alcohols phenols ethers
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
aliphatic
straight chain
alcohol formation
substitute —OH in H in aliphatic hydrocarbons
phenol formation

Ether formation

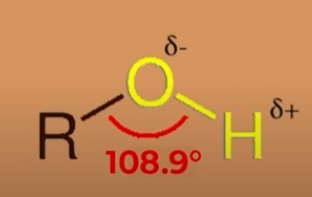
why is OH bond polar
O is electronegative
def electronegative
Electronegativity is a measure of how strongly an atom attracts shared electrons in a chemical bond. It essentially describes an atom's ability to pull electrons towards itself when forming a bond
which is more acidic? alcohols or water
In alcohols , the alkyl group has +I effect as a result it increases the electron density over the oxygen atom. Due to this, the release of ion from alcohol becomes more difficult than from water as a result alcohol is a weaker acid.
Conjugate acid and base meaning?
In the Brønsted-Lowry theory, a conjugate acid-base pair consists of two substances that differ by only one proton (H⁺). A conjugate acid is formed when a base accepts a proton, and a conjugate base is formed when an acid loses a proton. Essentially, they are related by the ability to donate or accept a proton, making them a joined pair.
which is more acidic? alcohols or phenols?
Phnols are more acidic:
because electron density over oxygen is not constant as the electron donating here is done by delocalised pi electrons in the benzene ring
because the oxygen is not not getting fixed electrons from the benzene ring it depends on H and pulls its electrons. Which in turn will easily come out as H+ ion than in alcohols
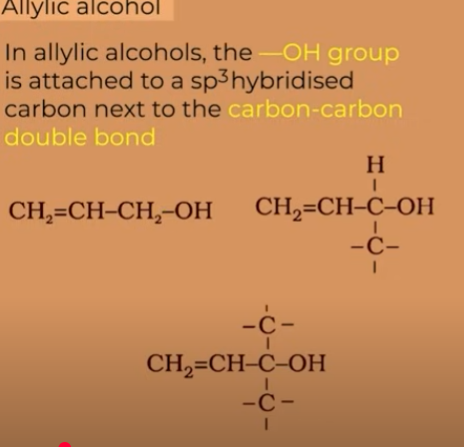
ALLYLIC
"allylic" describes a carbon atom that is directly attached to a carbon-carbon double bond (C=C bond) but is not part of the double bond itself. This carbon atom is referred to as the "allylic carbon".
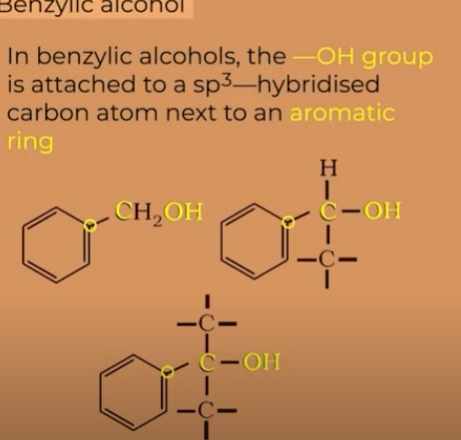
Benzylic
"benzylic" describes the position of a carbon atom that is directly attached to a benzene ring (or other aromatic ring). This carbon is saturated, and the term also refers to the group of atoms attached to that carbon
types of compunds with OH attached to C(SP3)

types of compunds with OH attached to C(SP2)

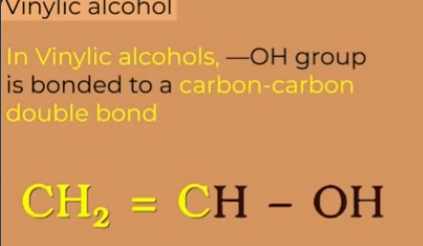
vinylic alcohol
Types of ETHER
SIMPLE ETHER/ SYMMETRICAL (same alkyl group on either side of the O
MIXED/UNSYMMETRICAL
Gylycerol structure

Phynyl
refers to the C6H5 group, also known as a phenyl group or phenyl ring
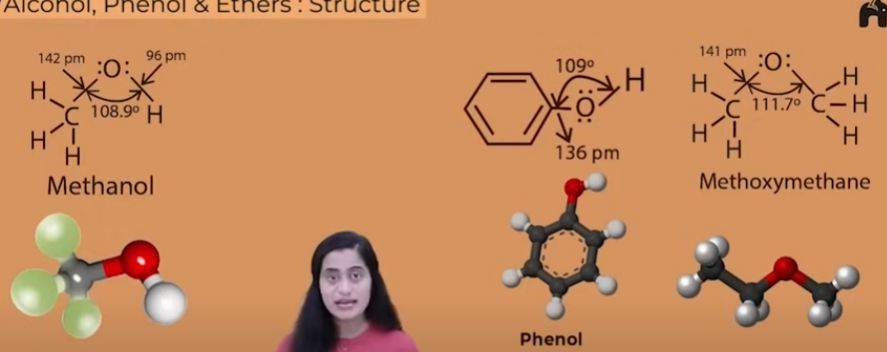
bond angle difference between alcohols, phenols, ethers (all of their stucture)
bond angle in phenols is tetrahedral 109degree
in alcohols its less than 109 as the unpaired electrons in the O repel ach other and the bond angle gets reduced
in ethers it is comparitively higher than both as on each side of the O there is a bulky group which repels each other, hence bond angle is more
BOND LENGTH
bond length of alcohols and ethers is appoximately equal
its the least in phenols as the benzene ring is and resonating stucture and the bond between O and the phenyl group is a partial pi bond
Preparation of alcohols (diff process)
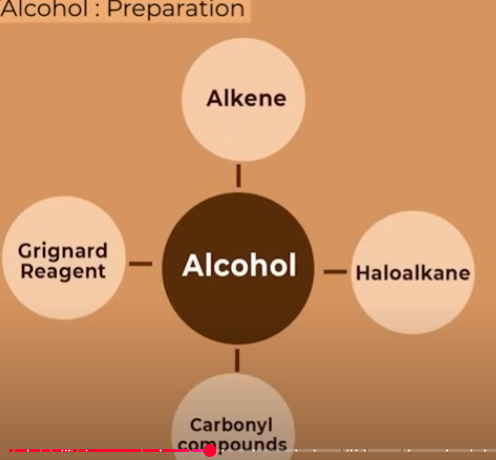
what and through how many types can alcohols be prepared from alkene:?
