Genetics CH 20
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
mutation
heritable changes in genetic information
change from wt
some adv some disadv like disease
wt
what is observed most often in population
mutation is the source for _____ that is necessary for ____
genetic variation, evolution
genetic variation is good , as it helps population adapt
mutations can be :
1) large scale/ chromosomal
2) small scale/ point
large scale mutations
affect chromosome structure or #
can be detected by viewing chromosomes using light microscope
deletions, inversions, duplications, translocations, entire chromosome added/deleted.
small scale/ point mutations
single base pair/few nucleotides changed, added or deleted
What are the small scale mutations that DO alter structure and function of protein?
1) missense - neutral or have no effect
2) nonsense
3) frameshift
What are the small scale mutations that DONT alter structure and function of protein?
silent
Transitions and transversions are ____
point mutations
transition
purine → purine A → G , G→ A
pyrimidine → pyrimidine T → C, C → T
transversions
purine → pyr A → T, C ; G → T, C
pyr → purine T → A, G ; C → A, G
transversions and translocations
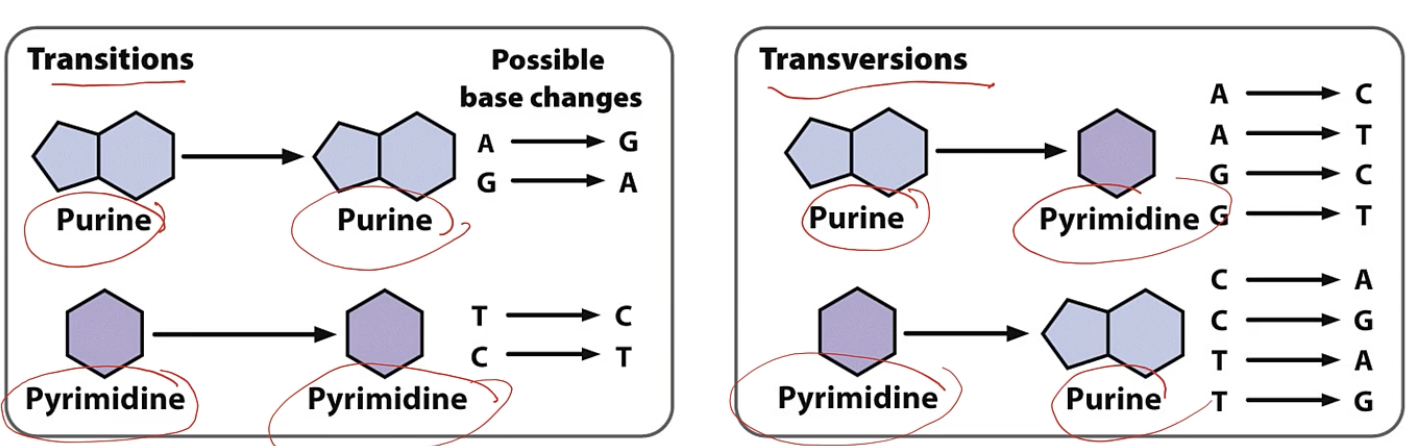
which is more common ? transition or transversion
transition
missense mutation
point mutation that leads to change in a single aa in product
considered neutral if no affect on protein function
eg) code for a neg aa, now codes for a dif neg aa → overall no effect in protein folding/ function
nonsense mutation
point mutation that changes sense (codes for aa) codon into non sense codon (STOP) → premature STOP → truncated/short protein that is nonfunctional
silent mutation
point mutation that changes on codon but aa stays same
frameshift mutation
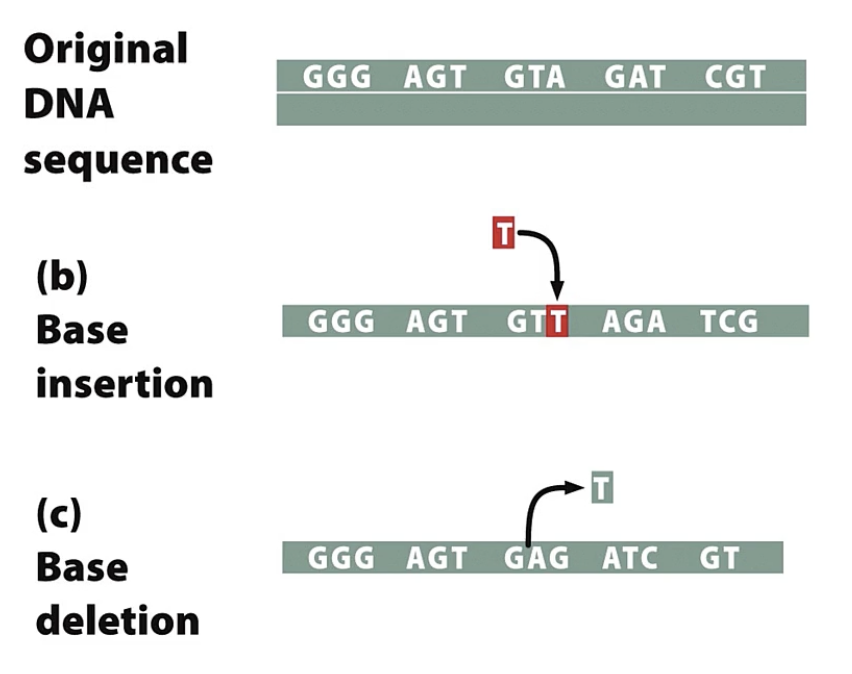
adding or deleting one or more bp
which alters reading frame of the mRNA downstream of the change
usually puts nonsense into frame → shorter protein
A point mutation that changes a codon in the mRNA but not the amino acid at that position in the protein is:
silent mutation
ways to categorize mutations based on where they happened
somatic mutations
germline mutations
somatic mutations
body cells
not heritable/cant be passed on
cancer is usually somatic mutation → increased cell division
NOT in all cells in body of affected peron
but ARE present in all DAUGHTER cells of initial affected cell
Are somatic mutations across all cells in the body of the affected indv?
