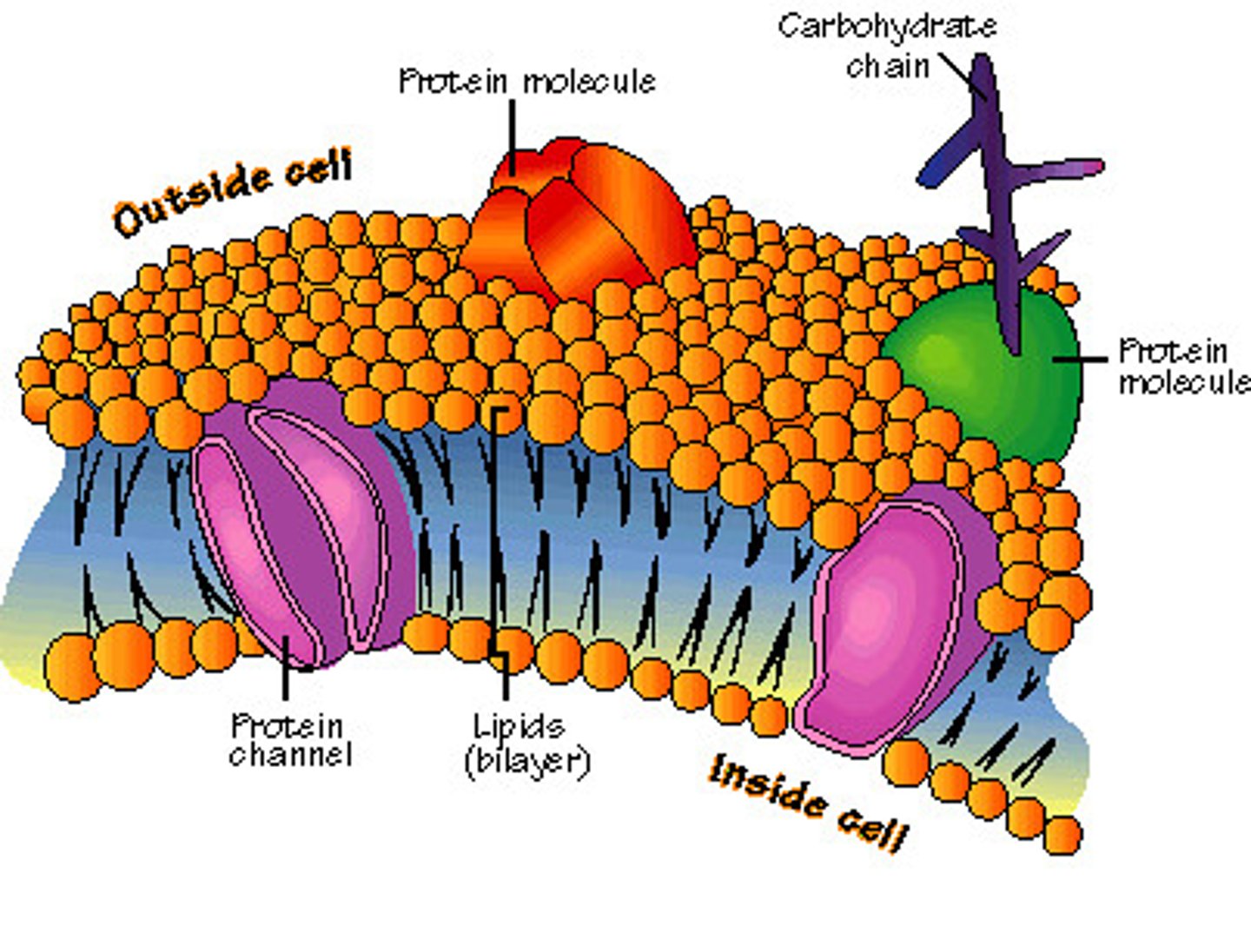
Cell membrane
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Plasma membrane
Another name for the cell membrane.
