Lesson 29 - Neuroanatomy of the Neck and Forelimb
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
What is the length of the spinal cord in relation to the vertebral column?
shorter
What does the neural canal extend to in most cases?
5th coccygeal vertebra
How many vertebra and spinal cord segments do dogs have?
35 vertebrae, 36 spinal cord segments
How many vertebra and spinal cord segments do horses have?
41 vertebrae, 42 spinal cord segments
How many vertebra and spinal cord segments do bovine have?
36 vertebrae, 37 spinal cord segments
What are the five major segments of the spinal cord?
1. C1 - C5 (Cervical)
2. C6 - T2 (Cervico-thoracic)
3. T3 - L3 (Thoraco-lumbar)
4. L4 - S1 (Lumbo-sacral)
5. S2 - Cd5 (Sacro-caudal)
What is the conus medullaris?
terminal conical part of spinal cord
Where is the conus medullaris in dogs?
L6 or L7
Where is the conus medullaris in cats?
variably between L6 and S3
Where is the conus medullaris in horses?
S2
What is the filum terminale?
thin extension of the modified pia matter surrounded by dura matter
What is the cauda equina?
bundle of spinal nerves spinal nerves L6-Cd5 that continue caudally after spinal cord terminates
What nerves are included in the cauda equina?
sciatic (L6-S2) and pudendal (S1-S3) nerves
Where do spinal nerves lie in relation to their respective vertebra in the cervical region?
in front of the respective cervical vertebra
Where does the 8th spinal nerve exit the neural canal?
caudal to the 7th cervical vertebra
What regions of the spinal cord have an equal number of spinal cord segments and vertebrae?
thoracic, lumbar, sacral
Where do spinal nerves lie in relation to their respective vertebra from the thoracic region to the end of the spinal cord?
behind/caudal to the respective vertebra
Which segments of the spinal cord are shorter?
caudal lumbar (L5, L6, L7), sacral (S1, S2, S3), and caudal/coccygeal (Cd1 to Cd5)
What is a sulcus?
groove in the brain/spinal cord
What are the sulci on the surface of the spinal cord?
dorsal median, dorsal intermediate, dorsolateral, ventrolateral
Where is the dorsal intermediate sulcus found?
cervical and cranial thoracic spinal cord only
What extends from the dorsolateral and ventrolateral sulci?
dorsal rootlets and ventral rootlets
What structures are seen on the surface of the spinal cord?
sulci, dorsal median septum, ventral median fissure, central canal
Where is the grey matter located in the spinal cord?
center (dorsal and ventral horns)
What does grey matter consist of?
neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, mostly unmyelinated axons, unmyelinated interneurons and neuroglia, blood vessels
Where do the dorsal and ventral roots/rootlets come from?
respective horns
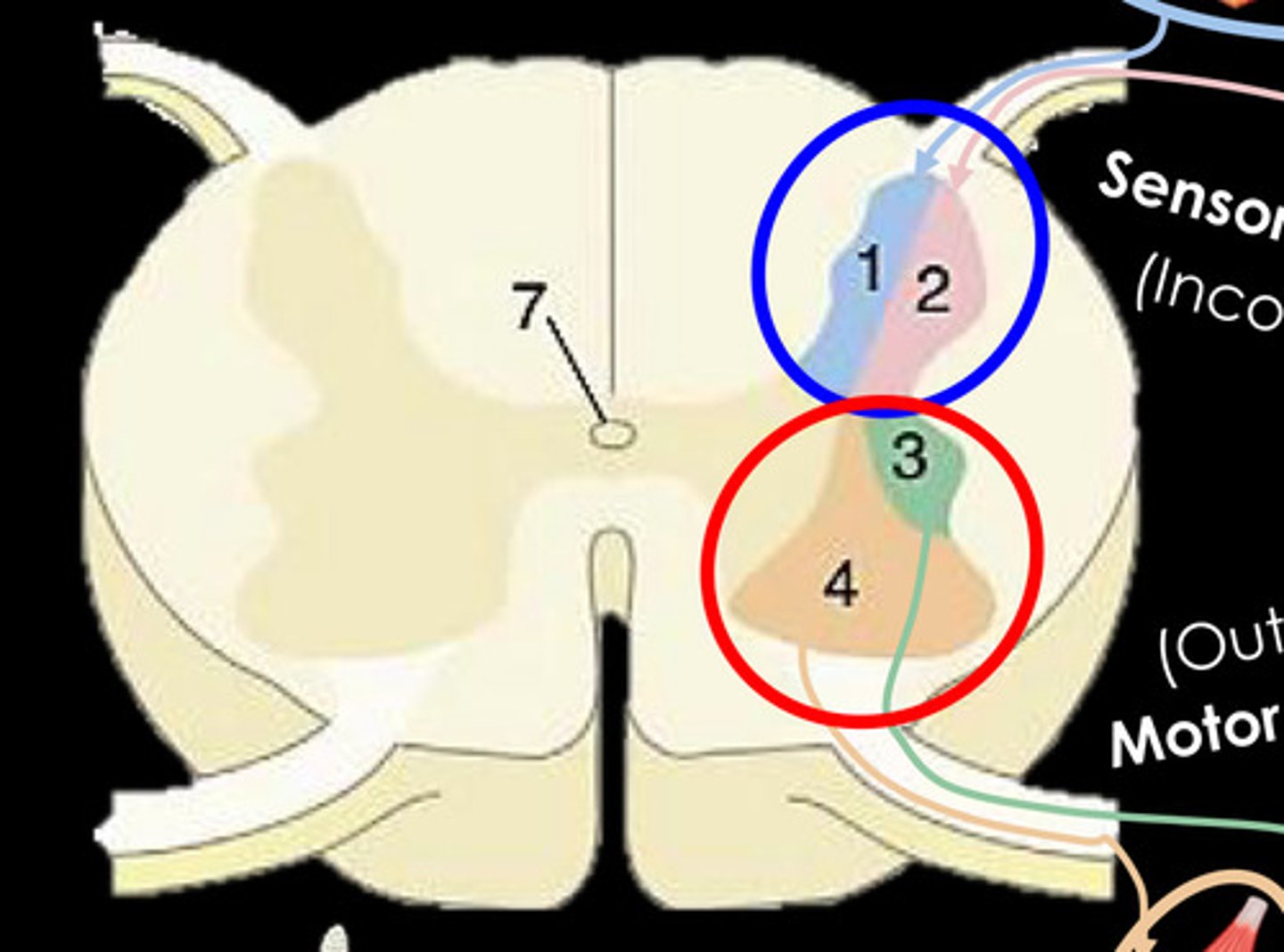
What is 1?
General Somatic afferent column - Somatic Sensory
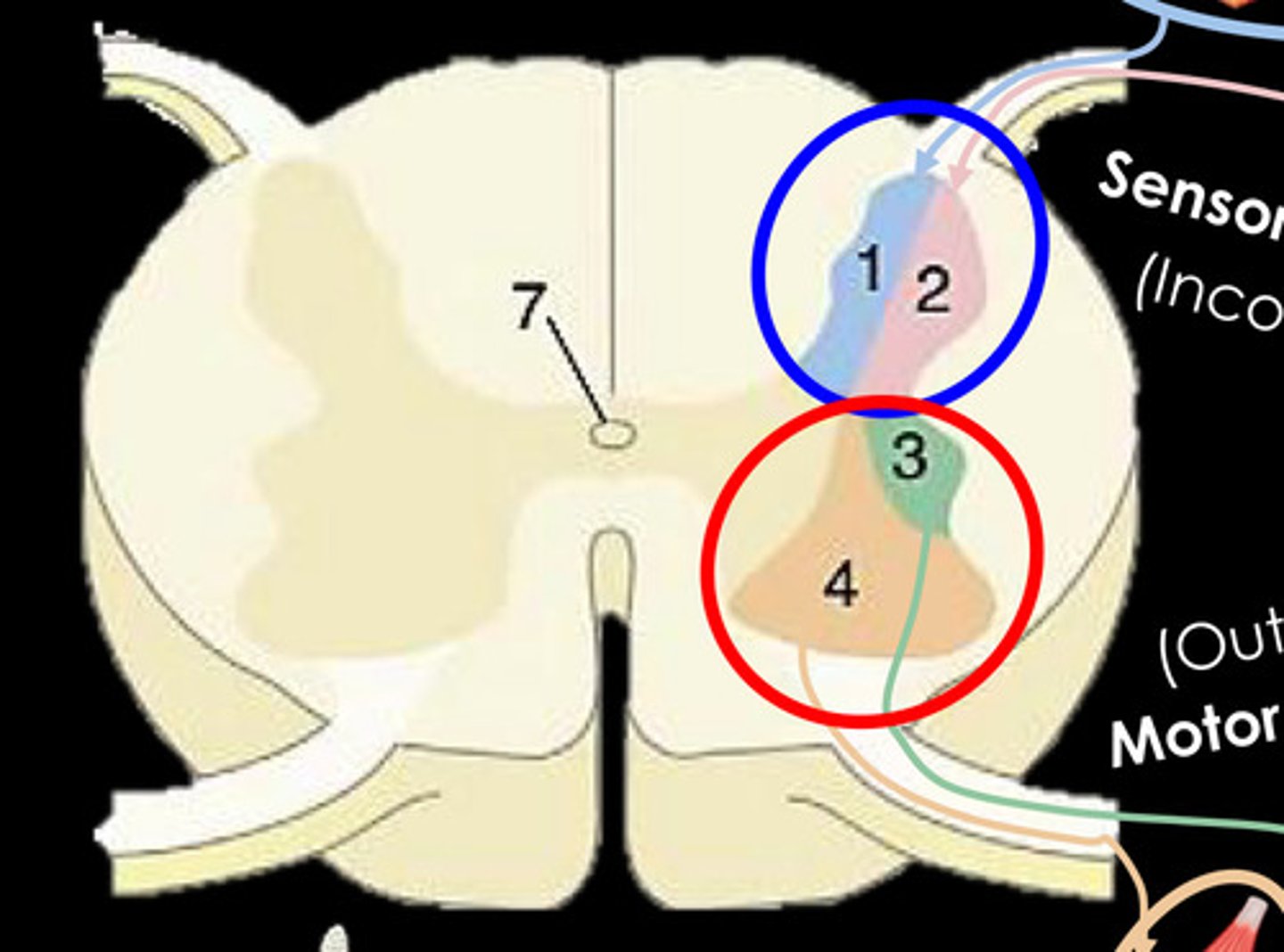
What is 2?
General visceral afferent column - Visceral sensory
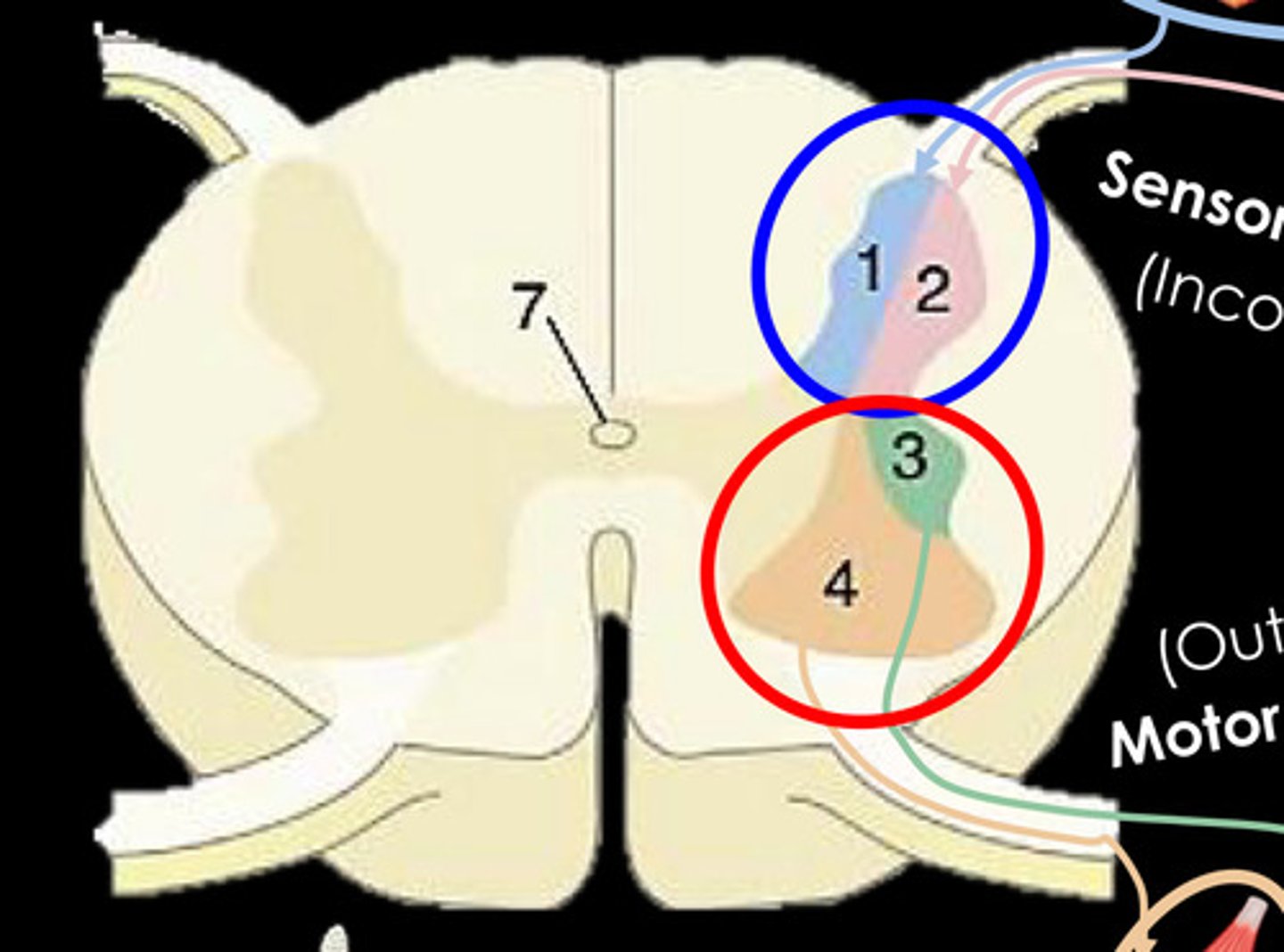
What is 3?