NO
but are present in the daughter cells that arise from initial affected cell in the affected individual (NOT present in progeny)
germline mutations
in gametes
heritable
ALL cells in affected individual have mutation
Are germline mutations across all cells in the body?
YES , passed onto progeny as well but not necessary that all the progeny are affected, but if affected then all cells affected
how can mutations happen?
1) spontaneous
2) induced
spontaneous mutation
during normal lifetime of cell
causes are :
1) errors made during DNA replication
2) normal biochem in cell, creating reactive forms of o2.
induced mutations
caused by external agent (mutagen)
mutagen examples
1) base analogues
2) base modifiers
3) intercalating agents
4) UV light
big butts in underwear
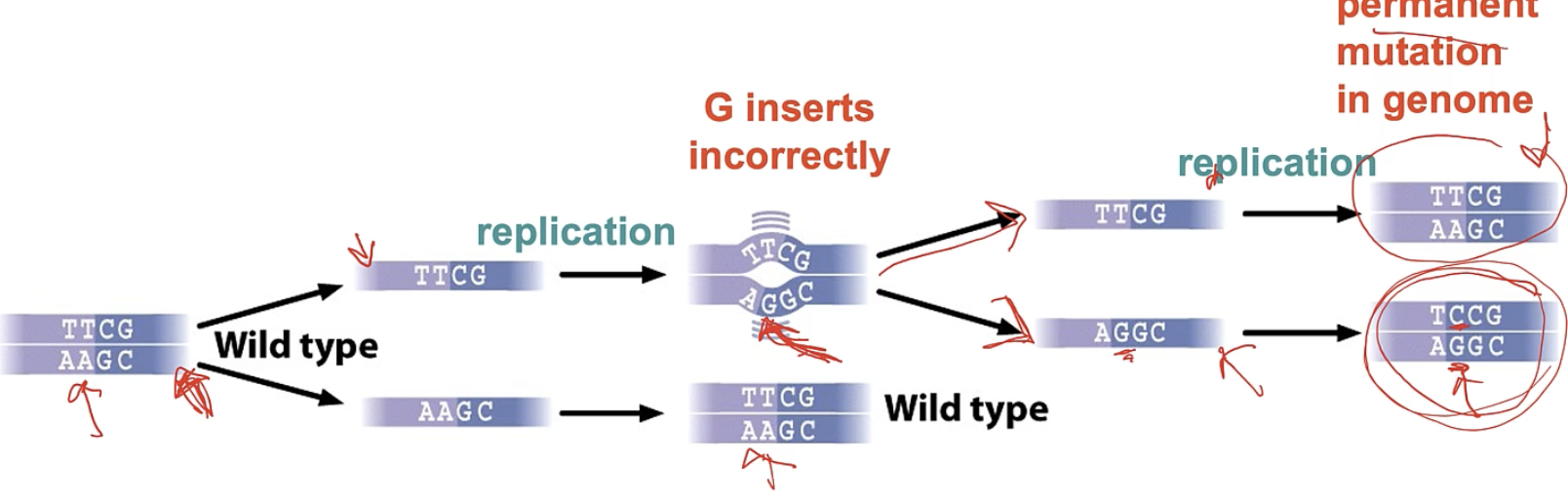
errors made during DNA replication
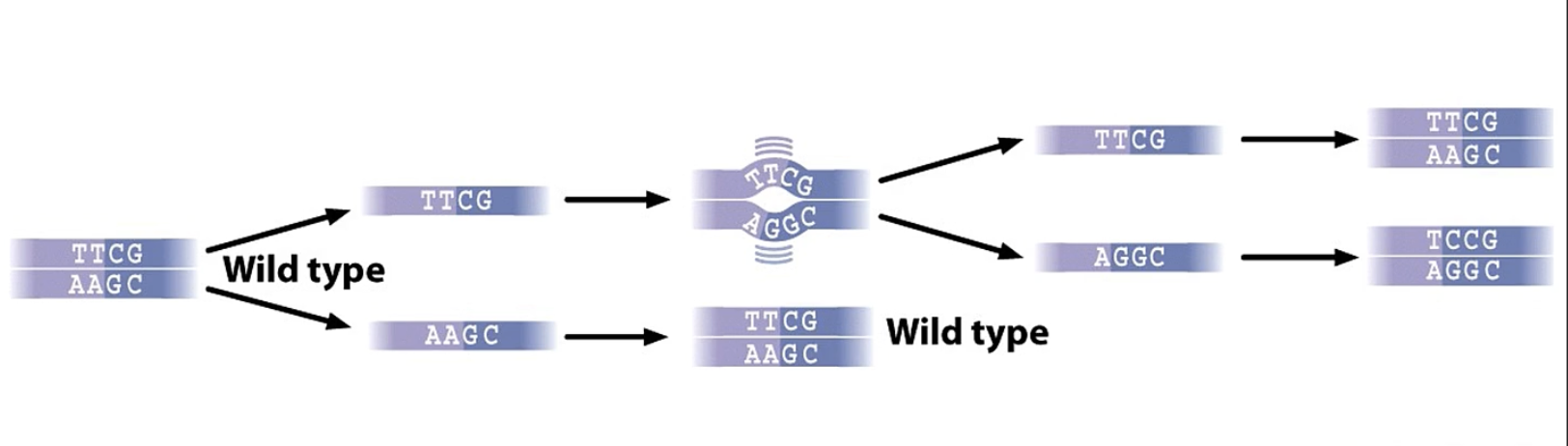
spontaneous
DNAP makes mistakes
usually corrected by 3’ → 5’ exonuclease activity
how do errors during DNA replication occur?
1) incorrect bases added due to wobble pairing
