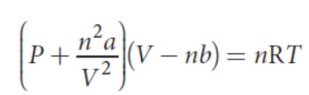MCAT General Chemistry - The Gas Phase
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
465
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
phases / states
different physical forms of matter; gas, liquid, solid
pressure (P)
expressed in units of atmospheres (atm), millimeters of mercury (mmHg), torr, SI unit for pressure pascal (Pa)
1 atm = 760 mmHg ≡ 760 torr = 101.325 kPa
sphygmomanometers
Medical devices that measure blood pressure; mmHg; normal adult blood pressure is considered less than 120 mmHg systolic and 80 mmHg diastolic; clinical blood pressure cuff creates a force that is opposed by the person’s systolic and diastolic arterial blood pressure
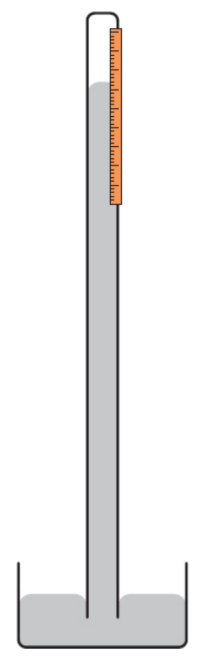
barometer
scientific instrument that is used to measure air pressure; atmospheric pressure creates a downward force on the pool of mercury at the base of the barometer; mercury in the column exerts an opposing force (its weight) based on its density; if PA > WHg, level rises, and vice versa
Atmospheric pressure
static pressure within the atmosphere of Earth
standard temperature and pressure (STP)
273 K (0°C) and 1 atm; used for gas law calculations
volume (V)
expressed in liters (L) or milliliters (mL)
temperature (T)
kelvin (K) or Celsius (°C)
standard state conditions
298 K, 1 atm, 1 M concentrations; used when measuring standard enthalpy, entropy, free energy changes, and electrochemical cell voltage
ideal gas
represents a hypothetical gas with molecules that have no intermolecular forces and occupy no volume
intermolecular forces
attraction and repulsion between molecules
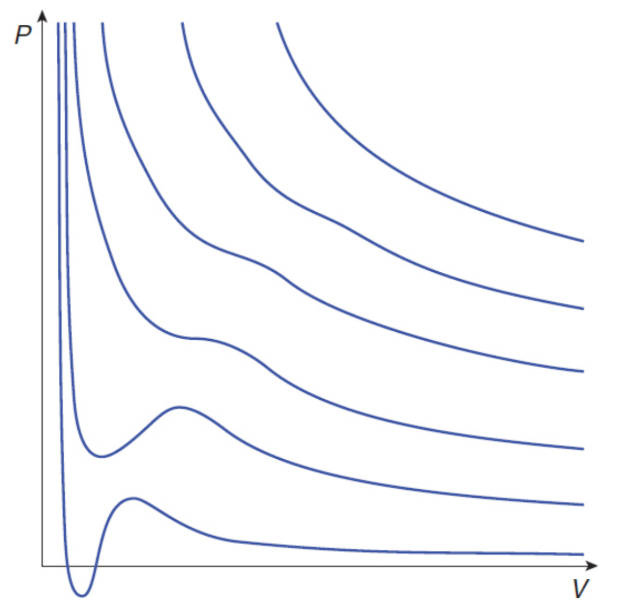
real gases
deviate from ideal behavior at high pressures (low volumes) and low temperatures
Ideal gas law
PV = nRT
where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles, T is the temperature and R represents the ideal gas constant
ideal gas constant (R)
8.21×10-2 L*atm/mol*K
8.314 J/K*mol
density (ρ)
ratio of the mass per unit volume of a substance; g/L
ρ = m/V = PM/RT
combined gas law
P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2
