L22 Dialysis
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Kidney Shape and size and basic structure
Bean shaped, is 150gm and has cortex+medulla. Lots of nephrons
Nephron components (5)
glomerular apparatus
proximal tubule
Loop of henle
Distal tubule
collecting ducts
3 types of nephrons
Cortical
Intermedial
Juxtamedullary
5 Things glomerular filtration can depend on
Molecular size, protein binding, ionization, polarity and kidney function
Tubular reabsorption when full
Renal clearance limited to amount of drug that leaves kidney as urine flows into bladder when there is 100% reabsorption
What does tubular secretion depend on?
The transporter, and how fast and efficient it is. Depends on fu.
What is normal urine output?
Without reabsorption would be 172.8L, but with is 1.73 L since about 99% drug gets reabsorbed.
CKD definition
Abnormalities of kidney structure or function, present for > 3 months, with implications for health
2 things to diagnose CKD
GFR <60 mL/min
One or more markers of kidney damage
EGFR ranges
Normal:>90 /1.73 m^2 (apply for everything)
Mildly decreased: 60-89
Mild to moderately decreased: 45-59
Moderate to severe decrease:30-44
Seere decrease:15-29
Kidney failure: <15
Albuminuria(Albumin/.creatinine) ranges
Normal to mildly increased: < 3mg/mmol
Moderate increase: 3-30mg/mmol
Severe increase: 30mg/mmol
CKD effect on Drug absorption and F (4)
Delayed gastric emptying and intestinal motility affecting T and Cmax of drugs
High gastric pH: excess urea in saliva turn to ammonia, alkalinization affect drugs
Drug F is more variable
Uremia decrease GI absorption and change first pass
CKD effect on distribution 2
Altered volume of distribution: (Dehydration/muscle wasting)
Altered plasma protein and tissue binding of drugs
CKD effect on metabolism (3)
Uremia slows rate of phase I metabolism and some phase II
Dependent on kidneys for removal of drug metabolites from body
Complicated impact on drug metabolism including changes in expression of several CYP enzymes and transporters
CKD effect on elimination (2)
Renal clearance depends on GFR, tubular reabsorption, and tubular secretion
GFR down leading to renal clearance down leading to higher plasma T 1/2.
Dialysis definition
Extracorporeal removal of waste products like creatinine and urea and free water from blood when kidneys are in a state of kidney failure
Done with IV catheter or areteriovenous fistula
4 parts of dialysis
remove blood, pump blood, filter blood, return filtered blood back to body
Dialyzers component:
Fibers, poly sulfone, methylmetacrylate, acrylonitrile
Dialysate description
Countercurrent flow
500-800mL/min has multiple solutes and anticoagulants
Waste and fluid removal mechanism for dialysis
Diffusion and ultrafiltration
Concentration gradient against dialyzer membrane
3 components of dialysis prescription
Flow rate
Duration of dialysis
Dialyzer
Urea Reduction Ratio equation (URR)
>70% is adequate
BUNpre-BUNpost/BUNpre *100%
Kt/V as measure of adequacy
Kt is dialyzer CL Of urea
T is duration of dialysis
V is volume of blood cleared from urea
What Kt/V > 1-3
4 properties of dialyzable drug
MW<5000 daltons
Vd<1 L/kg
Protein binding <90%
Low lipid solubility
Peritoneal dialysis description
Uses peritoneum in person's abdomen as membrane through which fluid and dissolved substances are exchanged with blood
Remove excess fluid, correct electrolyte problems and remove toxins in those with kidney failure.
