Quiz 2
5.0(1)Studied by 3 people
Card Sorting
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:36 PM on 3/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
1
New cards
How do cells solve the problem of protecting and compartmentalizing cellular components?
Lipid bilayers
2
New cards
Fluid-Mosaic Model
* Within the “sea” of membrane lipids, integral membrane proteins are floating around
* All cellular membranes have lots of proteins embedded in them
* All cellular membranes have lots of proteins embedded in them
3
New cards
What does it mean that lipid bilayers are selectively permeable?
Certain substances can readily diffuse across the membrane, certain substances can cross the membrane (but not easily), and certain substances cannot pass the membrane at all
4
New cards
What factors affect the rate of diffusion across a membrane?
1. Size
2. Charge
5
New cards
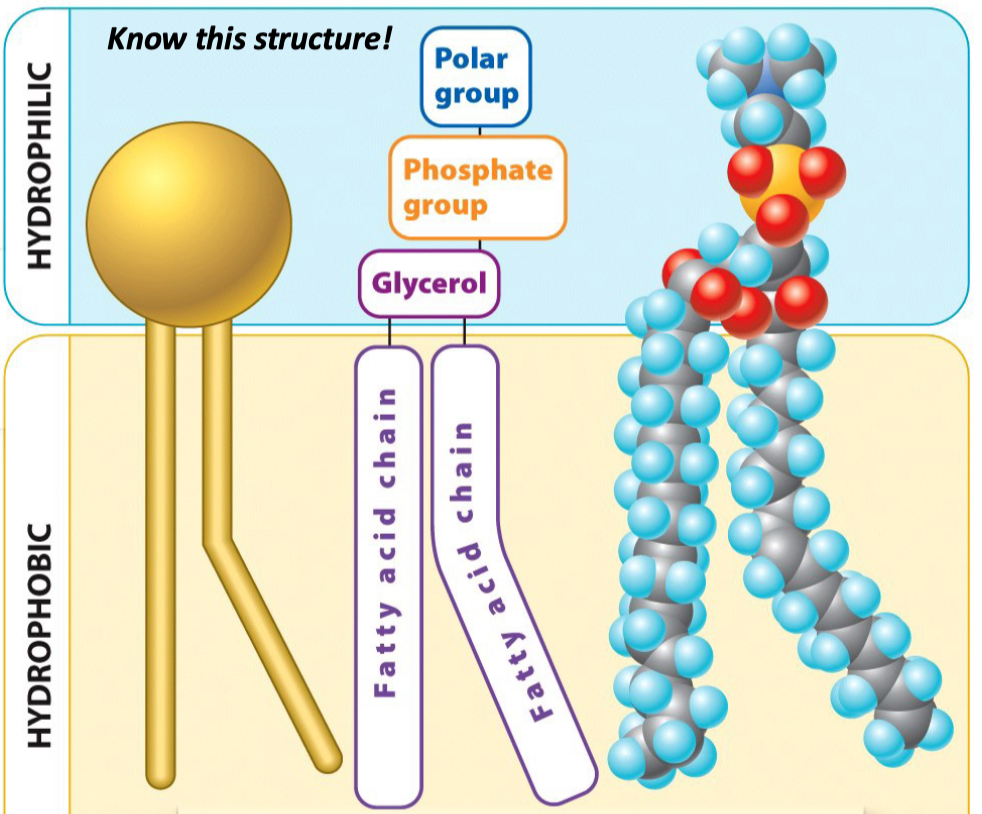
Structure of a phospholipid
Hydrophilic head
1. Polar group
2. Phosphate group
3. Glycerol
Hydrophobic tails
1. 2 fatty acid chains
1. Polar group
2. Phosphate group
3. Glycerol
Hydrophobic tails
1. 2 fatty acid chains
6
New cards
Amphipathic
Having a hydrophilic part and hydrophobic part (ex. phospholipid)
7
New cards
What is the most chemically variable portion of a lipid?
* The polar group/head group
* Can confer unique functions to the lipid
* Can confer unique functions to the lipid
8
New cards
How can fatty acid tails in a lipid vary?