General visceral efferent column - Visceral motor
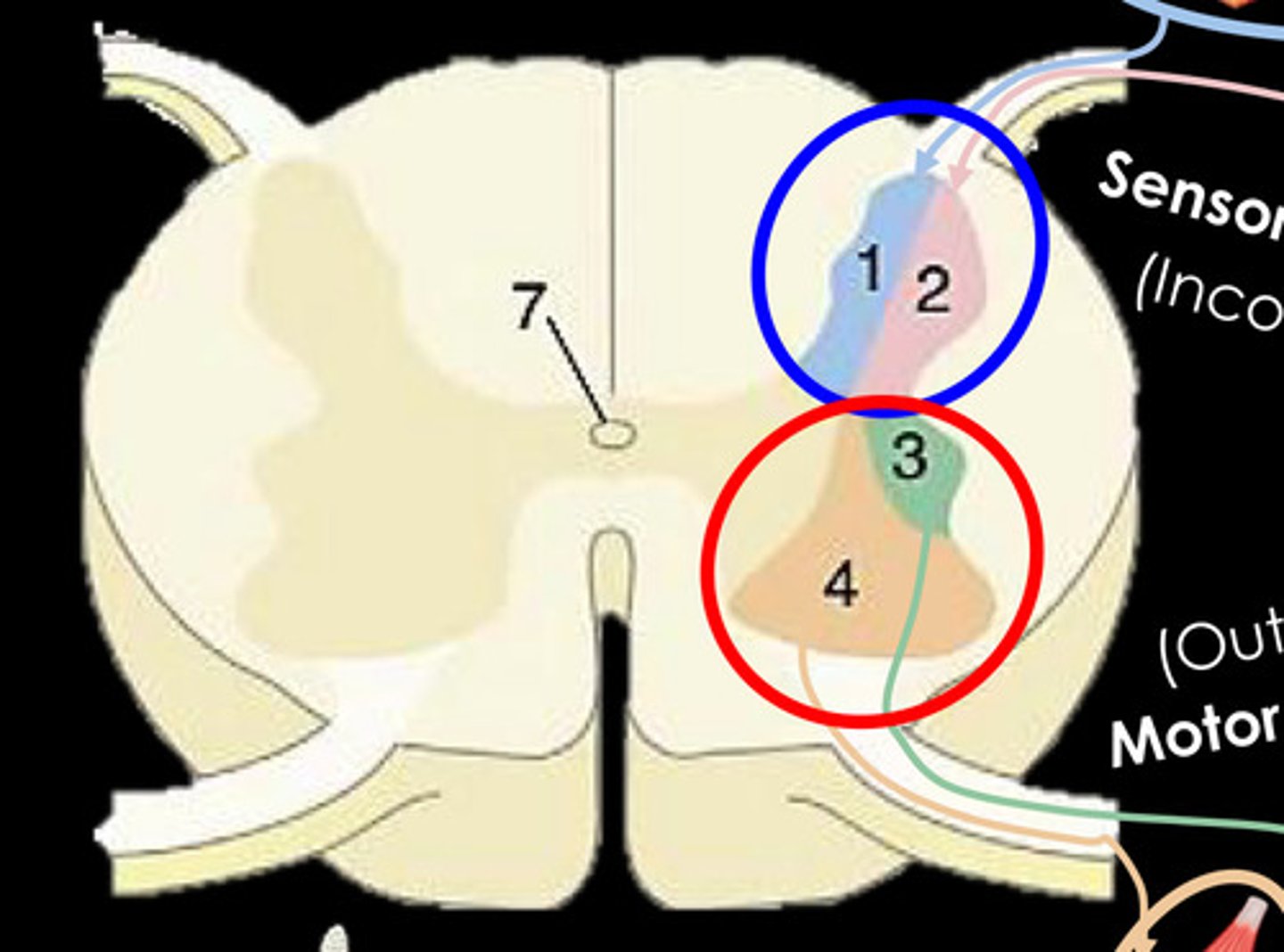
What is 4?
General somatic efferent column - Somatic motor (lower motor neurons)
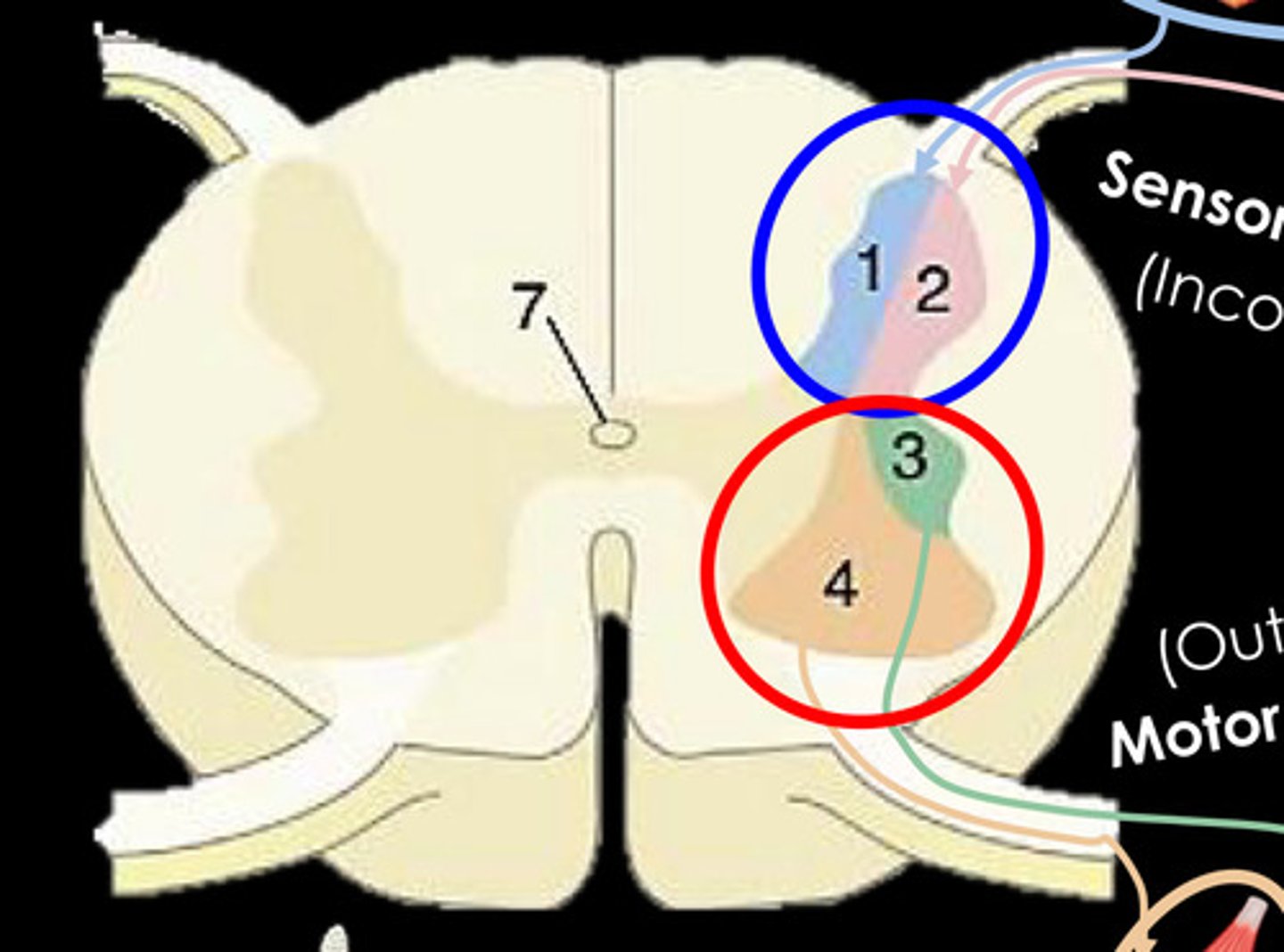
What is 7?
central canal
Where is white matter located in the spinal cord?
surrounding grey matter
Where do sensory/afferent axons originate?
dorsal horn
Where do motor/efferent axons originate?
ventral horn
Where do sensory/afferent axons carry impuses?
cranially to cranial segments of the spinal cord and then to the brain
Where do motor/descending axons carry impulses?
caudally in the spinal cord
What are funiculi made of?
ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) nerve fibers
What are the funiculi in the spinal cord?
dorsal, lateral, ventral
What is a fasiculus?
funiculus fibers grouped by common origin, destination, and function (sensory and motor pathways)
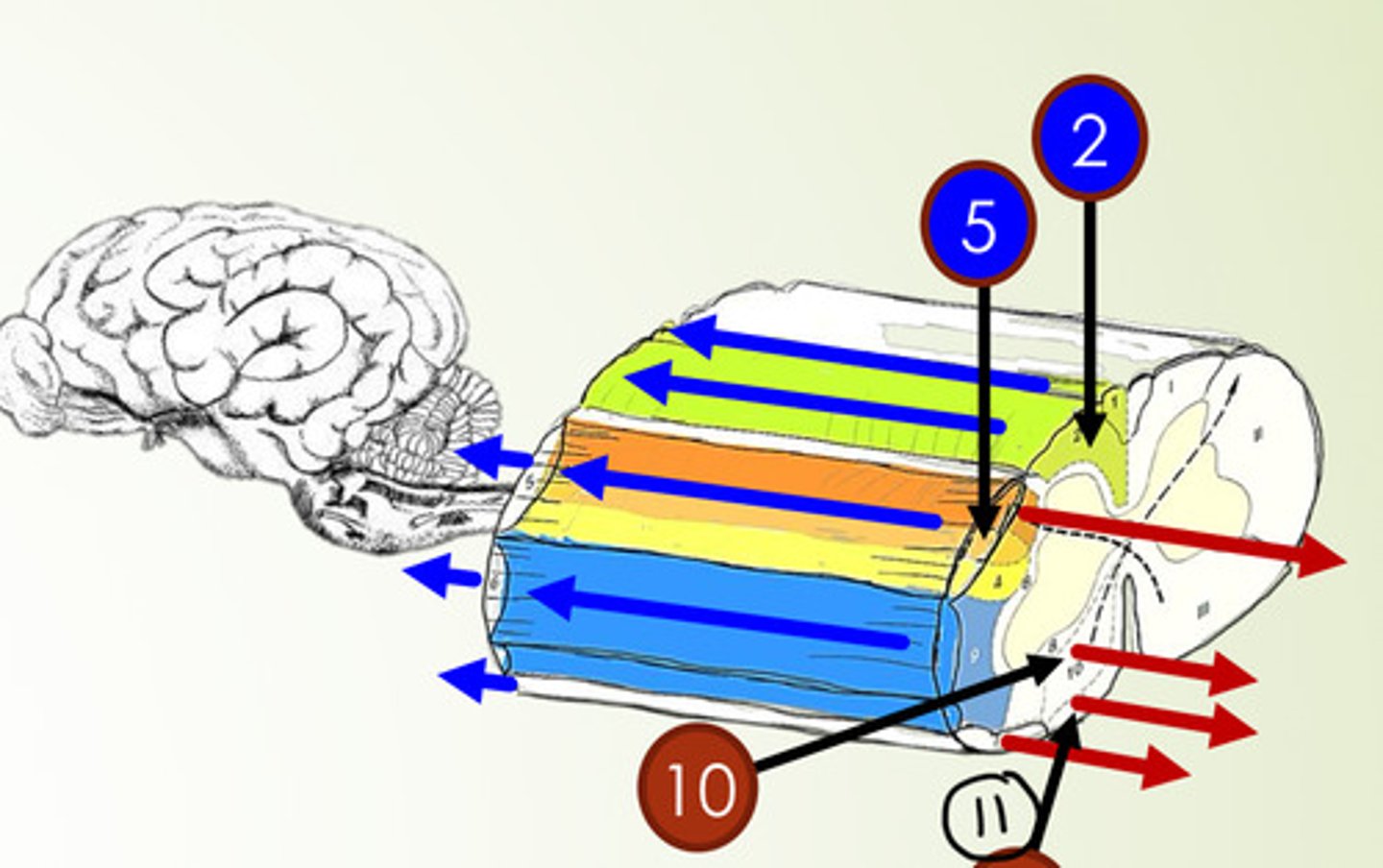
What is 2?
fasciculus cuneatus (sensory tract)
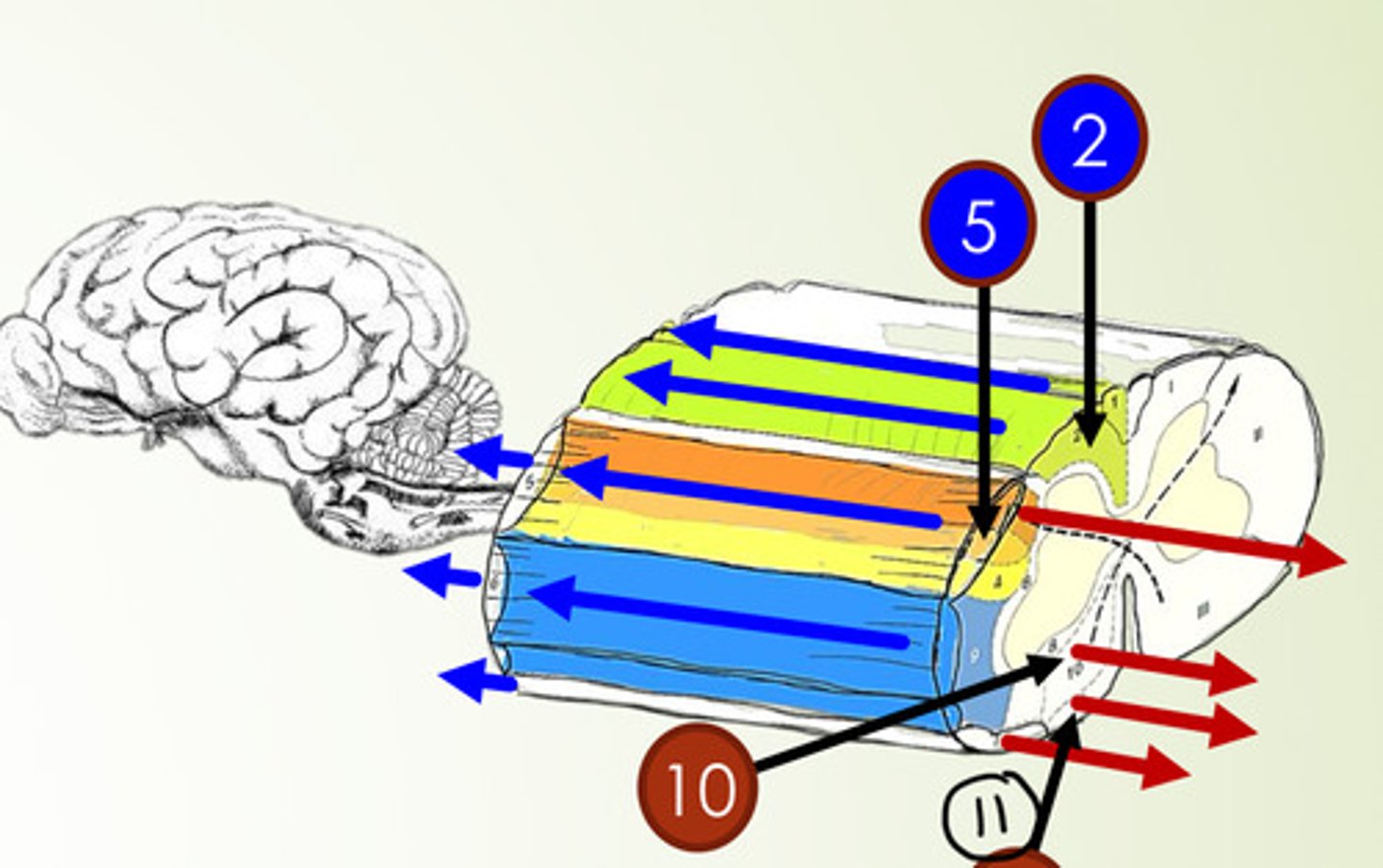
What is 5?
