IB1 economics sem 2
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Market failure
Resources are not allocated efficiently and to what is optimum for society
Negative externality of production
Production of good/service has a negative effect on a third party. MSC>MPC, MSB=MSC. Chicken farming
Negative externality of consumption
An individual's consumption of a good generates a negative effect on third parties not factored into decision to consume the good. MPB>MSB, MSC=MPB. Smoking
Positive externality of production
Resources are underallocated to the production of that good/service, production has a positive effect on third parties. MPC>MSC, MSB=MPB. Beekeeping
Positive externality of consumption
Underconsumption of a good, if external benefits were considered then demand would increase. MSB>MPB, MPC=MSC. Vaccinations
Public good
Provides benefits to society that are non rivalrous and non excludable. No free market for the good eg public parks
Merit good
Goods that are beneficial to individuals or society as a whole but are underconsumed, should be subsidised eg healthcare
Demerit good
Consumption occurs at a rate higher than what is considered socially optimal eg smoking cigarettes
Common access resources
Resources accessible to everyone but can't be used by everyone at the same time and not owned by anybody eg fishing lake
Carbon tax
Tax per unit output of pollutants emitted eg Sweden carbon tax gradually increasing over time
Collective self governance
Stakeholders in a community working together to combat negative externalities of production usually associated with common pool resources eg ecotourism in Borneo rain forests
Tradable permits
Government sets admitted level of pollution, splits it into permits and allocates them to firms- exist on a free market eg used in USA for sulphur dioxide emissions to mitigate acid rain
Pigouvian tax
Indirect tax to increase private costs and correct negative externalities eg UK alcohol tax
