Anatomy and Physiology Lab Final Exam BIOL2311 UNT
1/267
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
268 Terms
What is the functional classification for neurons that carry information from peripheral receptors to the central nervous system?
Sensory
What do we call neuronal processes that transmit membrane potentials away from the neuronal cell body?
Axon
What type of glial cell is responsible for producing and circulating cerebrospinal fluid?
Ependymal cell
Which labeled portion of the diagram corresponds to the repolarization of the axon?
C
What do we call the period during which initiation of an action potential requires a higher than normal threshold stimulus?
relative refractory period
Depolarization is the result of the rapid entry of which ion into the cell?
Sodium
In the PhysioEx exercise, what was the effect of curare on the nerve?
Inhibition
What fluid fills the scala tympani?
perilymph
A blurred area in the field of vision caused by unequal curvatures of the lens or cornea is called:
Astigmatism
Which cranial nerve supplies the medial rectus muscle of the eye?
Occulomotor
Which of the three tunics (layers) does the cornea belong to?
Fibrous
To which portion of the ear (outer, middle, inner) does the auricle belong?
Outer
With which sense (hearing, static equilibrium, dynamic equilibrium) is the tympanum associated?
Hearing
Identify one location in the body where dense irregular connective tissue is found.
Dermis of skin
Define "origin" as it applies to skeletal muscles.
immovable site of attachment
Identify one location in the body where fibrous cartilage is found.
intervertebral discs
The nuclear membrane reforms during which phase of mitosis?
telophase
What is the name of the dorsal bone of the pectoral girdle?
scapula
Name one origin of the flexor carpi radialis muscle.
medial epicondyle of humerus
How many tarsal bones are present on each side?
seven 7
The hip is _________ to the knee.
proximal
The distance between the bottom of the objective lens and the specimen is the __________.
working distance
Name one action of the infraspinatus muscle.
lateral rotation of arm
The humerus belongs to which of the two main divisions of the skeleton?
appendicular
You are examining a microscope slide under the 10X objective lens and you switch to the 4X objective lens. The height of the focal point will:
stay the same
What is the body cavity in which the brain and spinal cord are both located?
Dorsal
What is the name of the membrane lining the organ within the pericardial cavity?
visceral pericardium
You are examining a microscope slide under the 10X objective lens and you switch to the 40X objective lens. The field of view will:
decrease
What double walled organelle contains enzymes that oxidize foodstuffs to produce cellular energy?
mitochondrion
Which of the seven criteria used for naming a muscle applies to the trapezius muscle?
shape
What membrane bound organelle contains the genetic material that controls the functioning of the cell?
nucleus
What do we call an epithelial tissue that is composed of cells that are higher than they are wide and appears to be multi-layered, even though it is only one cell layer thick?
pseudostratified columnar
The hyoid belongs to which of the two main divisions of the skeleton?
axial
Identify one location in the body where skeletal muscle tissue is found.
muscles attached to bones and skin
Identify one location in the body where simple cuboidal epithelium is found.
kidney tubules
The ribs belong to which of the two main divisions of the skeleton?
axial
Identify the type of glial cells shown.
Ependymal cell
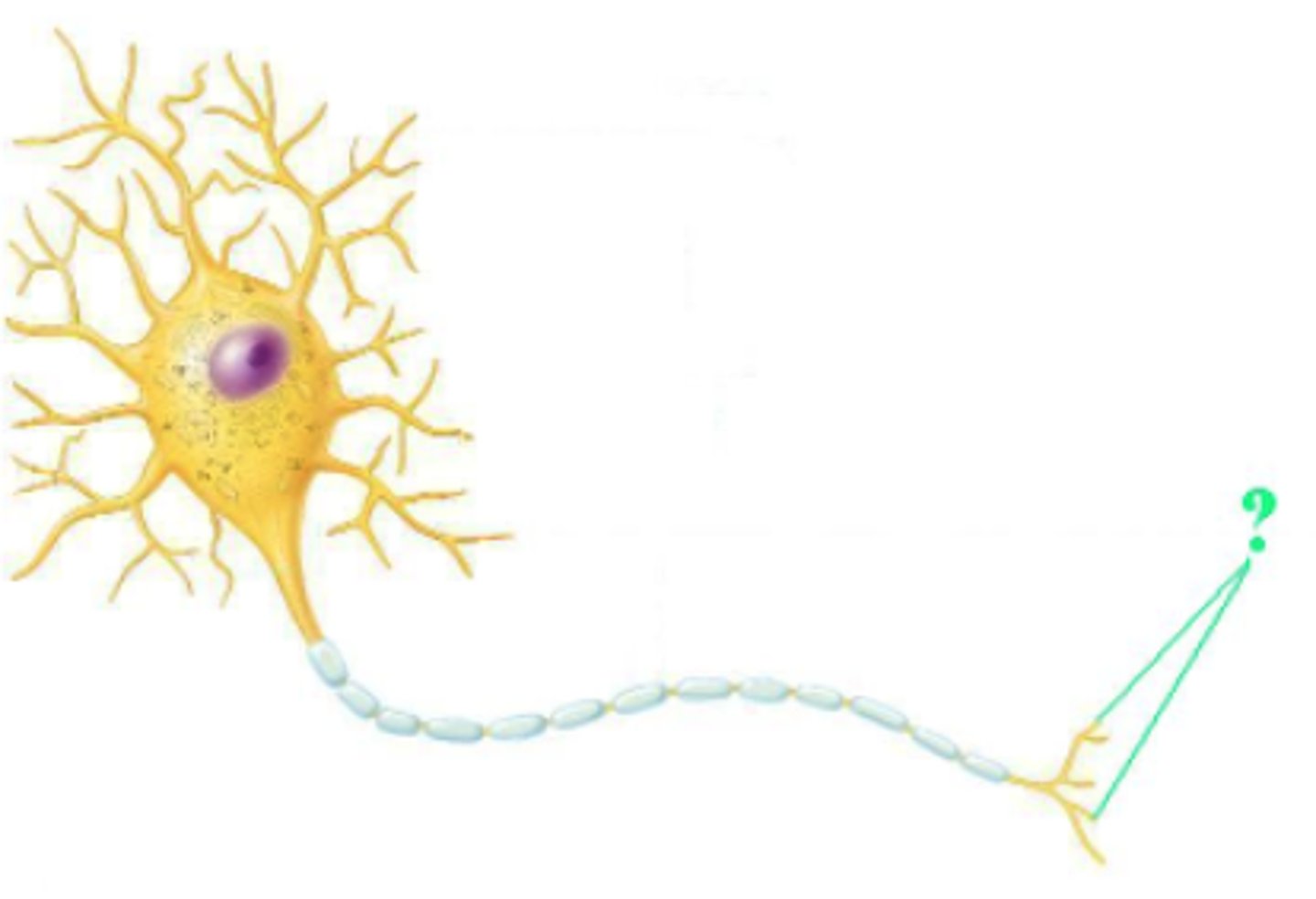
Identify the indicated part of a neuron.
axon terminal
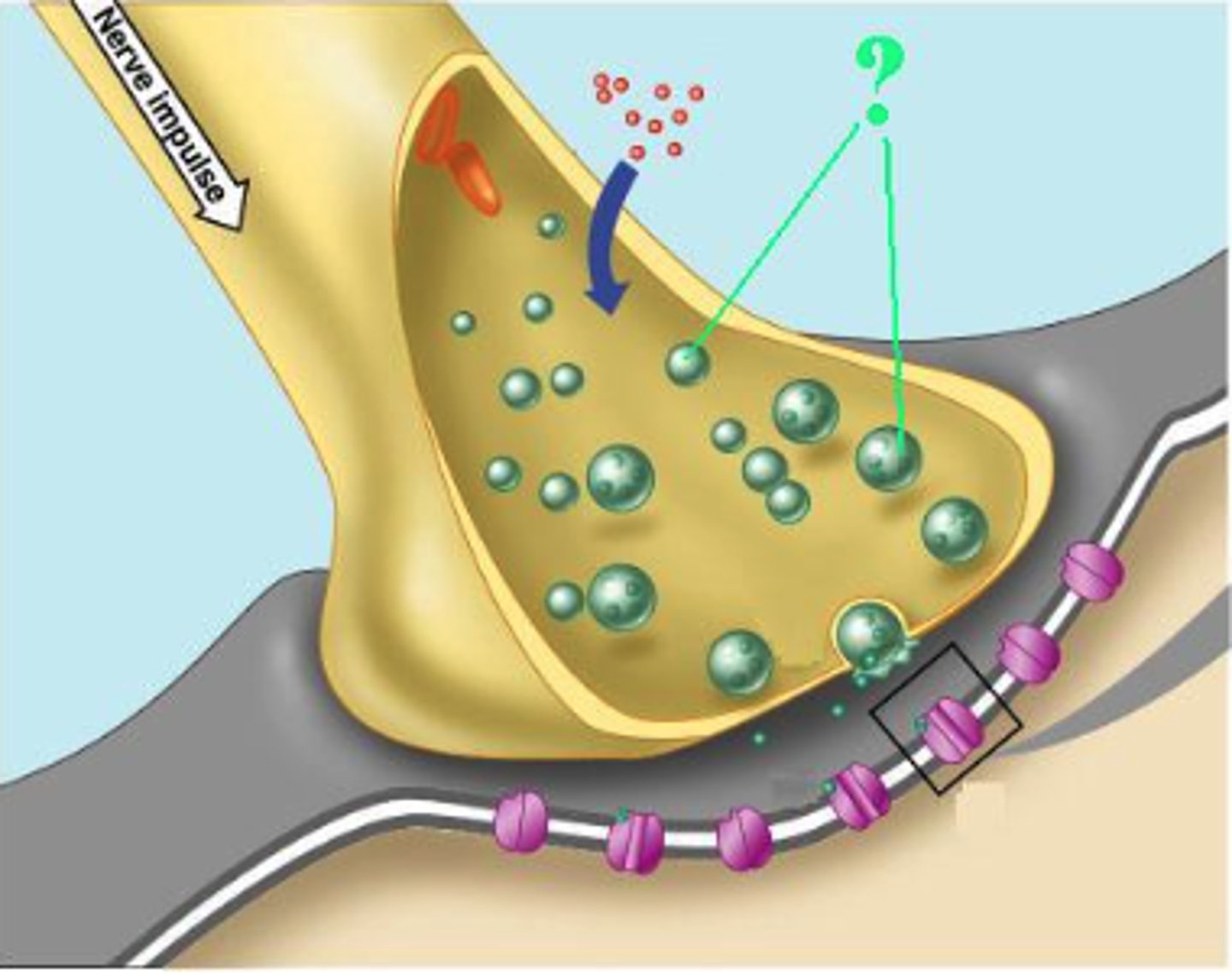
Identify the indicated part of a synapse.
synaptic vesicles
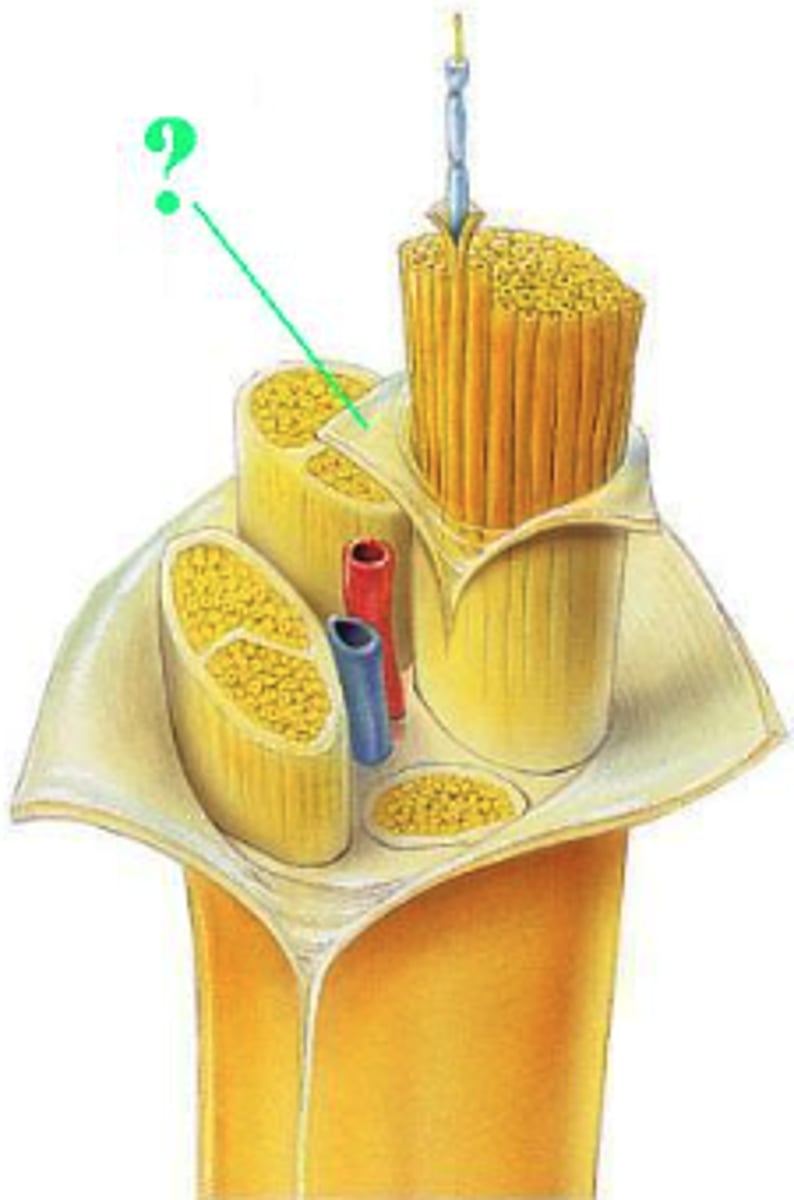
Identify the indicated connective layer of a nerve.
perineurium
Identify the indicated part of a nerve.
fascicle
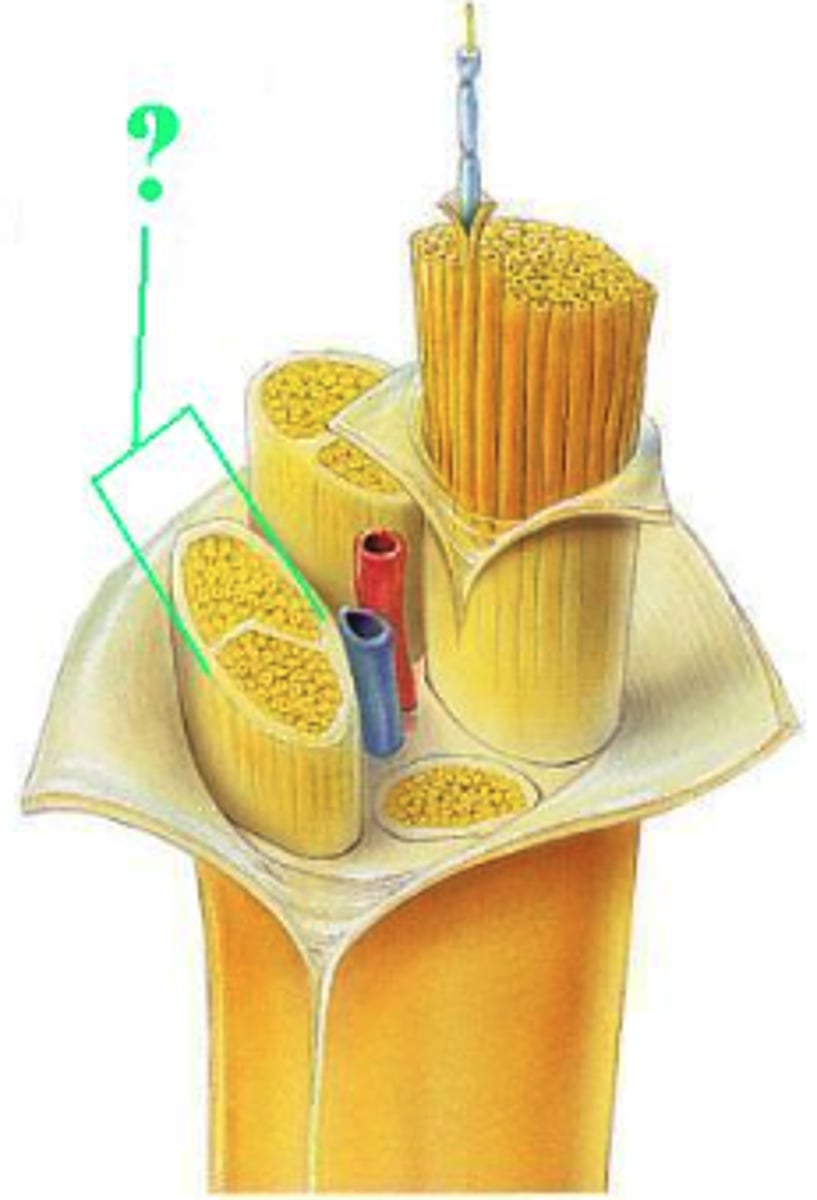
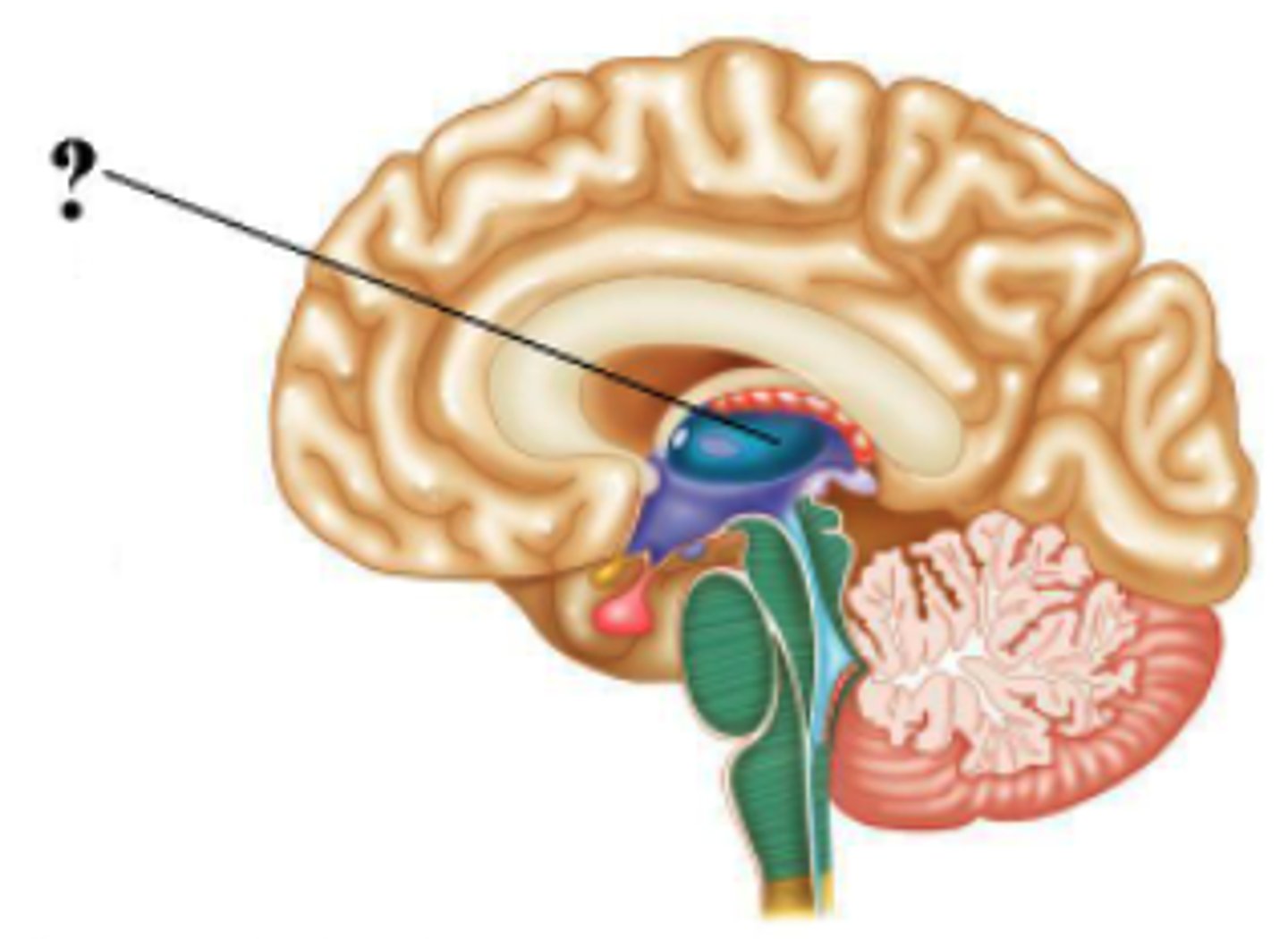
Identify the indicated space of the brain.
cerebral aqueduct
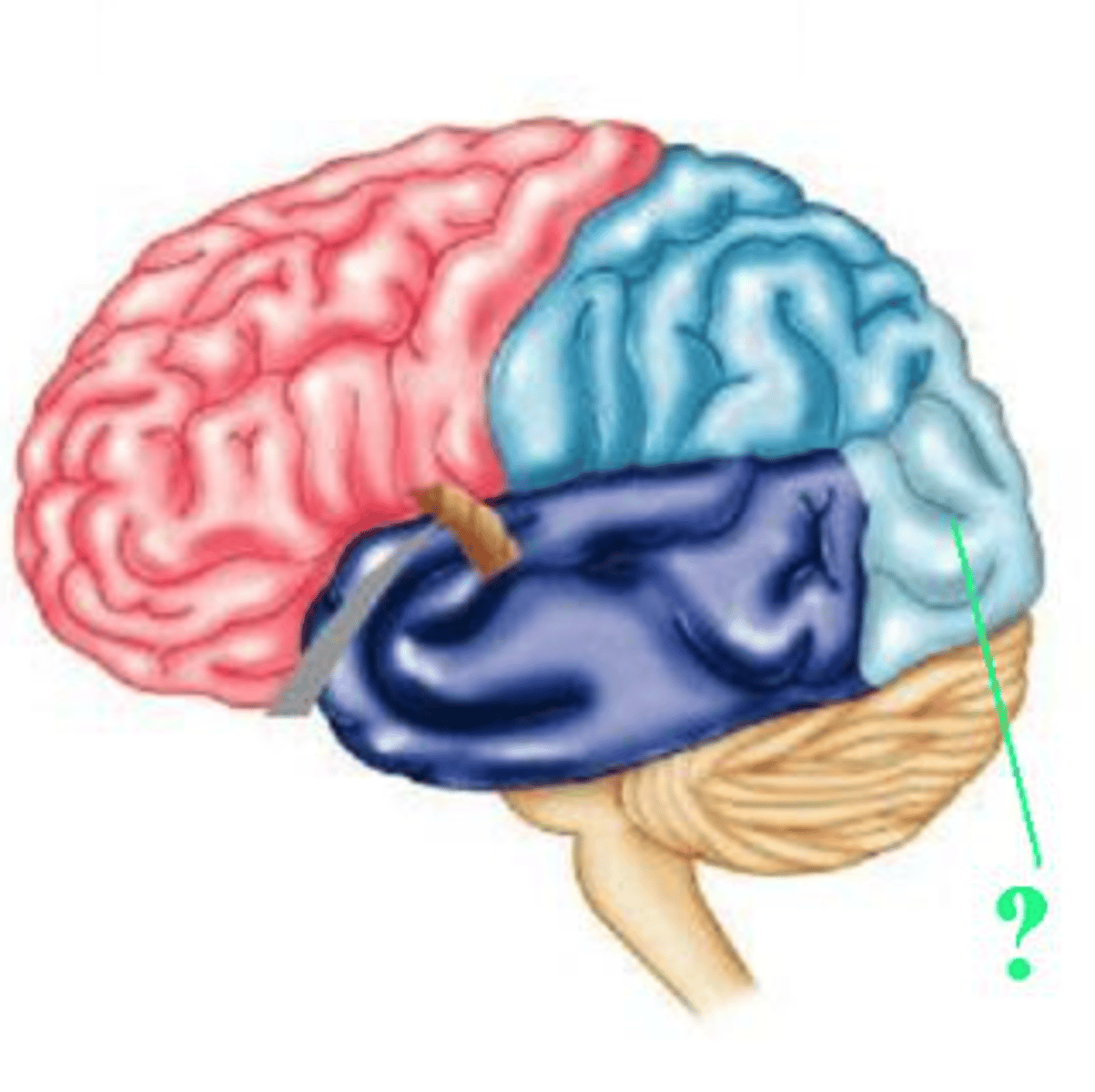
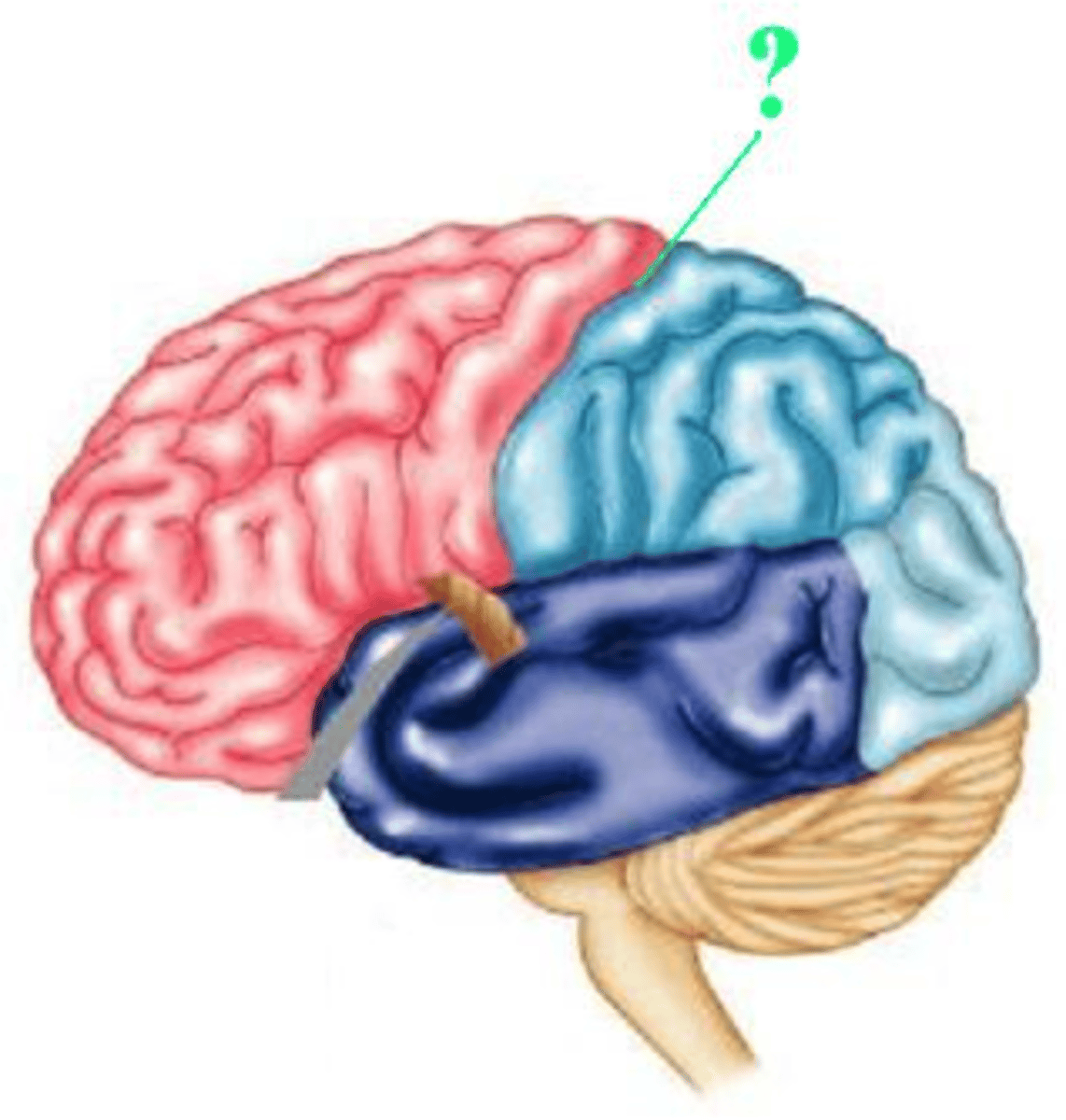
Identify the indicated lobe of the brain.