dorsal spinocerebellar tract (sensory tract)
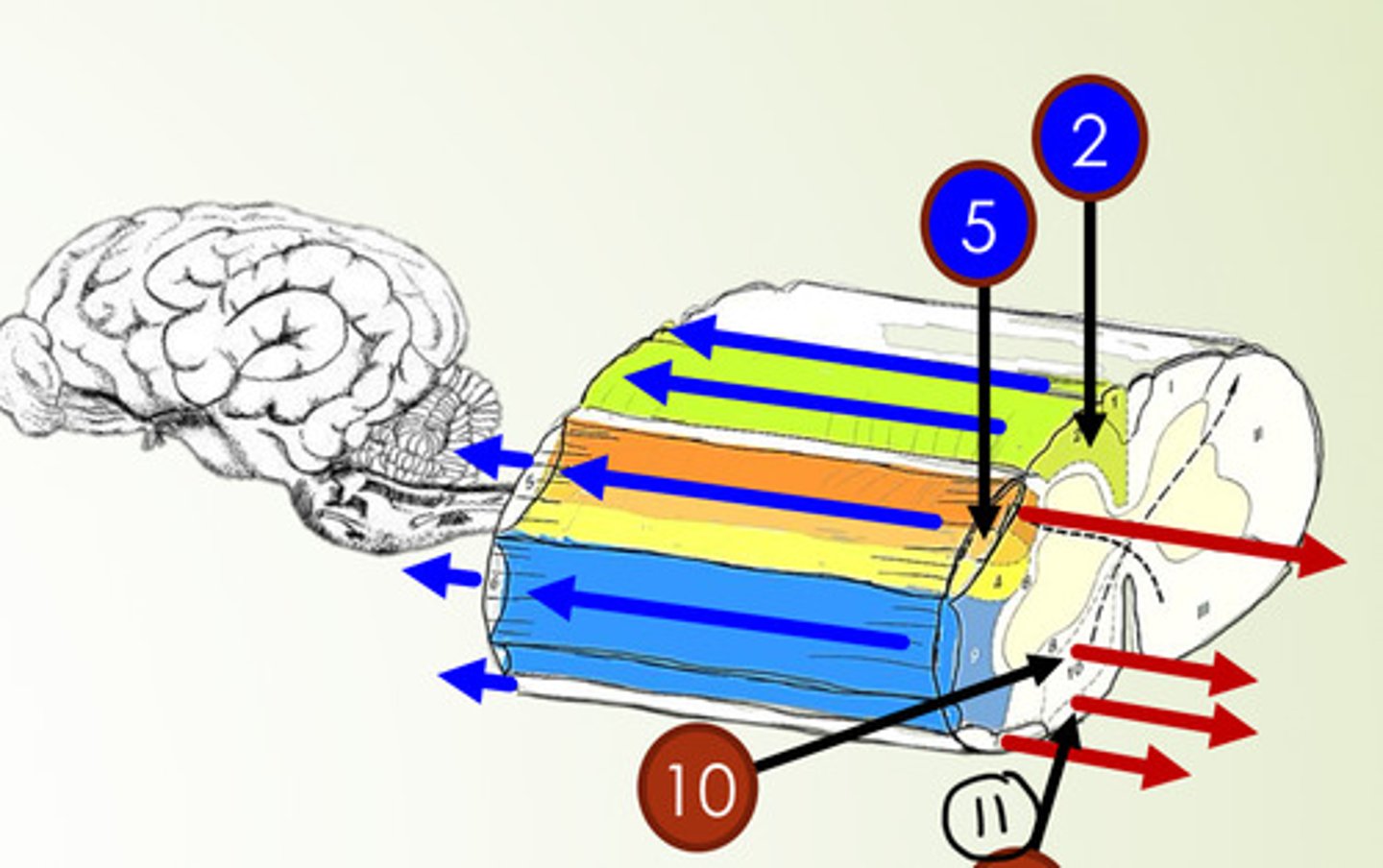
What is 10?
ventral corticospinal tract (motor tract)
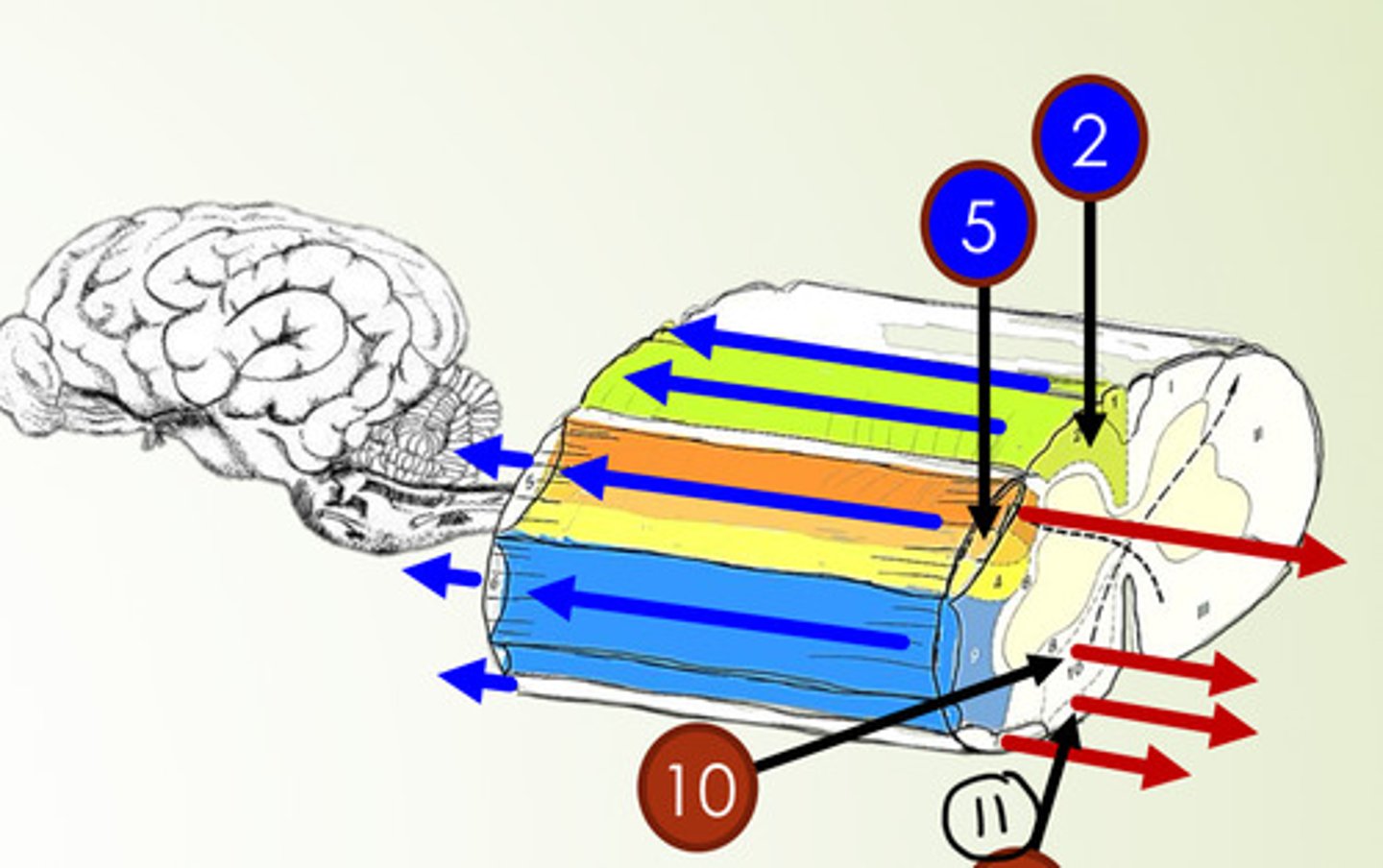
What is 11?
vestibulospinal tract (motor tract)
What is a dermatome?
area of the skin innervated by afferent nerve fibers (sensory innervation) from a single spinal nerve
How are dermatomes organized in the neck and trunk?
segments
What are myotomes?
set of muscles innervated (motor innervation) by a specific, single spinal nerve
What are the cervical spinal nerves?
ventral and dorsal branches, phrenic nerve, and fifth, sixth, and seventh cervical nerves
What are the superficial veins of the neck?
external jugular, omobrachial, axillobrachial
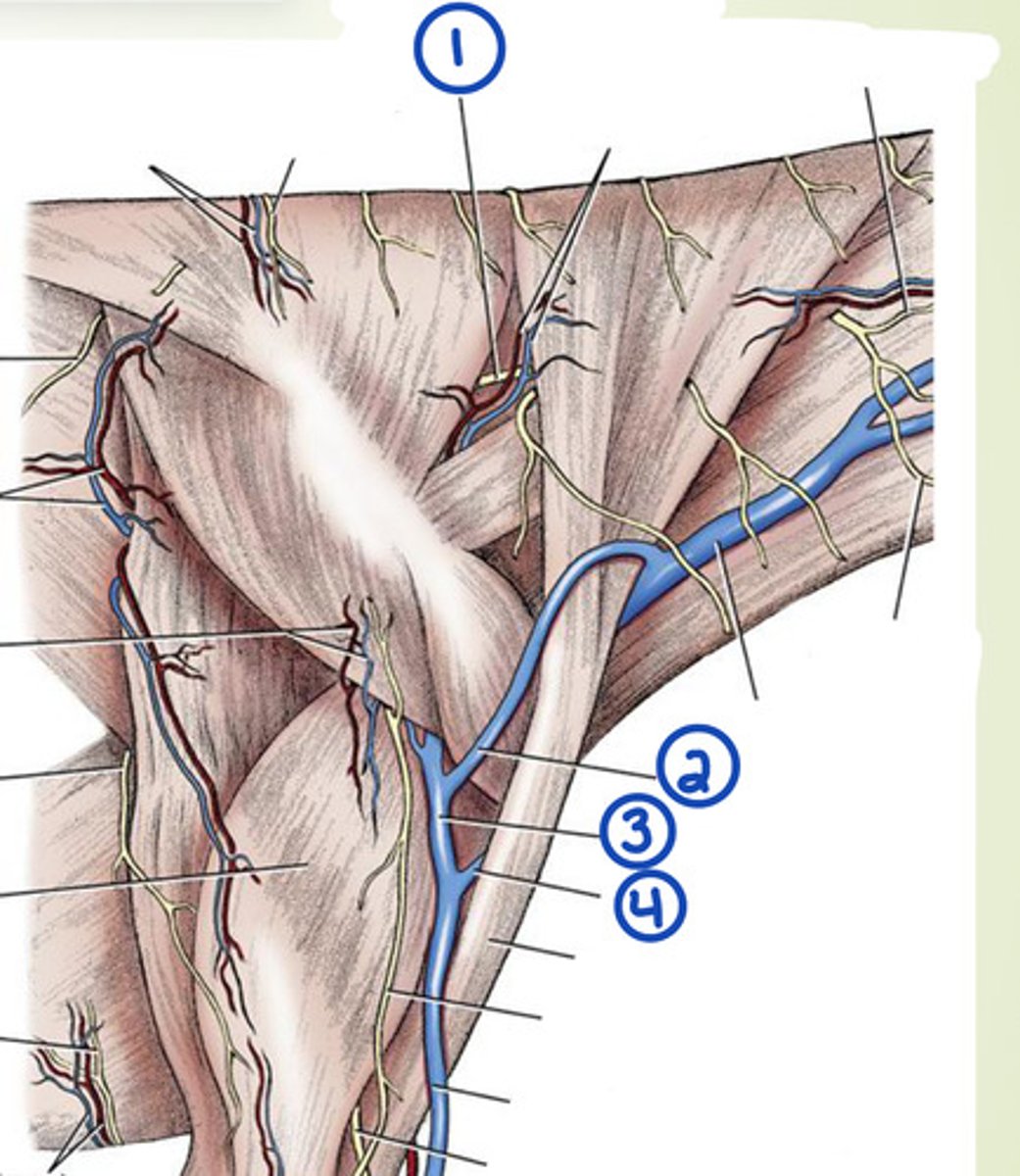
What is 1?
accesory n.
