BIOL 416 Invasion Biology Exam 1 Part 2
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
1
New cards
What is a propagule?
The set of individuals brought into a new habitat
2
New cards
Important Parts of propagule
Size = # of individuals
Number = # of release events.
Combine to make propagule pressure
Number = # of release events.
Combine to make propagule pressure
3
New cards
Propagule pressure vs Establishment curves
Redundant past threshold: Asymptotic. After a certain threshold, any amount of reduction does not help. You must meet that threshold
Consistent Marginal benefit: Linear. Any reduction to propagule pressure makes establishment less likely.
Consistent Marginal benefit: Linear. Any reduction to propagule pressure makes establishment less likely.
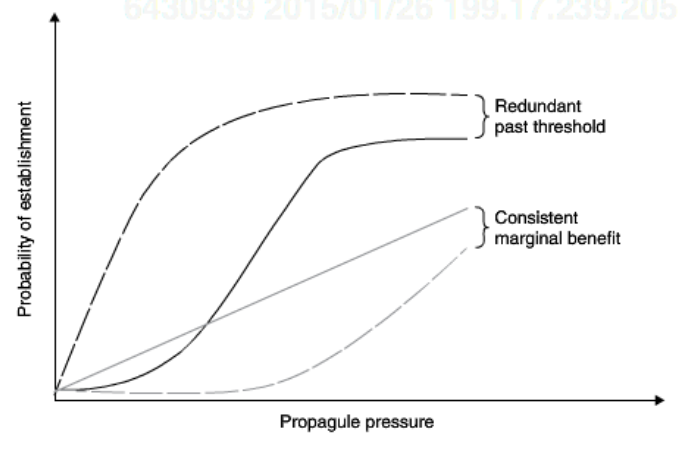
4
New cards
Why are larger population less likely to go extinct?
There is a safety margin against short term drops in survival/birth rates caused by variable weather events, sex ratio variation, randomly dying. Additionally, group size brings with it protection.
5
New cards
What is an allee effect?
Reduction in per capita population growth rates at low population densities. Small populations exhibit lower population growth.
6
New cards
Demographic allee effect
The positive relationship between large population sizes and higher fitness for each individual
7
New cards
Component allee effects
The reason there is a positive correlation between pop size and individual fitness
8
New cards
Strong allee effects
If the population dips below a certain size, growth rate is negative. A point of no return.
9
New cards
Weak allee effects
The population growth rate lowers with smaller populations, but it never dips negative
10
New cards
Mate-finding allee effect
Lower populations make it harder to find a mate (broadcast spawners cant mate if no one is near them)
11
New cards
Cooperative allee effects
Cooperative defense can confuse predators and help gather more resources, but low populations this is less effective (meercats). Predators that use group hunting take down less prey at lower levels (wolves).
12
New cards
Genetic allee effects
Lower populations lead to inbreeding and allows genetic defects to become fixed (white tigers are severely deformed)
13
New cards
What organisms are less likely to be influenced by allee effects?
Solitary (no cooperation allee effect), asexual (no mate finding allee effect), haplodiploid (inbreeding resistance)
14
New cards
How do allee effects influence invasion and how is that influence dependent on propagule number?
With no allee effects, everything falls under the redundant past threshold. As allee effects start occurring, everything except high propagule size are consistent marginal benefit. Higher propagule number means that the population is resupplied, counteracting the allee effects. (A has no allee effects, B has low allee effects)
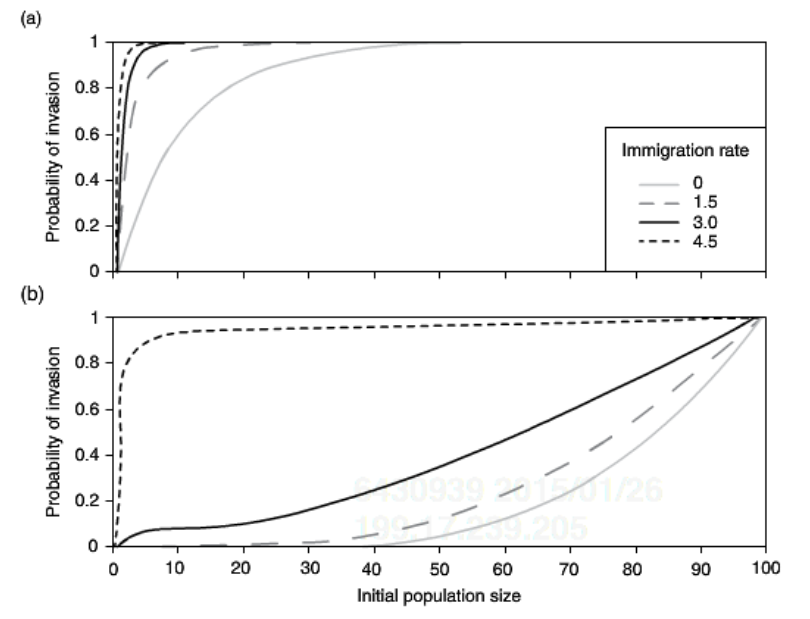
15
New cards
Why are biological control releases important in hypothesis regarding propagule pressure's effects on invasion?