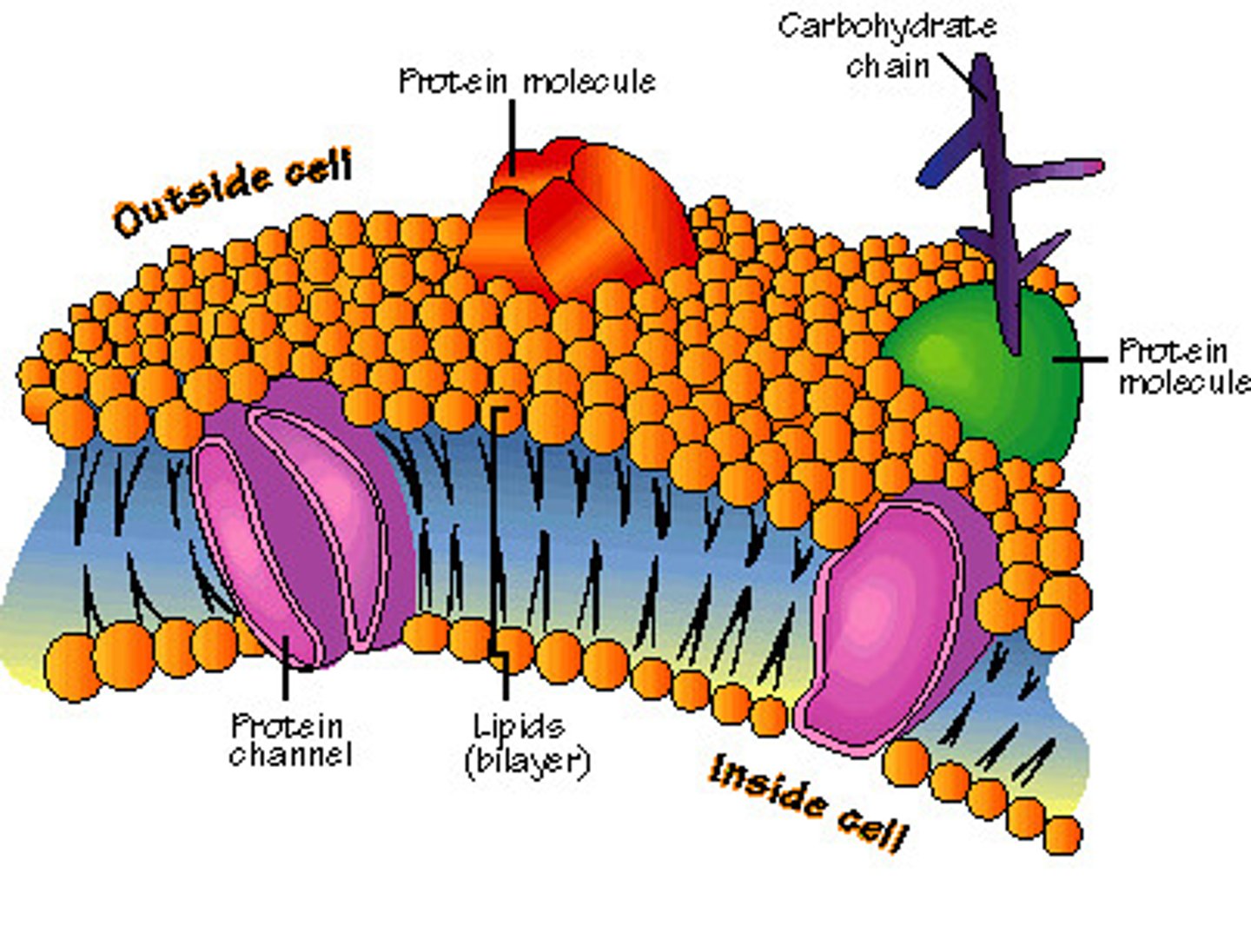
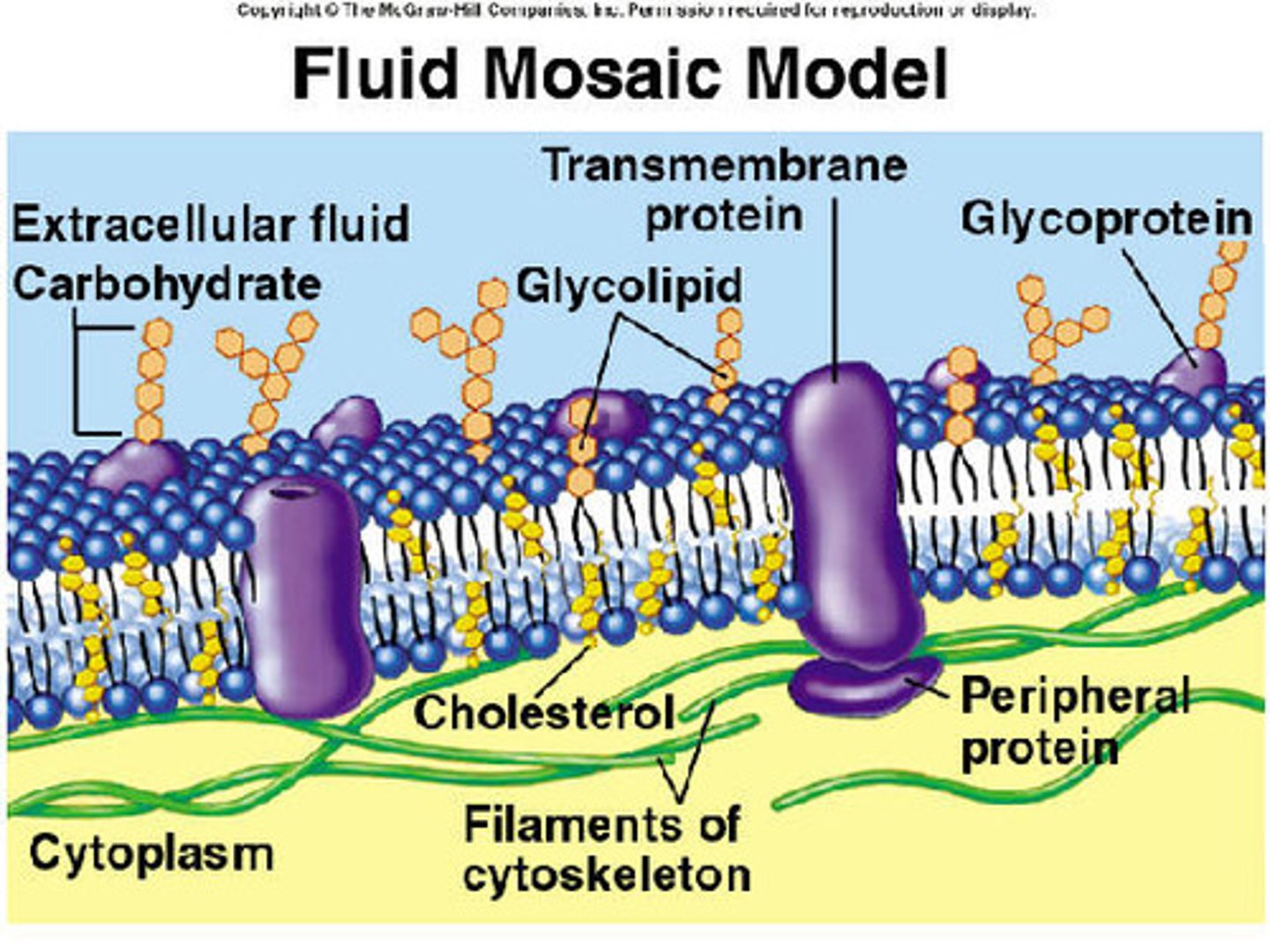
Fluid mosaic
A model that says the cell membrane tends to act more like a liquid than a solid and has proteins embedded in it.