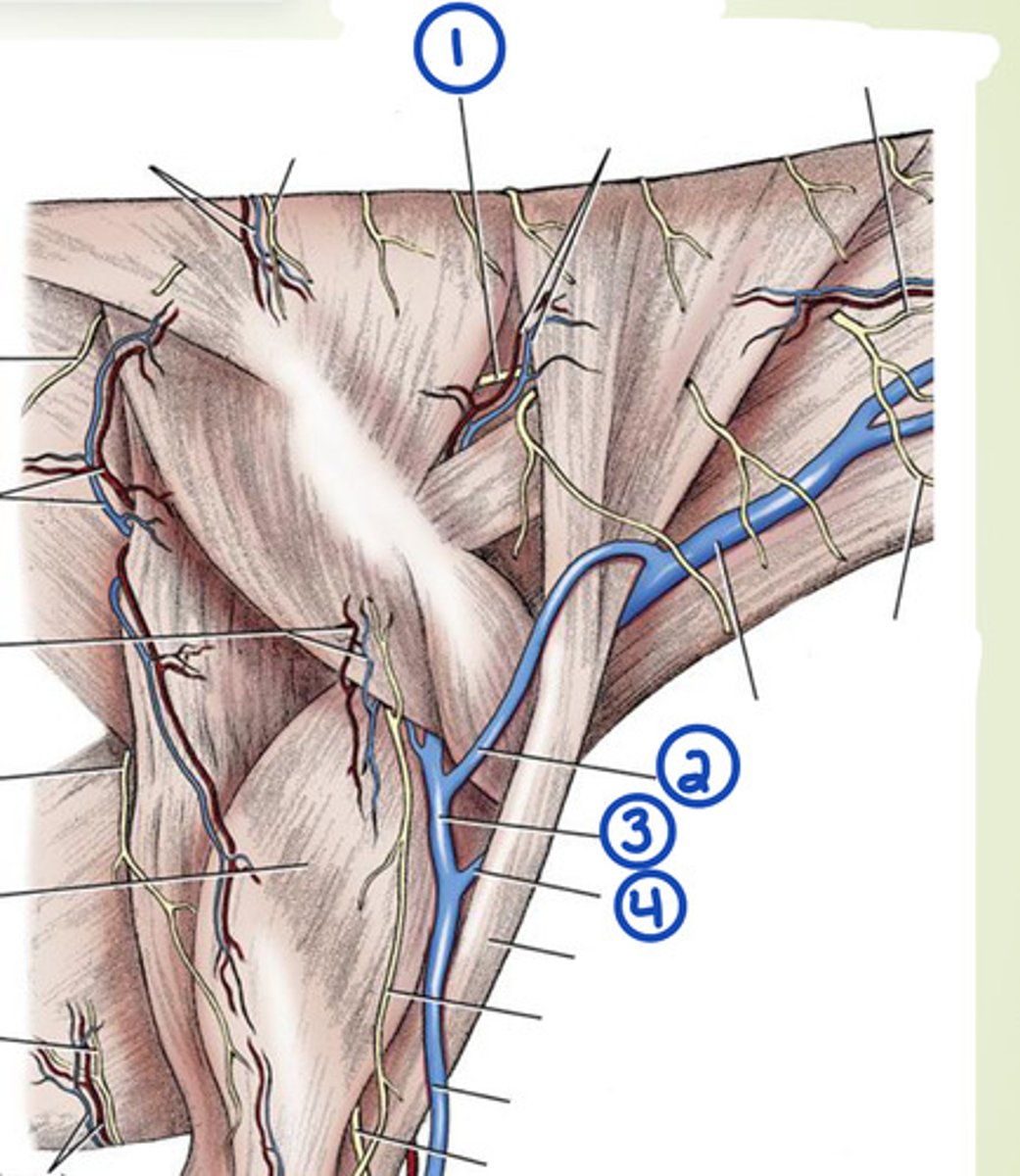
What is 2?
omobrachial v.
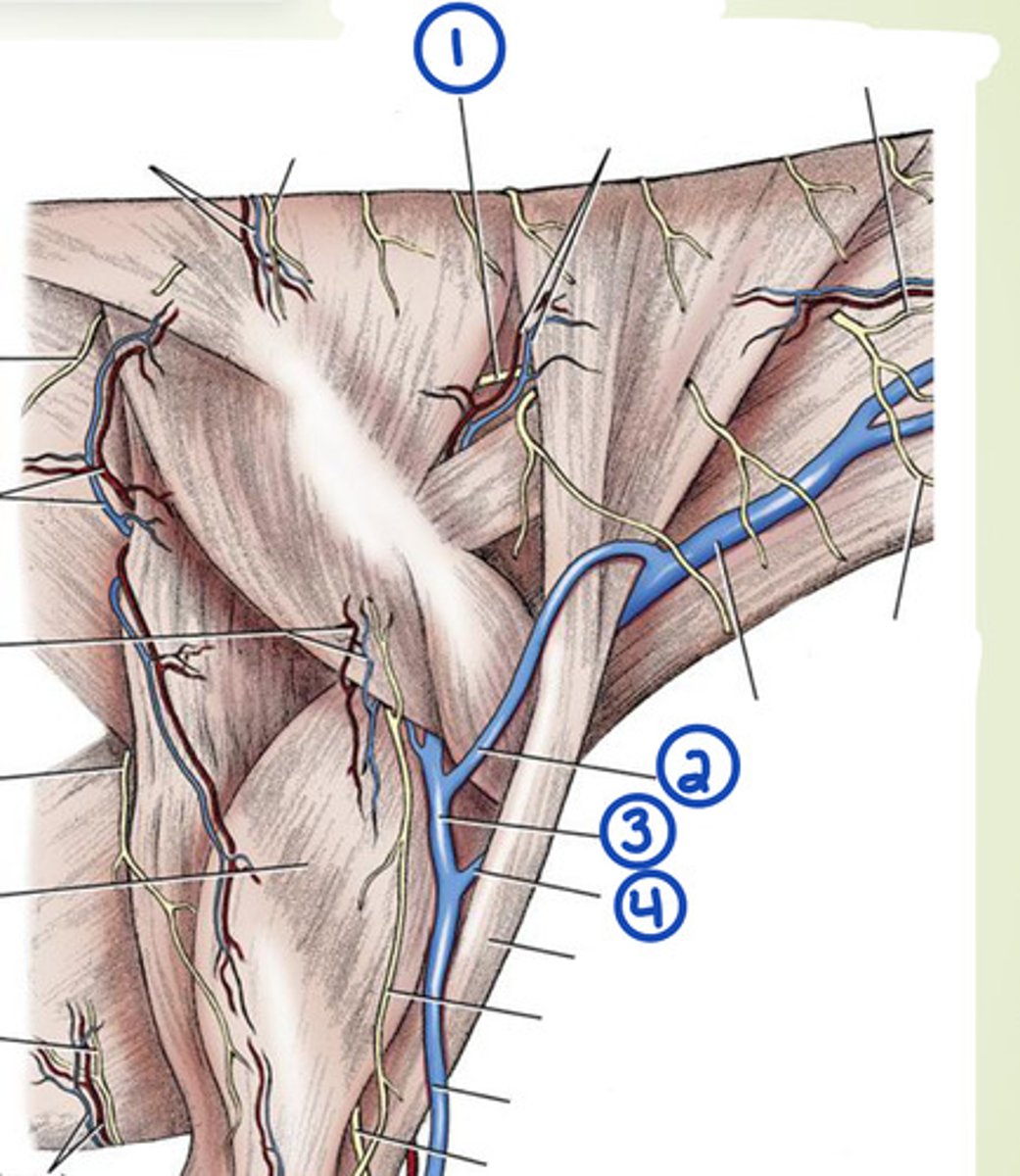
What is 3?
axillobrachial v.
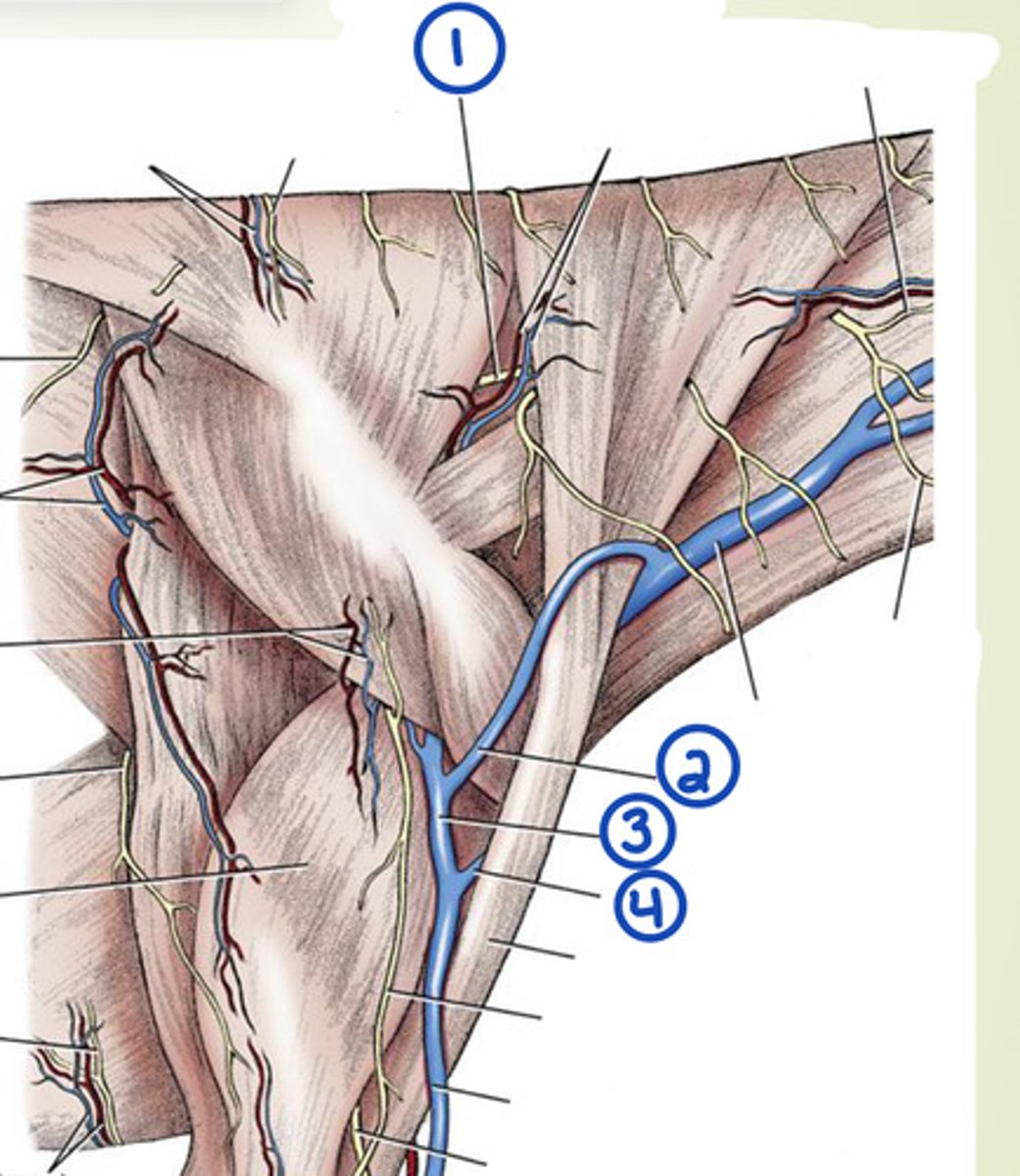
What is 4?
cephalic v.
What is the brachial plexus?
nerve network formed by the ventral branches of the spinal cord (sensory and motor innervation of the forelimb)
What kind of neurons are mostly present in the distal limb?
mostly sensory (loses motor)
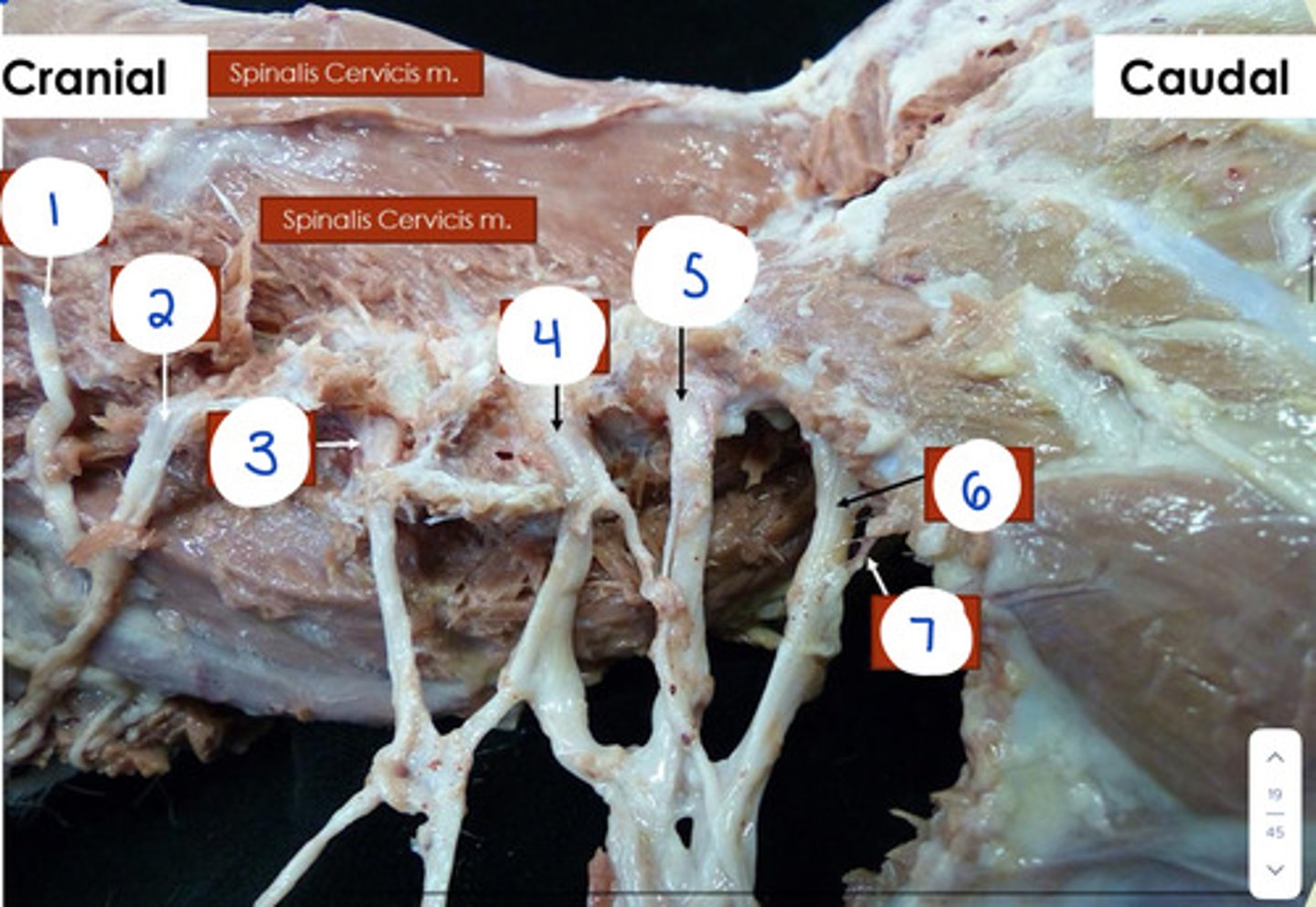
What is 1?
