20. Mechanical jaundice, Hemorrhoids and anal fissure & Traumatic injuries of the liver and spleen
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What is the definition of MECHANICAL JAUNDICE?
obstructive or post-hepatic icterus. It results from elevated bilirubin (> 2mg/dL)
What is the etiology of MECHANICAL JAUNDICE?
Choledocholithiasis,
biliary duct strictures
malformations of the bile ducts
Tumours
What is the pathophysiology of MECHANICAL JAUNDICE?
Biliary obstruction
Backflow of conjugated bilirubin into blood
Decreased bilirubin in the intestines
Clinical features: jaundice, dark urine, pale stools, pruritus
What is the clinical presentation of MECHANICAL JAUNDICE?
jaundice,
pale coloured stool,
dark urine,
pruritus
Fat malabsorption (steatorrhea, weight loss)
What are the diagnostic methods of MECHANICAL JAUNDICE and their positive results?
LABS:
increased ALP, GGT, and conj. bilirubin
increased AST, ALT
USG
intrahepatic obstruction = dilated intrahepatic bile ducts
Extrahepatic ““ = dilated common bile duct
Stones
ERCP (Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography)
MRI
CT
What is the surgical treatment of MECHANICAL JAUNDICE?
surgical excision of the obstruction
cholecystectomy if stones are present.
What is the definition of HEMORRHOID?
bulging veins or arteriovenous formations within the wall in the rectum, developing due to increased pressure in the rectal veins
What is the classification of HEMORRHOID and their features?
Gr. I — No prolapse
Gr. II — Prolapse when straining, but spontaneously reduce at rest
Gr. III — Prolapse when straining; only reducible manually
Gr. IV — Irreducible prolapse
What are the types of HEMORRHOID and their features?
Internal: painless, bright red hematochezia, perianal mass, pruritus, discharge, ulceration
external: painful perianal mass, pruritus
What is the etiology of HEMORRHOID?
Constipation
chronic diarrhea
obesity,
pregnancy,
low-fiber diet,
lifting heavy things,
anal sex.
What are the diagnostic methods of HEMORRHOID and their positive results?
anoscopy
proctoscopy
To exclude malignancy:
Flexible sigmoidoscopy,
colonoscopy,
barium enema
What are the measures to ease symptoms of HEMORRHOID?
Sitz baths (cleanses the perineum)
ice packs to the anal area, and bed rest.
High-fibre, high-fluid diet,
stool softeners,
topical steroids
What is the treatment of internal HEMORRHOID?
Rubber band ligation
What is the surgical treatment of HEMORRHOID?
sclerotherapy,
electrocautery
laser therapy
Hemorrhoidectomy = if conservative methods fail or for severe cases like strangulation or large tags.
What is the definition of ANAL FISSURES?
longitudinal tear of the perianal skin distal to the dentate line, often due to increased anal sphincter tone.
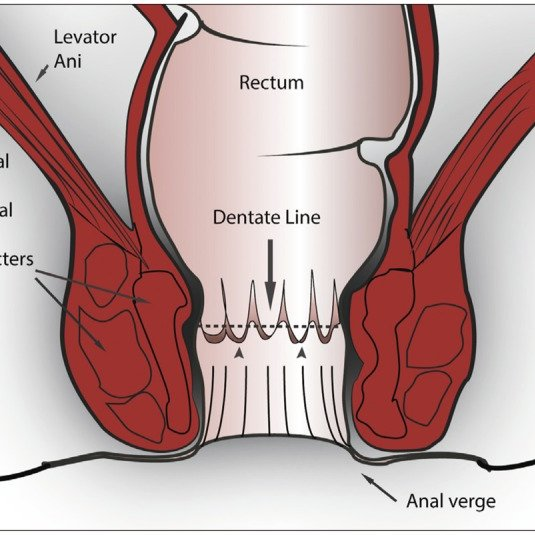
What is the classification of ANAL FISSURES and their features?
According to etiology or duration, such as acute or chronic.
What are the primary and secondary etiologies of ANAL FISSURES?
Primary etiologies (local trauma):
Chronic spasm/increased tone in the internal anal sphincter
chronic constipation or diarrhea,
low fiber intake,
anal sex,
vaginal delivery.
Secondary:
Previous anal surgery
IBD
Granulomatous disease
Infections (e.g. chlamydia, HIV)
Malignancy
What are the clinical features of ANAL FISSURES?
Sharp, severe pain during defecation
Rectal bleeding (often bright red and minimal)
Perianal pruritus
Chronic constipation
What are the diagnostic methods of ANAL FISSURES and their positive results?
Clinical examination
Digital rectal examination
Anoscopy = Indicated if clinical findings are unclear or if symptoms persist despite adequate treatment-
biopsy and histology
What is the conservative treatment of ANAL FISSURES?
Sitz bath
Ice packs + bed rest
Stool softeners
High-fiber, high-fluid diet
Topical steroids
What is the surgical treatment of ANAL FISSURES?
Lateral internal sphincterotomy = decrease sphincter spasming
Forceful anal dilation
What are the types of TRAUMATIC INJURIES OF THE LIVER AND SPLEEN?
Liver injuries can be caused by blunt or penetrating trauma.
Splenic injuries can include subcapsular hematoma or free rupture.
What is the epidemiology of TRAUMATIC INJURIES OF THE LIVER AND SPLEEN?
The spleen is the most commonly injured intraabdominal organ, especially from non-penetrating injuries.
The liver is the second most injured organ after blunt trauma and the most injured parenchymal organ after penetrating trauma.
What is the etiology of TRAUMATIC INJURIES OF THE LIVER AND SPLEEN?
blunt abdominal trauma and penetrating trauma
What is the clinical presentation of TRAUMATIC INJURIES OF THE LIVER AND SPLEEN?
hemorrhage
shock,
abdominal pain,
ABD distention
What are the diagnostic methods of TRAUMATIC INJURIES OF THE LIVER AND SPLEEN and their positive results?
USG or abdominal CT scan.
What is the conservative treatment of TRAUMATIC INJURIES OF THE LIVER AND SPLEEN?
Subcapsular splenic hematoma can be treated conservatively with close observation for 7 days.
What is the surgical treatment of TRAUMATIC INJURIES OF THE LIVER AND SPLEEN?
For liver injury, = suture, drainage, resection, and packing.
For splenic injury = splenectomy and embolisation (blocking off of the hemorrhaging vessels)
What is the definition of POST-TRAUMATIC HEMOPERITONEUM?
Post-traumatic hemoperitoneum is blood accumulating in the abdominal cavity following trauma and is associated with traumatic injuries of the liver and spleen.