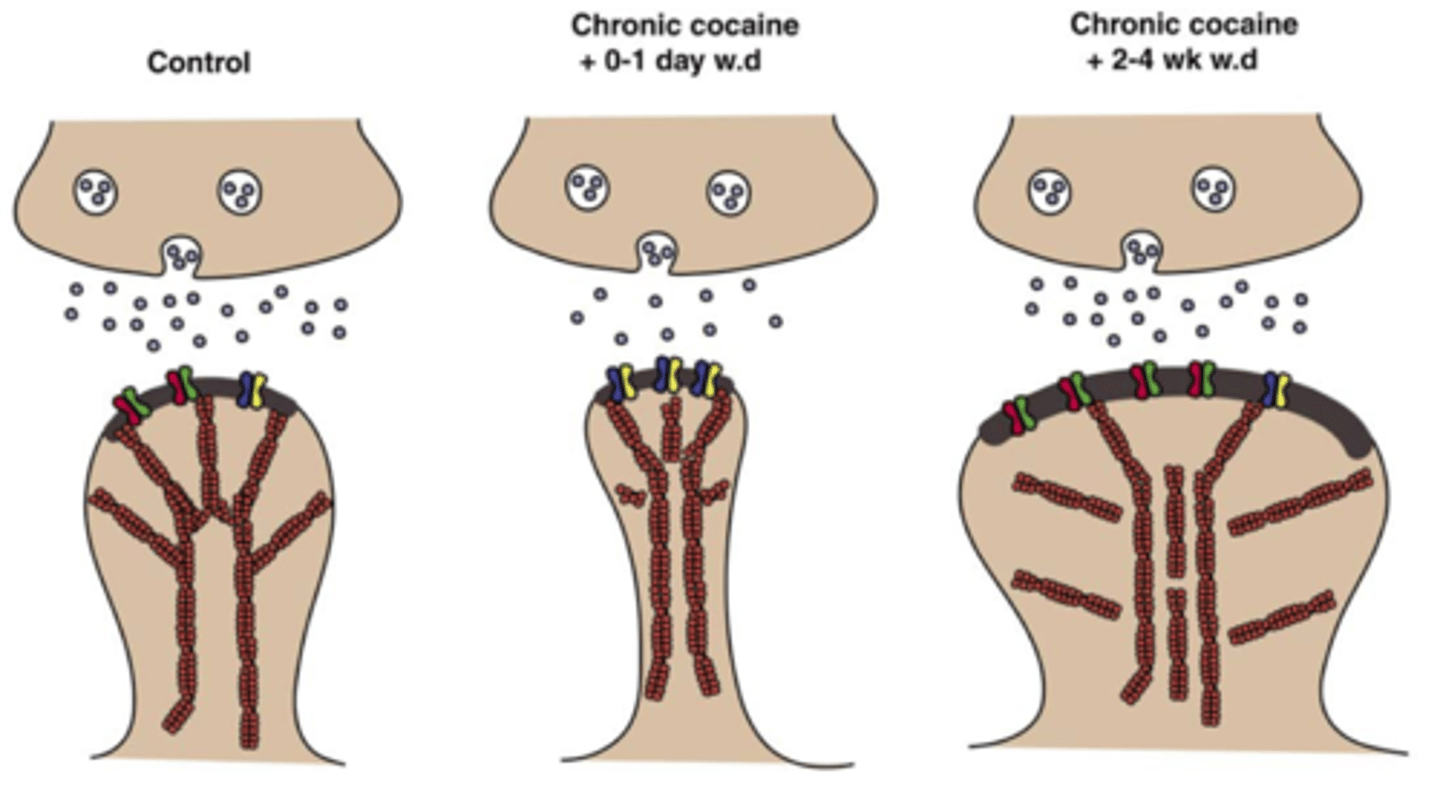
BRAIN, NERVOUS SYSTEM, EYES
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Sclera
outer protective layer of the eye (white of the eye)
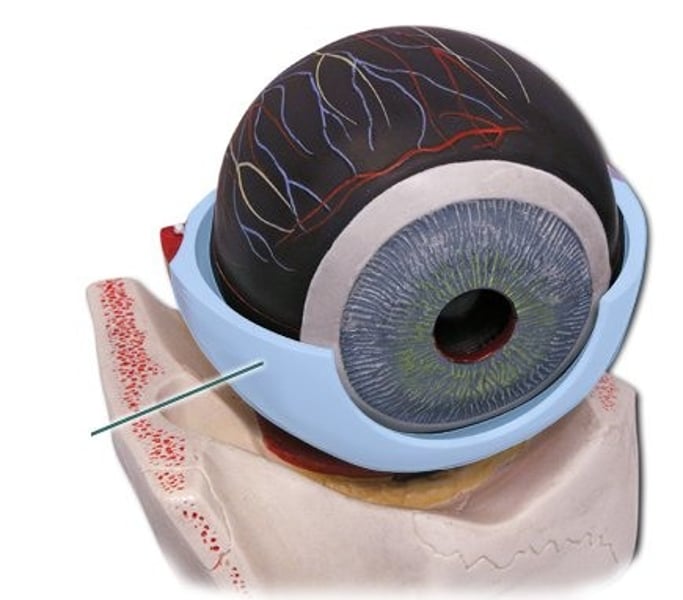
cornea
transparent anterior part of the sclera; allows light rays to enter the eye
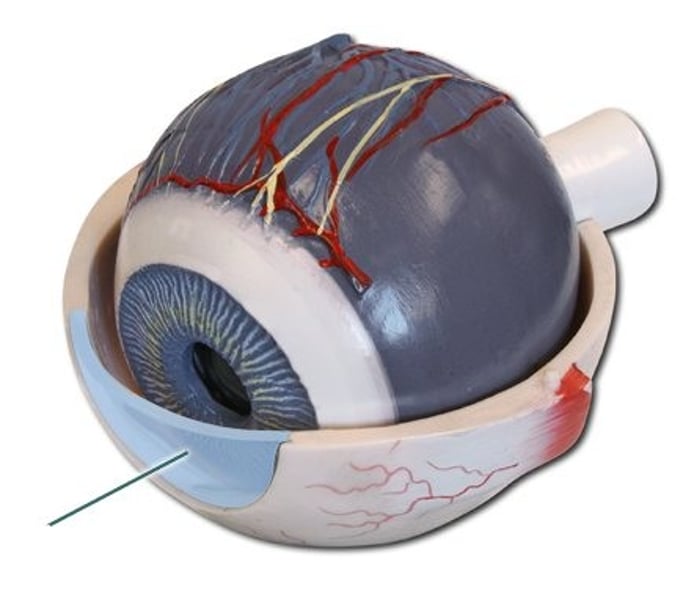
choroid
middle layer of the eye interlaced with blood vessels that supply nutrients to the eye; includes the iris.
iris
pigmented muscular structure that regulates the amount of light entering the eye by controlling the size of the pupil.