BC is tightly tracked. By observing data from releases, it is found that propagule size is important to establishment (mean of 5000 in 115 failures, mean of 31200 in 44 successes in Canada). Other studies have been done to see if the propagule number has an effect, and it was observed that 70% of individuals released 20 times established. However, it was refuted saying that they could have established early on. A comparison of a lot of data found that propagule SIZE is the most important factor.
16
New cards
How does resistance effect invasion probabilities?
Resistance is the native environment's ability to reject an invasion (a vertical line on a graph). The greater the resistance, the lower the chance of invasion (horiz S curve). Bigger propagule sizes are better at over coming defenses, so their S curve is shifted further right.
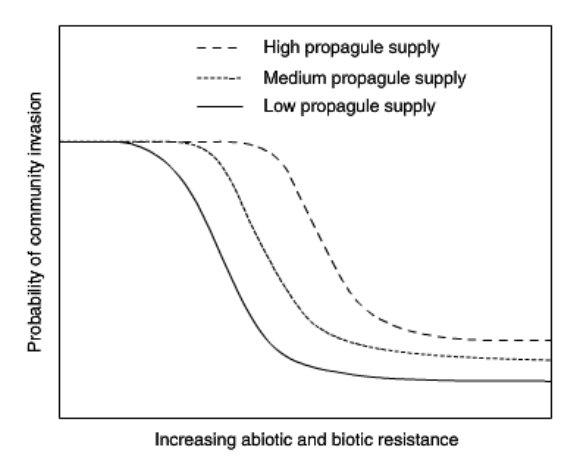
17
New cards
How does invasional meltdown effect invasion probabilities
Invasional meltdown is a bunch of exotics facilitating each other's invasion. This lowers the resistance of the native environment and lowers the threshold of invasion (the vertical line is further left).
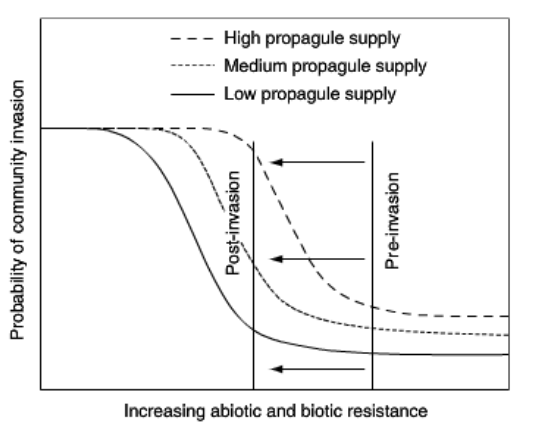
18
New cards
What is ecological disturbance
A discrete event that disrupts an ecosystem and changes the resources in some manner
19
New cards
How do disturbance regimes vary?
Intensity, frequency, duration, predictability, distribution (size and spatial extent), synergy (relationship to future disturbances)
20
New cards
How does disturbance typically influence native species richness and why?
Intermediate levels of disturbance allow greatest biodiversity. R types exploit areas quickly and poorly, favoring high disturbance. K types use competition to outlive things, favoring low disturbance. With intermediate disturbance, both can exist in greater numbers.