C4
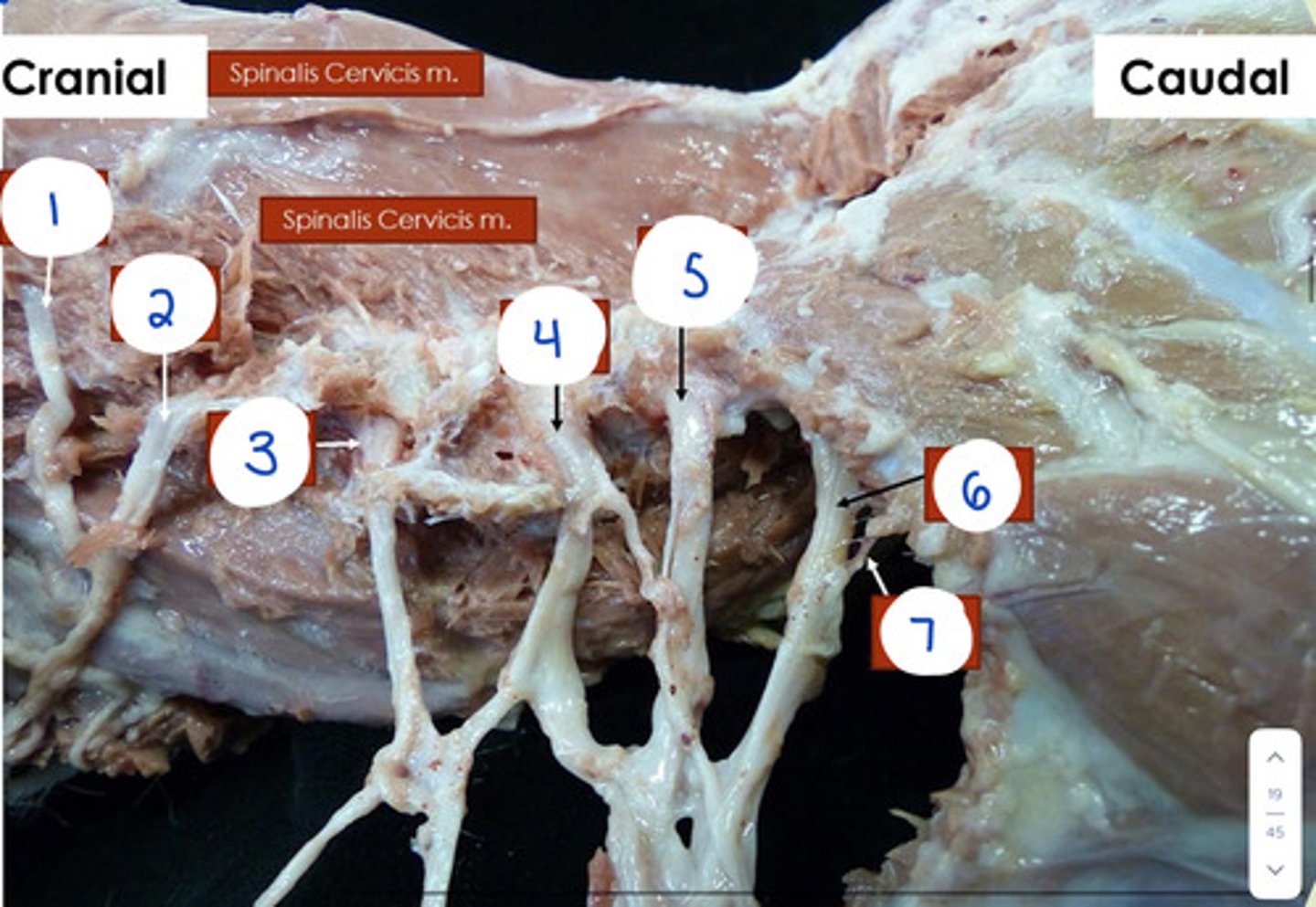
What is 2?
C5
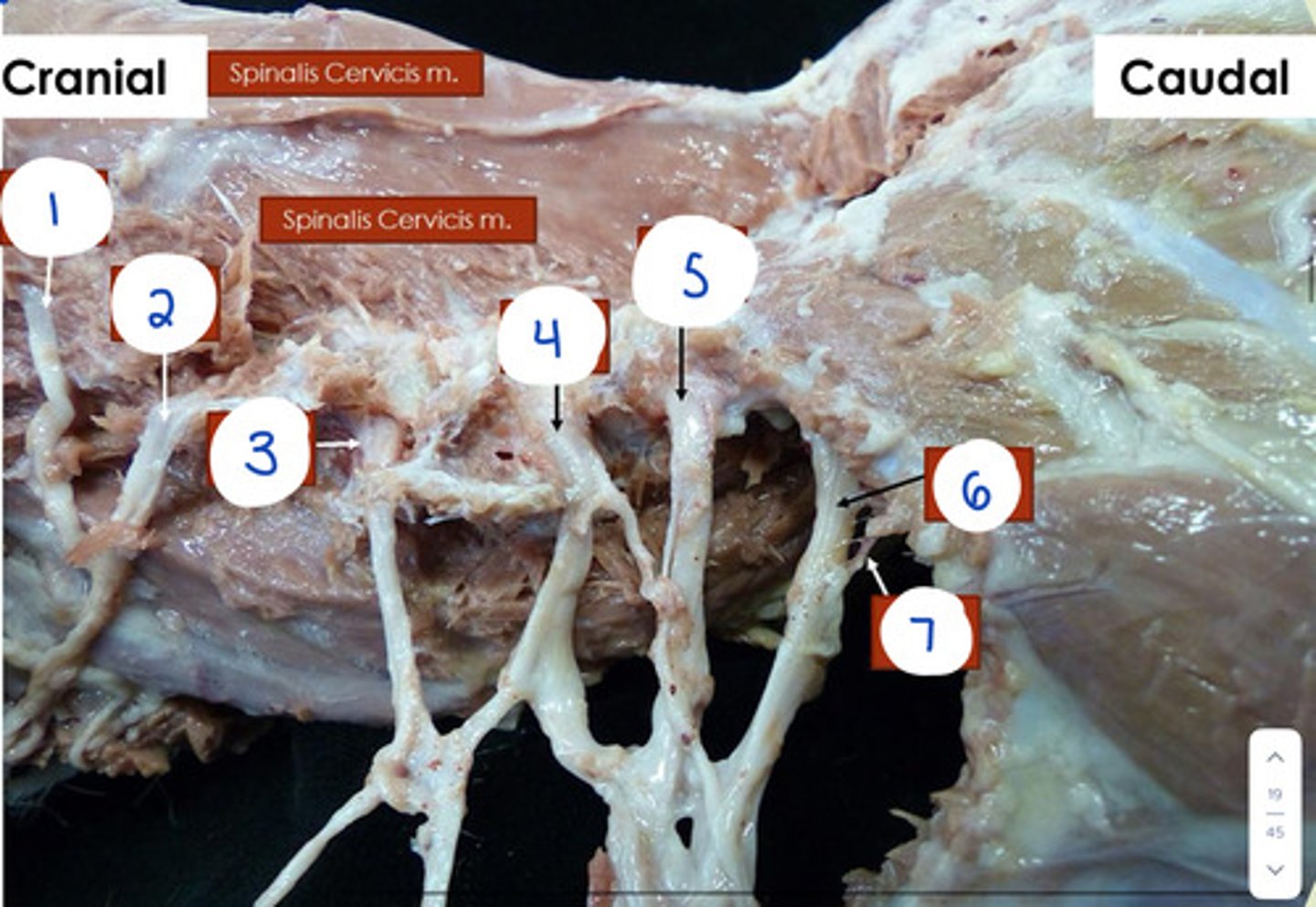
What is 3?
C6
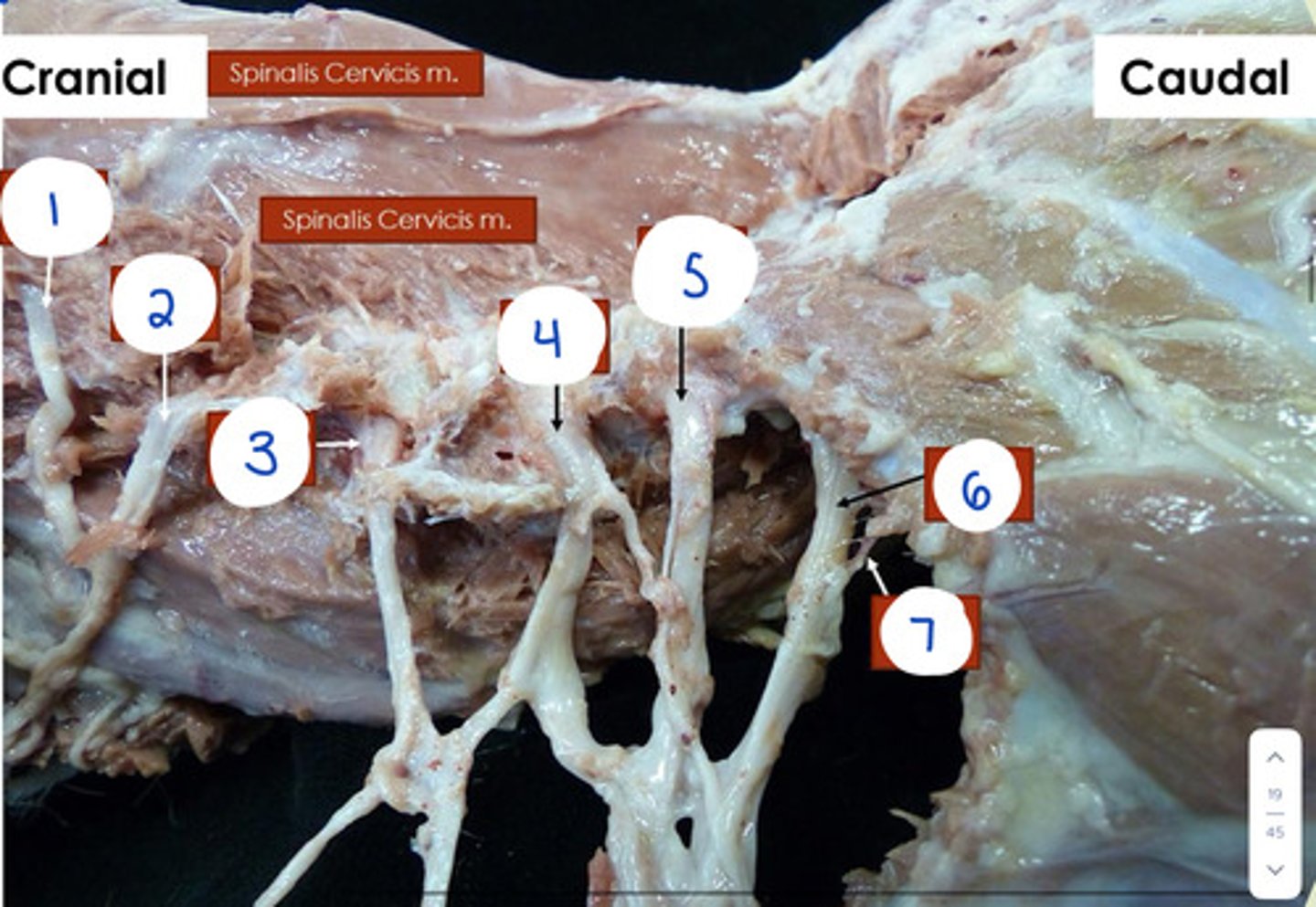
What is 4?
C7
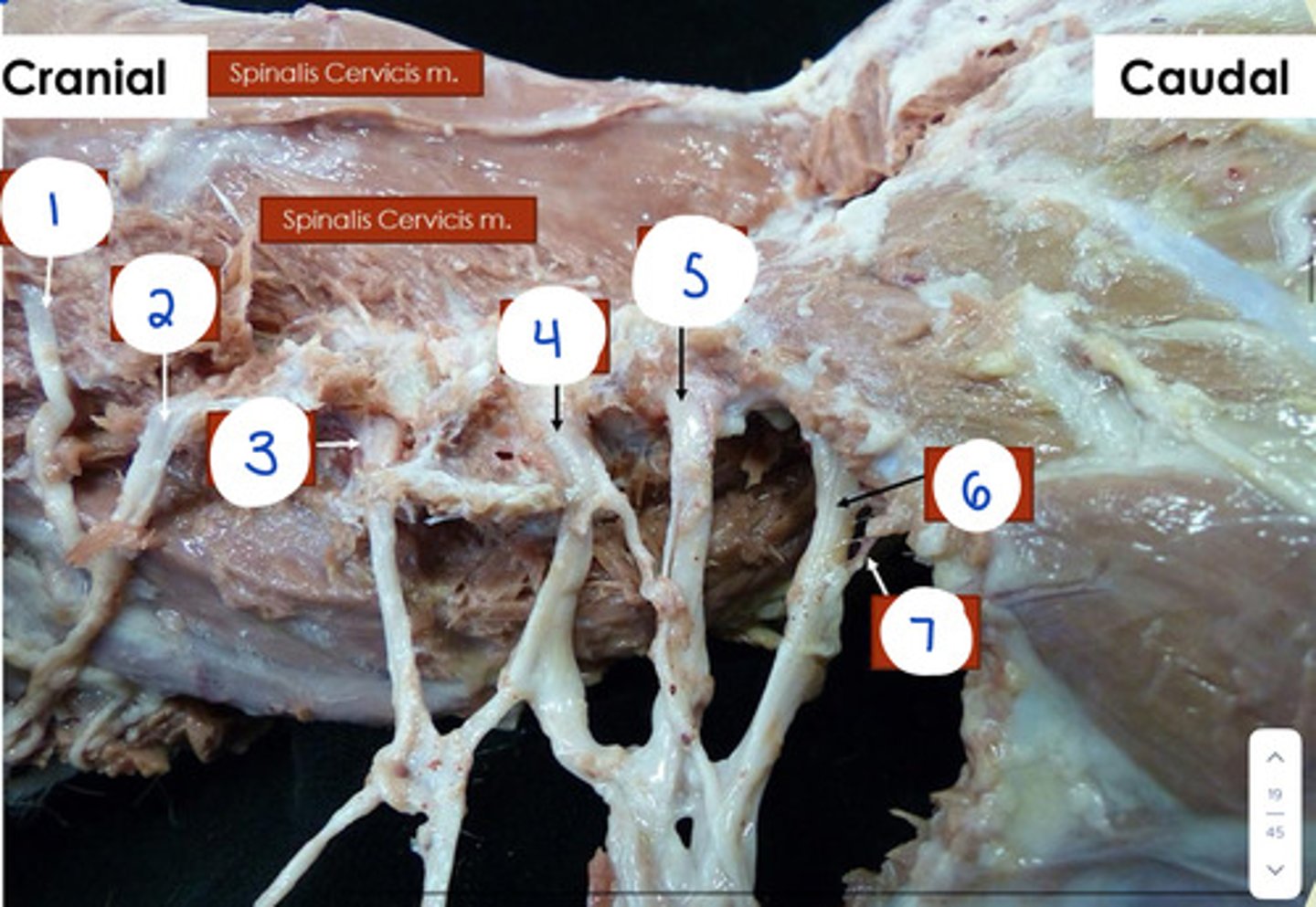
What is 5?