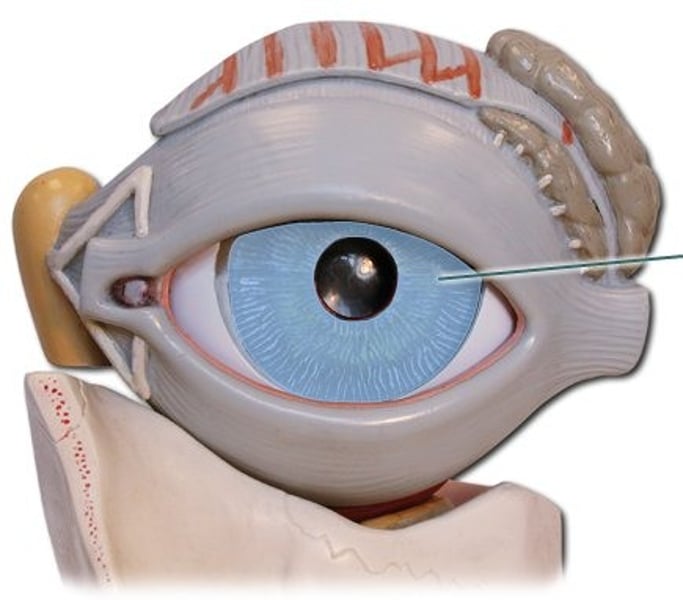
pupil
opening in the center of the iris through which light enters the eye
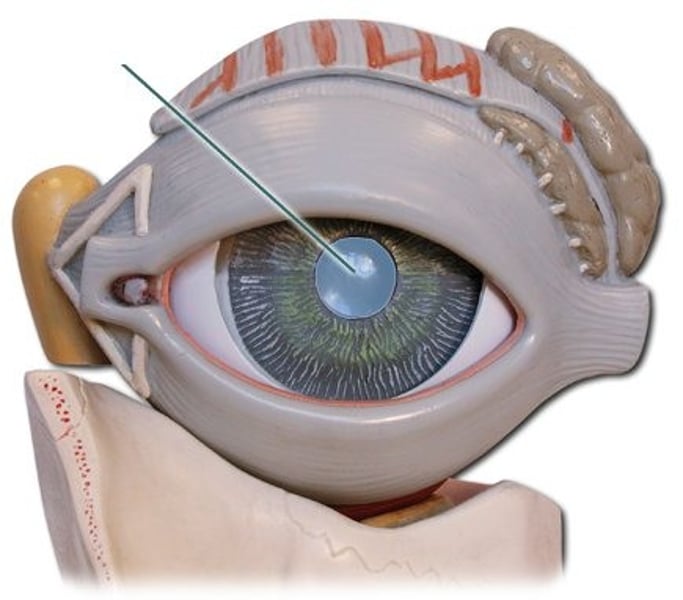
lens
directly behind the pupil; focuses and bends light
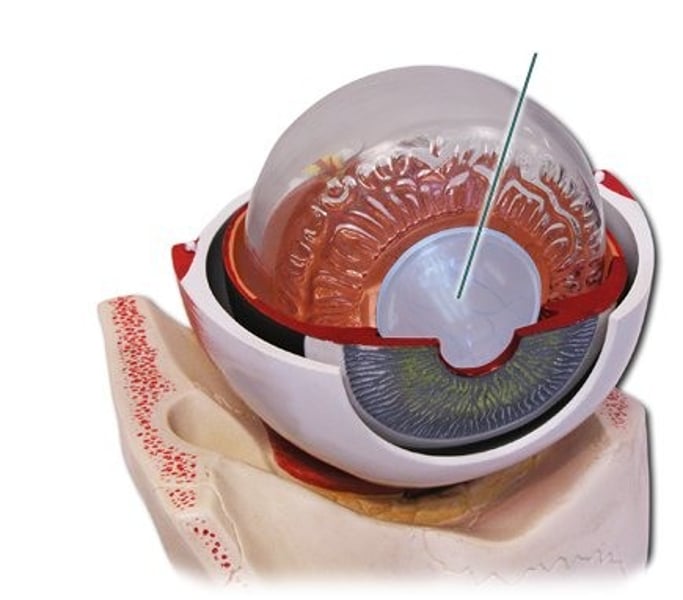
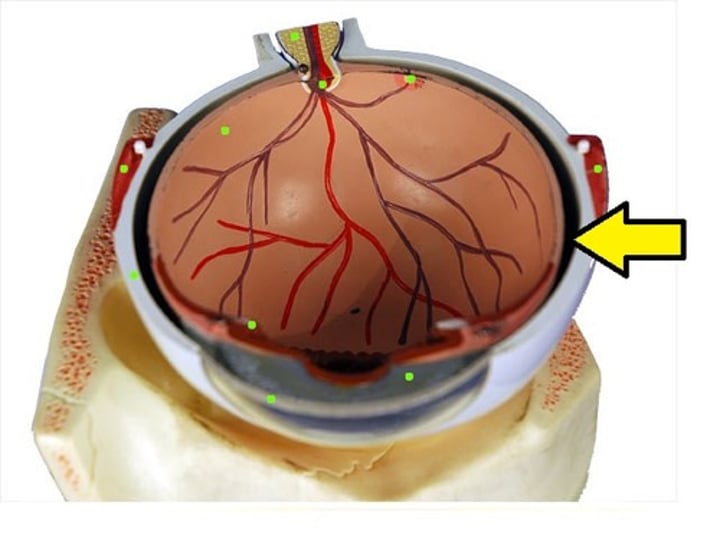
retina
innermost layer of the eye which contains photoreceptors (rods and cones)
aqueous humor
watery liquid in the anterior cavity of the eyes which provides nourishment and shape to the anterior eye
