CH 17 Skeletal Muscle System
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
X is the basis for all human movement.
Muscle contraction
X pulls on boney levers to cause movement.
Muscle shortening (contraction)
Functions of skeletal muscle
locomotion
body posture
venous return
thermogenesis
Irritability
ability to receive and respond to stimuli
Extensibility
ability to be lengthened or stretched
Elasticity
ability to return to resting length after being stretched
Contractility
ability to respond to stimuli by shortening
Thick filaments
Myosin
Thin filaments
actin
troponin
tropomyosin
All or none principal
motor neuron is stimulated, all the muscle fibers in that motor unit contract to their fullest extent or they do not contract at all
Muscle fibers
SR and T tubules
myofibrils and myofilaments
sarcomeres
t tubules
sarcoplasmic reticulum
muscle contraction occurs when
actin contains
sarcomeres are separated by
longitudinal muscle classification
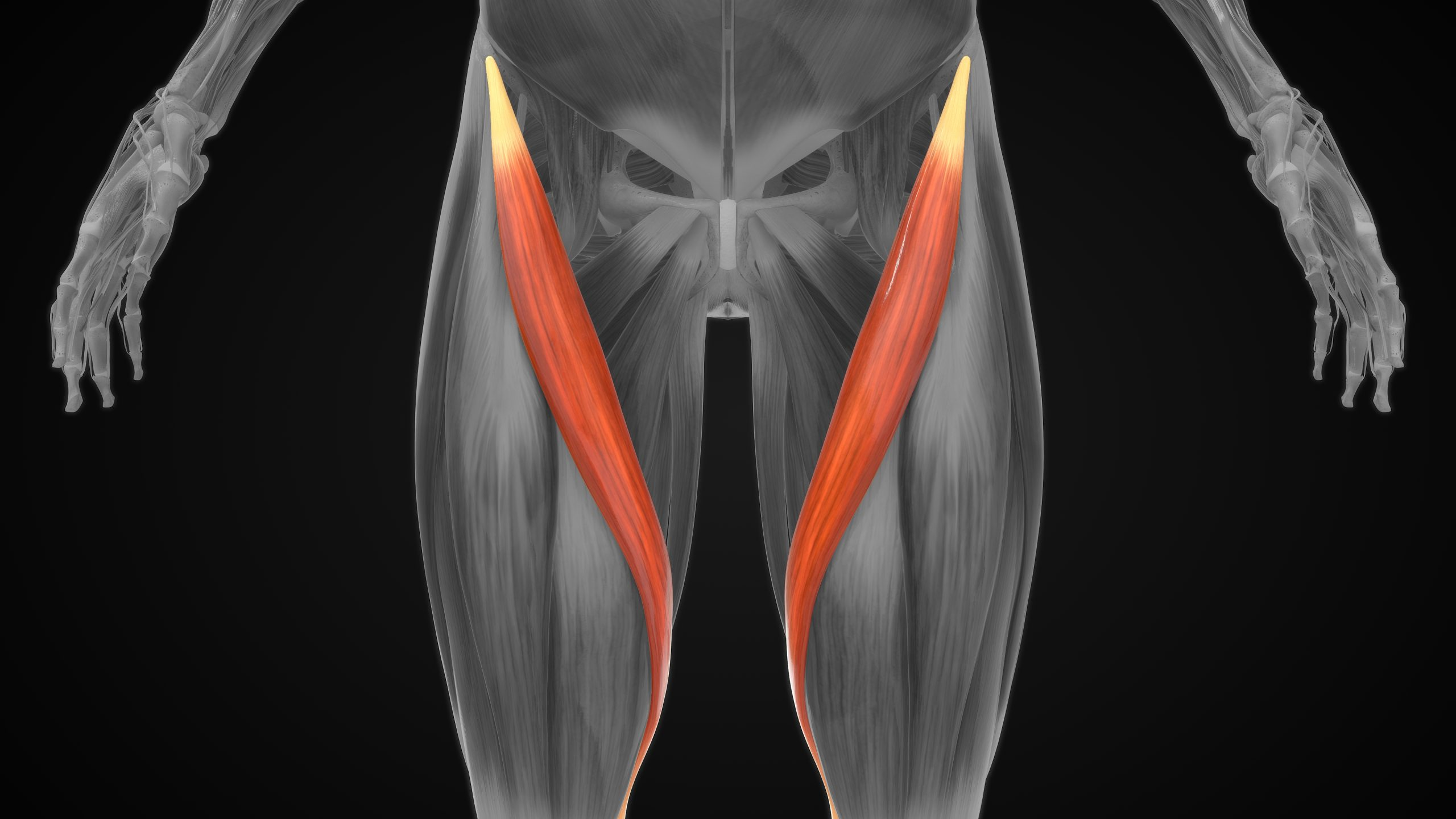
fusiform muscle classification
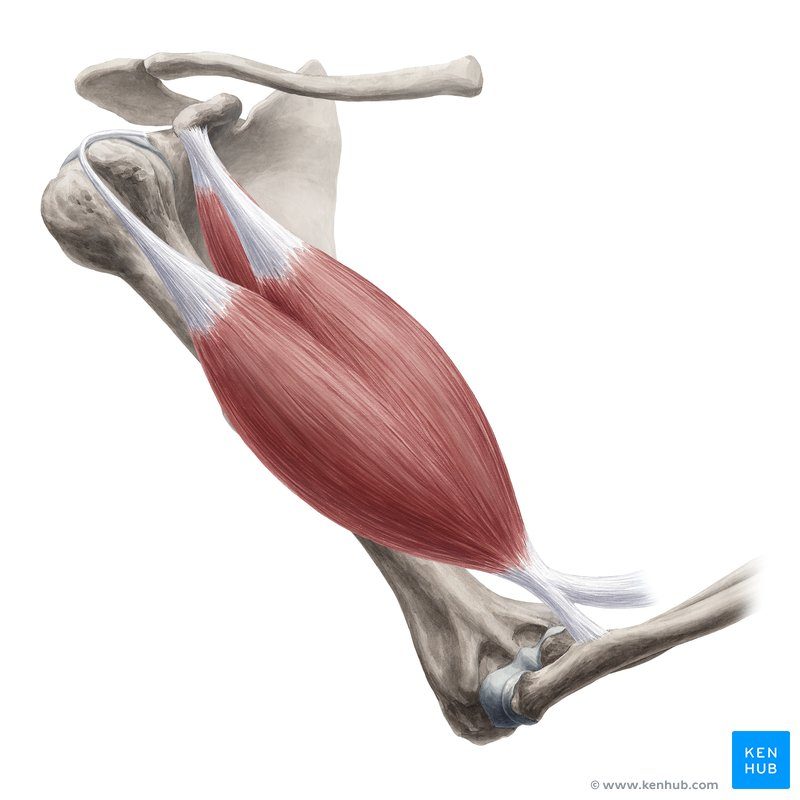
radiate muscle classification
unipennate muscle classification
Bipennate muscle classification
circular muscle classification