C8
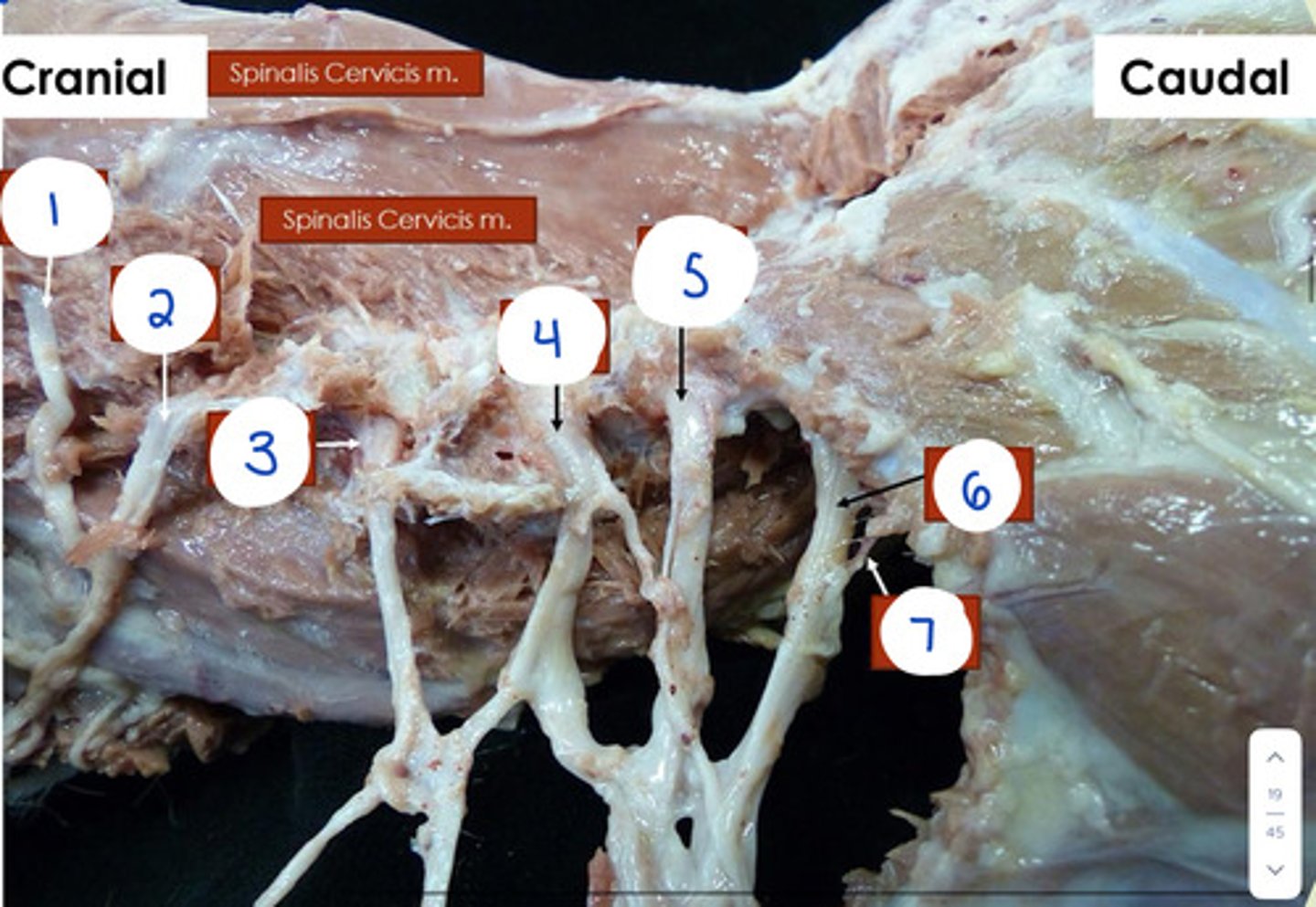
What is 6?
T1
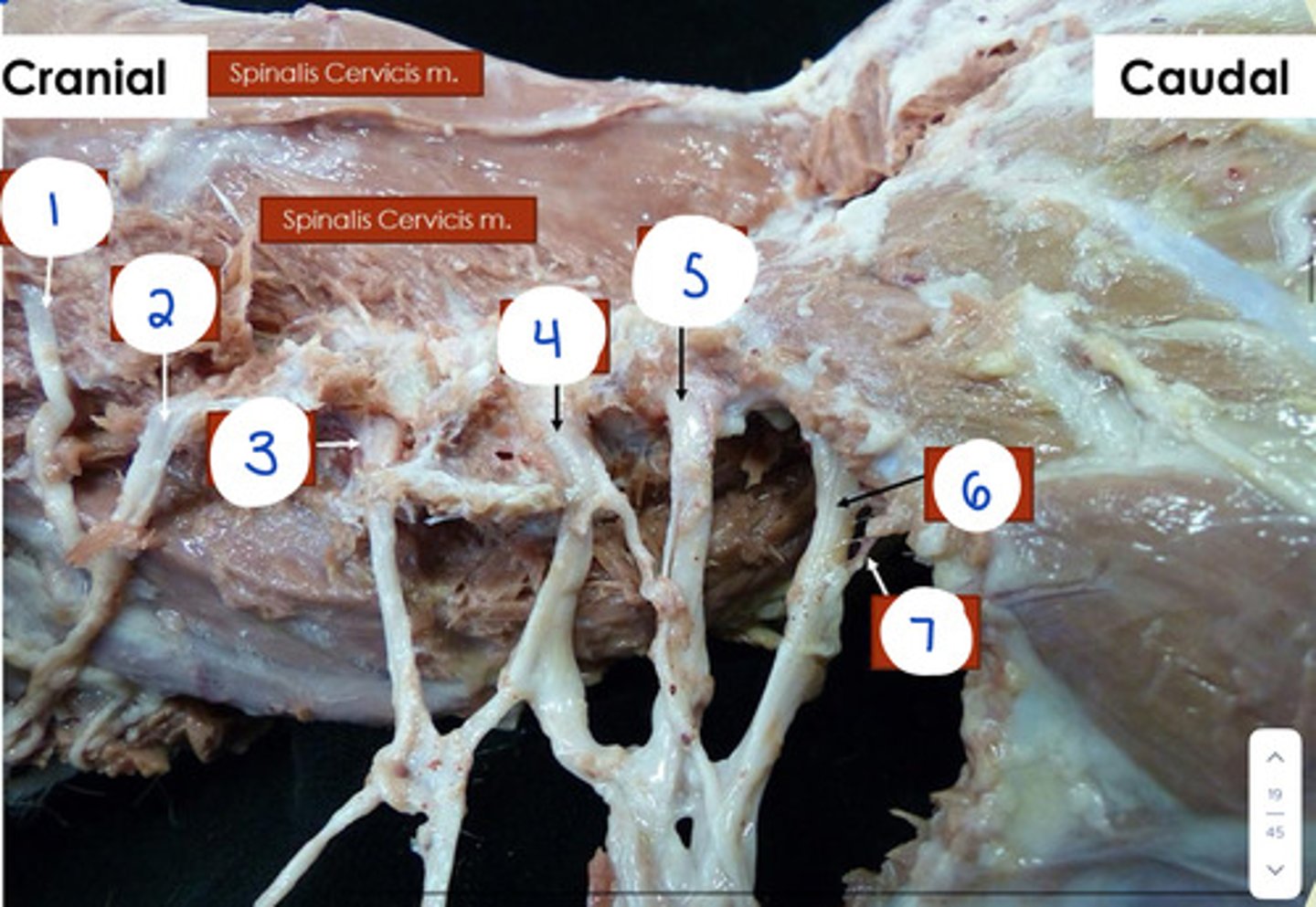
What is 7?
T2
Where does the suprascapular n. originate?
C6-C7
Where does the musculocutaneous n. originate?
C6-C8
Where does the radial n. originate?
C6-T2
Where does the median n. originate?
C7-T1
Where does the ulnar n. originate?
C8-T2
Where does the lateral thoracic n. originate?
C8-T1
Where does the axillary n. originate?
C6-C8
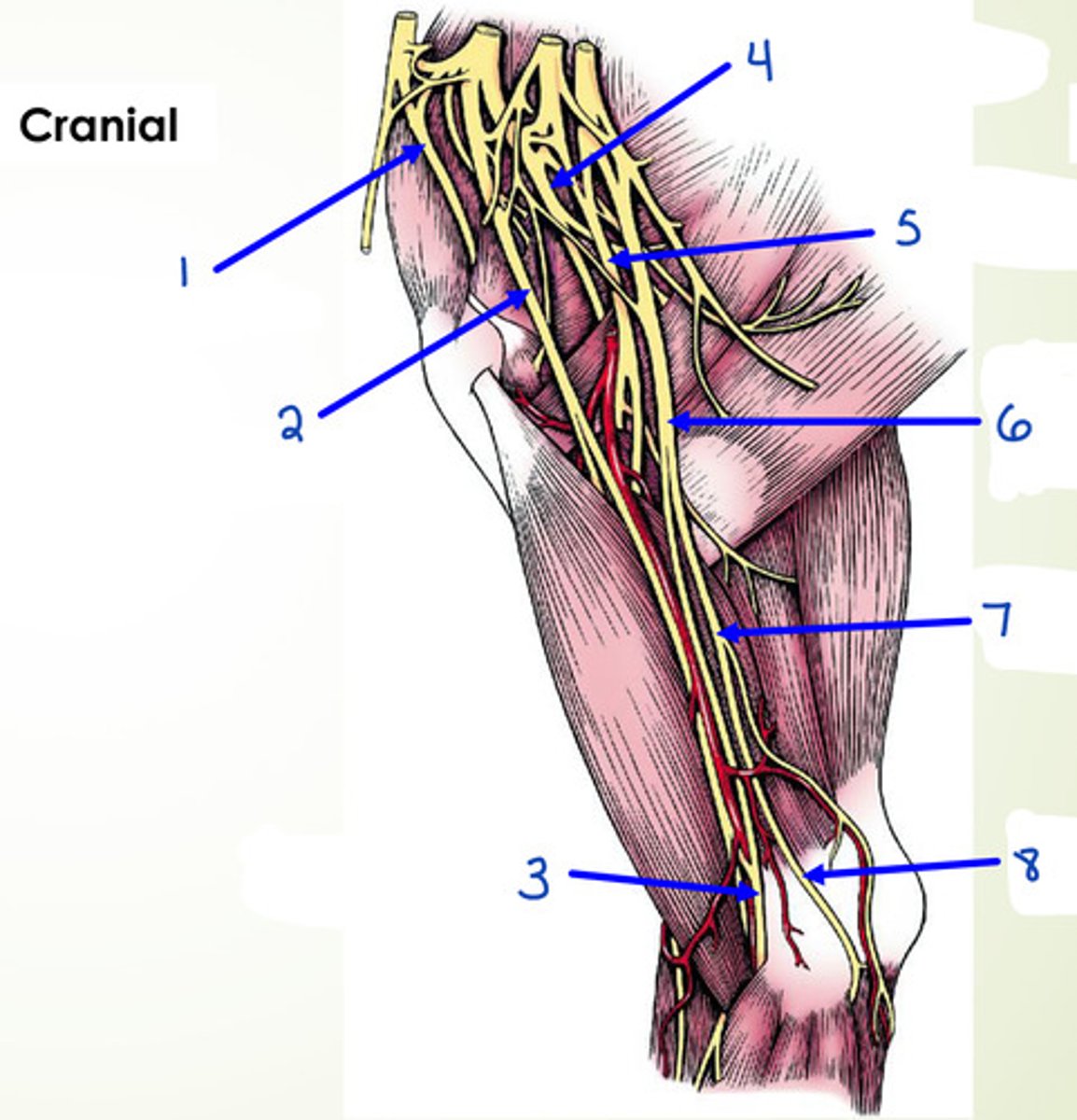
What is 1?
suprascapular n.
