Pharmacokinetics Absorption and Distribution 2
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
an important consequence of administering drugs by different routes is that there can be a?
Different Bioavailbility
The standard of comparison in determining bioavailability, against which all other routes are compared, is the?
IV Dose
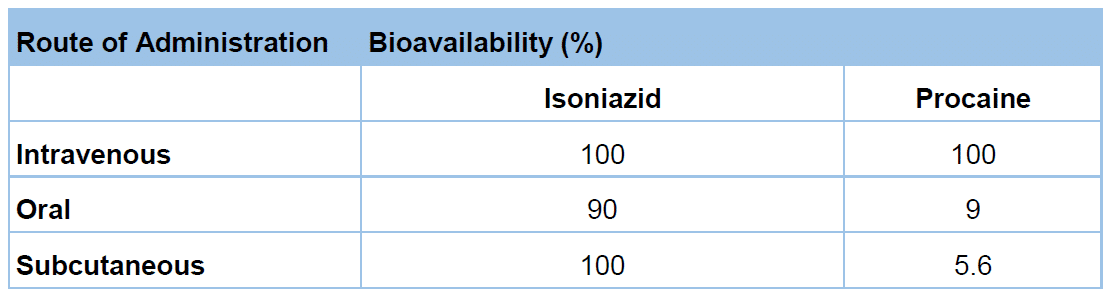
Factors that can affect bioavailability include?
Metabolism
Lipid Solubility
Chemical Stability
Drug Formation
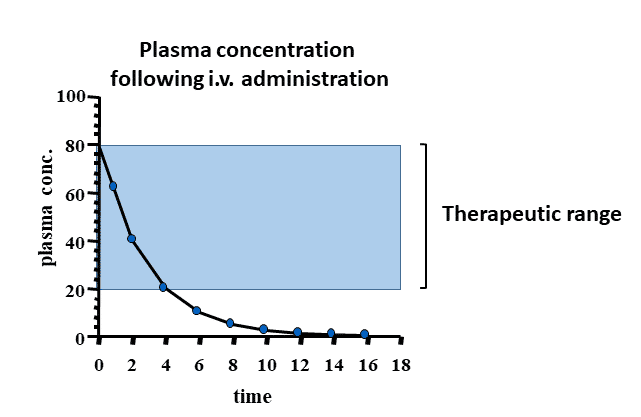
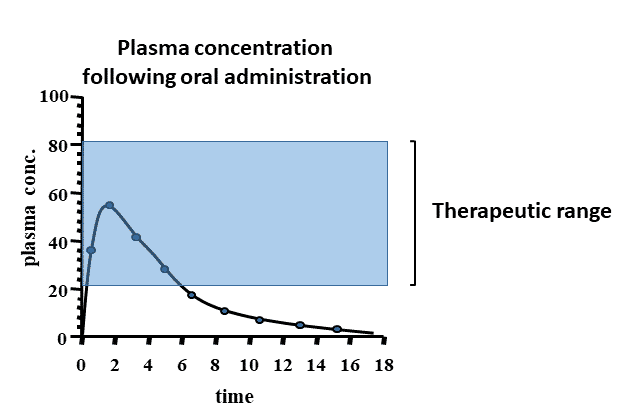
drug plasma levels decline over time, This decline is the result of?
The Drug being Metabolized and Excreted.
The plasma level reflects the concentration of drug at the target site more?
Closely than the dose and may indicate tissue exposure
Drug will produce a pharmacological effect when the plasma level…?
Falls within Therapeutic Range
IV plasma Concentration Diagram
Oral Plasma Concentration Diagram
The plasma half-life (t½) is time interval during?
During which the Drug Concentration is Reduced by 50% / 1/2
Plasma Half life provides an important indicator for the?
Duration of Drug Action
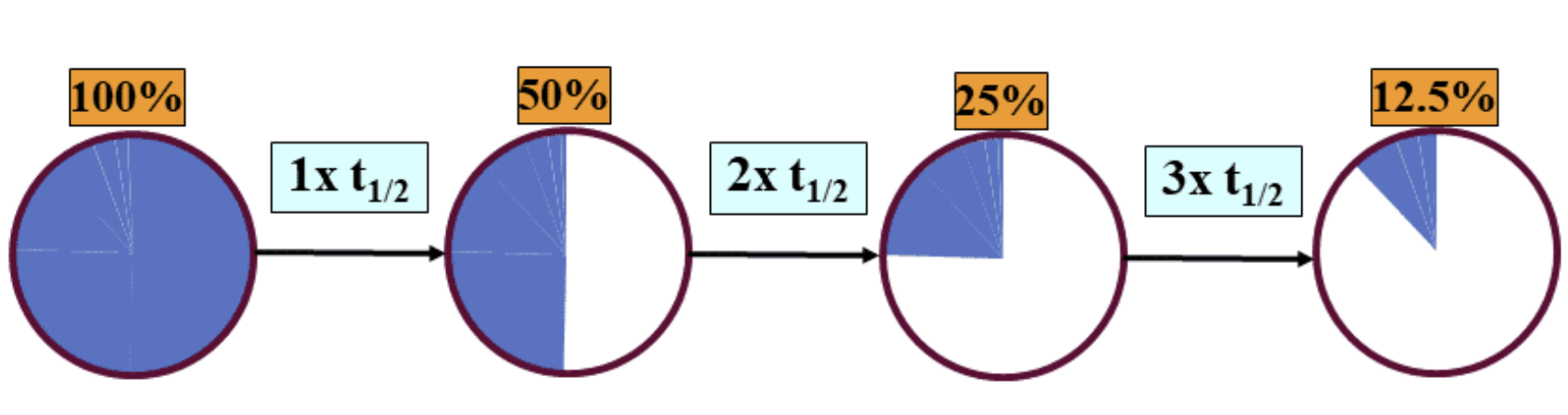
Therefore drugs with a short plasma half-life will have a?
