Engage Fundamentals Medication Administration
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
1
New cards
Dosage
A prescribed quantity of medication consisting of the dose and the frequency
2
New cards
Pharmacokinetics mnemonic
(ADME)
A- absorption
D-distrinbution
M-metabolism
E-excretion
A- absorption
D-distrinbution
M-metabolism
E-excretion
3
New cards
pharmacokinetics
Study of absorption, metabolism, distribution, and excretion of drugs in the human body
4
New cards
absorption
how will it get in?
5
New cards
Metabolism
Hoe is it broken down?
6
New cards
Excretion
How does it leave?
7
New cards
What factors can affect the rate of absorption?
\-route of administration
\-ionization
\-dissolution
\-blood flow
\-lipid soluability
\-surface area of the absorptive site
\-client-specific factors
\-ionization
\-dissolution
\-blood flow
\-lipid soluability
\-surface area of the absorptive site
\-client-specific factors
8
New cards
Ionization
affects the degree of absorption and the rate at which the drug permeates the cell membranes, which ultimately impacts the distribution of a medication
9
New cards
Dissolution
medication must be dissolved in a solution before absorption takes place. Dissolution of a medication is dependent upon its initial state and route of administration
10
New cards
Orally disintegrating tablets
drug form that rapidly dissolves on the tongue or oral cavity
11
New cards
Which route provides the most rapid rate of absorption?
Intravenous route because the medication is directly injected into the circulatory system through the patient’s vein
12
New cards
Enteral route
medications administered via the mouth, stomach, or intestines
13
New cards
Dose
the amount of the ordered medication
14
New cards
Metabolism or biotransformation
the chemical process of converting a medication’s structure
15
New cards
Toxicity
an adverse effect in which the body is unable to metabolize or excrete a medication, it can cause irreversible damage to organs
16
New cards
Prodrugs
contain inactive chemicals that are activated through metabolism to exert their herapeutic effects
17
New cards
Therapeutic effects
the desired effects of a medication
18
New cards
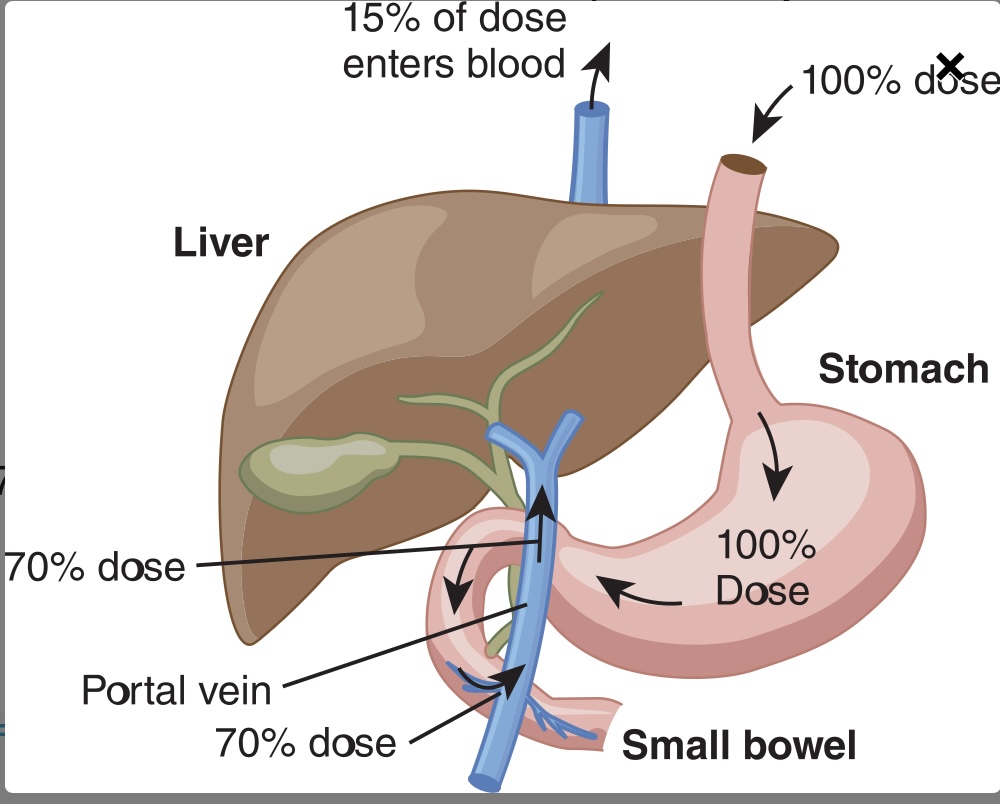
First-pass effect
passage of oral medications from small intestine to hepatic circulation via mesenteric & portal veins flowing to the liver, before reaching systemic circulation
19
New cards
CYP enzymes
on liver cells role in metabolism by regulating the rate at which medication is brown down and how long it stays in he body
20
New cards
The primary organ responsible for medication excretion ?