h bonding btw non watson/crick bases can lead to permanent mutation after 2nd round of replication
2) frameshift mutation due to strand slippage
common at repetitive seq
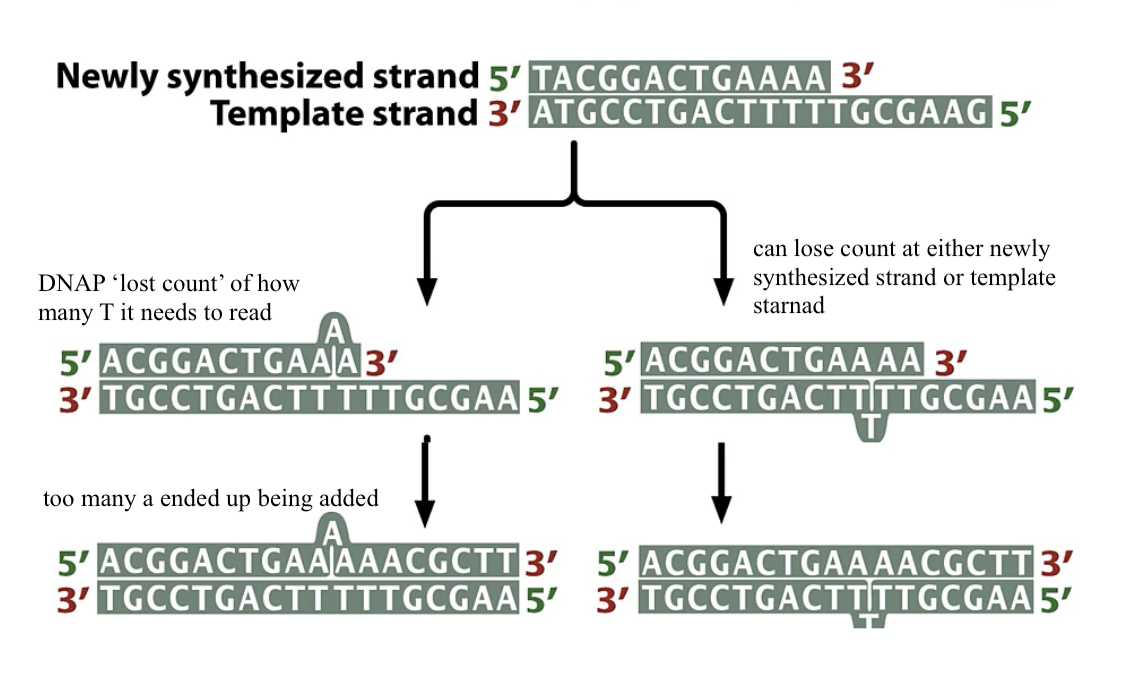
during errors made in DNA replication if proofreading does not correct the first error ____
a subsequent round of replication will establish a permanent change in genome
normal biochem in cell leading to …
spontaneous
depurination
loss of purine
deamination
loss of amine
depurination
loss of purine
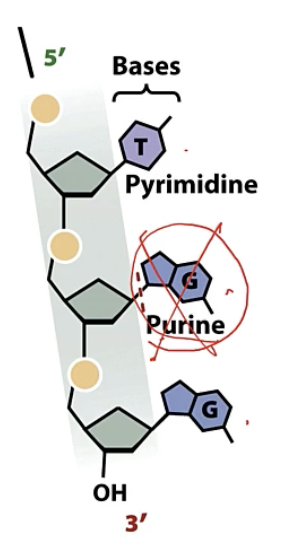
only lose the base, sugar phosphate backbone stays intact
2 rounds of replication needed for this change to be permanent (if not correct by proofreading it will become permanent at second round)
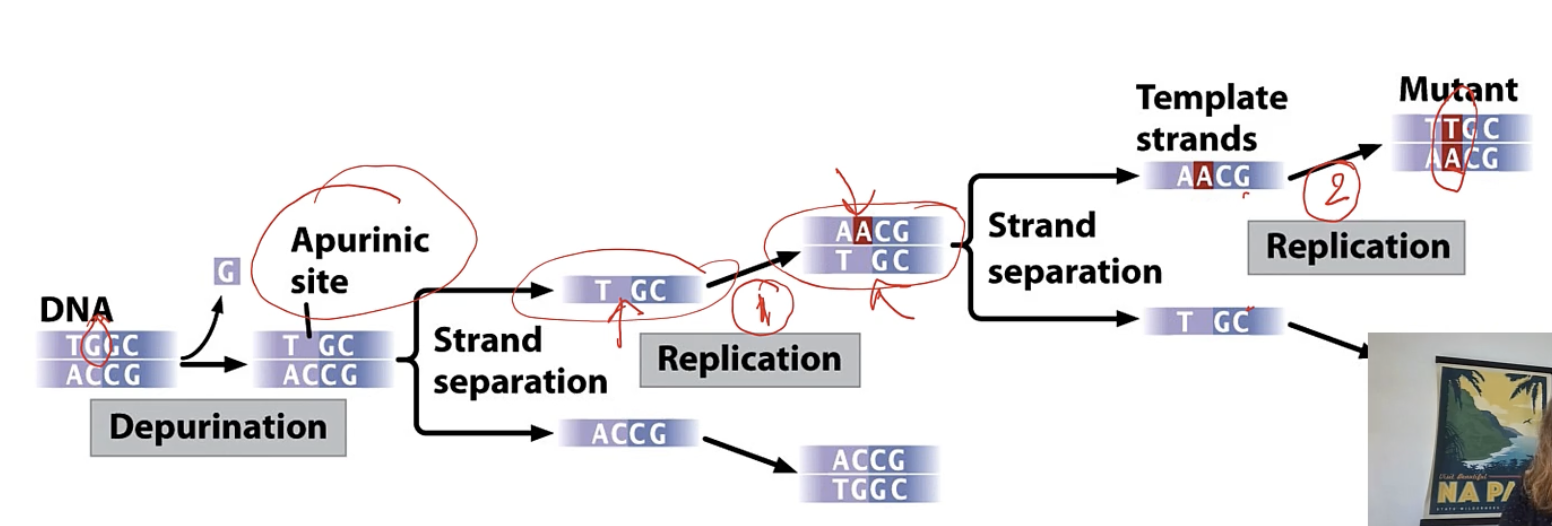
DNAP puts A where something is missing
deamination
loss of amino group from base
1) amino group lost from cytosine
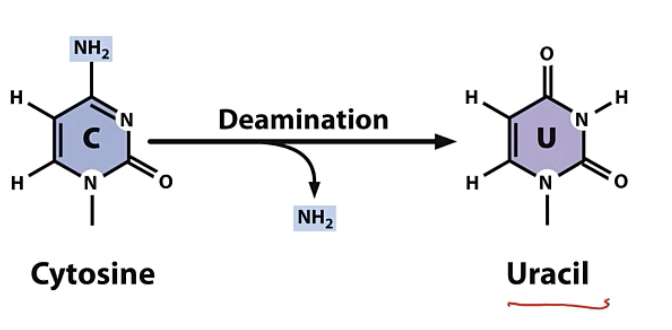
cytosine - amino group → uracil
U pair with A during synthesis
