Behavioral Science II Lesson 5: Classical and Operant Conditioning
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Your Mom starts to call you every so often. After she talks to you, she will send you a $5 Amazon gift card immediately via email, which makes you happy. After a while you start feeling happy as soon as your mom calls. What is the Neutral Stimulus, Conditioned Stimulus, Unconditioned Stimulus, Conditioned Response and Unconditioned Response in this example?
In this example, your mom's phone call is the Neutral Stimulus. The Amazon gift card is the Unconditioned Stimulus, which elicits the Unconditioned Response of you feeling happy. Once you begin to associate gift cards with your mom calling, your mom calling becomes the Conditioned Stimulus, which elicits a Conditioned Response of you feeling happy. What a tricky mother you have!
CRB True or false? A neutral stimuli could also be referred to as a Signaling Stimuli if it does not have the potential to be a conditioned stimulus.
False. A neutral stimuli could also be referred to as a Signaling Stimuli if it Has the potential to be a conditioned stimulus.
After some time, your mom stops giving you Amazon gift cards all the time, resulting in you no longer getting happy when she calls. This is an example of which of the following Conditioning terms?
(A) Spontaneous Recovery
(B) Extinction
(C) Generalization
(D) Discrimination
(B) Extinction
Extinction refers to a loss of the Conditioned Response in response to the Conditioned Stimulus. This is what happened when your mom stopped giving you Amazon gift cards.

CRB Before Extinction could have occurred, there must have been a process of learning the conditioned response of being excited when your mom calls. What would this process be called?
(A) Acquisition
(B) Spontaneous Recovery
(C) Generalization
(D) Discrimination
(A) Acquisition
Acquisition is the process by which a conditioned response is learned, like learning to be happy when your mom calls!
Let's say that your mom will sometimes text you before giving you a gift card. How might Generalization vs. Discrimination play out in this scenario?
Generalization would mean that you feel happy when your mom texts you as well as calls you whereas Discrimination would mean that you discern this to be different than a phone call and don't feel the same happiness (conditioned response).

What would Spontaneous Recovery look like in this gift card example?
After having not gotten gift cards for years, your mom calls you and you feel happy. The Conditioned Response randomly recovered, which is what is described by the term Spontaneous Recovery.
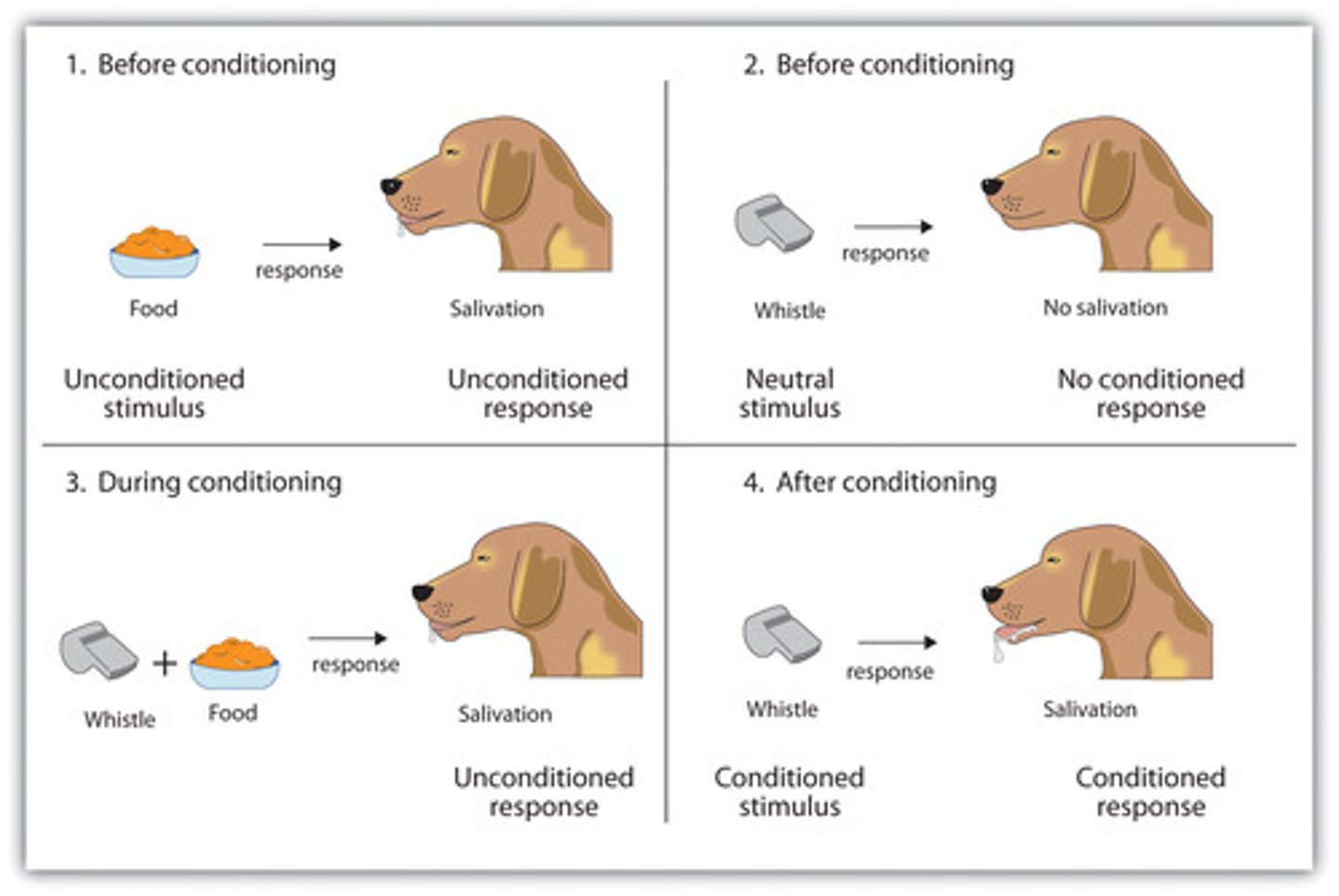
Compare and contrast Classical and Operant Conditioning. Give an example.