Short Duration of Action.
and require more frequent administration than drugs with a long plasma half-life.
Drugs are distributed throughout the body through the various?
Fluid Compartments of the Body
Body Water is between 50-70% of Weight.
Lower range being women.
Highly fat-soluble drugs may accumulate?
In fat.
Body water is distributed in the following main compartments?
Blood Plasma = 5% TBW
Interstitial and Lymph = 17% TBW
Intracellular Fluid = 30-40 % TBW
Transcellular Fluid = 5 % TBW
Fat = 20 % TBW
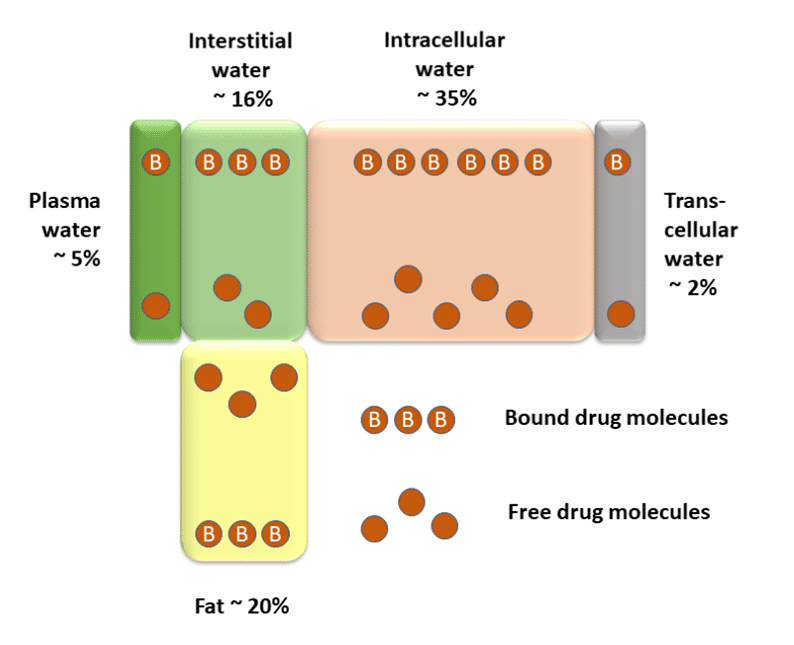
Drugs exist in what 2 Forms within Compartments?
Free and Bound Forms
What is the only Drug Form that can move between Compartments?
Free Drug
The equilibrium of distribution between the various compartments depends on?
Permeability between Tissue
Binding within Compartments
pH partition
Fat: Water Partition
Lipid-soluble drugs reach?
All Compartments
and may accumulate in Fat
lipid-insoluble drugs are mainly confined to?
Plasma and Interstitial Fluid.
Most do not enter the brain.
The blood brain barrier is caused by a continuous?
Layer of Epithelial Cells
joined by tight junctions and surrounded by pericytes.
making the brain inaccessible to drugs with?
Insufficient Lipid Solubility
Volume of Distribution Diagram Calculator
The two main reasons why a drug may be confined to blood plasma are?
Vd less than 5L
Molecular Size
Plasma Protein Binding
for example heparin.
Drugs distributed in the Extracellular Compartment have a Vd between?
Vd between 5L and 15 L
for example gentamicin and carbenicillin
Drugs distributed throughout all compartments and water have a vD of ?
Vd greater than 15L
Aka Lipid Soluble Drugs.
Morphine E.G
Pharmacokinetic interaction occurs when?
drug A alters the concentration of drug B that reaches the site of action.
Certain drugs can alter the rate of gastric?
Gastric Emptying
Results in Slower GI Absorption
Mainly in Small Intestine
atropine inhibits?
Gastric Emptying
metoclopramide hastens?
Gastric Emptying