* Length
* # of kinks (C=C bonds)
* # of kinks (C=C bonds)
9
New cards
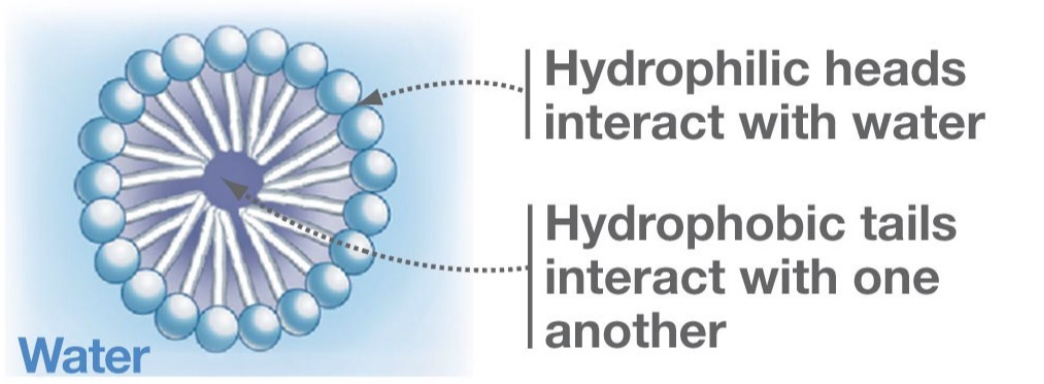
Micelles
* Spherical structure spontaneously formed by single layer of lipids
* Formed by cone-shaped phospholipids (1 fatty tail)
* Formed by cone-shaped phospholipids (1 fatty tail)
10
New cards
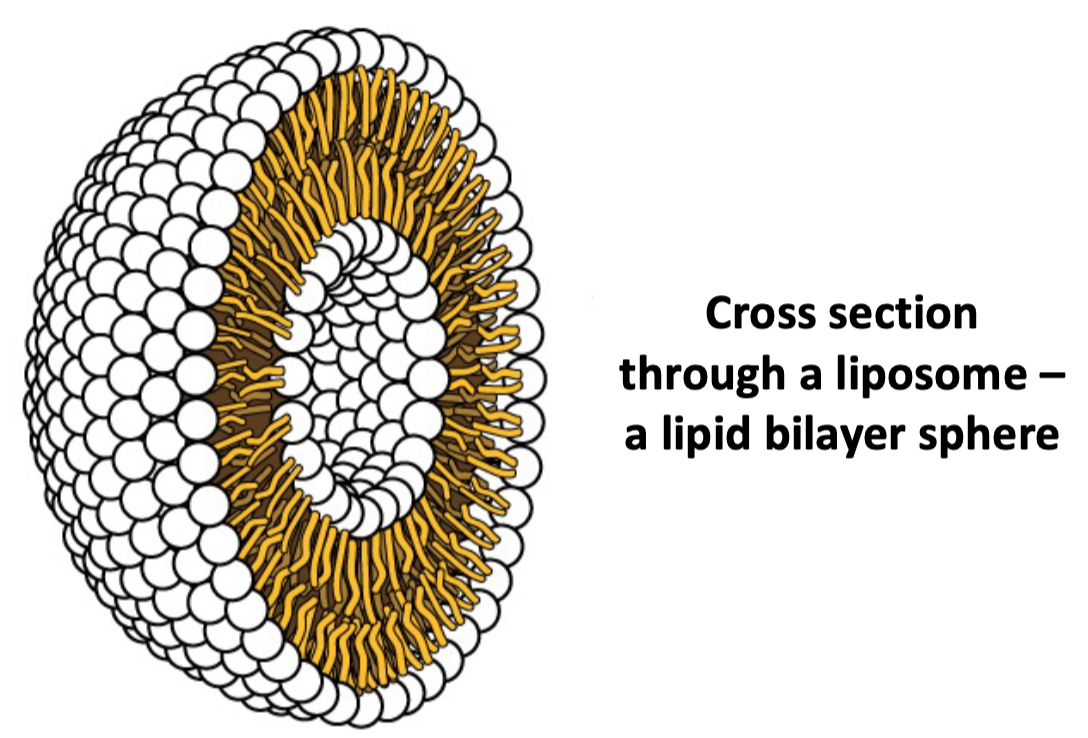
Liposome
* Spherical structure spontaneously formed by double layer of lipids
* Formed by cylinder-shaped phospholipids (2 fatty tails)
* Formed by cylinder-shaped phospholipids (2 fatty tails)
11
New cards
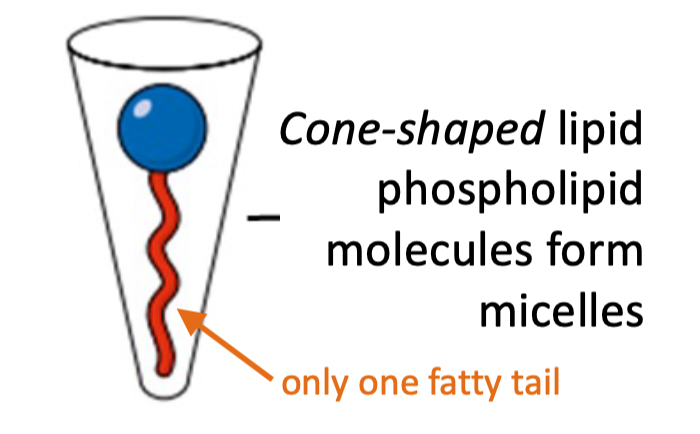
Cone-shaped phospholipid
* 1 fatty tail
* Forms micelles
* Forms micelles
12
New cards
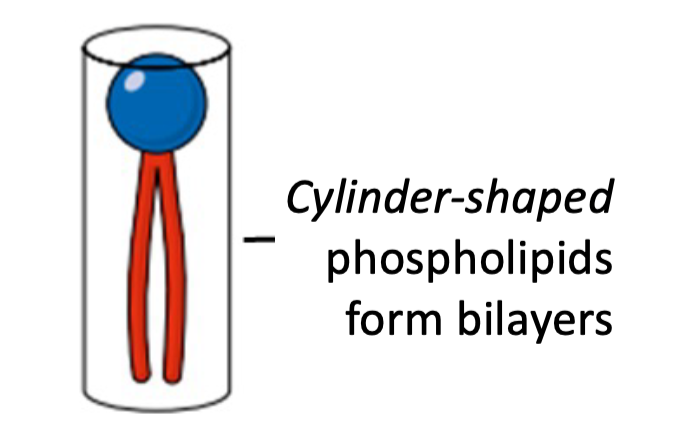