Classical Conditioning is when you learn to associate a stimulus with another stimulus (i.e. Pavlov's dogs associate bell ringing with getting food).
Operant Conditioning is when you learn to associate a consequence with a behavior (i.e. My dog associates getting a treat with going potty outside where he is supposed to).
CRB B.F. Skinner is strongly associated with Operant Conditioning, and he had a theory that all behaviors are conditioned. What is this theory called?
(A) Associative Learning
(B) Behaviorism
(C) Reinforcement
(D) Conditional Behaviorism
(B) Behaviorism
In Behaviorism, B.F. Skinner postulates that all behaviors are conditioned.
Every time you play your drumset really loud, your neighbor comes and knocks on the door to tell you to stop playing so loud. Which of the following Operant Conditioning terms is this an example of?
(A) Positive Punishment
(B) Negative Punishment
(C) Positive Reinforcement
(D) Negative Reinforcement
(A) Positive Punishment
Your neighbor telling you to stop is an example of Positive Punishment because your neighbor is an unpleasant stimulus being added to the situation.

You are conditioning your parents to stop asking you about your personal life. You keep your room clean except on days that your parents ask you about your personal life; on those days, you throw your clothes all over the floor. Which of the following Operant Conditioning terms is this an example of?
(A) Positive Punishment
(B) Negative Punishment
(C) Positive Reinforcement
(D) Negative Reinforcement
(B) Negative Punishment
To answer this, we need to see what the action is and when it is applied.
The action in question here is removing the positive stimulus of keeping your room clean (by throwing clothes on the floor).
The action occurs when you parents ask about your personal life. You are removing the positive stimulus to try and decrease the frequency of your parents asking about your personal life.
Since we are removing a stimulus to try and decrease the frequency of a behavior, this is Negative Punishment.
You are trying to teach your parakeet to say your name. Every time she says something close to your name, you give her a treat. Which of the following Operant Conditioning terms is this an example of?
(A) Positive Punishment
(B) Negative Punishment
(C) Positive Reinforcement
(D) Negative Reinforcement
(C) Positive Reinforcement
Giving your parakeet a treat is an example of Positive Reinforcement because you are adding a pleasant stimulus.

Come up with your own example of Negative Punishment.
You are teaching your son to eat his vegetables. On days that he doesn't eat his vegetables, he doesn't get to play his video games. This is an example of Negative Punishment because you are taking away a desired stimulus as a punishment.
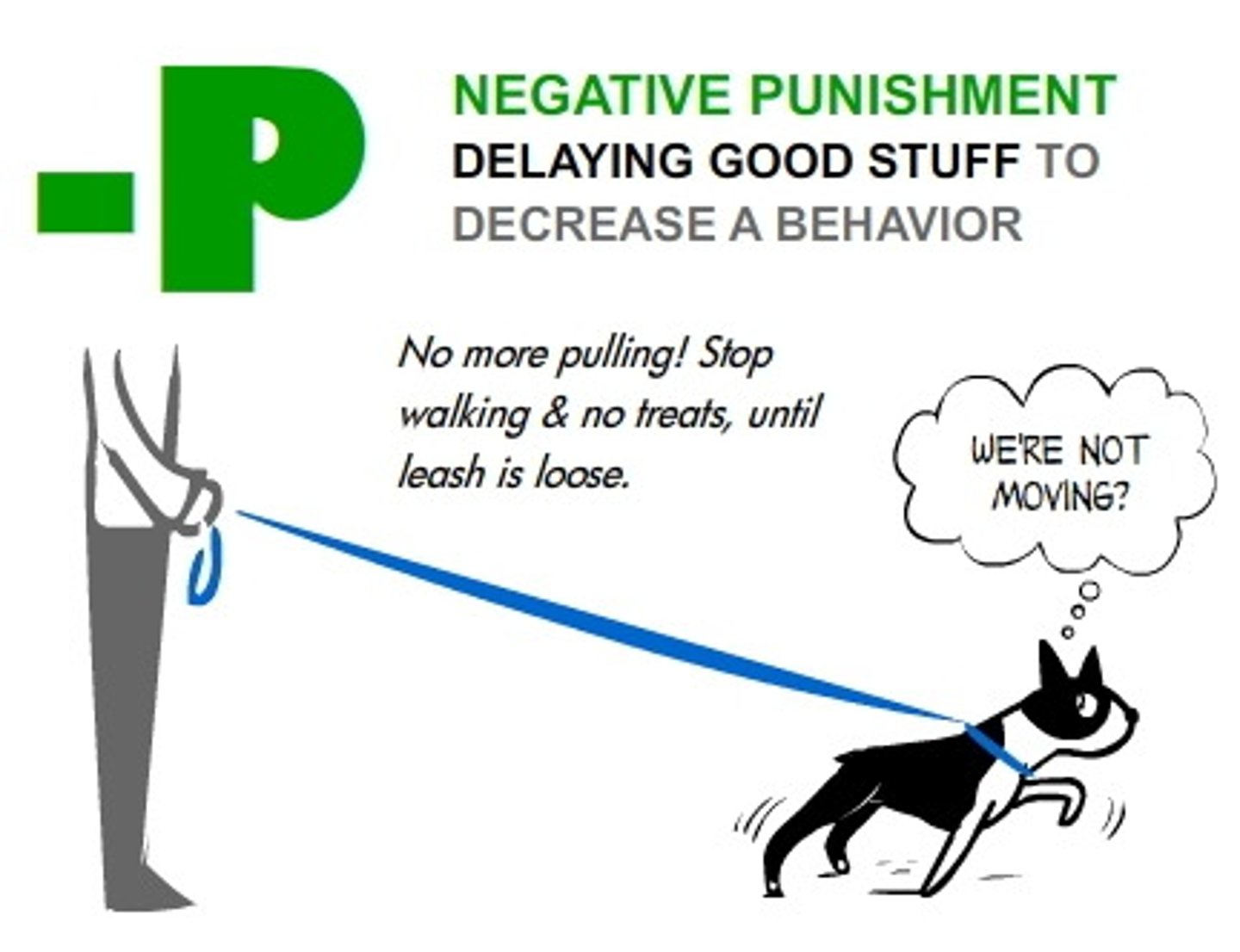
How might you use shaping to teach your dog to do a backflip?