the kidneys
21
New cards
The rate of medication excretion is affected by?
\-kidney
\-heart
\-liver
\-heart
\-liver
22
New cards
Pharmacodynamics
study of how a drug works, its relationships to drug concentrations and how the body responds
23
New cards
Therapeutic range
method used buy health care providers to monitor drug concentrations to determine therapeutic dose and avoid toxicity
24
New cards
Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM)
method used by health care providers to monitor drug level concentrations
25
New cards
Peak blood level
highest level of a drug in the bloodstream without being at a toxic level
26
New cards
Trough blood level
lowest concentration of a medication in the systemic circulation
27
New cards
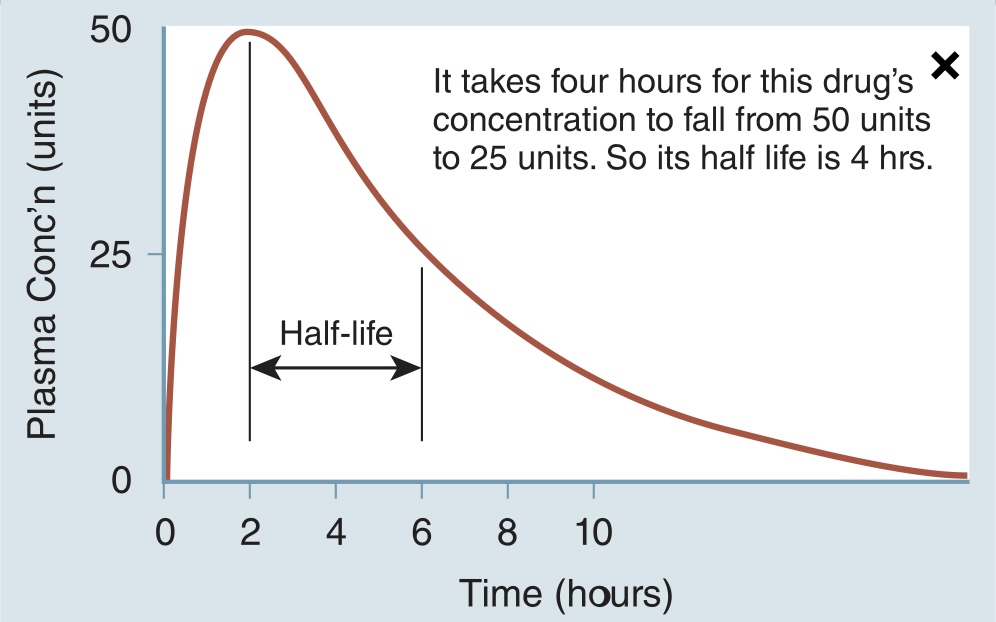
Half life
time it takes for the drug to fall to half its strength through excretion
28
New cards
Onset
the time the medication takes to produce a therapeutic effect after its administration
29
New cards
Peak
effect occurs whens absorption is complete, medication is distributed throughout the body, and medication is at its HIGHEST concentration
30
New cards
Duration
The period of time in which medication maintains its therapeutic effects
31
New cards
Agonist
medication that activates receptors to initiate a preferred response
32
New cards
antagonist
A medication that prevents the activation of a receptor
33
New cards
Adverse drug reactions
unwanted and non-therapeutic effects of medication can range from mild to severe
34
New cards
Adverse drug event
an injury caused from a medical intervention that is linked to a medication
35
New cards
Iatrogenic
an unforseeable or unintended physical condition, injury, or disorder caused by a treatment of procedure
36
New cards
Allergic reaction
a reaction resulting from a hypersensitivity to an antigen or a foreign substance, such as a medication
37
New cards
Steven-Johnson sydrome (SJS)
Potentially fatal medication reaction which develops 1 to 14 days following dose administration
\-symptoms include: respiratory distress, fever, chills, diffuse fine rash followed by blisters
\-symptoms include: respiratory distress, fever, chills, diffuse fine rash followed by blisters
38
New cards
Anaphylaxis
acute allergic reaction to an antigen that may result in life threatening shock, producing vasodilation, bronhcospam, and laryngeal edema
39
New cards
Drug-drug interactions
the effect that two or more drugs that the client is administered have on each other
\-enhance actions or block actions
\-enhance actions or block actions
40
New cards
Drug-food interactions
effects of nutrients on the absorption, distribution, metabolism or excretion of medications
41
New cards
If medications are ordered to be taken on a n empty stomach the nurse should administer the medication when?
At least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal
42
New cards
Teratogenic
medications that can cause fetal defects, pregnancy loss, prematurity or developmental disabilities
