PD Exam 2: Heart/Lungs/Abdominal/Male Genitalia
1/733
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
734 Terms
what is the largest chamber of the heart?
left ventricle
3 multiple choice options
what are the 4 valves of the heart?
tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, aortic
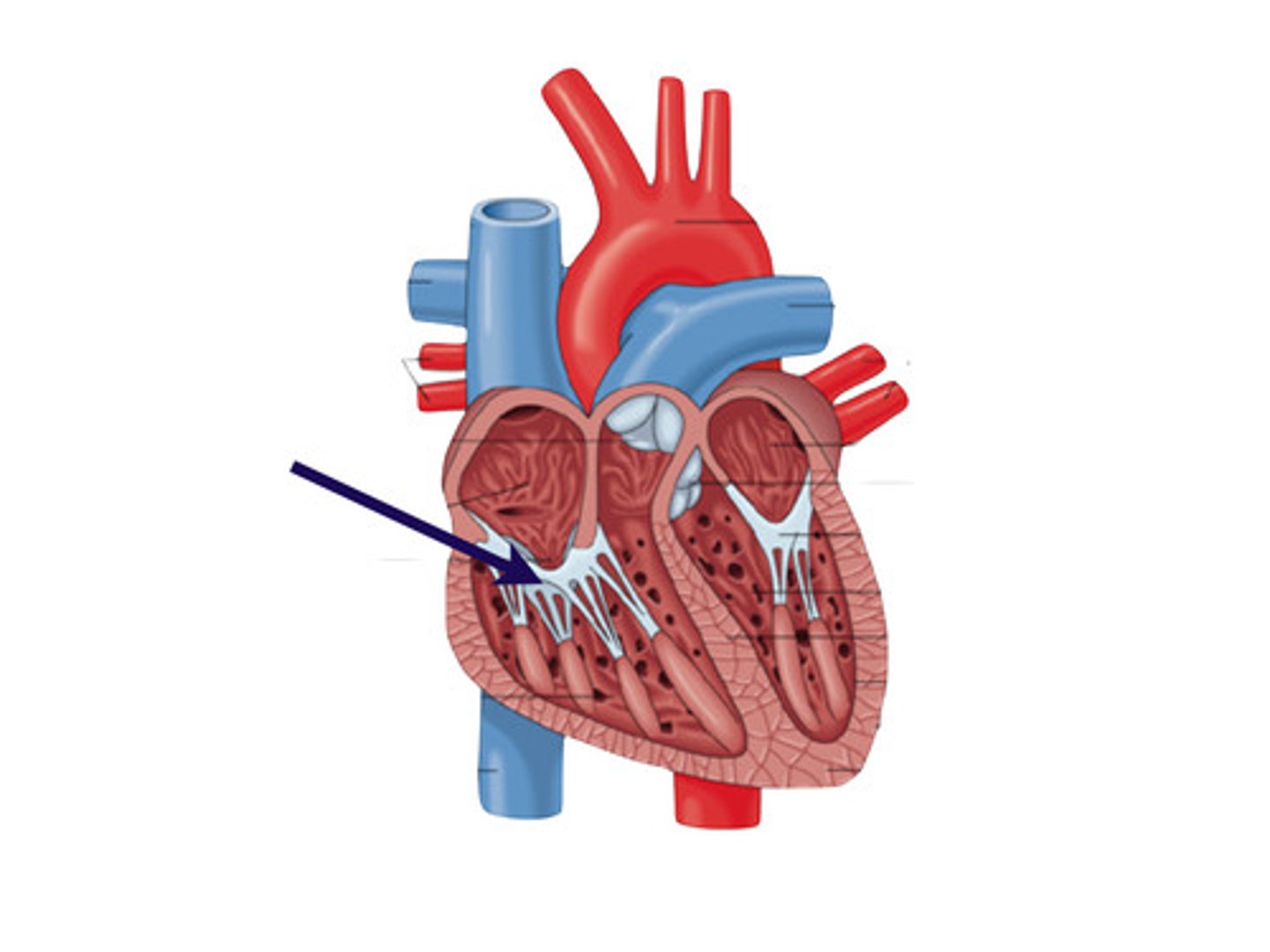
tricuspid valve