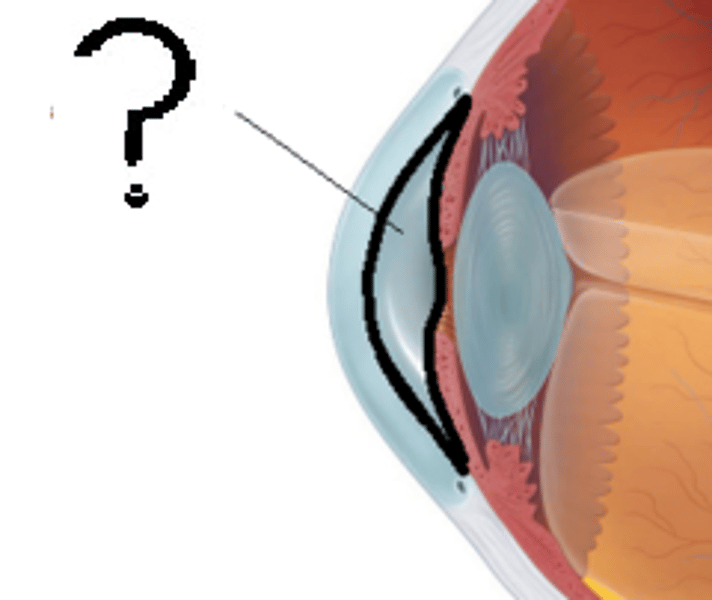
vitreous humor
Jellylike liquid found behind the lens in the posterior cavity of the eye that maintains its shape
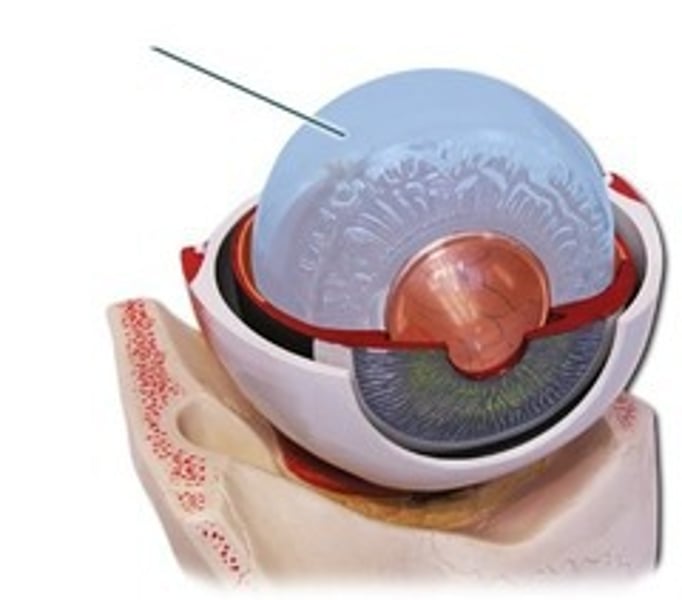
optic nerve
carries visual impulses from retina to brain
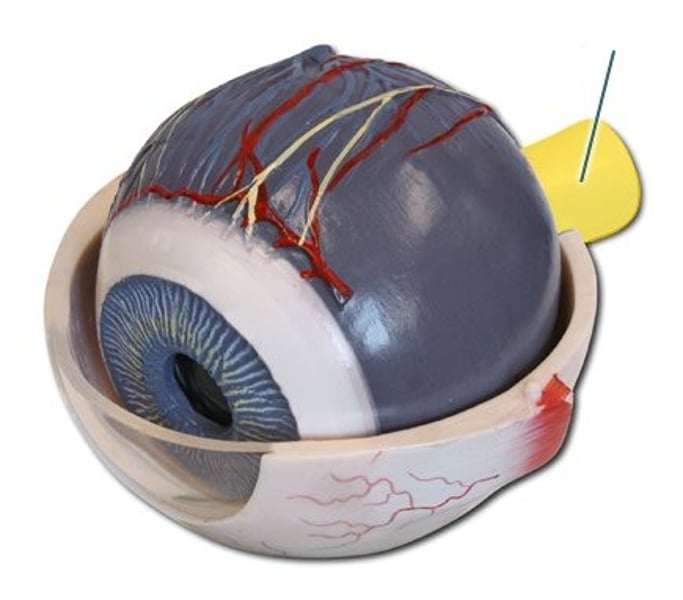
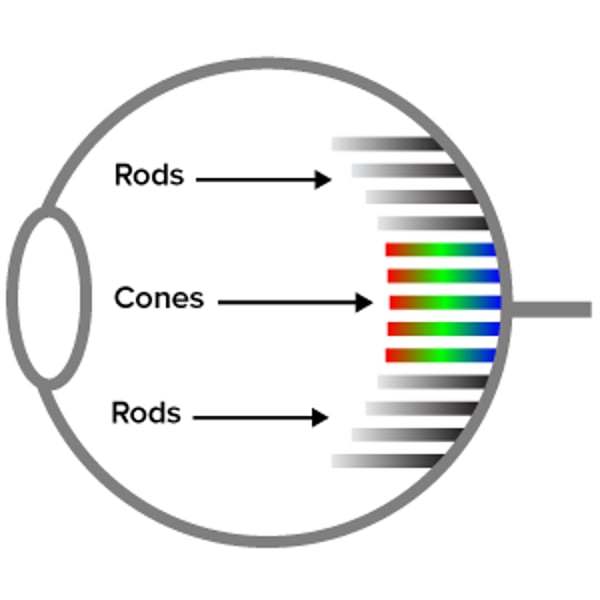
cones
Photoreceptors in the retina that distinguish different colors
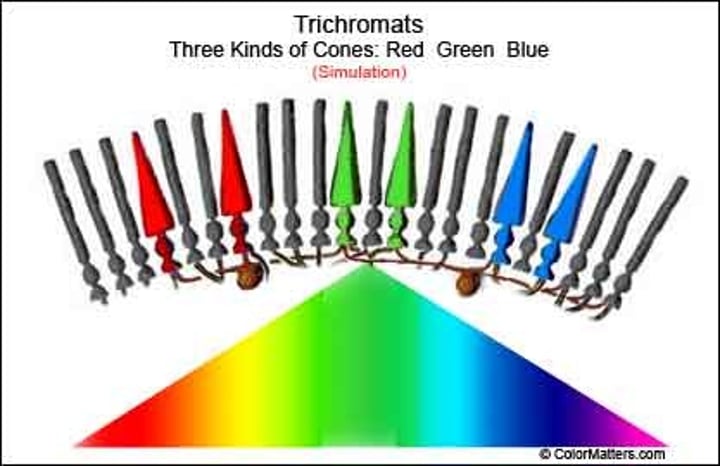
rods
Photoreceptors in the retina of the eye for black and white vision.
