Biology - A Level Practical
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
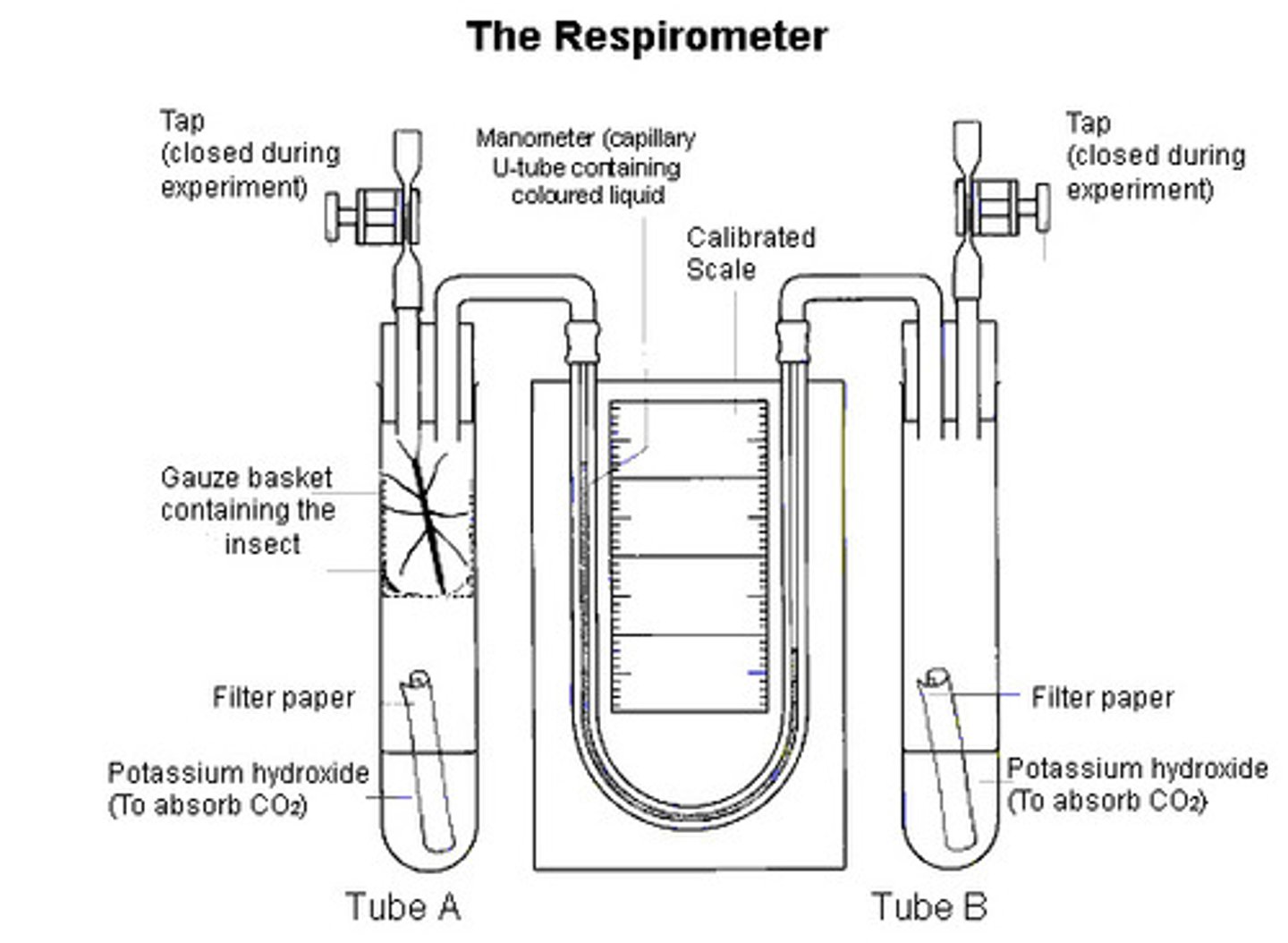
.Explain how to use a respirometer.
Using a respirometer to measure the rate of uptake of oxygen:
1. Place living organism in one side of the tube, and a non-living object of the same mass in the other
2. Soda lime is placed in each tube, to absorb all carbon dioxide
3. Add cotton wool to prevent contact of the soda lime with the organisms.
4. Coloured fluid is poured into the reservoir of each manometer and allowed to flow into the capillary tube
NOTE: It is essential that there are no air bubbles. You must end up with exactly the same quantity of fluid in the two manometers.