between the right atrium and the right ventricle
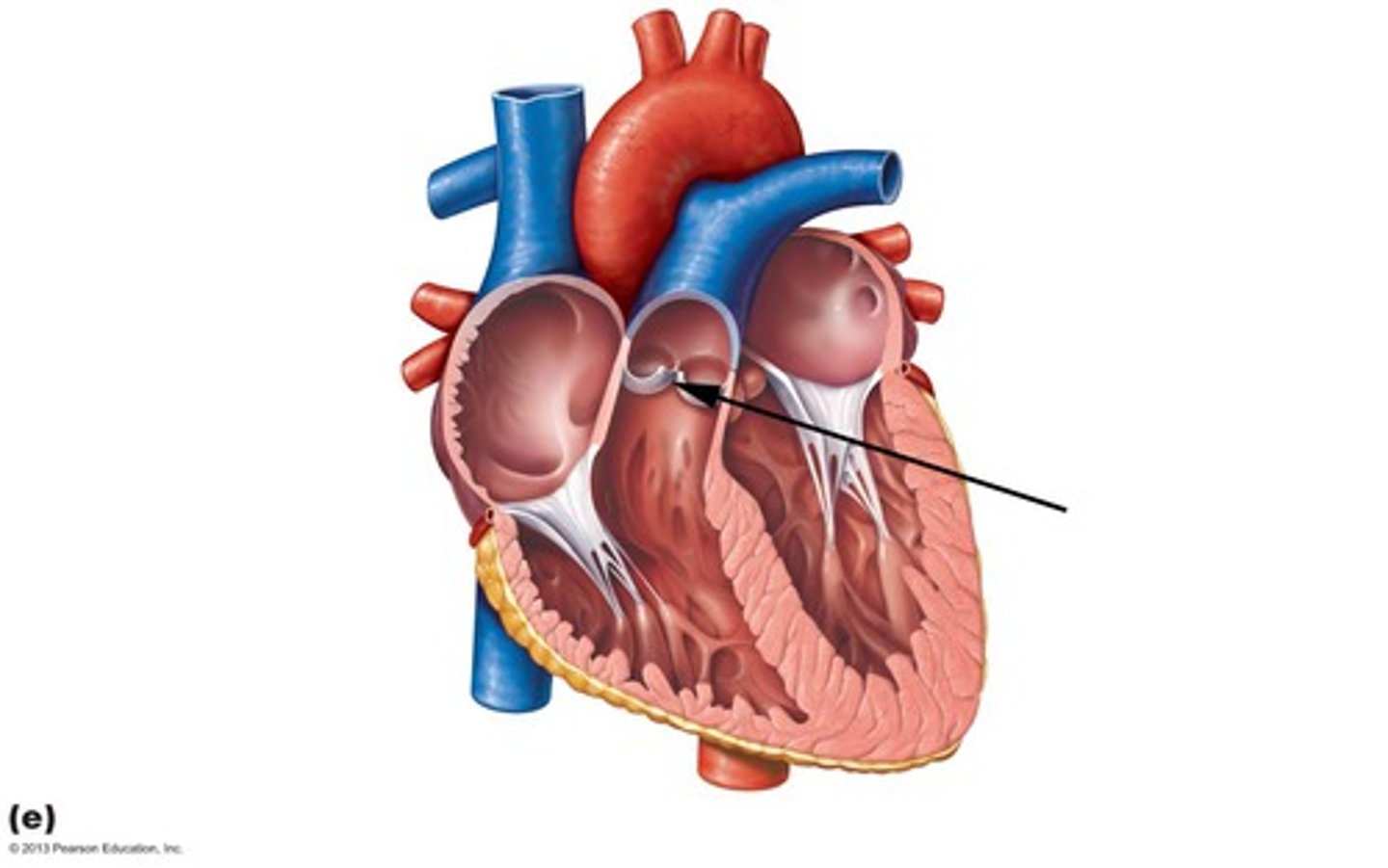
pulmonary valve
between right ventricle and pulmonary artery
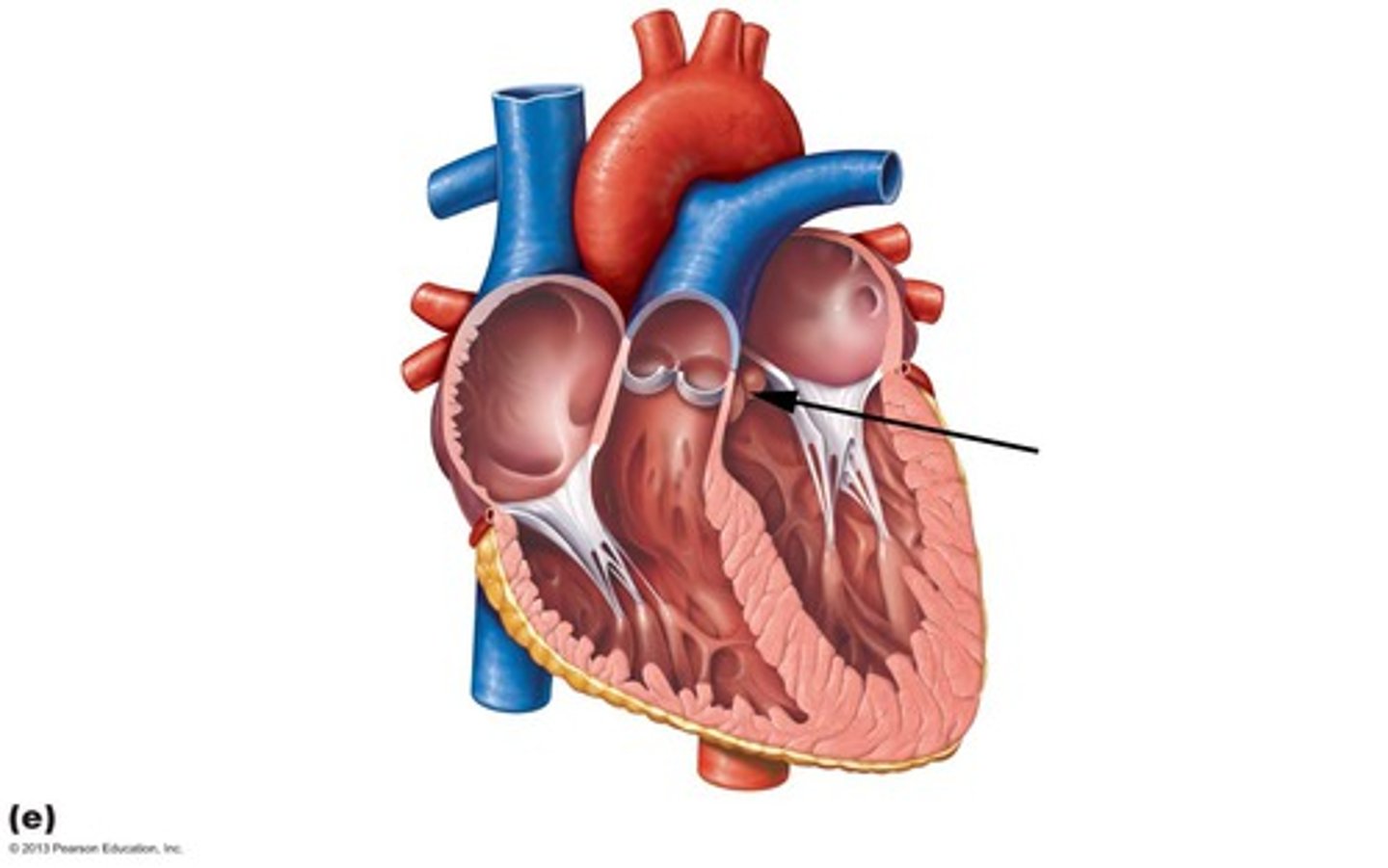