You would reward your dog for each successive good step in the right direction. For instance, first reward him for getting up on two feet. Then reward him for falling backwards. Then reward him for the attempt at a flip, and finally reward him for the full, successful flip.
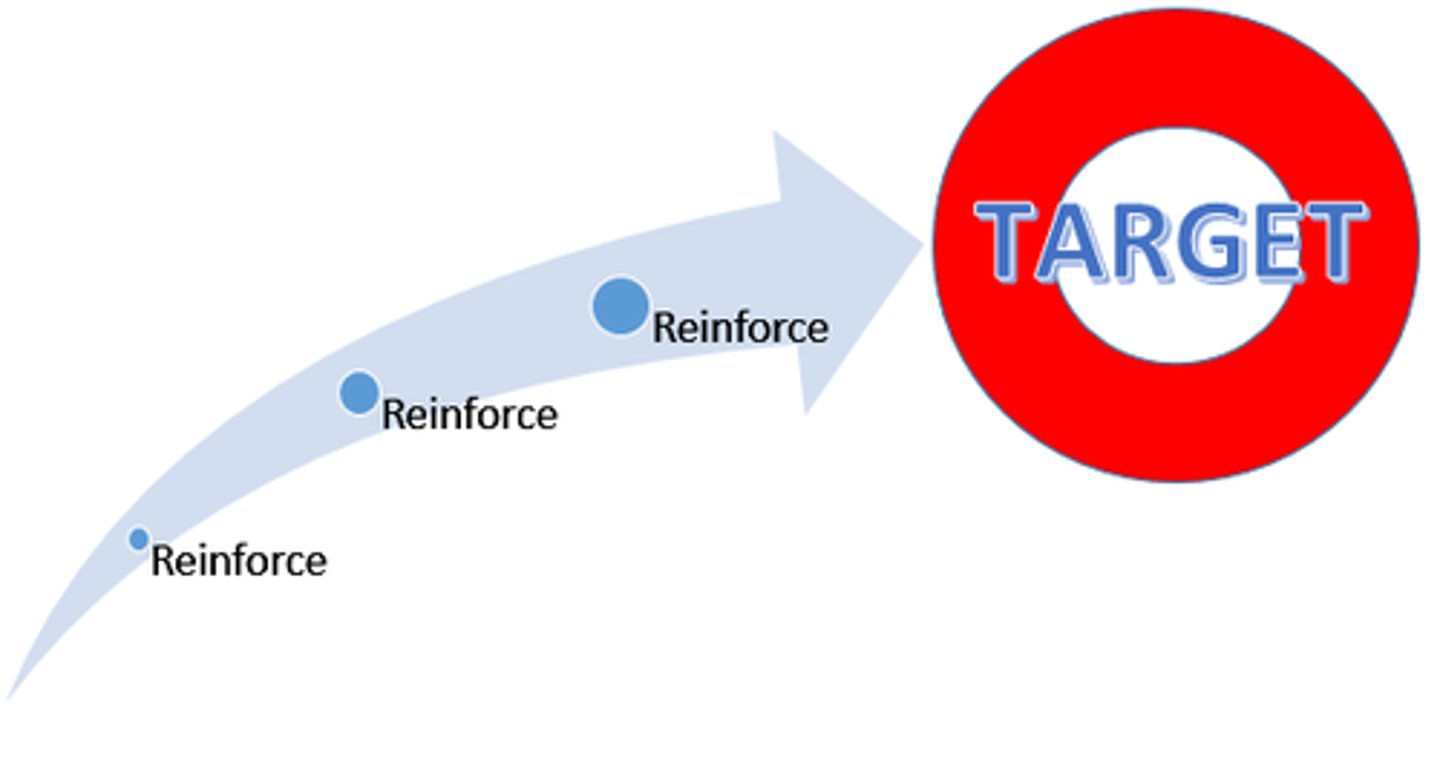
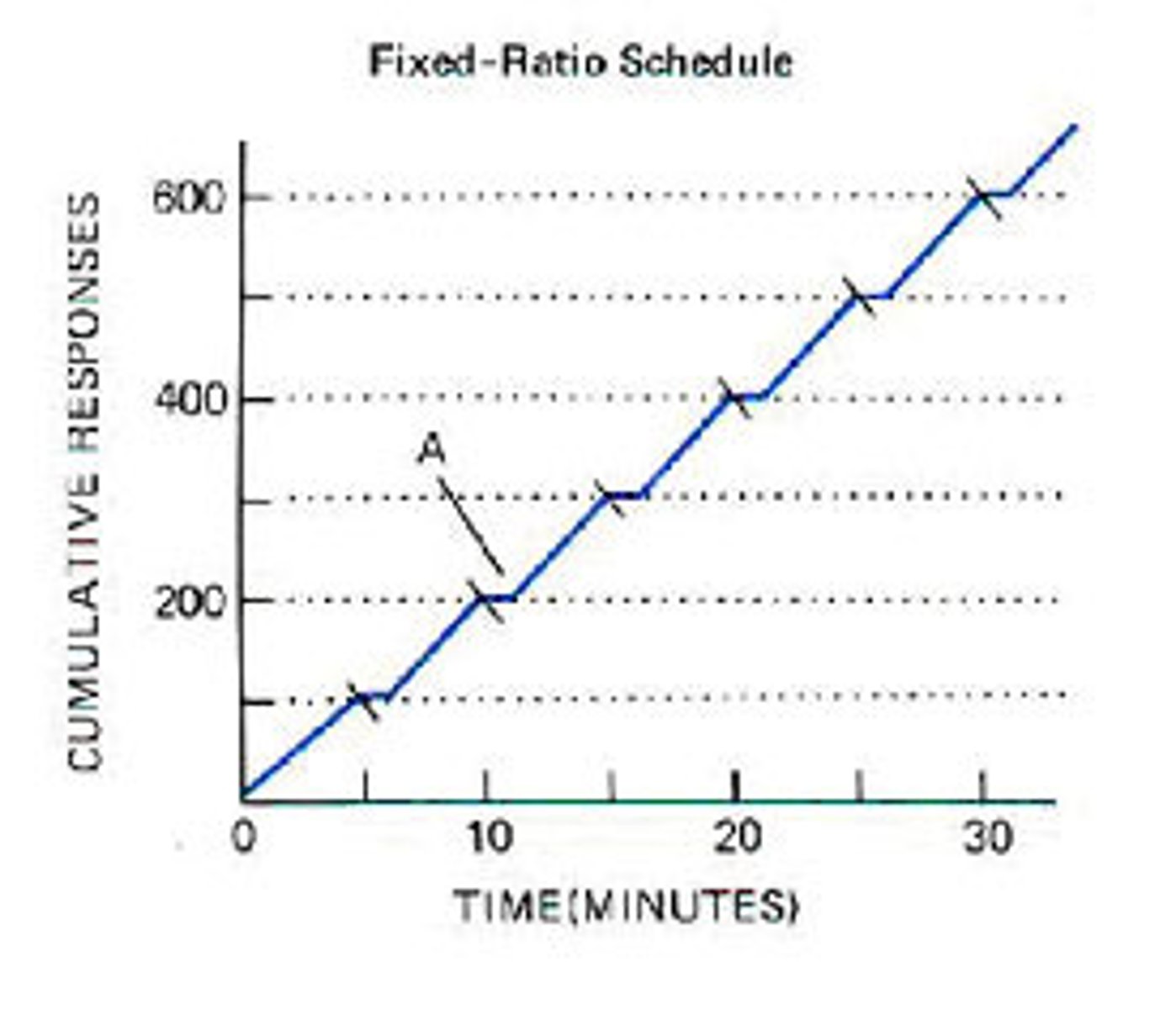
You give your dog a treat after every time it goes potty outside. This example is most illustrative of which partial reinforcement schedule?
(A) Fixed-ratio
(B) Variable-ratio
(C) Fixed-interval
(D) Variable-interval
(A) Fixed-ratio
Giving your dog a treat after each successful attempt is an example of a fixed-ratio schedule.
The ratio does not have to be 1:1, as in this scenario, to be a fixed-ratio.
CRB True or false? A Continuous reinforcement schedule would need to have every occurrence of the behavior enforced (a 1:1 ratio), whereas an intermittent reinforcement schedule must not have that 1:1 ratio.