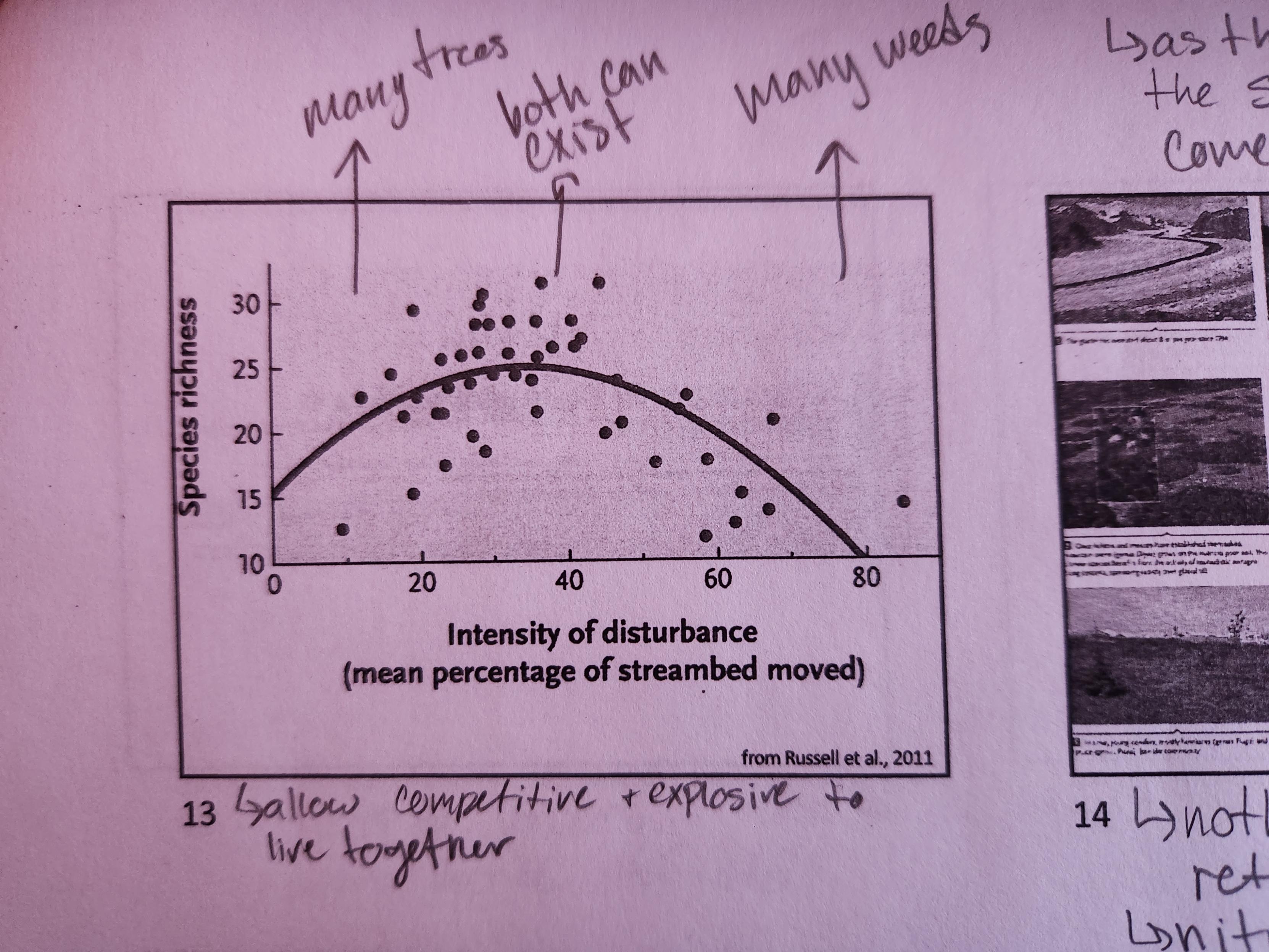
21
New cards
Theory of Fluctuating Resource Availability
Disturbance changes amount of resources available in an environment. If resources are increased, invasives can come in easier.