neuron
A nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system.
dendrites
part of neuron that receives stimuli from the environment or from other neurons
axon
part of neuron that carries information towards other cells
cell body
Largest part of a typical neuron; contains the nucleus and much of the cytoplasm
myelin
a fatty covering around the axon of some neurons that speeds up transmission of the neural impulse
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath of the axons. Action potentials can 'jump' from node to node, thus increasing the speed of conduction.
multiple sclerosis
The immune system attacks myelin, forming scar tissue (sclerosis) which gives the disease its name. This damage interrupts nerve impulses traveling to and from the brain and spinal cord.
neuroglia
Supporting cells ("glue") of the nervous system that support, insulate, and protect neurons but do not transmit nerve impulses
action potential
A neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon. The action potential is generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon's membrane. It is an "all-or-nothing" event.
axon terminal
the end ("terminal") of the axon on the presynaptic cell
synaptic vesicles
contain neurotransmitters
presynaptic cell
neuron that transmits a signal toward the synapse
postsynaptic cell
The neuron, muscle, or gland cell that receives the signal from a neuron
synaptic cleft
space separating presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes
Acetylcholine (ACh)
neurotransmitter widespread in CNS and PNS
polarized membrane
An axon membrane at rest where the inside of the cell is negative (-70 mv) compared with the outside of the cell
depolarized membrane
An axon membrane that becomes less negative (closer to 0 mv) than the resting potential of -70 mv
repolarized membrane
An axon membrane that is restored to its resting potential of -70 mv after depolarization
hyperpolarization
A change in the axon membrane potential from -70 mV (resting) to -90 mV, becoming more negative
sodium channels
voltage-gated channels in the axon's plasma membrane that allow sodium to move into the cell
potassium channels
voltage-gated channels in the axon's plasma membrane that allow potassium to move out of the cell
sodium-potassium pump
A protein pump in the plasma membrane of an axon that restores the membrane to its original polarized condition by using ATP to pump sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell
calcium channels
voltage-gated channels in the presynaptic terminal that allow calcium to enter and trigger the release of acetylcholine
resting potential
The difference in electric charge between the inside and outside of a neuron's cell membrane (more K ions inside, more Na ions outside); -70 mv
threshold
The level of stimulation required to activate a neuron
all-or-none principle
If the threshold is reached the action potential in the axon occurs either 100% or not at all.
central nervous system
A division of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
A division of the nervous system consisting of all sensory and motor neurons that are not part of the brain or spinal cord
somatic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's voluntary skeletal muscles
autonomic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls involuntary activity of smooth and cardiac muscle, and internal organs and glands.
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations; the "GAS"
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy; the "BRAKE"
reaction time
the amount of time needed for your brain to respond to a stimulus and initiate a response
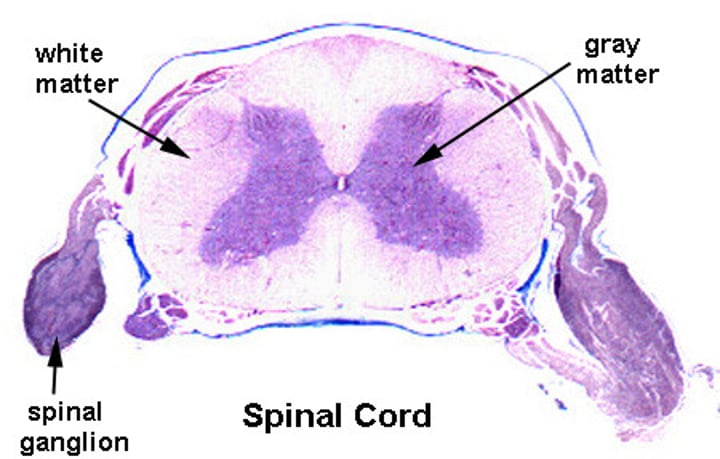
gray matter
Grayish nervous tissue of the CNS containing unmyelinated axons, neuron cell bodies, and dendrites
white matter
Whitish nervous tissue of the CNS consisting of neurons and their myelinated axons
brainstem
the major route by which the forebrain sends information to and receives information from the spinal cord and peripheral nerves; comprised of the medulla oblongata, the pons, and the midbrain.
medulla oblongata
the portion of the brainstem that controls respiration and regulation of heart rhythms
pons
the portion of the brainstem that "bridges" or connects the medulla oblongata with the cerebral cortex
midbrain
the portion of the brainstem that processes information from the superior colliculus [visual] and inferior colliculus [auditory], and helps maintain consciousness
cerebellum
the "little brain" structure located dorsal to the brainstem that helps control movement, balance, and muscle coordination
cerebral hemispheres
the two halves of the cerebrum
left cerebral hemisphere
brain area specialized for speech, writing, language, and calculations
right cerebral hemisphere
brain area specialized for spatial abilities, facial recognition, analyzing emotional context ("Get lost"), and some aspects of music perception and production
cerebrum
the largest of the three divisions of the brain; sub-divided into four lobes (frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital) and responsible for all forms of conscious experience including decision-making, perception, emotion, thought, language and vision
corpus callosum
a large bundle of nerve fibers (myelinated axons) that link the right and left hemispheres of the brain
meninges
three vascular membranes (the dura, arachnoid and pia mater) that cover and protect the brain and spinal cord against shocks, knocks, and vibrations
dura mater
tough, leathery outermost layer of the membranes surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord; Latin for 'tough mother'
arachnoid mater
spiderweb-like middle layer of the membranes surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord; Latin for 'spider(web) mother'
pia mater
delicate, innermost layer of the membranes surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord; Latin for 'delicate mother'
gyrus (plural = gyri)
the ridges or bumps of the cerebral surface
sulcus (plural = sulci; "sulky")
the valleys or depressions between the folds (gyri) of the brain
frontal lobe
front region of the cerebrum concerned with cognitive processes that include planning, inhibition of instincts and drives, and declarative memory
temporal lobe
brain lobe located near the temples and ear region of the cerebrum; functions include smell, taste, hearing, visual associations, some aspects of memory, and a person's sense of self
parietal lobe
cerebral lobe that interprets sensation; processes higher sensory and language functions
occipital lobe
in the posterior region of the cerebrum; receives sensory information from the eyes
hippocampus
C-shape band of fibers that sends memories out to the cerebral hemisphere for long-term storage, and retrieves them when necessary
thalamus
almost all sensory input and motor output goes through this "regulatory gateway" in the middle of the brain
hypothalamus
regulates homeostasis: emotions (joy, rage, sadness), thirst, hunger, body temperature, and sleep patterns; produces hormones.