Cylinder-shaped phospholipid
* 2 fatty tails
* Form liposomes/bilayers
* Form liposomes/bilayers
13
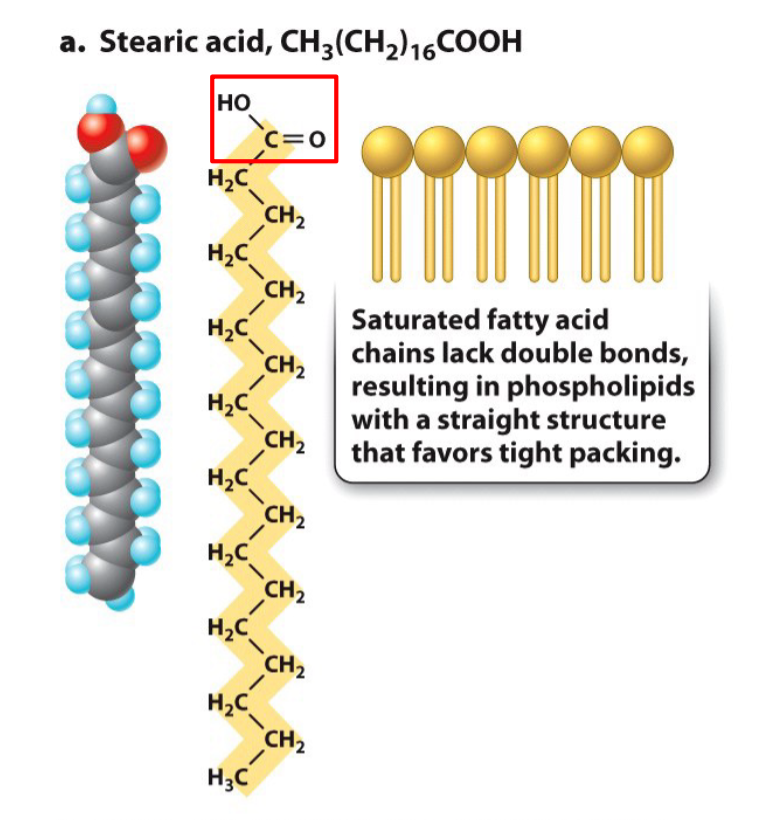
New cards
Saturated hydrocarbon chains
Hydrocarbons have maximum hydrogen bonding and no C=C double bonds
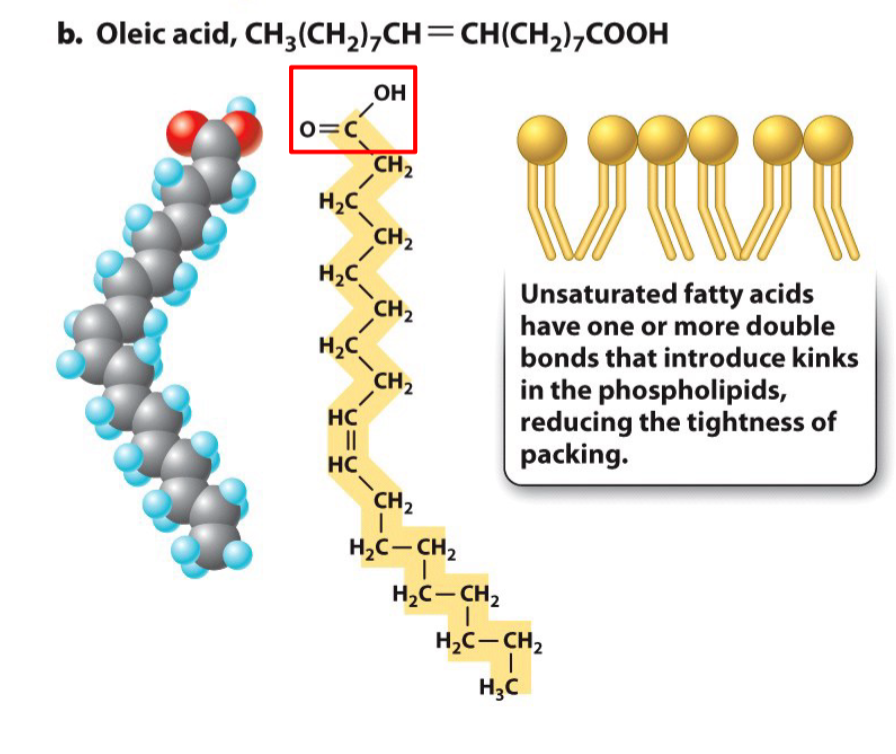
14
New cards
Unsaturated hydrocarbon chains
* Missing some hydrogens, so have C=C bonds
* Causes a bend or __**kink**__ in the chain
* Prevents close packing of hydrocarbon tails and reduces hydrophobic interactions
* Causes a bend or __**kink**__ in the chain
* Prevents close packing of hydrocarbon tails and reduces hydrophobic interactions
15
New cards
Why are hydrocarbon chains called (fatty) acids?