occipital lobe
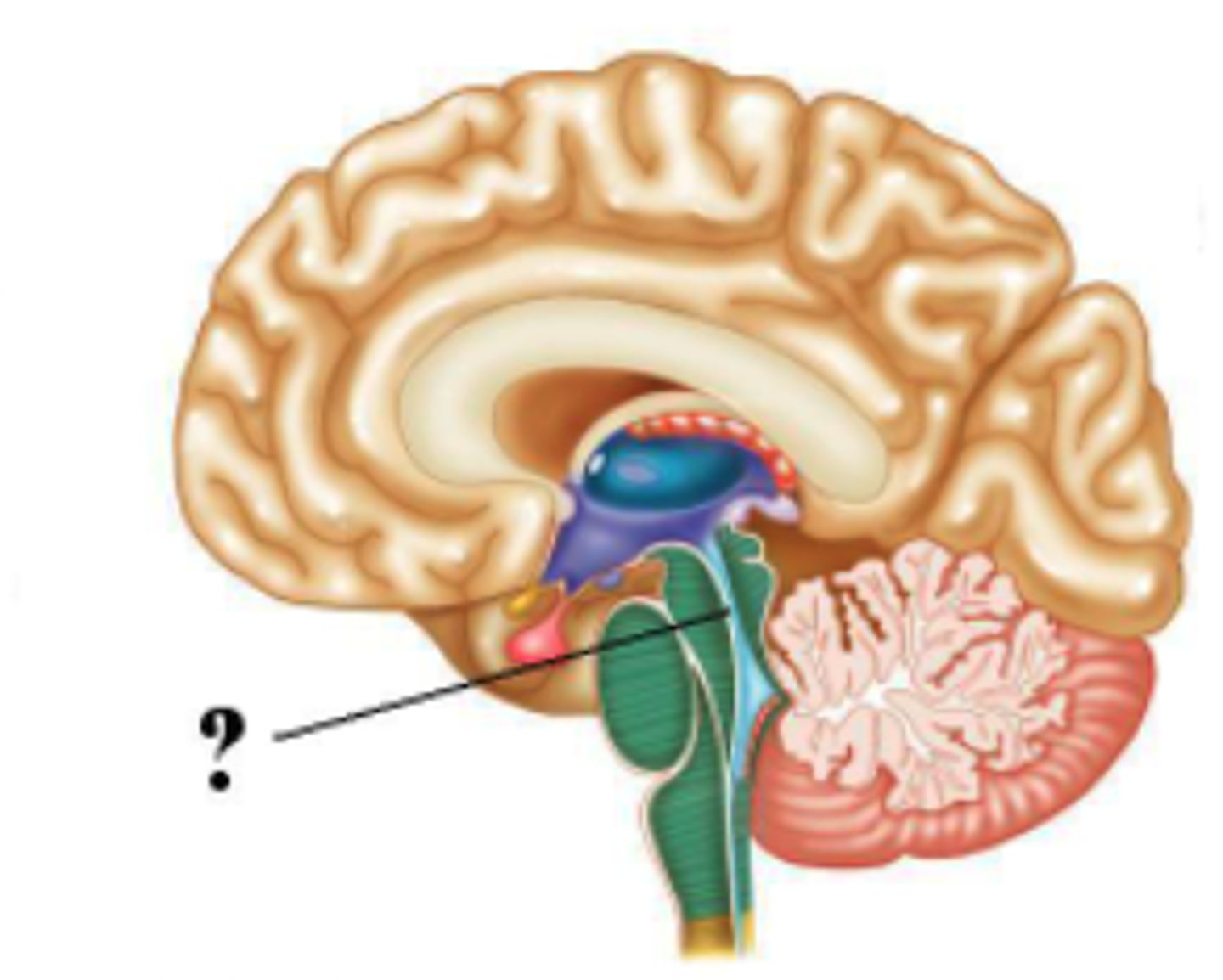
Identify the indicated structure of the brain.
thalamus
Identify the indicated groove of the brain.
central sulcus
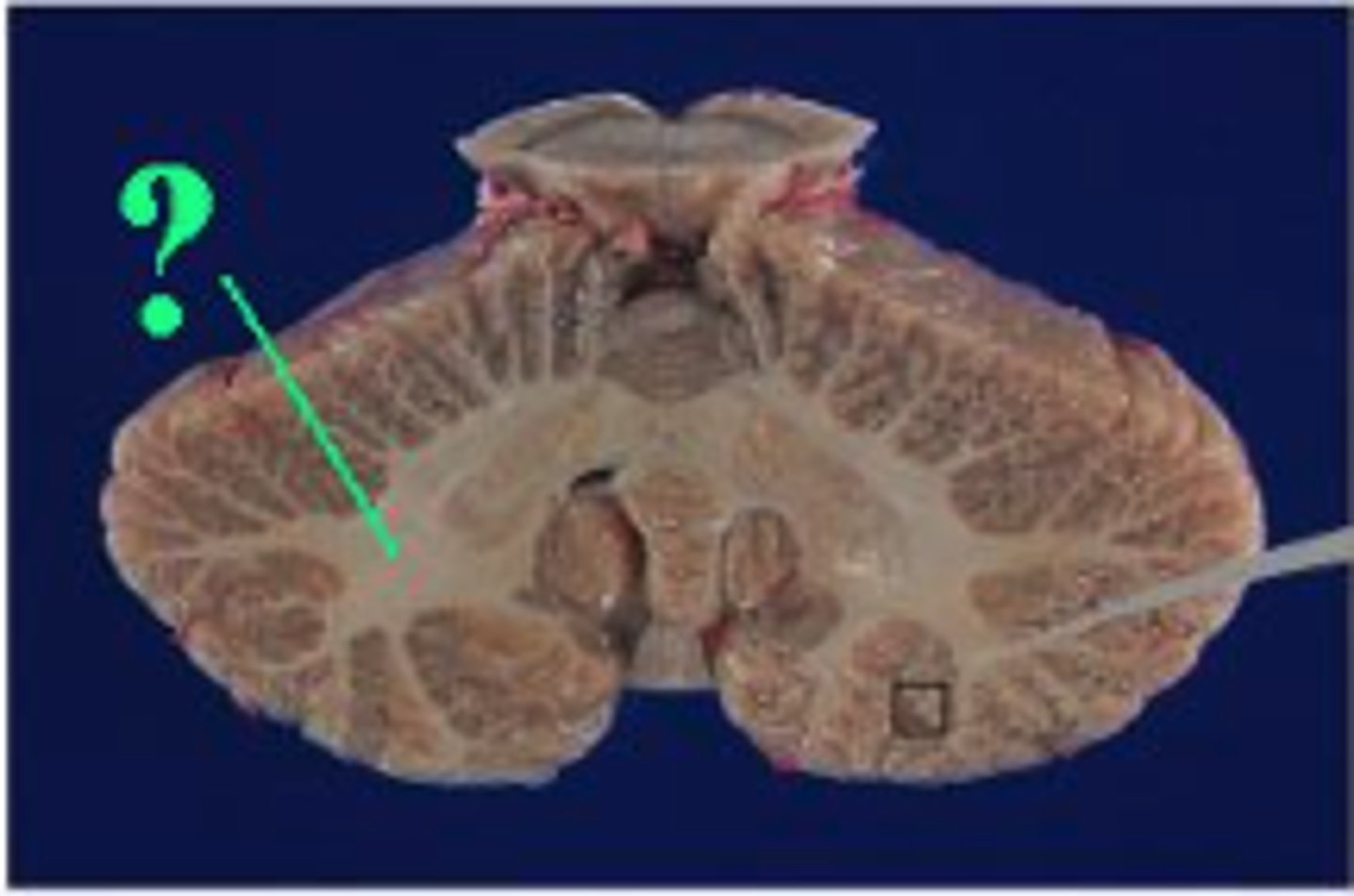
Identify the indicated portion of the cerebellum.
white matter
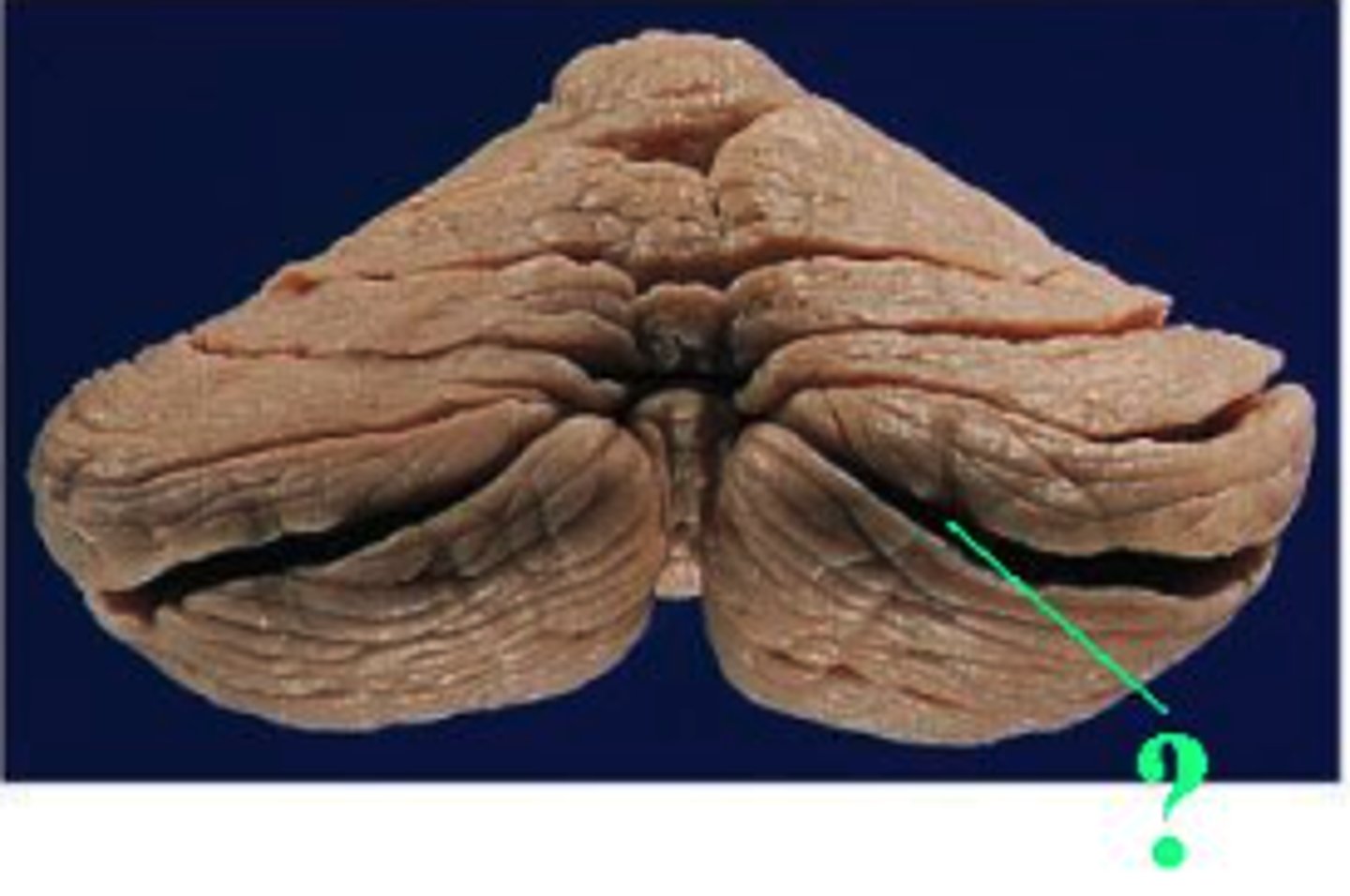
Identify the indicated groove of the cerebellum.
horizontal fissure
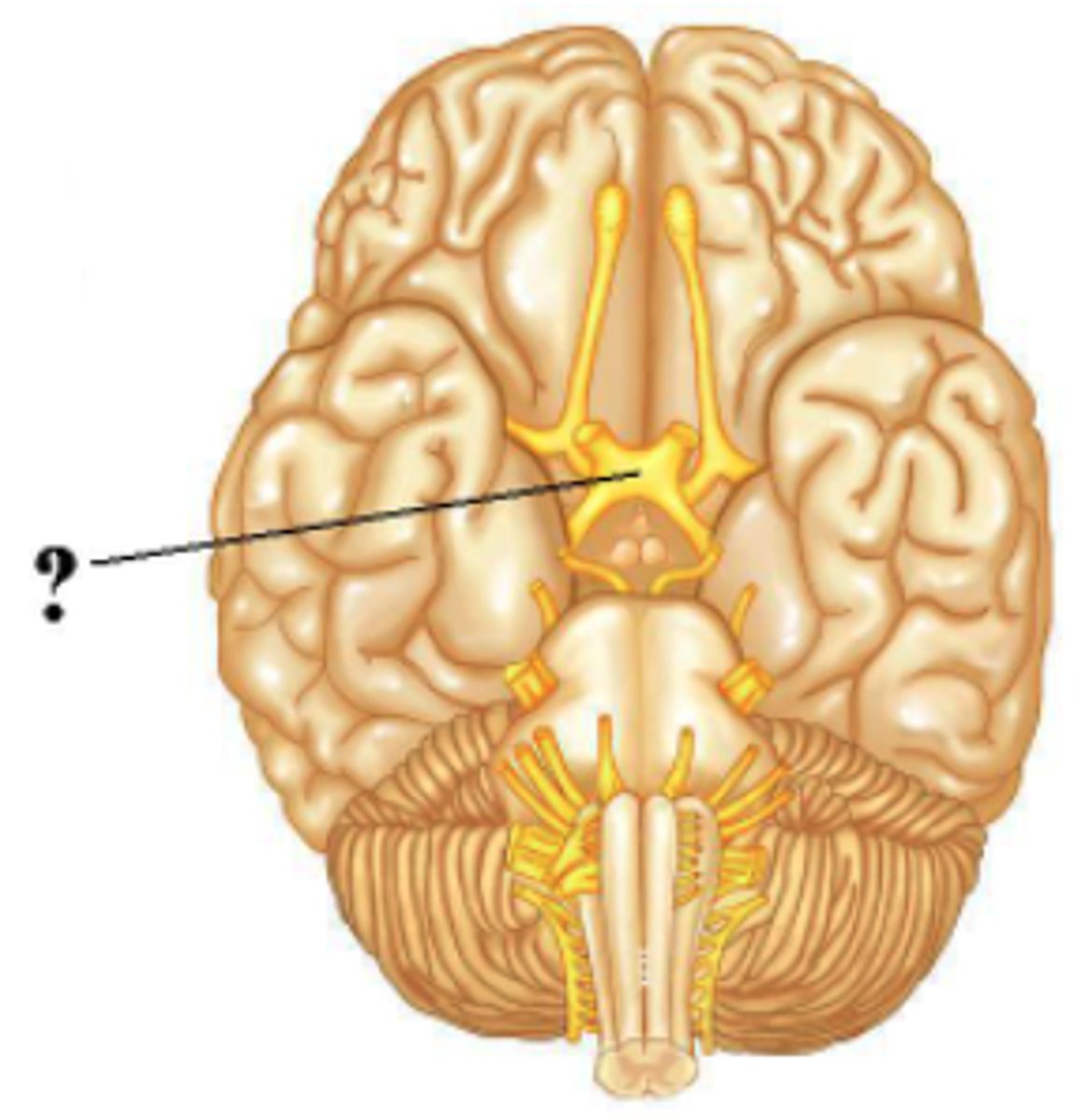
Identify the indicated structure.
optic chiasm
Identify the indicated cranial nerve.
Vestibulocochlear
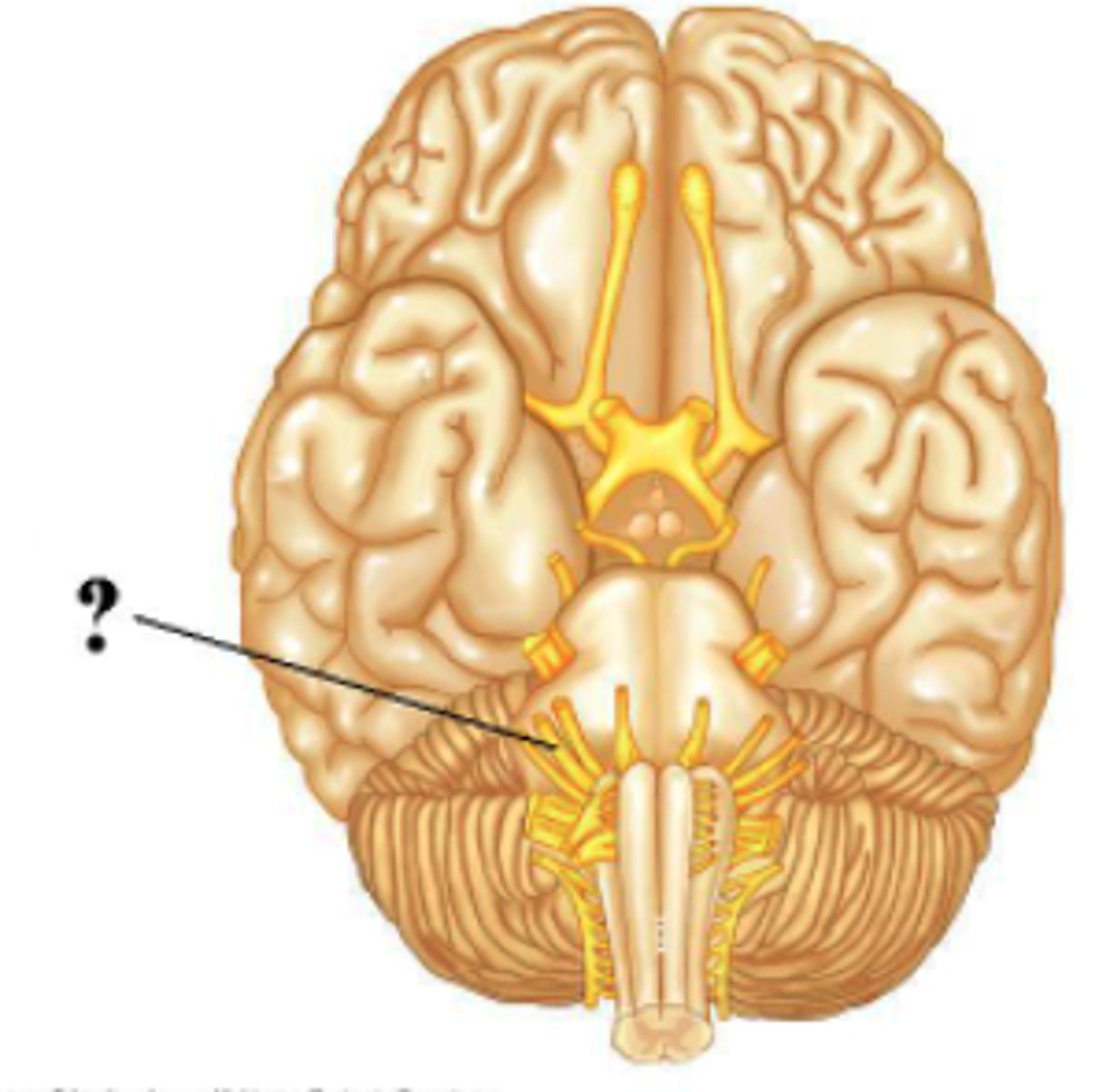
Is the indicated cranial nerve sensory only, motor only, or both sensory and motor?
motor
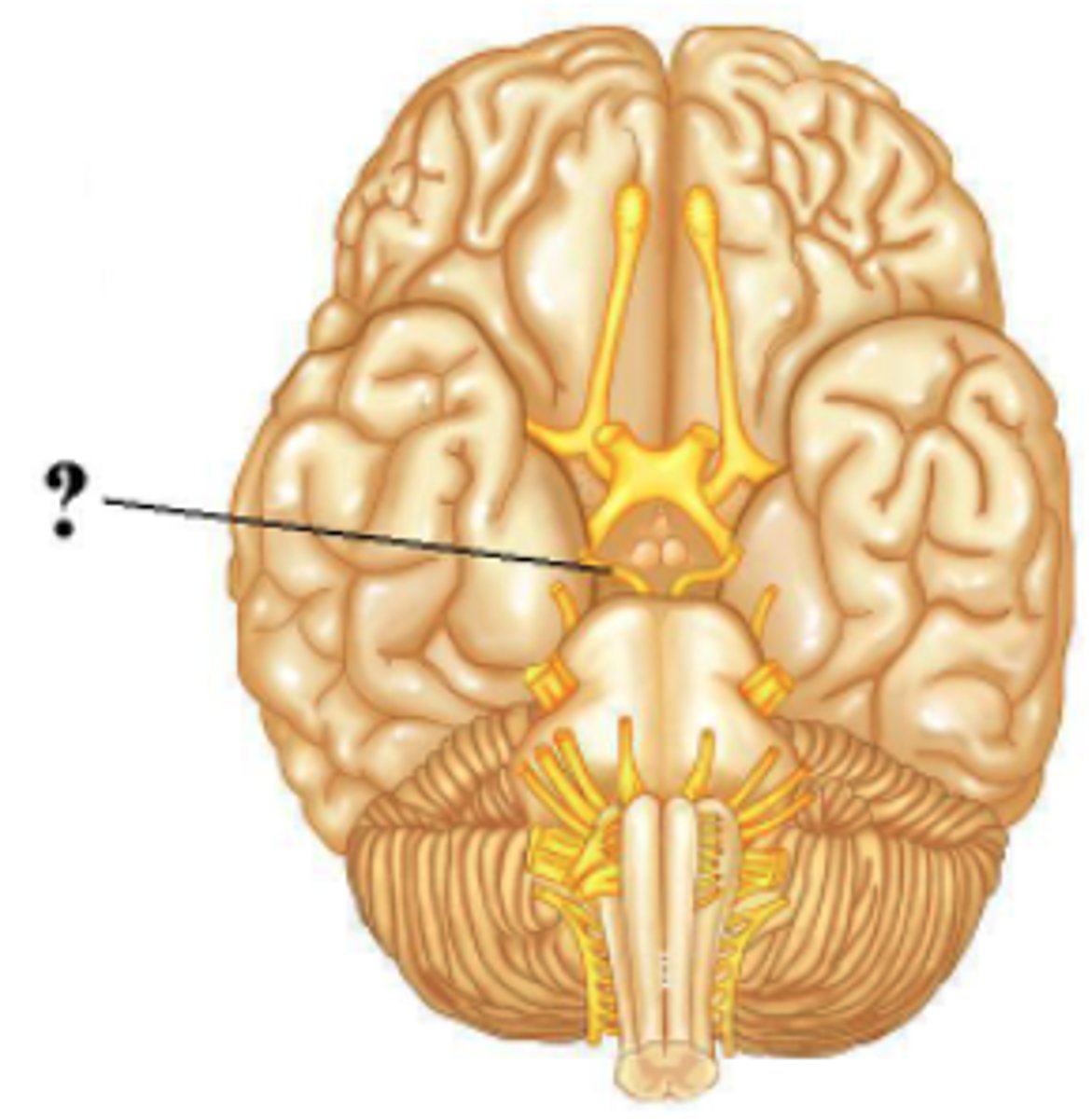
Is the indicated cranial nerve sensory only, motor only, or both sensory and motor?
both
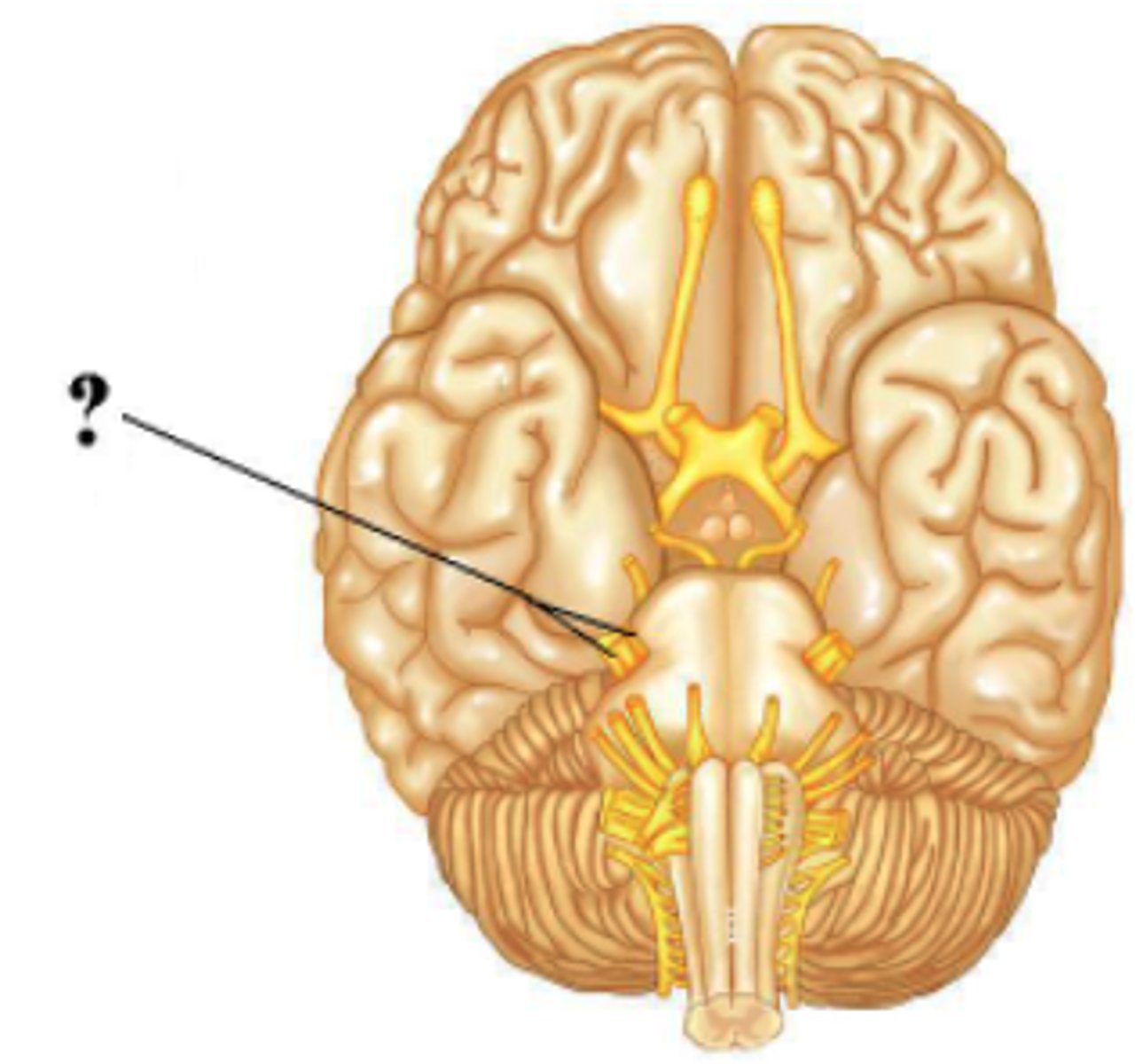
Identify the indicated space.