Active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration gradient.
Passive transport
Movement across the cell membrane that does not require energy from the cell and moves with the concentration gradient.
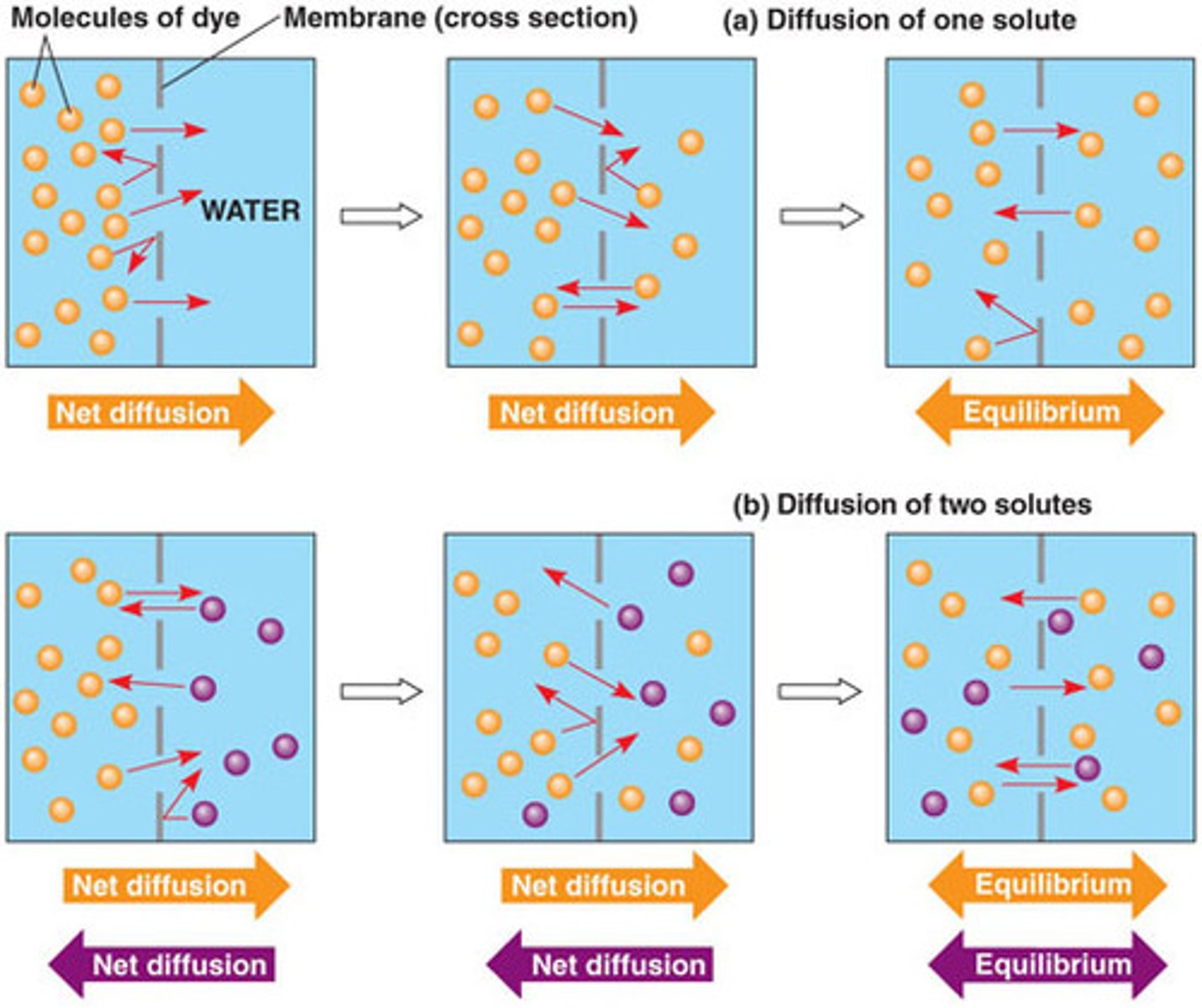
Diffusion
Movement of molecules (oxygen, caron dioxide, natural steroid