Geometry Ch 2 Reasoning & Proof
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Counterexample
a specific case for which the conjecture (or statement) is false
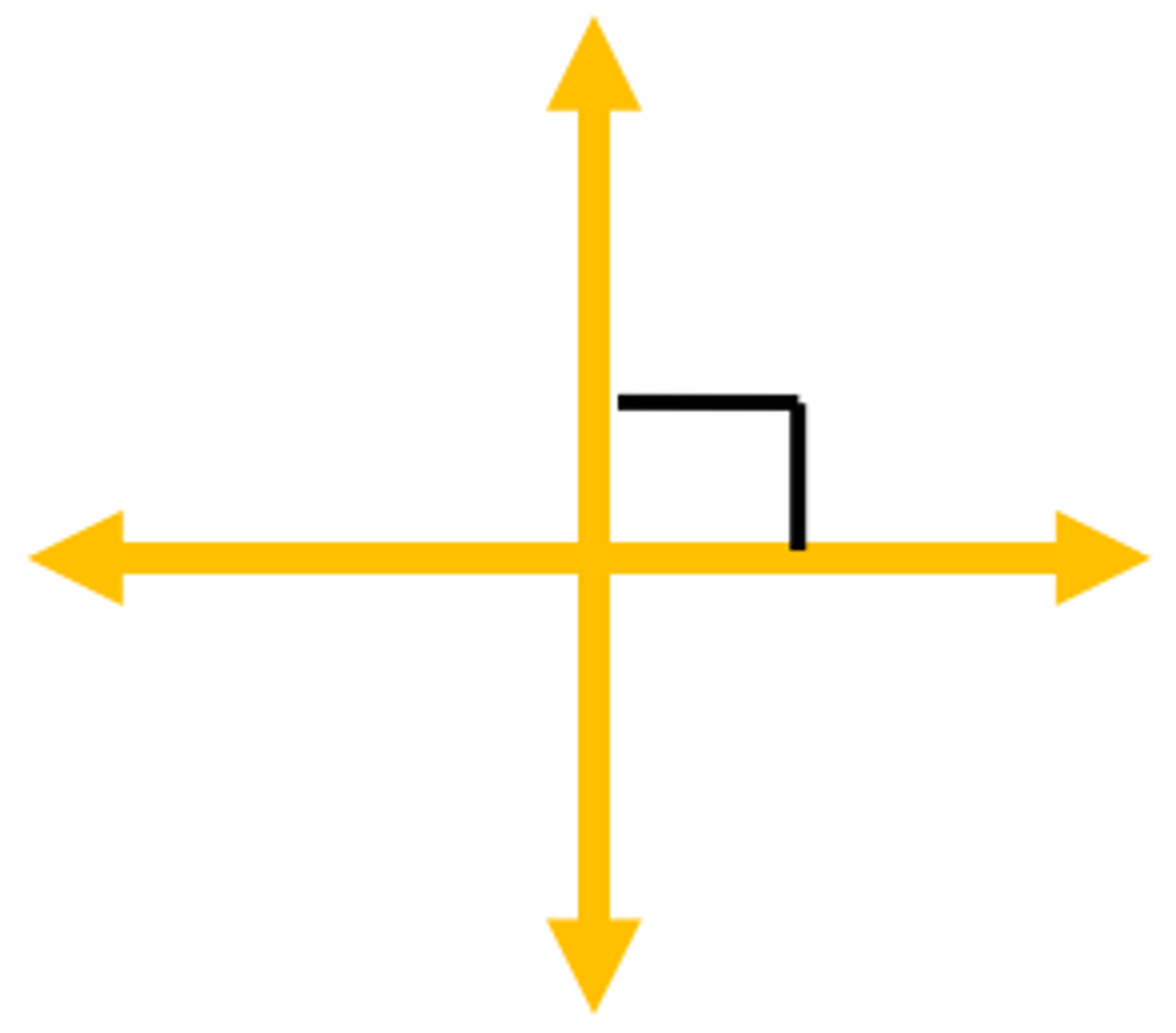
Perpendicular lines
two lines that intersect to form right angles
Converse Statement
the hypothesis and the conclusion of a conditional statement are switched
Inverse Statement
A conditional statement that negates the hypothesis and negates the conclusion.