fourth ventricle
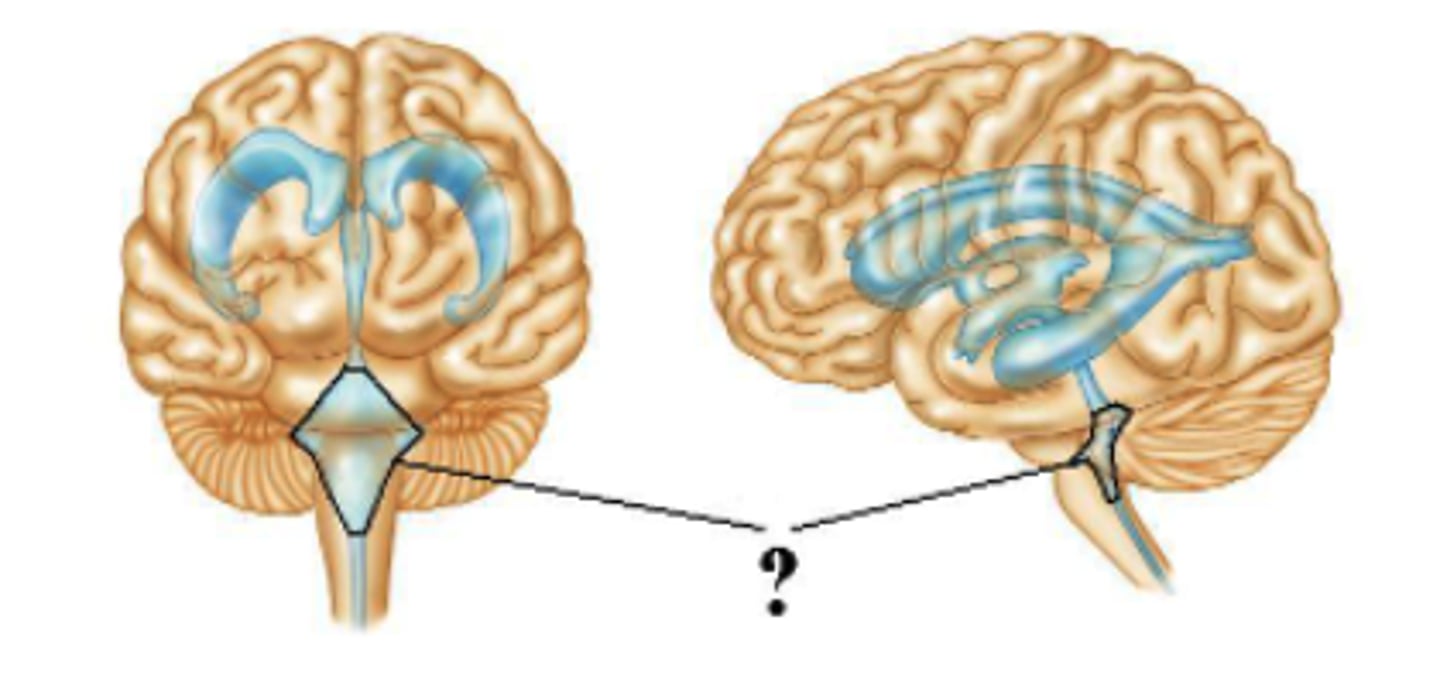
Identify the indicated part of the coverings of the brain.
arachnoid mater
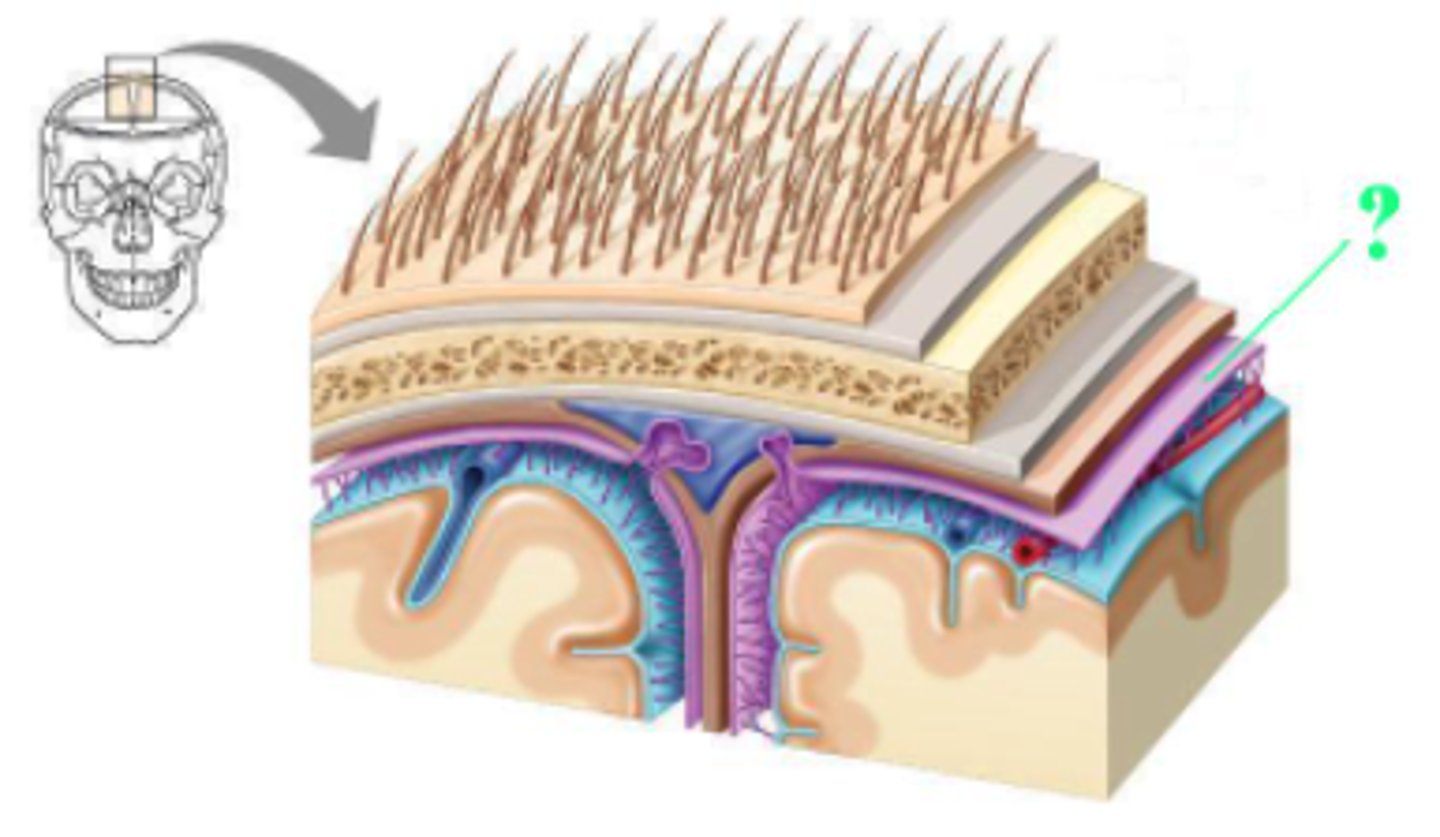
Identify the indicated structure.
falx cerebelli
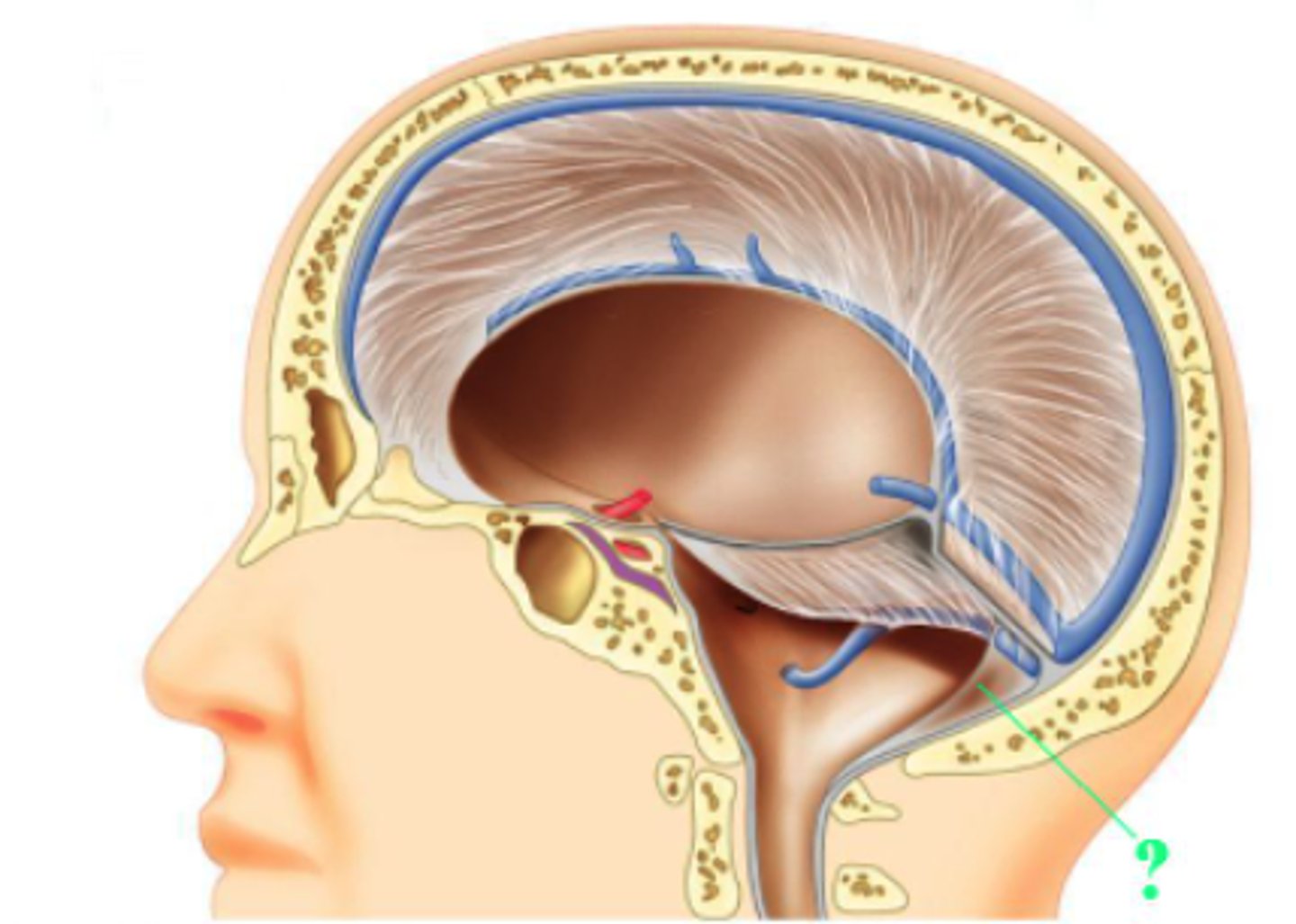
Identify the indicated structure.
dorsal root
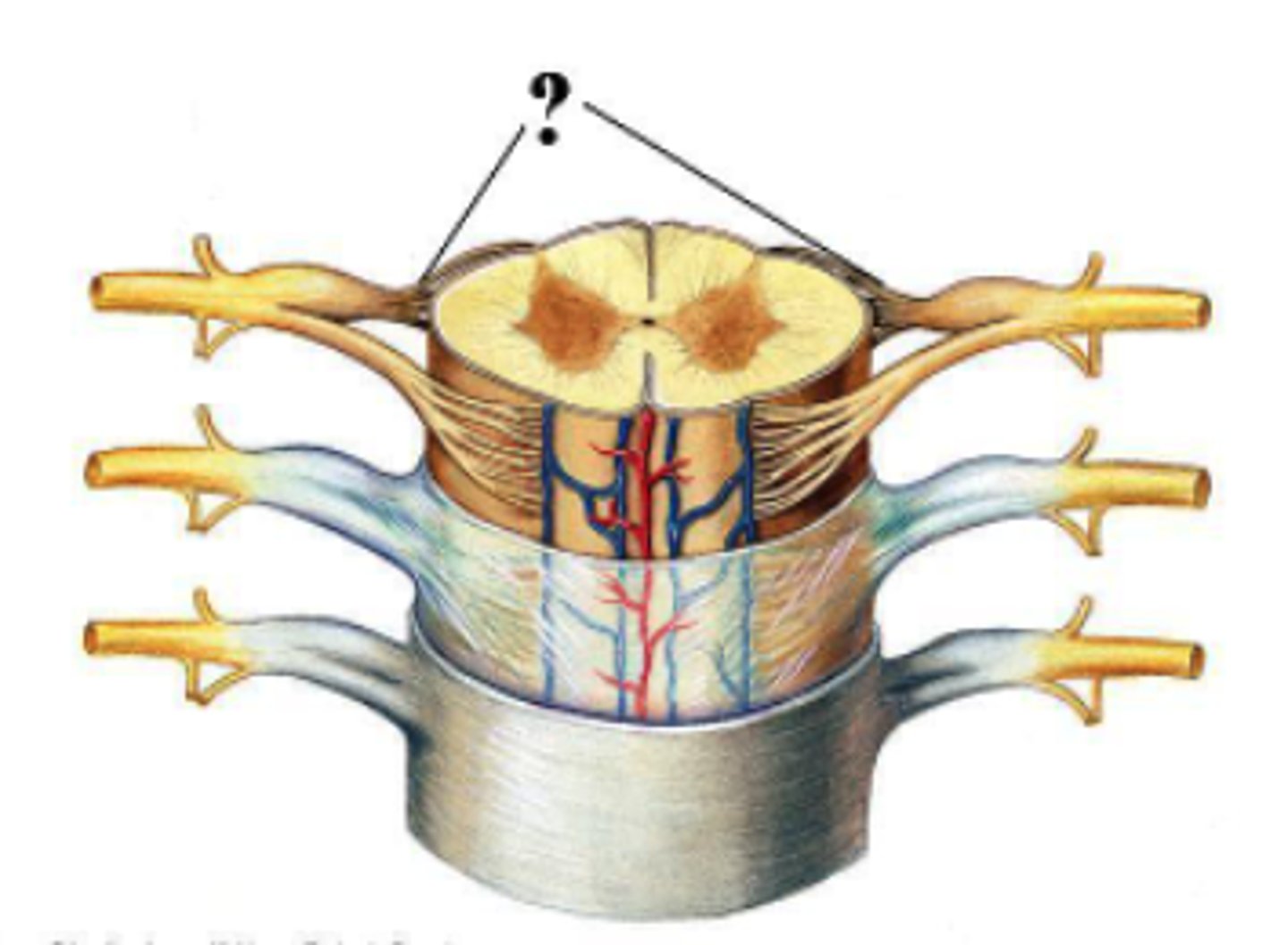
Identify the indicated structure.
lumbar enlargement
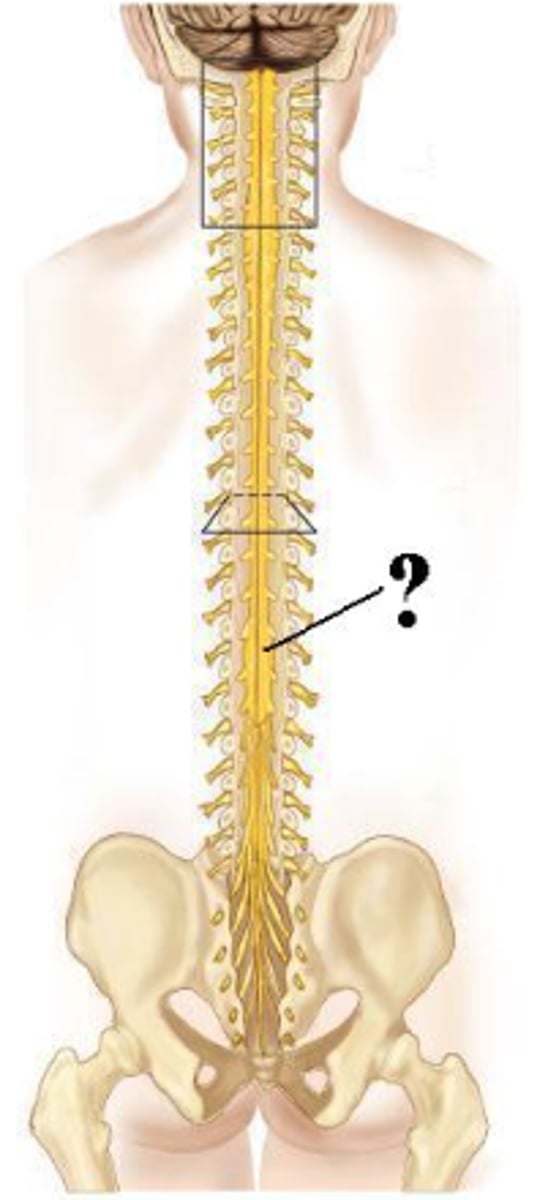
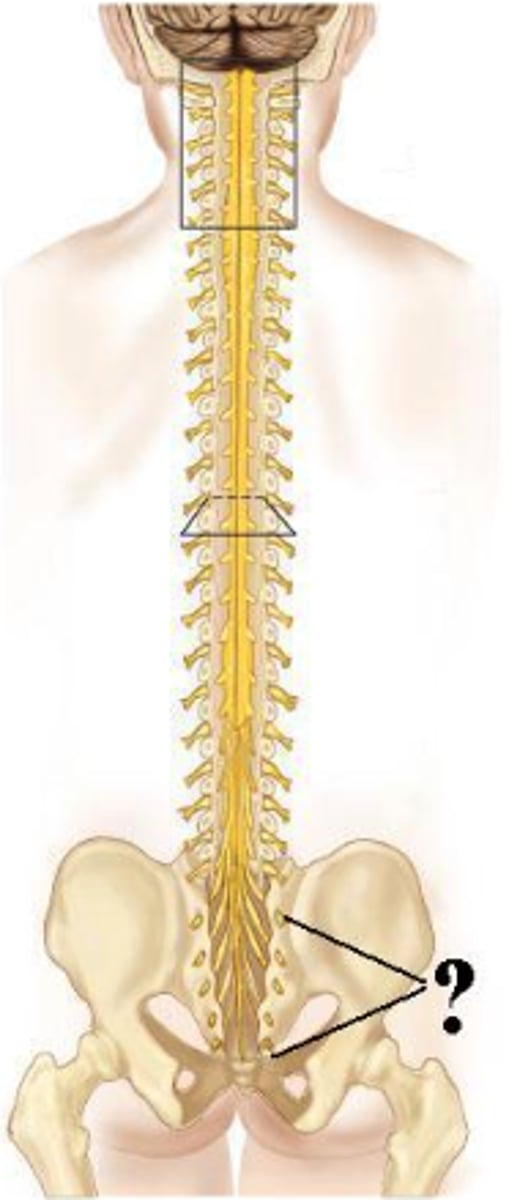
Identify the indicated structures.
sacral spinal nerves
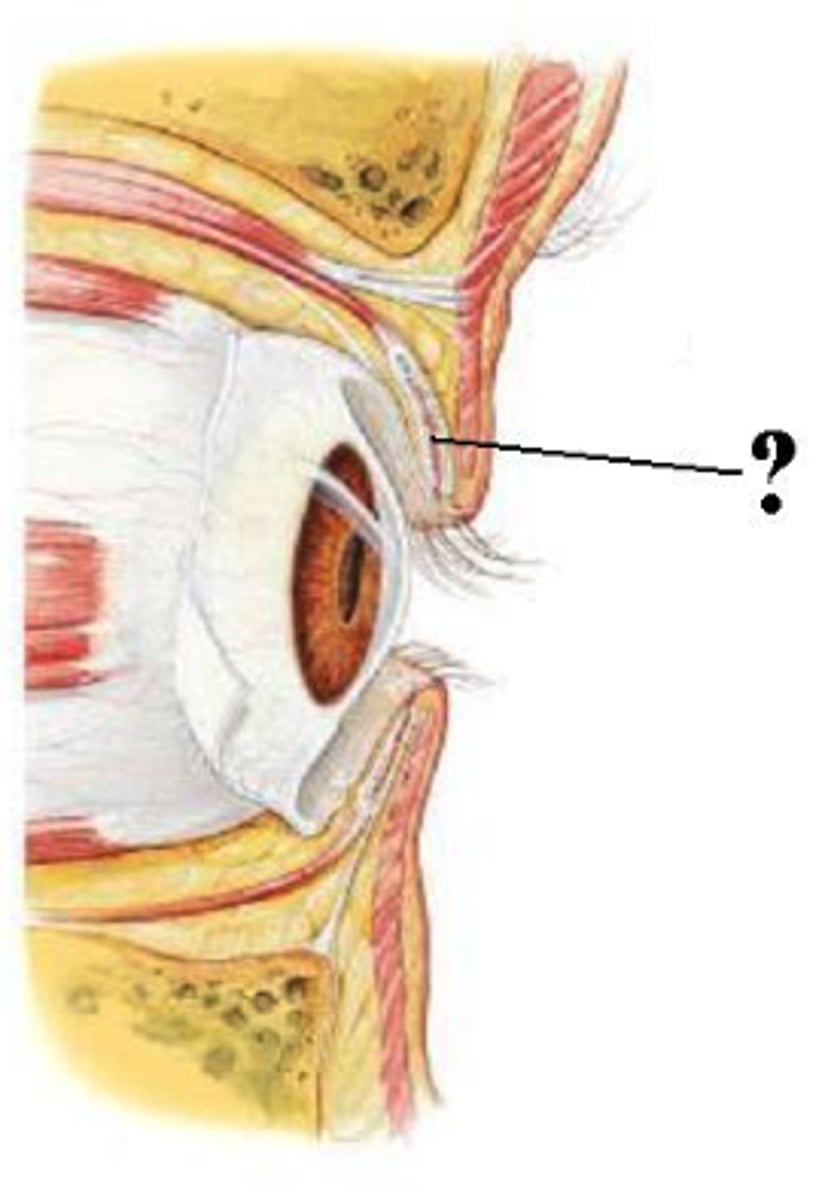
Identify the indicated structure.
tarsal glands
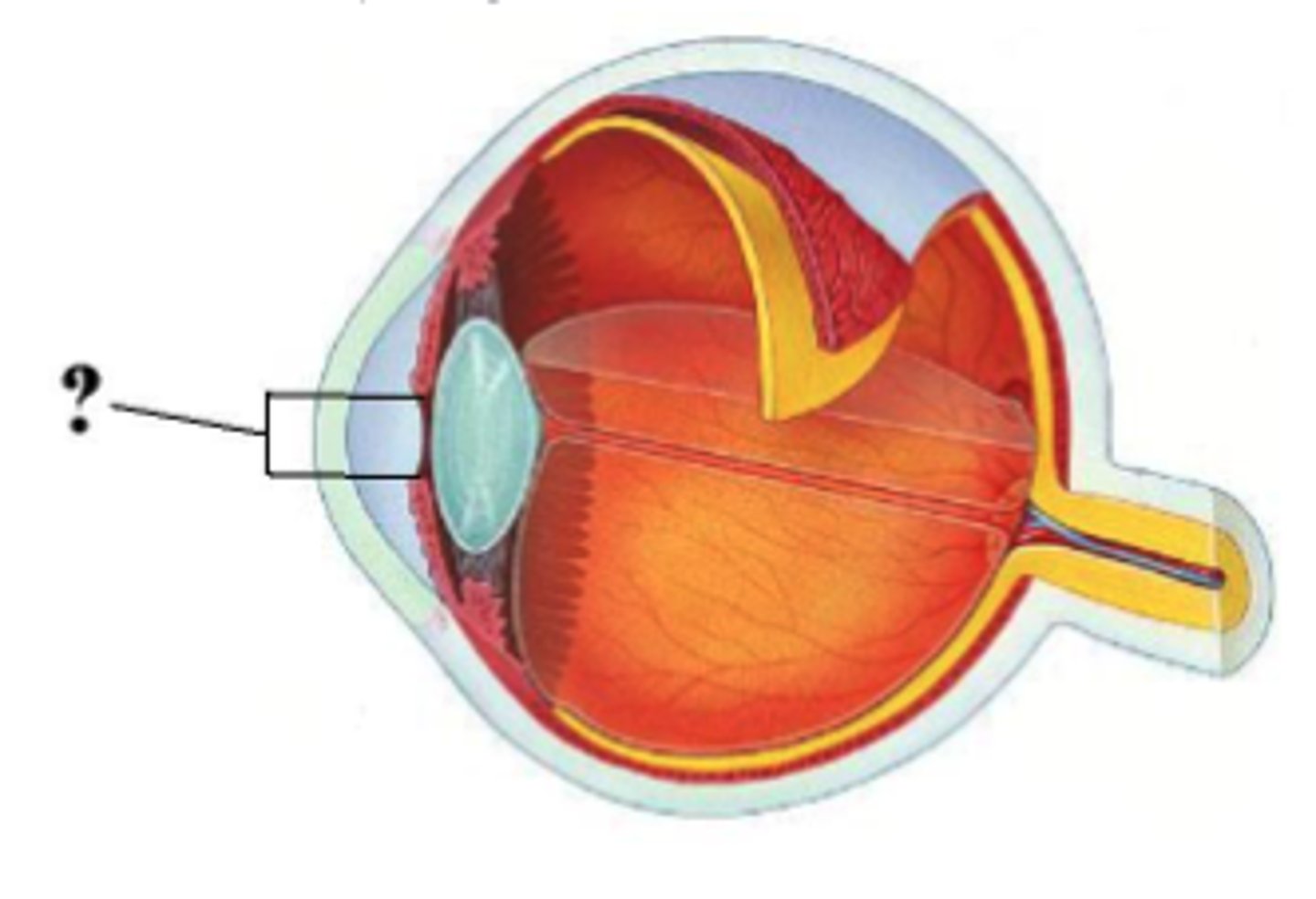
Identify the indicated opening.
pupil
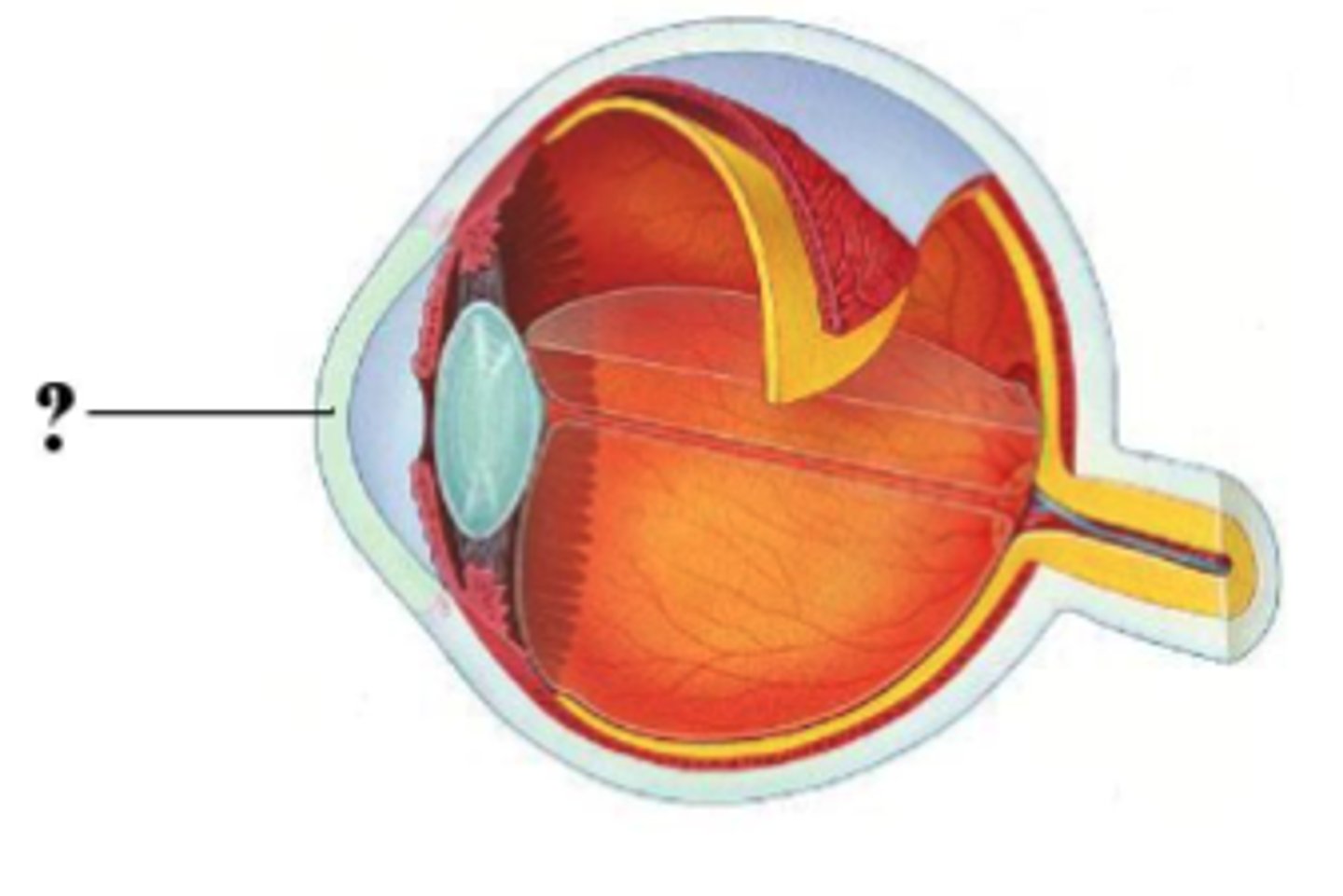
Identify the indicated structure.
cornea
Identify the indicated structures.