43
New cards
Polypharmacy
multiple (5 or more) medications that one person is taking
44
New cards
The rights of medication administration (10)
\-right client
\-right medication
\-right dose
\-right route
\-right time
\-right assessment (allergies/vitals)
\-right documentation
\-right to refuse
\-right education
\-right evaluation
\-right medication
\-right dose
\-right route
\-right time
\-right assessment (allergies/vitals)
\-right documentation
\-right to refuse
\-right education
\-right evaluation
45
New cards
How many times should you check for confirmation of the correct client when administering medication?
3 or more times
46
New cards
Medication administration record (MAR)
a record of the medications prescribed for the client by the provider, used by the nurse to record and confirm medication administration per the prescription
47
New cards
Generic
non-trademarked name of a drug assigned by the FDA
48
New cards
STAT medication prescriptions
medications that are required to be given immediately
49
New cards
PRN
as needed, medications given as required for specific conditions such as pain, nausea
50
New cards
Time-critical medications
medications that should be given within either 30 minutes before or after the scheduled administration time
51
New cards
Non-time-critical medications
medications that can be administered between 1 to 2 hours before or after the scheduled time
52
New cards

A complete medication prescpriton should include?
Name of the drug, amount to be given, route and frequency of administration, clients name, fate and time the order wears written and providers name/title
53
New cards
Over the counter (OTC) medications
medications that can be purchased without a healthcare providers prescription
54
New cards
Medication reconciliation process
\-document an accurate & comprehensive list of at home medications
\-compare at home meds with newly prescribed meds
\-update med list (repeat process)
\-communicate reconciled med list to next care provider
\-educate client and caregivers upon discharge, with written info about their meds
\-compare at home meds with newly prescribed meds
\-update med list (repeat process)
\-communicate reconciled med list to next care provider
\-educate client and caregivers upon discharge, with written info about their meds
55
New cards
Override
the nurse removes a medication for the automatic dispensing system before a pharmacist has reviewed an order
56
New cards
Workaround
the practice of a voiding a policy or procedure in a system that is there to protect client safety
57
New cards
Unit dose medication
a medication that is prepared and packaged by the hospital’s pharmacist or the drug manufacturer in a single unti dose container that is specific to the provider’s prescription for the client
58
New cards
Multi-dose vial
container of medications that holds more than a single dose and can be used for multiple clients
59
New cards
What are the three major categories of medication administration?