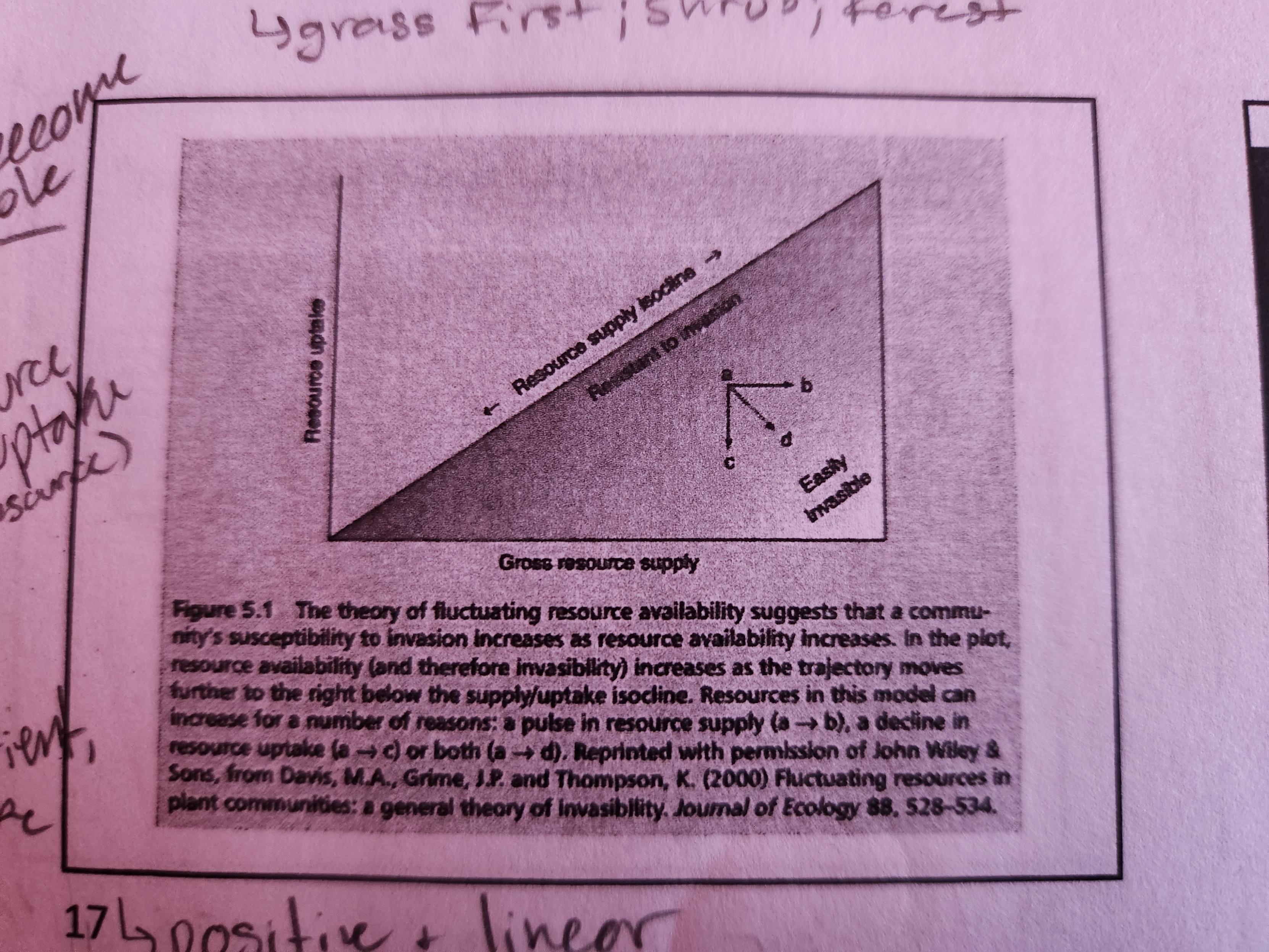
22
New cards
Fluctuating resource availability graphically
Positive slope between gross resource supply and resource uptake. The further away from the line you get, the more invasible the environment is. To become invasible, an environment can increase resource with no uptake (horizontal), decrease the amount of uptake (vertical), or both for the fastest (diagonal towards right corner)
23
New cards
What are some issues with taking the statement "disturbance facilitates invasion" as an axiom?
Taxonomically biased towards plants and towards cold temperatures. Studies show that in cold environments, disturbance helps plants invade. In animals, disturbance is not necessary. In temperate forests, it was shown that disturbance had no distinct effect. Disturbances creates opportunities for invasives and natives. Disturbance also does not create propagules.
24
New cards
What are the four signatures of agricultural disturbance?
Crops with long roots that stay behind after harvest, crops leave behind parts that change soil chemistry, agricultural weeds persist (exotics), the effects of fertilizers and herbicides remain
25
New cards
What is biotic disturbance?