True. A Continuous reinforcement schedule would need to have every occurrence of the behavior enforced (a 1:1 ratio), whereas an intermittent reinforcement schedule must not have that 1:1 ratio.
You will randomly give your cat a treat throughout the day as long as she has continued to avoid scratching the furniture. This example is most illustrative of which partial reinforcement schedule?
(A) Fixed-ratio
(B) Variable-ratio
(C) Fixed-interval
(D) Variable-interval
(D) Variable-interval
Giving your cat a treat at random times is an example of a variable-interval schedule because it is based on a random time table and not on number of actions.
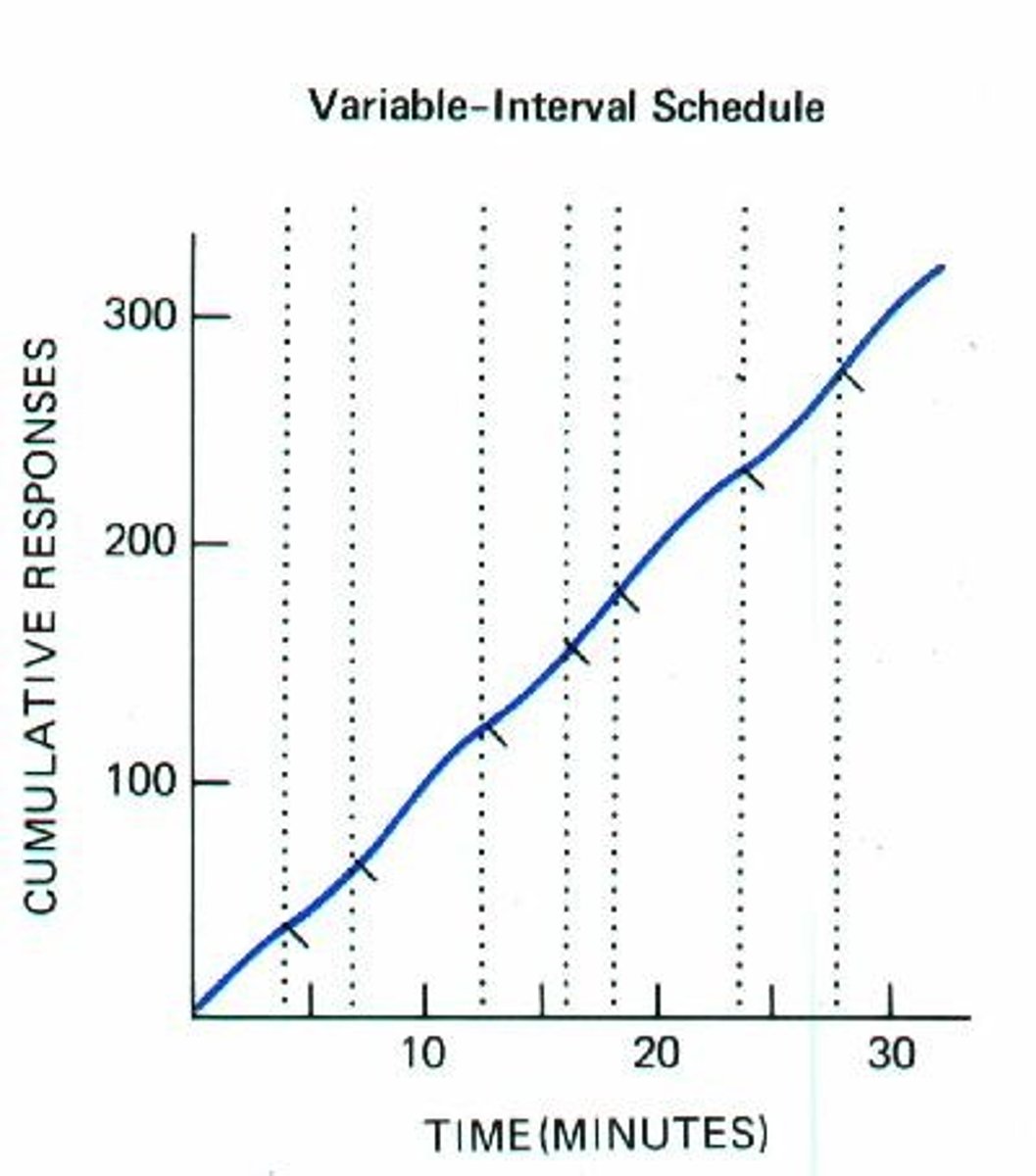
You give your sister some licorice at the end of each hour that she avoids annoying you. This example is most illustrative of which partial reinforcement schedule?