5. Two rubber bungs are now taken, fitted with tubes as shown in the diagram. Close the spring clips
6. Attach the manometers to the bent glasstubing, ensuring an airtight connection. Next, place the bungs into the tops of the tubes.
7. Open the spring clips. (This allows the pressure throughout the apparatus to equilibrate with atmospheric pressure.) Note the level of the manometer fluid in each tube. Close the clips. Each minute, record the level of the fluid in each tube.
Calculate the mean (adjusted) distance moved by the manometer fluid per minute. If you know the diameter of the capillary tube, you can convert the distance moved to a volume:
volume of liquid in a tube - length x πr2
This gives you a value for the volume of oxygen absorbed by the organisms per minute.
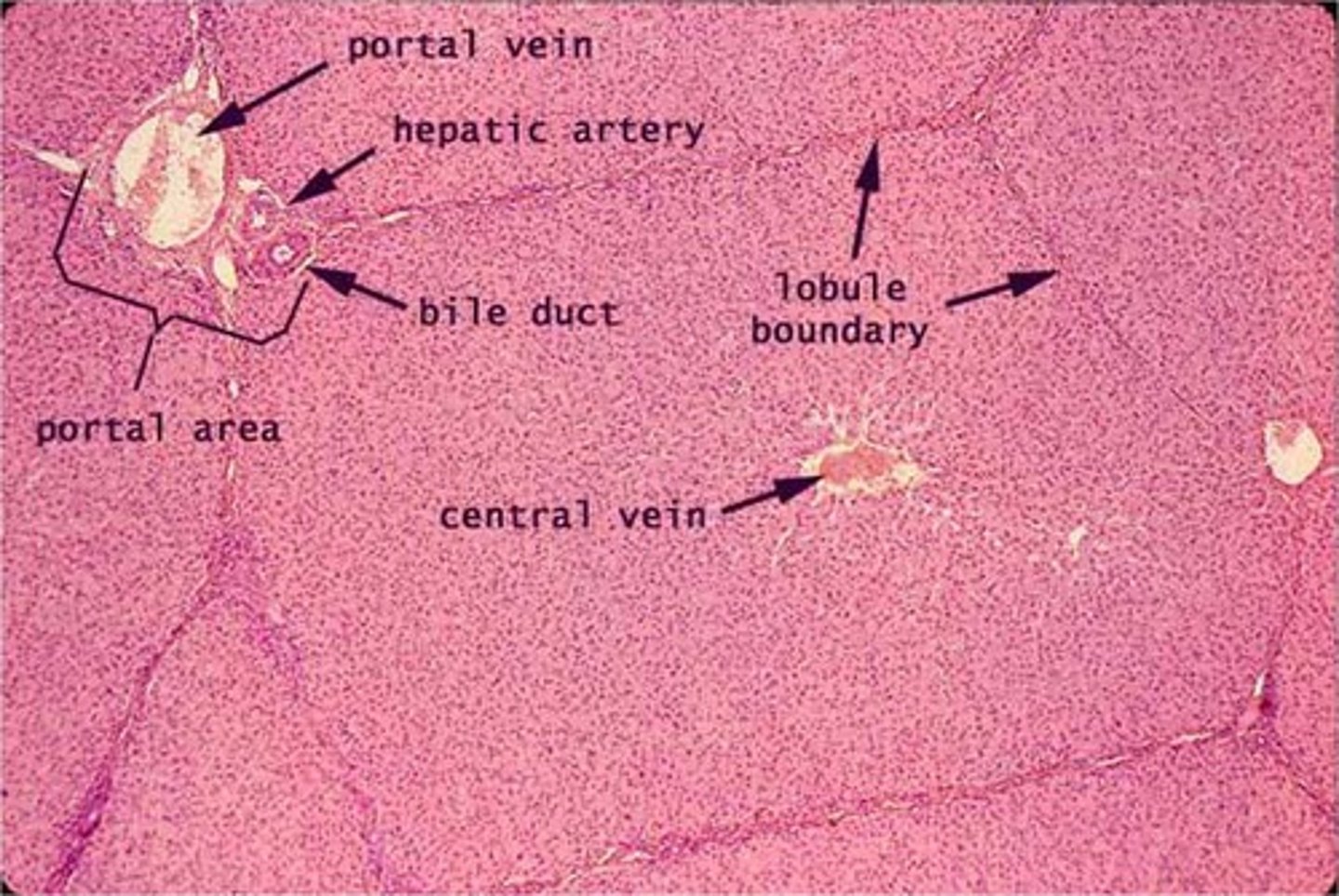
Label a photomicrograph of liver lobules.