1) Acid catalyst hydration
2)Hydroboration oxidation(indirect addition of water)
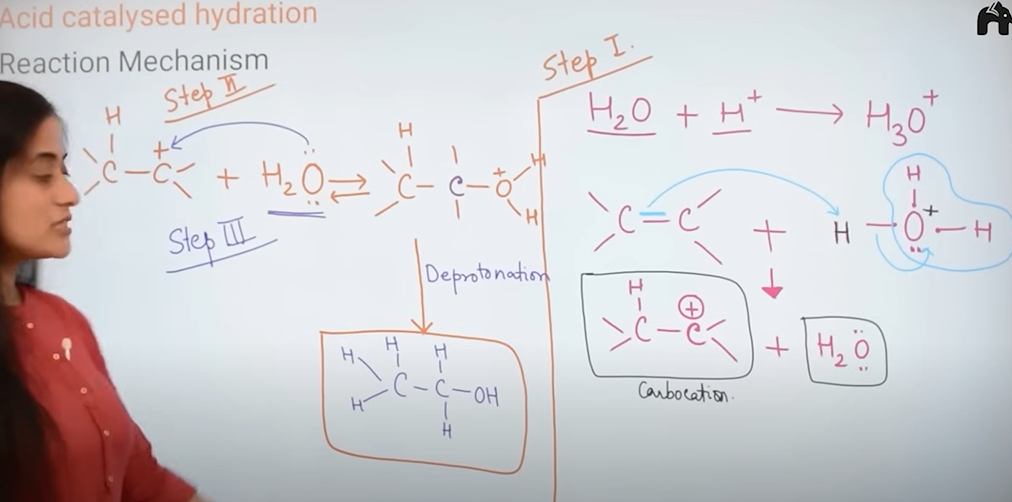
explain the mechanism of acid catalyst hydration
Hydrogen peroxide formula
H2O2
Explain the mechanism of Hydroboration oxidation
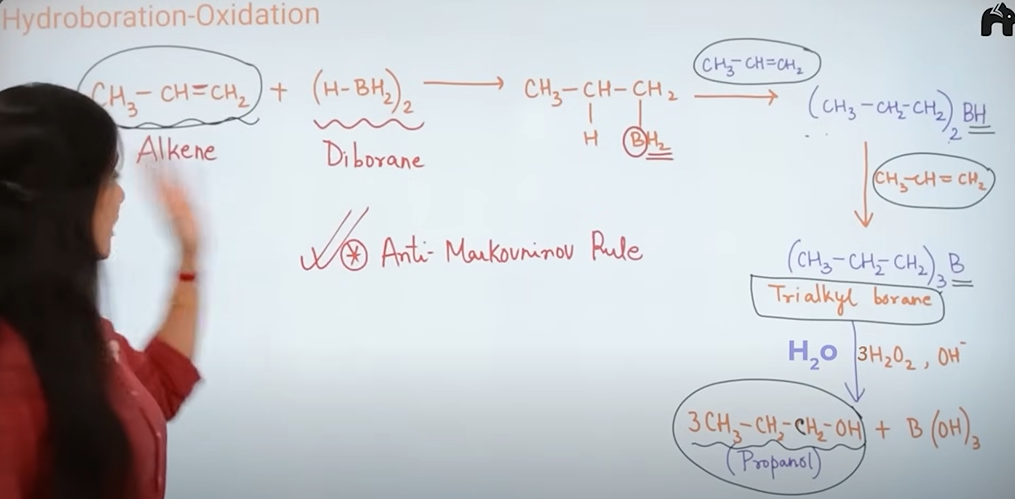
what rule does acid catalyst hydration and hyroboration oxidation follow?
acid catalyst hydration—> Markovnkov rule
Markovnikov and Antimarkovnikov rule
Markovnikov Rule — "Rich gets richer"
H goes to the carbon that already has more H, and the other part (like Br, OH) goes to the carbon with fewer H
Happens only with HBr + peroxide (ROOR).
H goes to the carbon with fewer H, and Br goes to the one with more H.