When the invasive itself is the biological disturbance
26
New cards
Aveneus of biotic disturbance
Exotic's presence messed up the abiotic disturbance regime (exotic plants being more/less flammable and messing up fire regimes)
Exotic directly altered the habitat (feral hogs directly cause 8% of soil turnover)
Exotic directly altered the habitat (feral hogs directly cause 8% of soil turnover)
27
New cards
Mutualism
Both benefit from interaction
28
New cards
Consumer/host
One benefits other is harmed
29
New cards
Competition
Neither benefit from the ineraction, someone just loses less
30
New cards
Why is competition important for biotic resistance?
Rich communities have more niches filled, which leads to competitive exclusion of exotics. If the niche is already filled, the invader cannot fill it
31
New cards
Competitive Exclusion theory
When grown separately, things do well. When put into competition, one species will win, but they will do worse than if they never fought in the first place.
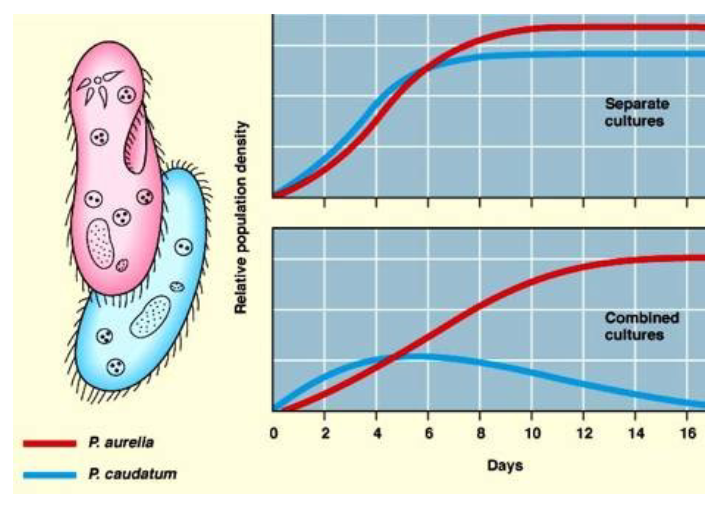
32
New cards
Niche theory
There are components of a niche. The realized environmental space is the range that the environment had. The fundamental niche space is the range that a species can live in. Where these two overlap is the potential niche space. Within that potential is the realized niche, the area within the potential space that the organism actually lives
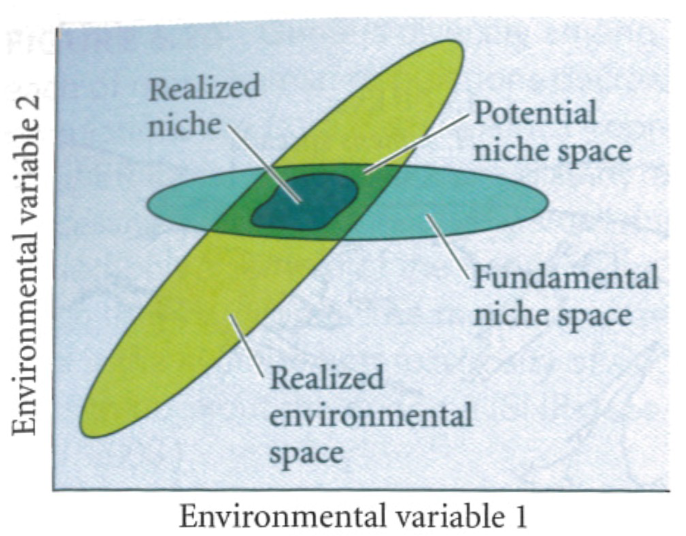
33
New cards
What is the invasion paradox?
small scale studies show that species richness decreases invasibility. Large scale studies show that species richness increase invasibility. Graphically, to a certain point, you get more variability and mostly negative. But as you let larger, diversity decreases, and it very quickly becomes a positive correlation
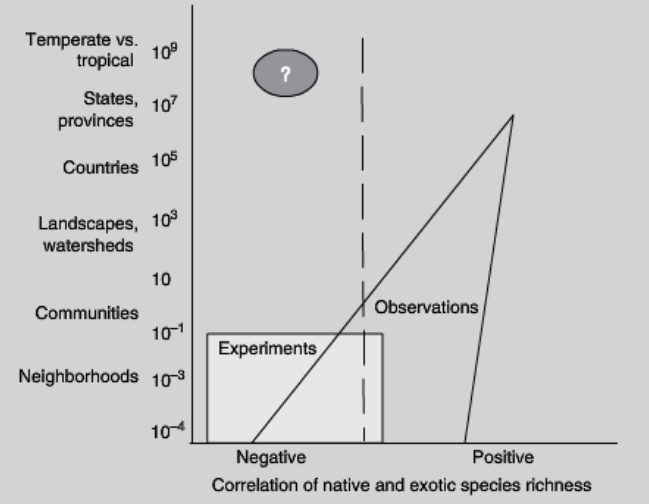
34
New cards
How to solve the invasion paradox
At small scales, abiotic conditions are all the same, so only biotic factors matter. At larger scales, the abiotic factors vary more, there are more niches to fill, and biotic factors don't matter as much.