pituitary gland
endocrine gland at the base of the brain that makes and releases hormones into the blood stream
myelin
fatty material that surrounds axons of many neurons creating white matter; speeds transmission of action potential movement down axons
ventricles
cavities inside the brain filled with cerebrospinal fluid to nourish and protect the brain and spinal cord
olfactory bulb
anterior part of the brain concerned with the sense of smell; innervated by Cranial Nerve I
optic nerve
nerve that connects the retina to the brain; Cranial Nerve II (2)
rostral
directional term referring to anterior portion of brain/towards the front ("rhymes with nostril")
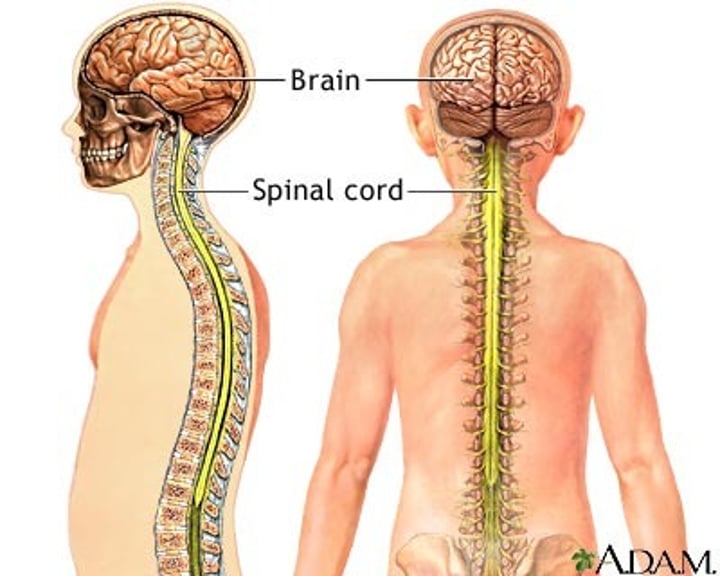
spinal cord
bundle of nerve fibers located inside the vertebrae that connects via the brainstem to the brain, and conducts sensory and motor information between brain and body
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
a progressive neurodegenerative disease causing motor neurons in the brain and the spinal cord to die; the brain can no longer control voluntary muscle movement. (Disorder name means "No muscle nourishment.")
rabies
a viral infection transmitted to humans by the bite of an infected animal; the virus travels up the axons by retrograde flow to the CNS
multiple sclerosis
a chronic disease of the central nervous system marked by damage to the myelin sheath; causes weakness, impaired vision and speech, and loss of muscle coordination
cerebral palsy