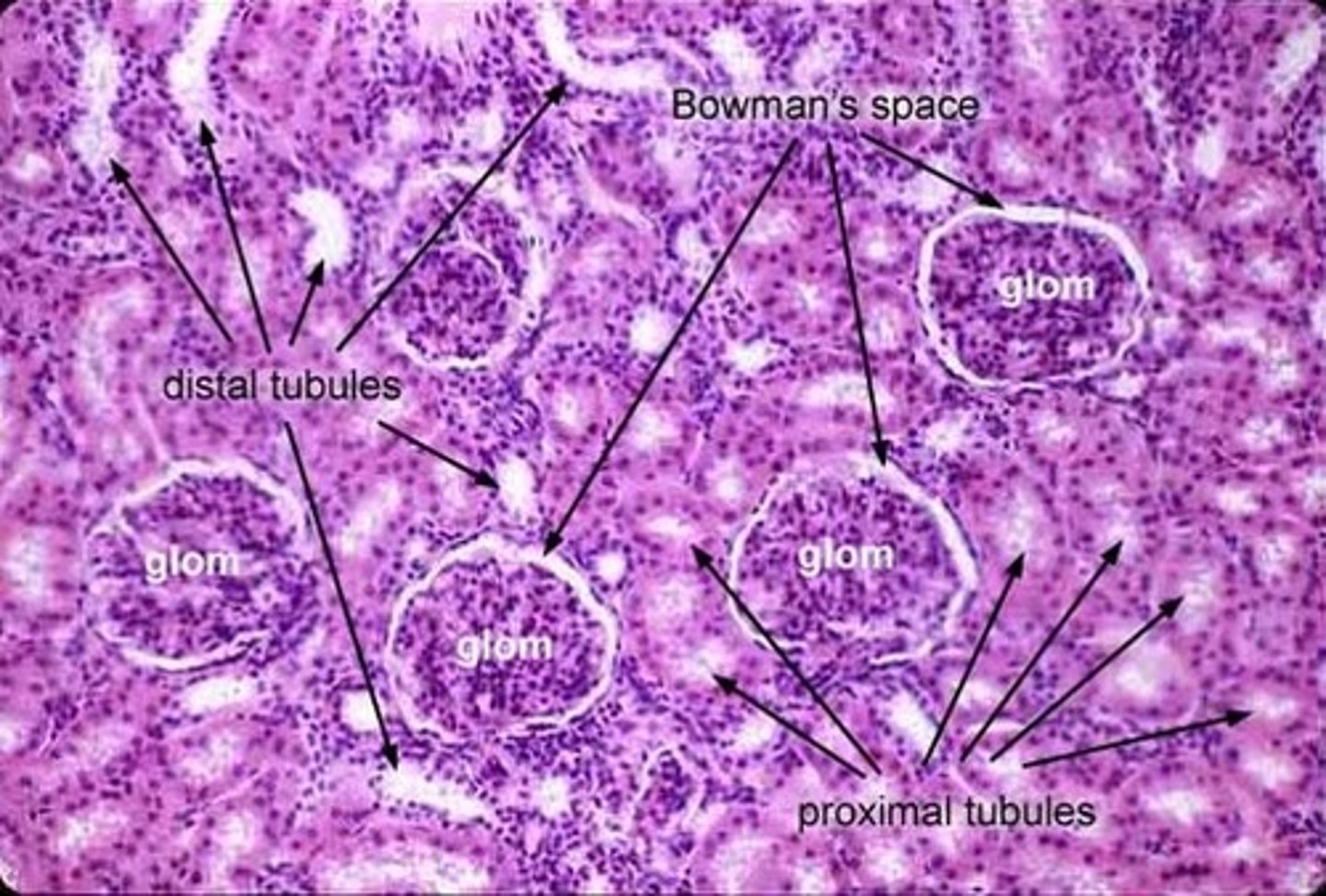
Label a photomicrograph of the kidney tissue.
Explain how to investigate the sodium potassium pump.