excretory ducts of lacrimal glands
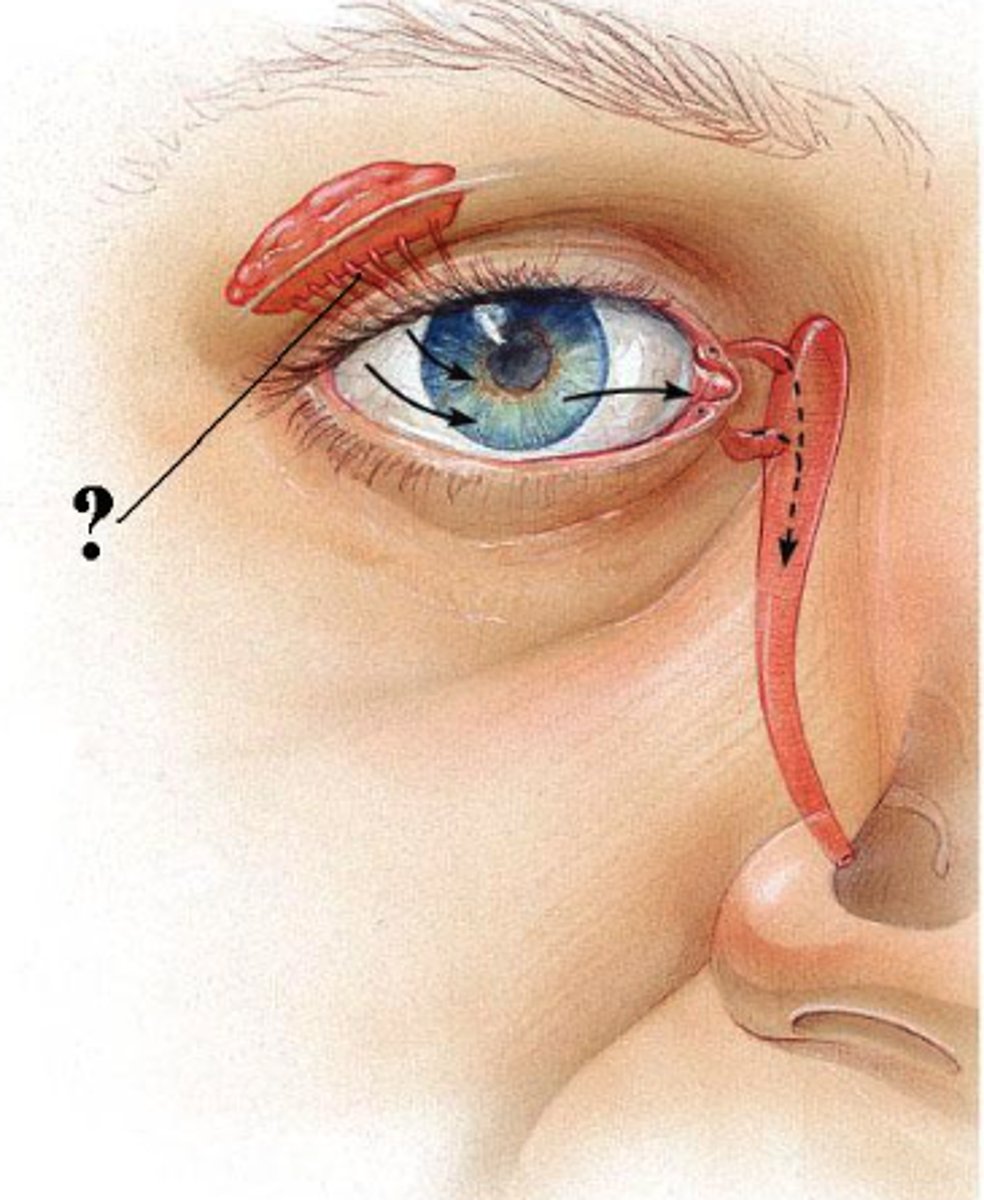
Identify the indicated structure.
caruncle
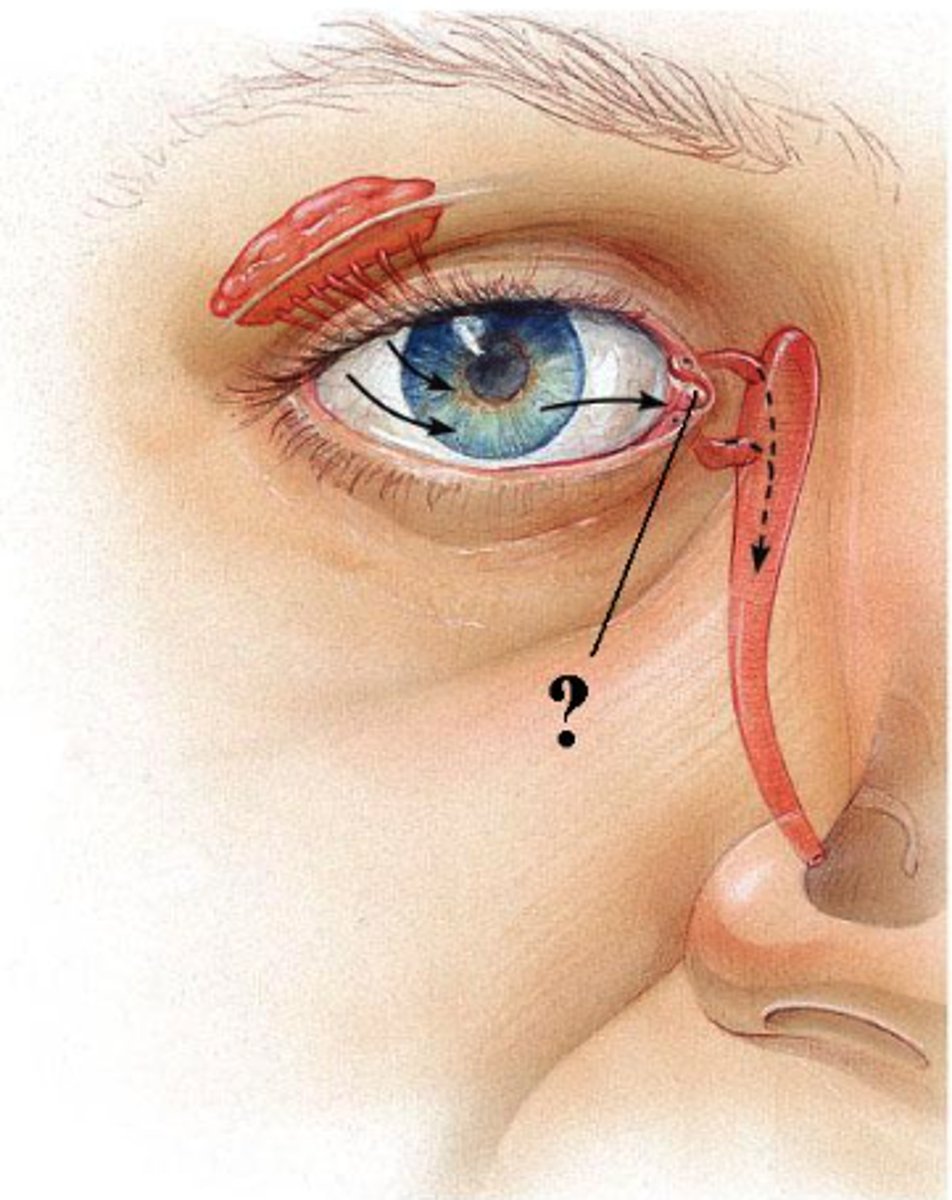
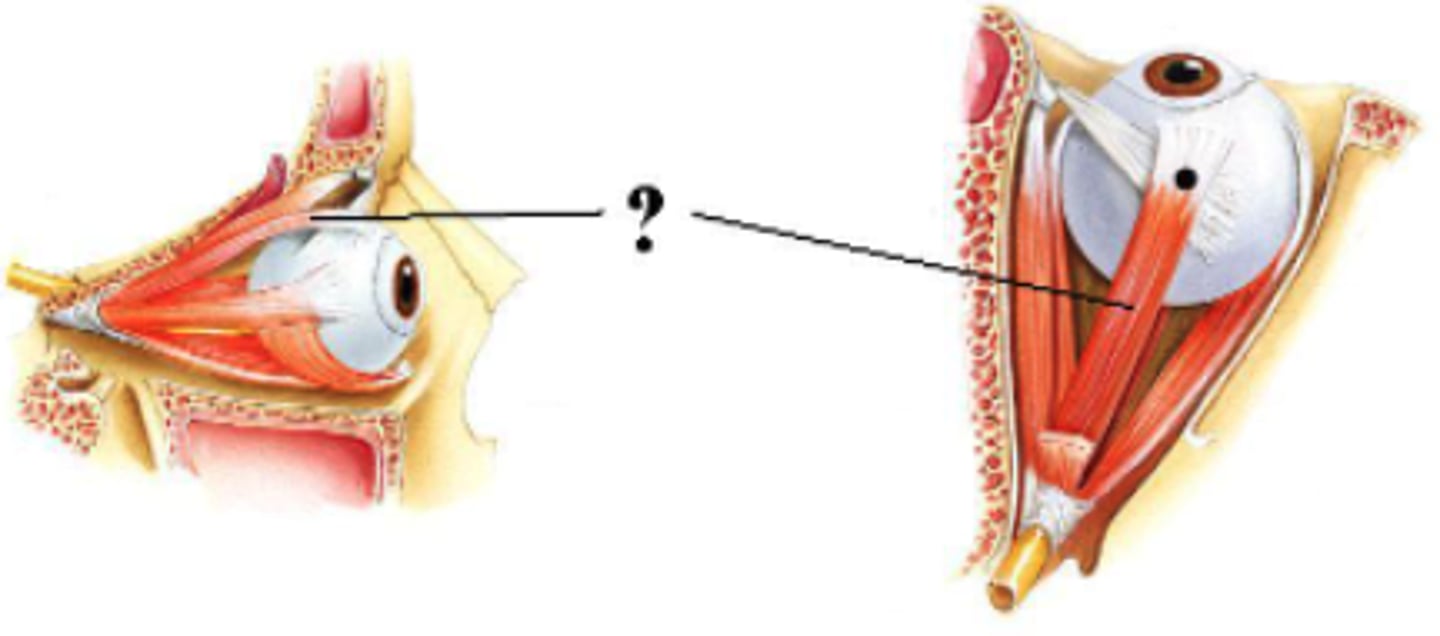
Identify the indicated structure.
superior rectus muscle
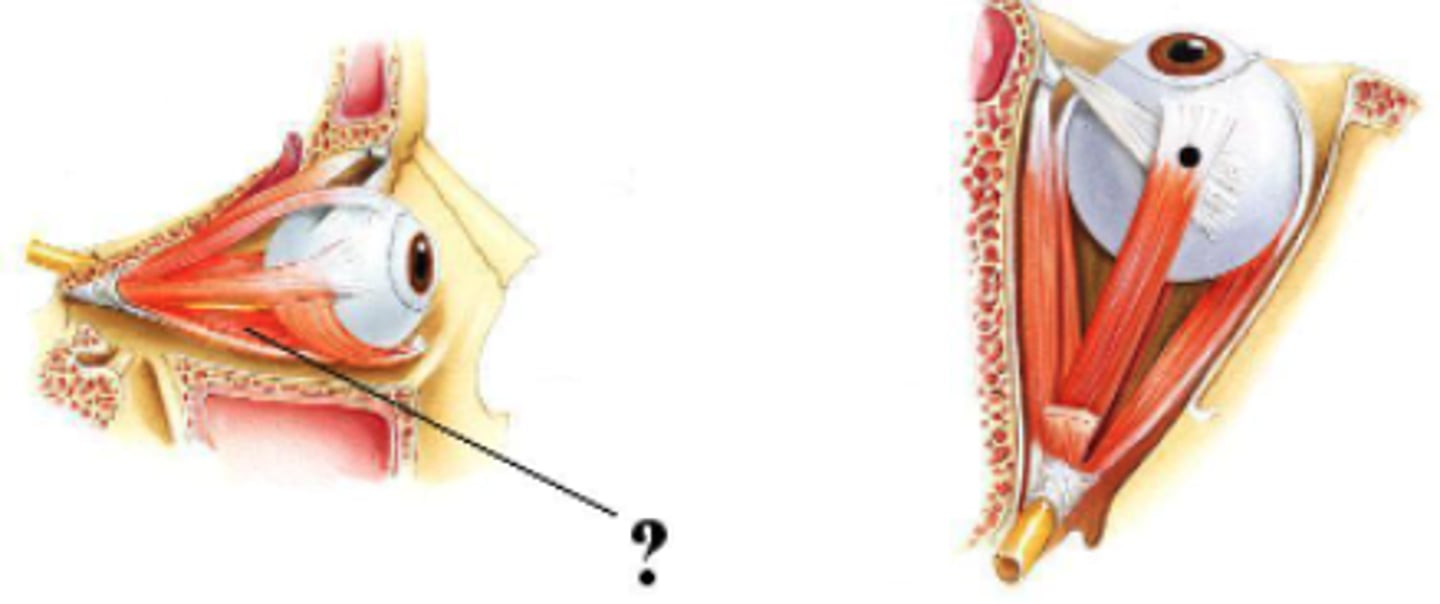
Identify the indicated structure.
inferior rectus muscle
Identify the indicated layer of the retina.
photoreceptor cell layer
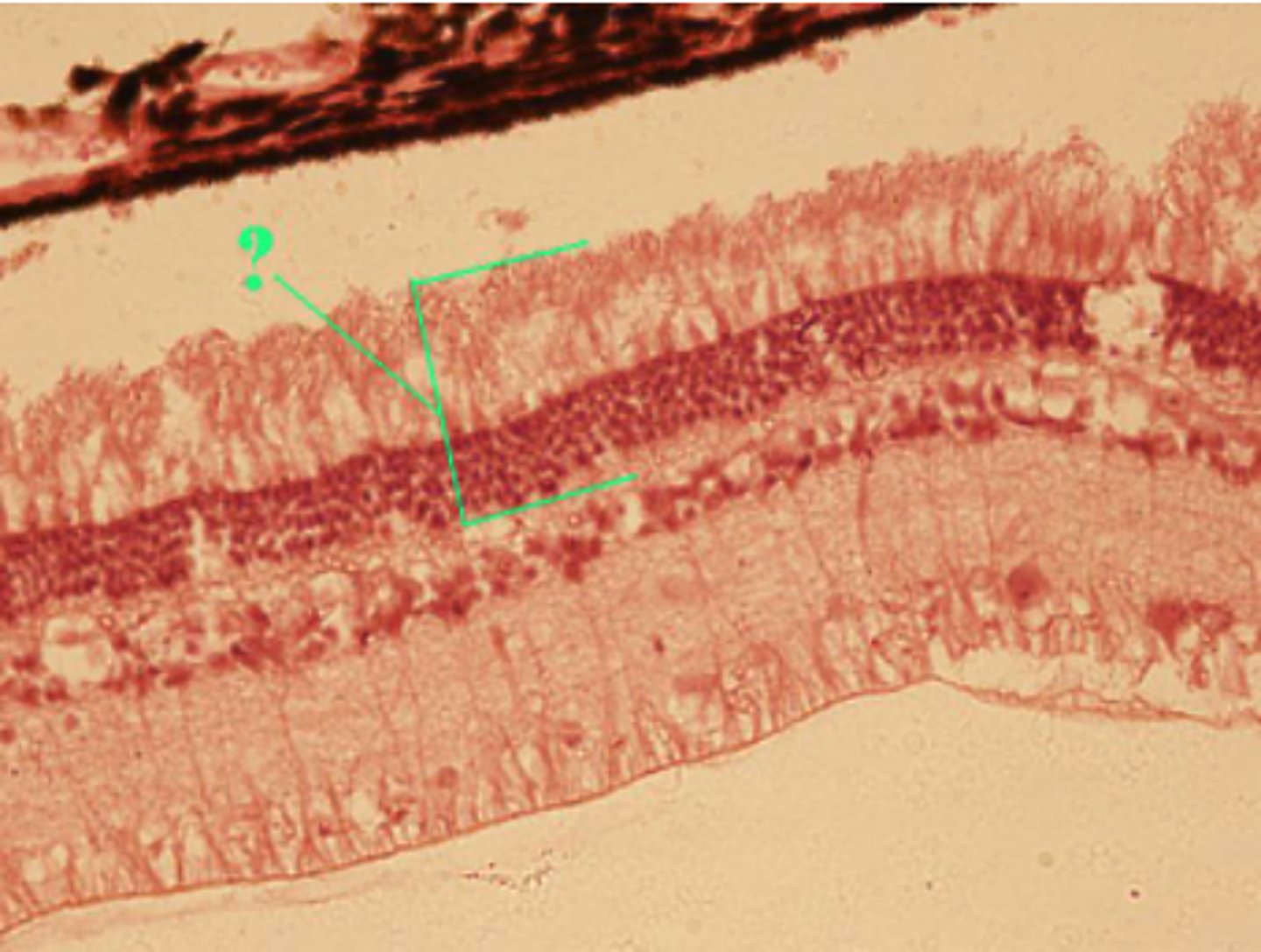
Identify the indicated structure.
tympanic membrane
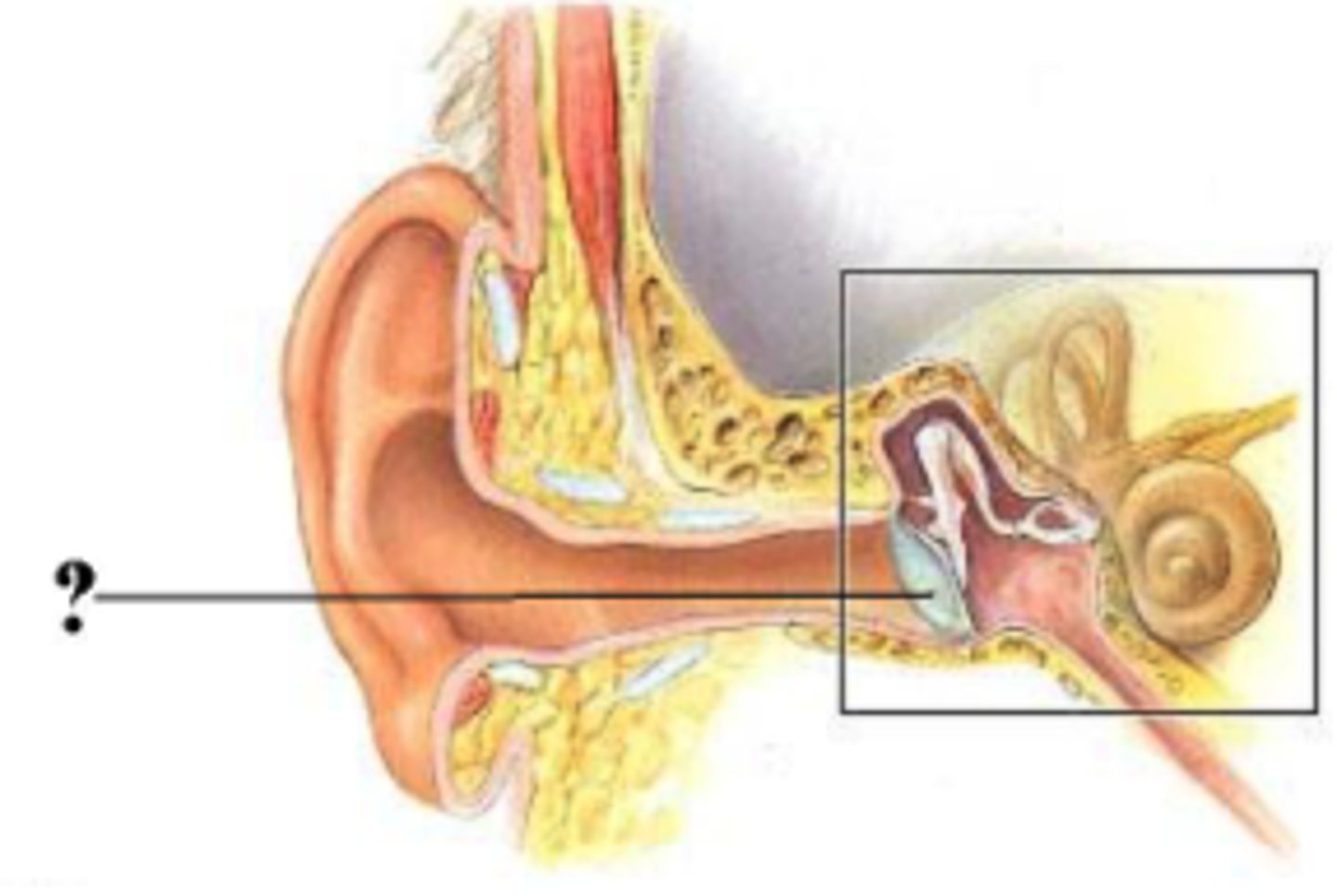
Identify the indicated structure.
auricle
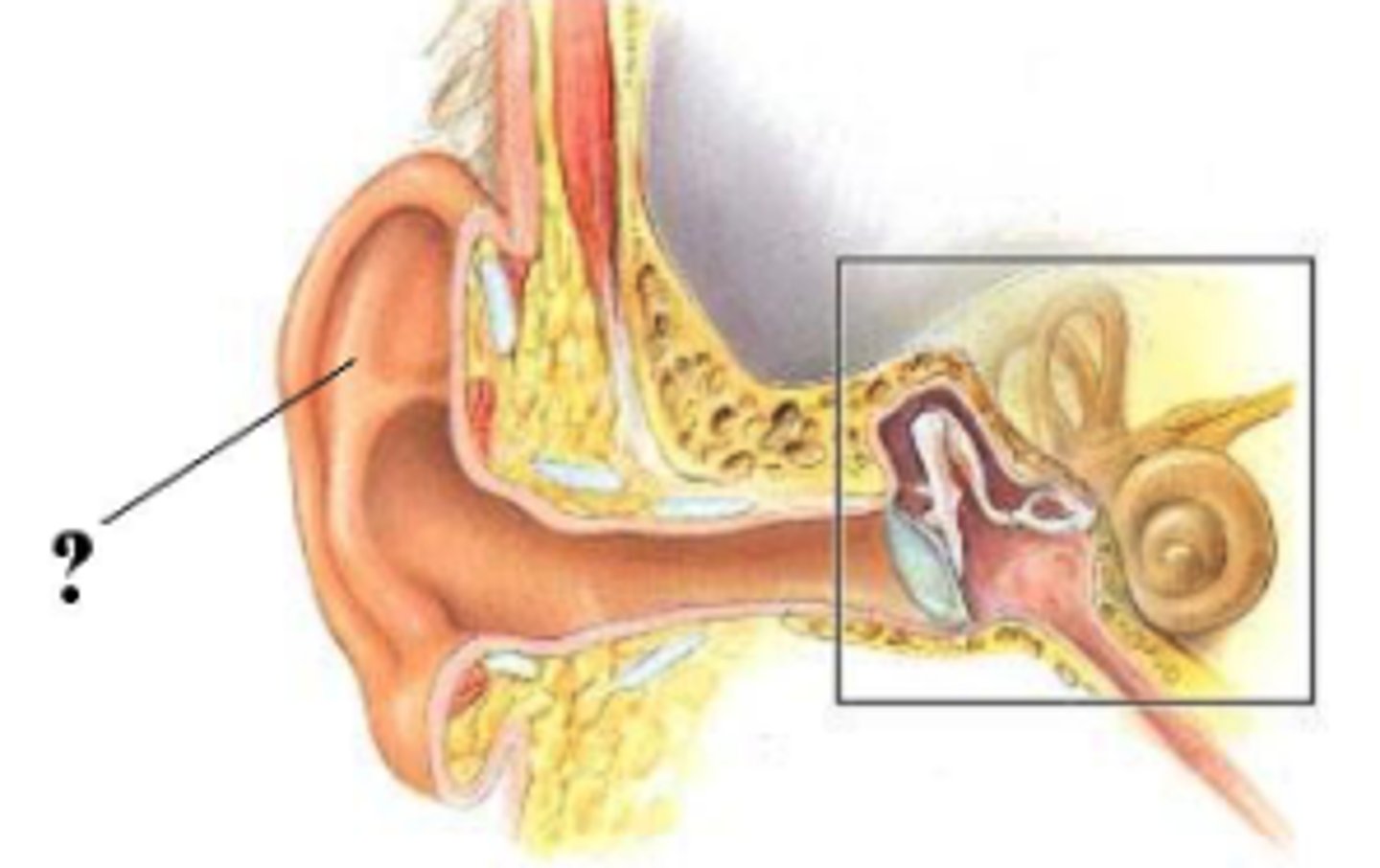
Identify the indicated region of the ear.
middle ear
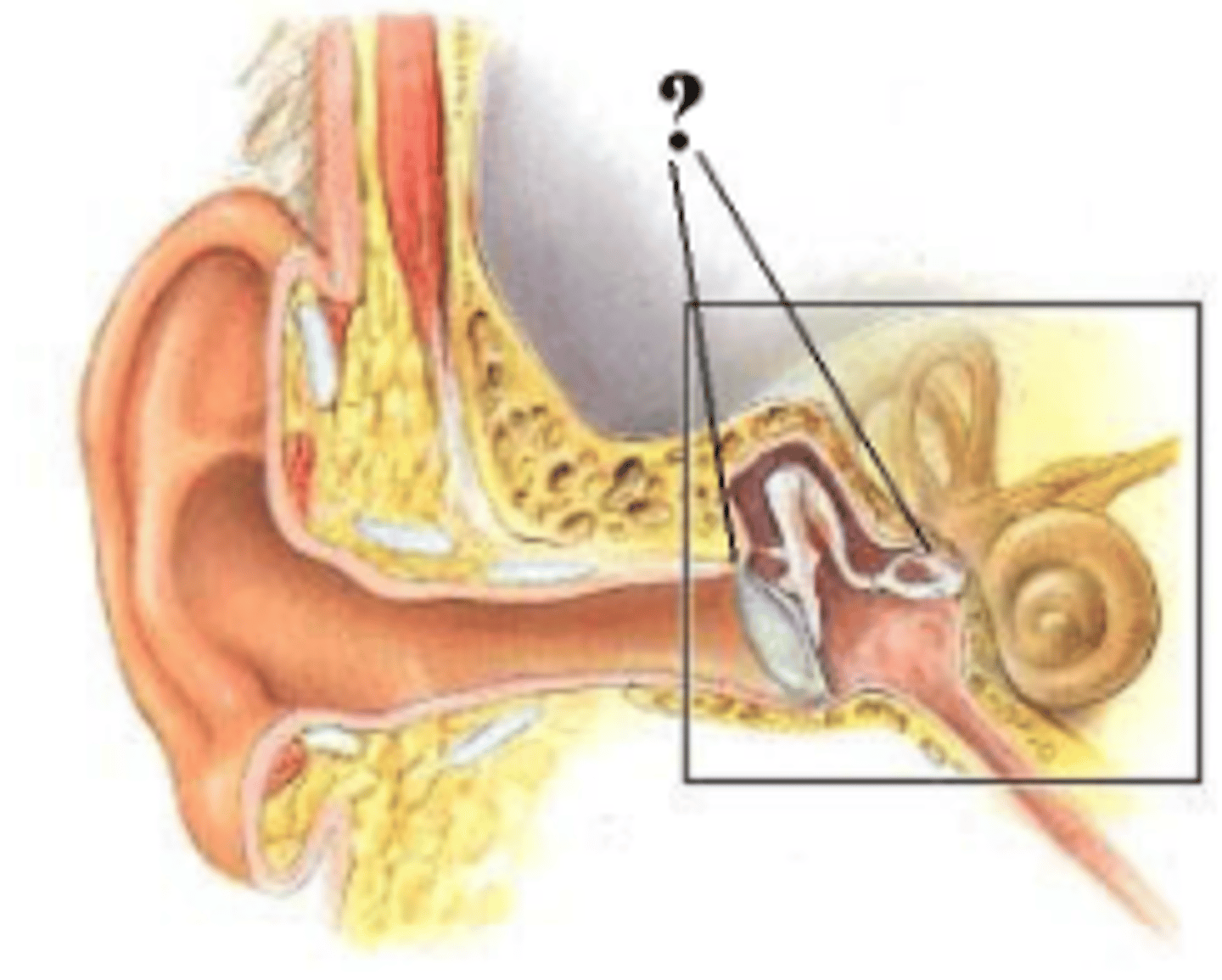
Identify the indicated structure.