(A) Fixed-ratio
(B) Variable-ratio
(C) Fixed-interval
(D) Variable-interval
(C) Fixed-interval
You are rewarding your sister according to a timetable that is fixed.
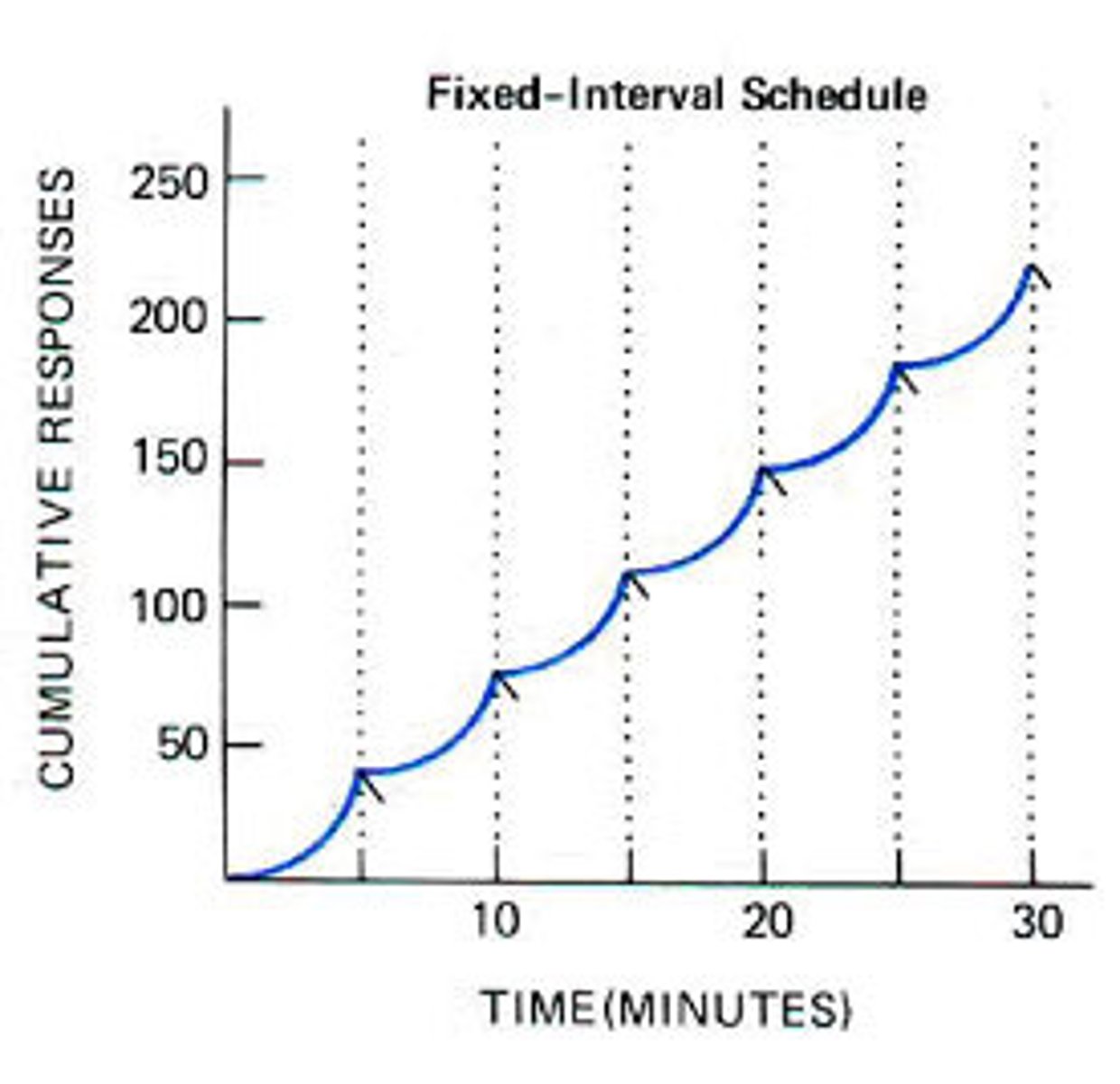
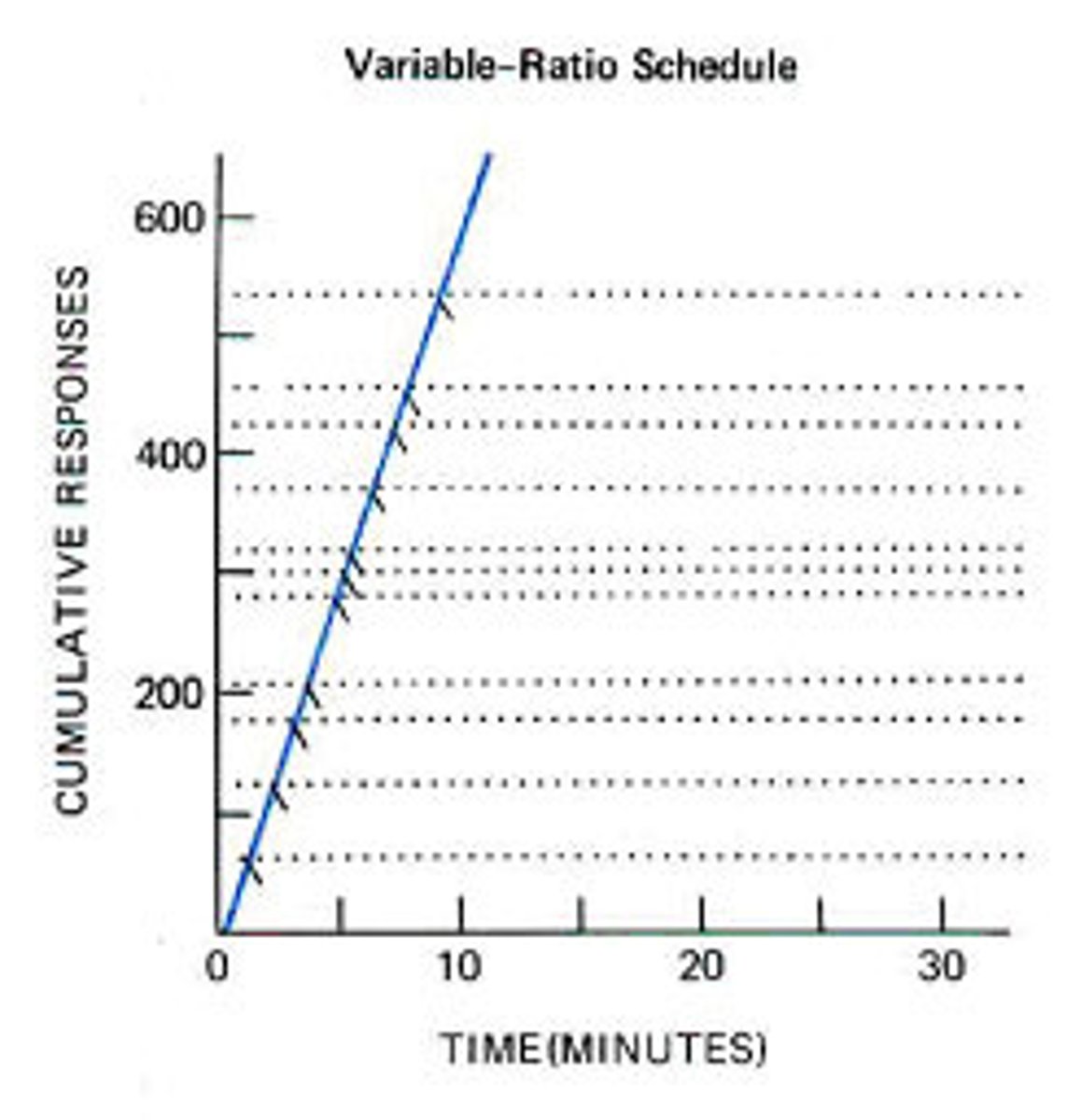
In some forms of gambling, the user is rewarded at random. This example is most illustrative of which partial reinforcement schedule?
(A) Fixed-ratio
(B) Variable-ratio
(C) Fixed-interval
(D) Variable-interval
(B) Variable-ratio
Gambling utilizes variable-ratio conditioning, as it rewards after a random number of actions.
Which reinforcement schedule is the best at causing the repetition of behavior?
Variable-ratio is best at causing repetition of behavior, which is why gambling is so addictive.

CRB Compare Primary and Secondary reinforcers, using a Las Vegas buffet at a casino as an example.
A Primary reinforcer would be innately satisfying, like eating a big dinner at a Las Vegas buffet. A Secondary reinforcer would have to be learned to be a reinforcer, like learning to play all day at the casino so your buffet meal is comped by the casino.
CRB An early caveman is used to working hard to get the direct reward of finding food to eat. This caveman is dropped into modern society, and instead of offering him food for his work, they are offering to pay him in Dogecoin, which he can use to buy food. What role does this Dogecoin best fill?
(A) Conditioned Stimulus
(B) Primary Reinforcer
(C) Unconditioned Stimulus
(D) Secondary Reinforcer
(D) Secondary Reinforcer