use for patients who are hemodynamically stable
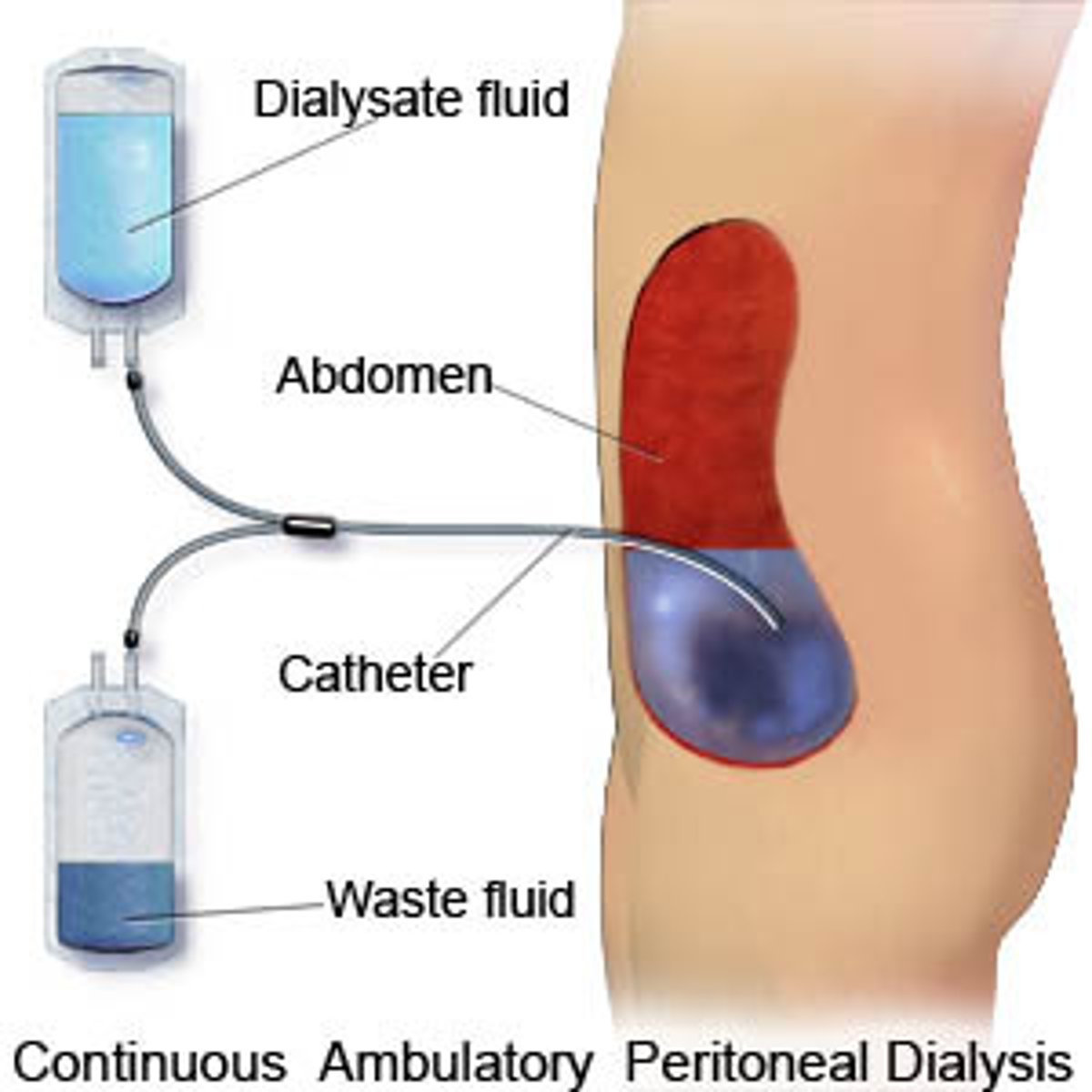
Peritoneal physiology (5)
Contains 100 mL liquid
Can expand to hold several liters
Surface area of 1-2 m^2
Allows passage of larger MW substances
Catheters used to gain access to peritoneal cavity
Dialysate for peritoneal dialysis
High dextrose solution containing various solutes and anticoagulants
2 types of peritoneal dialysis
Continuous cyclic: cycler at night, day dwell (chill)
Continuous ambulatory: 3 daily exchanges, 1 longtime bedtime dwell
Kv/T for peritoneal dialysis
Kt=D/P: dialysate to plasma urea concentration
should be ~2 per week
3 components of peritoneal dialysis prescription
Number of exchanges (CAPD)
Volume
Concentration of solutes
3 properties of dialyzable drug for peritoneal dialysis
Vd<1L/kg
Protein binding<96%
Can better clear large molecules up to 15,000-20,000 daltons
Absorption changes for hemodialysis
Increased absorption from paracellular leakage, decreased efflux transporter activity and decreased CYP450 activity
Distribution changes for hemodialysis
increased fu cause decreased albumin, uremic toxin mediated decrease in protein binding
Metabolism changes for hemodialysis
Decreased Phase I and Phase II metabolism
Excretion changes for hemodialysis
Decreased renal and biliary drug excretion
Hemodialysis changes for hemodialysis
Dialytic drug clearance leading to decreased plasma conc
Normalization of non renal drug clearance pathways
How does change in CYP and transporters affect renal vs non renal cleared drugs for patients on hemodialysis
Renal has a higher AUC
Non renal has a lower AUC for those with chronic hemodialysis.
3 questions to ask for influence of dialytic therapy on PK of drug
If drug dosage should be adjusted cause of dialysis
How much?
Timing of drug admin relative to dialysis
IHD/Intermittent hemodialysis
most common method used, need to record blood flow, dialysate flow and type of dialyzer used for studies
CRTT/continuous renal replacement therapy
For critical care meds, IHD studies might not be enough.