Types of Bones and Joints
1/40
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
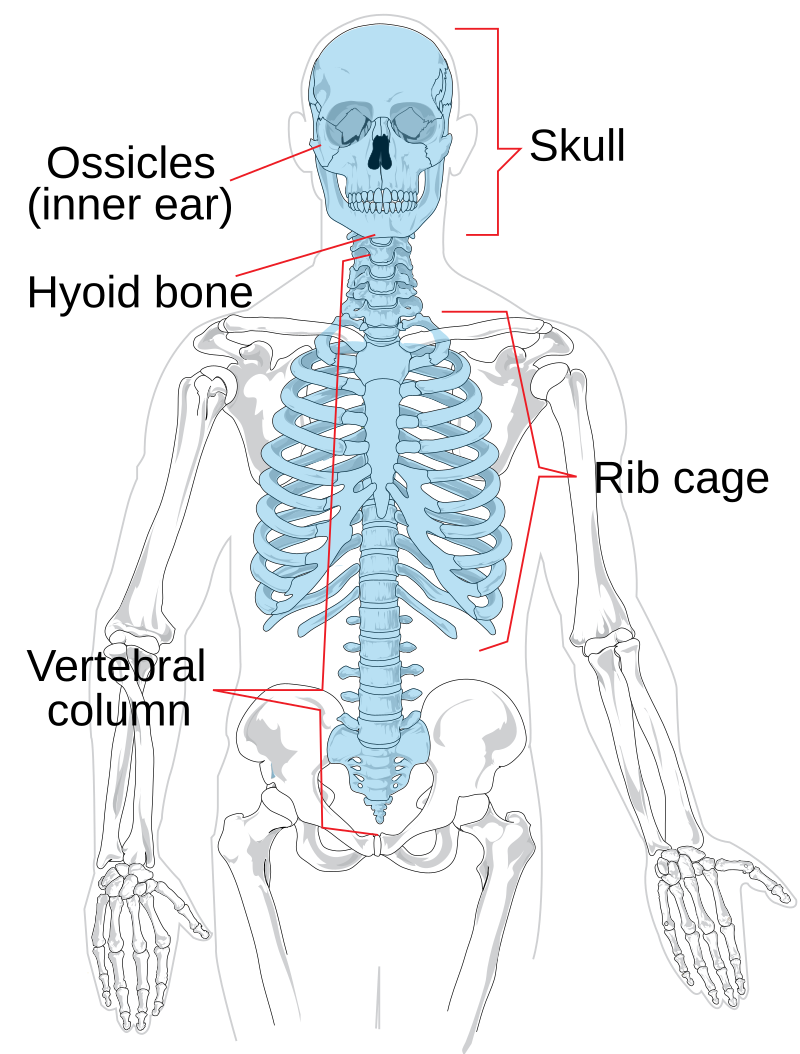
Axial Skeleton
Skull, hyoid bone, sternum, ribs, vertebral column (sacrum and coccyx)
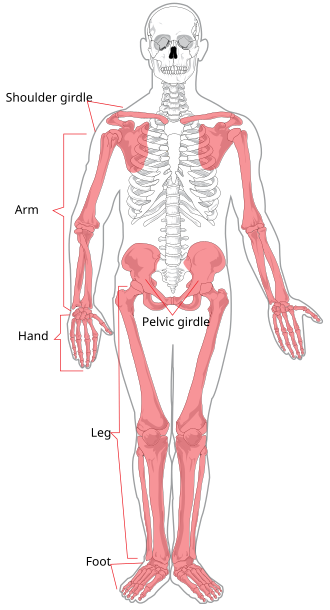
Appendicular Skeleton
Bones of appendages or extremities, including scapula, clavicle, and pelvis
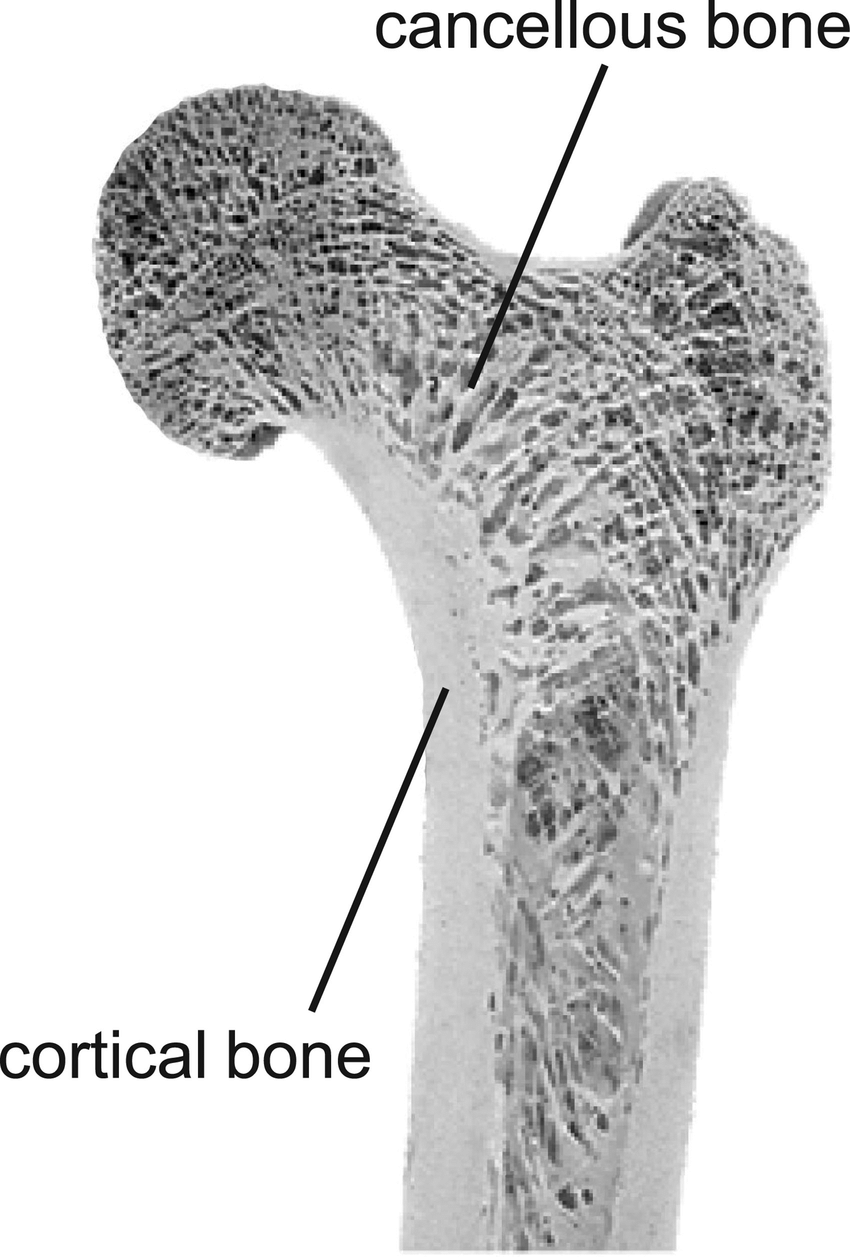
Cortical (Compact) Bone
Dense bone lining the outermost portion of bones
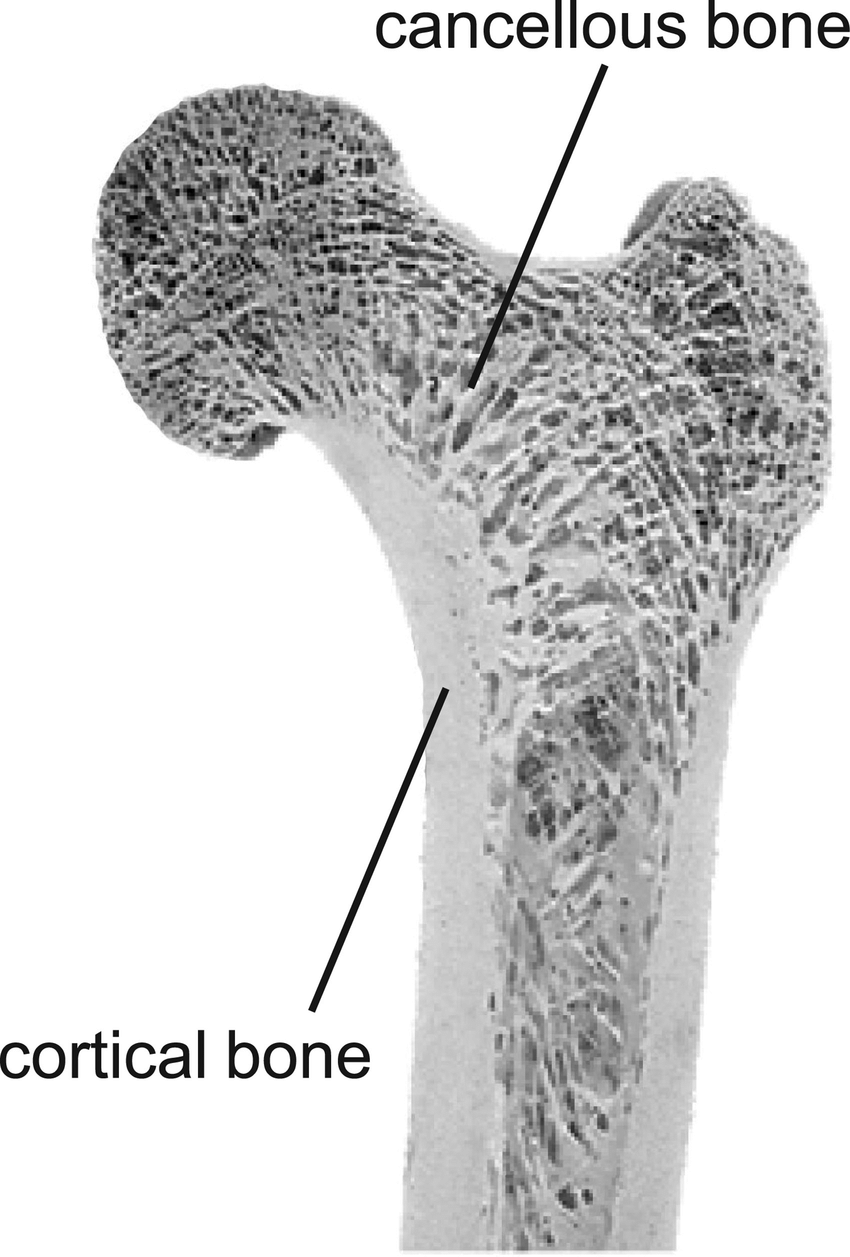
Cancellous Bone
Porous bone composing the inner portions of bone, redirects forces toward weight-bearing surfaces
Diaphysis
In blue