if not proofread then after 2 rounds becomes permanent
G/C → A/T transition
2) amino group lost from adenine
adenine - amino group → hypoxanthine (pairs with C)
A/T → G/C transition
permanent after 2 rounds of DNA replication
Test used to idenity mutagens
mutagens cause inducible mutations
Ames Test
Ames Test
used to identify mutagens/ chemical carcinogens
uses mutant bacterial strains that
have no DNA repair system
cannot make histidine (His-)
aka will only grow on minimal media supplemented with his
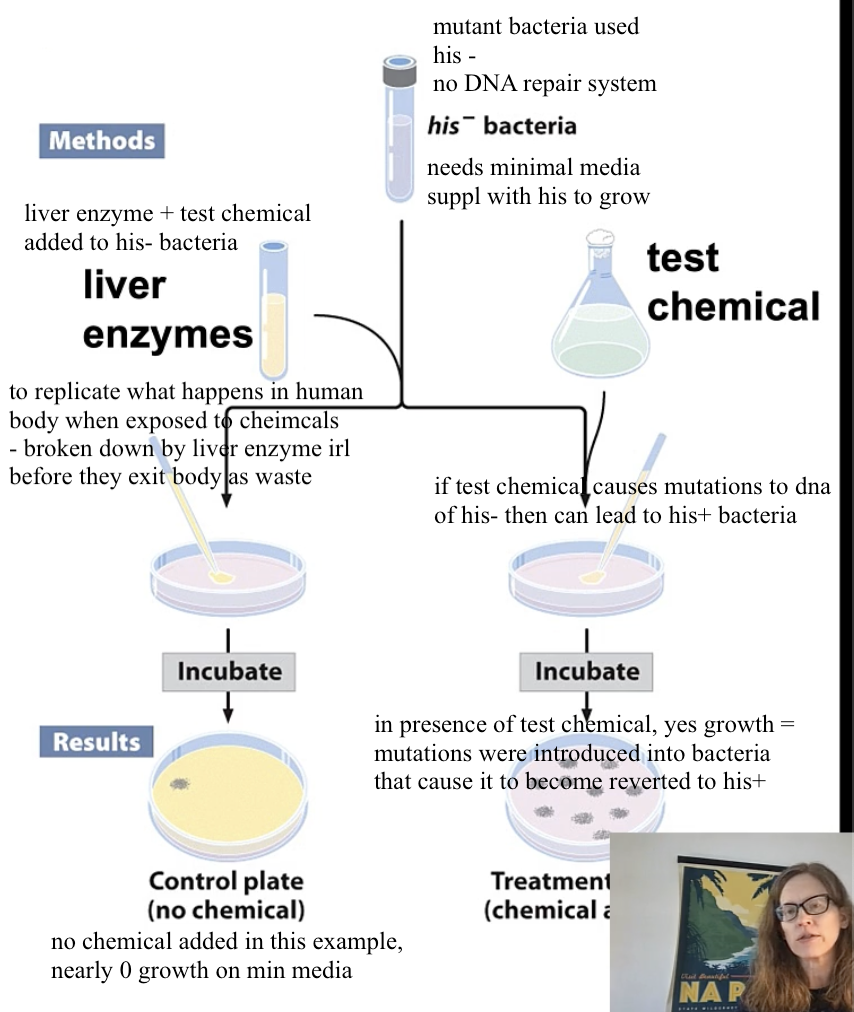
since test chemical is mixed with liver enzyme, we don’t know if the growth was caused by mutagen in test chemical or by mutagen byproduct of liver enzyme+ test chemical
this is why we run control of test chemical itself + his- bacteria and check for growth
what can be concluded if Ames test shows growth when chemical+liver enzyme+ bacteria his-
body metabolism converted the chemical into mutagen
You use the Ames test to study a chemical commonly found in plastic packaging materials. You have 2 plates containing minimal media. Untreated bacteria is added to Plate 1. Bacteria mixed with the test chemical is added to Plate 2. You observe no growth on Plate 1 and 150 colonies on Plate 2. What do you conclude?
test chemical is mutagen
induced mutations 4 ways
big booty in underwear
base analog
chemical with structure similar to normal base
can be incorporated into the newly synthesized DNA, during S phase (as it looks like base)
DNAP cannot differentiate btw base analog and base
why is base analog a problem
as ionization of base analog will change bp properties during subsequent rounds of replication
base modifiers
add or remove chemical group from base → changes its bp properties → so it wont pair properly when it is a template
intercalating agents
flat, planar molecules that can insert themselves between stacked bases in DNA
causing contorted helical structure → leads to mistakes by DNAP
UV light
cause adjacent pyrimidines to bond tg
changing structure of helix
what stage do all inducible mutation mutagens act as mutagens or cause problems?