Enteral (oral), topical, and Parenteral
60
New cards
Oral (enteral) medication advantages
\-safer
\-cheaper
\-convenient
\-painless
\-silent can self-administer
\-cheaper
\-convenient
\-painless
\-silent can self-administer
61
New cards
oral (enteral) medication disadvantages
\-slow onset of action
\-subject to first-pass effects
\-may have an unpleasant taste
\-not appropriate for unconscious clients
\-not appropriate for clients with vomiting/diarrhea
\-subject to first-pass effects
\-may have an unpleasant taste
\-not appropriate for unconscious clients
\-not appropriate for clients with vomiting/diarrhea
62
New cards
sublingual (SL) medication advantages
\-rapid onset of action
\-bypasses first-pass effects
\-can be self-administered by the client
\-bypasses first-pass effects
\-can be self-administered by the client
63
New cards
Sublingual (SL) medication disadvantages
\-not appropriate for children
\-may cause membrane irritation
\-may cause membrane irritation
64
New cards
Rectal (PR) medication advantages
\-can be admistered to children, unconscious clients, clients unable to swallow
\-increased concentration is achieved quickly
\-increased concentration is achieved quickly
65
New cards
rectal (PR) medication disadvantages
\-not liked by clients
\-absorption varies
\-rectal mucosa can’t become irritated/swollen
\-absorption varies
\-rectal mucosa can’t become irritated/swollen
66
New cards
Intravenous (IV) advantages
\-rapid onset
\-can be used with unconscious clients, non compliant, or unable to tolerate oral medications
\-can be used with unconscious clients, non compliant, or unable to tolerate oral medications
67
New cards
intravenous (IV) medication disadvantages
\-sterilization and aseptic technique are essential
\-high cost
\-invasive technique is required
\-can injure nerves, tissues, or vessels
\-high cost
\-invasive technique is required
\-can injure nerves, tissues, or vessels
68
New cards
Buccal medication advantages
\-rapid onset or action
\-bypassses first-pass effects
\-can be self-administered by the client
\-bypassses first-pass effects
\-can be self-administered by the client
69
New cards
buccal medication disadvantages
\-can cause irritation to open sores in mouth
\-exact site location can be difficult
\-Decrease in the effect of meds if swallowed
\-client may experience nausea/vomiting if med has an undesirable taste
\
\-exact site location can be difficult
\-Decrease in the effect of meds if swallowed
\-client may experience nausea/vomiting if med has an undesirable taste
\
70
New cards
Inhalation medication advantage
\-rapid onset
\-smaller dose required
\-medication dosage can be regulated
\-smaller dose required
\-medication dosage can be regulated
71
New cards
Inhalation medication disadvantage
local irritation can precipitate respiratory secretions or bronchospasms
72
New cards
Intramuscular (IM) medication advantages
\-faster absorption as compared to oral route
\-soluable and suspension substances can be administered
\-soluable and suspension substances can be administered
73
New cards
Intramuscular (IM) disadvantages
\-must be administered using aseptic technique
\-painful
\-can cause nerve damage
\-painful
\-can cause nerve damage
74
New cards
Subcutaneous medication advantages
\-can be self-admistered by the client
75
New cards
subcutaneous medication disadvantages
\-maximum volkume delivery is 1-2mL
\-slow absorption
\-slow absorption
76
New cards
transdermal medication advantages
effects can last for several days
77
New cards
transdermal medication disadvantages
medications dosing varies due to client factors
78
New cards
Enteral tube
goes directly into the stomach or small intestine
79
New cards
Buccal route
administration of a tablet by placing it in the oral cavity between gum and cheek
80
New cards
Enteric-coated
medications formulated to be dissolved and released in the small intestines for a slower release and can be administered less frequently during the day
81
New cards
Sustained-release
tablets designed to release medication slowly over am extended period
82
New cards
Transdermal
delivery of a specifically prepared medication designed to be absorbed by the skin
\-should be rotated to different sites to avoid irritation
\-should be rotated to different sites to avoid irritation
83
New cards
Ophthalmic
Medication administration into the eyes nurse places index finger at the inner corner of client’s eye maintaining gentle pressure for 30-60 seconds
84
New cards
Otic medications
medication administered in the ears, make sure it is room temperature, pull pinna up back and gently to help straighten ear canal
85
New cards
Nasal
medication administered via the nostrils absorbed through the mucous membranes and into the bloodstream
86
New cards
Vaginal route
Delhi every of a specifically prepared medication designed to be absorbed through the vaginal mucosa
87
New cards
Rectal route
administered via the rectum/anus discuss with clients to wait a minimum of 20 minutes before passing stool to provide enough time for the medication to enter the systemic circulation and have effect
88
New cards
Parenteral route
medication administered by a route that does not involve the GI tract, an injection that is administered by a needle such as IV or IM
89
New cards
What size needle should you use for a TB syringe?