hormones) from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
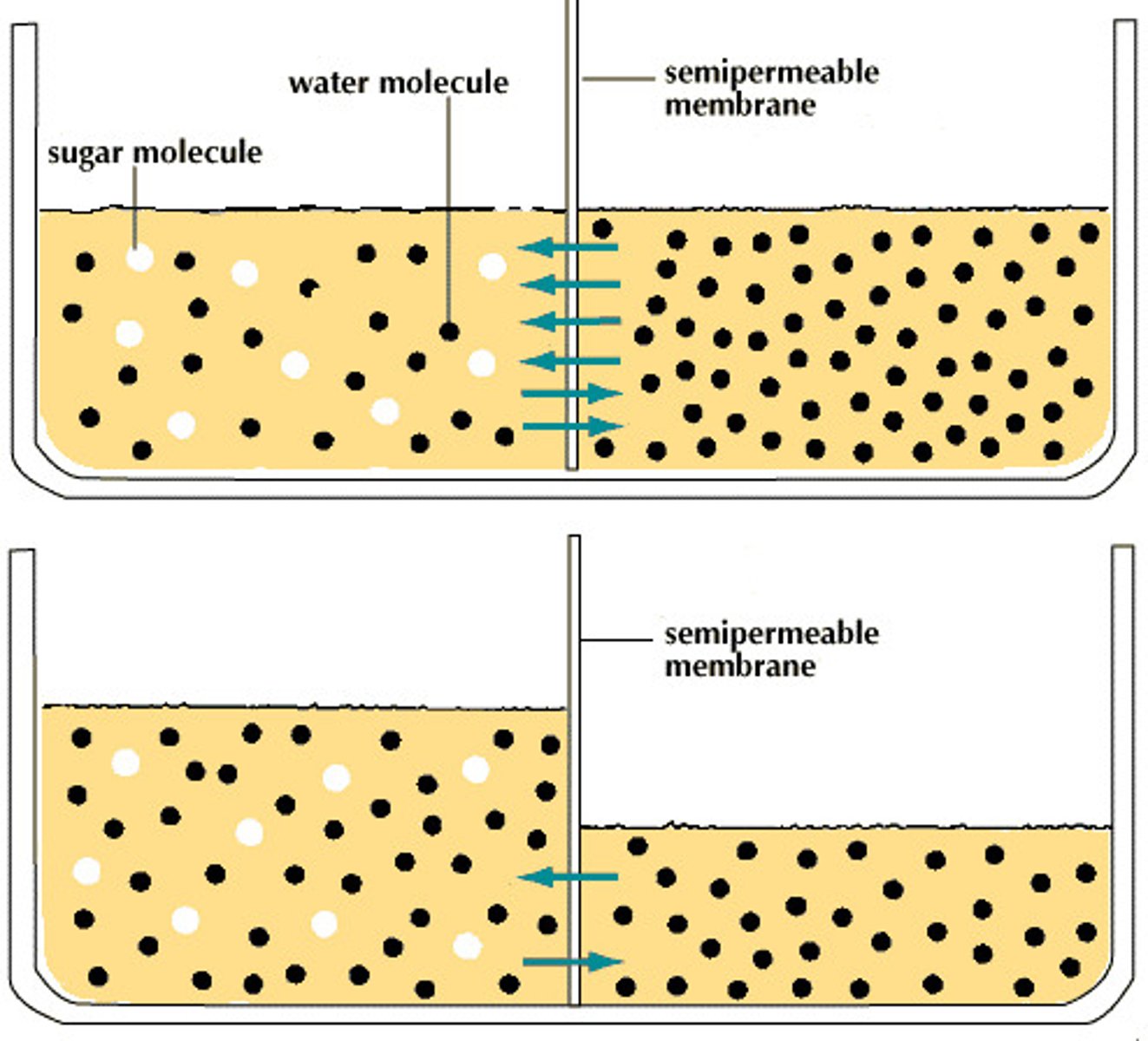
Osmosis
Diffusion of water from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. .
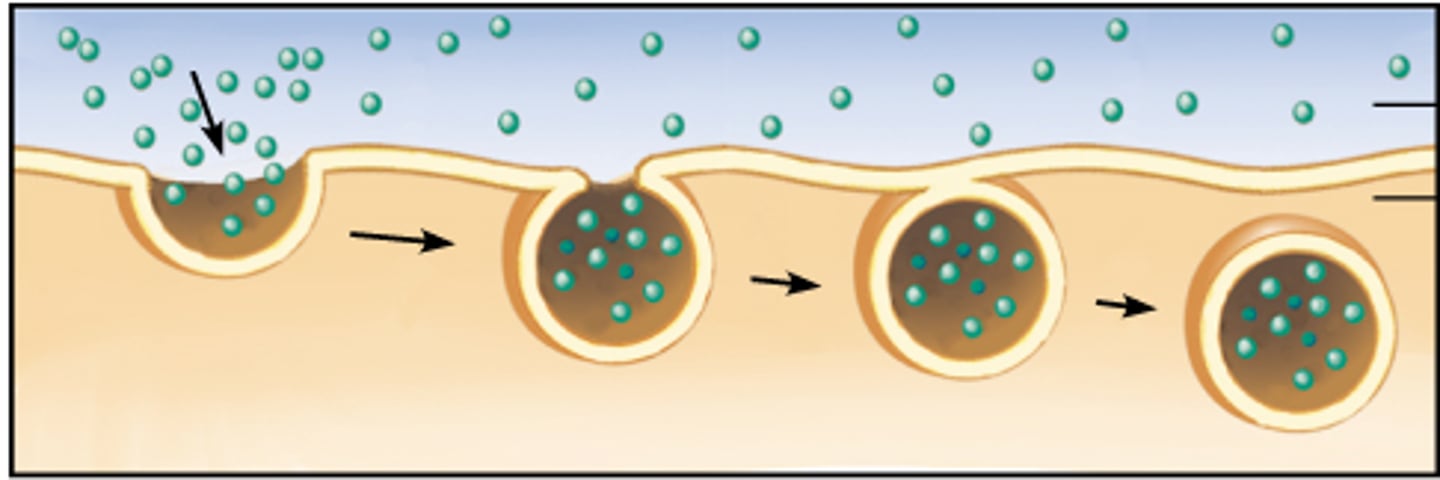
Endocytosis
Movement of materials into the cell by the formation of a vesicle from the infolding of the cell membrane.