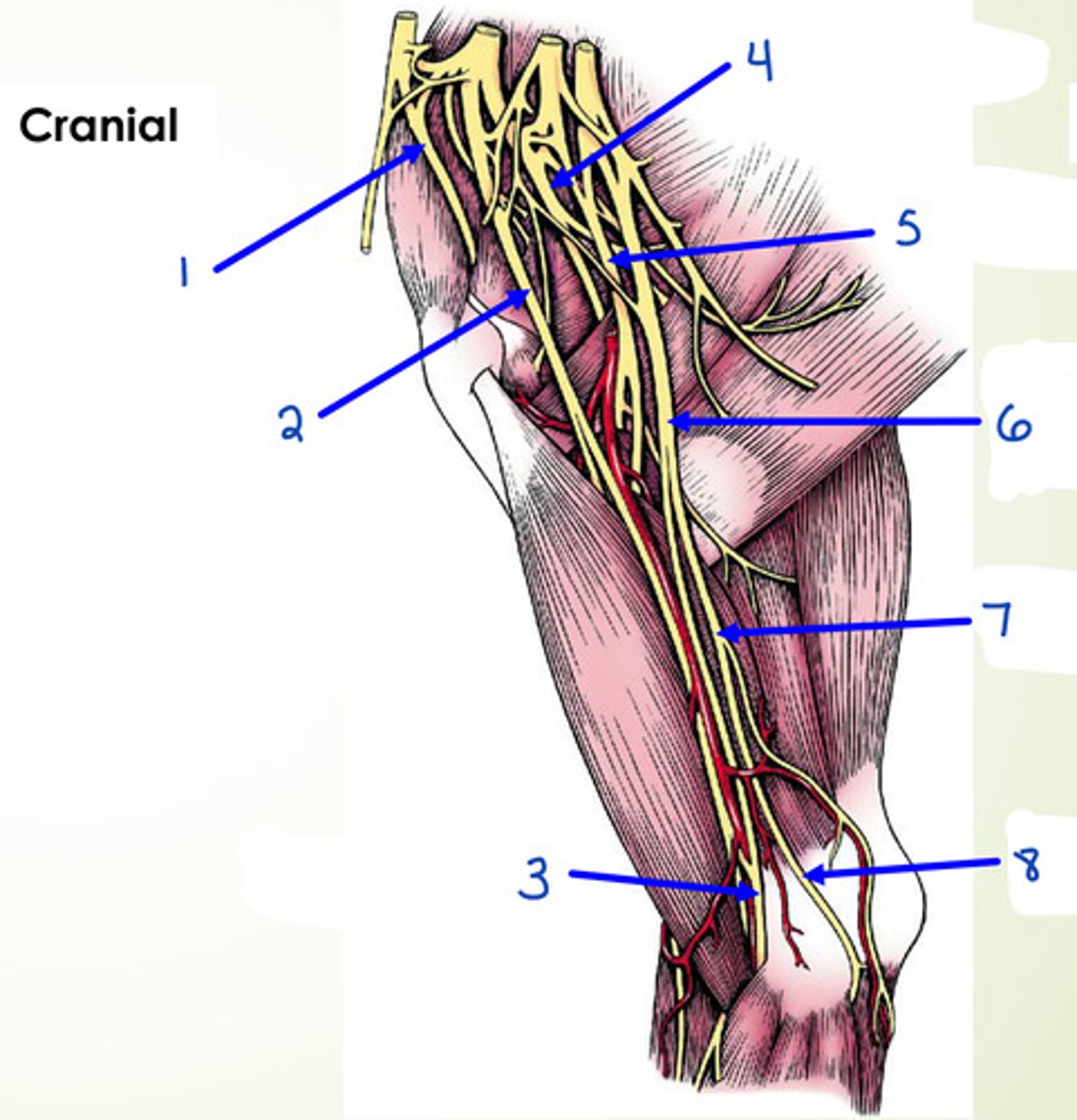
What is 2?
musculocutaneous n.
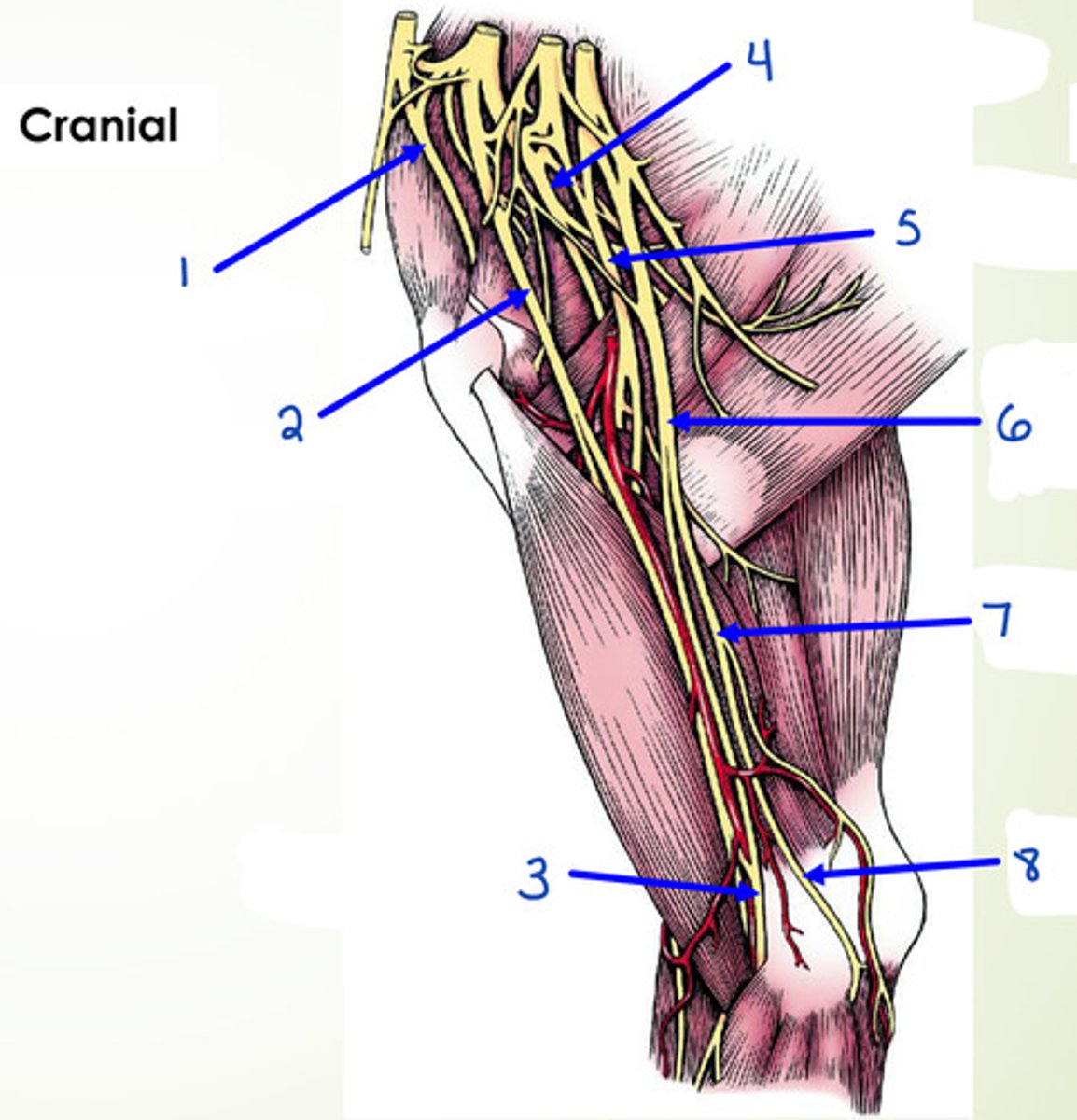
What is 3?
median n.
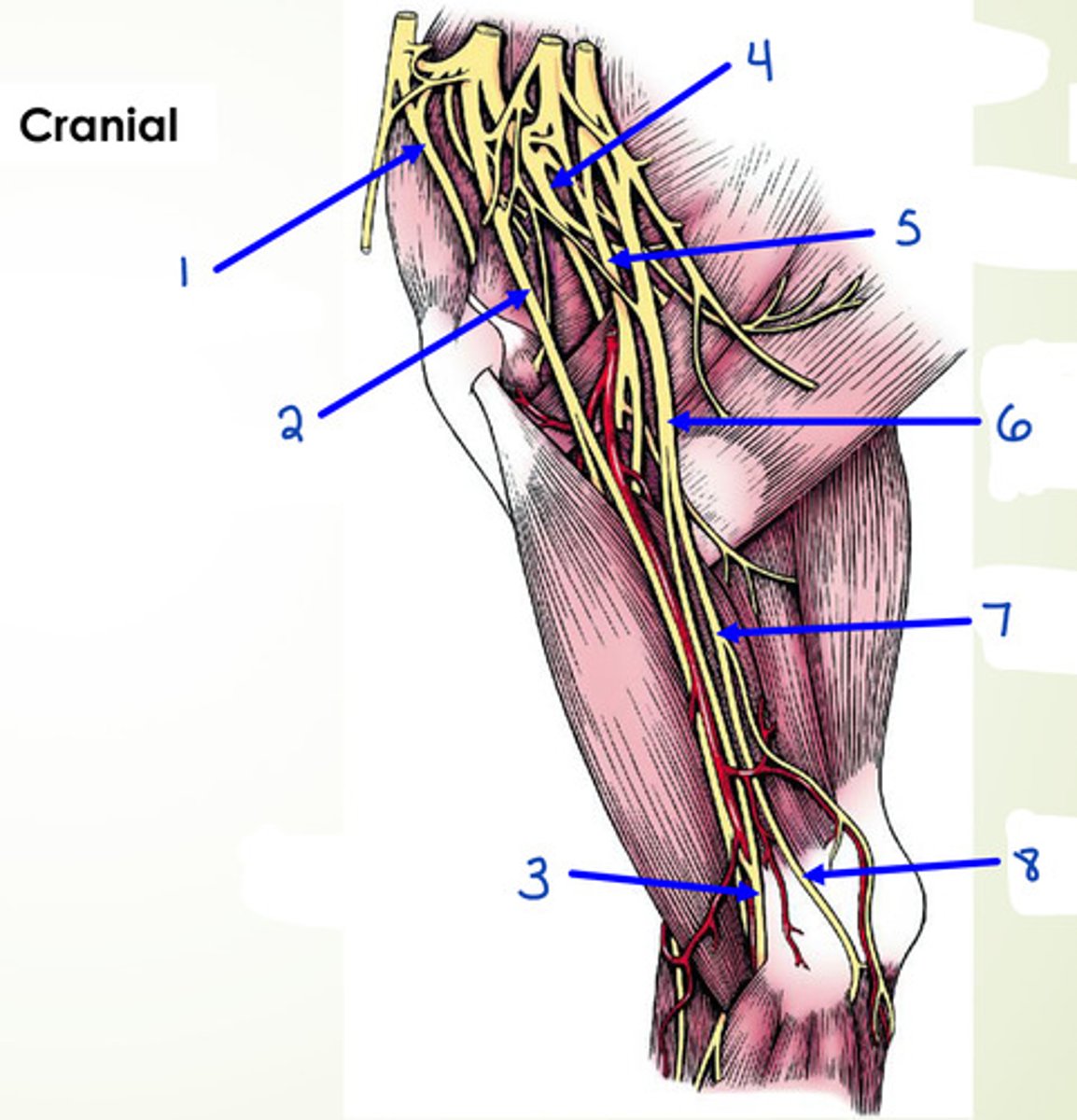
What is 4?
axillary n.
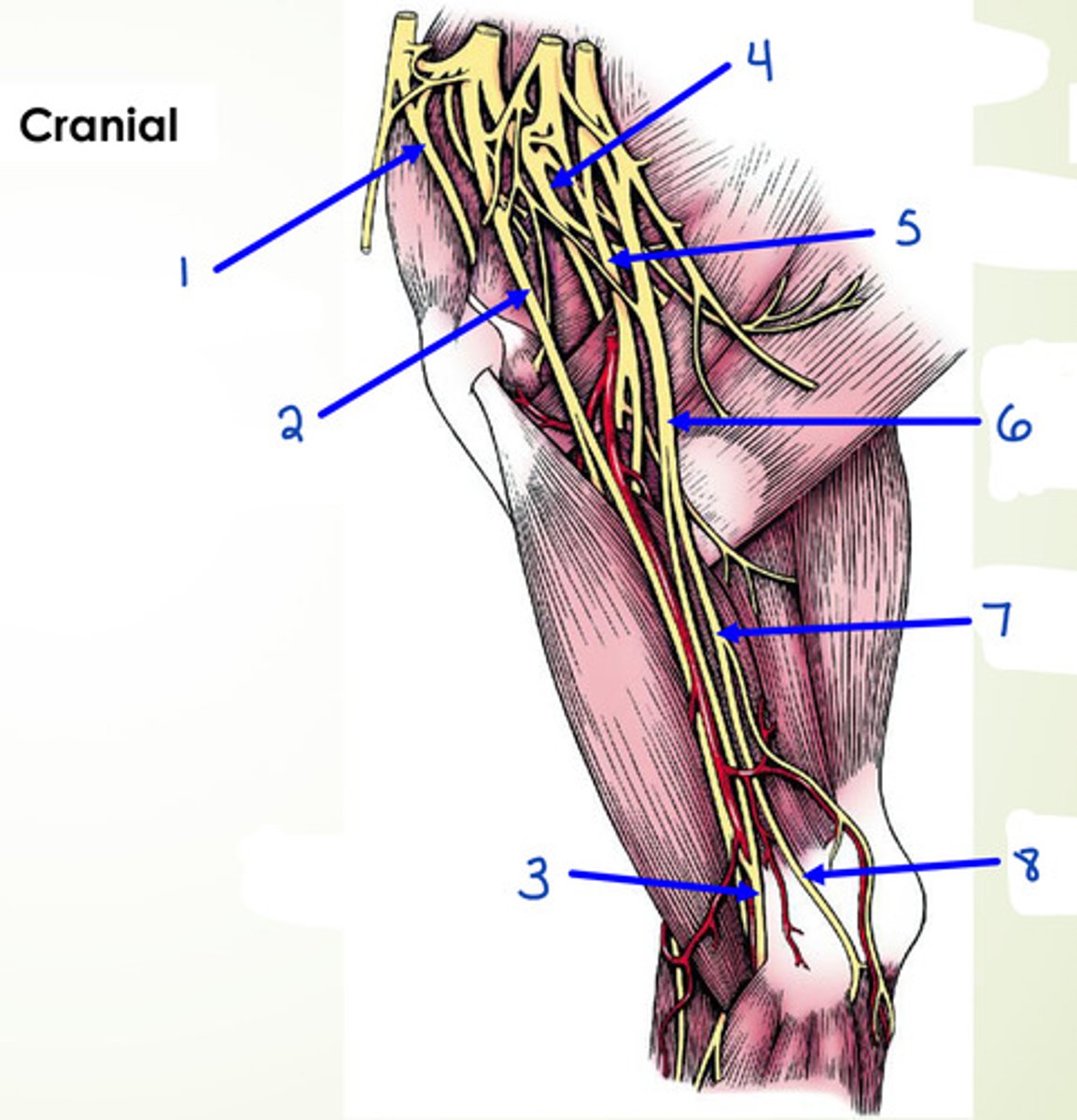
What is 5?
radial n.