in actively DNA replicating cells
gene interaction epistasis = supressor mutation
supressor expressed at one locus of gene masks the phenotype expressed by another locus in gene
double mutant : individual has one mutation and a mutation at another locus supresses this mutation
mutant purple (p) eye in fly , wt red (p+)
supressor (ss) vs non supressor (s+ dom) makes red
1st mutation caused mutant phenotype purple, 2nd mutation at dif site supress the effect of first mutation and give wt
ppss → purple got supressed and became red
methods of supression
1) intergenic supression
mutation in 2 different genes
1st mutation gives mutant phenotpe
2nd supressor mutation restores to wt
2) intragenic supression
both mutations in same gene / single codon of gene
intergenic supression eg) eye color
indv that shows supression will be double mutant
1st mutation in gene that codes for eye color : nonsense mutation
2nd/ supressor mutation in gene that codes for tRNA
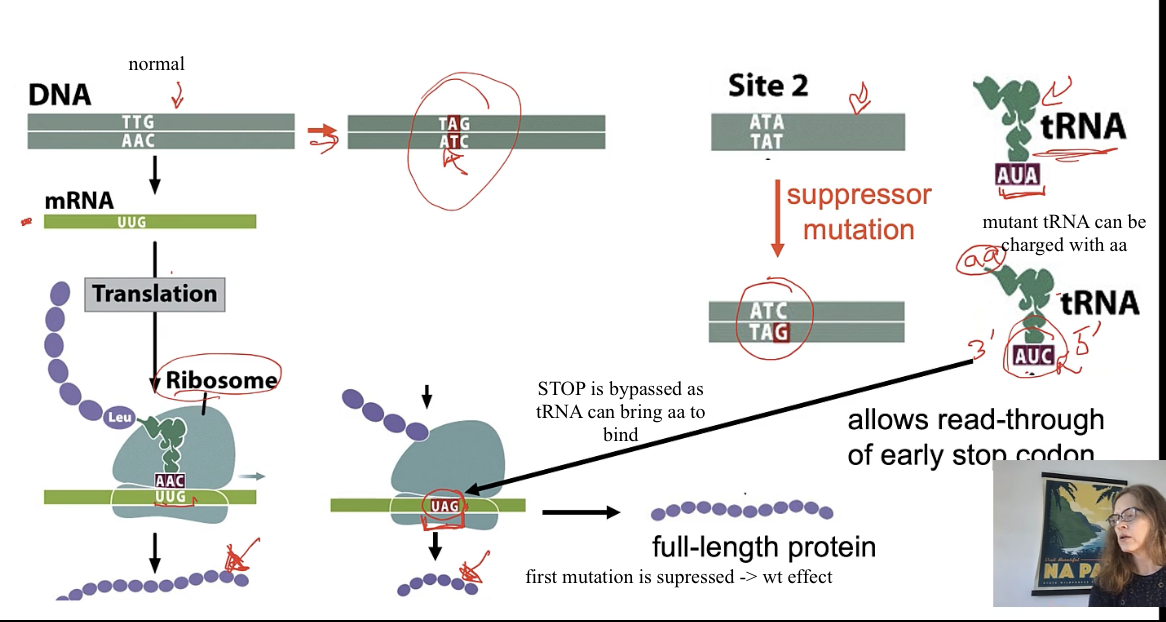
mutation 1 gives mutant phenotype of eye color