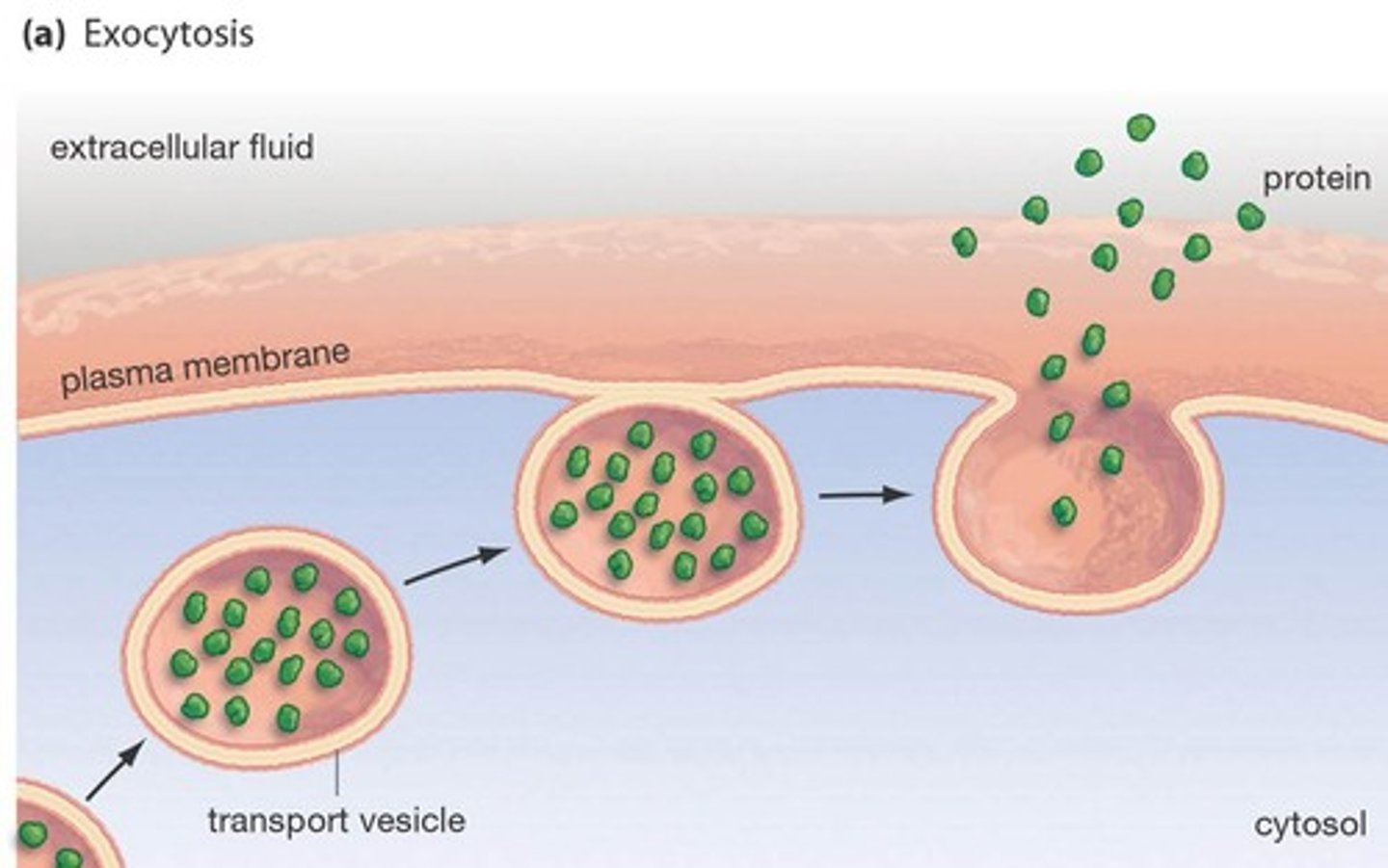
Exocytosis
Removal or secretion of materials from a cell by use of a vesicle. The molecules to be exported are modified by the Golgi body
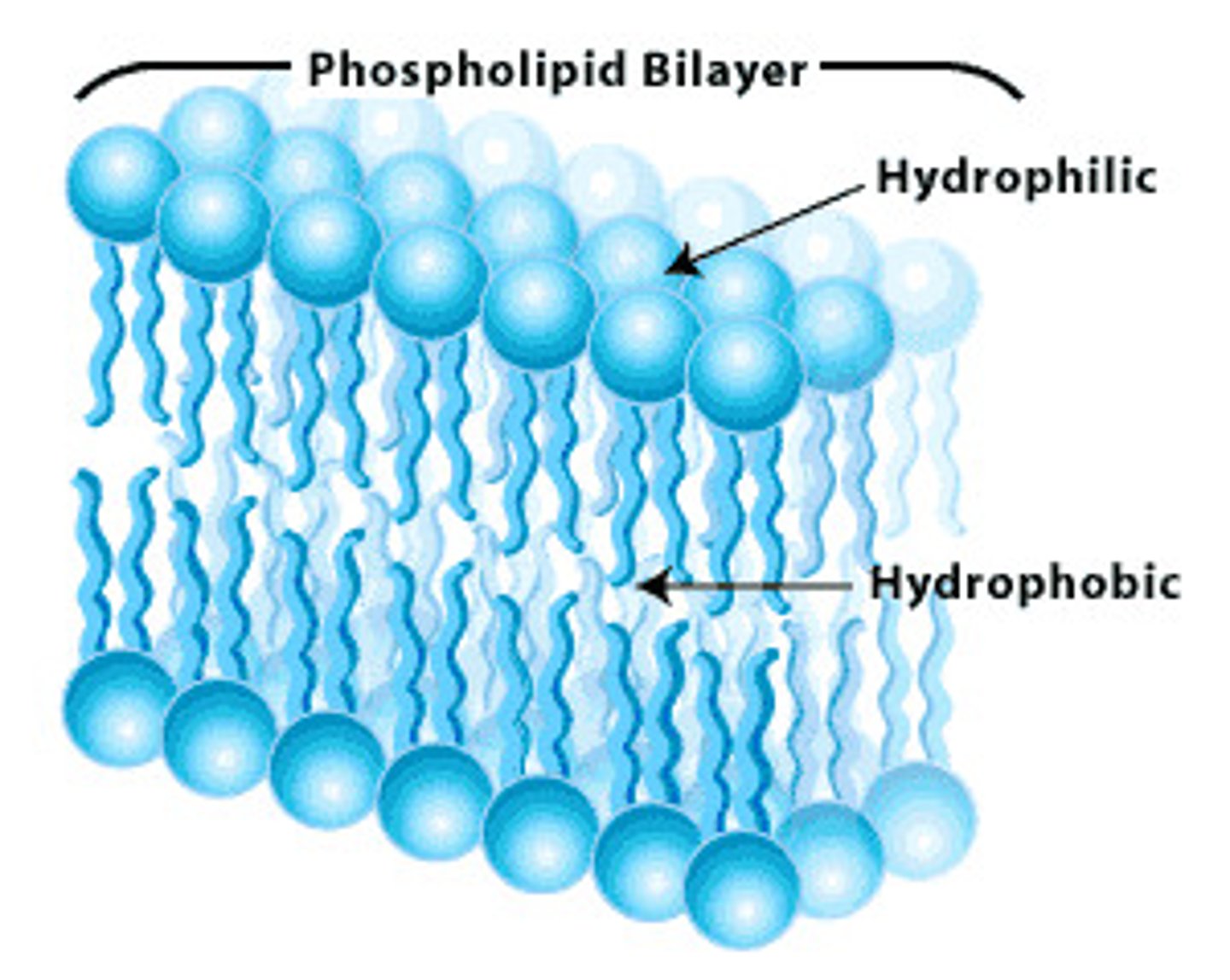
Phospholipid
specialized lipid made of a phosphate (polar), hydrophilic head and two fatty acid (nonpolar), hydrophobic tail.