a group of disorders caused by brain injury or abnormal brain development before birth or early in life, resulting in the permanent (though not progressive) loss of a child's muscle control and coordination
Alzheimer disease
progressive disease of structural changes (plaques and tangles) in the brain resulting in an irreversible deterioration; progresses from forgetfulness and disorientation to loss of all intellectual functions, total disability, and death
What is the primary function of the spinal cord?
to integrate and process information
spinal meninges
specialized membranes that provide protection, stability, and shock absorption; continuous with cranial meninges
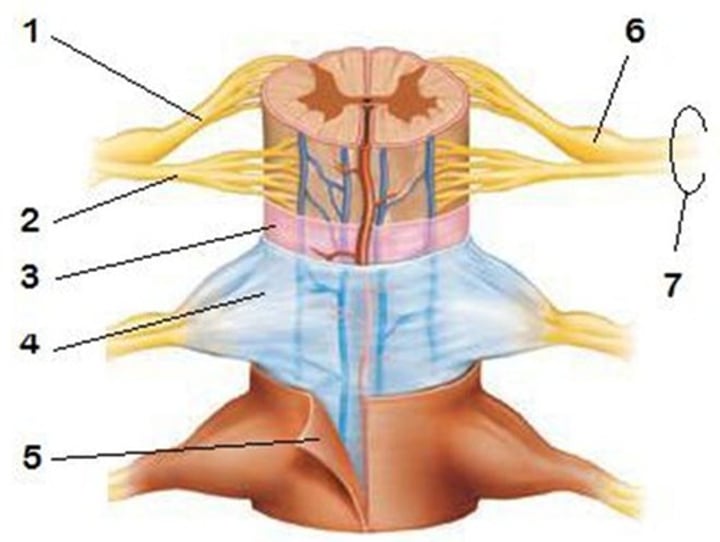
Name the spinal meninges from exterior to interior:
-dura mater
-arachnoid mater
-pia mater
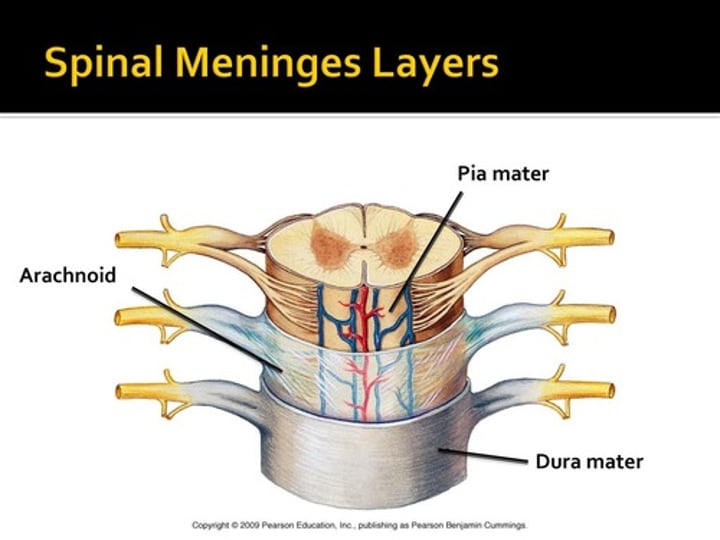
Dura mater
Tough, fibrous outermost layer of meninges that stabilizes the spinal cord within vertebral canal ("tough mother")
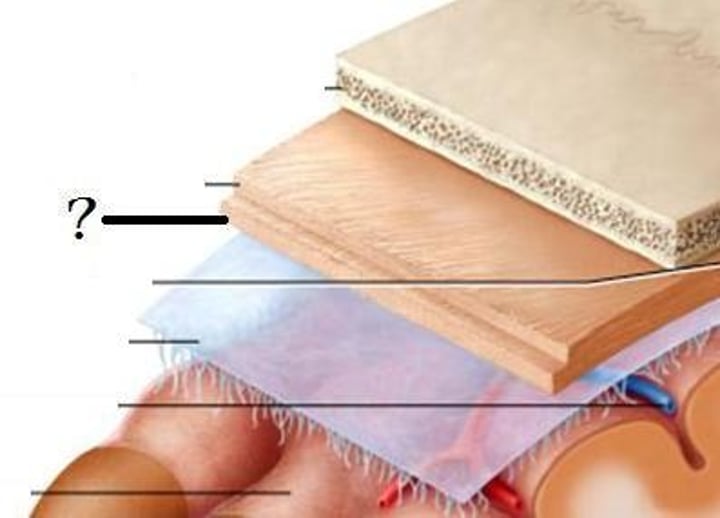
Arachnoid mater
"Spidery" middle layer of the meninges ("spider mother")
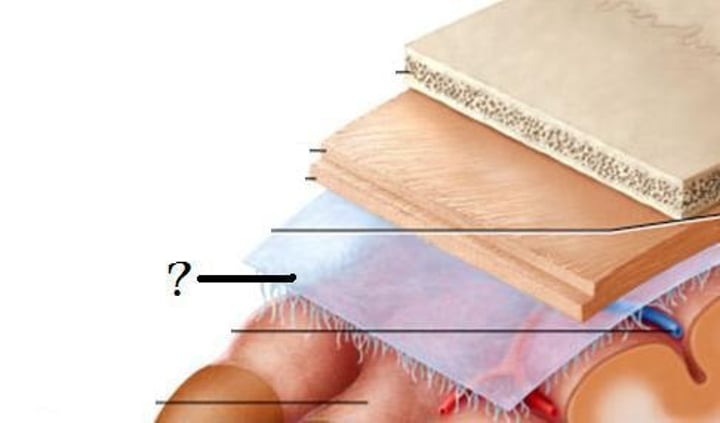
Pia mater
The deepest meningeal layer; blood vessels are found in this layer. This tissue is firmly bound to brain tissue and spinal cord tissue ("delicate mother")
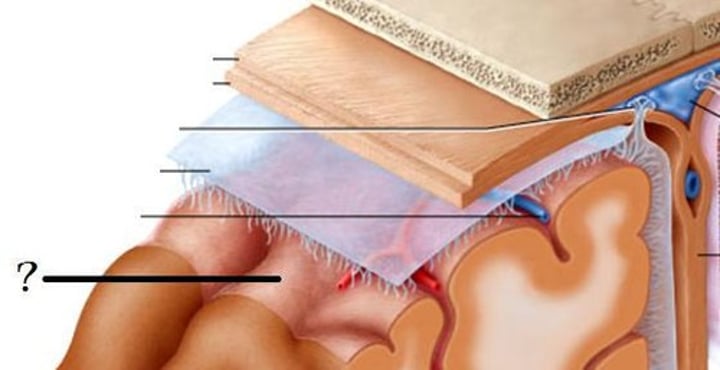
What does gray matter consist of?
neuron cell bodies and glial ("glue"; supporting) cells that are mostly unmyelinated
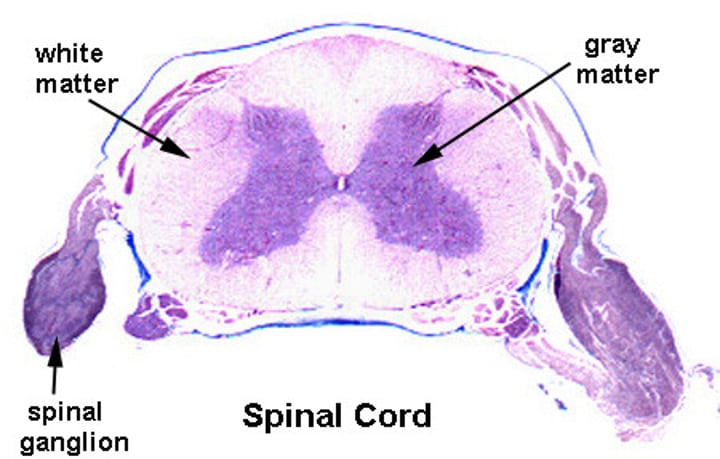
What does white matter consist of?