mutation 2 supresses mutant eyecolor and expresses wt
intergenic supression eg) enzyme
enzyme needs many subunits to function
1st mutation in code for subunit A : missense mutation
subunit A and B cannot bind
2nd/ supressor mutation in gene that codes for subunit B
restores binding btw A and B
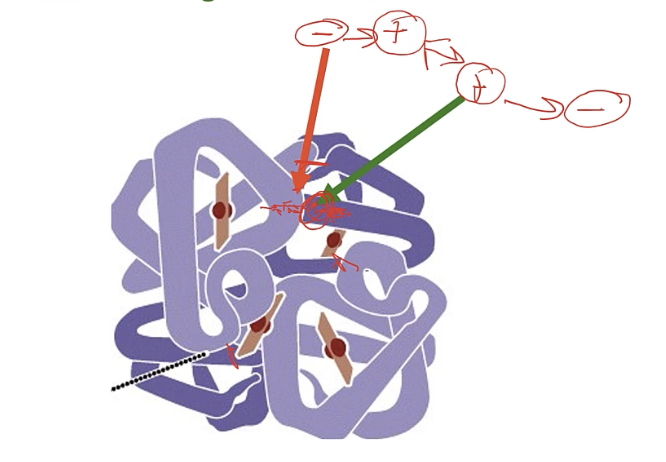
at first mutation at red site
- → + so no longer binding as + vs +
at second mutation at green site
+ → - so now + and - can bind
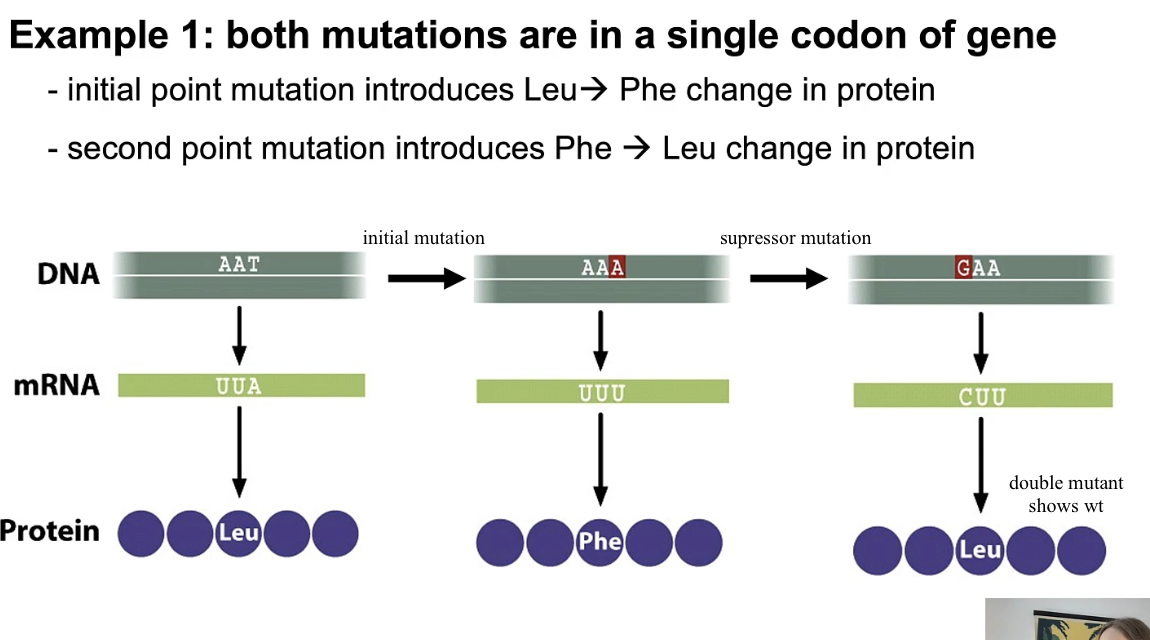
intragenic supression eg) leu → phe → leu
both mutations in SINGLE codon of gene
intragenic supression eg) - → + → -
mutations in DIFFERENT codons of same gene
mutation 1 - → + so no longer folding correct
mutation 2 + → - now folding correct
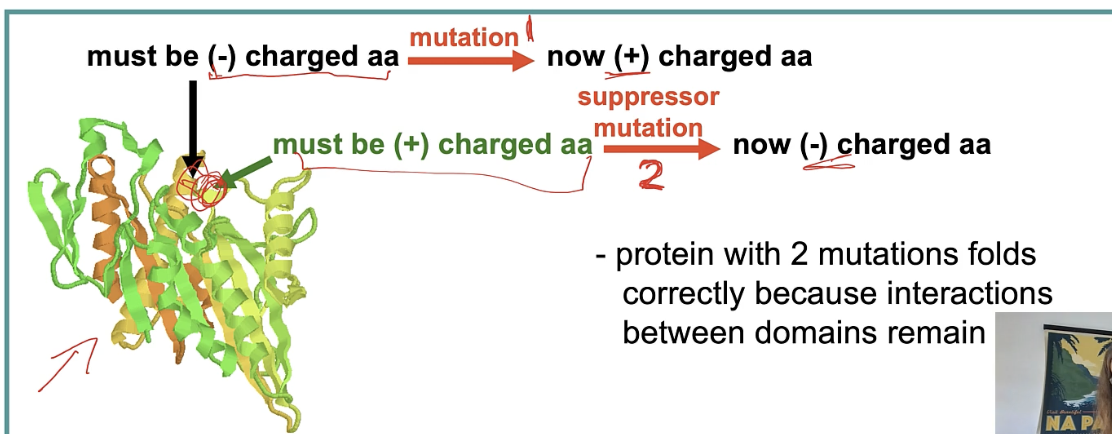
2 wrongs → right
DNA repair mechanism
1) direct repair
2) excision repair
3) mismatch repair
dont envy me
2 strands of DNA
1 mutated , 1 template/ non mutated
What is true about BOTH intergenic suppression and intragenic suppression?
a double mutant shows wt phenotype
DNA repair mechanisms are ___ meaning?