Central shaft of a long bone, composed of cortical bone, withstands compressive forces
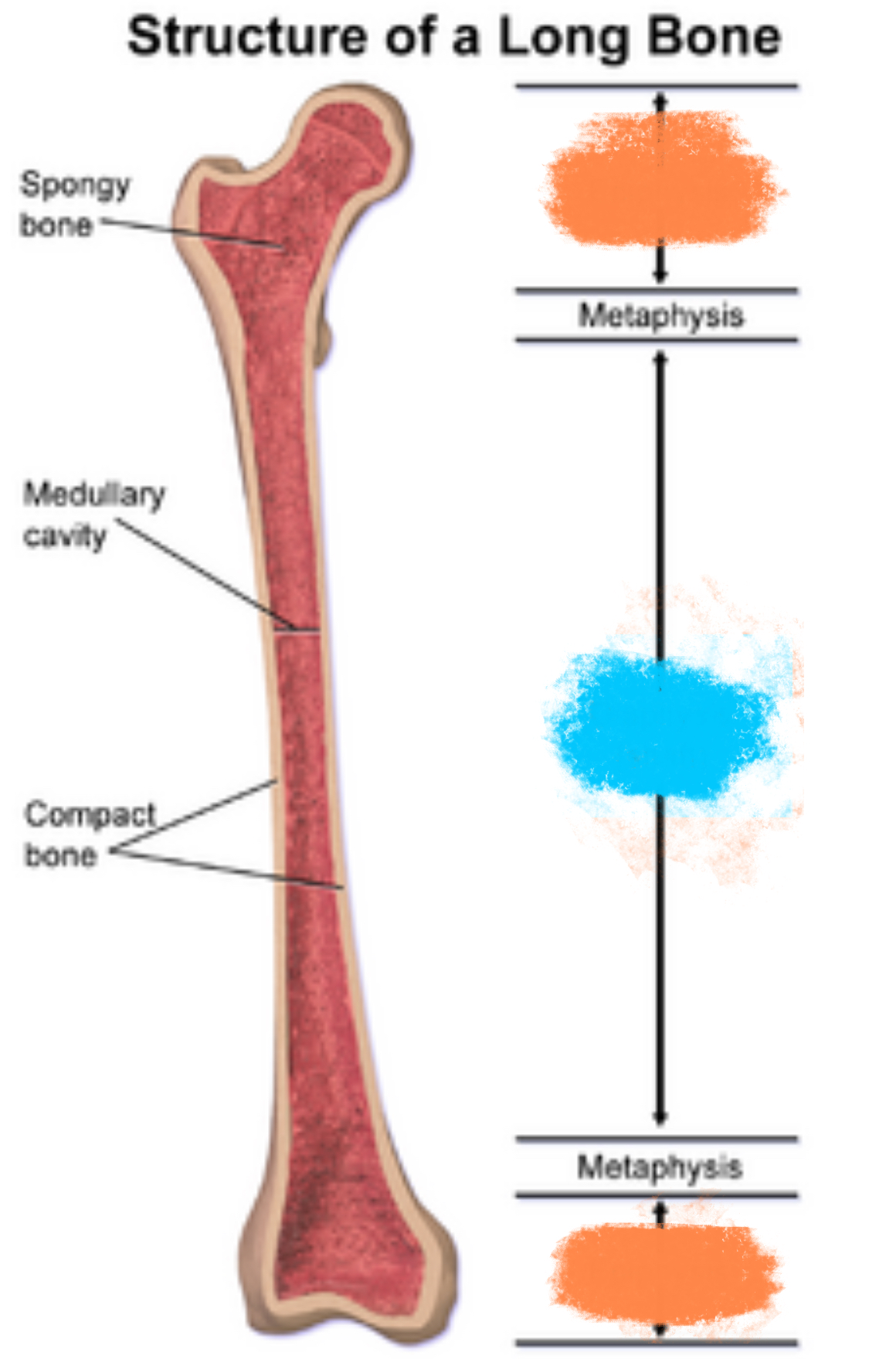
Epiphyses
In orange
Expanded portions of bone arising from the diaphysis, composed of cancellous bone, typically makes up the joint
Articular Cartilage
Lines the articular surface of each epiphysis, acts as a shock absorber between joints
Periosteum
Tough membrane covering each long bone, highly vascularized and innervated, secures attachments of muscles and ligaments
Medullary Canal
Central hollow tube within the diaphysis of a long bone, stores bone marrow and provides passage for nutrient-carrying arteries
Endosteum
Membrane that lines the surface of the medullary canal