consists of axons (mostly myelinated); located outside gray matter area
31
Number of pairs of spinal nerves in the human body
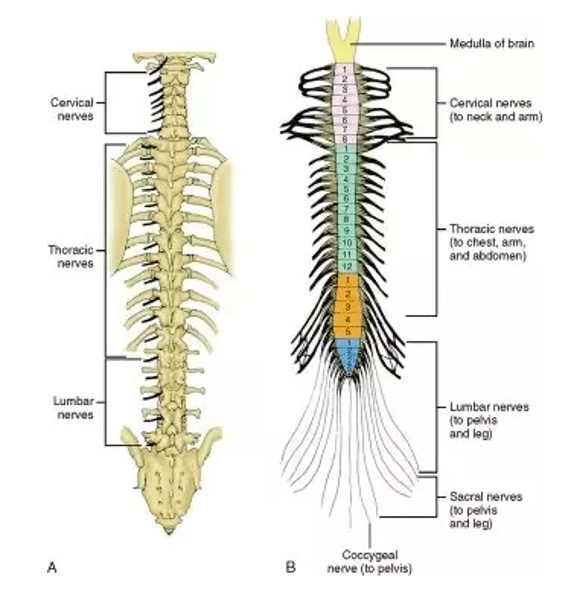
Order of spinal nerves from superior to inferior, with the number of spinal nerves in each division
-8 cervial nerves
-12 thoracic nerves
-5 lumbar nerves
-5 sacral nerves
-1 coccygeal nerve
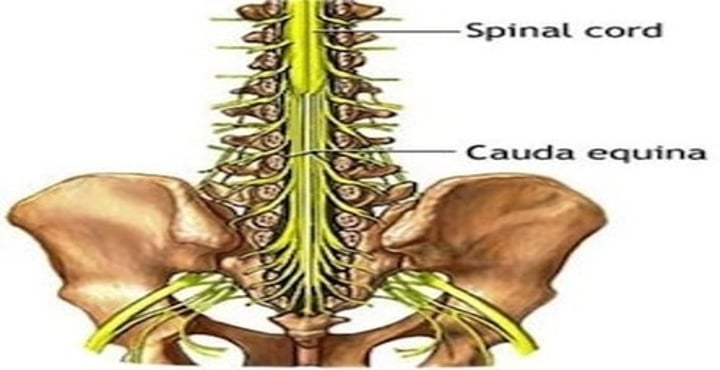
cauda equina
"horse's tail," a fan of nerve fibers at the inferior end of the spinal cord
reflex
a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus
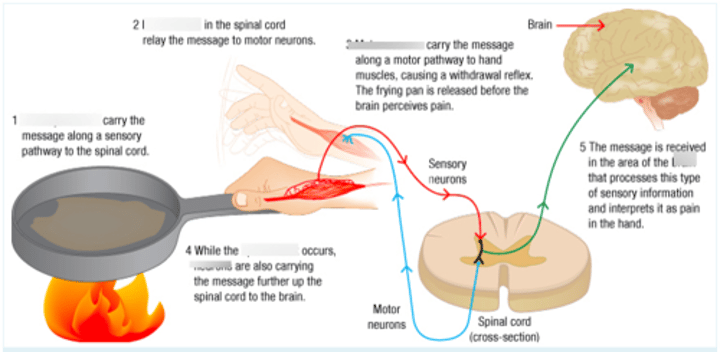
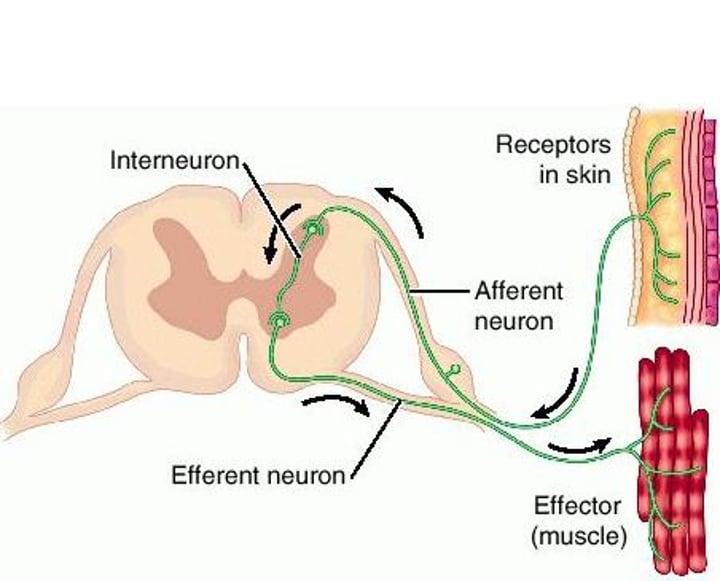
reflex arc
The nerve pathway involved in a reflex action, from receptor to effector. In vertebrates, most sensory neurons do not pass directly into the brain, but synapse in the spinal cord.