saccule
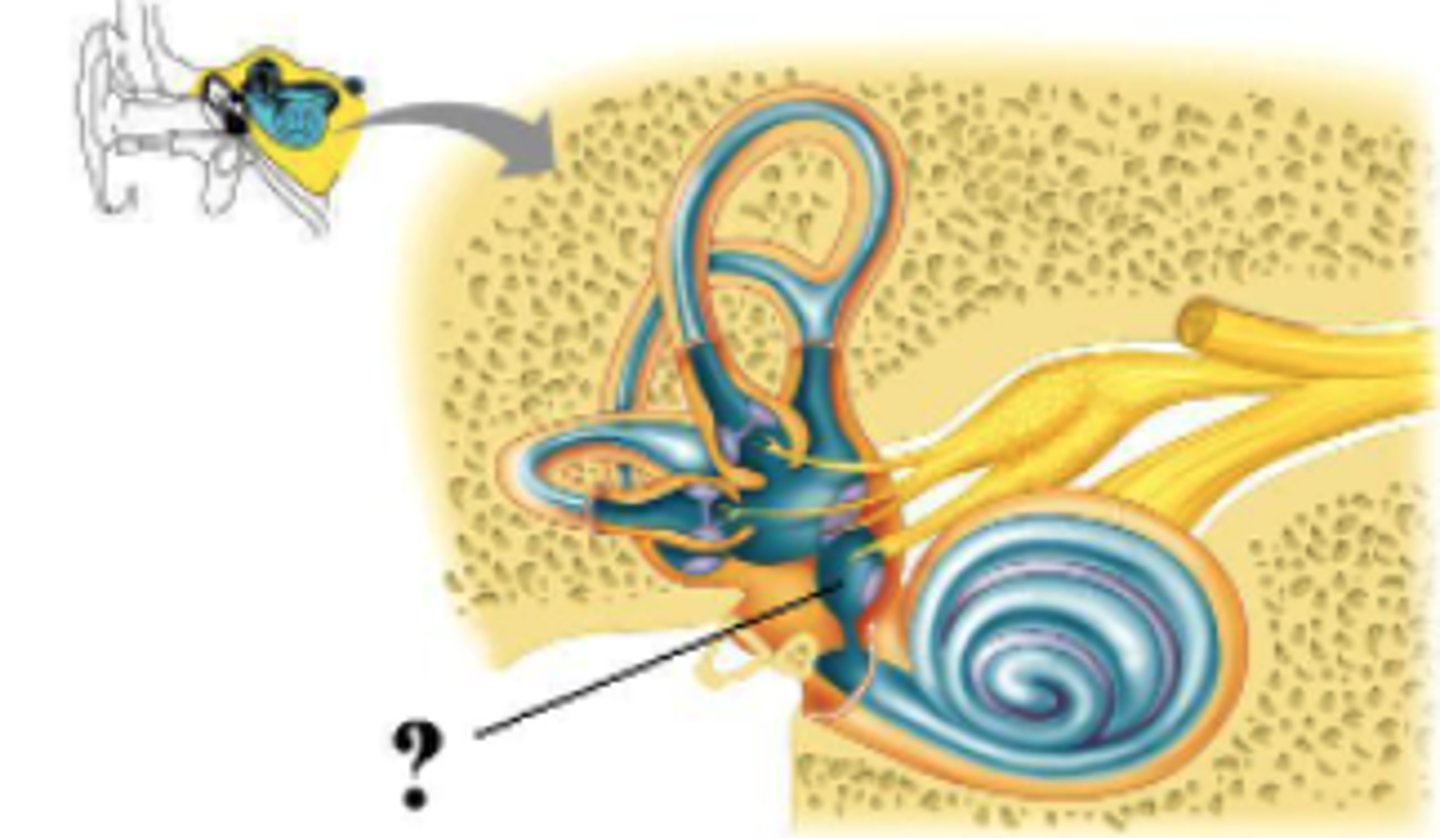
Identify the indicated region.
vestibule
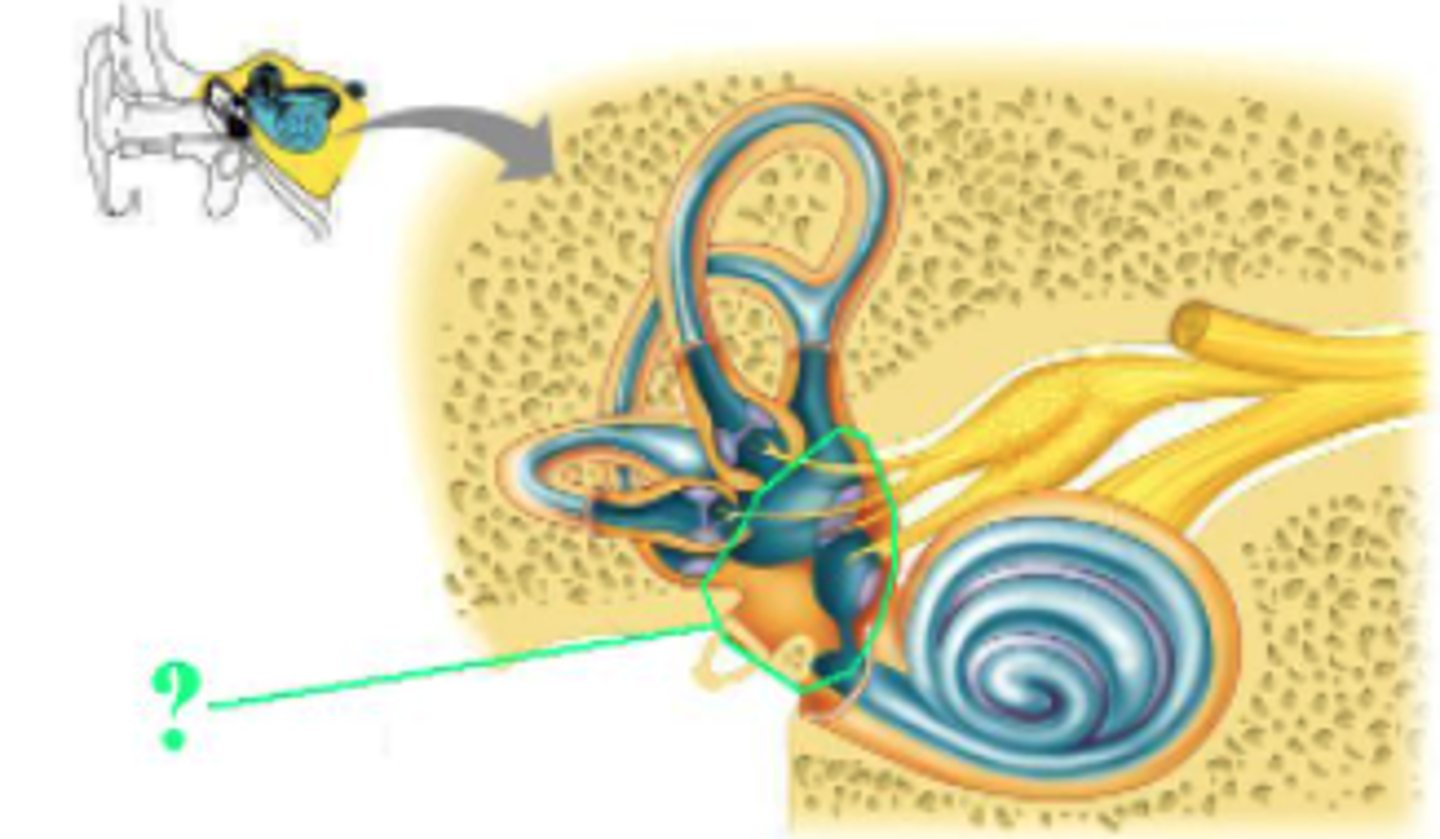
What phenomenon does the indicated structure sense?
hearing
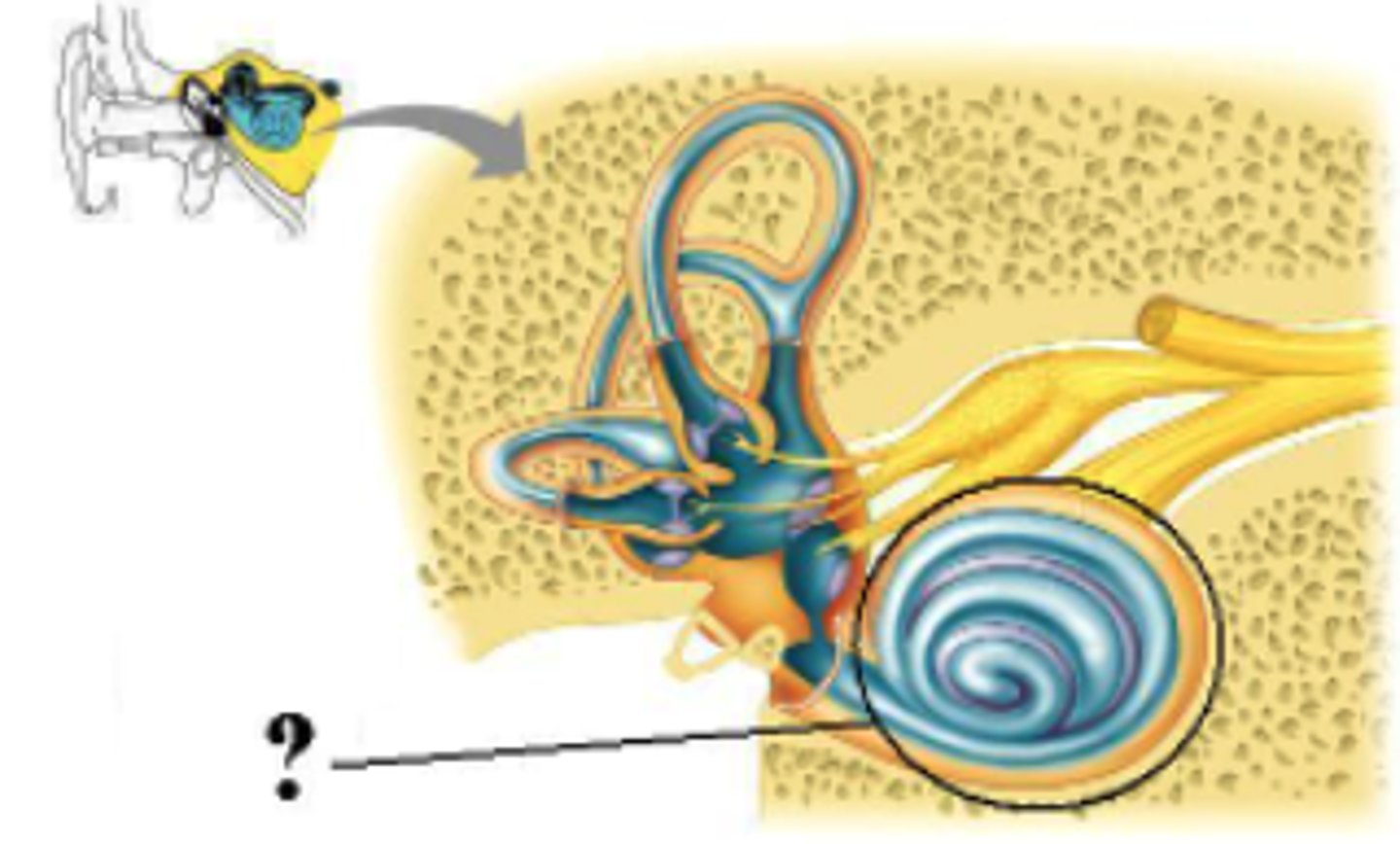
Identify the indicated structures.
hair cells
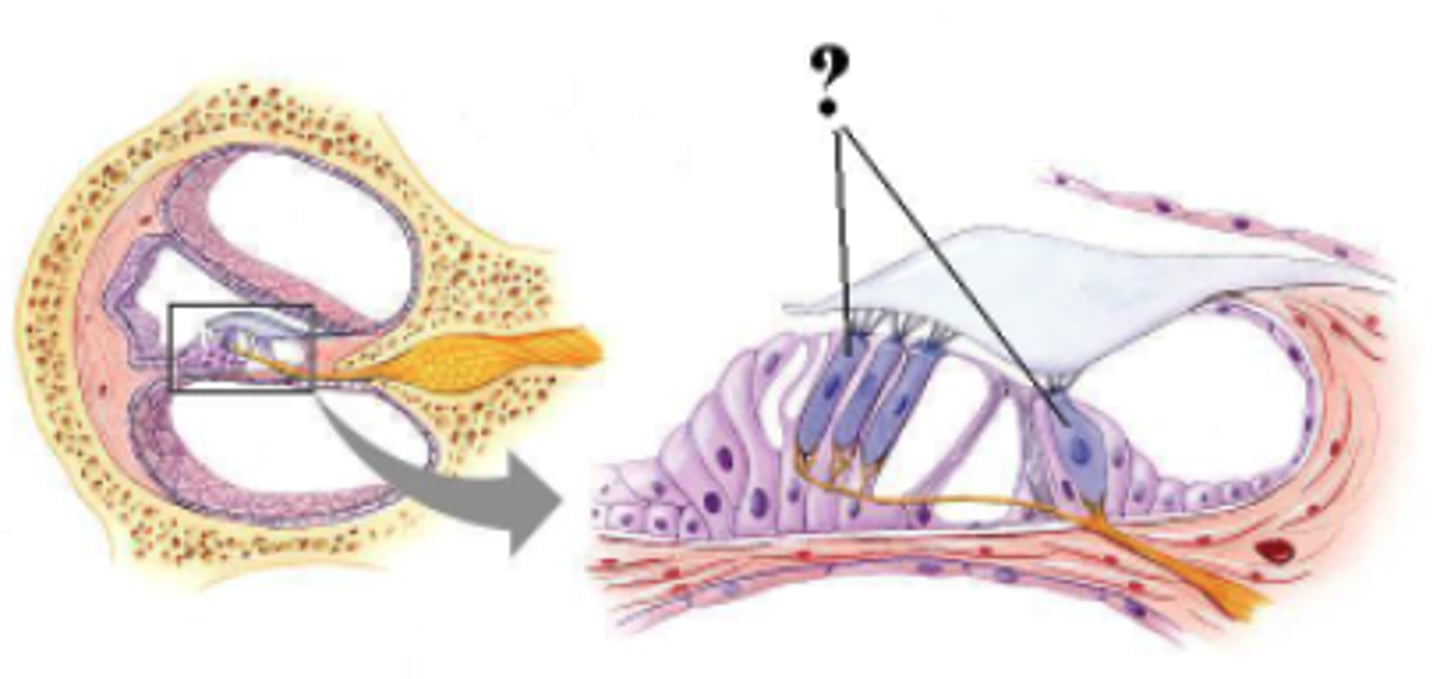
Identify the indicated structure.
spiral ganglion
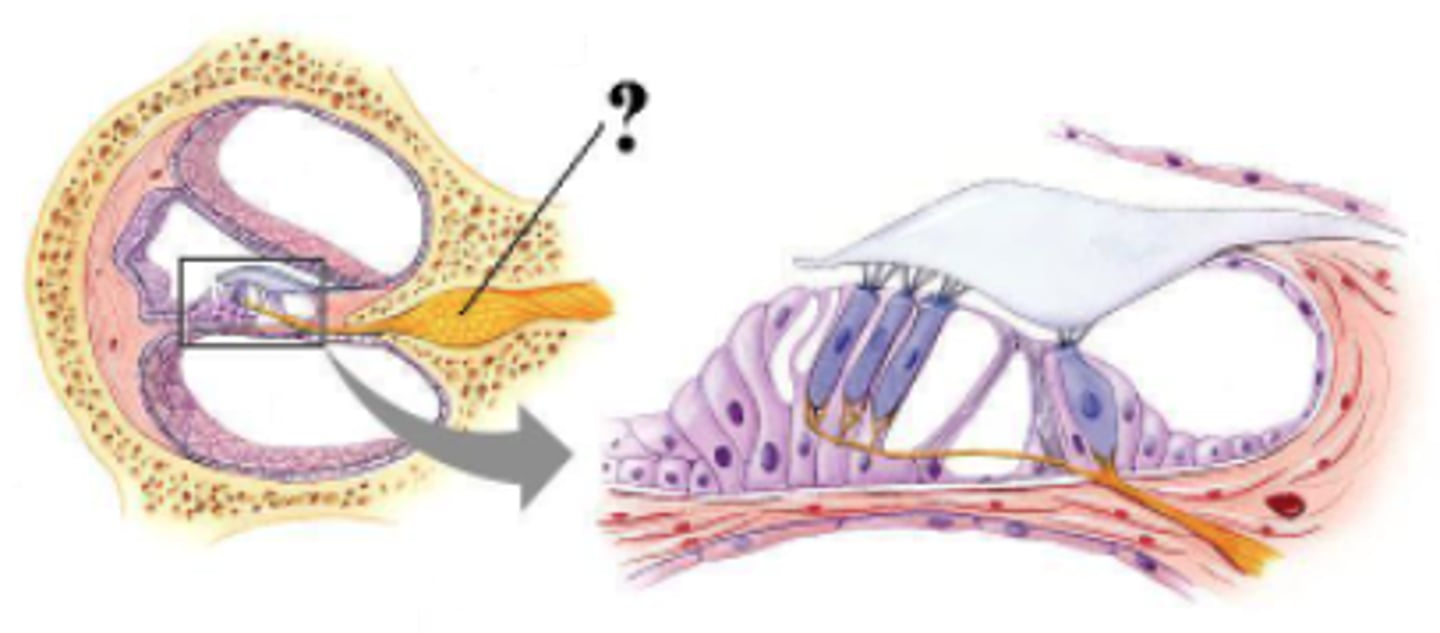
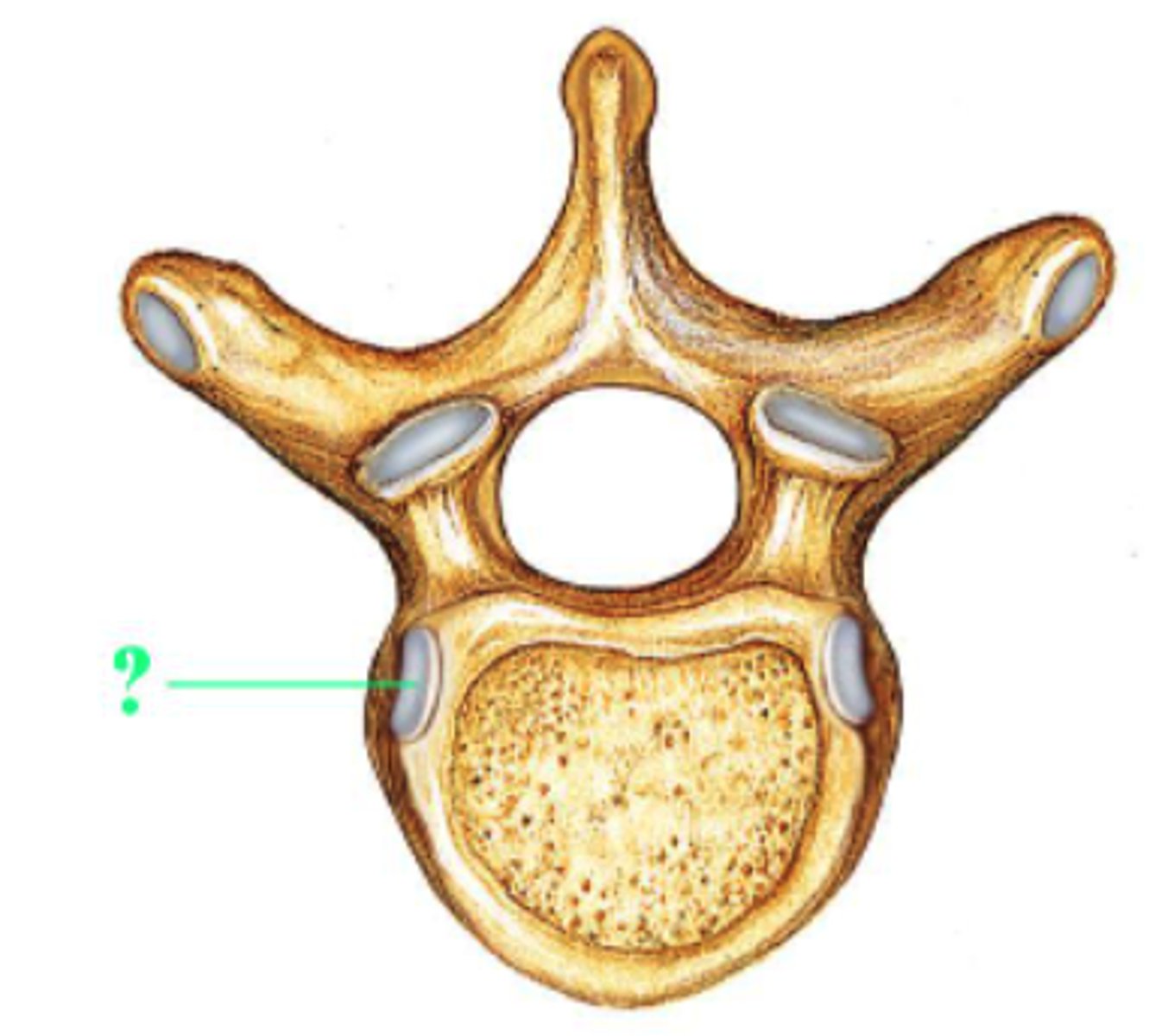
Identify the indicated bone marking (surface).
costal demifacet
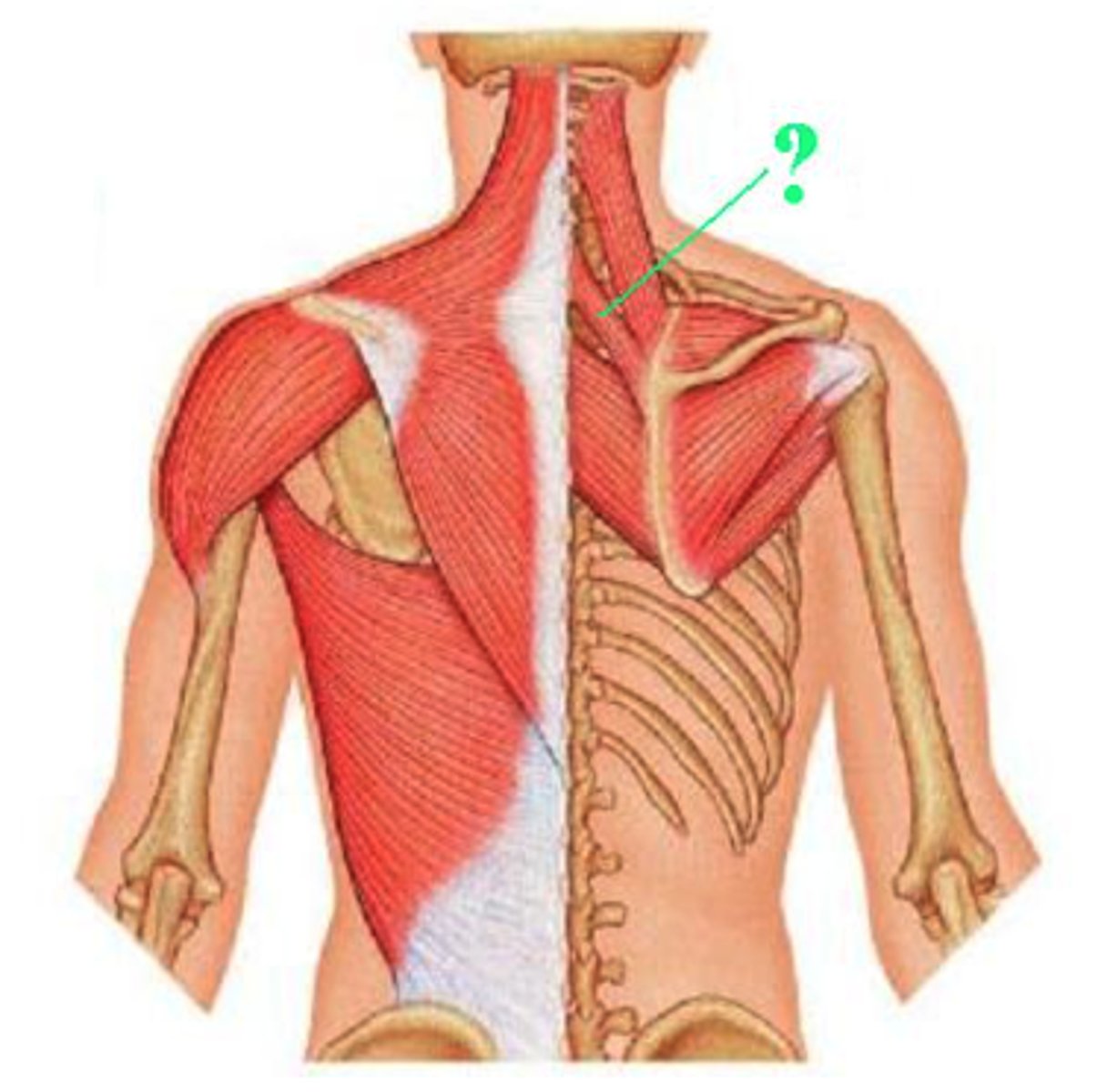
Identify the indicated muscle.
rhomboid minor
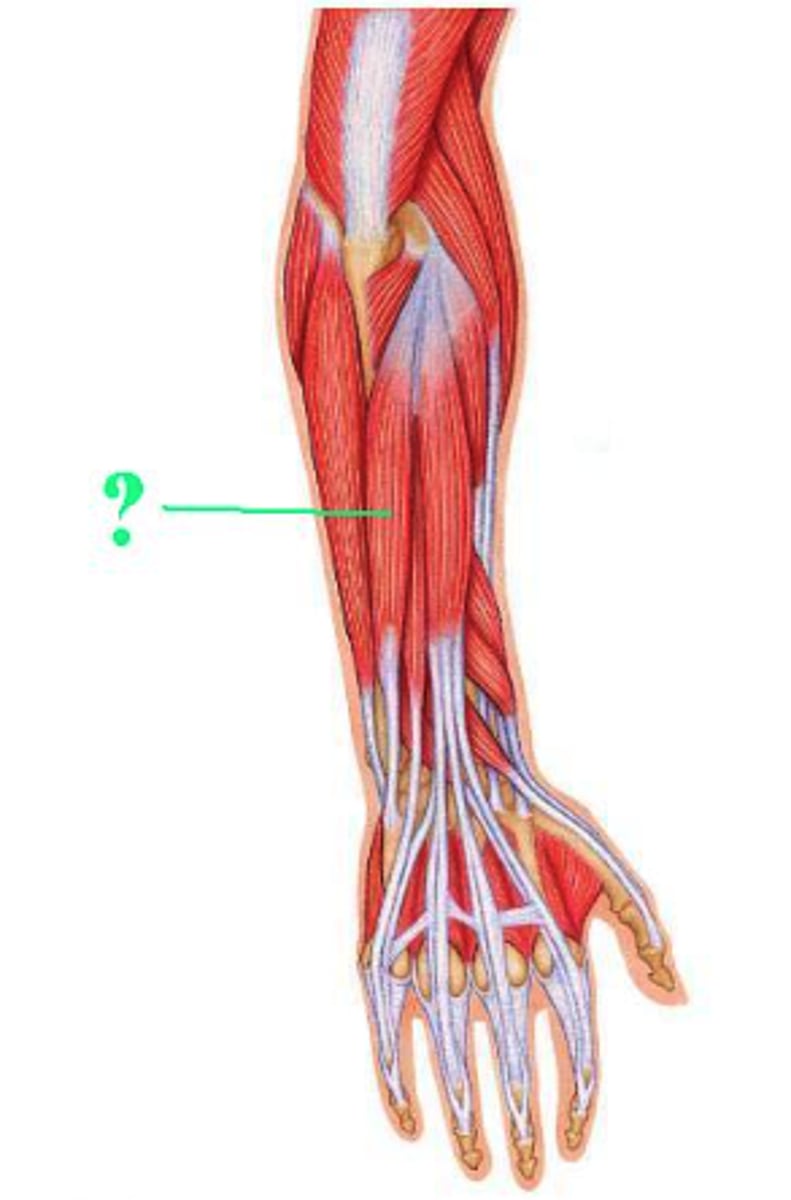
Identify the indicated muscle.
