brain and spinal cord
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
integrative control center
peripheral nervous system
peripheral nerves (cranial and spinal)
communication between CNS and body
afferent (PNS)
sensory neurons
efferent (PNS)
motor neurons
somatic nervous system
voluntary movements
sympathetic (automatic nervous system)
mobilizes body systems
fight or flight
parasympathetic (automatic nervous system)
conserves energy
rest and digest responses
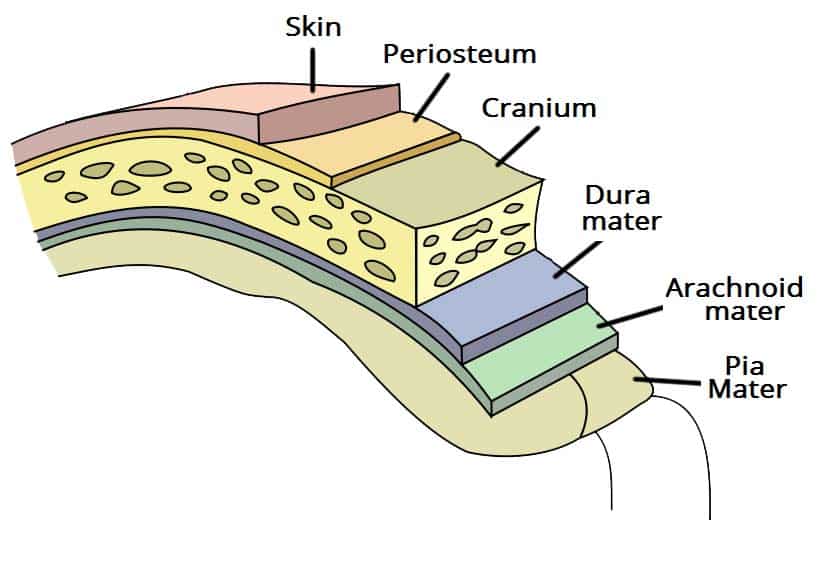
meningeal layers
dura mater
arachnoid mater
pia mater
grey matter
40% of the brain
contains brain neural cell bodies
conducts processes, sends info to various parts of the body
white matter
60% of the brain
interprets sensory information from various parts of body
cerebellum
balance and motor planning center
when disrupted: ataxia and apraxia
(difficulty planning and executing movements)
how is information passed through the brain?
from prefrontal cortex————-occipital lobe
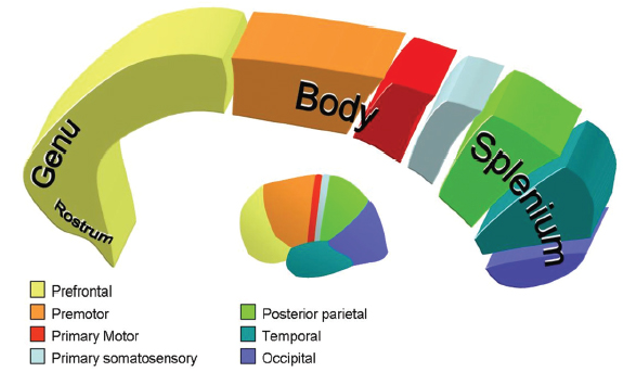
Precentral gyrus
Premotor area
◦ Control movement on the opposite
side of the body
Postcentral gyrus
Sensory area
◦ Receives and interprets sensatons
of pain, temperature, touch, and
pressure from the opposite side of
the body
Superior temporal gyrus
Primary auditory cortex
◦ Receives and interprets sounds
Broca’s area
Controls motor components of speech
◦ Dominant in lef hemisphere of right handers…
◦ Expressive aphasia
expressive aphasia
you know what to say but you can’t say it
Wernickes area
Understanding writen and spoken language
◦ Receptve aphasia
receptive aphasia
they can’t understand what you are saying
frontal lobe key function
Personality,
emoton, higher-order thinking,
motor functon
frontal lobe key areas
Primary Motor Cortex
Broca’s Area
temporal lobe key functions
Learning, memory,
auditory processing,
integrating other senses with memory
temporal lobe key areas
primary auditory cortex
parietal lobe key functions
Sensory functon,
speech and language
comprehension
parietal lobe key areas
Primary Sensory Cortex
Wernicke’s Area
occipital lobe key functions
vision
occipital lobe key areas
primary visual cortex
diencephalon
Limbic system
◦ Thalamus, hypothalamus,
hippocampus, amygdala, basal
ganglia, mammillary bodie
thalamus
the “gate keeper”
virtually every pathway in the brain synapses
within the thalamus before continuing to fnal
destnaton
thalamus functions