aortic valve
between left ventricle and aorta
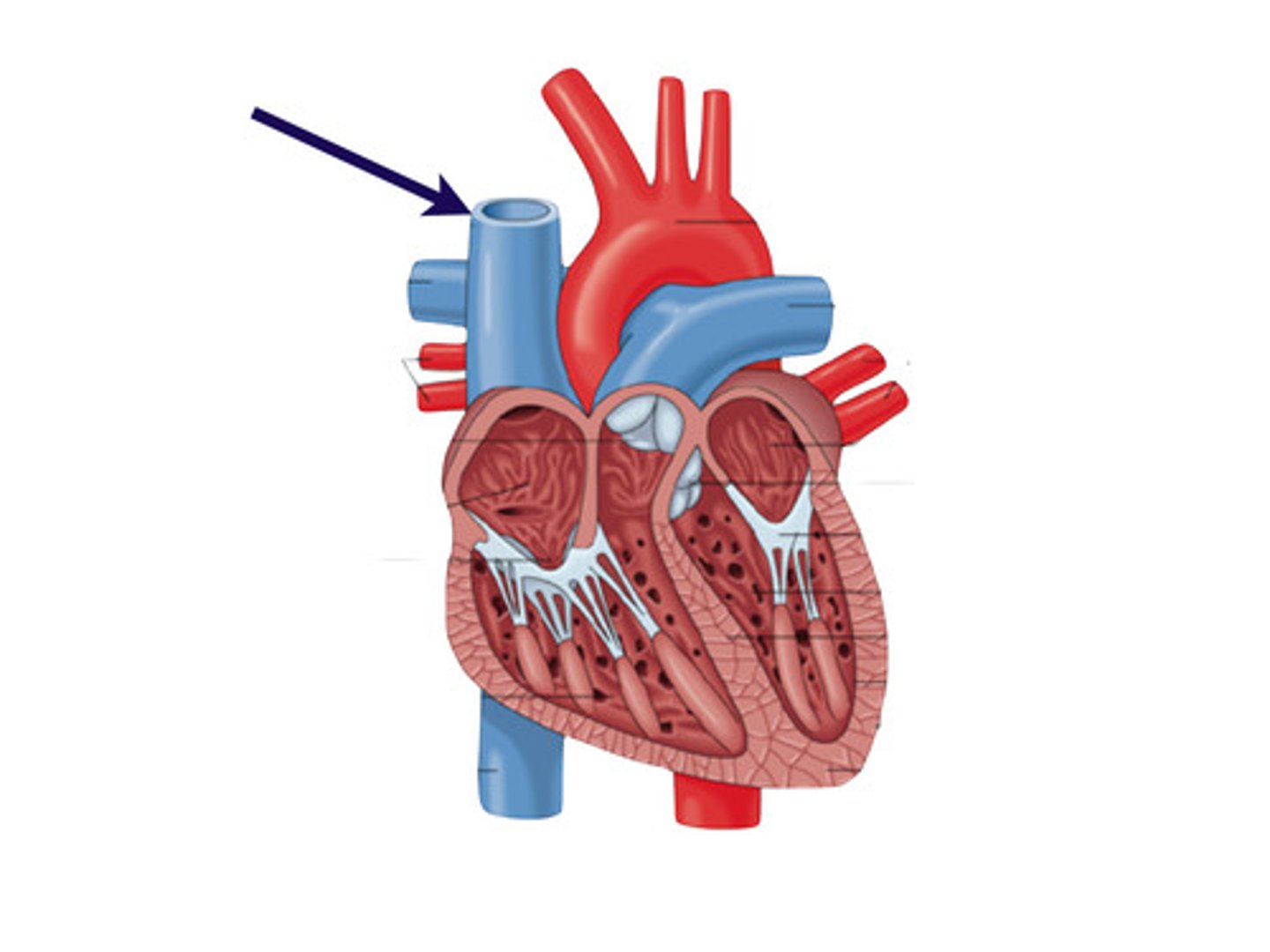
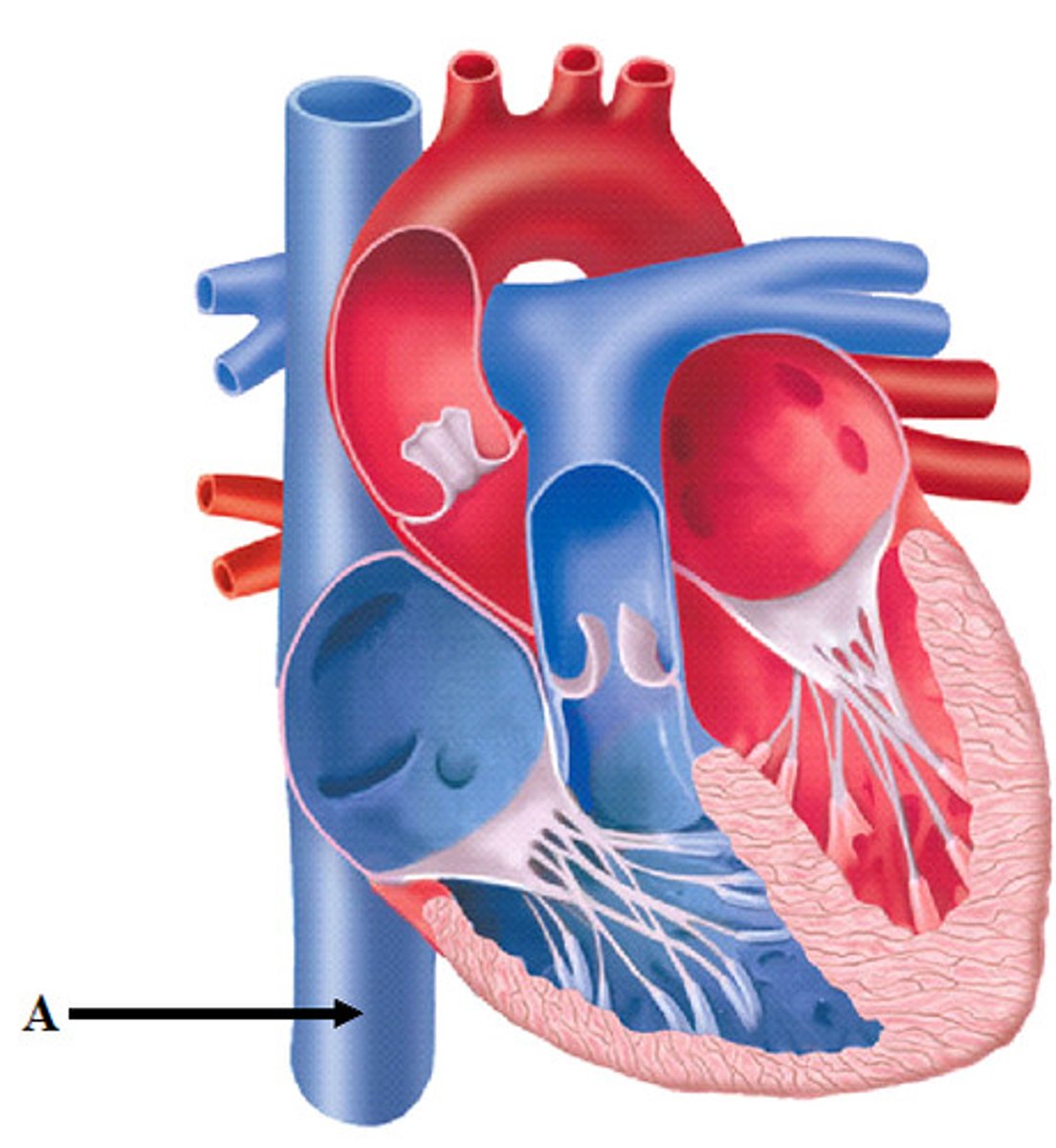
what does the superior vena cava do?