Aim: To examine sodium efflux (sodium ions pumped out of a neurone)
-particular experiment examines the sodium efflux of a giant axon of a cuttlefish with dinitrophenol
-DNP is an uncoupling agent which prevents the production of ATP in respiration
Method:
1. Isolate an axon and place in artificial sea water at 18 degrees
-the artificial sea water should contain radioactive sodium ions which are detectable
2. Electrically stimulate the axon
3. Replace the artificial sea water with sea water that doesn't contain a radioactive isotope
4. Collect samples of fluid that pass through the axon at intervals, and measure the concentration of radioactive sodium
NOTE: this indicates the amount of sodium ions pumped out by the sodium potassium pumps
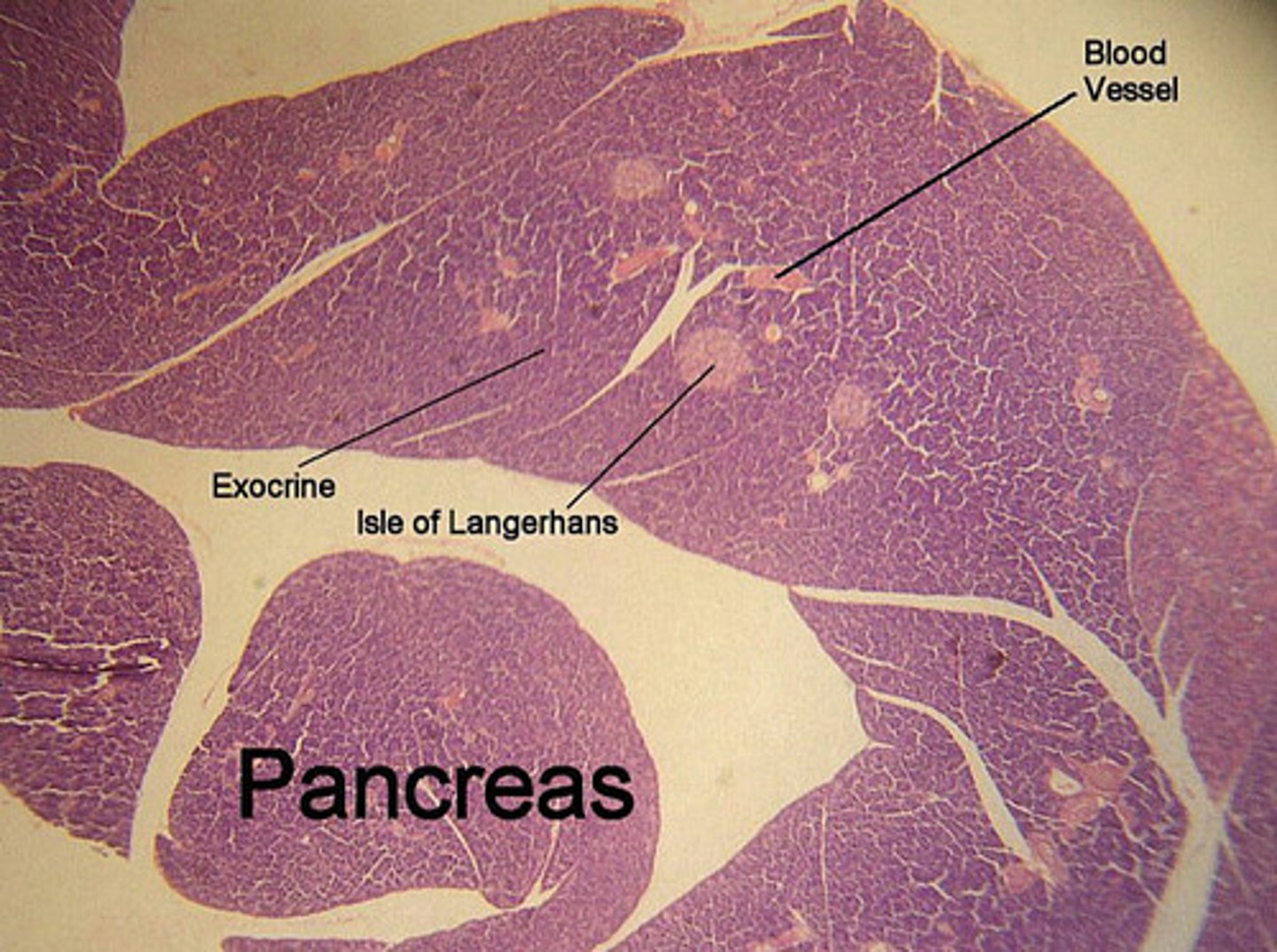
Label a section of the pancreas.