Because they have a hydroxyl group that can act as an acid and give up H+
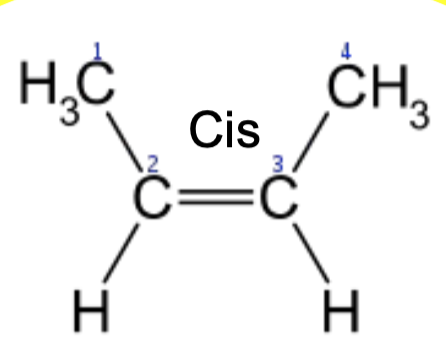
16
New cards
Cis-double bonds in fatty acid tails
* Occur naturally
* Two H on the same side
* Two non-H on the same side
* Cis = same
* Two H on the same side
* Two non-H on the same side
* Cis = same
17
New cards
How do saturated vs. unsaturated fatty acids affect membrane permeability?
* No unsaturated fatty acids = low permeability
* Many unsaturated fatty acids = high permeability
* More porous
* Many unsaturated fatty acids = high permeability
* More porous
18
New cards
Cholesterol
* Makes membranes more rigid, less permeable, a stabilized to fluidity changes
* Steroid molecule
* Present in most eukaryotic membranes
* Amphipathic structure
* Steroid molecule
* Present in most eukaryotic membranes
* Amphipathic structure
19
New cards
How does temperature affect membrane fluidity and permeability?
* ==Higher temperature== = higher fluidity = higher permeability
* ^^Lower temperature^^ = lower fluidity = less permeability
* ^^Lower temperature^^ = lower fluidity = less permeability
20
New cards
How does the length of fatty acid tails affect membrane permeability?
* Longer tails = less permeable
* Shorter tails = more permeable
* Shorter tails = more permeable
21
New cards
Diffusion
* Ions and molecules diffuse spontaneously from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration
* Driven by entropy (tendency of the universe to become more disordered)
* Driven by entropy (tendency of the universe to become more disordered)
22
New cards
What types of molecules can diffuse through a membrane?
* Small mostly non-polar molecules
* Very small polar molecules (ex. water)
* Very small polar molecules (ex. water)
23
New cards
Osmosis
* The movement of water across a semipermeable membrane
* Water is drawn toward higher *solute* concentration
* Water is drawn toward higher *solute* concentration
24
New cards
What happens to a cell in a hypertonic solution?
Cell shrinks
* Water moves out of the cell to area of higher solute concentration
* Water moves out of the cell to area of higher solute concentration
25
New cards
What happens to a cell in a hypotonic solution?
Cell swells/lyses
* Water moves into the cell to an area of higher solute concentration
* Water moves into the cell to an area of higher solute concentration
26
New cards
Hypertonic solution
Compared to cell, solution has higher solute concentration
27
New cards
Hypotonic solution
Compared to cell, solution has lower solute concentration
28
New cards
Transmembrane/integral membrane proteins (def’n, characteristic, shape)
* Transverse the entire membrane
* Tend to contain hydrophobic amino acid residues (that interact with the hydrophobic core of the membrane)
* Usually form alpha helix
* Tend to contain hydrophobic amino acid residues (that interact with the hydrophobic core of the membrane)
* Usually form alpha helix
29
New cards
Peripheral membrane proteins
* Reversibly associated with either the internal or external side of the membrane
* Could be bound to a lipid or another protein embedded in the membrane
* Could be bound to a lipid or another protein embedded in the membrane
30
New cards
How do ion channels and transporters influence membrane permeability?