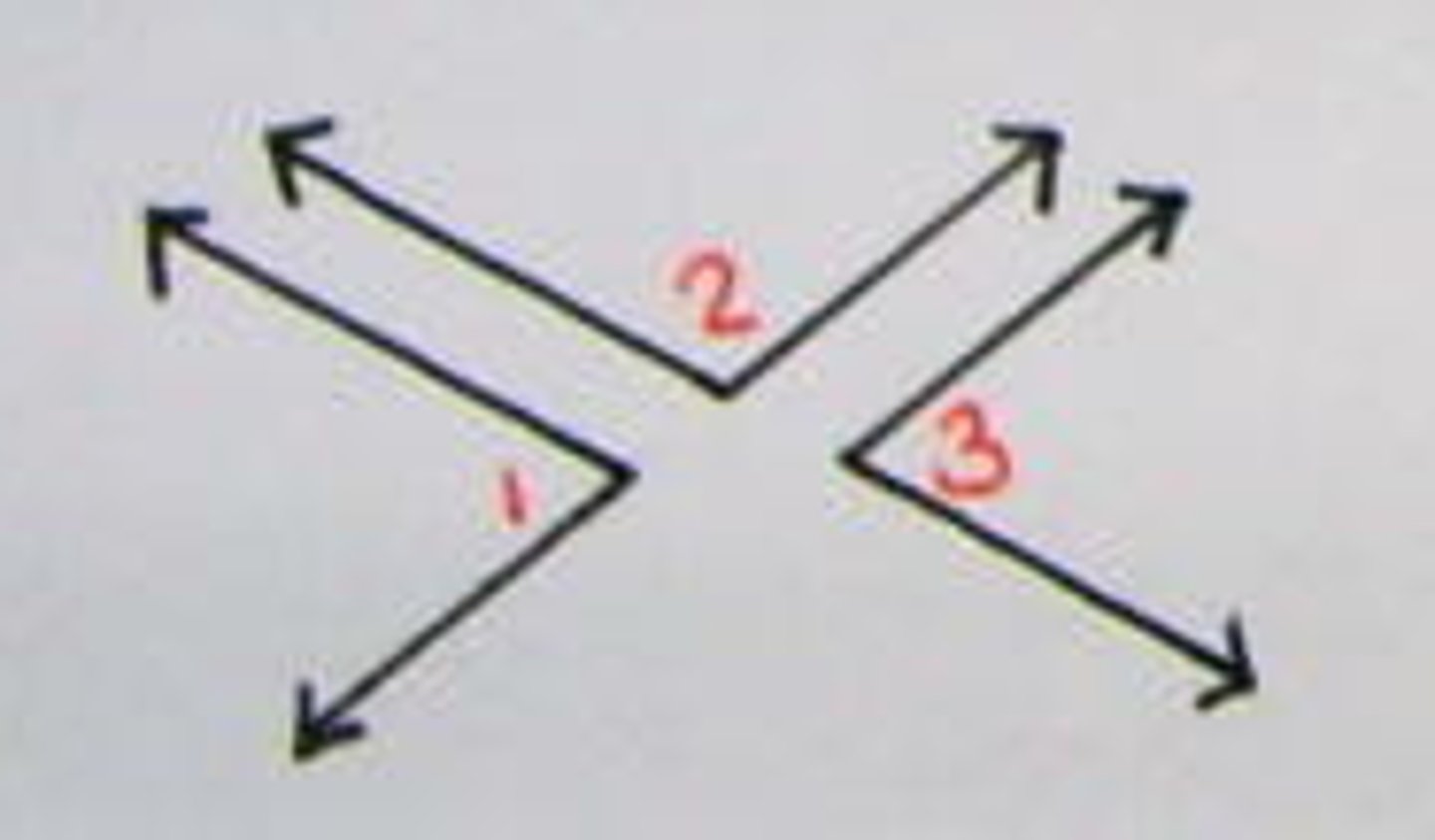
vertical angles
A pair of opposite congruent angles formed by intersecting lines
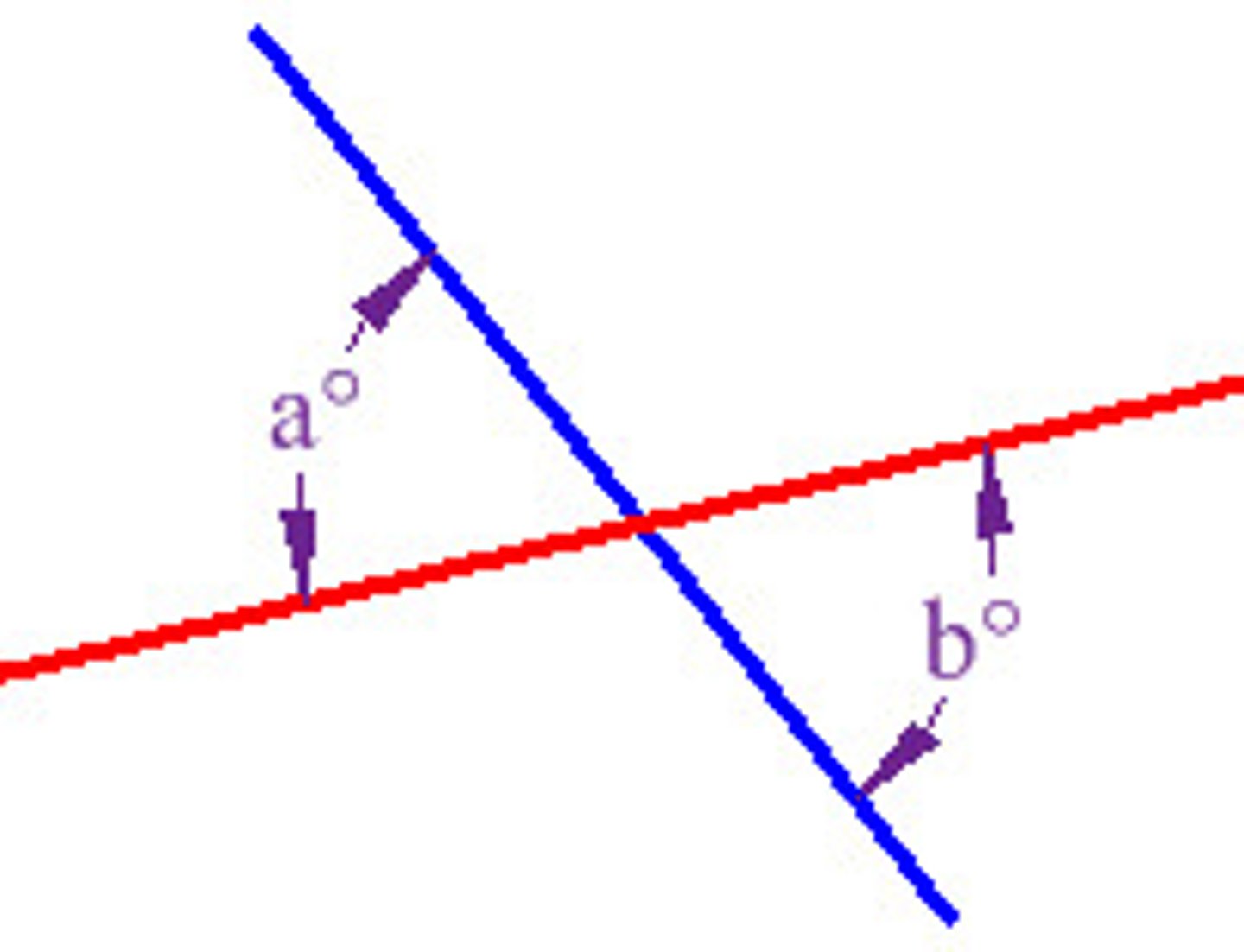
linear pair