Because this scenario relies upon Dogecoin not being innately satisfying, but rather being used as a means to get something satisfying, Dogecoin is best considered a Secondary Reinforcer.
Dogecoin, for those who don't know, is a cryptocurrency (like Bitcoin).
Which of the following are examples of Simple Innate Behaviors?
I. Reflexes
II. Kinesis
III. Migration
(A) I Only
(B) I and II Only
(C) II and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(B) I and II Only
Reflexes, Kinesis (random movement in response to stimulus), and Taxis (purposeful moving towards or away from stimuli) are examples of Innate Behaviors.
Complex Behaviors include Fixed Action Patterns, Migration, and Circadian Rhythm.
An Amoeba can sense and move toward food. What is this an example of?
An Amoeba can sense and move toward food. This an example of Taxis as it is purposeful movement.
You shine a light in a dark room and cockroaches scurry in all directions. What is this an example of?
You shine a light in a dark room and cockroaches scurry in all directions. This is an example of Kinesis.
When you drop a baby, it will throw its arms up in the air instinctively. What is this an example of?
When you drop a baby, it will throw its arms up in the air instinctively. This is an example of a reflex.

Give an example of a Fixed Action Pattern, Migration, and Circadian Rhythm as it might apply to a fish.
The fish may swim in circles when it is trying to attract a mate. This would be an example of a Fixed Action Pattern.
The fish may swim upstream to lay its eggs at a certain time of the year. This would be an example of migration.