returns deoxygenated blood from the upper body to the right atria
what does the inferior vena cava do?
returns deoxygenated blood from the lower body to the right atria
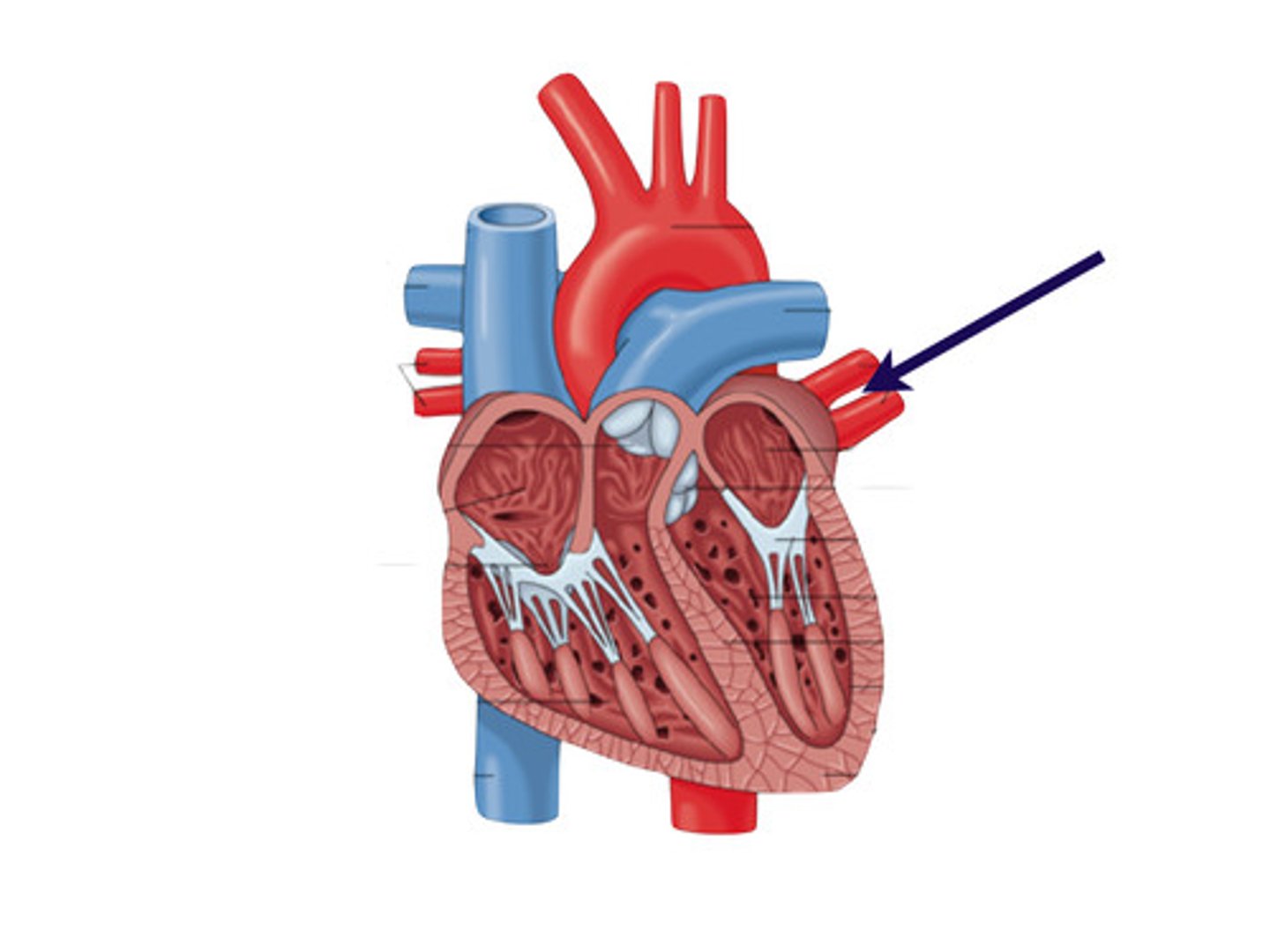
what does the pulmonary artery do?
carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs
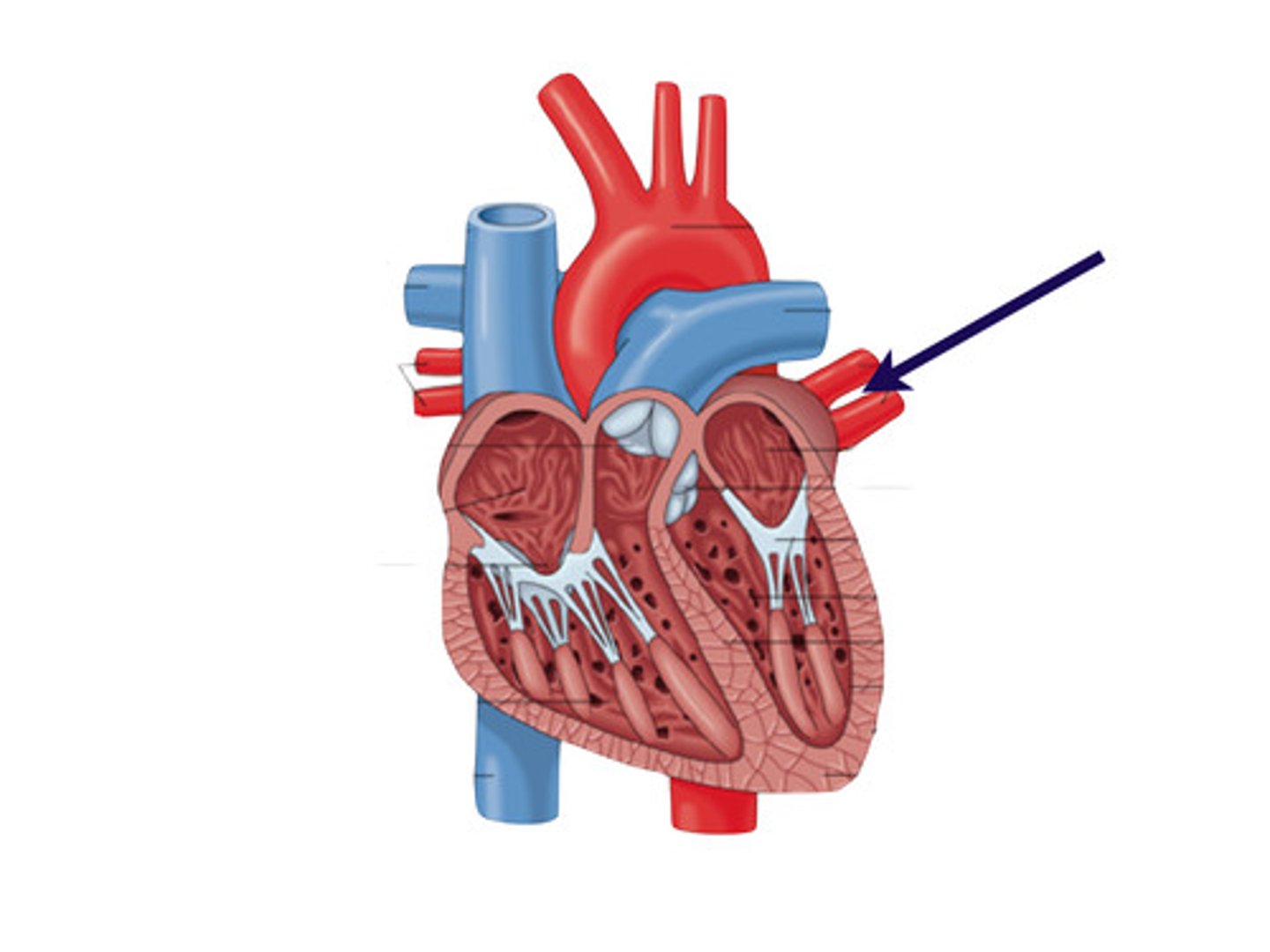
what does the pulmonary vein do?
carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atria
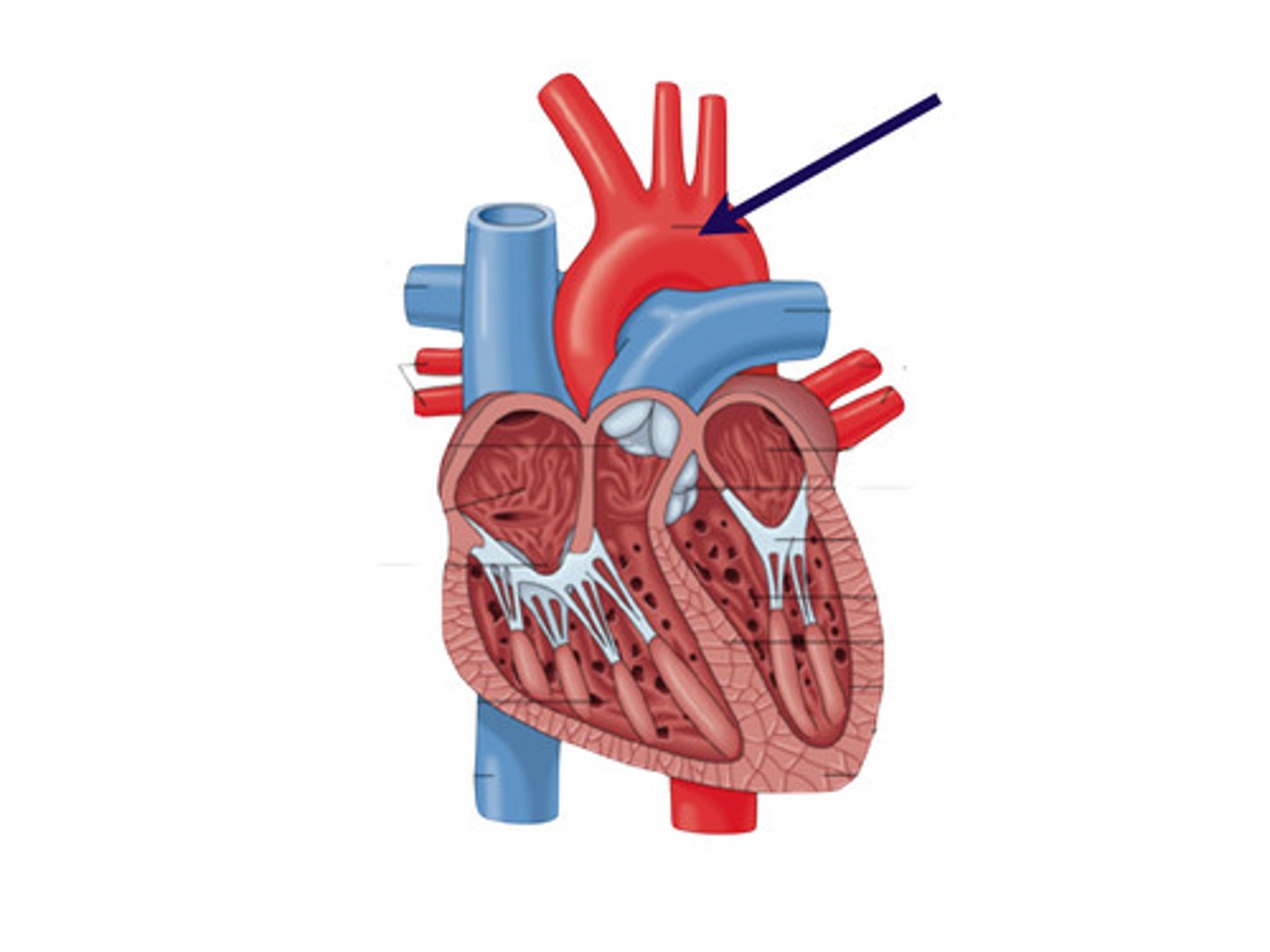
what does the aorta do?
carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the body
what is the first structure the heart feeds and through what?
heart itself through coronary arteries