26-27 gauge
Syringe holds a max amount of 1mL and is able to measure amounts to the hundredths (0.01 mL)
Syringe holds a max amount of 1mL and is able to measure amounts to the hundredths (0.01 mL)
90
New cards
PPD
protein derivative test
91
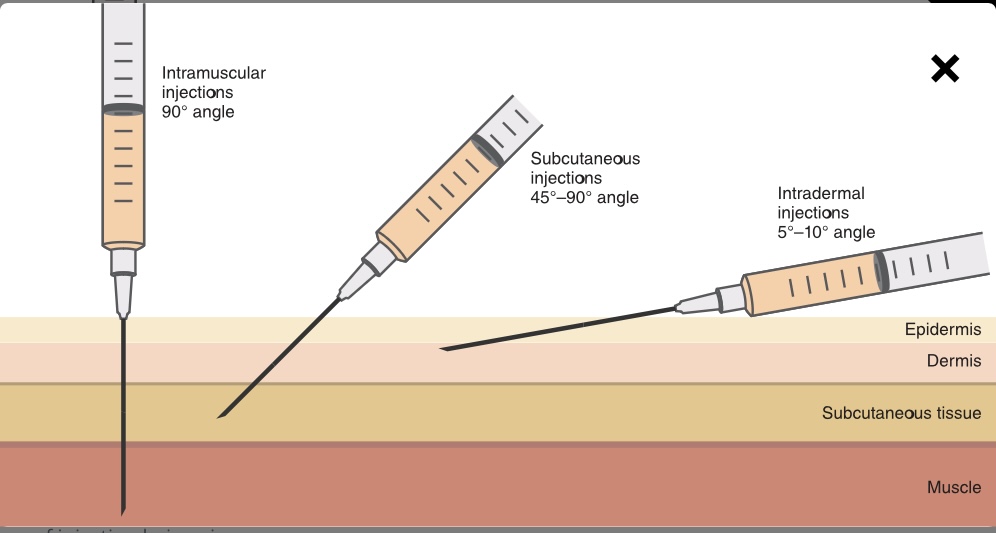
New cards
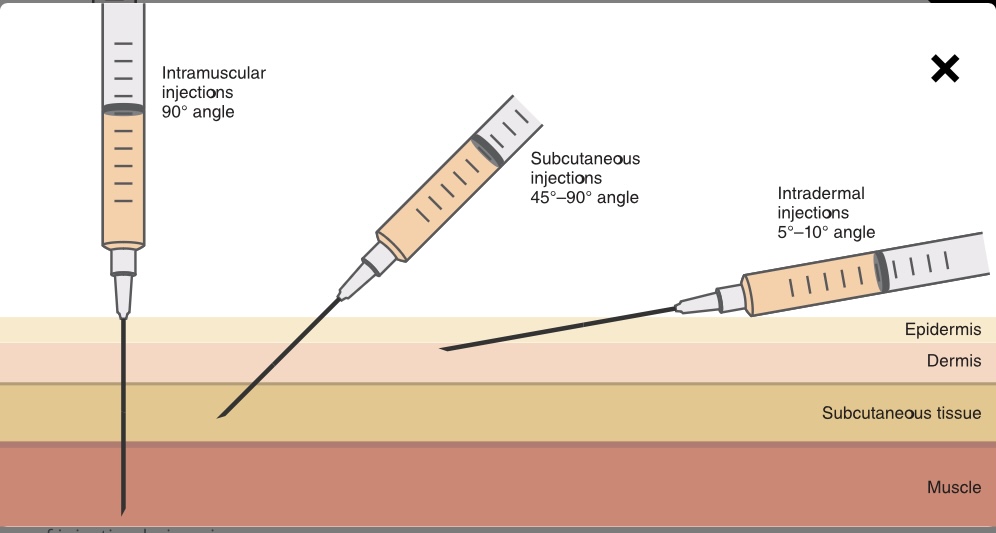
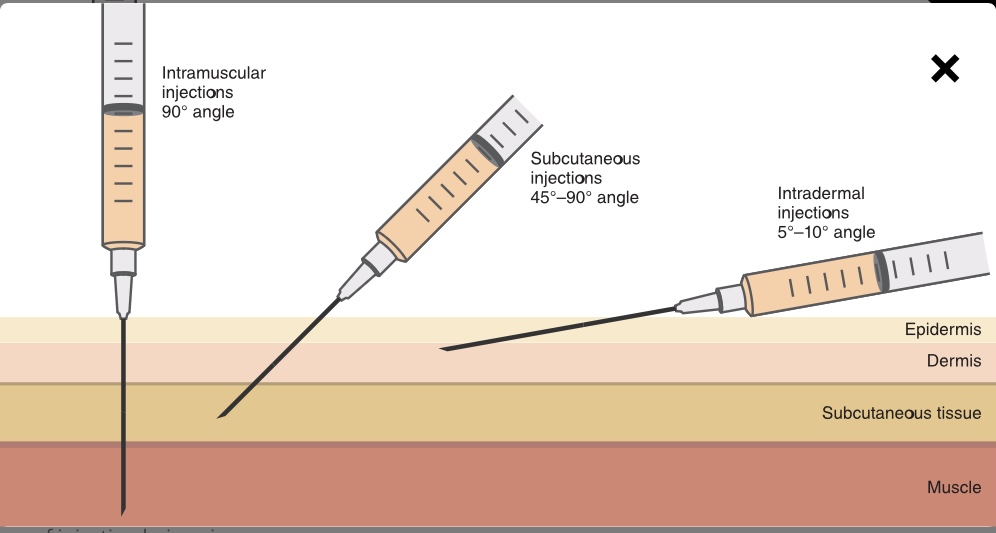
At what angle should you administer a intramuscular (IM) injection?
90 degree angle
92
New cards
At what angle should you administer a subcutaneous injection?
45-90 degree angle
93
New cards
At what angle should you administer an intradermal angle?
5-10 degree angle
94
New cards
Ampule
glass container that stores liquid medications neck is cored which aids the nurse in breaking the ampule before withdrawing the medication
95
New cards
What syringe should a nurse use when drawing medication from an ampule?
As syringe with a filter needle to prevent glass particles from the ampoule being pulled into the syringe, this needle is not used to administer the medication
96
New cards
What technique should the nurse use when administering injections?
Aseptic technique
97
New cards
Intradermal
medication administered via the dermal layers of the skin
\-often used for allergies/TB
\-max amount to administer would be 0.1mL
\-often used for allergies/TB
\-max amount to administer would be 0.1mL
98
New cards
Subcutaneous route
a medication administered beneath the skin or dermal layer (adipose tissue)
\-insulin/low molecular weight heparins
\-selected site of injection should be pinched to reduced risk of admistering to the muscle
\-insulin/low molecular weight heparins
\-selected site of injection should be pinched to reduced risk of admistering to the muscle
99
New cards
Lipohypertrophy
the formation of small lumps beneath the skin due to irritated fatty tissue
100
New cards
Aspirate
to pull back on the plunger of a syringe after the needle has been inserted, too determine if the needle is within a blood vessel, if so blood will flow into the syringe