By allowing specific polar solutes to pass that are normally impermeable
31
New cards
Ion channels
* Open to allow a specific solute to pass (usually ions)
* Either open or closed
* Open/closed status is regulated: “gated”
* Either open or closed
* Open/closed status is regulated: “gated”
32
New cards
Transporters/carrier proteins
* Undergo conformational (shape) change
* Bind solutes on one side of the membrane and release them on the other
* Bind solutes on one side of the membrane and release them on the other
33
New cards
Passive transport
* Occurs when a solute moves down its concentration gradient (high to low concentration)
* Occurs spontaneously (no energy input needed) due to diffusion
* Can occur through the membrane directly or through a channel/transporter protein
* Occurs spontaneously (no energy input needed) due to diffusion
* Can occur through the membrane directly or through a channel/transporter protein
34
New cards
Active transport/pumping
* Occurs when a cell expends energy (usually ATP) to move a solute against its concentration gradient (low to high concentration)
* Requires a protein pump
* Requires a protein pump
35
New cards
Simple diffusion
Solute passes through the membrane along its concentration gradient by itself (no channel/transporter protein or energy required)
* Passive transport
* Passive transport
36
New cards
Facilitated diffusion
Solute passes through membrane via a transporter or channel protein along its concentration gradient
* Passive transport
* Passive transport
37
New cards
Sodium-potassium pump (+ where does it get energy)
* Uses energy of ATP hydrolysis to create electrochemical gradient
* Animal cells
* Pumps Na+ ions out of the cell
* As a result, Na+ higher outside the cell
* Pumps K+ ions into the cell
* As a result, K+ is higher inside the cell
* Animal cells
* Pumps Na+ ions out of the cell
* As a result, Na+ higher outside the cell
* Pumps K+ ions into the cell
* As a result, K+ is higher inside the cell
38
New cards
Gradients are a form of ________ energy
Stored (potential)
39
New cards
Coupled transport
* One molecules moves down its concentration gradient, releasing energy
* Potential energy of electrochemical gradient (generated by active transport)
* Another molecule is driven with this energy to move against its concentration gradient
* Potential energy of electrochemical gradient (generated by active transport)
* Another molecule is driven with this energy to move against its concentration gradient
40
New cards
What types of things can pass through cell surface transporters? Why?
* Amino acids and nucleotides can pass
* Small monomers
* Nucleic acids and proteins cannot pass
* Larger
* Reason: there is a size limit to what can enter cells through transporters/channels; transporters/channels are selective
* Small monomers
* Nucleic acids and proteins cannot pass
* Larger
* Reason: there is a size limit to what can enter cells through transporters/channels; transporters/channels are selective
41
New cards
Selective
Binds/recognizes or allows passage of some things but not others
42
New cards
What do all cells have?
1. __Plasma membrane__ (separates cell from its environment)
2. __DNA__ (genome = entire chromosomal DNA seq. of cell)
3. __Cytosol__ (aqueous interior of cell)
4. __Ribosomes__ (‘machines’ for protein synthesis)
5. __Cytoskeleton__ (structural support)
43
New cards
What are things that only some cells have?
1. Nucleus (encloses genome)
2. Organelles (membrane-enclosed sub compartments)
3. Cell wall (protective outer layer)
4. Flagellum/cilium (projection for movement)
44
New cards
Plasma membrane
Acts as a selective barrier against the extracellular environment
45
New cards
What is characteristic of eukaryotic cells?
* Nucleus
* Bigger
* Organelles (many intracellular membranes)
* Bigger
* Organelles (many intracellular membranes)
46
New cards
Motile
Many __bacteria__ are motile (can move) due to the presence of __flagella__
47
New cards
Plasmid
Prokaryotes may contain a small, __circular piece of extra-chromosomal DNA__ called a plasmid
* Easily shared
* Often where bacteria have genes conferring antibacterial resistance
* Easily shared
* Often where bacteria have genes conferring antibacterial resistance
48
New cards
Nucleoid
Circular chromosome is supercoiled into nucleoid (one big packaged chromosome)
49
New cards
Cell wall (bacteria)
Almost all bacteria have a __semi-rigid__ but __permeable__ cell wall composed of __peptidoglycan__ that __prevents osmotic lysis__
50
New cards
Mitochondria
* Harness energy from chemical compounds (e.g. glucose, fats)
* Convert energy into ATP
* Present in virtually all eukaryotes (including plant cells)
* Double membrane with aqueous compartment in between
* Convert energy into ATP
* Present in virtually all eukaryotes (including plant cells)
* Double membrane with aqueous compartment in between
51
New cards
Chloroplasts
* Capture the sun’s energy
* Synthesize simple sugars via photosynthesis
* Double membrane with additional third interior membrane (thylakoid membrane)
* Synthesize simple sugars via photosynthesis
* Double membrane with additional third interior membrane (thylakoid membrane)
52
New cards
Life originated as _____________
Prokaryotic (no nucleus nor intracellular membranes)
53
New cards
Endomembrane system
* Evolved from inner folds of the plasma membrane
* Pinched off and enclosed DNA (nucleus)
* Created eukaryotes
* Refers to the set of intracellular organelles that are interconnected via vesicular traffic
* Pinched off and enclosed DNA (nucleus)
* Created eukaryotes
* Refers to the set of intracellular organelles that are interconnected via vesicular traffic
54
New cards
Membranes of which organelles are __*not*__ part of the endomembrane system?