a pair of adjacent angles that form a line, have a sum of 180 degrees
Reflexive
a=a
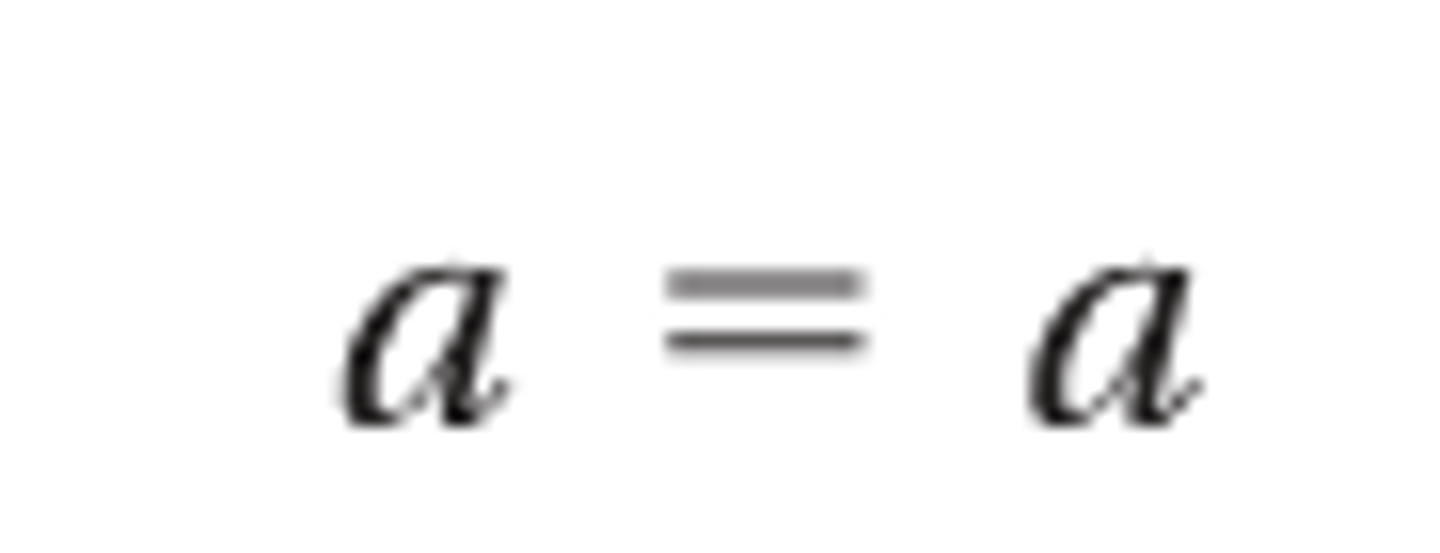
Symmetric
if a=b, then b=a
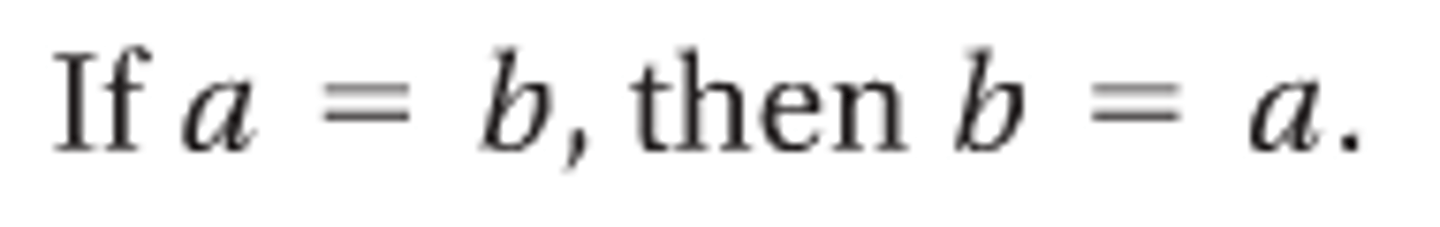
Transitive
If a=b and b=c, then a=c