extensor carpi ulnaris
Identify the indicated bone.
proximal phalanx
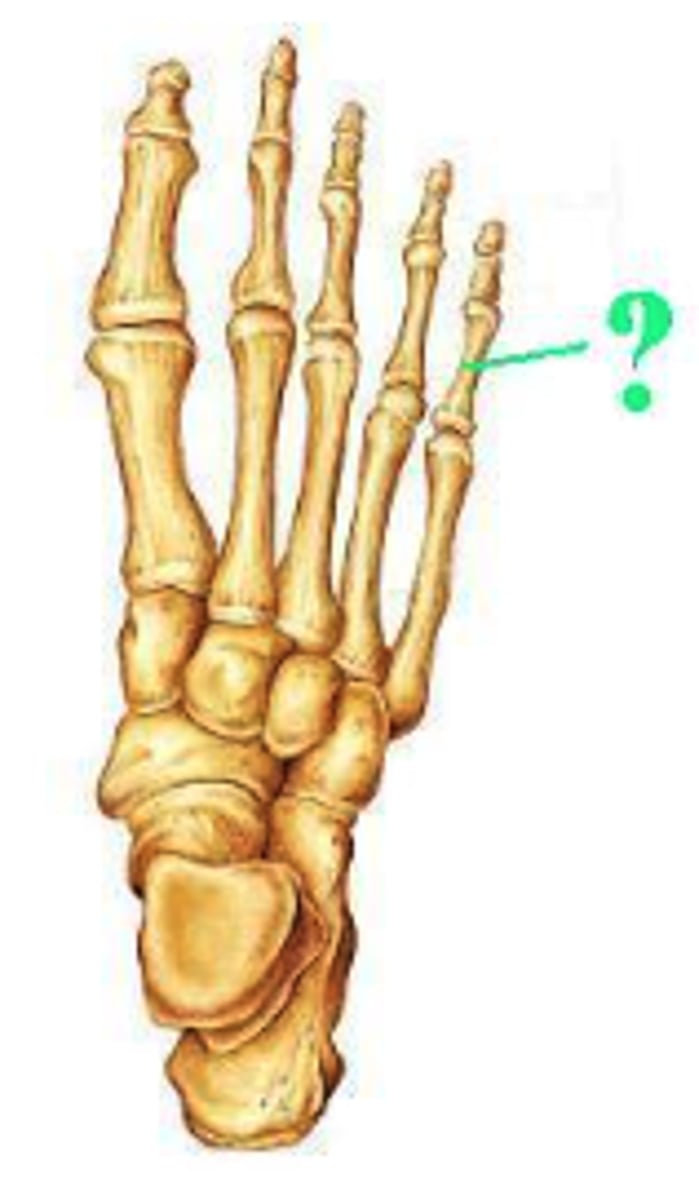
Identify the indicated bone marking (projection)?
lateral condyle
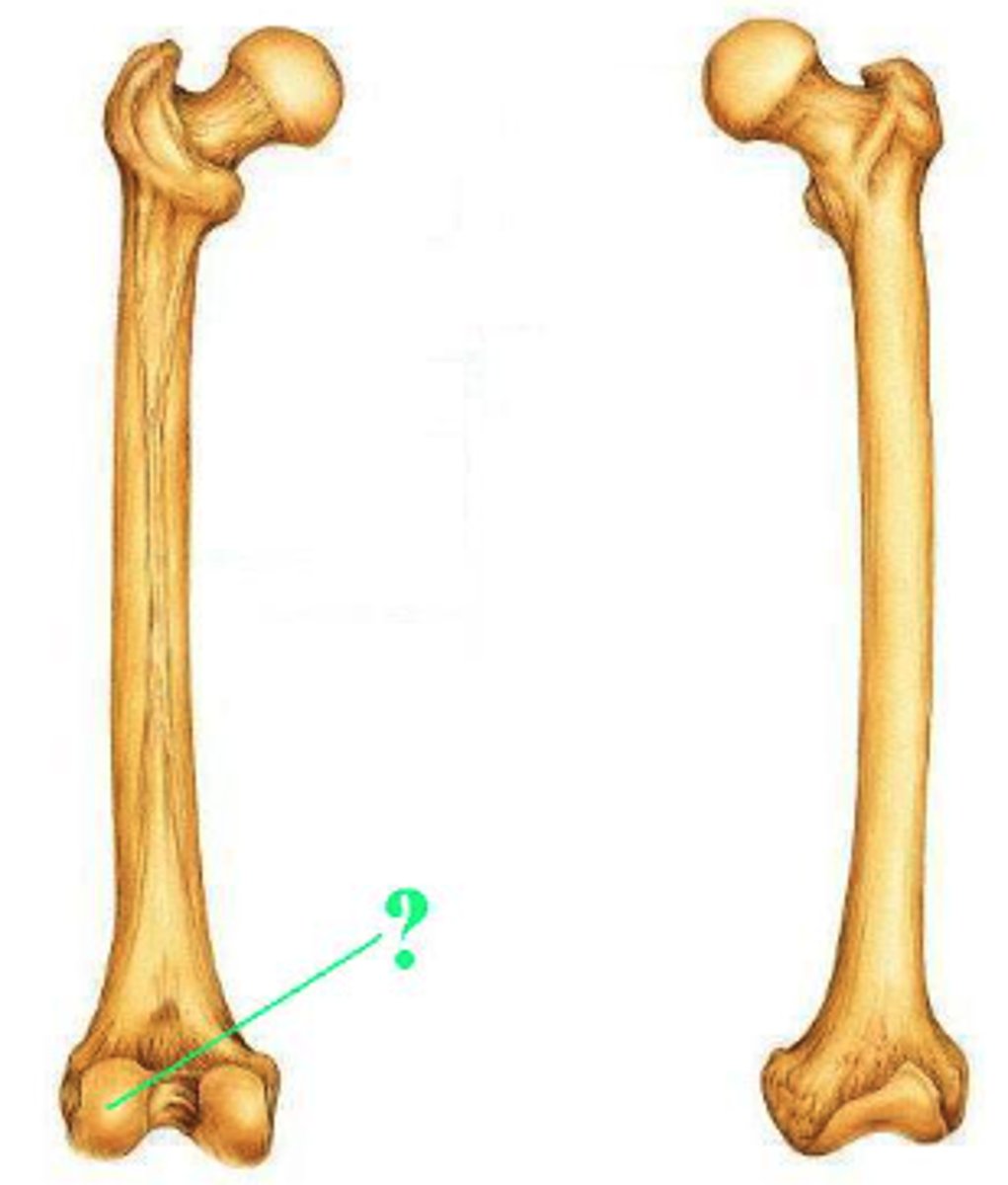
Identify the indicated bone.
lateral cuneiform
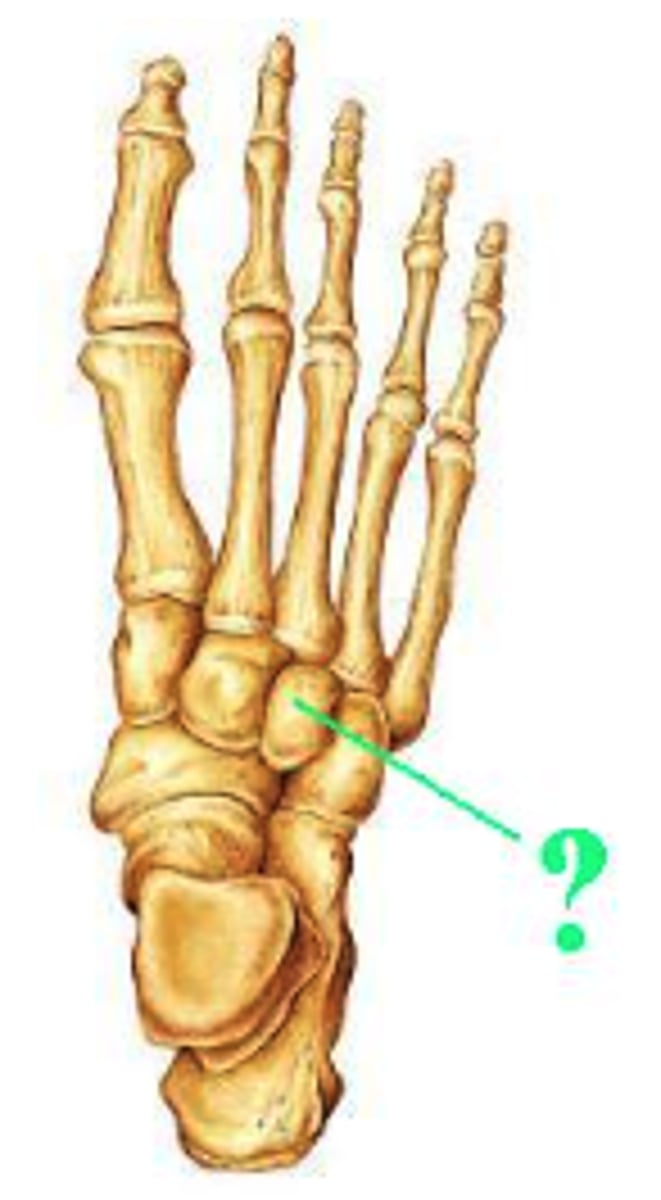
Identify the indicated muscle.
sternocleidomastoid
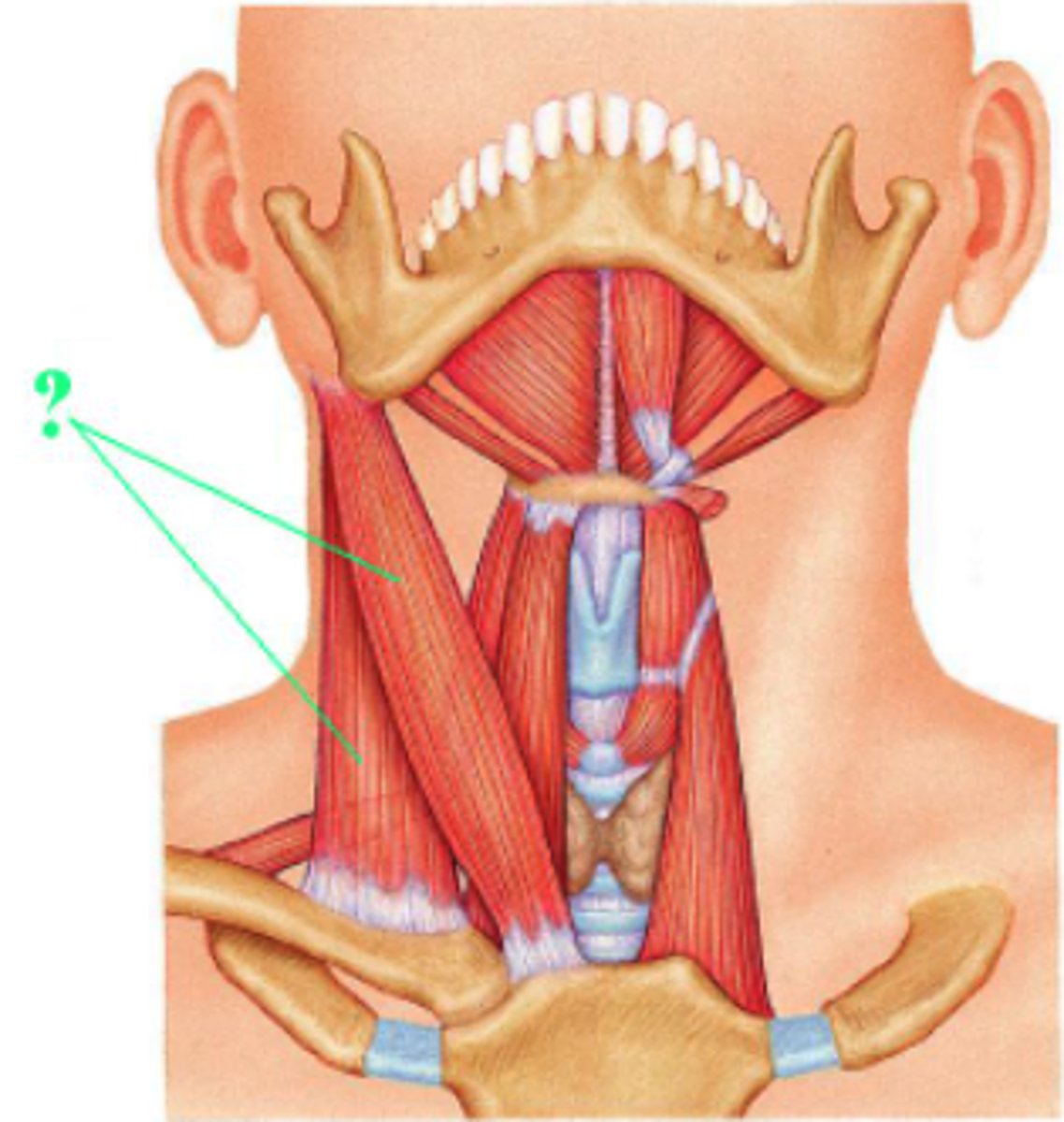
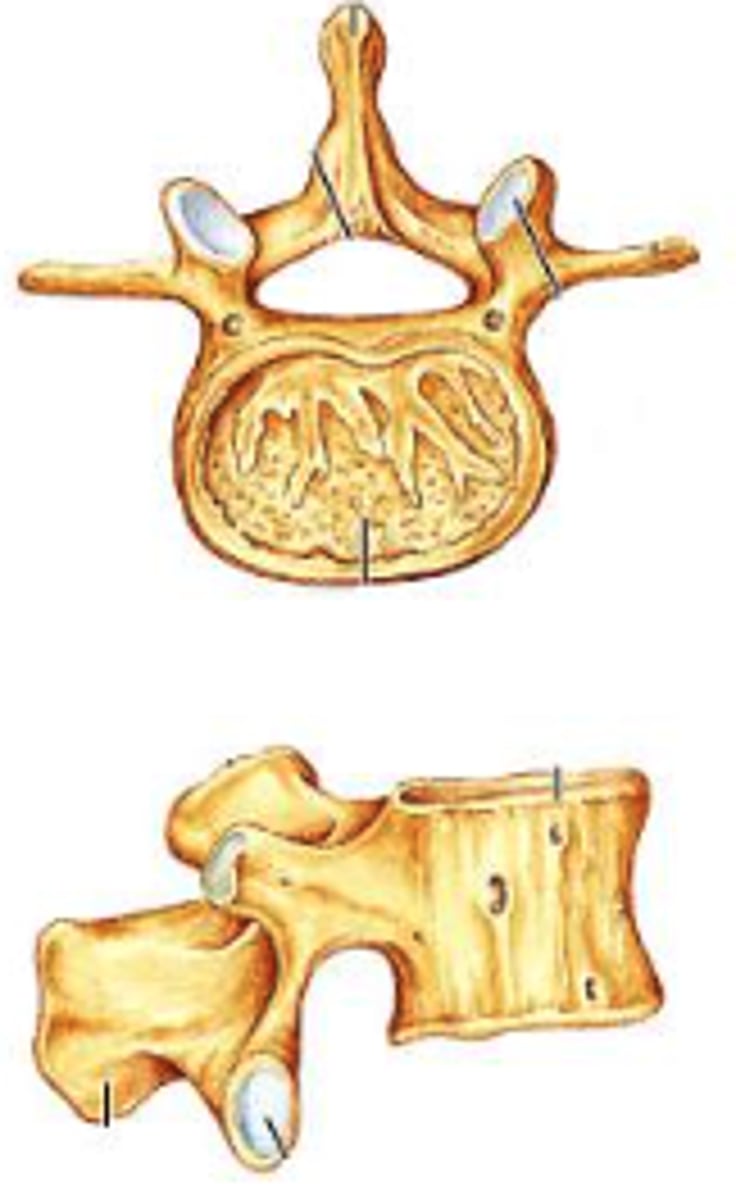
Identify the indicated type of vertebra.
lumbar
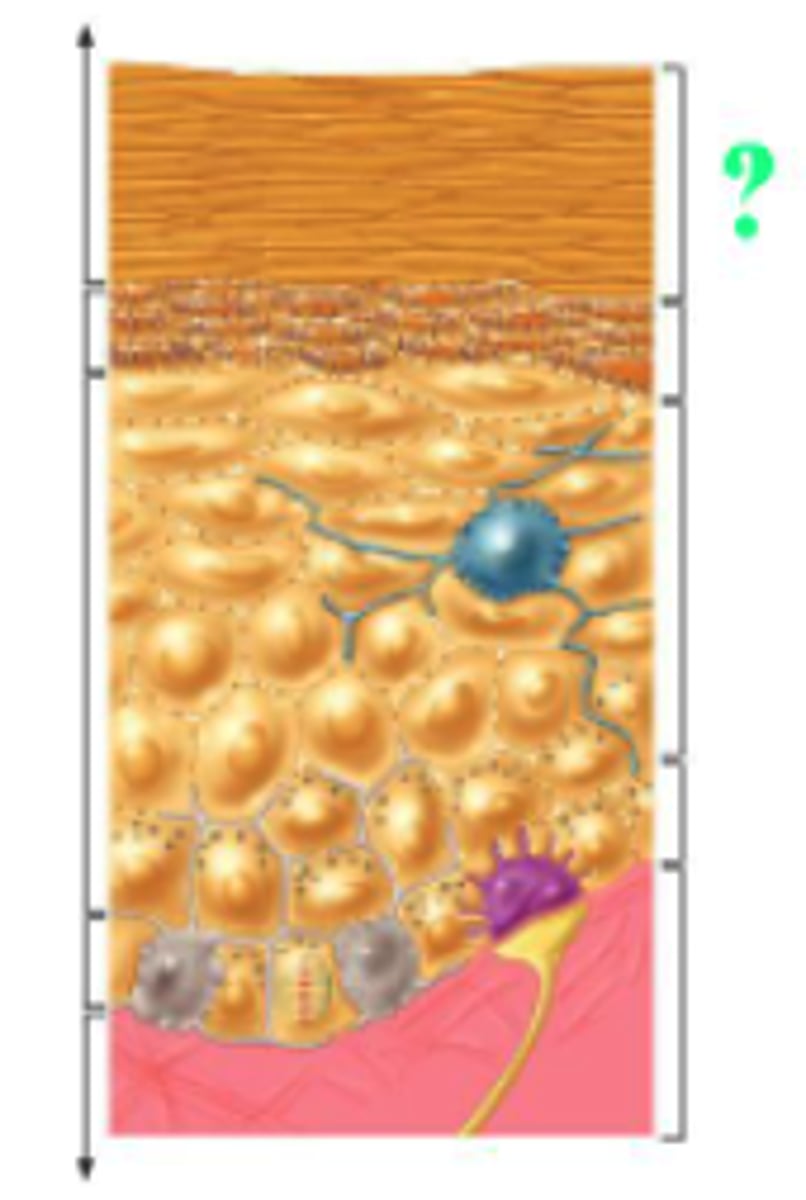
Identify the indicated region of the epidermis.
stratum corneum
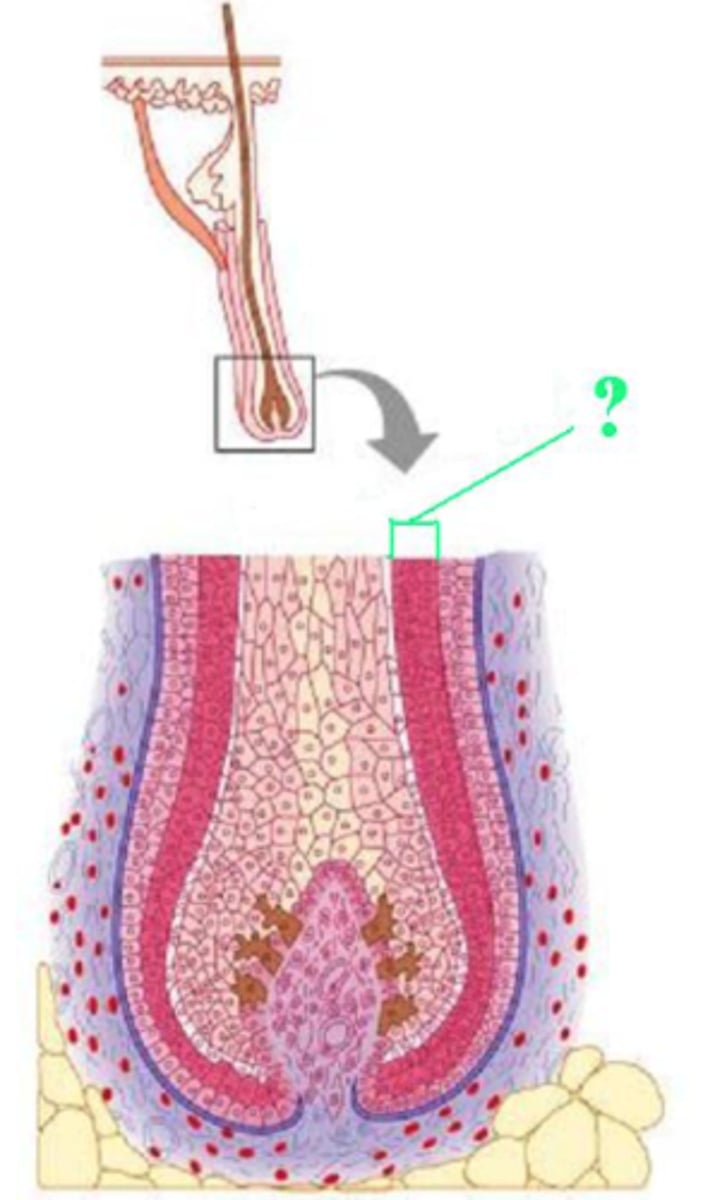
Identify the indicated layer of a hair.
internal epithelial root sheath
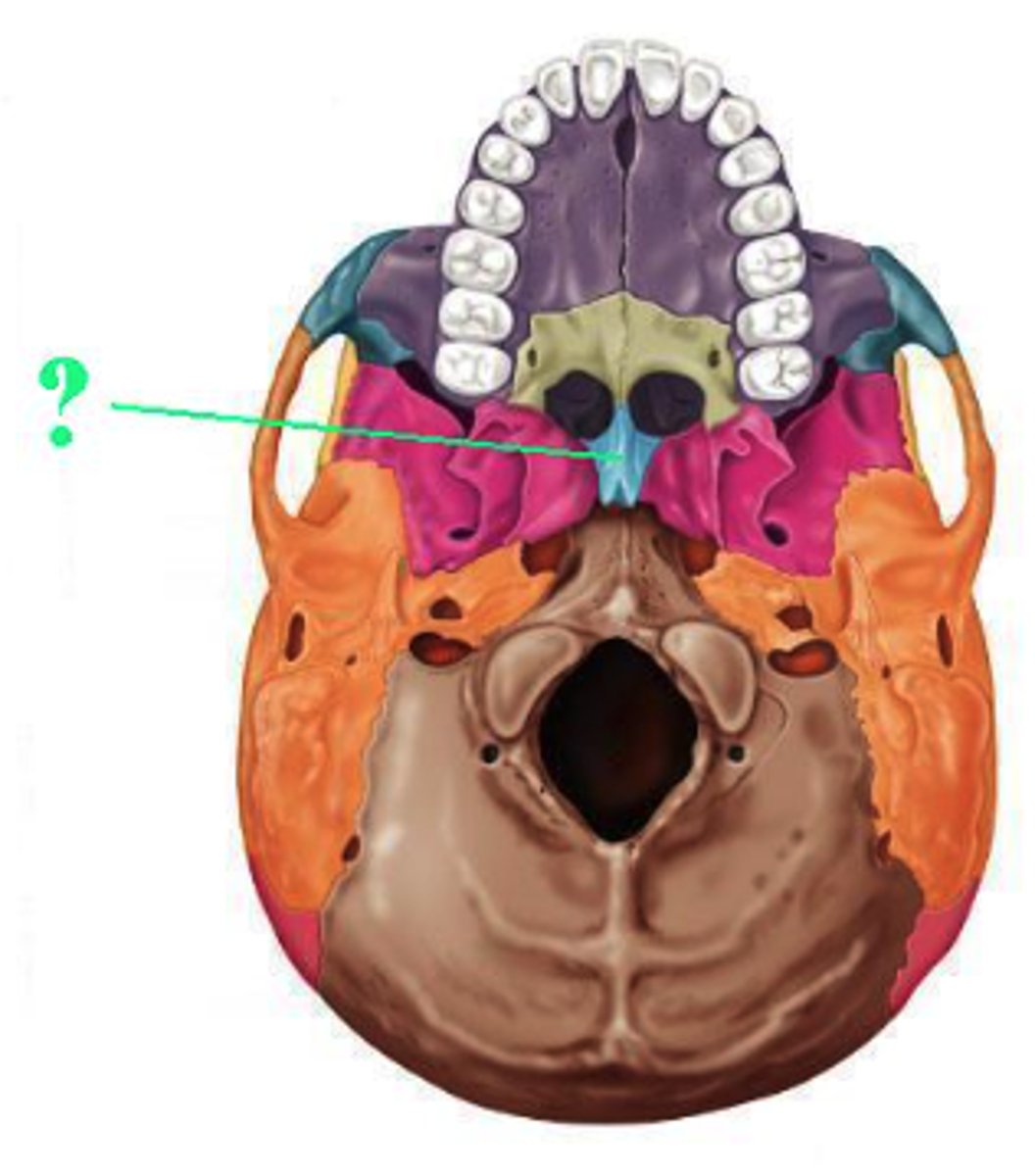
Identify the indicated bone.
vomer
Identify the indicated bone marking (opening).