Avogadro’s principle
all gases at a constant temperature and pressure occupy volumes that are directly proportional to the number of moles of gas present
one mole of any gas, irrespective of its chemical identity, will occupy 22.4 liters at STP
where k is a constant, n1 and n2 are the number of moles of gas 1 and gas 2, respectively, and V1 and V2 are the volumes of the gases, respectively
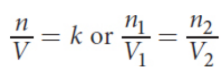
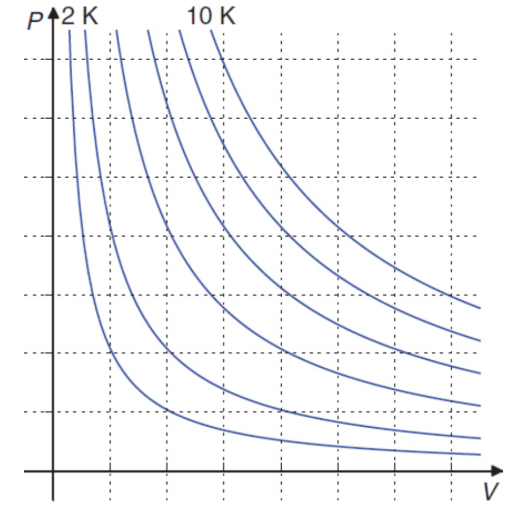
Boyle’s law
in isothermal conditions, the volume of the gas is inversely proportional to its pressure
PV = k or P1V1 = P2V2
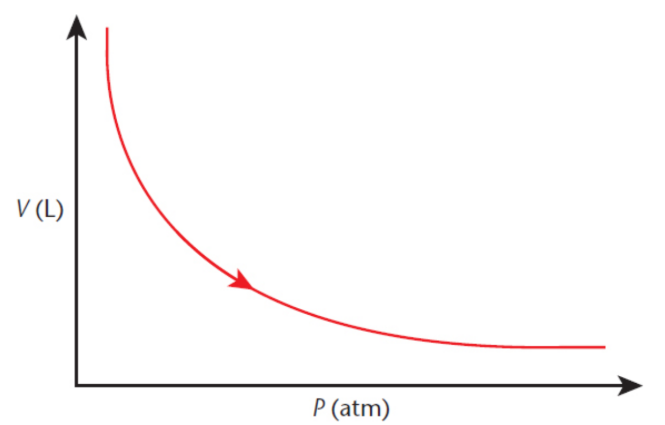
Charles’s law.
at constant pressure, the volume of a gas is proportional to its absolute temperature, expressed in kelvin
V/T = k or V1/T1 = V2/T2
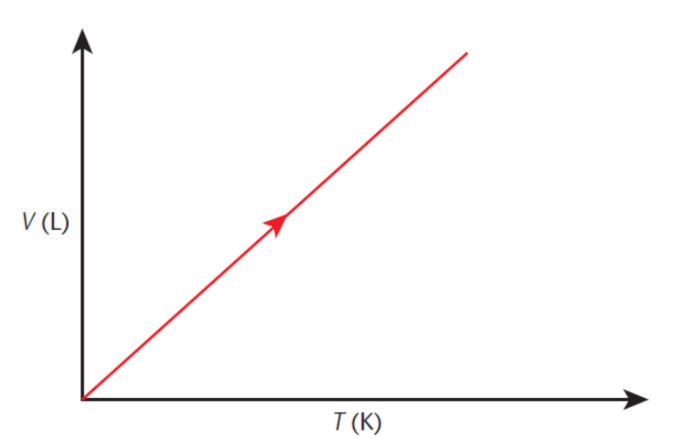
Gay-Lussac’s law
at constant volume, the pressure of a gas is proportional to its absolute temperature, expressed in kelvin
P/T = k or P1/T1 = P2/T2
partial pressure
pressure exerted by each individual gas in a mixture
Dalton’s law of partial pressures,
the total pressure of a gaseous mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the individual components
PT = PA + PB + PC + ...
where PT is the total pressure in the container, and PA, PB, and PC are the partial pressures of gases A, B, and C, respectively
Vapor pressure
pressure exerted by evaporated particles above the surface of a liquid
Henry’s Law
at various applied pressures, the concentration of a gas in a liquid increased or decreased; Vapor pressure from the evaporated molecules forces some of the gas back into the liquid phase, and equilibrium is reached between evaporation and condensation
[A} = kH * PA
where [A] is the concentration of A in solution, kH is Henry’s constant (depends on the gas), and PA is the partial pressure of A
kinetic molecular theory
explain the behavior of gases; all gases show similar physical characteristics and behavior irrespective of their particular chemical identity
Gases are made up of particles with volumes that are negligible compared to the container volume.