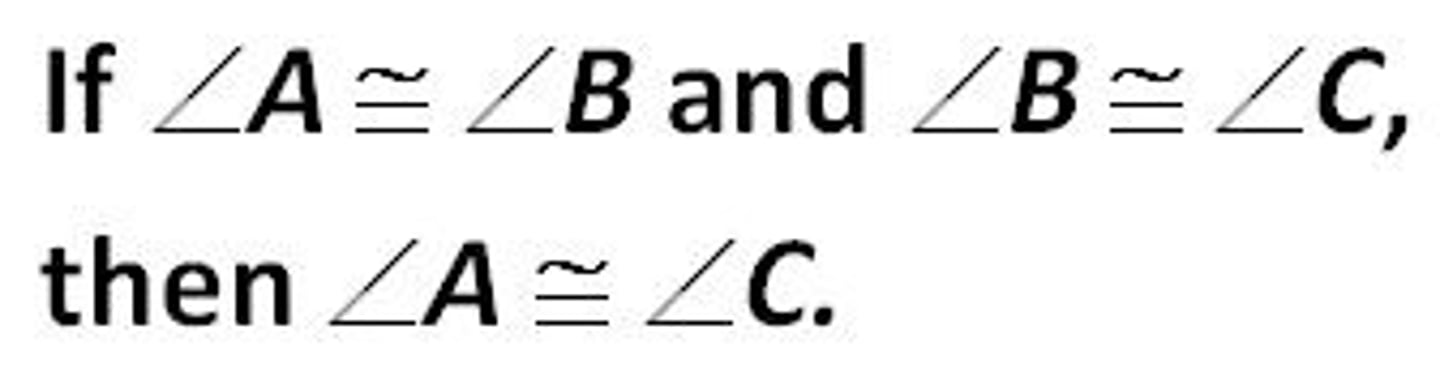
complementary angles
Angles with a sum of 90 degrees
supplementary angles
Angles with a sum of 180 degrees
addition property
If a = b, then a + c = b + c
subtraction property