the great relayer
Sensory, motor, consciousness, alertness
hypothalamus
link between nervous systems and endocrine system
function: homeostasis
pituitary gland included
pituitary gland
secretes hormones to control many body processes, particularly autonomic processes
Function: growth, blood pressure, metabolism, body temperature
hippocampus
crucial for memory
Key region afected in Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimers disease
Progressive memory loss due to excessive formation of abnormal plaques on neurons
hippocampus shrinks
amygdala
plays important roles in emotion and behavior
•It is best known for its role in the processing of fear and anger
mammillary bodies
Recollective memory
• Memory information begins within the
hippocampus
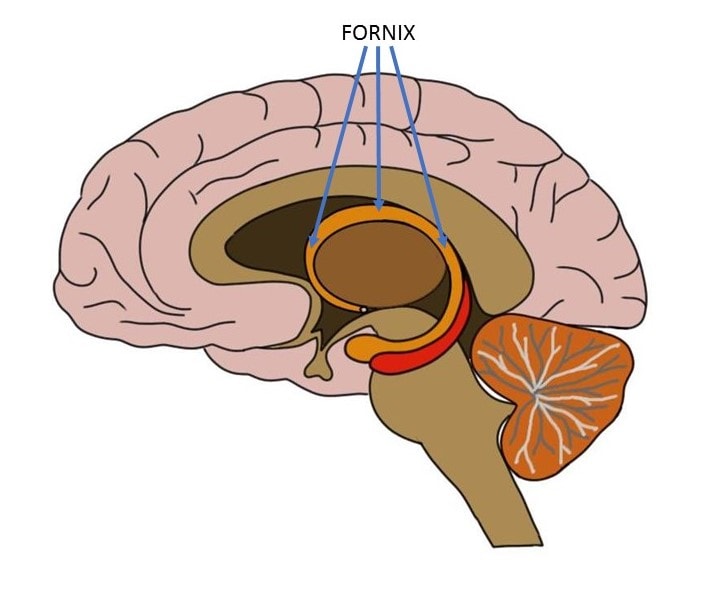
fornix
• Limbic system
verbal memory info
• Largest pathway for the hippocampus
midbrain
Origin of cranial nerves III(oculomotor) and IV (trochlear)
Produces dopamine = muscle coordination
◦ Parkinson’s disease
midbrain function
function: Role in reward, addiction, and movement
cerebellum
Contributes to coordinaton, balance, fne motor control, equilibrium,
motor learning
medulla oblongata
Cardiac, vasomotor, and respiratory centers
pineal gland
produce and secrete melatonin
◦ Internal clock, circadian rhythms: sleep-wake cycles
◦ Third eye- connecton with light
Olfactory Bulbs
Crainall nerve I
◦ Sense of smell
spinal cord
Spinal nerves of PNS emerge from above individual vertebra
Cranial nerve 1 and cranial nerve 2
do not exit the skull
not PNS
spinal nerves
Emerge from spinal cord above individual vertebra, part of PNS
choroid plexus
Specialized cells in pia mater that filter blood and produce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
CSF
supply CNS tissue with nutrients and CNS tissue exchanges with waste products
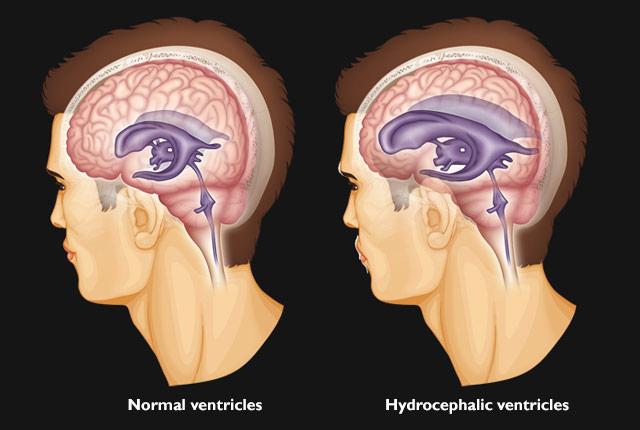
hydrocephalus
buildup of fluid in the cavities (ventricles) deep within the brain
seizures/ epilepsy
Abnormal neuronal activity in the cerebral cortex
problems frontal lobe
Lack of Focus, Irritability, Language Difficulty
problems with parietal lobe
Difficulty with Reading, Spatial Misperception
problems with occipital lobe
blind spots, blurry vision
problems with the temporal lobe
Problems with Short- & Long-Term Memory
problems with cerebellum
Difficulty Walking, Slurred Speech
problems with brainstem
Changes in Breath, Difficulty Swallowing