The fish may consistently sleep at night as opposed to the daytime, which would be an example of Circadian Rhythm.
You are working on your homework and although you originally noticed the clock ticking in the background, you've stopped noticing it for the past hour. This example is most closely aligned with which Learned Behavior?
(A) Habituation
(B) Classical Conditioning
(C) Operant Conditioning
(D) Insight Learning
(A) Habituation
And when you answered this question, I bet you noticed a clock ticking in the background if there was one, huh?
You are trying to solve a difficult physics practice question. How might insight learning help you in this instance?
Maybe you will go take a shower, and then randomly the solution will come to you as an insight.

A mouse is on a diving board that can sometimes administer electric shocks. The researcher shocks the diving board, and the mouse jumps in the water. Before the shock, however, the researcher made a beeping noise. Next time, when the researcher makes the beeping noise, the mouse jumps off the diving board before the researcher has time to apply the electric shock. How does this example relate to Avoidance Learning, Escape Learning, and Aversive Control, respectively?
Escape Learning applies to the mouse jumping off the bridge to escape the continuous electric shock.
Avoidance Learning applies to the mouse jumping off when it hears the beep noise in order to avoid getting shocked.
Both Escape and Avoidance Learning are examples of Aversive Control.
Describe how Sensitization and Habituation may relate to trying to sleep in a new noisy neighborhood.
Sensitization would entail you having a harder and harder time trying to sleep because the noises start bothering you more and more.
Habituation would entail you having and easier and easier time trying to sleep because the noises begin to blend into the background and affect you less and less over time.

CRB The majority of Pavlov's dog experiments relied upon associative learning. Which of the following are examples of Non-Associative learning in dog experiments?
I. When the bell is rung and then food is brought out, the dog learns to salivate when the bell is rung.
II. A light will go on right before the bell is rung. The dog learns to salivate when the light is lit.
III. The bell malfunctions and has rung every five minutes for a week. By the end, the dog no longer salivates when the bell is rung.
(A) I only
(B) III only
(C) I and II only
(D) I, II and III
(B) III only
In this example, the dog becomes habituated to the bell ringing; the dog is not learning to associate this ringing with any other stimulus.
CRB Which of the following would NOT be considered Non-associative Learning?
(A) Habituation
(B) Dishabituation
(C) Sensitization
(D) Extinction
(D) Extinction
Extinction would be considered a part of Classical Conditioning, which is associative learning.
Habituation, Dishabituation and Sensitization are all types of Non-associative learning.
Why are Sensitization and Habituation referred to as Non-associative Learning?
They are called this because the learner is not learning to associate something with something else.
CRB When I first moved into college, my roommate's Doomsday morning alarms used to startle me the six times they went off each morning. By the middle of the semester, I wasn't even aware of these alarms going off, and easily slept through them. Which of the following terms best describes this phenomenon?
(A) Associative Learning
(B) Dishabituation
(C) Habituation
(D) Sensitization
(C) Habituation
Because a single stimulus is being repeated often, and my response has decreased over time to the stimulus, this would best be characterized as Habituation.
CRB I went home for winter break, and when I returned, my roommate still used his same alarm setup. However, I was startled and woke up the first morning back. Which of the following terms best describes this phenomenon?
(A) Associative Learning
(B) Dishabituation
(C) Habituation
(D) Sensitization
(B) Dishabituation
Because the stimulus that I had habituated was removed for a long period of time, I was no longer habituated to it when the stimulus returned. This is best described as Dishabituation.
CRB Dick "Night Train" Lane was a feared football player for many years. When he was younger, he wouldn't even feel sore after a big game or tough double-sessions. Near the end of his career, these same double sessions and hard-fought games would leave him extremely tight and in a lot of pain the next morning. Which of the following terms best describes this phenomenon?
(A) Associative Learning
(B) Dishabituation
(C) Habituation
(D) Sensitization
(D) Sensitization
"Night Train" Lane had very little response to the constant stimulus of practices or games when he was younger. However, his responsiveness increased as this noxious stimulus continued to be applied. This would best be described as Sensitization.

CRB Kelub went to his local Newport Creamery and ordered a burger to pair with his typical Holy Cow sundae. A few hours later, Kelub had food poisoning, and says he will never have another burger from a creamery again. The next week, he is really hungry and decides to order another burger from Newport Creamery anyways. Would this count as a taste aversion? Why or why not?
A Taste-Aversion is an extremely strong, long-lasting association that an individual will have with that type of food. Because Kelub had already forgotten this association in one week, this would not be considered a taste aversion.
Explain why the rats who got shocked when administered sweet water only did not develop an aversion to sweet water?
It is not natural to associate a shock with food poisoning whereas it is natural to associate an upset stomach with food poisoning. This illustrates that we are evolutionarily predisposed to learn certain things.
CRB After training my dog to not eat the dead squirrels it sees in the woods, after a few months of winter, my dog forgets what I taught him and starts eating the dead squirrels again in the spring. What would this be an example of?
(A) Dishabituation
(B) Instinctive Drift
(C) Extinction
(D) Poor Training
(B) Instinctive Drift
Instinctive drift is a difficulty in overcoming behaviors that are natural to the individual. For my dog, eating the dead animals it sees is a natural source of food for him, so over time he forgot the behaviors I had tried to teach him.
Explain why my one-year-old child really wants to touch the outlets in my house, but he gets scared of a barking dog.
This is because my child is predisposed by evolution to know that barking dogs are dangerous whereas outlets have not been around long enough to result in any sort of evolutionary adaptation.
