psych 1010 exam 1
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ekker goat
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Who is the founder of psychology
Wilhelm Wundt and his laboratory
When was psychology founded
December of 1879
What are the schools of thought
structuralism and functionalism
structuralism
seeks to understand the structure of the mind and how they related to one another
methods:
introspection and experiments
promotors of structuralism
Wundt and Titchener
functionalism
seeked the functions of the mind and mental processes.
methods:
naturalistic observation
promotors of functionalism
James and influenced by Darwin
what is the definition of psychology
science of behavior and mental processes
related disciplines of psychology
physiology
philopsophy
humanistic psychology
historically significant perspective that emphasized human growth potential
cognitive psychology
the study of mental processes
What are the 6 psychological perspectives
- psychoanalytic/psychodynamic
- behaviorism
- humanism
- cognitive
- biological/neuroscience
- socio-cultural
PsychoANALYTIC/PsychoDYNAMIC
focus on unconcious experiences
Biological Urge (sex)
Aggressive Urge (fight)
Early childhood
Behaviorism
Focus on observable behavior
“did they get rewarded or punished for their actions.”
Enviroment > Genetics
Visual Learning
Founders of Behaviorism
Watson, Skinner, Pavlov
Founders of Psychoanalytic/Psychodynamic
Frued, Jung, Adler
Humanism
Focus on uniqueness and individuality
Freedom of choice
Founders of Humanism
Maslow, Rogers
Cognitive
Focus on the working mind
Decision making
problem solving
memory
Founders of cognitive
Piaget, Simon, Vygotsky
Biological/Neuroscience
Focus on genetics, biochem
stress reactions
founders of biological / neuroscience
Sperry, Olds, Gazzaniga
Socio-cultural
Focus on impact of others + situation on thoughts
Beauty and cultural standards
founders of socio-cultural
Bandura, Milgrim, Zimbardo
Biopsychological approach
integrated approach that incorporates biological, psychological, and social-cultural levels of analysis
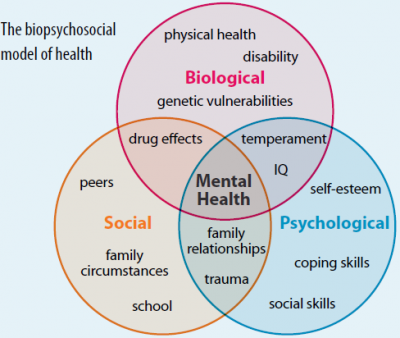
Applied Psychologies
clinical
counseling
psychiatry
industrial/organization
Dendrites
recieve
axons
transmit away
All or none law
neuron will fire once it hits the threshhold. Same power as if the threshold was hit quicker or slowly
absolute refractory period
times when a neuron resets
What is the hindsight bias
“i knew it all along” phenomenon
overconfidence error
thinking you were right when you werent
confirmation bias
“i believe this sm that idc to see other perspective”
barnum effect
accepting info as true (tarot card readers)
THE SCIENTIFIC ATTITUDE
curiosity
skepticism
humility
ethical safegrounds of psychological research (DRIPCF)
informed consent
confidentiality
freedom from coercion
protection from harm
risk benefit analysis
debriefing
hypothesis vs. theory
testable idea vs. well supported idea
types of psychological research
case study
naturalistic observation
survey
random sampling
equal chance of subjects
causation vs. correlation
correlation predicts
causation is the actual cause
random assignment
equal chance to be in either group
blind study
person doesn’t know which group they’re in
double blind study
neither groups know what group theyre in
pros of experiments
isolates the cause and effect
cons of experiments
costly
unethical
logistics
CNS
brain and spinal cord
decisions for the body
PNS
rest of the nervous system
gathers and sends info to and from the body
Neuron types
sensory, motor, and interneurons
sensor neurons
carry messages from sensory recpetor to CNS
interneuron
in the brain and spinal cord
processes info
motor neuron
carry instructions out from CNS to body tissue
agonist
mimic neurotransmitter action
antagonist
oppose neurotransmitter action
Acetylcholine Ach (NT)
attention and learning
deficit relates to alzheimers
Dopamine (NT)
motivation, pleasure movements,
high levels —> schizo
low levels —> parkinsons disease
Glutamate (NT)
excitement; increases information transfer
high levels —> seizures
GABA (NT)
slows down information transfer
low levels —> seizures
Norepinephrine (NT)
Mood, arousal
low levels —> mood disorders
serotonin (NT)
sleep, eating, mood, agression
abnormal levels —> depression and OCD
Endorphin (NT)
similar to opiate drugs
but they’re naturally and internally produced
Can dull pain and elevate mood
sympathetic NS vs parasympathetic NS
arousing vs. calming
autonomic (PNS)
controls self regulating actions
somatic (PNS)
control of voluntary movements of skeletal muscles
research methods to studying the brain
damage studying (leisions)
electrical stimulation
brain imaging
left side of brain
Logic and analytic thinking
right hand
right side of brain
creativity
left hand
split brain surgery
difficulties coordinating tasks w both hands
Phineas gage
a guy that got a pole stuck in his head. still survived just had seizures and had personality changes but sitll had memory