Carbonyl group
C=O
Different carbonyl groups to form alcohols from
You can form alcohols by the reduction of the following compunds
Aldehydes
ketones
carboxylic group
esters
Alcohols from aldehydes and ketones
catalytic hydrogenation

Alcohols from Carboxylic acid

Alcohols from Esters
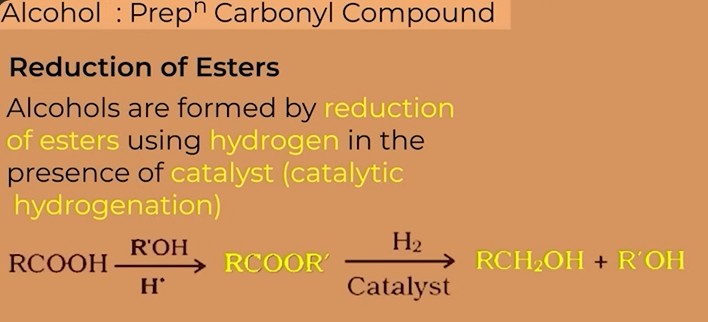
Grignard reagent
R-Mg-X
Alcohols from Grignard
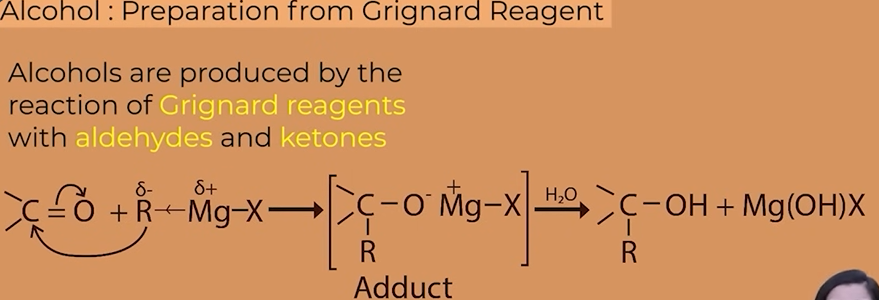
different alcohols from methanal,aldehydes and ketone

Preparation of phenols(carbolic acid)
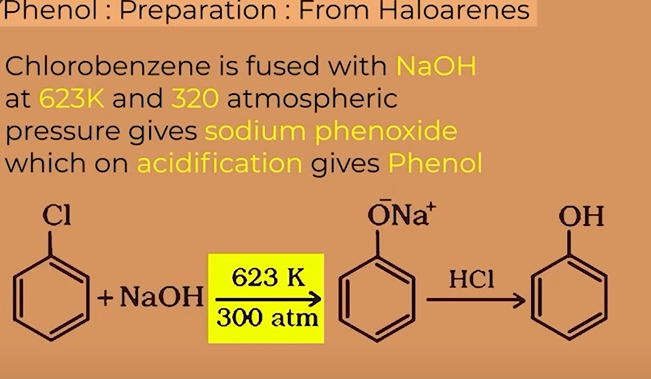
Chlorobenzene
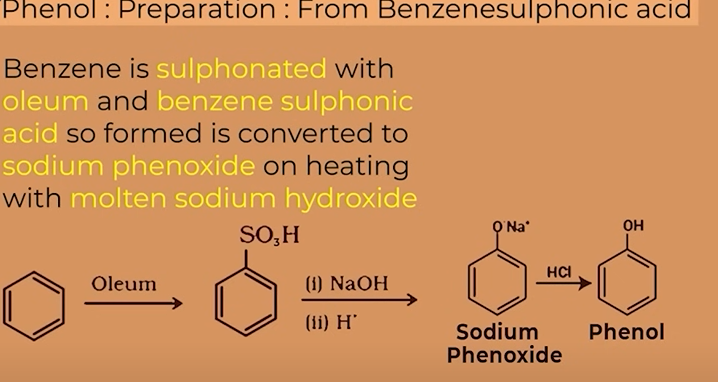
benzene sulphonic acid
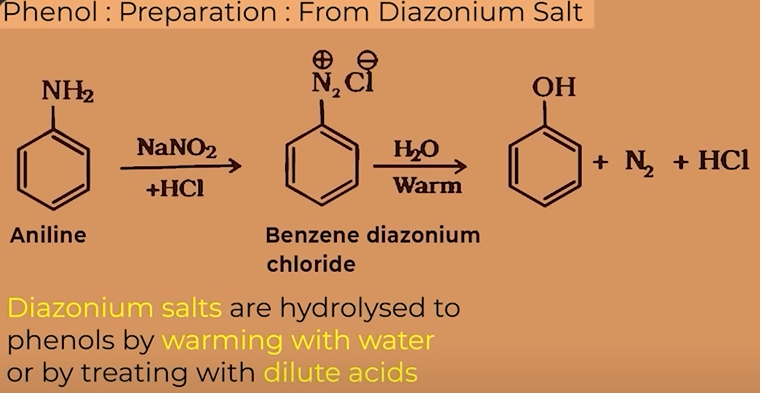
ANILINE (to diazonium salts to phenol)
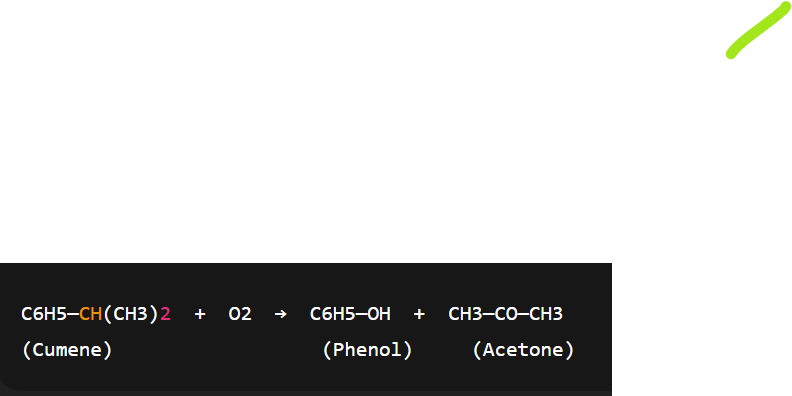
cumene-industrial name aka isopropyl benzene
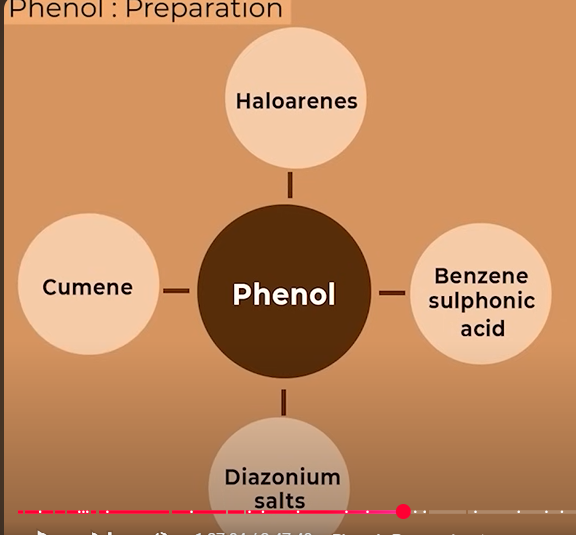
prep of phenol from chlorobenzene
prep of phenol from benzene sulphonic acid
BENZENE sulphonic acid is obtained from benzene through sulphonation with oleum(H2S2O7)
What is oleum
it is a oil. basically fuming suphuric acid
prep of phenol from Anilne
aniline first converted to benzene diazonium salt (DIAZODISATION) followed by warming with water or with dilute acid
prep of phenol from Cumene(Isopropylbenzene)
this is industrial method for prep of phenol
cumene is oxidised to cumene hydroperoxide using air which on acid hydrolysis produces phenol along with acetone
write the properties of alcohol
BOILING POINT OF ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS:
boiling point of lower alcohols is more than that of other classes of compounds
increses with increase in molecular mass
decreases with increase in branching
SOLUBILITY:
CHEMICAL PROPERTY OF ALCOHOLS:
versatile compounds, acts as both nucleophile (O—H Bond breaks) and electrophile (C—O breaks)
ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS ACT LIKE BRONSTED ACIDS
(BRONSTED LOWRY ACID- a substance that can donate a proton (hydrogen ion, H+) to another substance

when do alcohols act as electrophiles?
