Evolution mid term (ch 1-8)
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Aristotle
Proposed scala nature ( believe species were fixed )
Erasmus Darwin
Proposed evolutional change “single living filament
Lamarck
Proposed theory of inheritance of acquired characteristics
Patrick Matthew
Proposed circumstance adaptive law → similar to darwin idea
Lyell
Proposed that Geological formations result from slow, gradual processes (uniformitarianism and gradualism )
Darwin
Proposed evolution by natural selection and that species descended from a common ancestor
Wallace
Darwin’s friend who came to the theory of natural selection independently
Problems with darwin theory
Complex structure: eye
Could not explain traits of little importance : example the limb
Lack of understanding of how variation persists in the face of natural selection:
Natural selection
Individuals with advantageous traits that survive and reproduce with more successful traits passing it on to offspring
Artificial selection
human choose which individual with the desired traitor to reproduce
Genotype
the genetic makeup of an organism
Locus
a unique physical location on the chromosome where the gene exist
Gene
A sequence of DNA that codes for a trait
Allele
An alternative version of a specific gene
Phenotype
An observable characteristic of an organism caused from the interaction of genotype with its environment
Component of natural selection (evolve)
Variation , Variation need to be heritable and Difference in reproduction success
Mutation
Generate variation → occurs randomly
Evolutionary unit
the population evolves not individual
Genetic drift affects what group
Population size matters → smaller pop is more affected
Selection is more efficient in large pop
Directional selection
favors individual with one extreme version of a trait
Diversifying or disruptive selection
favors individual at both extreme ends
ex: birds with small beaks or large beak are successful
Stabilizing selection
favors intermediate phenotype trait reducing variation
example: Average-sized babies are more likely to survive compared to very small or very large babies.
Natural selection constraints
Physical constraints,
rapid change in environment
Natural selection lacks foresight (mutations are random even if favorable).
Modern synthesis
The Modern Synthesis showed that both discrete and continuous traits follow the same genetic principles.
Phylogeny
shows relationship among population in a group or taxa
Phylogeny nodes
Populations
Pedigree
track genetic traits
Pedigree nods
individuals , each nods has two ancestor
Monophyletic group
group including common ancestor + its descendents
Paraphyletic
group includes a common ancestor and some of its descendants
polyphyletic
a group that does not share a common recent common ancestor
Phylogram branch length
this means the amount of evolution change (longer = more change)
Analogous traits
similar traits evolved independently due to similar selective pressure
example bats and birds wing
Convergent evolution
when two or more pop become more similar to one another because they are exposed to the same condition
Divergent
when closely related pop diverge from one another because Natural selection acts
Vestigial traits
traits with unknown function but believed to be functional in the past
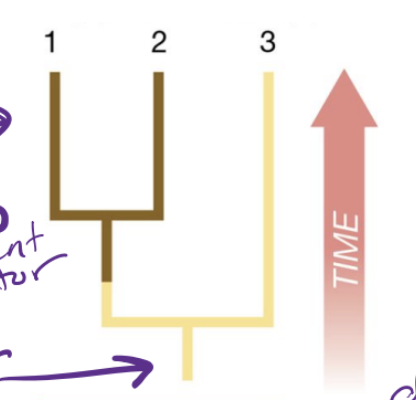
Synapomorphies
A shared derived trait that groups organisms together * new trait
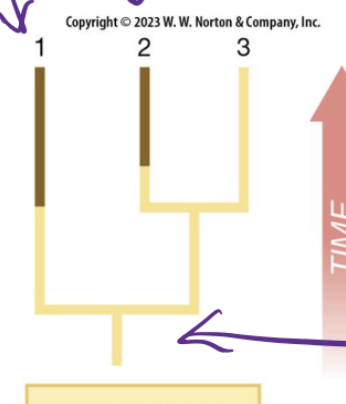
Homoplasy
similar trait in species but independent origin
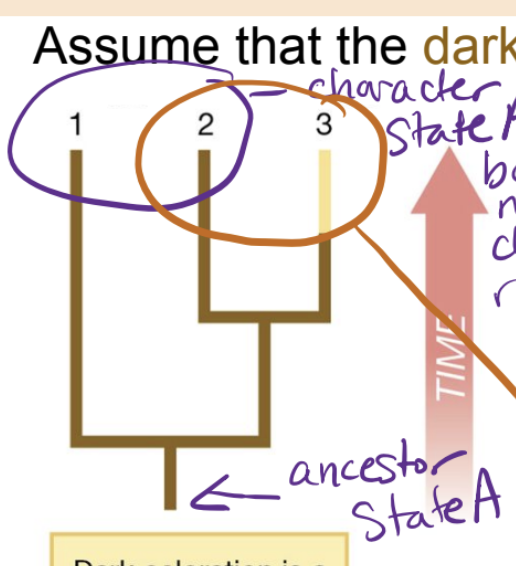
Symplesiomorphy
shared ancestral trait that appears in only one of the sister taxa
Parsimony
minimum number of evolutionary change is better
Fitch algorithm
helps calculate parisony, sum number of changes per trait , if there is one trait similar don’t count it
Bootstrap
test phylogeny tree strength by randomly reusing data many time to see what patter consistently show up, Acceptable support level 70% - 80%, very supported 90% - 95%
Bootstraps steps
Original data 2. Randomly pick traits and reorder them or repeat them ect, 3. The new table is made using resampled table 4. Repeated many times
Odds Ration
measures how strong data supports claude being monophyletic likelihood of tree X likelihood of tree Y
Odd ration HO
no difference between trees
Reject HO (odds ratio)
P < 0.05 tree X has a significant higher likelihood then tree Y
Fail to reject HO (odds ratio)
P > 0.05 The tree are equally supported by the data
Law of segregation
Each individual has 2 gene copies at each loci these gene copes segregate during gametes production so only 1 gene copy goes into each gamets
Law of independent assortment
Alleles of genes assort independently of one another
Epigenetic inheritance
Heritable mechanism altering gene expression withou changing DNA Sequence
Source of variation
mutation
recombination
migration
lateral gene transfer
Mutation location
Somatic : not heritable
ex: cancer
Sex cells : heritable
Synonymouse mutiation (silent)
Base change but no amino acid changes
Nonsynonymous mutation
Base change alter amino acid sequence (can cause problems)
Missense Mutation
a base pair changes codon to encode a different amino acid
nonsense (NO!)
A base pair change that creats a stop codon
Frameshift (mutation)
insertion/deletion of nucleotides not in multiple of 3
disruption of reading frame
In Frameshift
Insertion/deletion in multiple of 3 may not disrupt reading
Most mutation are…
deleterious or neutral few are beneficial
synonymous : netural
Nonsense: deleterious