* **Mitochondria**
* **Chloroplast**
* These were engulfed: endosymbiotic theory
* They grow and multiply independently of other membrane compartments
* **Chloroplast**
* These were engulfed: endosymbiotic theory
* They grow and multiply independently of other membrane compartments
55
New cards
Endosymbiotic theory
Mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved from __engulfed prokaryotes__ that gave an advantage to the host eukaryotic cell
56
New cards
Zip code hypothesis
Proteins are directed to the correct cellular location by signals within their amino acid sequence
* Usually encoded by primary amino acid sequence
* Zip codes are most prevalent in eukaryotes
* Usually encoded by primary amino acid sequence
* Zip codes are most prevalent in eukaryotes
57
New cards
What is the default location for a protein in the absence of a specific signal/zip code?
Cytoplasm/cytosol
58
New cards
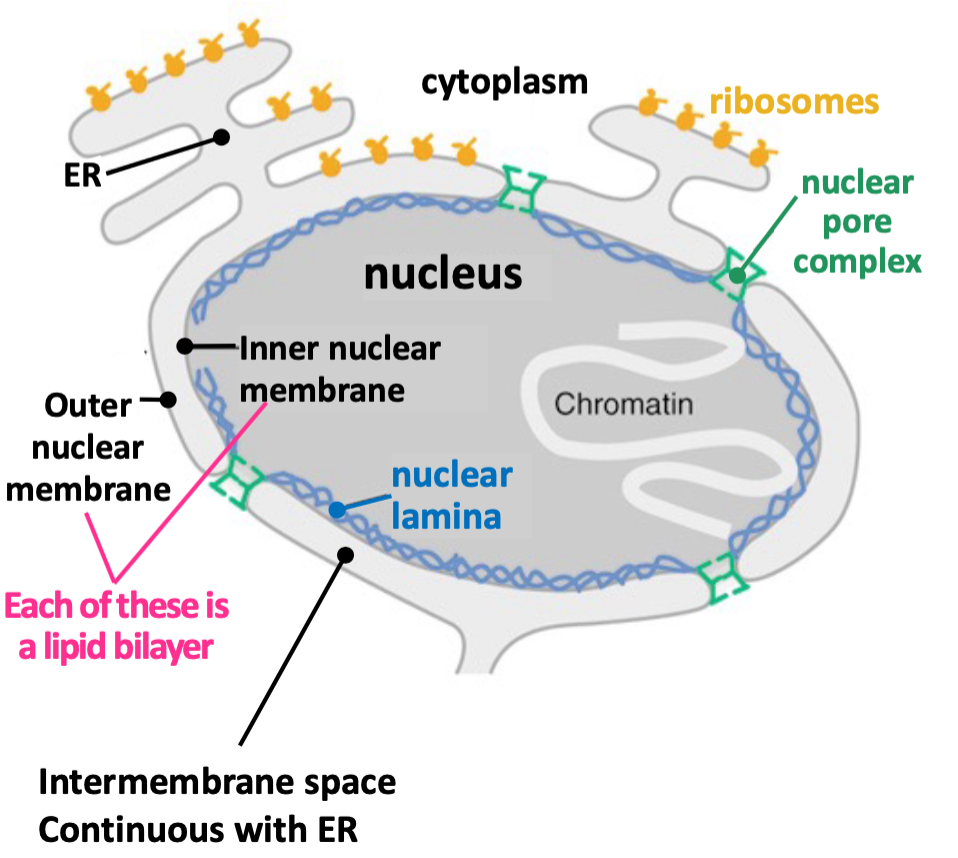
Nuclear envelope
* Double-membrane structure that contains nucleus
* Continuous with __ER__
* Supported by __nuclear lamina__ (cytoskeletal structure)
* Perforated by __nuclear pore complexes__ that act as gates
* Continuous with __ER__
* Supported by __nuclear lamina__ (cytoskeletal structure)
* Perforated by __nuclear pore complexes__ that act as gates
59
New cards
Nuclear pore complexes (NPCs)
Allow selective passage of molecules between nucleus and cytoplasm
60
New cards
Vesicular traffic
Refers to when membrane bound structures are budding off and/or fusing with another membrane bound structure
61
New cards
Members of endomembrane system
1. ER
2. Golgi
3. Lysosome
4. Endosomes
5. Plasma membrane
62
New cards
Exocytosis
A vesicle that has budded off from the endomembrane system can fuse with the plasma membrane and deliver its contents into the extracellular space
* Things are sent out of the cell
* Things are sent out of the cell
63
New cards
Endocytosis
Material from outside the cell is brought into a vesicle that can then fuse with other organelles
* Bringing things into the cell
* Bringing things into the cell
64
New cards
Vesicular transport
A vesicle can pinch off of one membrane and fuse with another
65
New cards
What characteristic of cells allows vesicular transport to occur?