If a = b, then a - c = b - c
multiplication property
If a = b, then a·c = b·c
division property
if a = b and c is not equal to 0, then a/c = b/c
distributive property
a(b+c)=a·b+a·c
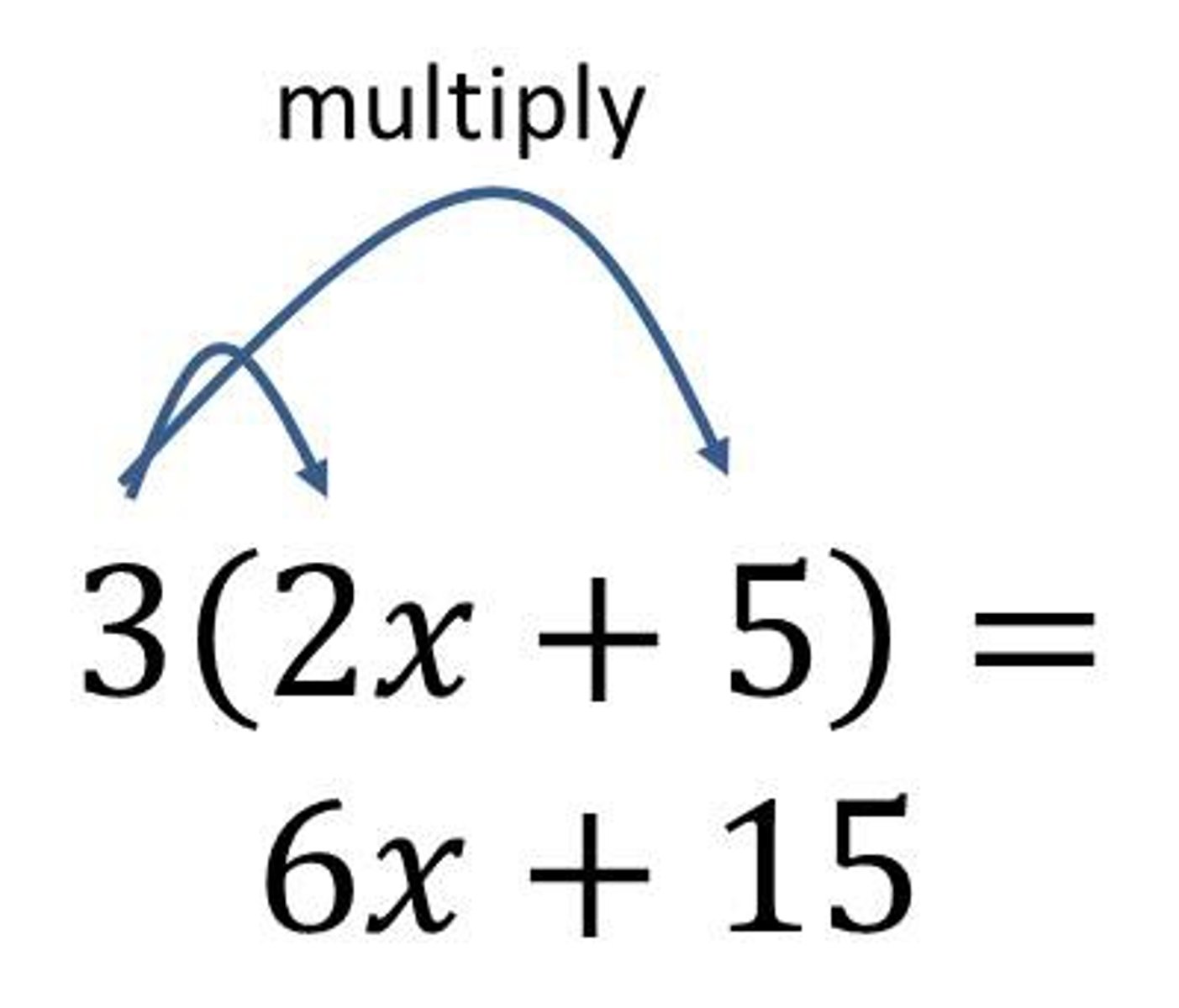
substitution property
If a=b, then b can replace a in any expression
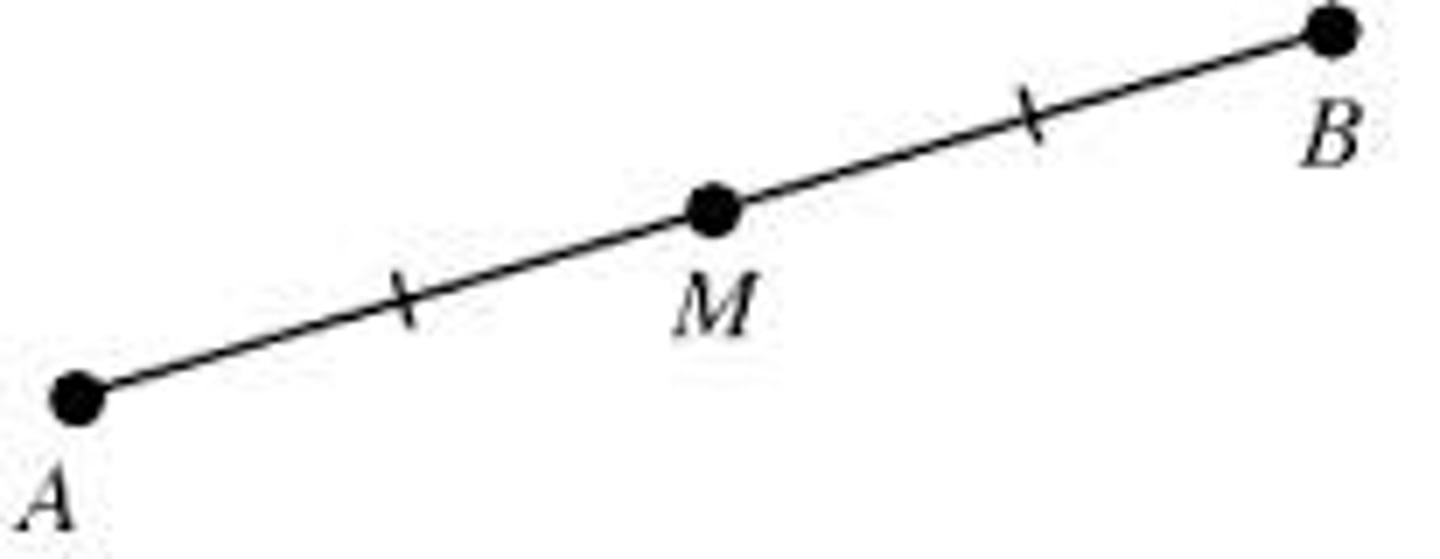
Definition of Midpoint
A point that divides a segment into two congruent segments