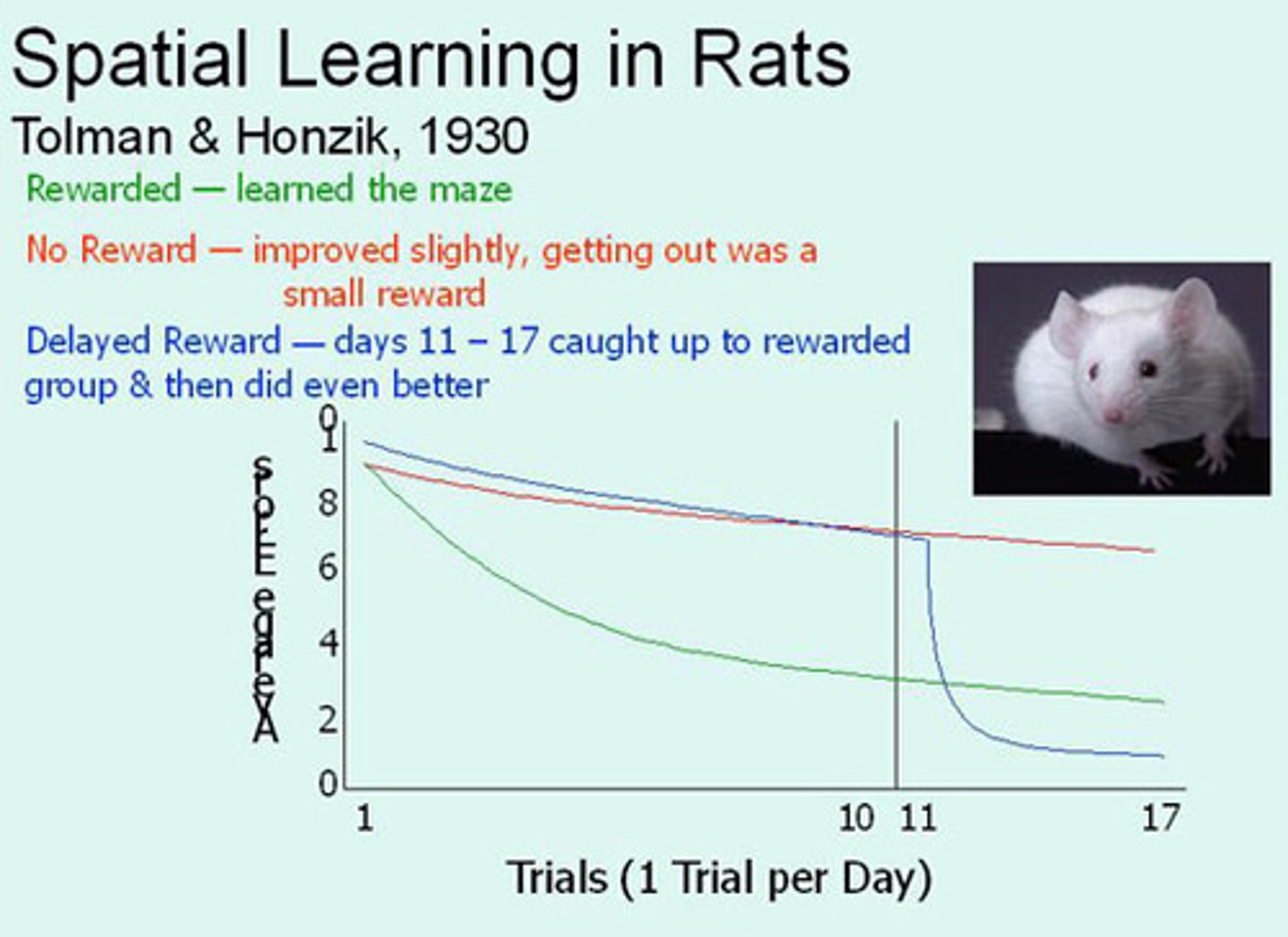
CRB In a famous Tolman and Hoznek experiment, there were three groups of mice that ran mazes. One group always had a reward at the center of the maze; one group never had a reward at the center of the maze; the third group had no reward for the first ten trials, but had a reward for all subsequent trials. That third group had similar speeds to the unrewarded group for the first ten trials, but showed a steep decrease in time running the maze once the reward was introduced. What would this effect be called?
(A) Latent Learning
(B) Insight Learning
(C) Late Learning
(D) Masked Learning
(A) Latent Learning
In Latent Learning, something is learned, but not necessarily represented by any behavioral change. There was no incentive for the mice to run the maze without a reward; once a reward was introduced, they exhibited their learning.
CRB True or false? Advanced organisms are able to learn not only through direct experience, but also through Vicarious Learning.
True. Advanced organisms are able to learn not only through direct experience, but also through Vicarious Learning.
This Vicarious Learning can also be called Social or Observational Learning.
CRB Janelle was trying to learn how to play Fortnite so she could beat all of her friends. Knowing almost nothing about video games, she went onto Twitch and watched a couple of hours of a popular streamer. She then logged onto Fortnite and won her first Victory Royale! What would this be an example of?
(A) Associative learning
(B) Secondary Reinforcement
(C) Consolidation
(D) Modeling
(D) Modeling
Modeling is a type of Observational learning, in which somebody observes somebody else's behavior and imitates it. Here, Janelle imitated the Twitch streamer's Fortnite behaviors and won a game.
CRB Jerry the Macaque monkey has been trained how to play chess. Fill in the blanks about moving the pieces: Whenever _____________ would pick up a pawn, ____________ would fire action potentials in Jerry's brain.
(A) Jerry, Mirror Neurons
(B) Jerry, Cortical Neurons
(C) Jerry or his opponent, Mirror Neurons
(D) Jerry or his opponent, Cortical Neurons
(C) Jerry or his opponent, Mirror Neurons
Jerry the Macaque monkey has been trained how to play chess. Fill in the blanks about moving the pieces: Whenever Jerry or his opponent would pick up a pawn, mirror neurons would fire action potentials in Jerry's brain.
Mirror neurons fire when a higher mammal either performs or observes somebody else performing a particular task! This could be one way that observational learning is possible.
CRB True or false? It is also possible that Vicarious emotions, like Empathy, could be caused by Mirror Neurons.
True. It is also possible that Vicarious emotions, like Empathy, could be caused by Mirror Neurons. Instead of the action being the focus of these mirror neurons, the emotion would be. This is an active area of research!