where is the right ventricle located?
anterior, behind and to the left of the sternum
where is the base of the heart located?
right and left 2 nd intercostal spaces
where is the left ventricle located?
posterior (and lateral) and left of the right ventricle
where is the apex of the heart located?
5th intercostal space, midclavicular line
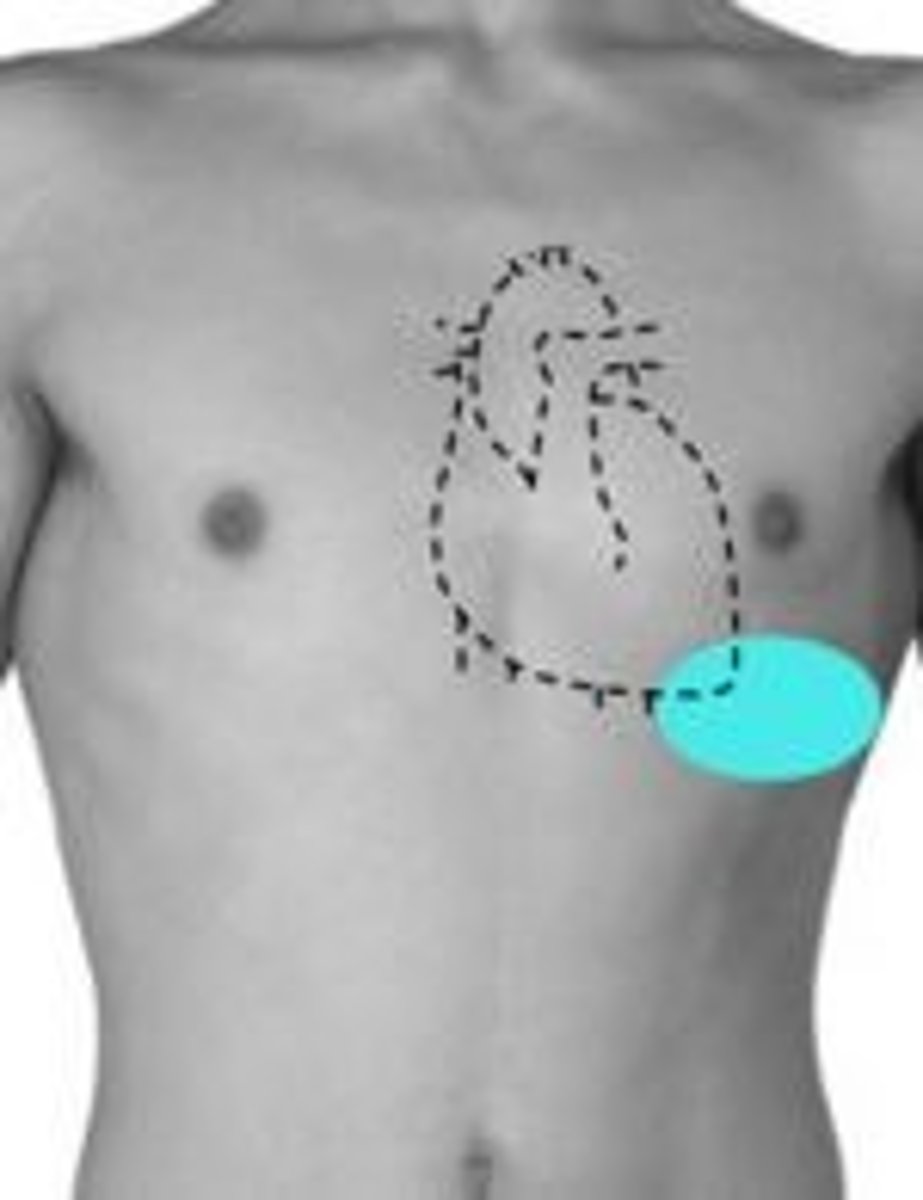
what is the point of maximal impulse?