Long Bones
•Majority of appendicular skeleton
•longitudinal shafts
•contain expanded portions at ends that make up the joint (e.g., femur, humerus, metacarpals, radius)
Short Bones
Lengths, widths, and heights are typically equal (e.g., carpal bones of the hand)
Flat Bones
Typically flat or slightly curved, broad surface provides an expansive base for muscular attachments (e.g., scapula, sternum)
Irregular Bones
Wide variety of shapes and sizes (e.g., vertebrae, bones of face and skull, sesamoid bones)
Sesamoid Bones
Subcategory of irregular bones, small, rounded appearance, encased within tendon of muscle, protects tendon and increases muscle leverage (e.g., patella)
Synarthrosis
A junction between bones that allows little to no movement. Functions to firmly bind bones together and transmit force from one bone to another. (Skull sutures)

Amphiarthrosis
Formed by fibrocartilage and hyaline cartilage. Limited motion allowed. Play an important role in shock absorption. (Intervertebral discs)
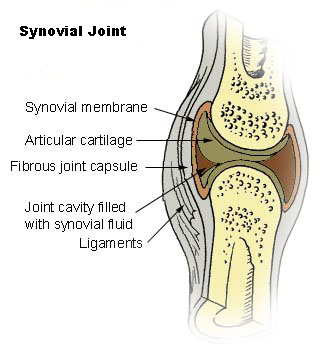
Diarthrosis/Synovial Joint
An articulation that contains a fluid filled joint cavity between two or more bones. Referred to as synovial joints because of the synovial fluid in the joint cavity. (Most joints)
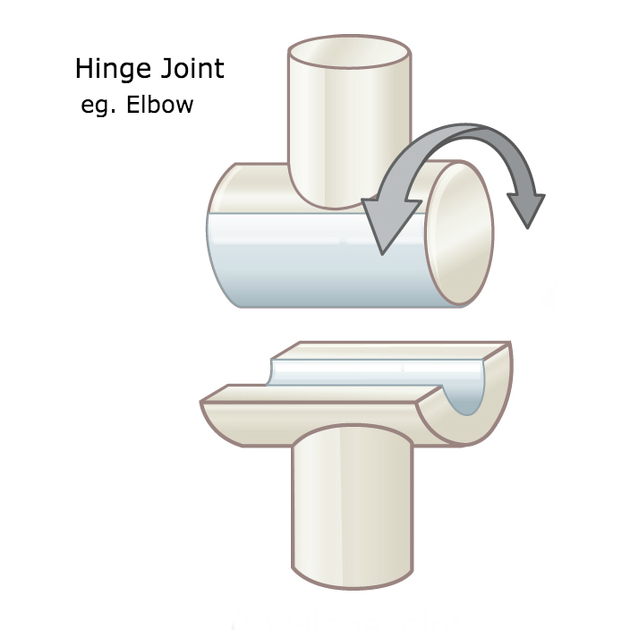