C—O breaks
when h+ (proton) is joined with an alcohol, we get protonated alcohol which acts as an electrophile.
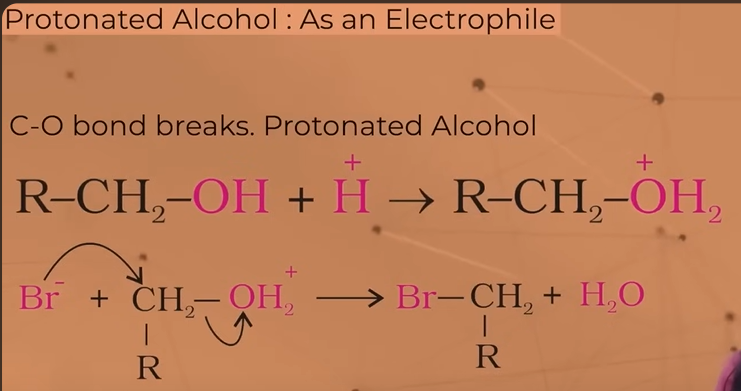
what are the Reactions invoving the cleavage of O—H Bond in alcohols (acts as a nucleophile)
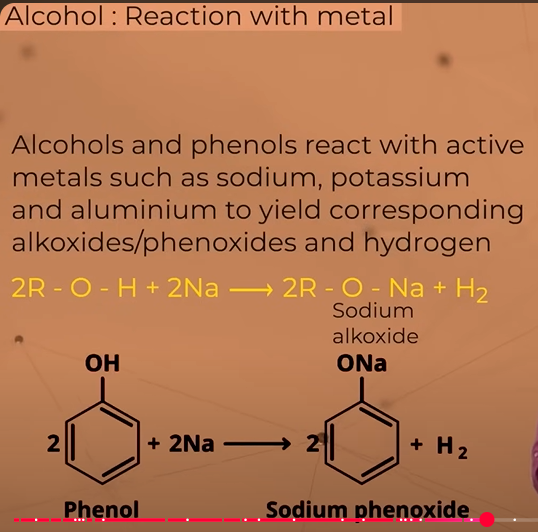
reactions with metal
esterification
acetylation
what are the Reactions invoving the cleavage of C—O Bond in alcohols (acts as a electro)
Reaction of alcohols or phenols with metals
order of acidity among alcohols
in tertiary alcohols the number of alkyl groups is more, they donate electrons to C as well so the dependence of C on H reduces and the bond does not break easily. a compund is said to be acidic if it donates H+ and thats not the case here (the polarity of O—H is less here
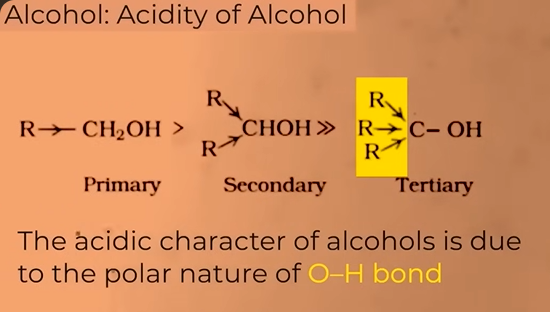
alcohols are weaker acids than water
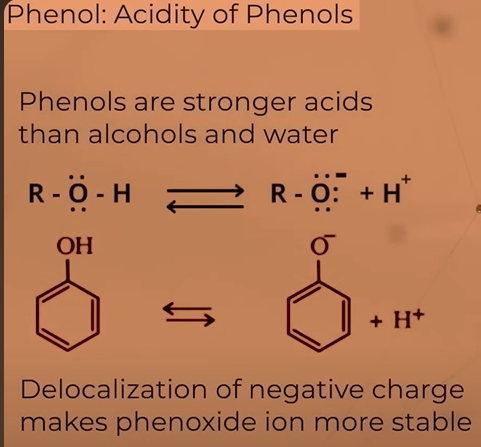
Acidity of phenols
strongerr acid than water and alcohols
as OH attached to sp2 ccarbon (greater the s character more is the electronegativity) the electron density over O is less so it’ll pull electron towards itself from H, releasing H+ ions(acid behaviour)
when alcohol and phenol ionised, they from alkoxide and phenoxide
how is the acidity of phenols affected when substituted by an electron withdrawing group
acidity increases, because when the substituent withdraws electron the electron density over oxygen decreases which will now pull electron from H releasing H+ more easily
happens more when the substituent is present in ortho/para position
ex- nitro group- electron withdrawing