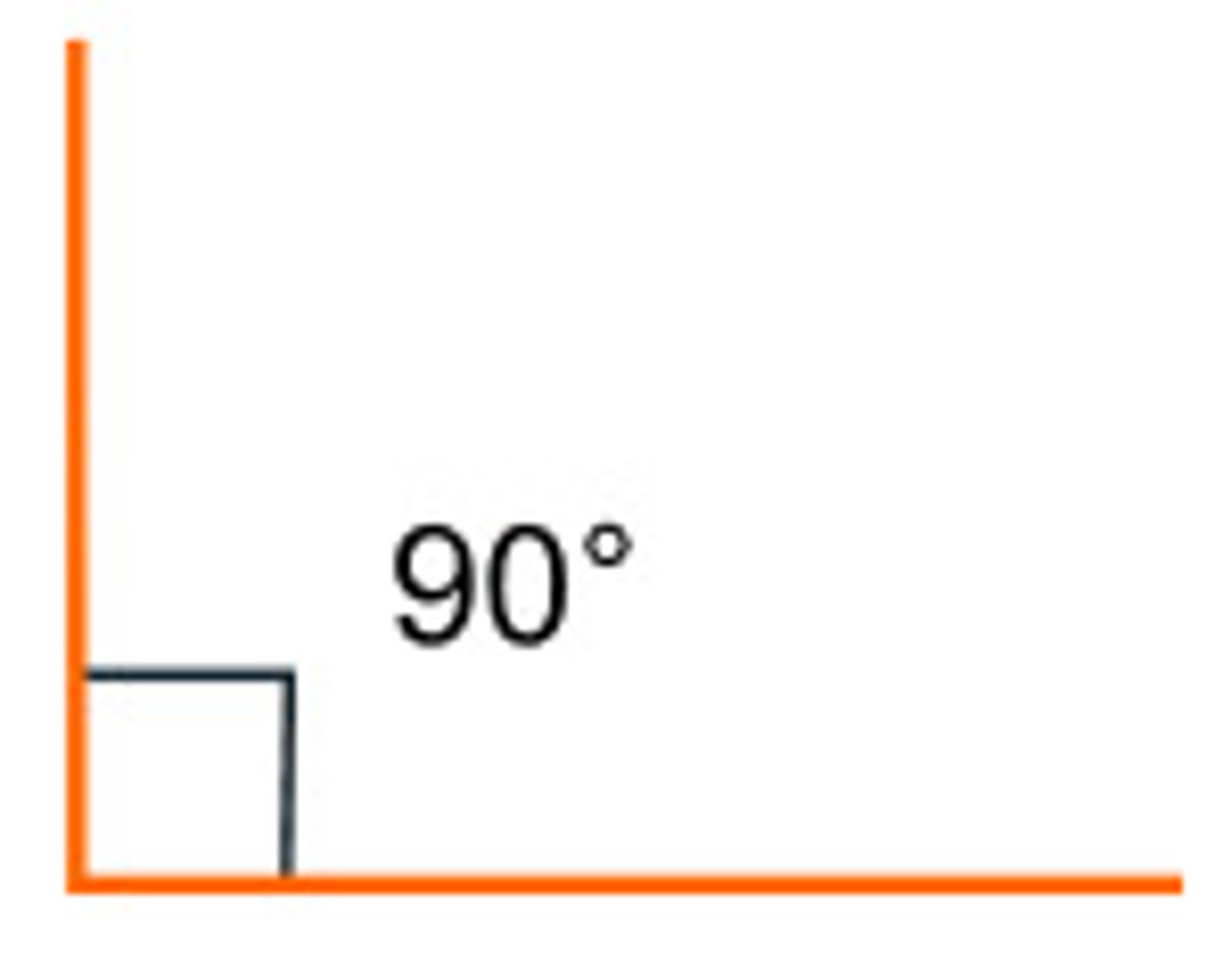
Definition of right angles
angles that equal 90 degrees
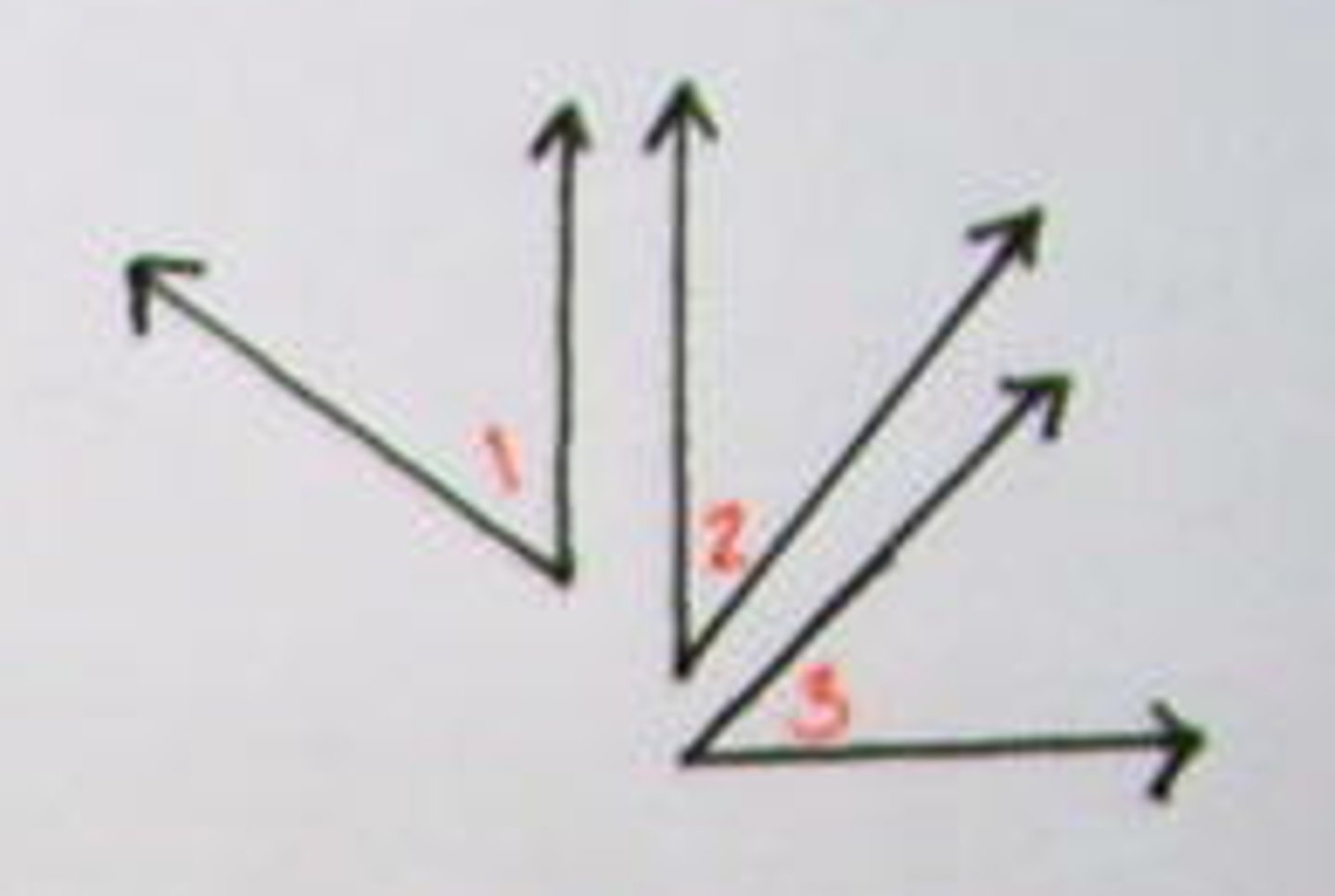
Congruent Complements Theorem
If two angles are complementary to the same angle (or to congruent angles), then they are congruent.
Congruent Supplements Theorem
If two angles are supplementary to the same angle (or to congruent angles), then they are congruent.