Force and Motion
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Science GACE
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Ideal Mechanical Advantage
the amount of output force divided by the input force in the case of no friction
Mass
The amount of matter in an object, measured in kg in the SI system of units.
Power
the rate at which work is done or at which energy is transferred; measured in watts (W)
Actual Simple Machine
a simple machine that has friction
Weight
The amount of force of gravity on an object, measured in newtons (N) or pounds (lb) on a scale.
Conservation of Angular Momentum
The angular momentum before an event = the angular momentum after an event.
Height (Projectile Motion)
The maximum vertical displacement of a projectile above the ground.
Screw
a simple machine that is an inclined plane wound around a shaft
Moveable Pulley
a pulley that moves up and down and changes the direction and strength of a force
Newton (N)
the SI unit of force, equal to 1 kilogram meter per second squared (kg∙m/s²)
Torque (𝜏)
the perpendicular component of a force (FF) perpendicularly applied at some distance (dd) from an object's axis of rotation
Input
something put into a system that causes change
Compound Pulley
a combination of several pulleys, usually some that are fixed and some that are moveable
Fixed Pulley
a pulley that is held in place and only changes the direction, not the magnitude, of a force
Momentum
The product of an object’s mass and its velocity.
Pitch (of a screw)
the distance between threads on a screw
Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation
An equation relating the force of one mass on the other to the gravitational constant multiplied by the product of the masses divided by the square of the distance between their centers.
Range (Projectile Motion)
The horizontal displacement of a projectile.
Fulcrum
the pivot point of a lever
Gravitational Constant
An experimentally determine constant used in calculating the force of gravity between two masses.
Conservation of Momentum
The total momentum before an event = the total momentum after the event.
Angular Momentum
product of an object's rotational inertia and its angular velocity about an axis
Rotational Inertia
The tendency of an object to keep rotating at a constant rate unless acted upon by an external torque.
Acceleration (Due To Gravity)
The rate at which an object accelerates as it falls due to the force of gravity.
Wedge
a triangular simple machine that pushes objects apart and changes the direction and amount of the input force
Actual Mechanical Advantage
the actual output force divided by the input force
Wheel and Axle
a simple machine that is composed of two attached wheels of different diameters
Lever
a simple machine with a fulcrum,an output force or weight, and an applied force
Simple Machine
a device that makes work easier by reducing the force (but increasing the application distance) or reducing the distance (but increasing the force)
Output
a result of input into a system
Ideal Simple Machine
a simple machine with no friction
Inclined Plane
a simple machine that is a ramp with one end higher than the other
Work
the process by which energy is changed in a system; calculated from the product of force and distance
the object must move for work to have been done
Pulley
a simple machine that can change the direction and size of a force
Projectile
An object under the influence of gravity alone.
A 150 kg box rests on a ramp inclined at 30° above the horizontal.
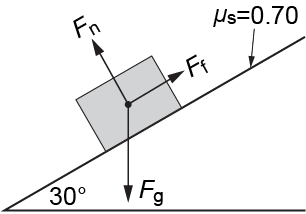
The coefficient of static friction between the box and the ramp is 𝜇s = 0.70. The component of gravity that points down the ramp, parallel to the ramp, is 75 N. The component of gravity that points into the ramp, perpendicular to the ramp, is 130 N. What is the magnitude and the direction of the static friction force that acts on the block? (Use g = 10 m/s2.)
75 N up the ramp
A train car of mass 3m initially traveling at speed v collides with a train car at rest of mass 2m. If the cars couple together, what is the speed of the two cars immediately after the collision?
3v/5
Which of the following is an example of Newton's law of inertia?
A bowling ball continues rolling down the bowling lane until it strikes the pins.
Imagine a future generation living under a dome on Mars. If two children are playing catch with a baseball inside this dome, which of the following is true during the time the ball is in flight above the surface of Mars?
The ball exerts a gravitational force on Mars that is the same magnitude as the gravitational force of Mars on the ball.
Compare the force of gravity of the Sun on Mercury with the force of gravity of Mercury on the Sun.
Both are non-zero and their magnitudes are the same.
An object accelerates at 3 m/s2 when the net force on the object is 12 N. What is the mass of the object?
4 kg
A mass on a spring oscillates from left to right across a frictionless table. In the figure below, the spring is to the right of equilibrium.
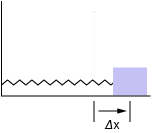
The spring oscillates with an angular velocity of ωω. Which of the following represents the relationship between the displacement and the acceleration of the mass as a function of time?
a(t)=−ω^2 x(t)
A car travels at a constant speed of 88 ft/s (60 mi/hr). Suddenly the driver sees a deer in the road. How far does the car move at this speed during the driver's reaction time of 0.5 s?
(The reaction time is the time it takes the driver's foot to come off the accelerator after the driver first sees the deer.)
44 ft
An applied force of 15 N is used to push on an 8 kg box at rest on a rough floor. The coefficient of static friction between the box and the floor is 0.2. Which of the following correctly answers the question of whether the box will accelerate and why or why not? (Use the acceleration of gravity g = 10 m/s2 in your analysis.)
No, because the static friction force equals the applied force.
The graph below shows the velocity versus time of a toy car moving across the floor.
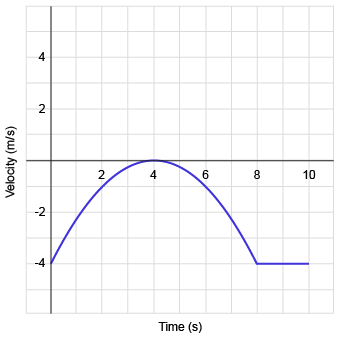
Which of the following best approximates the displacement of the car between 0 and 8 seconds?
10 m
work (equation)
W=Fd
work (equation torque)
W=τ⋅θ
ideal mechanical advantage
IMA = ideal output force/ input force
Actual Mechanical Advantage
AMA = actual output force/ input force
displacement (equation)
Δx = x – x0
average velocity (equation)
vaverage = Δx/t
change in velocity (equation)
Δv = v – v0
average acceleration (equation)
a = Δv/t
projectile motion (equation)
d = v0t + 1/2at²
v = v0 + at
momentum (equation)
p = mv
force of gravity between two masses (equation)
Fg = G (m1m2)/d²
force of the spring (equation)
Fspring=−kΔx
magnitude of downward force of gravity (equation)
mg=kΔx
k=mg/Δx
period of oscillation
T=2π √(m/k)
angular frequency
ω=√(k/m)
energy
KE=1/2mv²
PEgravity=mgh
v in terms of k
v = √(k/m) Δx