Lipid bilayers are fluid and can fuse and intermix with each other
66
New cards
Rough ER vs. smooth ER
* Rough ER: integral membrane and lumenal protein synthesis
* Has ribosomes bound to it (in the process of translating something)
* Smooth ER: primary site of lipid synthesis
* No ribosomes
* Has ribosomes bound to it (in the process of translating something)
* Smooth ER: primary site of lipid synthesis
* No ribosomes
67
New cards
Where are integral membrane proteins and proteins inside the endomembrane system synthesized?
ER
68
New cards
Secretion/exocytosis
Vesicular transport out of the cell
69
New cards
What is the secretary pathway through the cell?
1. ER
2. Golgi
3. Plasma membrane
Note: some proteins that are needed to function in the ER or Golgi can be retained there by mechanisms similar to the zip code concept
70
New cards
Glycosylation
* Proteins that go through the ER and Golgi are __glycosylated = covalently attached to carbohydrate chains__ (modified by carbohydrates)
* Occurs in the lumen of the Golgi
* This is why cell-surface and extracellular proteins are glycoproteins
* For integral plasma membrane proteins, the lumenal, glycosylated portions end up in the extracellular space
* Occurs in the lumen of the Golgi
* This is why cell-surface and extracellular proteins are glycoproteins
* For integral plasma membrane proteins, the lumenal, glycosylated portions end up in the extracellular space
71
New cards
Endoplasmic reticulum structure
Forms a continuous network of __interconnected membrane tubules__ (some rough, some smooth)
72
New cards
Cisternae
The Golgi apparatus consists of a series of __flattened membrane sacs__ called cisternae
73
New cards
Endocytic pathway
Stuff outside the cell or in the plasma membrane can be brought __into the cell__ by endocytosis
* Endocytic cargo can be recycled (sent back to the plasma membrane) or directed to a lysosome
* This is *not* done because the cell wants the protein it is bringing in (if that were the case, the cell would just make the protein itself); it is usually about bringing something in to be degraded
* Endocytic cargo can be recycled (sent back to the plasma membrane) or directed to a lysosome
* This is *not* done because the cell wants the protein it is bringing in (if that were the case, the cell would just make the protein itself); it is usually about bringing something in to be degraded
74
New cards
Lysosomes
* Acidic and degradative organelles
* They break down any biological molecule brought to them into building blocks for reuse
* Cellular compost bin
* They break down any biological molecule brought to them into building blocks for reuse
* Cellular compost bin
75
New cards
How do lysosomes maintain an acidic pH?
Proton pumps
76
New cards
Lysosomal/acidic hydrolases
Degrading enzymes that only work at low pH
77
New cards
Signal/signal sequence
* Signal within protein that is currently being translated directed a ribosome to the surface of the ER