innate reflex
an inborn reflex
learned reflex
an acquired response to a stimulus; these are learned over time, and typically more complex (reactions that 'evolve' into reflexes)

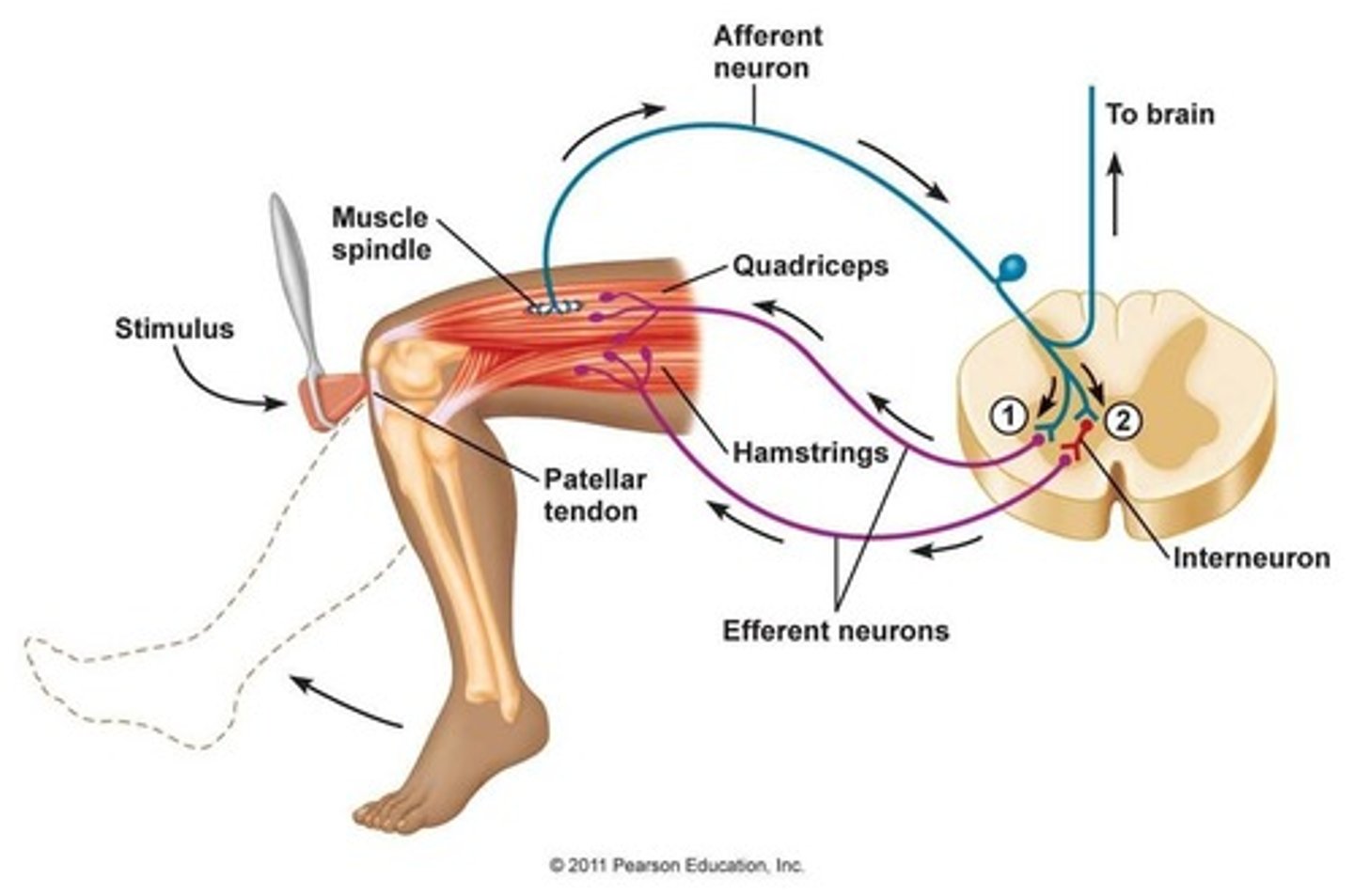
Name in order the 5 stages of a stretch reflex:
-1) stimulus stretches a muscle
-2) stretch receptors activated
-3) information is processed in spinal cord
-4) motor neurons are activated
-5) muscle (effector) contracts
Neural plasticity
The brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life. The brain can grow and change!
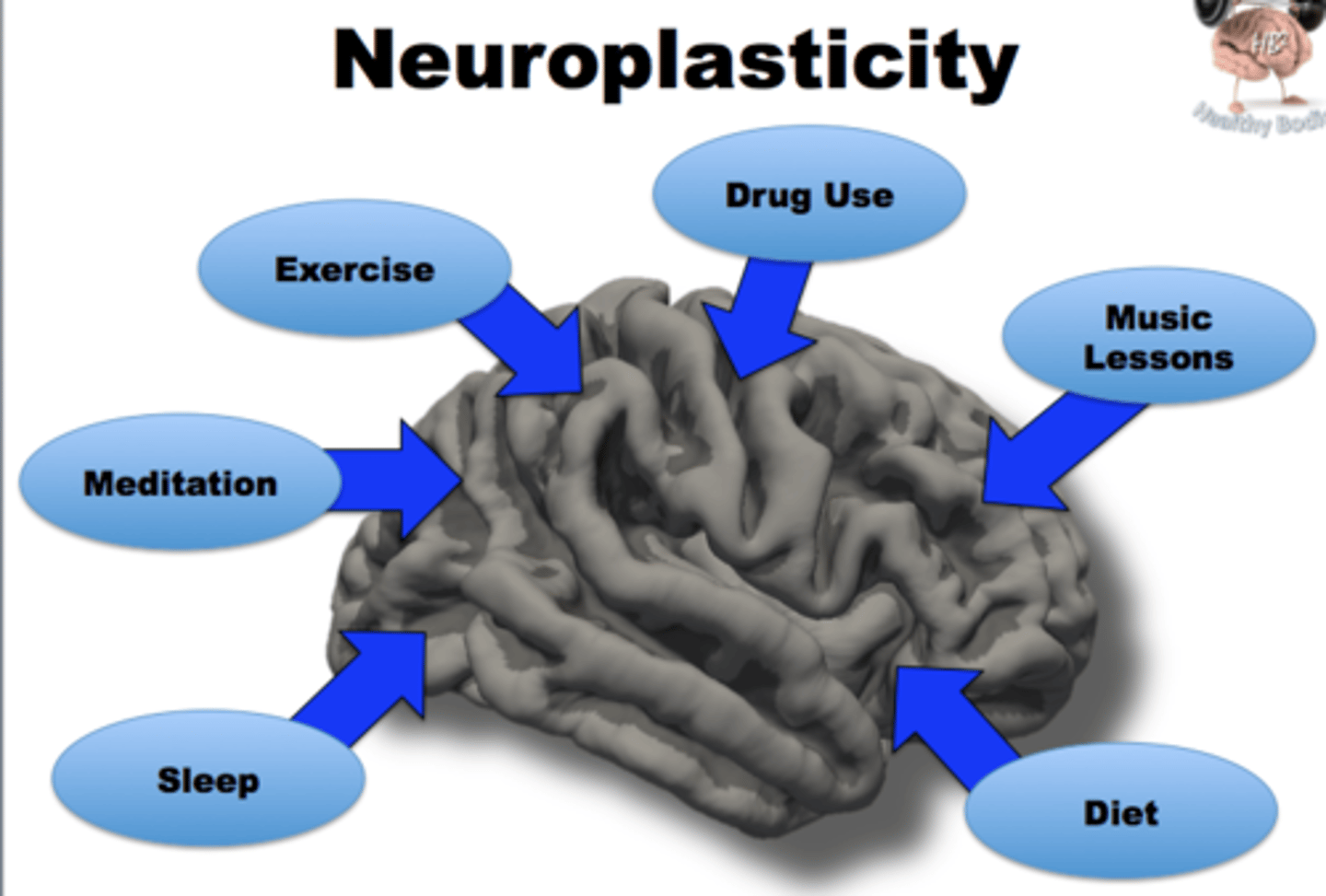
synaptic plasticity
the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, in response to increases or decreases in their activity (so "use it or lose it!")