Adverse selection
One party in a transaction has more information than the other eg in insurance market highlighting risks of your lifestyle
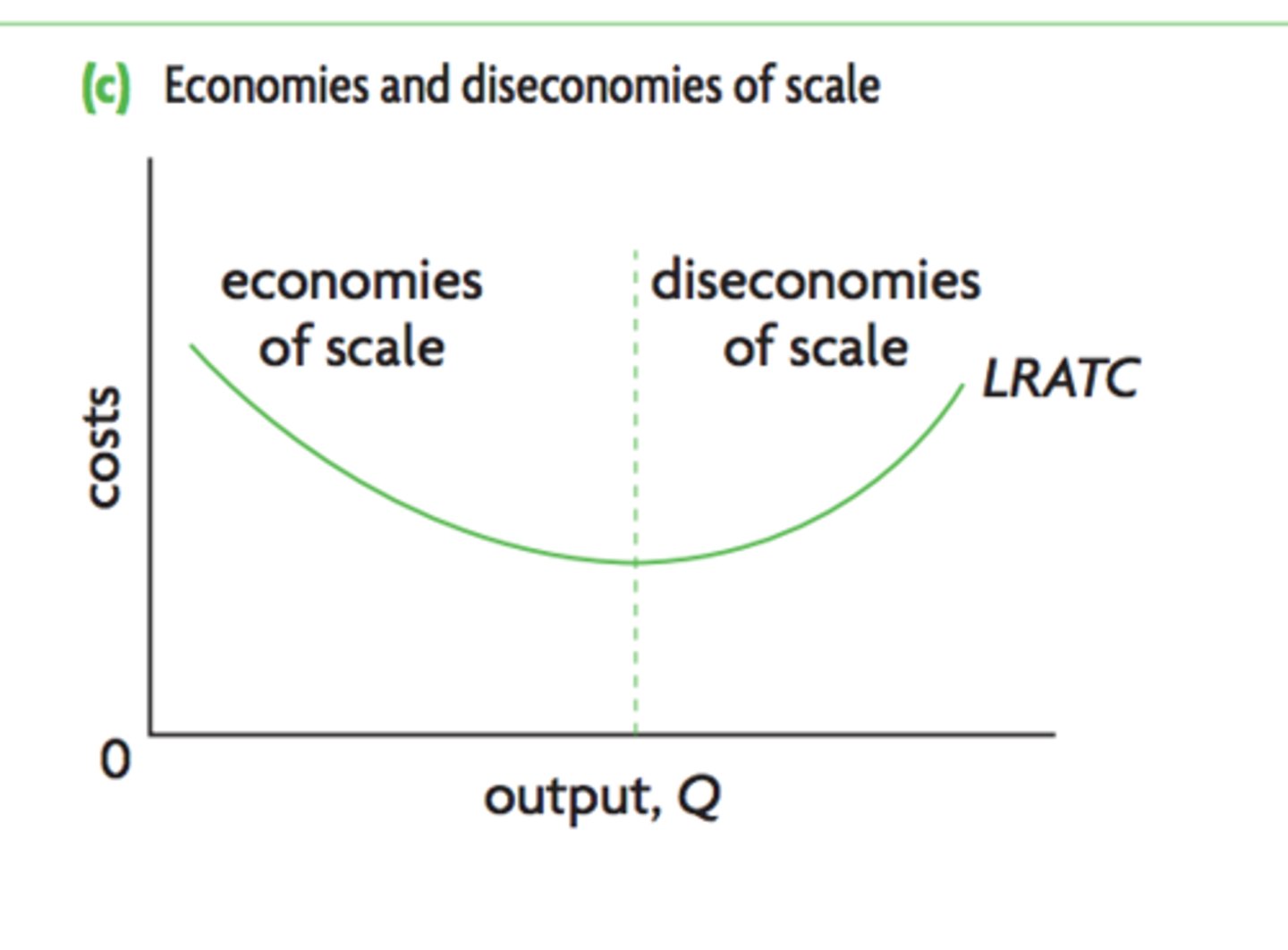
Economies of scale
Decreases in average costs of production over the long run as firms increase all factors of production (downward sloping portion of LRAS curve). Specialisation of labour, bulk buying of FOPs, lower interest rates, spreading of costs like marketing
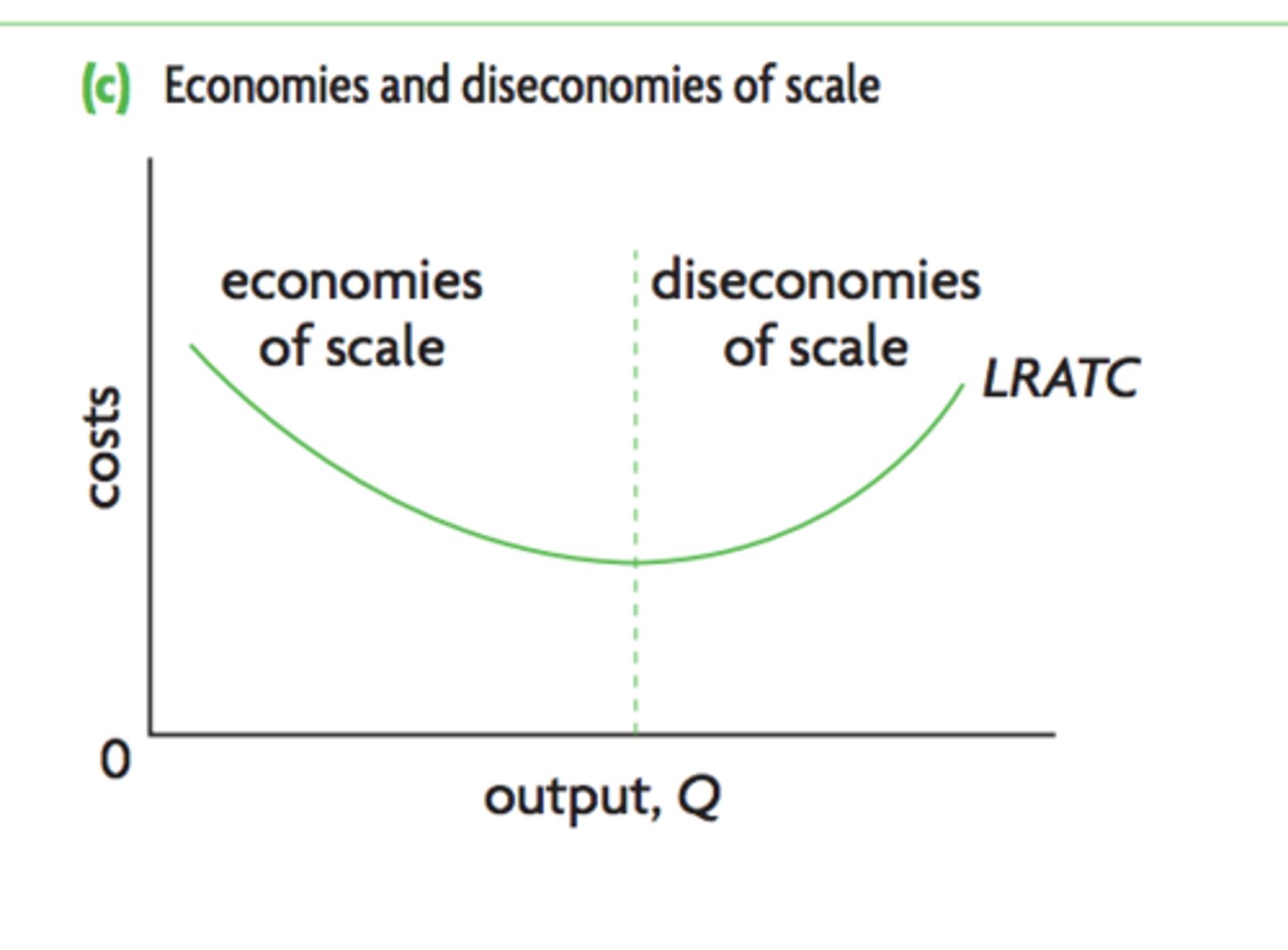
Diseconomies of scale
Company is so big that average costs increase. Coordination and monitoring difficulties eg time zones, multiple levels of management creating slow communication, poor worker motivation (upward sloping of LRAS curve)
Total revenue formula
Price x quantity
Marginal revenue formula
Change of total revenue / change in quantity
Average revenue formula
Total revenue / quantity
Profit formula
Total revenue - total costs
Total costs
(fixed + variable costs) x quantity
Marginal cost
Change in total costs / change in quantity
TR/TC approach to profit maximisation
Output where difference between TR and TC is highest is where profit maximisation occurs
MR/MC approach to profit maximisation
Where MR=MC is the point that profit maximisation occurs at
Market power
Ability of a firm to set price and their relative share of the market
Characteristics of perfectly competitive firms
Many firms, homogenous goods, price takers, only earn normal profit in long run, low barriers to entry/exit (theoretical)
Characteristics of monopolistic competition
Large number of sellers, price takers, similar but not identical goods that are differentiated by advertising eg clothing
Characteristics of oligopolies
Small number of firms, high competition, price makers, high barriers to entry/exit eg supermarkets
Characteristics of monopolies
One firm with all market power, high barriers to entry, no competition eg water companies