Hinge Joint
Allows motions in one plane about a single axis of rotation. (Humeroulnar joint)
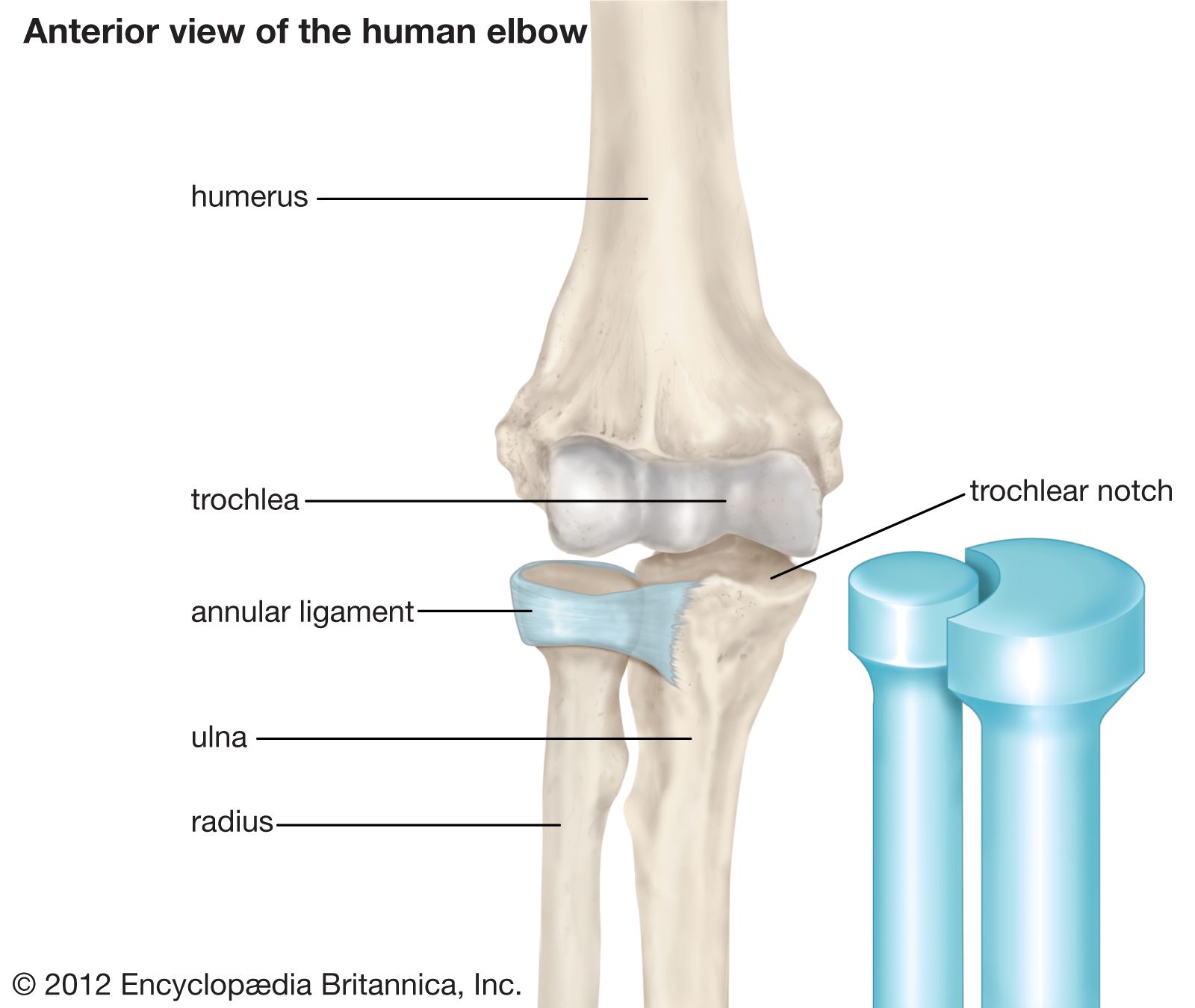
Pivot Joint
Allows rotation about a single longitudinal axis of rotation. (Proximal radioulnar joint)
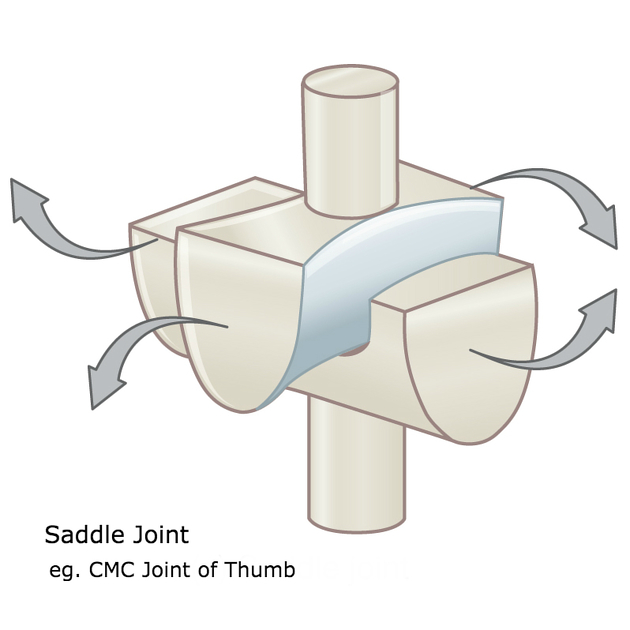
Ellipsoid Joint
Has one convex elongated surface in one dimension mated with a matching concave surface. Allows motion in two planes (Radiocarpal joint)
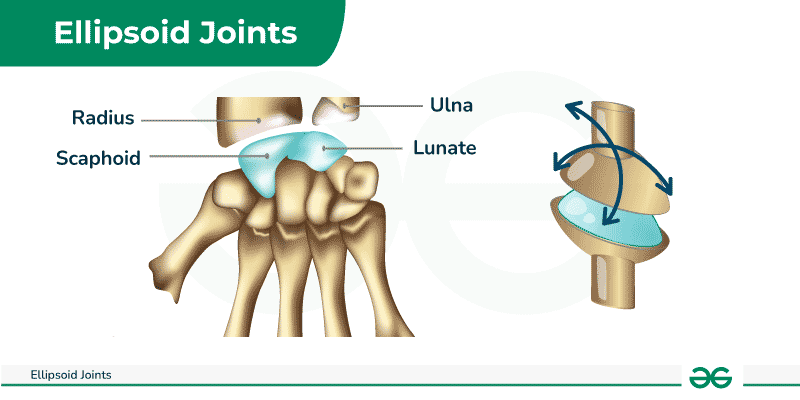
Ball and Socket Joint
Composed of the articulation between a spherical convex surface and a matching cup-like socket. (Glenohumeral joint)
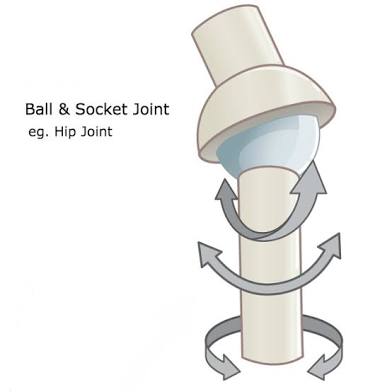
Plane Joint