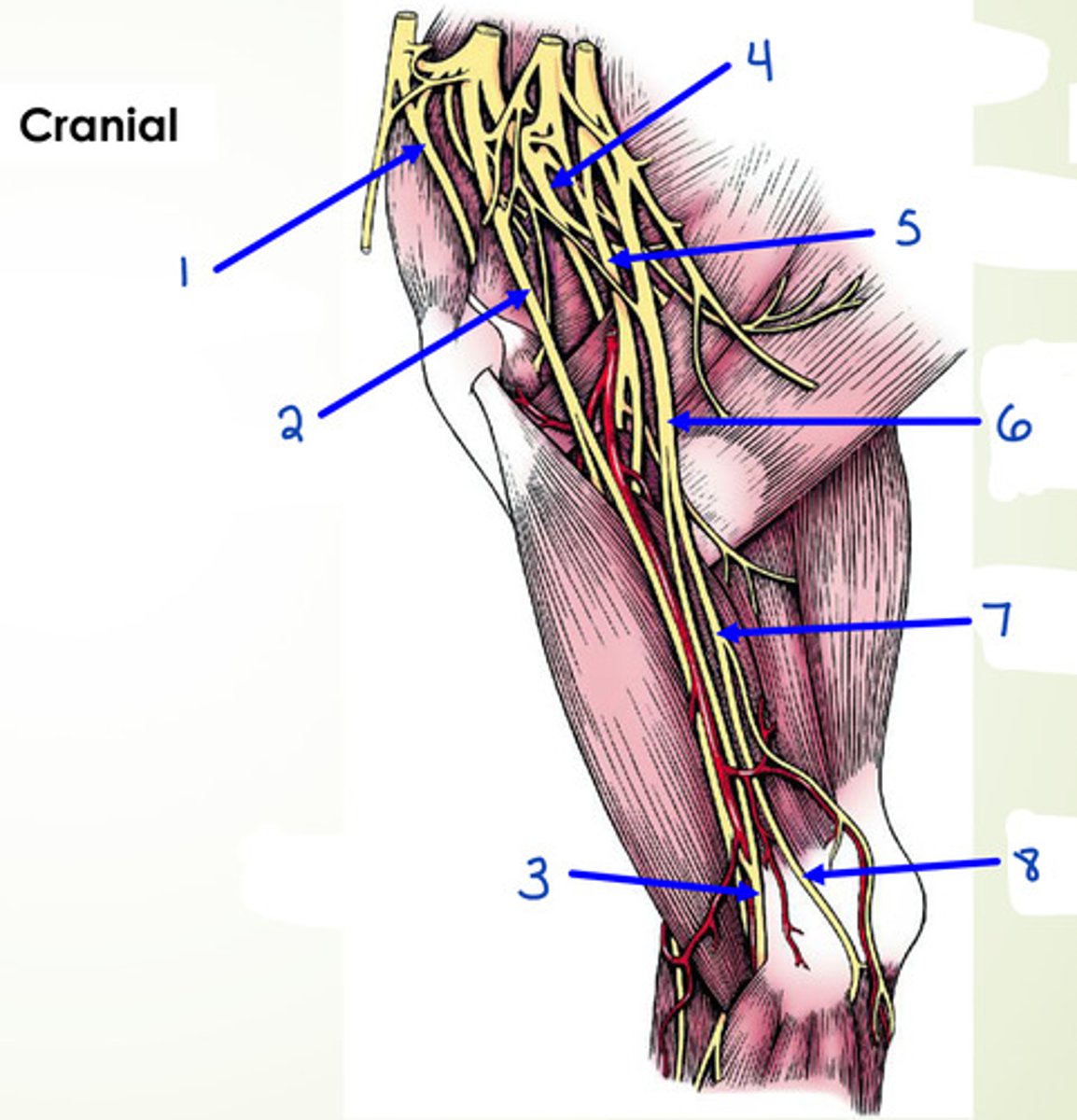
What is 6?
median and ulnar n.
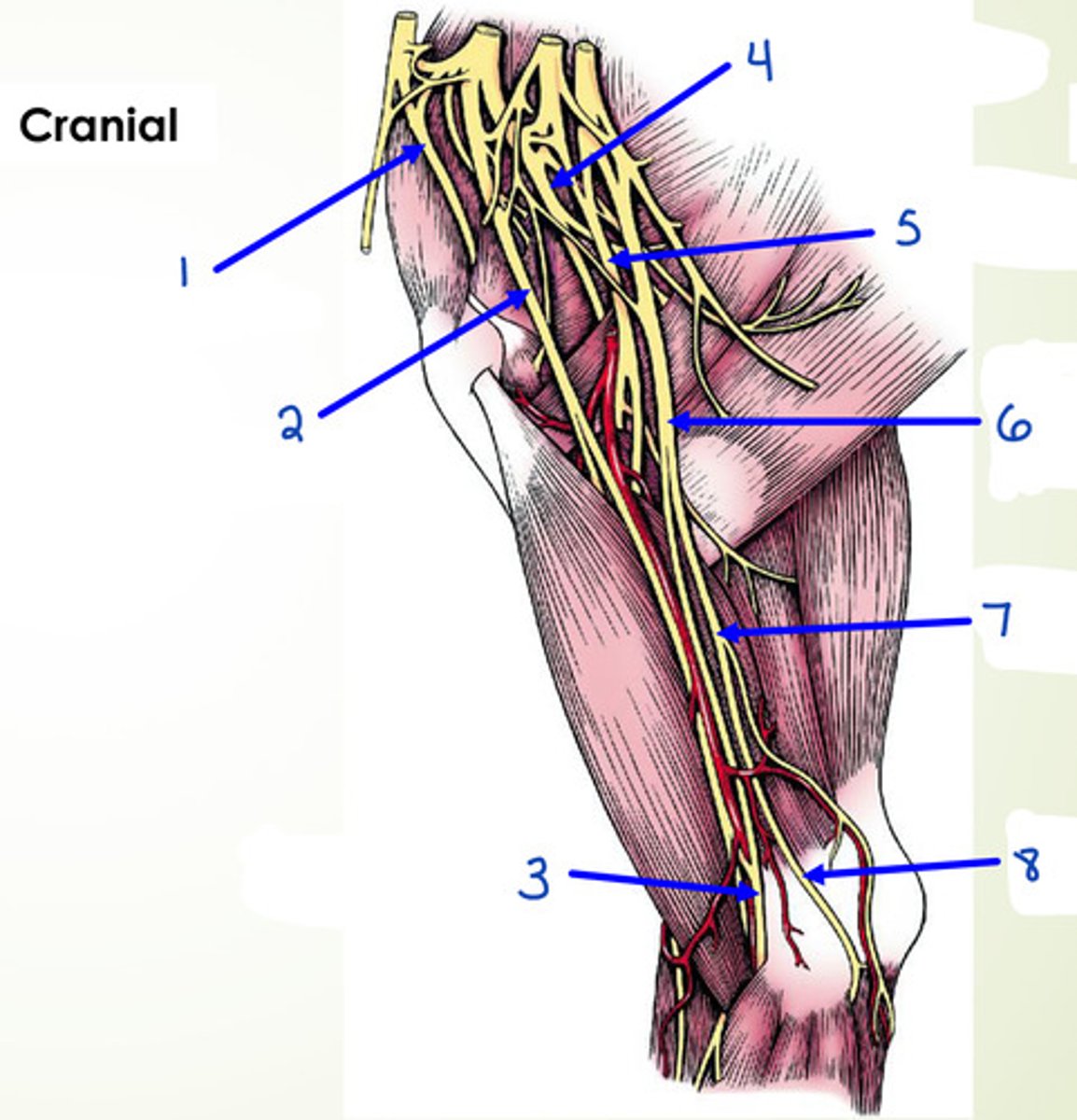
What is 7 and 8?
ulnar n.
What does the suprascapular n. innervate?
supraspinatus, infraspinatus
What does the subscapular n. innervate?
subscapularis (one or more branches)
What does the musculocutaneous n. innervate?
coracobrachialis, biceps brachii, brachialis
What does the axillary n. innervate?
deltoideus, teres major, teres minor
What does the thoracodorsal n. innervate?
latissimus dorsi
What does the cranial pectoral n. innervate?
superficial pectoral muscles
What does the caudal pectoral n. innervate?
deep pectoral muscles
What does the radial n. innervate?
Triceps brachii (all heads), Tensor fasciae antebrachii, Anconeus, Extensors of the carpus and digits (Extensor carpi radialis, Common digital extensor, Lateral digital extensor, Ulnaris lateralis, Abductor digiti I longus, Supinator)
What does the median n. innervate?
Flexor carpi radialis, Pronator teres, Superficial digital flexor, Deep digital flexor (humeral, radial, ulnar heads), Pronator quadratus
What does the ulnar n. innervate?
Flexor carpi ulnaris (ulnar & humeral heads), Deep digital flexor (ulnar head), Interossei
What does the lateral thoracic n. innervate?
cutaneous trunci
What does the long thoracic n. innervate?
serratus ventralis thoracis
What are the nerves of the manus in the horse?
median and ulnar
What is the main innervation of the manus in the horse?
median n.
Where does the median n. divide into medial and lateral palmar nerves?
above the carpus
What does the ulnar nerve branch into above the carpus?
dorsal and palmar branches
Where does the median palmar n. lie?
between the interosseus muscle and deep flexor tendon
Where does the medial palmar n. go in the mid-metacarpus region?
sends a communicating branch obliquely and ventrolaterally to the lateral palmar n.
What does the medial palmar n. become just above the fetlock?
medial (palmar proper) digital n
Which branch of the median n. has ulnar n. contribution?
lateral palmar n.
What does the lateral palmar n. branch into in the metacarpal groove?
medial and palmar metacarpal nerves
What does the lateral palmar n. become just above the fetlock?
lateral palmar proper digital nerve
What is the dorsal aspect of the distal forelimb innervated by?
1. dorsal branch of the ulnar nerve
2. medial cutaneous antebrachial nerve (branch of musculocutaneous n.)
3. dorsal branches from medial and lateral (palmar proper) digital nn.
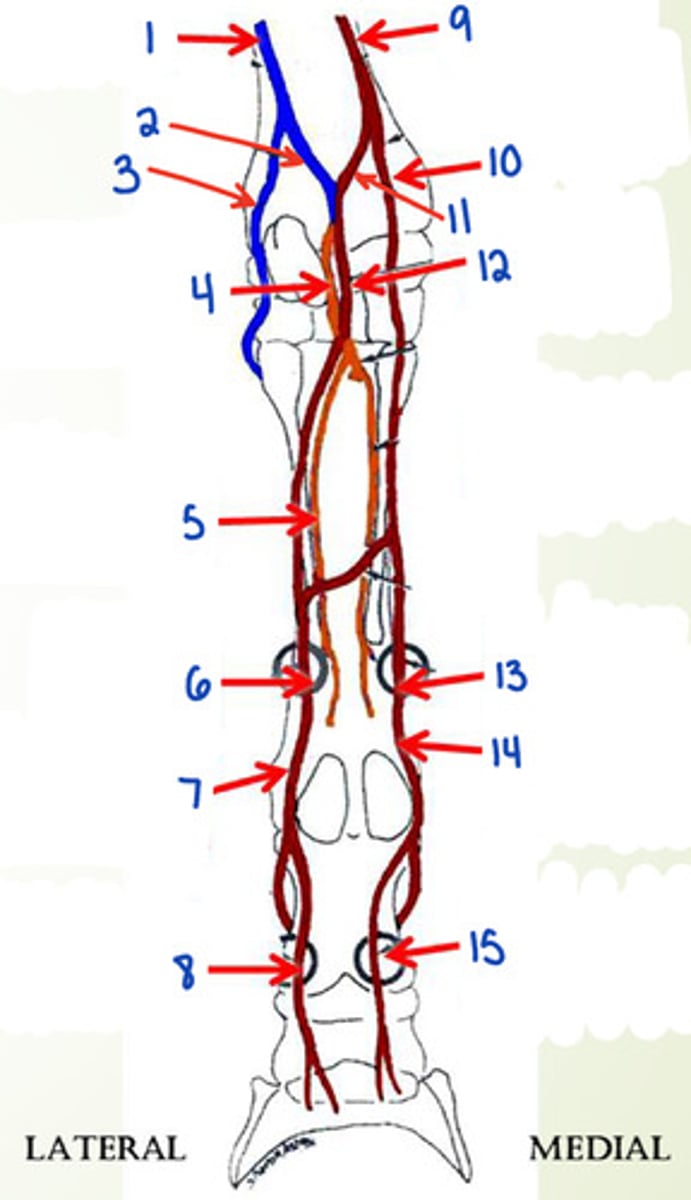
What is 1?
ulnar n.
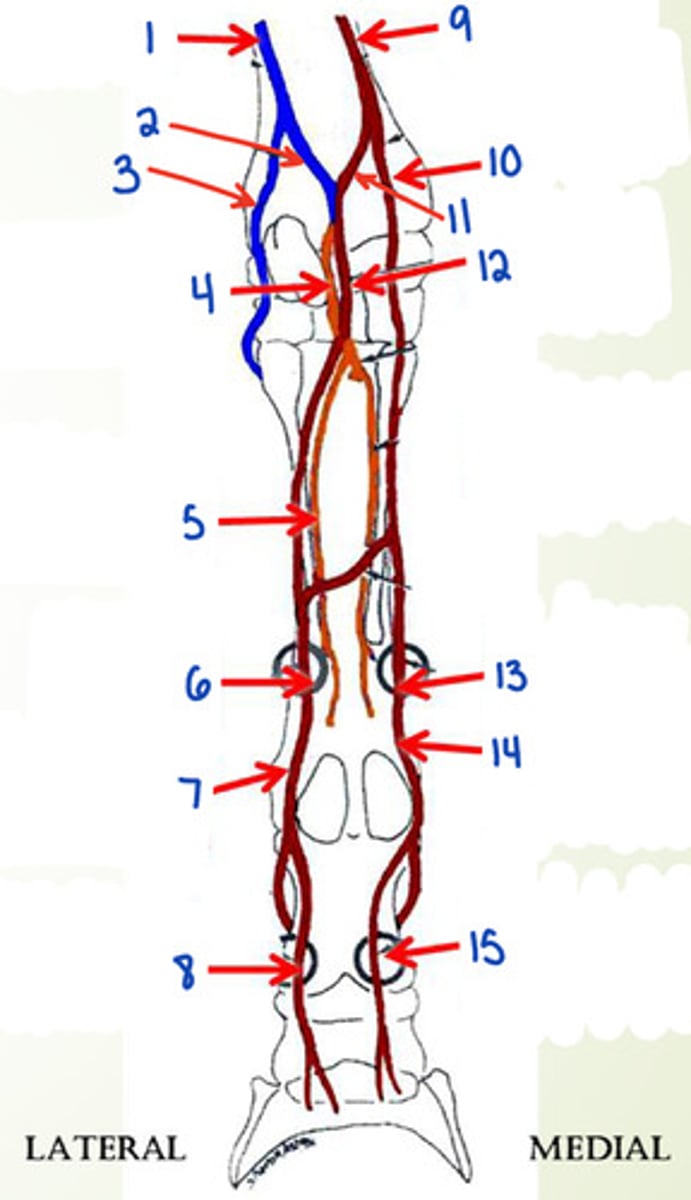
What is 2?
palmar br. of ulnar n.