Explain how to investigate the relationship between pulse rate and BMI.
Aim: to investigate the effect of being overweight on pulse rate in exercise in children
1. Calculate the BMI of 10 normal weight and 10 overweight children
2. Monitor their heart rate for 5 minutes before exercise, and find a value for beats per minute
3. Monitor the children on an exercise bike for 5 minutes using a heart rate data-logger attached wirelessly to a computer
4. Measure the time taken for heart rate to return to normal
5. Carry out a student t-test to look for an association between means
Explain how to use TLC to separate photosynthetic pigments.
Method:
1. Draw a pencil line across the plate, just above where the solvent line will reach
2. Extract a sample of chloroplast by grinding a leaf
3. Spot the extract into the middle of the pencil line multiple times, allowing it to dry between each spot
NOTE: this creates a very concentrated area of pigment which doesn't spread out
4. Lower the plate into the chromatography chamber which should already by saturated in vapour (to prevent the pigment from rising too fast)
5. Leave the apparatus until the solvent is close to the top of the plate (this is the solvent front)
6. Use a pencil line to record where the solvent front is
7. Calculate the Rf (retention factor) values of all the pigments
8. Compare the Rf values to known values to determine pigments present
Explain how to find the effect of light intensity on photosynthesis in pond weed.
NOTE: rate of oxygen production is used to determine rate of photosynthesis
Method:
1. Set up a shoot of pond weed in a photometer
2. Fill the capillary tubing with coloured dye to make tracking the oxygen bubbles easier
3. Set up a UV lamp at a measured distance away
NOTE: find light intensity at each distance using 1/d^2
4. Allow the plant to equilibrate for 5 minutes
5. Track the length of bubble produced in 2 minutes
Explain how to investigate the effect of carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis.
Method:
1. Cut leaf discs from thing leaves such as cress
2. Use a 5cm^3 syringe to draw up 5cm^3 of 0.2 mol dm^-3 sodium hydrogen carbonate solution, and add 5 leaf discs
3. Evacuate air from the discs by allowing them to drop to the bottom of the syringe
4. Record the time taken for the discs to reach the top of syringe
5. Make recordings at different values of light intensity
NOTE: use freshly cut leaf discs for each measurement
Explain how to measure respiration rates in yeast.
Method:
1. Make a yeast and sugar mixture, so the yeast has material to respire
2. Place it in a test tube with a rubber stopper
NOTE: there should be rubber tubing coming out of the tube, which feeds into an inverted graduated cylinder through a trough of water
-therefore what is being measured is the volume of oxygen being produced which displaces the water
3. Record the volume of gas produced at 30 second intervals for three minutes
4. To investigate different substrates, repeat the experiment with a yeast and glucose mixture
Explain how to use a respirometer to calculate respiratory rate and RQ.
Apparatus:
1. Assemble a yeast suspension in a large syringe with a plunger
2. The syringe should have 1mm glass tubing coming out of the bung
Method:
1. Assemble yeast mixtures with yeast with different sugars
NOTE: this is to find RQ of different substrates
2. Record the distance travelled by the meniscus at a set time interval
3. Convert this into rate of respiration, then compare
Explain how to dissect plant material to take cuttings.
1. Cut the plant at a terminal bud or growing point
2. Treat the cutting with lanolin and IBA in the soil
3. Firmly press the cutting into the soil, and allow to grow
4. Assess the cuttings after 60 days to observe
-percentage of samples with adventitious roots
-mean number of roots
-length of the longest root
5. Transplant the plants into larger pots when necessary
Explain how to dissect plants to grow them as a tissue culture.
1. Remove meristem cells
2. Sterilise the cells in bleach solution as part of aseptic technique
3. Remove meristems for subculturing
4. Transfer the plant lets to a rooting medium
5. Remove plants from agar
Explain how to culture bacteria on a streak plate.
1. Heat agar in a water bath at 42-45 degrees to melt it
2. Open the lid of the petri dish to 45 degrees and pour in the molten agar
3. Sterilise the collecting loop using the white flame of the bunsen burner
4. Remove the plug from the culture and flame the neck to sterilise it
5. Take a sample
6. Flame the neck again and replace the plug
7. Make the streak patter, and quickly close the petri dish again