35
New cards
What is EICA?
Evolution of Increased Competitive Ability. There will be a trade off between defense and growth (competition). You can only put your resources into one place.
36
New cards
EICA graphically
Negative correlation. When enemies are present (native range) you will allocate more resources to defense. When you are released from enemies (invasive range) you can put all your resources into competition.
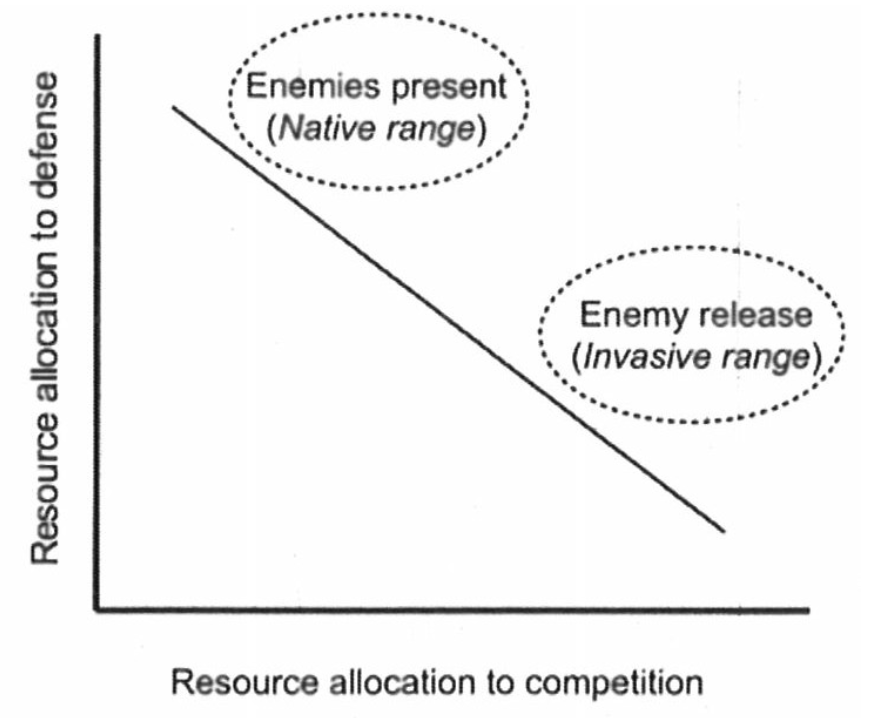
37
New cards
Issues with EICA as a generalized principle in plant invasion?
Studies into EICA grew native and exotic phenotypes of the same plant. Natives are expected to put more into defense, while exotics would put more into growth. Only ¼ of EICA studies measured BOTH growth and defense traits, aka the bare minimum. Studies also ignored other forms of competition that are not growth
38
New cards
Predation for biotic resistance
Predators can increase biotic resistance by competing with the invasives, either indirectly or by hunting them (like medium-large red rock crabs fight and prevent establishment of European green crabs)
39
New cards
Predation for facilitation
An exotic consumer may eat a native predator, which makes it safer for other exotics to ender. (European cows graze fields which allows exotic plants to invade)
40
New cards
Mutualism for biotic resistance
If an exotic is brought over without its obligate mutualism, then the exotic will die (European fig trees cant survive in the Florida without European fig wasps. Florida fig wasps don't work)
41
New cards
Mutualism for facilitation
Exotic species can form new mutualisms with native species, which would help them invade. Also, at some point an obligate mutual can be reunited with the exotic and they can both establish (exotic fig wasps being brought to florida for exotic figs)
42
New cards
When can multiple ecological interactions create stronger barriers to establishment than either one individually?
Mutualisms and Competition can increase resistance. For example, the presence of specialist mutualists for natives can make them better competitors with exotics. For example, the presence of competition (a grassland) and herbivory by rabbits made invasives almost die out completely.