* At the ER, the ribosome associates with a translocation channel through which the protein’s synthesis is completed, resulting in a lumenal protein or integral membrane protein
* At the ER, the ribosome associates with a translocation channel through which the protein’s synthesis is completed, resulting in a lumenal protein or integral membrane protein
78
New cards
Series of events leading to synthesis of lumenal/membrane protein
1. Signal recognition particle __(SRP)__ binds to a signal sequence in the amino end of the growing polypeptide, __halting translation__
2. SRP binds to SRP receptor on ER membrane
3. SRP receptor brings ribosome to transmembrane channel (SRP dissociates)
4. Protein synthesis resumes; growing polypeptide chain is threaded through the channel
5. Protein ends up in the lumen of the ER where it will remain, be transported to the lumen of another organelle, or be secreted out of the cell
79
New cards
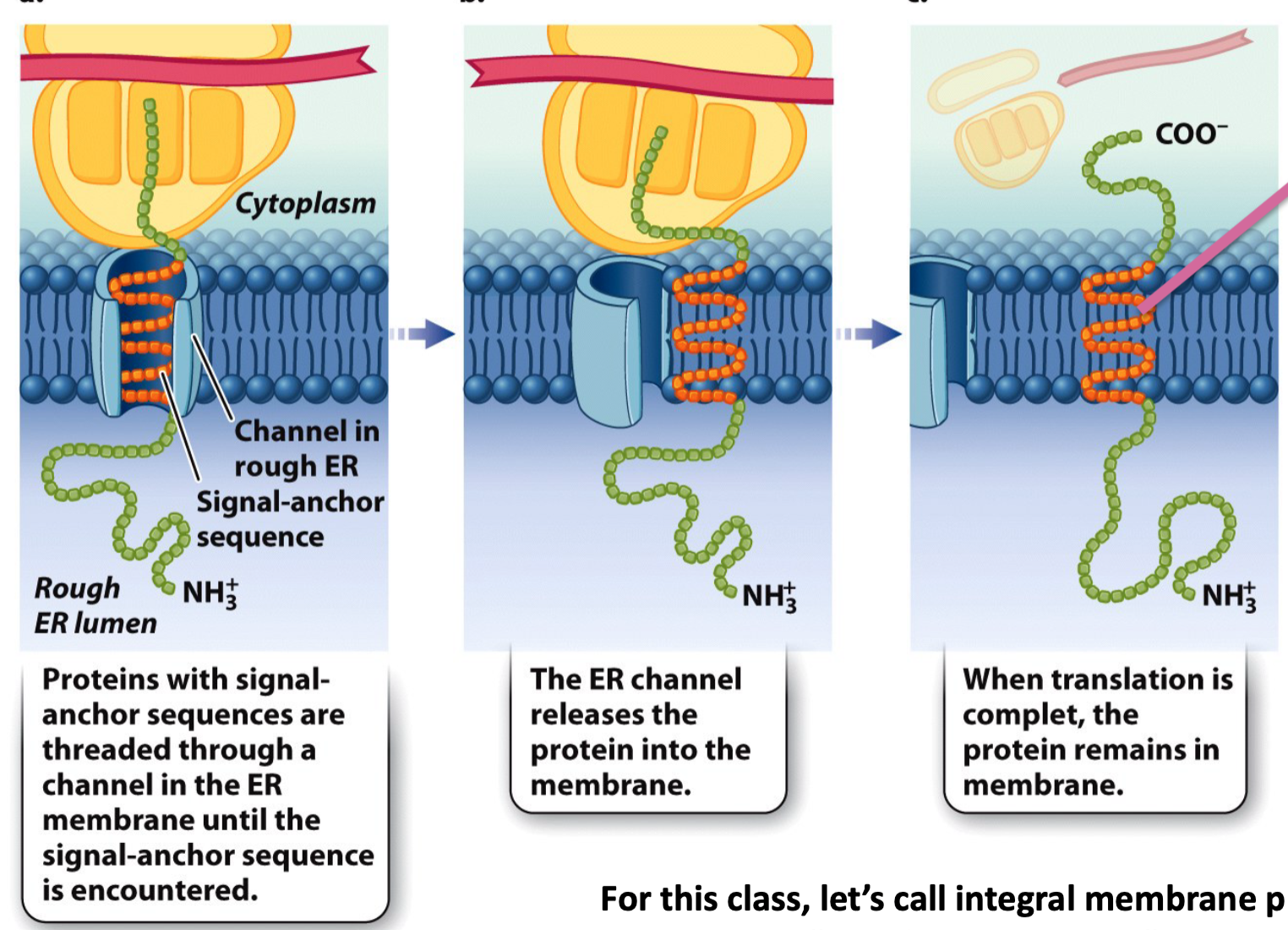
Signal anchor sequences
* Signal anchor sequences become transmembrane domains in transmembrane proteins
* Hydrophobic portion
* They are released from the translocation channel into the ER membrane and diffuse laterally into its lipid bilayer
* Hydrophobic portion
* They are released from the translocation channel into the ER membrane and diffuse laterally into its lipid bilayer
80
New cards
General cytoskeletal functions
1. Structure and support
1. Shape, strength
2. Shape could include controlling membrane projections
2. Intracellular transport
3. Contractility and motility
4. Spatial organization
81
New cards
What types of subunits does the cytoskeleton consist of?
Noncovalent polymers of protein
* Microtubules (smallest)
* Microfilaments (biggest)
* Intermediate filaments (middle)
* Microtubules (smallest)
* Microfilaments (biggest)
* Intermediate filaments (middle)
82
New cards
Microtubule
* Smallest
* Hollow tube formed from tubulin dimers
* More rigid than actin or intermediate filaments and rupture when stretched
* Globular shaped
* Consists of alpha and beta tubulin
* Hollow tube formed from tubulin dimers
* More rigid than actin or intermediate filaments and rupture when stretched
* Globular shaped
* Consists of alpha and beta tubulin
83
New cards
Microfilaments
* Largest
* Double helix of actin monomers
* Actin = 3º protein structure that binds to itself
* Flexible
* Most concentrated just beneath the plasma membrane
* Double helix of actin monomers
* Actin = 3º protein structure that binds to itself
* Flexible
* Most concentrated just beneath the plasma membrane
84
New cards
Intermediate filaments
* Strong fiber composed of intermediate filament proteins
* Fibrous (stringy) subunits; rope-like
* Doesn’t fold into globular shape
* Provide cell mechanical strength
* Very flexible
* Fibrous (stringy) subunits; rope-like
* Doesn’t fold into globular shape
* Provide cell mechanical strength
* Very flexible