how is the acidity of phenols affected when substituted by an electron donating group
electron donating groups such as alkyl groups, in general do not favour the formation of phenoxide ion decreasing in acid strength
Why are cresols less acidic than phenols
there are alkyl groups attached in cresols
they donate electrons
various process through which we can get esters from alcohols and phenols
reaction with carboxylic acid
reaction with Acid anhydrides
reaction with acid chlorides
reaction of alcohols or phenols with CARBOXYLIC ACID
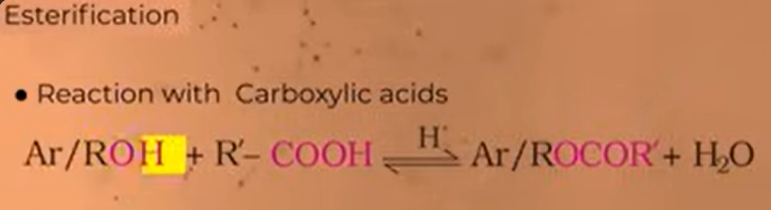
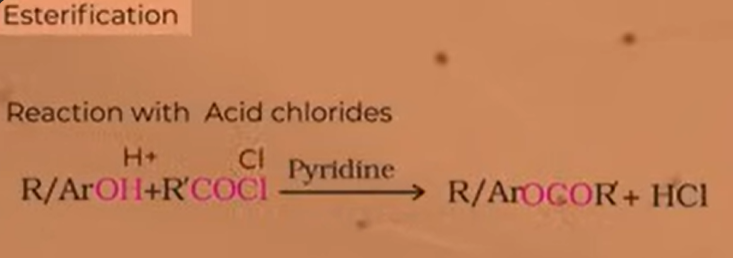
reaction of alcohols or phenols with ACID CHLORIDES
pyridine is a base used to neutralise the acid that is release in the product-HCl
because of pyridine which reduces the produc or neutralises it; it creates forward reaction
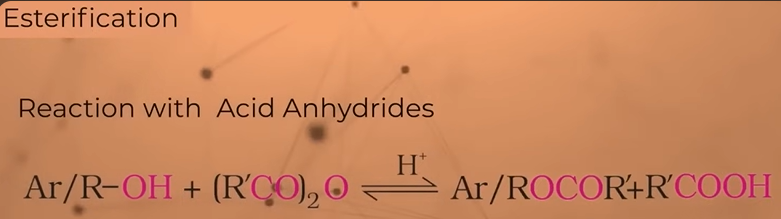
reaction of alcohols or phenols with AcId ANHYDRIDES
Takes place in the presence of small amt of sulphuric acid
anhydrides structure
Acyl grp—O—acyl grp
Acyl grp- (R—CO)
Anhydrides (R—CO)2O
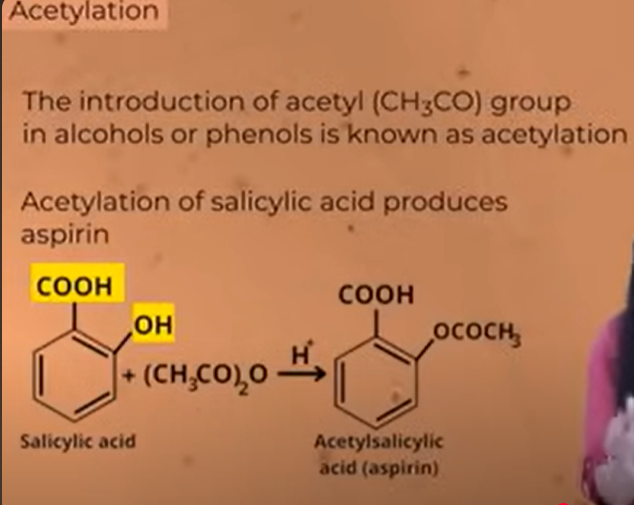
process of acetylation to make asprin
Why is C=O cleavage only seen in alcohols and not phenols
Alcohols have a C-OH bond that is more easily cleaved due to the lack of resonance stabilization, while in phenols, the oxygen lone pair is delocalized into the aromatic ring, making the C-OH bond stronger and less reactive.
reactions where C=O bond clevage is seen in alcohols
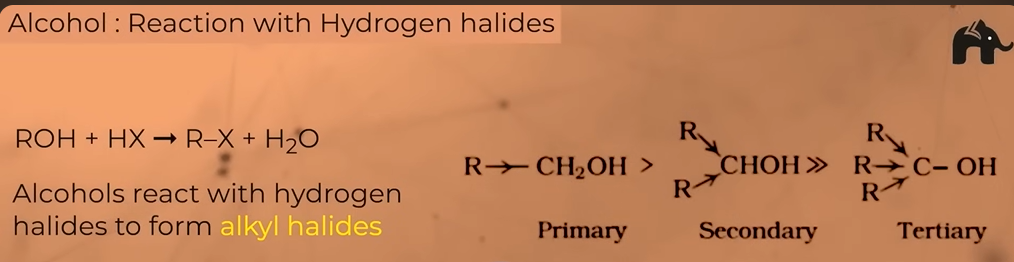
Rn with hydrogen halides HX