Lipid Bilayer
Term used to describe the 2 layer thick phospholipid structure of the cell membrane.
Hydrophobic
Describes a substance that resists dissolving in water.
Hydrophilic
Describes a substance that is able to mix with water.
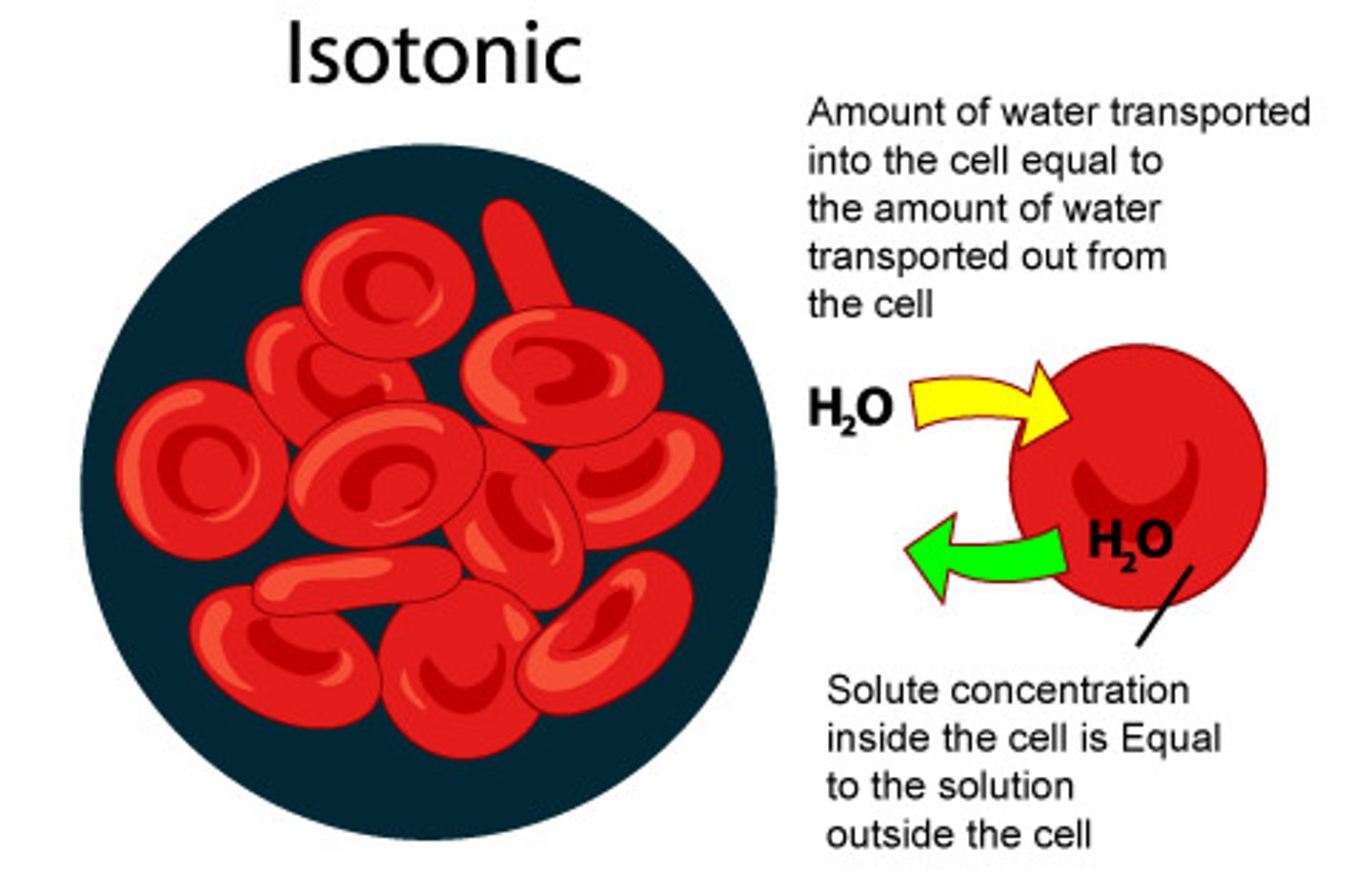
Isotonic