Composed of the articulation between two relatively flat boney surfaces. Limited motion allowed. Sliding and rotating allowed in many directions. (ex: Intracarpal joints of hand)
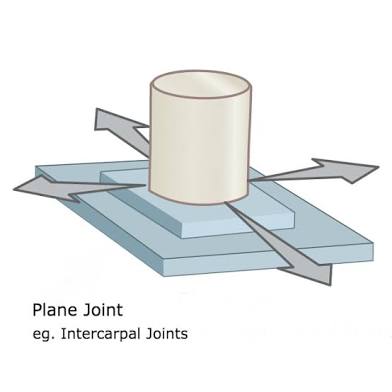
Saddle Joint
Typically allow extensive motion primarily in two planes. Each partner of the has two surfaces: one concave and one convex. Curved surfaces are oriented approximately at right angles, producing stability. (Sternoclavicular Joint)
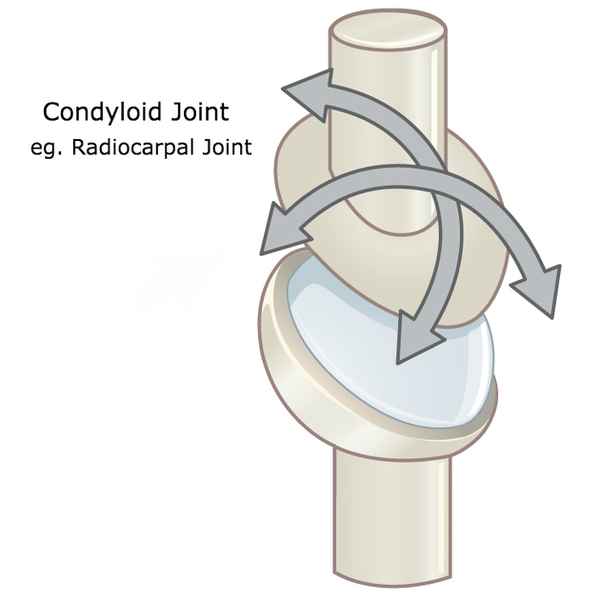
Condyloid Joint
Composed of the articulation between a large, rounded, convex member and a relatively shallow concave member. Allow 2 degrees of freedom.