Rn with phosphorous trihalde PX3
Rn with Thionyl chloride (SOCl2)
Dehydration
Oxidation
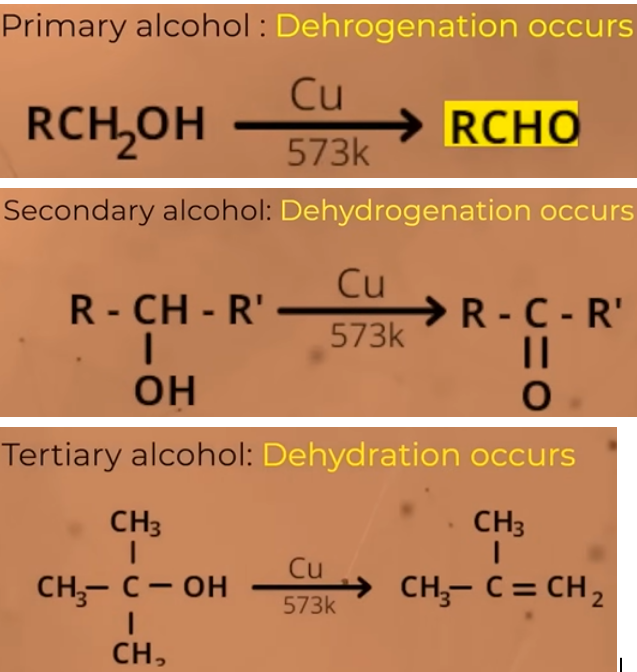
Rn with heated copper
Reaction of alcohols with HYDROGEN HALIDES
FORMS AKLYL HALIDES
DIFFERNT PRODUCTS WITH PRIMARY SECONDARY AND TERTIARY ALCOHOLS
LUCAS TEST TO FIND THE DEGREE OF THE ALCOHOL
LUCAS TEST
REAGENT: Conc HCl and ZnCl2
(alcohols dissove in lucas reagent, while their halides are immisible )
PRIMARY- do not produce tubidity at room temp
SECONDARY-turbidity produced but not immediately
TERTIARY- instant turbidity
Reaction of alcohols with PX3(phosphorous trihalide)
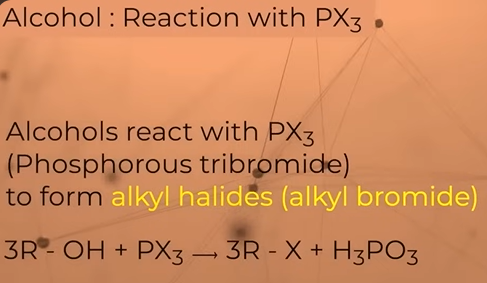
Reaction of alcohols with Thionyl chloride (SOCl2)

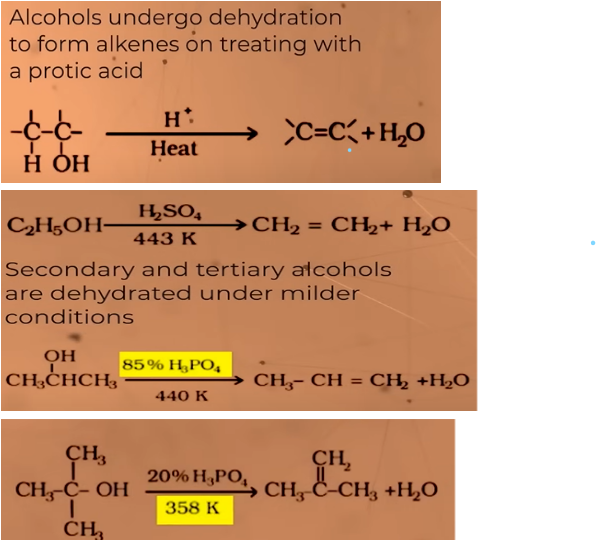
what do we get from dehydration of alcohols
ALKENES
In the presence of protic acids(gives H+ easily like H2SO4 or H3PO4 phosphoric acid)
relative ease of dehydration in alcohols:
tertiary>secondary >primary
reason: in this reaction carbocation is formed. 3o carbocation is more stable in comparison to 2o and 1o
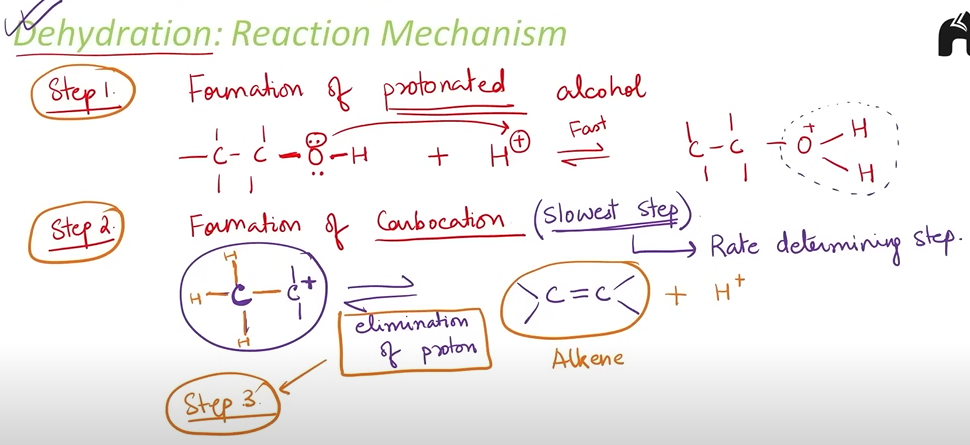
Explain the mechanism of DEHYDRATION
Oxidation of alcohols
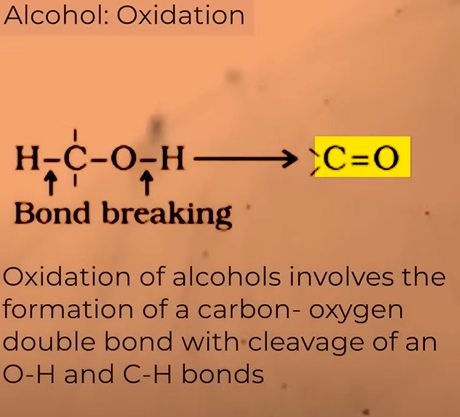
What do you get from the oxidation of alcohols ?
alcohols(oxidation)——>aldehydes(oxidation)——>carboxylic acid
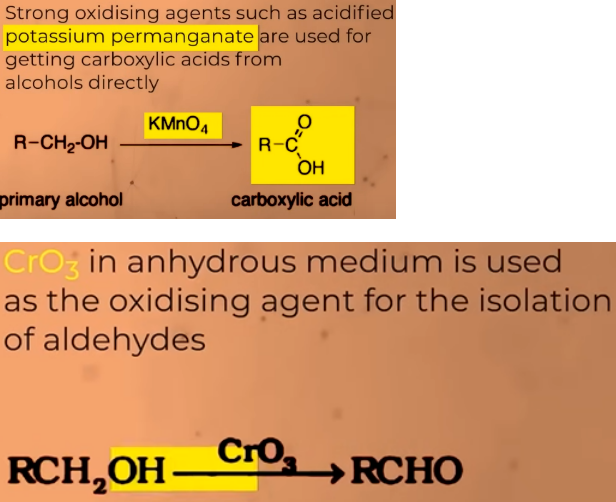
Oxidation of PRIMARY ALCOHOLS
gives aldehydes in good yield

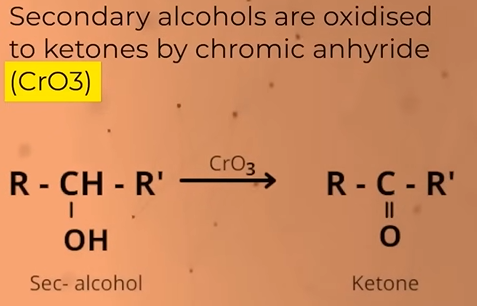
Oxidation of SECONDARY alcohols
gives KETONES
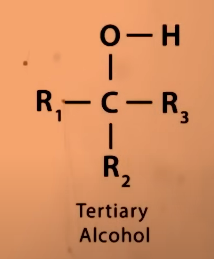
Do tertiary alcohols undergo Oxidation?