Describes a solution whose solute concentration is equal to the solute concentration inside a cell. No change in the cell shape.
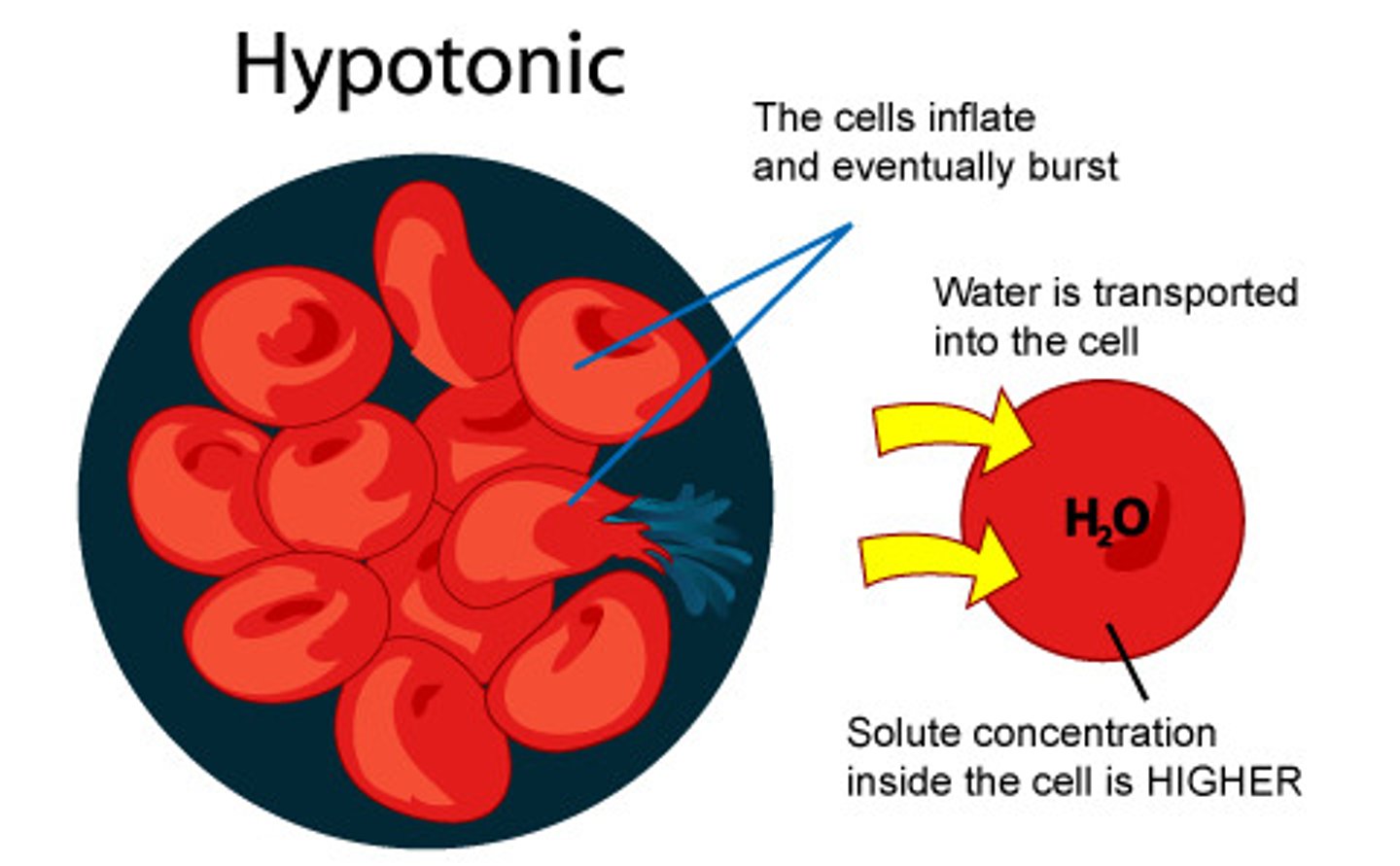
Hypotonic
Describes a solution whose solute concentration is lower than the solute concentration inside a cell. Causes a cell to swell or increase in size from water entering into the cell.