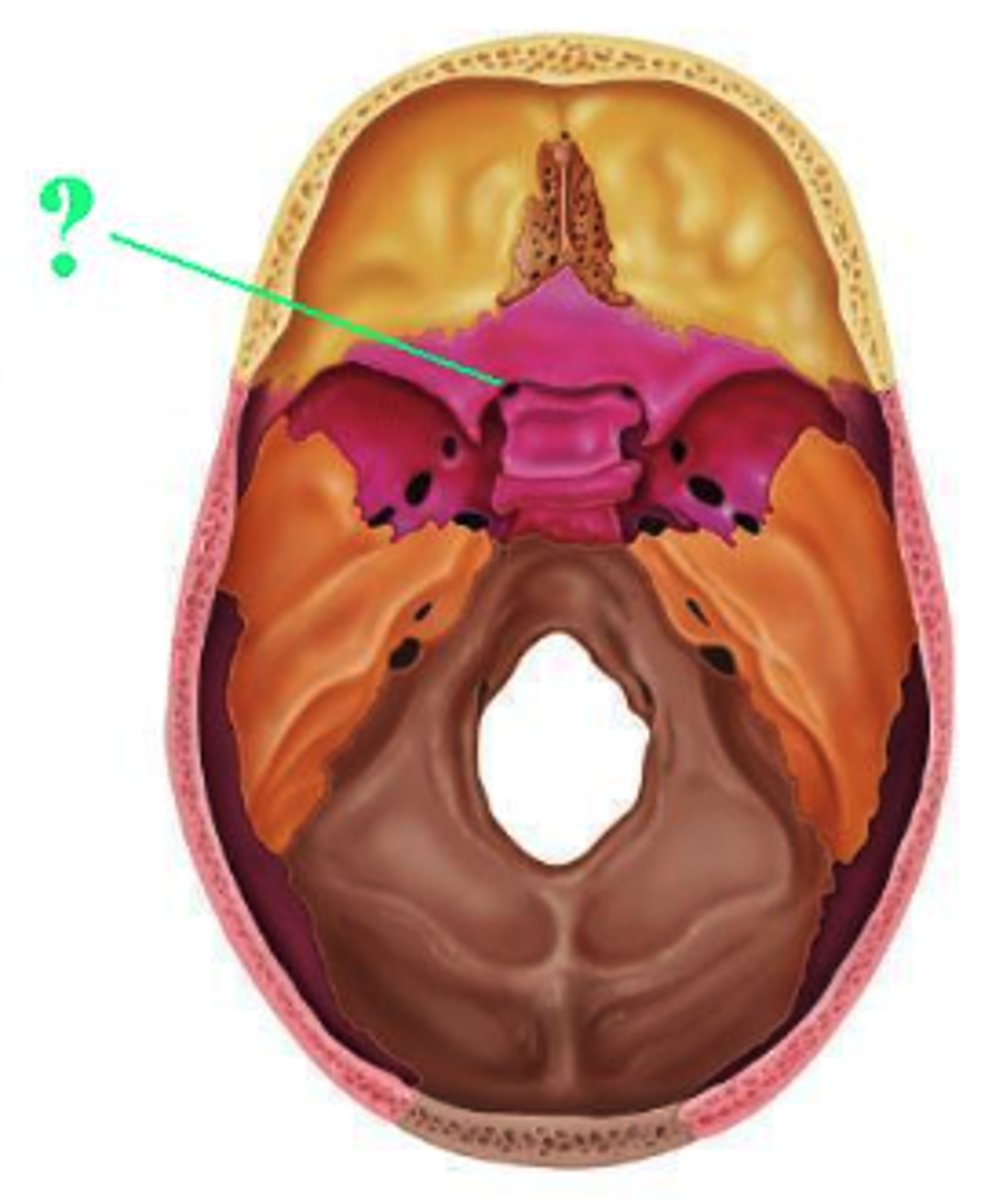
optic canal
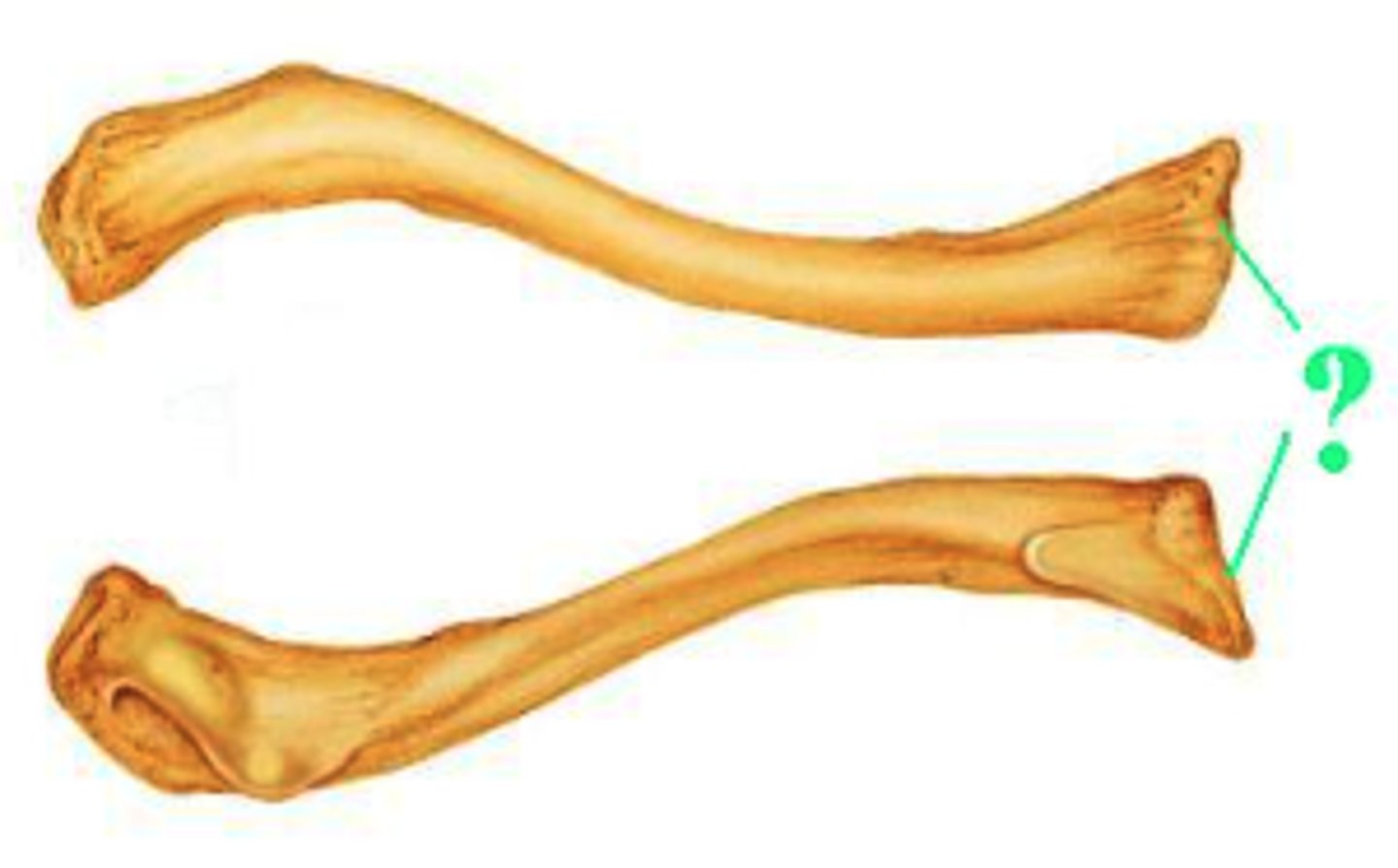
Identify the indicated bone marking.
sternal end
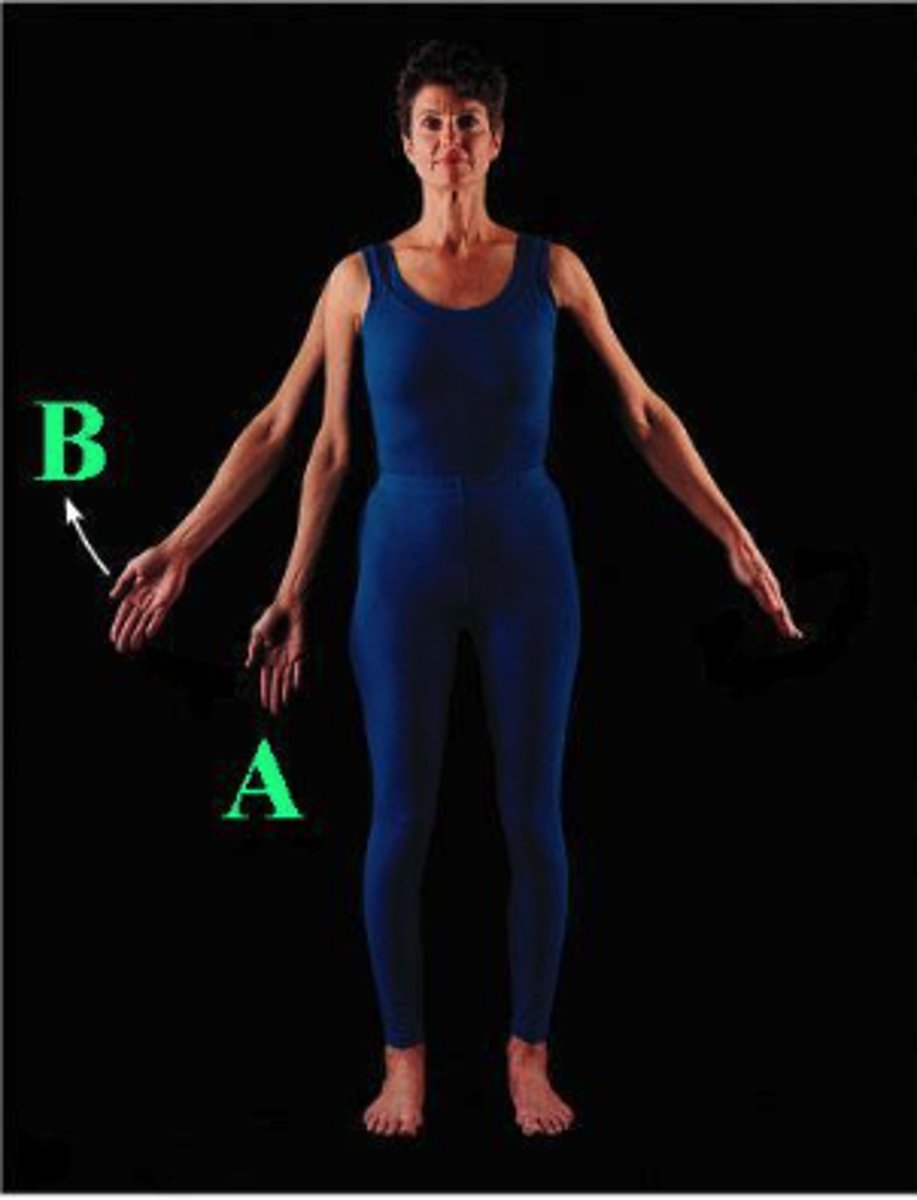
Identify the indicated body movement from A to B.
abduction
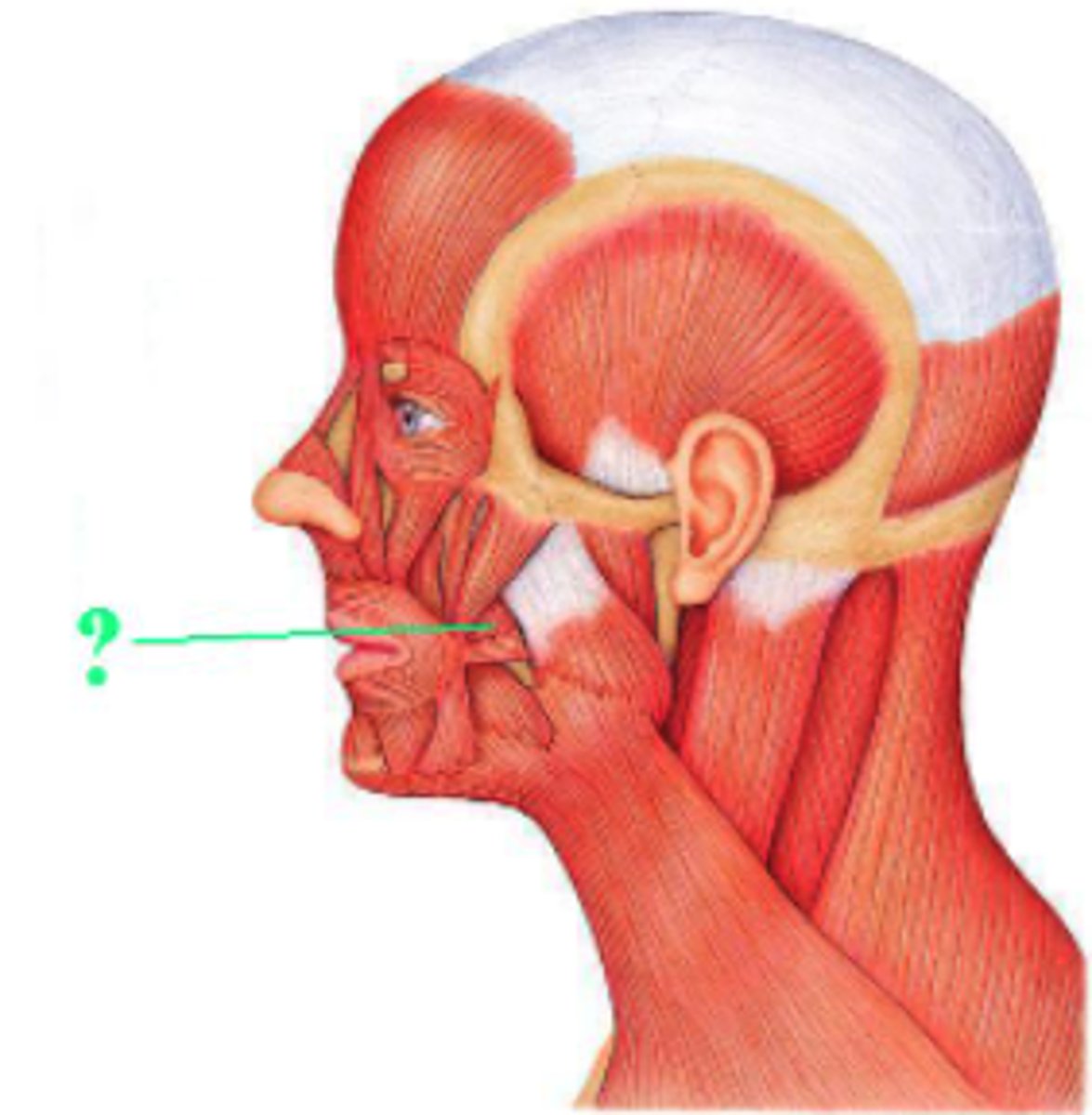
Identify the indicated muscle.
buccinator
Identify the indicated bone marking?
neck
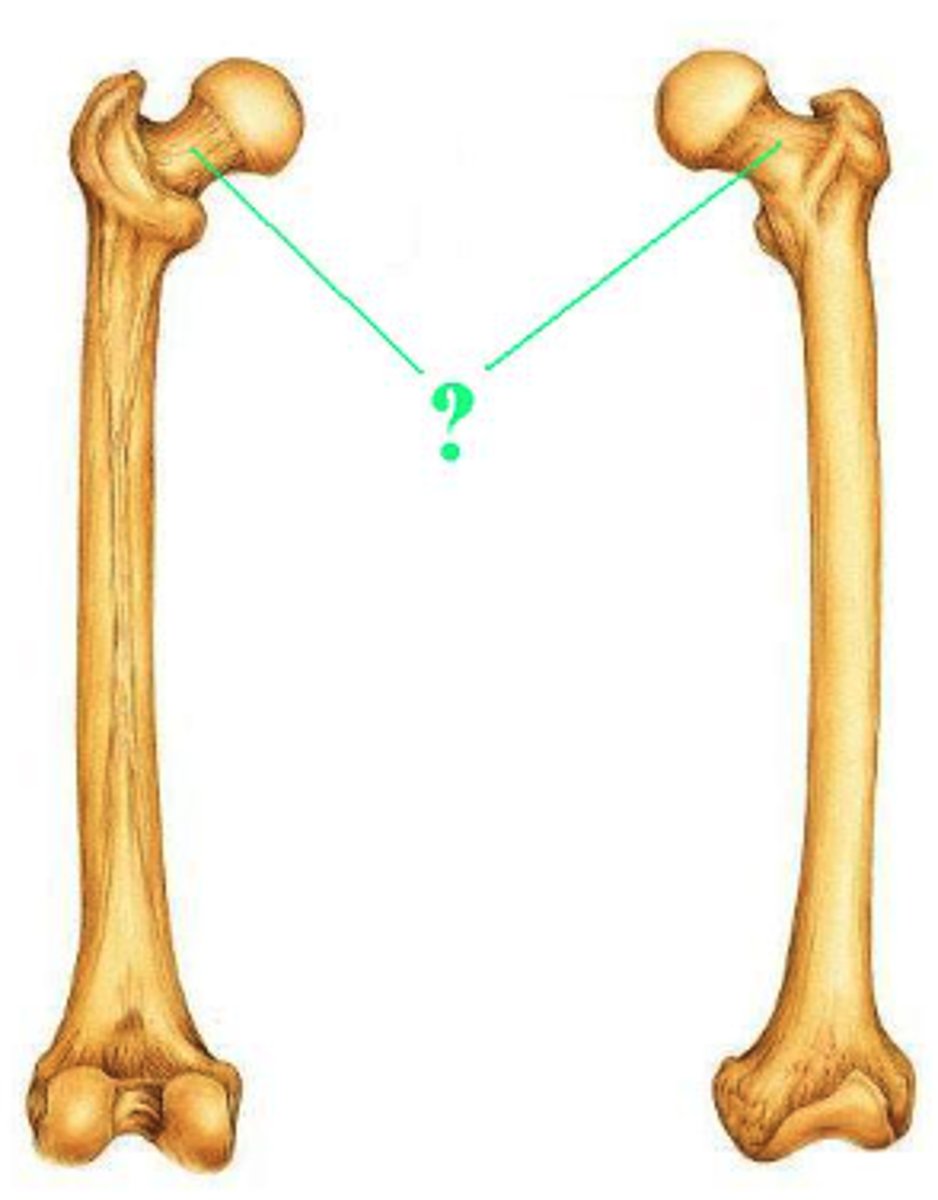
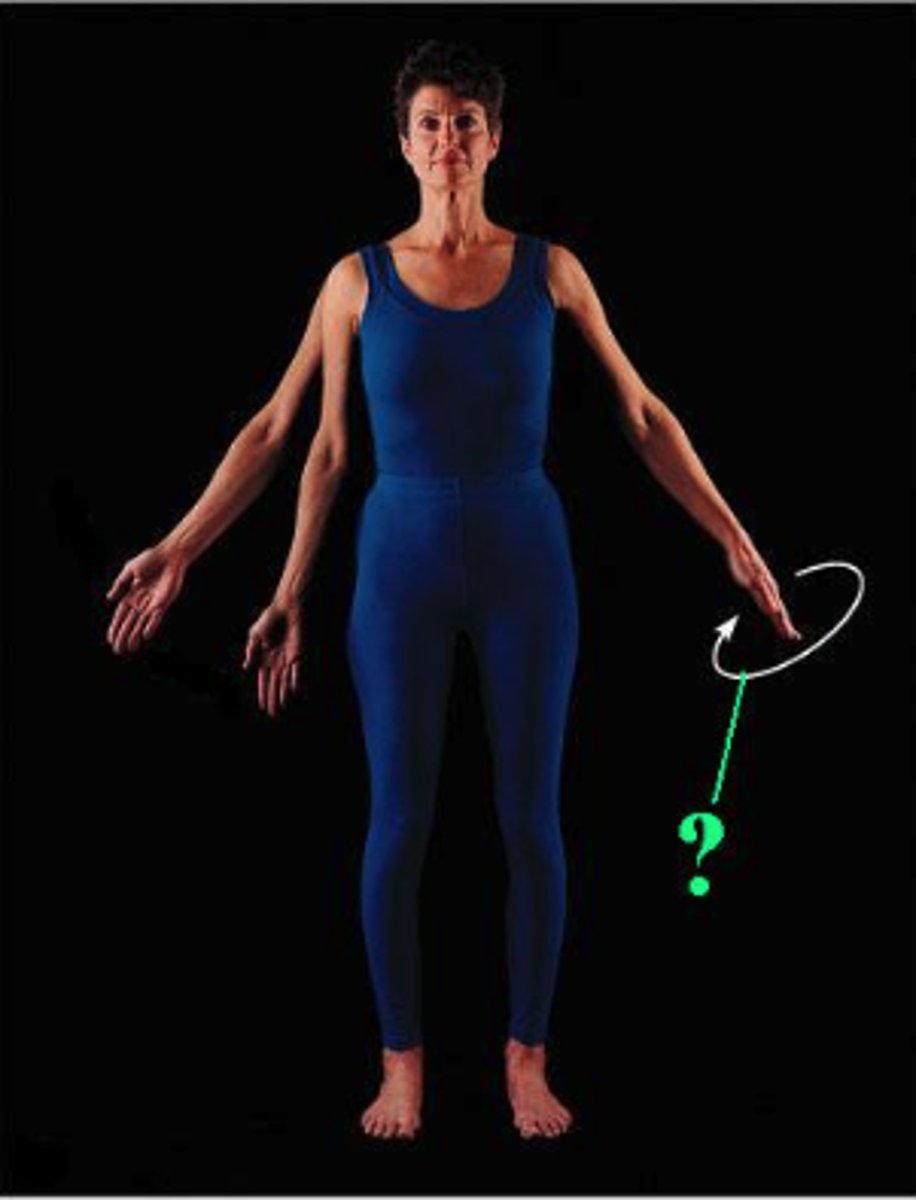
Identify the indicated body movement.
circumduction
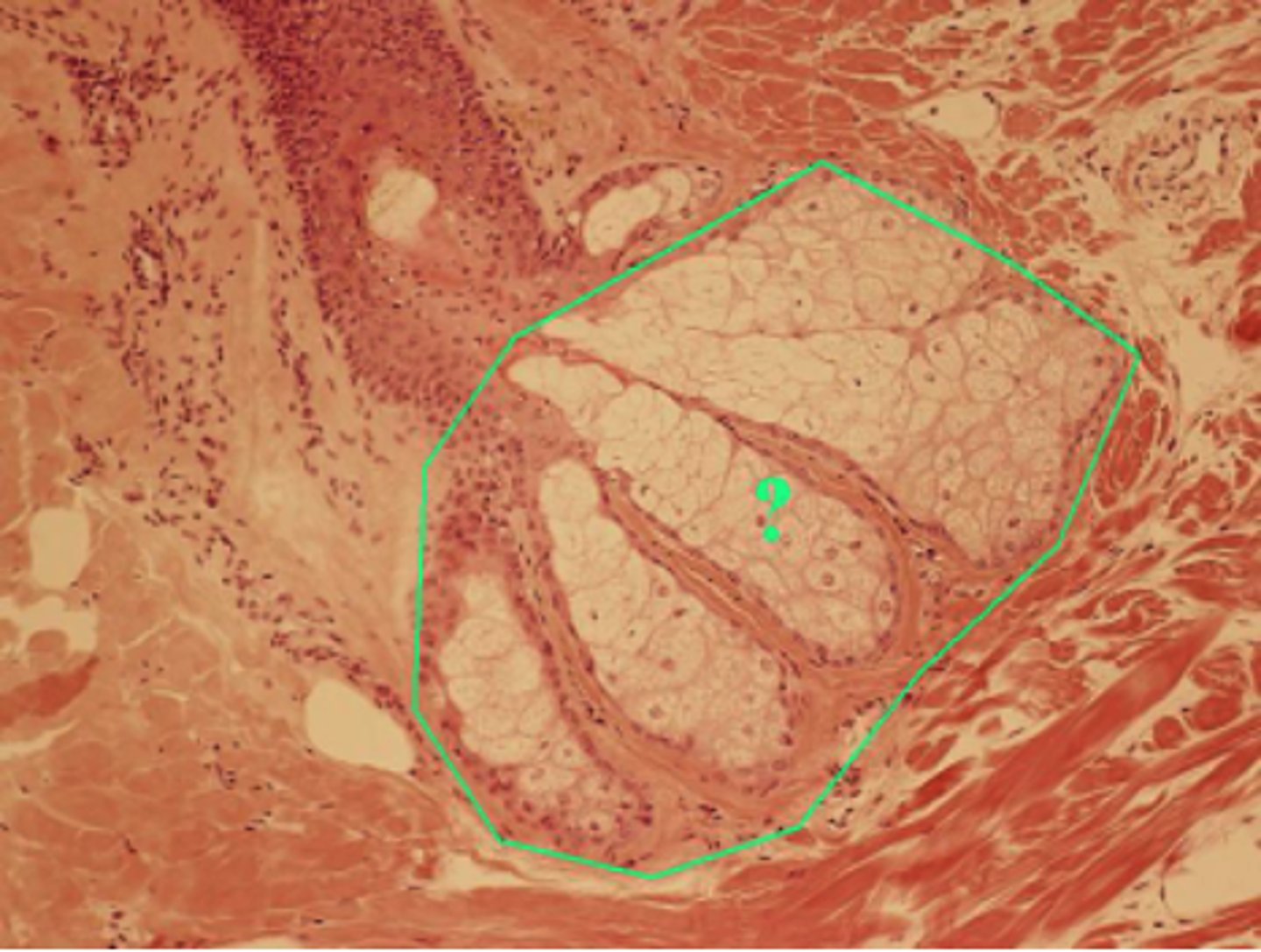
Identify the indicated structure of the integument
sebaceous gland
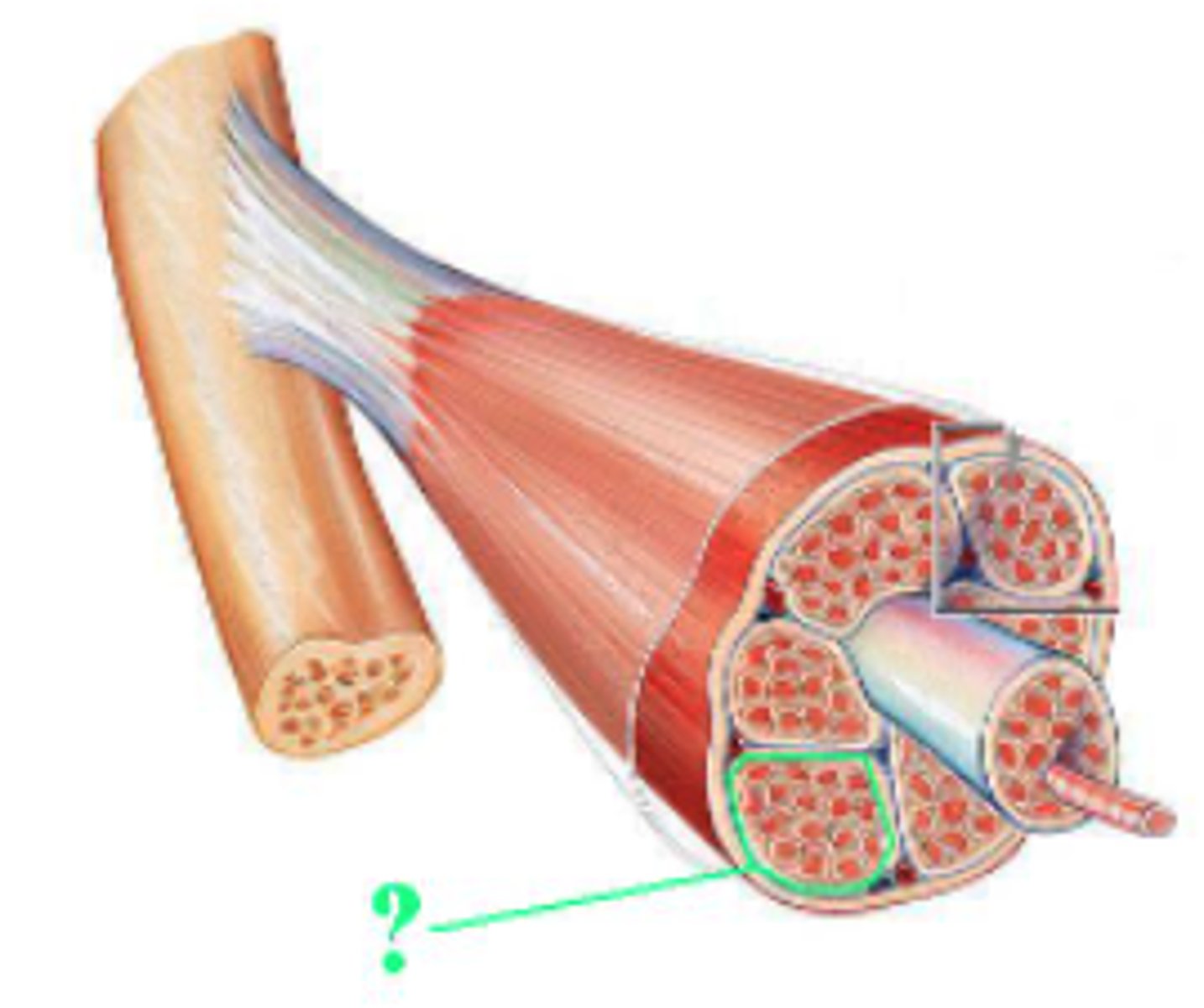
Identify the indicated structure.
fascicle
Identify the indicated bone.