Type 1 Collagen
Thick and rugged, designed to resist elongation. Ligaments, tendons, and fibrous capsules.
Type 2 Collagen
Thinner and less stiff. Flexible woven framework for maintaining the general shape and consistency of structures such as hyaline cartilage.
Elastin Fibers
Elastic in nature, resist stretch(tensile) forces but have more give when elongated.
Tendon
Connects muscle to bone
Ligament
Connects bone to bone
Plantar
Sole or bottom of the foot
Dorsal
Refers to the top or superior portion of the foot
Dorsiflexion
Movement at the ankle that decreases the angle between the foot and the shin.
Plantarflexion
Movement at the ankle that increases the angle between the foot and the shin (pointing the toes).
Inversion
Lifting the medial border of the foot.
Eversion
Lifting the lateral border of the foot.
Talocrural Joint
Ankle joint formed by the tibia, fibula, and talus.
Subtalar Joint
Located between the talus and calcaneus.
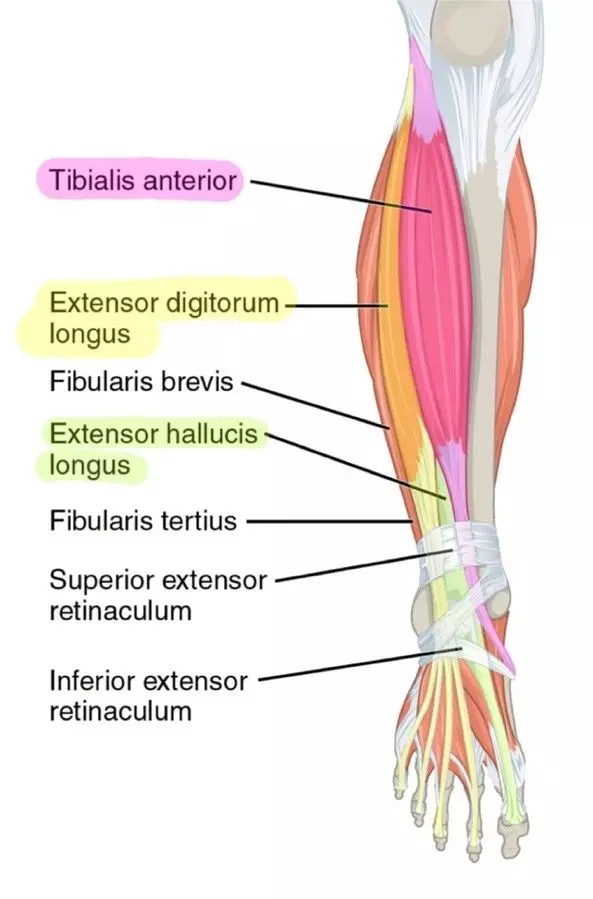
Anterior Compartment Muscles
Tibialis Anterior, Extensor Digitorum Longus, Extensor Hallucis Longus, Fibularis Tertius
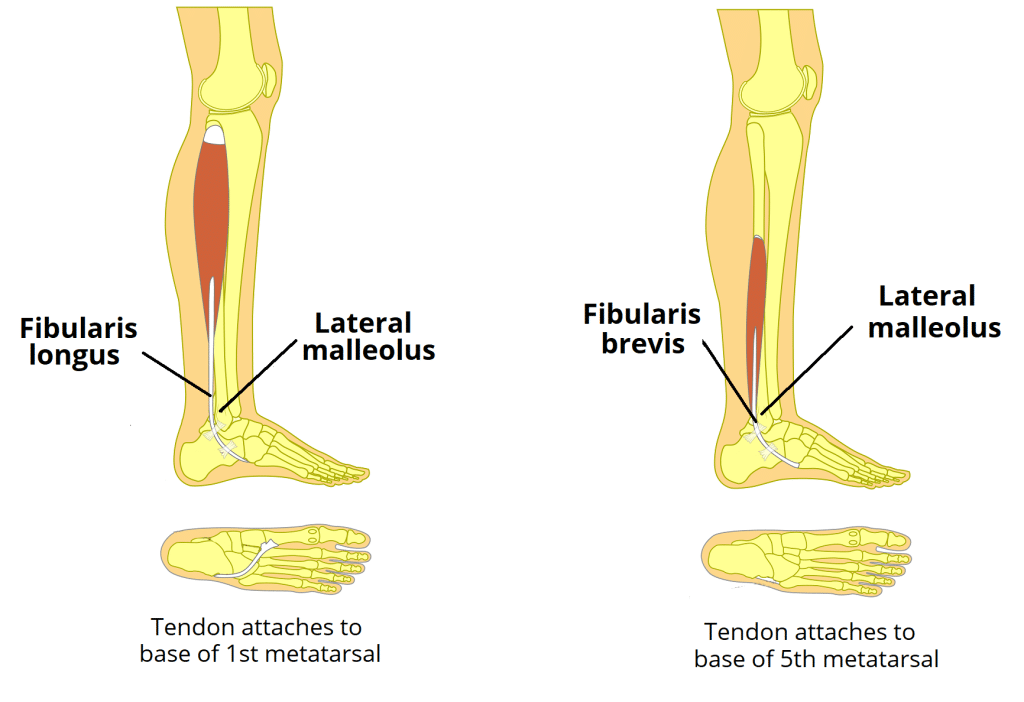
Lateral Compartment Muscles
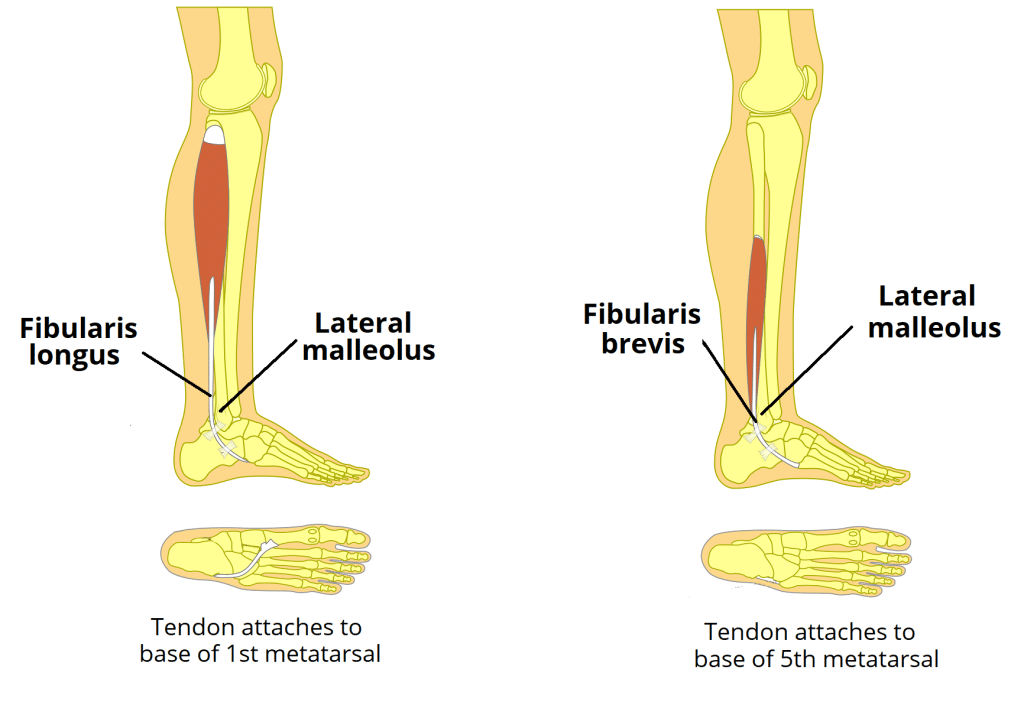
Fibularis Longus, Fibularis Brevis
Posterior Compartment Muscles
Gastrocnemius, Soleus, Plantaris, Tibialis Posterior, Flexor Digitorum Longus, Flexor Hallucis Longus