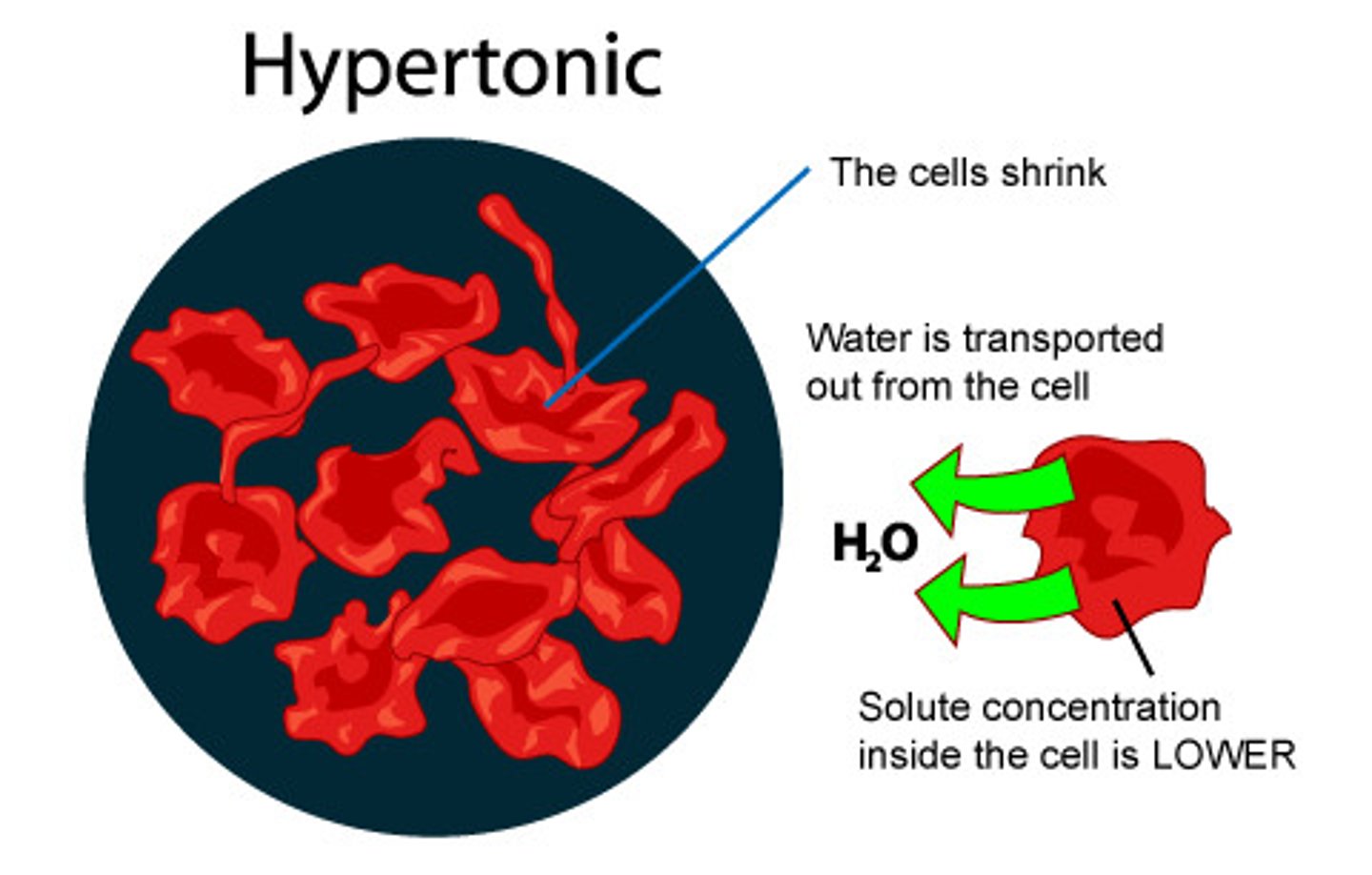
Hypertonic
Describes a solution whose solute concentration is higher than the solute concentration inside a cell. Causes a cell to shrink in size from water exiting a cell.
Channel proteins
A type of transport protein in the membrane whose role is to pass large molecules (ions, sugars, & amino acids) that cannot go through the membrane.

pump
transport protein used to move substances against the gradient
marker protein
A special type of protein found in the cell membrane that helps to identify a cell
facilitated diffusion
A type of passive transport that uses a transport protein to move substances down the concentration gradient.
Homeostatsis
The maintenance of stable internal conditions (98.6F temperature, 7 pH body cells, 2 pH stomach) in a changing environment.
Equilibrium
spaced is filled with the same amount of molecules on the inside as they're are on the outside
Concentration gradient
substances move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
Carrier protein
A type of transport protein in the membrane whose role is to only pass substances through the cell membrane that can fit their binding sites.
concentration
The amount of a particular substance in a given volume.
Sodium-potassium pump
ATP (energy) is used to pump sodium ions outside of the cell and potassium ions inside the cell
vesicles
membrane bound sacs