Gas atoms or molecules exhibit no intermolecular attractions or repulsions.
Gas particles are in continuous, random motion, undergoing collisions with other particles and the container walls.
Collisions between any two gas particles (or between particles and the container walls) are elastic, meaning that there is conservation of both momentum and kinetic energy.
The average kinetic energy of gas particles is proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas (in kelvin), and it is the same for all gases at a given temperature, irrespective of chemical identity or atomic mass.
Average Molecular Speed
average kinetic energy of a gas particle is proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas
KE = ½ mv2 = 3/2 kBT
Boltzmann constant (kB)
1.38 × 10-23 J/K
serves as a bridge between the macroscopic and microscopic behaviors of gases
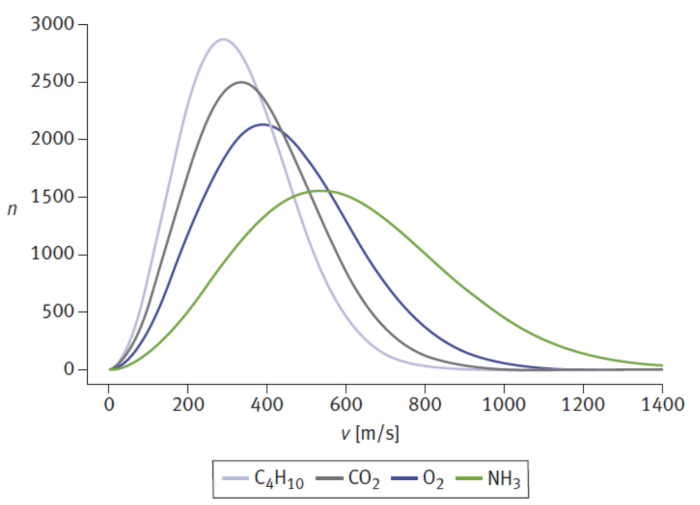
root-mean-square speed (urms)
average speed is to determine the average kinetic energy per particle and then calculate the speed to which this corresponds
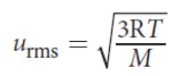
Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution curve
shows the distribution of gas particle speeds at a given temperature; T2 > T1
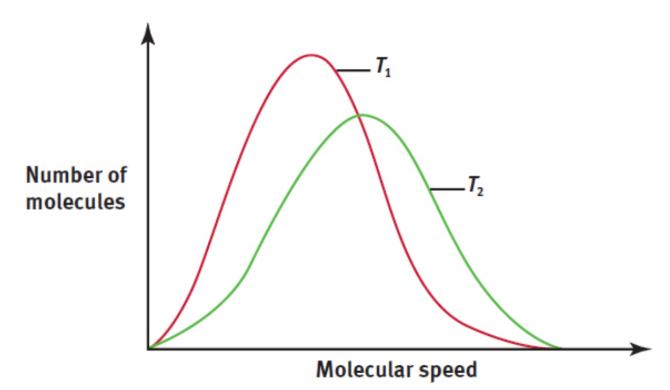
diffusion
movement of molecules from high concentration to low concentration through a medium (such as air or water); heavier gases diffuse more slowly than lighter ones because of their differing average speeds
Graham’s law
under isothermal and isobaric conditions, the rates at which two gases diffuse are inversely proportional to the square roots of their molar masses
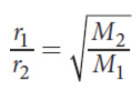
Effusion
the flow of gas particles under pressure from one compartment to another through a small opening; for two gases at the same temperature, the rates of effusion are proportional to the average speeds; follows Graham’s law
Deviations Due to Temperature
T down → average speed of the gas molecules decreases and the attractive intermolecular forces become increasingly significant → liquid
closer a gas is to its boiling point, the less ideally it acts
van der Waals Equation of State
where a (corrects for the attractive forces between molecules) and b (corrects for the volume of the molecules themselves) are physical constants experimentally determined for each gas