration. This is known as ________
Proliferation stage
A wound is filled with new connective tissue during which stage of the healing process? this take about 2-3 weeks and begins on 3rd or 4th day.
Wet to wet
______ to ______ dressing are used to keep a wound moist and promote healing. The main purpose of this dressing is to reduce inflammation; cleanse the skin of the thick exudates, crusts or scales; and to maintain drainage of the affected area
wet to dry dressing
This serve multiple purposes. They prevent microorganisms from freely entering or escaping the wound while also absorbing any drainage. These dressings help debride wounds and encourage cellular growth from the base of the wound to the surface.
Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma, (FAST exam)
This is performed on trauma patients. It is a rapid ultrasound assessment as a screening tool used to test or look for blood around the heart or free fluid in the abdominal organs after trauma has happened.
hemothorax, pneumothorax
FAST is now used to also screen or detect for _________ and ___________ and other cardiac related traumas.
Cardiac is the first area, Followed by:
Right Upper Quadrant
Left Upper Quadrant
Pelvic
During a FAST exam, what area will you inspect first?
these can give a false " bleed" in the patients output.
For clear liquid diets, patients with potential GI issues, or post- surgical, Why do patients need to avoid clear liquids that are red/pink, orange or purple?
orange juice.
What is an example of a non-clear juice would be?
bland diet
These are ordered for patients who suffer from "ULCERS" or any irritants to the GI tract. These diets are designed to eliminate chemical, mechanical and thermal irritants. This diet consists of foods cooked without oils and seasoning/spices.
fat restricted diet
These are ordered for patients with gallbladder disease, malabsorption syndrome, and hyperlipidemia.
Protein restricted diet
These are ordered for patients who have an impaired ability to excrete waste products of protein due to kidney or liver disease. These vary from total elimination of protein to diets around 80 grams per day.
Calorie restricted diet
This diet is designed to either lose weight or maintain a desirable weight. Foods allowed on this kind of restricted diet include foods that are low in fats and carbs, such as lean meats, fruits, vegetables,
Mineral restricted
These diets are ordered to treat certain diseases and conditions for test purposes. This includes: sodium (Na), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), phosphorus, (P), copper (Cu) and oxalate (OX).
low sodium
These consist of 4 gram (no added salt), 2 and 1 gram, or 500-mg sodium diets. These can vary from no salt, to sever sodium restrictions.
Sodium restricted, 6-18
Sodium is a mineral commonly found in almost all food and even water. The average daily intake is between ______ grams. This diet is ordered for patients who are subject to edema, hypertension, congestive heart failure, renal disease and cirrhosis of the liver.
kidney disease.
Potassium Restricted is ordered for patients with __________ _________. Damaged kidneys have difficulty eliminating potassium. On occasion, some patients have a potassium depletion and require a high-potassium diet.
pro-longed IV feedings, severe diarrhea, diuretic therapy, diabetic acidosis or renal disease.
What conditions that require high potassium?
Calcium Restricted
800 mg
This diet is ordered for patients who have recurrent renal calculi or hypercalcemia. The average daily intake of this is _____ mg . A 400 mg reduction in calcium intake will lower the renal load.
anywhere in the urinary tract
Where can calculi from urine develop?
normal sinus rhythm; pulse on palpitation
Pulseless electrical activity (PEA) may show ______ while being unable to obtain a ______ for the patient.
Bowl of soup
Ice chips
Intravenous fluids
Which of the following are included when calculating a patient's intake?
cranberry juice
What juice has a strong acidifying effect on urine, and may be effective in increasing urinary calcium excretion?
Stronger side of the mouth
In patient with unilateral weakness, which side do you place the food?
Absent gag reflex,
dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) or
decreased level of alertness. These patients are high risk for aspiration
Give the contraindication of oral feeding.
difficulty with maintaining placement.
Why is an endotracheal tube not recommended for long term use?
Uncorrectable coagulopathy
Severe refractory hypoxemia
Unstable hemodynamic status
Facial trauma
Unstable cervical spine
what are a contraindication for a bronchoscopy?
Standing, speaking or swallowing during the test
What can change the pressure of the middle ear and invalidate the tympanometry test results?
Gastric gavage
____________ _________is the procedure of feeding a patient through a tube inserted through the mouth or nose and into the stomach.
Semi-fowler
When performing a gastric gavage, in what position should the patient be placed?
is to lubricate the feces in the rectum and colon.
These are called oil-retention enemas. These are typically for patients who are experiencing constant constipation. What is one of the main purposes of a retention enema?
2 tablespoons
When collecting feces for testing, what amount should be placed into a specimen container?
20 minutes, 2 hours
The oil or solution for a retention enema should be retained for at least ___ minutes and no more than ____ hours.
Irrigation of the bladder
prostate or bladder surgery
This is done to remove and flush out any blood, bacteria and waste products that may remain post-surgery. Continuous irrigation is performed after __________ or _________ surgery via the three-way, also known as foley, catheter system
Open and close
What are the types of intermittent bladder irrigations?