Collusive agreement
Non competitive, secret agreement between rival firms to disrupt market equilibrium and gain an unfair market advantage
What does game theory tell us about the characteristics of oligopolies?
Firms are highly interdependent, display strategic behaviour, become worse off as a result of price competition, strong interest in avoiding price wars
Cartel
Formal agreement between firms to take actions to limit competition eg fixing quantity produced by each firm, dividing the market geographically, setting higher prices eg OPEC
Concentration ratio
Percentage output of the market of the largest firms in an industry. If 4 firms produce 45% of the market's output, the 4-firm concentration ratio is 45%
Natural monopoly
A market that runs most efficiently when one large firm supplies all of the output
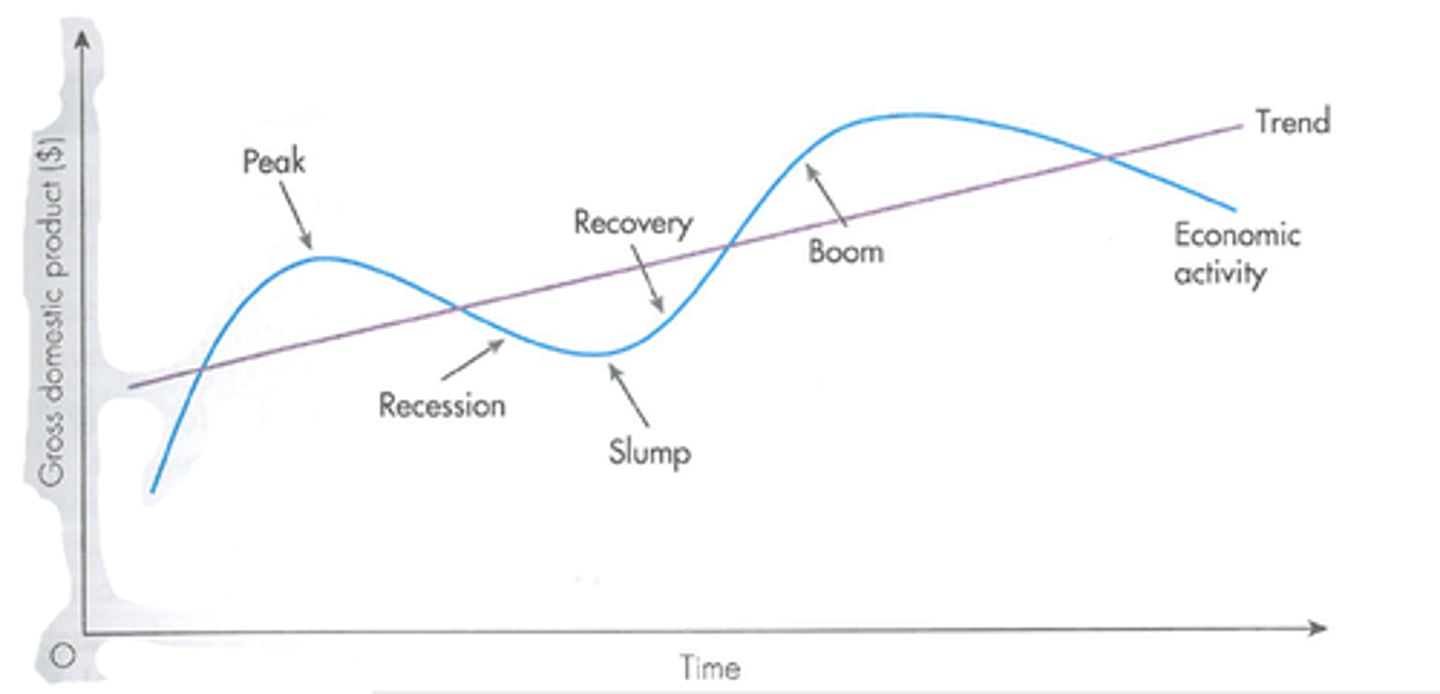
Business cycle
Charts changes in real GDP that occur in an economy over time
Leakages (circular flow)
Taxes, spending money on imports, money saved in banks- all income not spent on goods and services so don't contribute to total output
Injections (circular flow)
Government spending, investment, exports
Expenditure approach for GDP
Sum of 4 components of GDP (household consumption, investment, government spending, net exports)
Income approach for GDP
Sum of costs of production (wages, interest, rent, profits) earned by a nation's household in a year
Output approach for GDP
Sum of outputs of primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors (finished goods to avoid double counting)
GDP
Total value of a nation's output in a particular period of time
GNI
GDP + (income from abroad - income sent abroad)
Happy Planet index
Gives HPI score measured by (wellbeing x life expectancy) / ecological footprint to rank countires by sustainability and happiness
OECD Better Life index
Measures 11 variables such as housing, income, and safety