NO. because for oxidation to take place C—H and O—H bond needs to break then only C=O is formed.
in tertiary alcohols there is no C—H bond to break that is attached to O—H
what happens when you pass the vapours of 1o 2o and 3o alcohols through heated copper?
TEMP: 573 K
Chemical reactions of Phenol

why is electrophillic aromatic substituition exclusive for phenols?

2 reaction of electrophillic aromatic substituition:
Nitration
halogenation
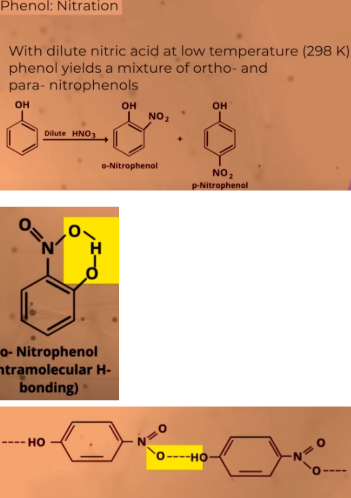
Nitration (DILUTE NITRIC ACID)
both the products can be separated
o-Nitrophenol is steam volatile(evaporate) due to INTRAMOLECULAR hydrogen bonding
p-Nitrophenol is less volatile due to INTEMOLECULAR hydrogen bonding
can be separated through DISTILLATION
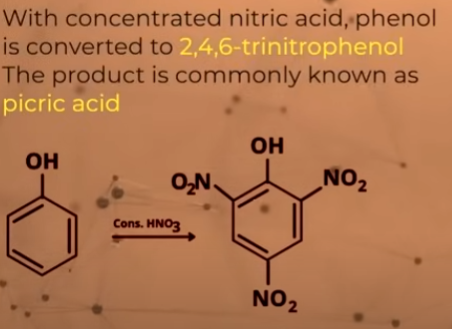
What happens when nitration of phenols is done with concentrated nitic acid
halogenation of phenol
para is major product
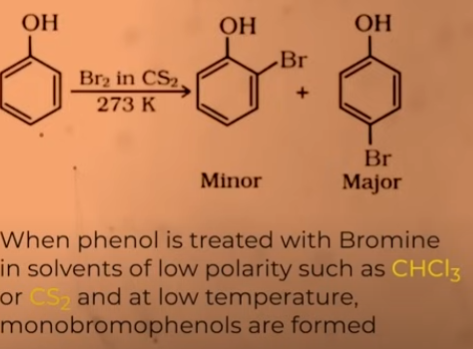
Halogenation of benzene takes place in the presence of a lewis acid. why is a lewis acid not required for the halogenation of phenols?
OH is a highly activating group as well hence the presence of lewis acid is not needed
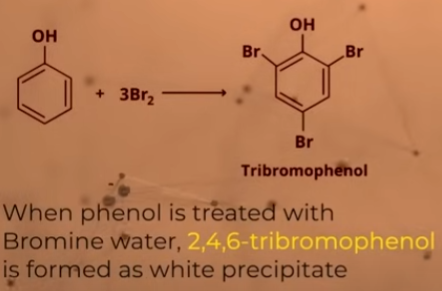
What happens when phenol reacts with bromine water
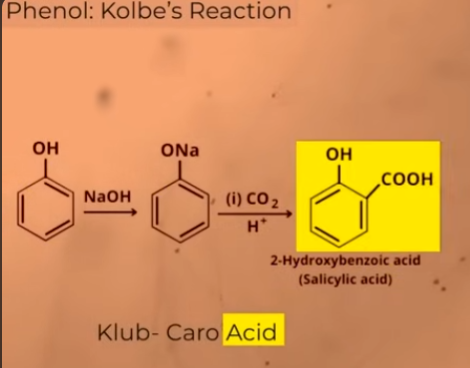
KOLBE’S REACTION
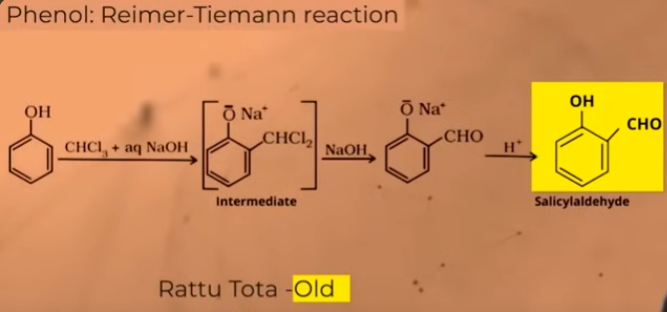
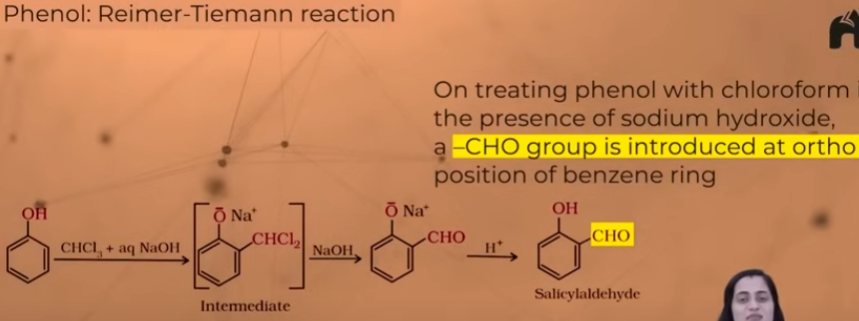
Reimer-Tieman reaction
(ortho formation of phenols - aldehyde gets added to ortho position of phenols)
Choloroform formula
CHCl3
Mechanism of Reiman tieman reaction
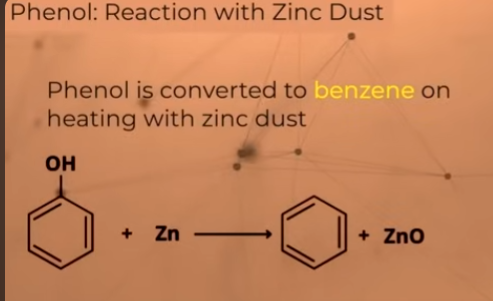
Reaction with Zinc Dust
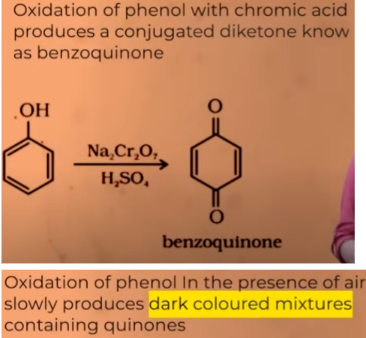
Oxidation of phenons
comercially important alcohol- METHANOL
aka “wood spirit”
solvent for fats, oils, paints etc
added to ethanol to make it unfit for drinking(denatures industrial alcohol)
used to prepare FORMALDEHYDE which is in turn used to make plastics
