Chapter 3.2: Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What are nucleotides?
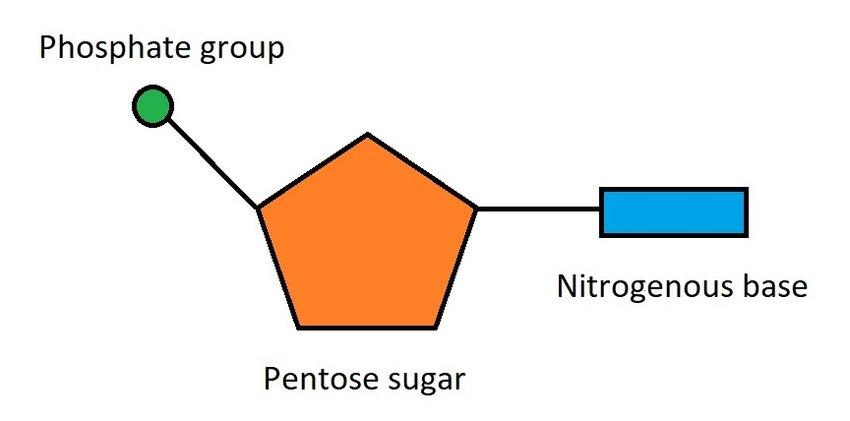
The monomers used to form nucleic acids. Made up of a pentose monosaccharide, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base.
What three things is an individual nucleotide made up of?
A pentose monosaccharide, containing five carbon atoms
A phosphate group that is acidic and negatively charged
A nitrogenous base- contains one or two carbon rings
Draw the general structure of a nucleotide.
What are pyrimidines?
The smaller bases, contain single carbon ring structures.
What are purines?
The larger bases, they have two carbon rings.
What are the two purines?
Adenine
Guanine
What are the three pyrimidines?
Cytosine
Thymine
Uracil
What is the difference between DNA and RNA?
Deoxyribose contains one less oxygen atom than a ribose sugar.
What base does thymine always complementary base pair with?
Thymine always pairs with adenine or uracil in RNA.
What base does guanine always complementary base pair with?
Guanine always pairs with cytosine.
What is complementary base pairing?
The specific hydrogen bonding between nucleic acids, adenine and thymine always form two hydrogen bonds with each other, guanine and cytosine always form three hydrogen bonds with each other.
What are phosphodiester bonds?
The covalent bonds formed between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the hydroxyl group of another.
How is a polynucleotide formed?
A condensation reaction between the phosphate group at the fifth carbon of the pentose sugar and the hydroxyl group at the third carbon of the adjacent nucleotide.
This forms a covalent bond called a phosphodiester bond.
This forms a long, strong sugar-phosphate backbone with a base attached to each sugar.
How is a polynucleotide broken?
The phosphodiester bonds are broken by hydrolysis, which released the individual nucleotides.
What three main things do cells require energy for?
Synthesis- large molecules like proteins
Transport- pumping molecules or ions across cell membranes by active transport
Movement- protein fibres in muscle cells that cause muscle contraction
What is the general structure of ATP?
Nitrogenous base
Pentose sugar
Three phosphate groups
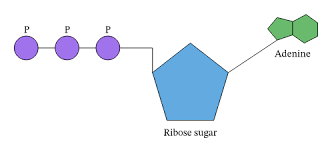
What are the main similarities and differences between ATP and DNA/ RNA?
In ATP the base is always adenine, whereas in DNA or RNA they can be others
The sugar in ATP is ribose like in RNA nucleotides.
Why is ATP known as the universal energy currency?
Used for energy transfer in all cells of all living things.
How is ATP made?
During respiration via a condensation reaction and using the enzyme ATP synthase.
What is the reaction for the condensation of ATP?
ADP + Pi → ATP + H2O
What is the reaction for the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP?
ATP + H2O → ADP + Pi
What is phosphorylation?
Reattaching a phosphate group to an ADP molecule, this releases a small amount of energy.
Why are DNA molecules described as antiparallel?
The two parallel strands that are held together by hydrogen bonds, are arranged so they run in opposite directions so are said to be antiparallel.
How does the structure of DNA relate to its function?
It is a stable structure due to the sugar-phosphate backbone and the double helix structure.
Double-stranded so replication can occur using both strands as a template.
Weak hydrogen bonds between bases for easy separation of the two strands during replication.
Complementary base pairing allows identical copies to be made.
Describe how to extract a DNA precipitate from plant material.
Grind the sample with a pestle and mortar- this breaks down the cell walls.
Homogenise with detergent- this breaks down the cell surface membrane, releasing the cells contents.
Filter to remove large debris.
Add salt to break hydrogen bonds between the DNA and water molecules.
Add protease to digest the proteins associated with the DNA.
Add ice-cold ethanol to precipitate out the DNA from the solution. It should appear as white strands.
What are the three polymers of RNA?
mRNA
rRNA
tRNA
What is rRNA?
Ribosomal RNA, makes up the bulk of ribosomes.
Made up of rRNA and proteins.
What is mRNA?
A copy of a gene from DNA made in the nucleus.
It is much shorter than DNA and it is very short-lived.
What is a codon?
A three-base sequence of DNA or RNA that codes for one amino acid.
What is tRNA
A single-stranded but folded into a cloverleaf shape that brings a specific amino acid to the ribosome.
It is found in the cytoplasm.
the specific amino acid is determined by the three bases on the tRNA, the anticodon.
Why is DNA replication described as semi-conservative?
In replication one strand is conserved and one new strand is created.
When does replication occur during the cell cycle?
S-phase in interphase.
What are the stages of DNA replication?
Helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between the complementary bases of the two DNA polymers, causes the double helix to unwind and the two strands to separate.
Both strands act as a template for replication.
Free floating DNA nucleotides align opposite their complementary base on the template strand of DNA. Hydrogen bonds will form between base pairs.
DNA polymerase joins adjacent nucleotides together, forming a phosphodiester bond between these nucleotides to create a new polymer chain of DNA.
What is the role of the enzyme helicase in replication?
Unwinds and separates the two strands of the DNA double helix.
What is the role of the enzyme DNA polymerase?
Catalyses the formation of phosphodiester bonds between the adjacent nucleotides.
Why is the genetic code considered degenerate?
Amino acids are coded for by more than one triplet of bases.
Why is the genetic code considered universal?
The same triplet of bases codes for the same amino acid in all organisms.
Why is the genetic code considered non-overlapping?
Each base in a gene is only part of one triplet of bases that codes for one amino acid. Each codon, or triplet of bases, is read as a discrete unit.
What is a mutation?
A random change to the sequence of bases in a newly-copied strand.
What is a gene?
A section of DNA that contains the complete sequences of bases (codons) to code for a protein.
What is the triplet code?
The genetic code is a sequence of three nucleic acid bases, called a codon. Each codon codes for one amino acid.
How many different base codons are possible?
64 or 4×4×4
What are the two stages of protein synthesis?
Transcription- where the DNA sequence for one gene is copied into mRNA
Translation- mRNA joins with a ribosome and a corresponding tRNA molecule brings the specific amino acid the codon codes for.
What are introns?
Sequences of bases in a gene that do not code for amino acids and therefore polypeptide chains. These get removed through splicing after transcription.
What are exons?
Sequences of bases in a gene that code for sequence of amino acids.
What are start and stop codons?
Start codon at the beginning of every gene allows the ribosome to attach.
At the end of the gene there are three bases that do not code for an amino acid, these are stop codons.