Aggregate demand
Total demand for final goods and services in an economy at a given time
Aggregate suppy
Total amount of goods and services in the economy available at all possible price levels
Household consumption effect on AD
Consumer confidence, interest rates, income tax, household debt, future price expectations, wealth
Capital investment effect on AD
Interest rates, business confidence, technology (efficiency), level of corporate indebtedness, excess capacity available
Government spending effect on AD
Political and economic priorities
Net exports effect on AD
Foreign and domestic incomes, exchange rate, protectionism
Recessionary/deflationary gap
Real GDP is less than potential GDP created by a fall in aggregate demand. Recession part of business cycle
Inflationary gap
Real GDP is greater than potential GDP created by a rise in aggregate demand. Expansion part of business cycle
Natural rate of unemployment
The unemployment rate that exists when an economy is producing at full employment levels- includes frictional, seasonal, and structural but NOT cyclical
Frictional unemployment
Unemployment that results because it takes time for workers to search for the jobs that best suit their tastes and skills
Seasonal unemployment
Unemployment caused by seasonal changes in the demand for certain kinds of labor
Structural unemployment
Unemployment that occurs when workers' skills do not match the jobs that are available
Cyclical unemployment
Unemployment caused by a business cycle recession
Short term growth
Increase in actual output from reductions in unemployment and inefficiency- increases In AD/SRAS
Long term growth
Increase in resource quantity or quality creating an increase in production possibilities- an increase in potential output
Budget defecit
When the government spends more than it takes in
Debt servicing
Payment of interest and principal of debt (of a country or individual).