redundant, many ways to repair all mutations
direct repair
reverse the change that happened to DNA
A) thymine dimers caused by UV light can be reversed using photolyase
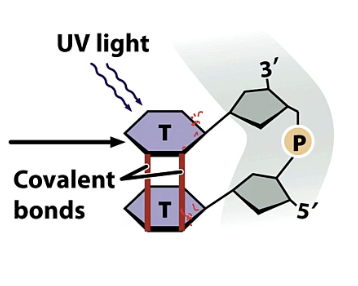
UV light causes T to bond to neighbour T instead of complementary A
B) Methyltransferase
removes CH3 added by mutagen
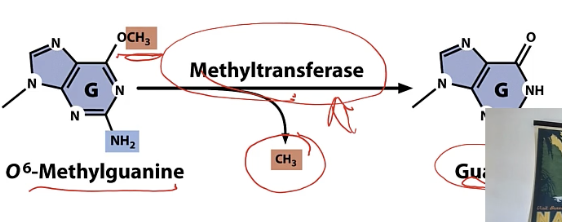
photolyase
needs light to work
does direct repair and repairs thymine dimers caused by UV light
breaks T-T helping T-A form
Excision repair
1) nucleotide excision repair
2) base excision repair
nucleotide excision repair
remove multiple nucleotide
needs DNAP , DNA ligase
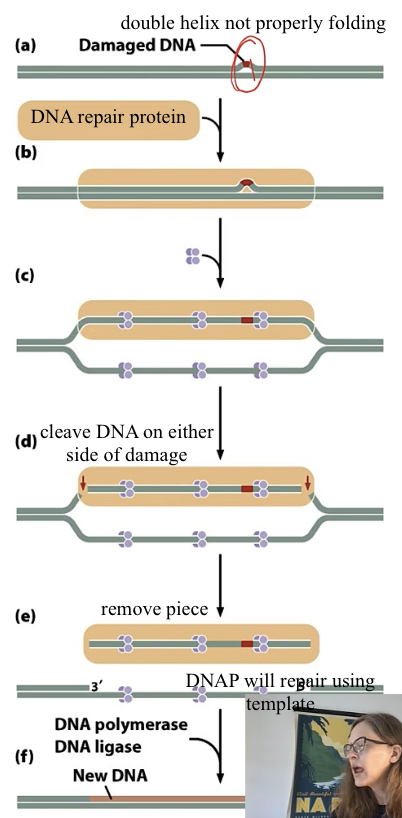
base excision repair
remove damaged base
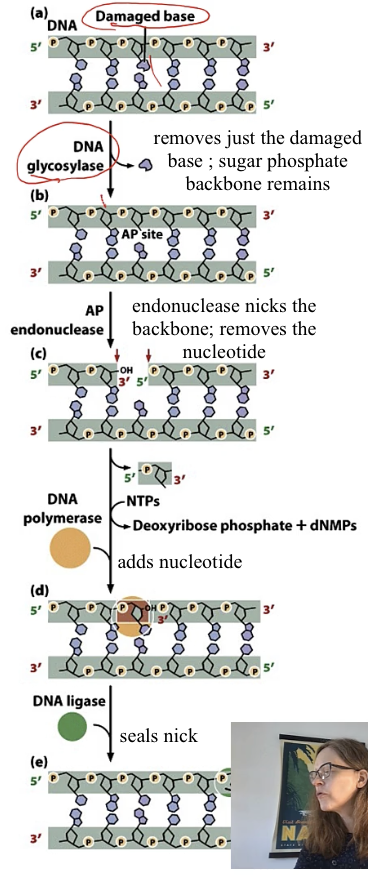
Compare both the excision repair mechanisms
both use DNAP and DNA ligase
in first step nucleotide excision repair - removes nucl
in first step base excision repair - DNA glycosylase removes base
mismatch repair
during S phase as replication is happening
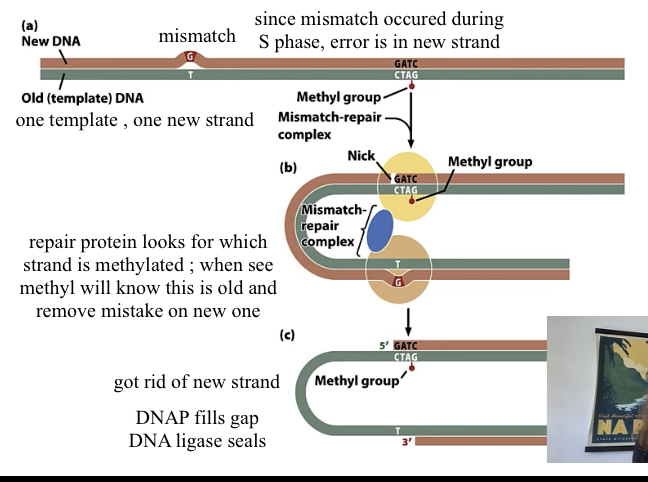
enzyme identifies old vs new strand
how to distinguish old and new DNA
many A’s in DNA are methylated after replication; but this takes time
so right after replication, new wont be methylated but old will be
Which repair is the only one that acts during DNA replication not after?
mismatch repair
Which repair acts on cells that are not actively dividing?
direct repair
excision repair