Preparation of Methanol

comercially important alcohol- ETHANOL
commonly known as alcohol
substitute of petrol
acts as solvent for paints
preservative for biological species
fuel for lamps
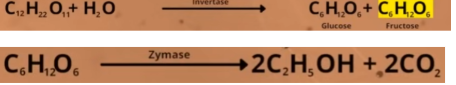
preparation of ethanol(commercially important)
ether used for anastesia
Diethyl ether
how is an ether formed
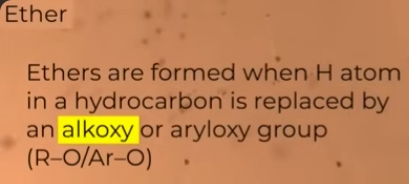
Preparation of ether
dehydration of alcohol
williamson synthesis
dehydration of alcohol
gives ether
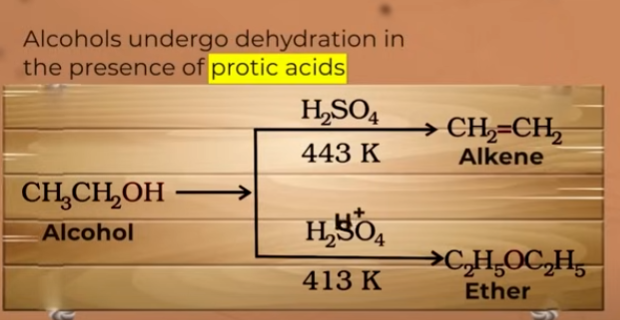
do you get wther everytime alcohol is dehydrated?
no. when alcohol is treated at 413K you get ether
and at 443K you get alkene
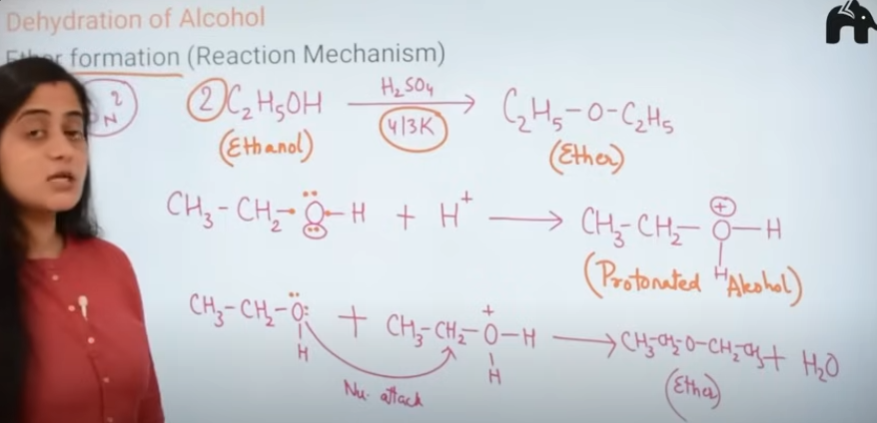
mechanism of dehydration of alcohol to form ether
Nucleophillic substitution
protonated alcohol
mechanism of dehydration of alcohol to form alkene
elimination reaction
at a higher temp alcohol behaves like a base
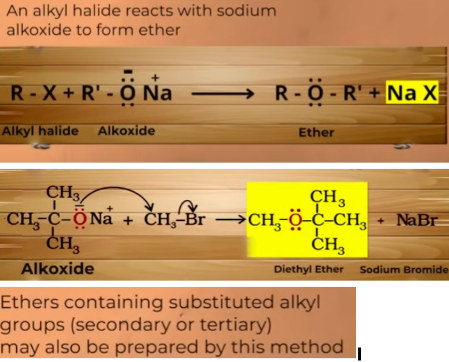
prep of ether by williom synthesis
you can make symmetrical as well as unsymmetrical
it can be done for 2o and 3o as well
nuclephillic substituition
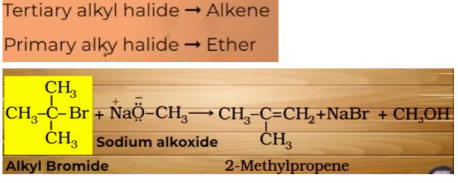
what would happen if alkoxide group is secondary or tertiary instead of alkyl halide in the reaction of Williamson synthesis
elimination takes place instead of nucleophillic substituition
ALKOXIDES ARE NOT ONLY NUCLEOPHILES BUT STRONG BASES ASWELL
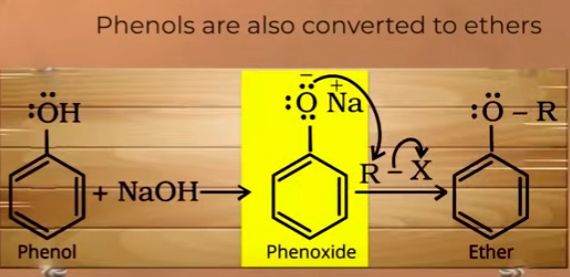
USING williamson reaction phenols can also be converted into ethers
physical properties of ether
dimethyl ether and diethyl ether are gasses while others are colourless liquids
soluble in water
highly volatile and inflammable
increse in boiling point with increase in molecular mass
slight polarity hence have net dipole momet (weak polarity)
which has lesser BP alcohols or ethers
ether<<<alcohols
because of stronger H bonding of alcohols