nasal
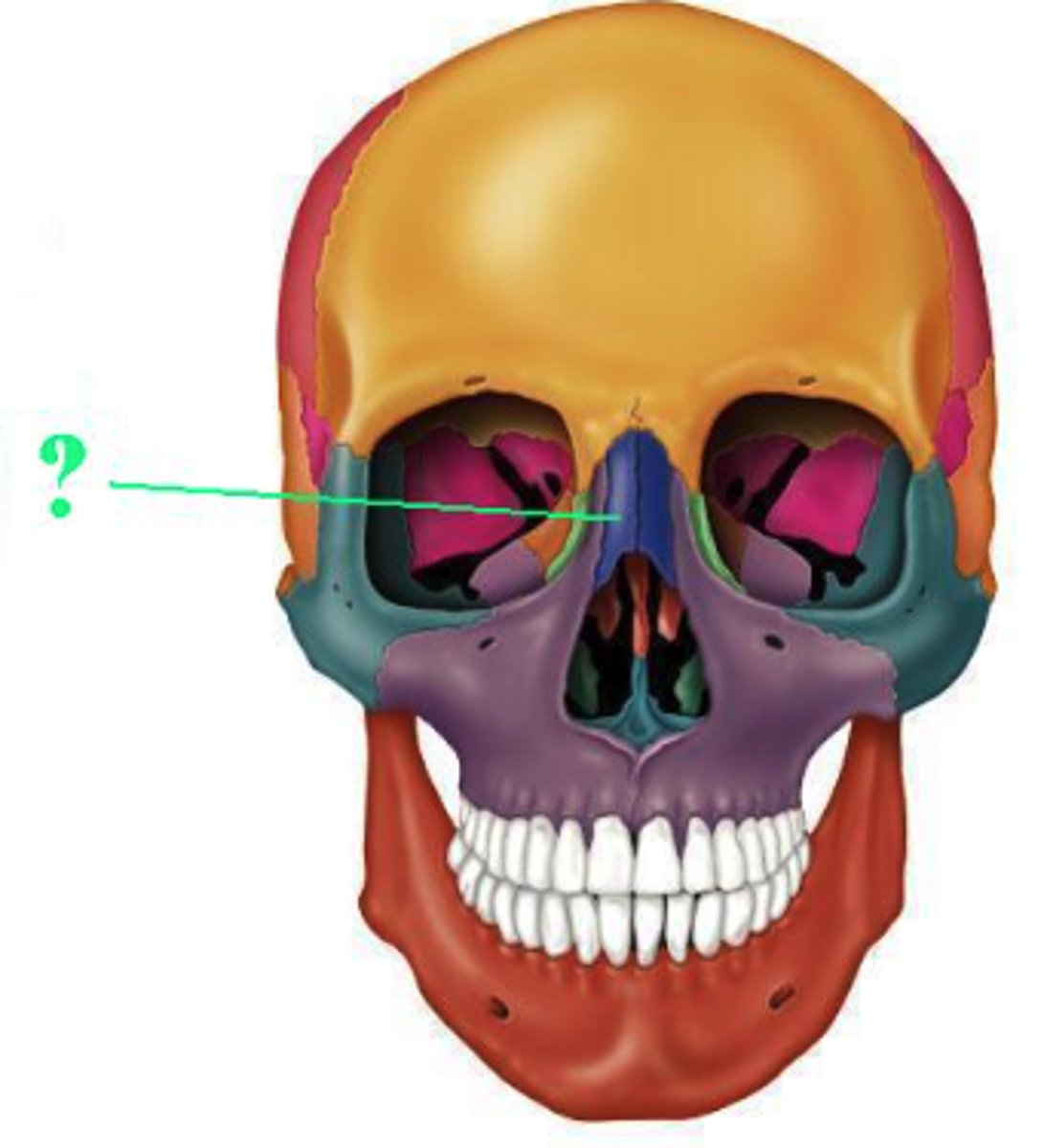
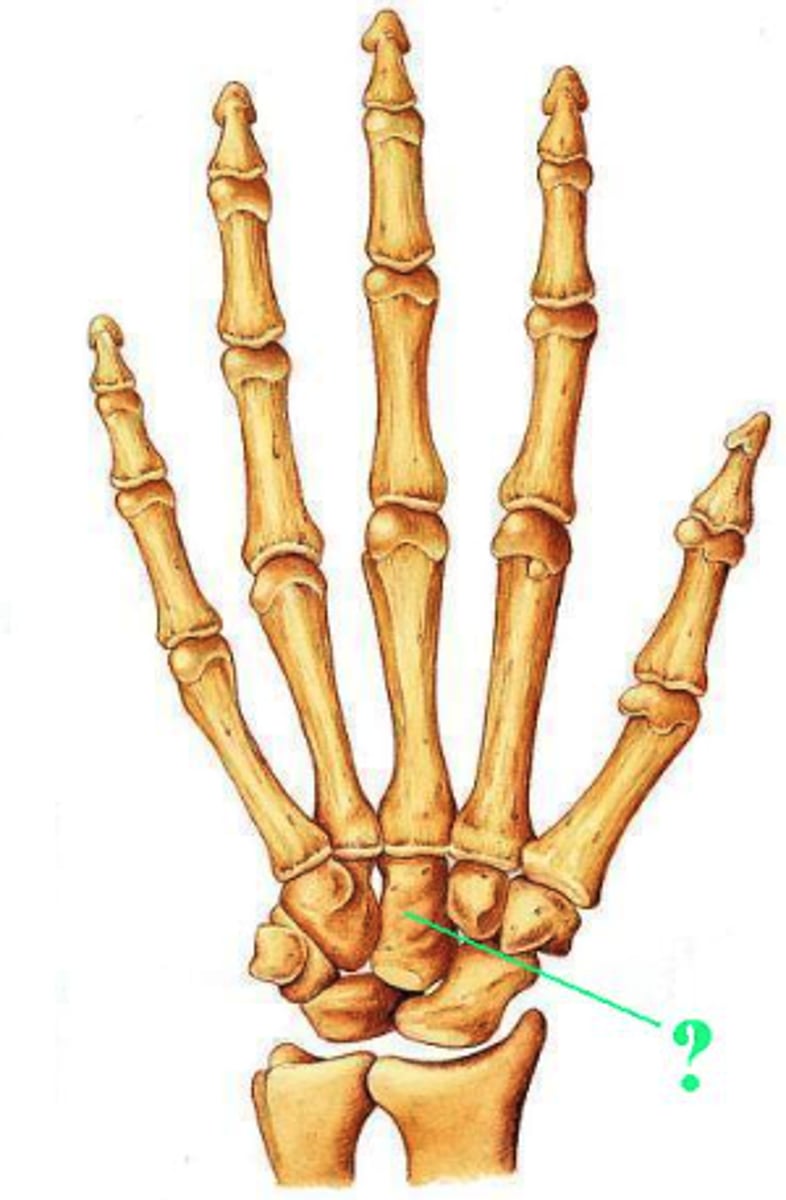
Identify the indicated bone.
capitate
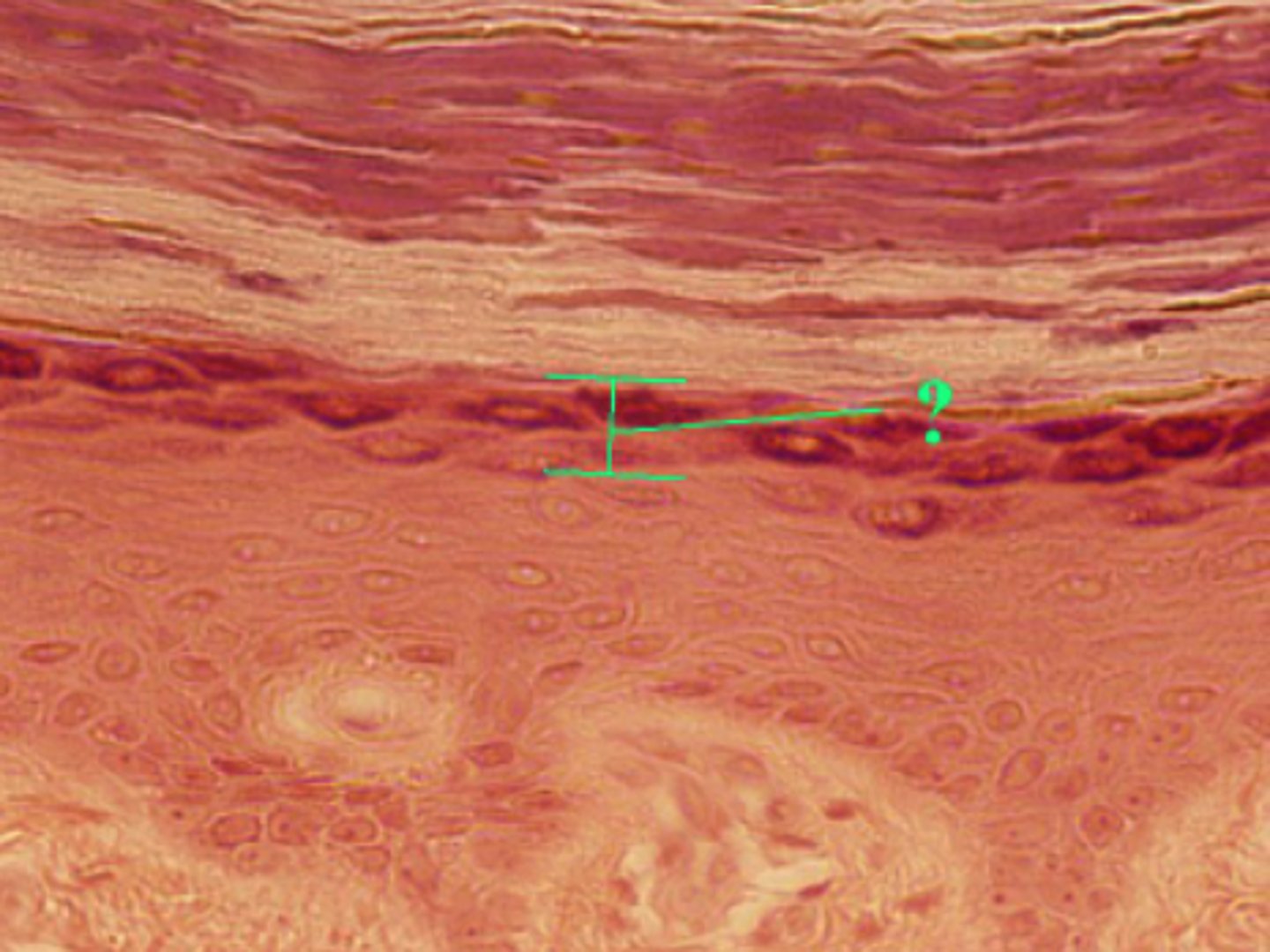
Identify the indicated layer of thick skin.
stratum granulosum
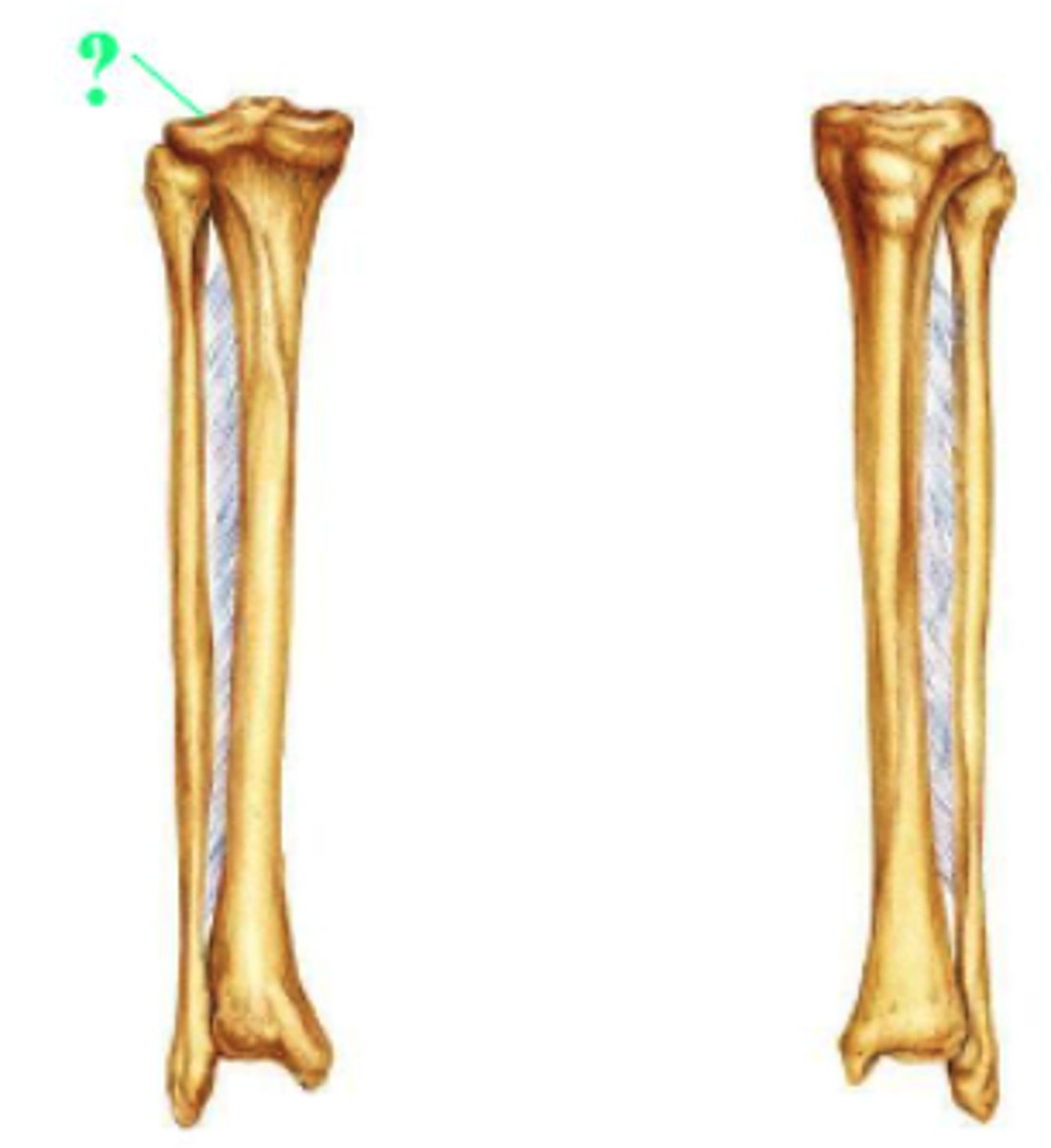
Identify the indicated bone marking (surface).
articular surface of lateral condyle
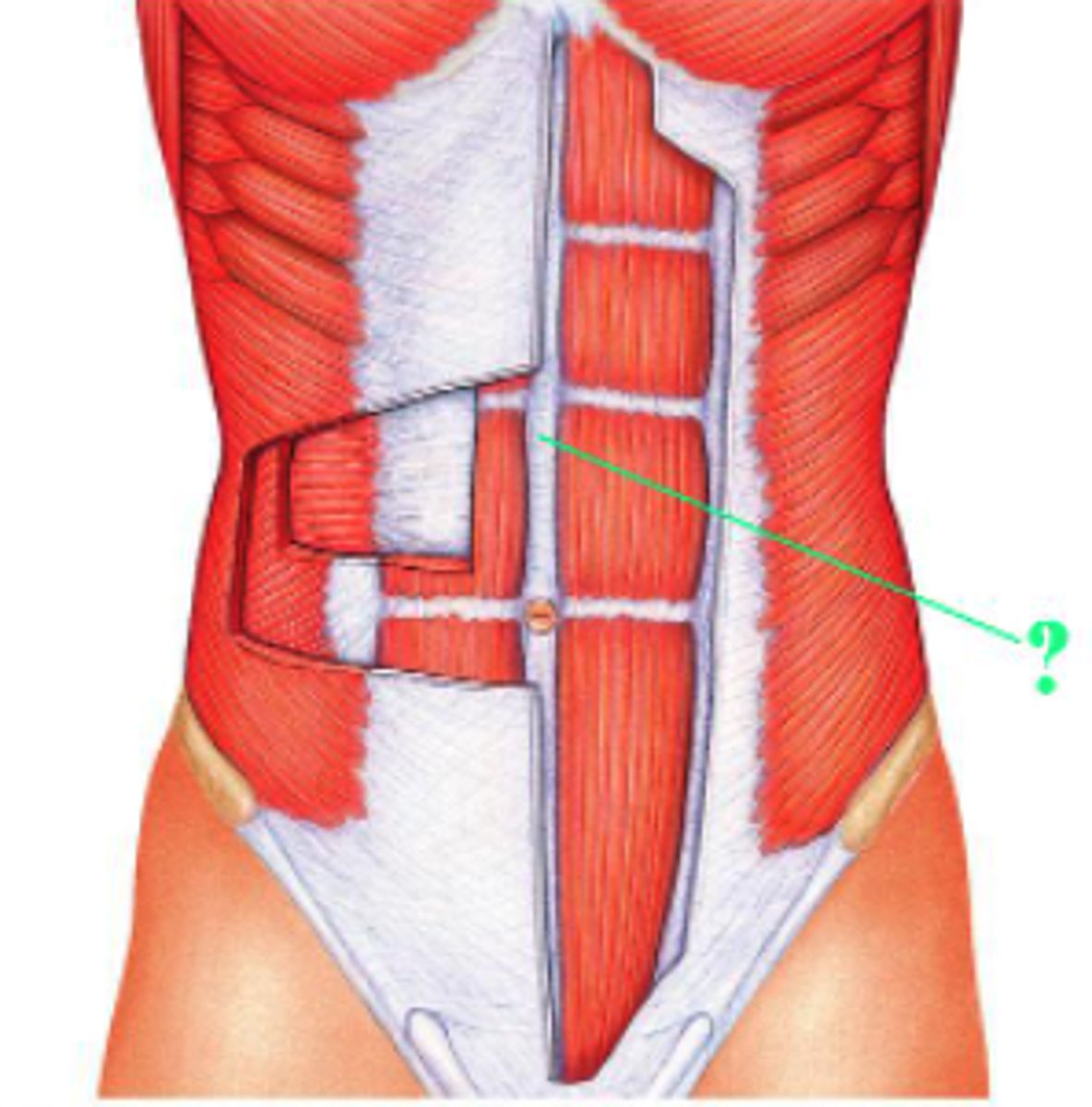
Identify the indicated structure.
linea alba
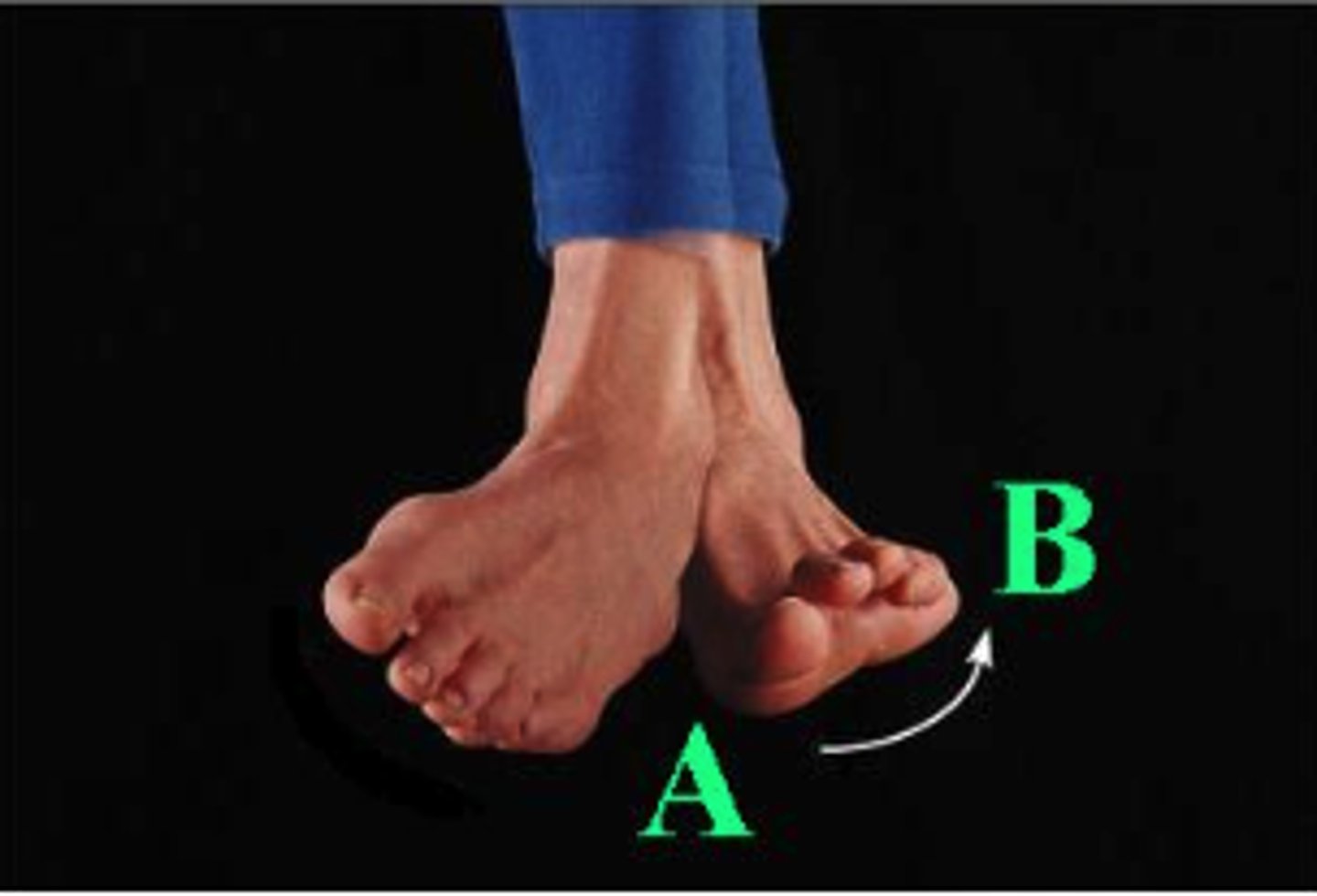
Identify the indicated body movement from A to B.
eversion
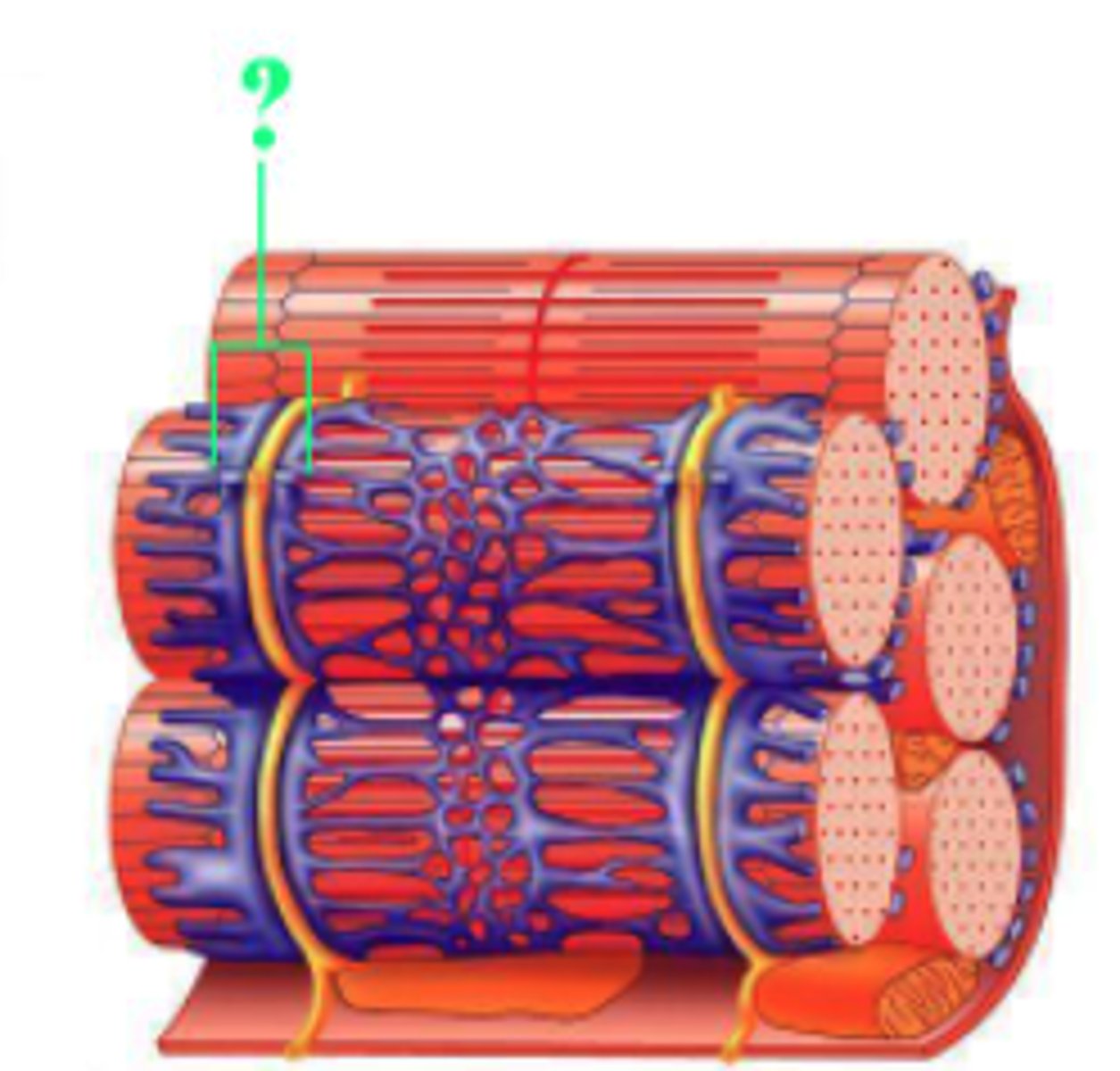
Identify the indicated structure.
triad
Identify the indicated bone.
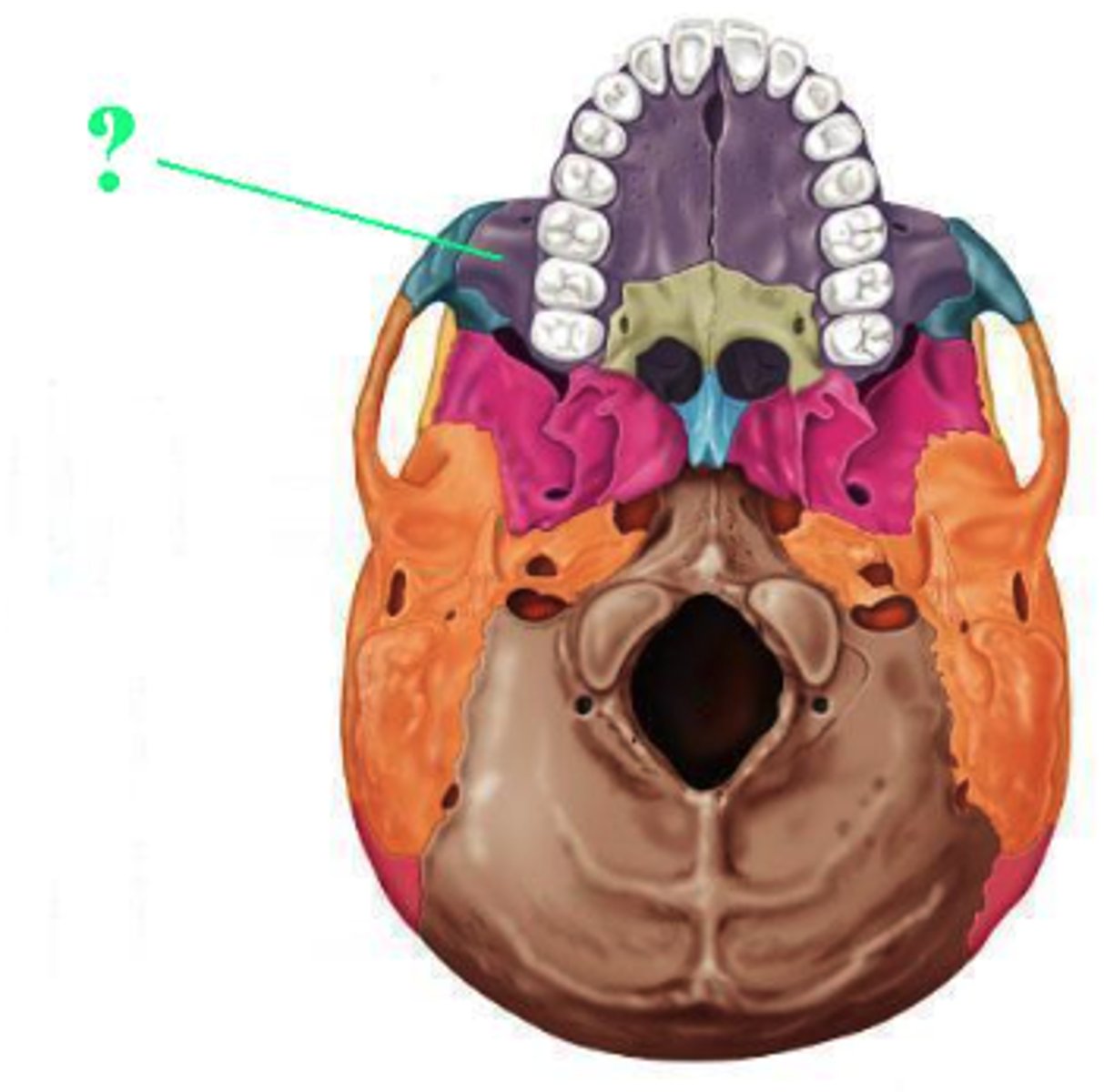
maxilla