apical impulse
where is the aortic valve located?
right 2nd intercostal space
where is the pulmonic valve located?
left 2nd intercostal space
where is the tricuspid valve located?
left 4th and 5th intercostal space close to the sternum
where is the mitral valve located?
left 5th intercostal space near the left midclavicular line
cardiac cycle diastole
relaxation
in diastole, whats the pressure in the left atrium and left ventricle?
left atrium: increased
left ventricle: decreased
cardiac cycle systole
contraction
in systole, whats the pressure in the left ventricle and left atrium?
left atrium: decreased
left ventricle: increased
as space decreases, what happens to volume and pressure?
volume decreases, pressure increases
in diastole, pressure in blood filled left atrium slightly exceeds that in the relaxed LV and blood flows from left atrium to left ventricle across the open mitral valve. Just before the onset of systole, atrial contraction produces a slight pressure rise in both chambers which creates what?
atrial kick (S4)
in systole, LV starts to contract and ventricular pressure rapidly exceeds left atrial pressure, closing the mitral valve. Closure of the mitral valve (left) and the tricuspid valve (right) produce what?
first heart sound S1
As the LV pressure continues to rise, it quickly exceeds the pressure in the aorta and forces the ________ ______ open
aortic valve
__________ ____ ________ corresponds to systolic blood pressure. LV ejects most of its blood, ventricular pressure begins to fall. When LV pressure drops below aortic pressure, aortic valve closes. Aortic valve closure, as well as closure of the pulmonic valves, produces the S2 and another diastolic begins
maximal LV pressure
In diastole, LV pressure continues to drop and falls below left atrial pressure. What valve opens and what sound does it make?
mitral valve opens - silent
After mitral valve opens, period of _______ _______ ______ as blood flows early in diastole from LA to LV. What sound can be associated with this?
rapid ventricular filling; S3
preload
load that stretches cardiac muscle before contraction
volume of blood in the right ventricle at the end of diastole is the ________ for the next beat
preload
Increased right ventricular preload occurs with _________ venous return
increased
Decreased right ventricular preload occurs with _______ venous return
decreased
afterload
Load against which the heart has to contract to eject blood or degree of vascular resistance to ventricular contraction
myocardial contractility
ability of muscle to shorten
what increases myocardial contractility?
stimulation from sympathetic nervous system
what decreases myocardial contractility?
blood flow or oxygen delivery to myocardium is impaired
stroke volume
volume of blood ejected from the heart with each heartbeat
cardiac output
volume of blood ejected from the heart each minute
equation for cardiac output
HR x SV = CO
S1 closure from what valves? systole or diastole?
mitral and tricuspid valves; systole
S2 closure from what valves? systole or diastole?
aortic and pulmonic; diastole
ejection sound
heard in some pathologic conditions when the aortic valve opens
opening snap
opening sound created by a calcified mitral valve in mitral stenosis
S3 occurs during what? caused by what?
occurs during rapid ventricular filling; caused by the rapid deceleration of the column of blood against the ventricular wall
what can cause S3?
physiologic or pathologic
what is S4 typically caused by and is it typically heard?
atrial contraction; no
which valves close slightly later? left or right
right
1 multiple choice option
whats a split heart sound?
one of the normal heart S1 or S2 is perceived as two distinct sounds
what are more common S1 or S2 split
S2
1 multiple choice option
physiologic S2 split
normal, closure of aortic and pulmonary valve
physiologic S2 split in expiration and inspiration
one sound during expiration
splitting sound during inspiration
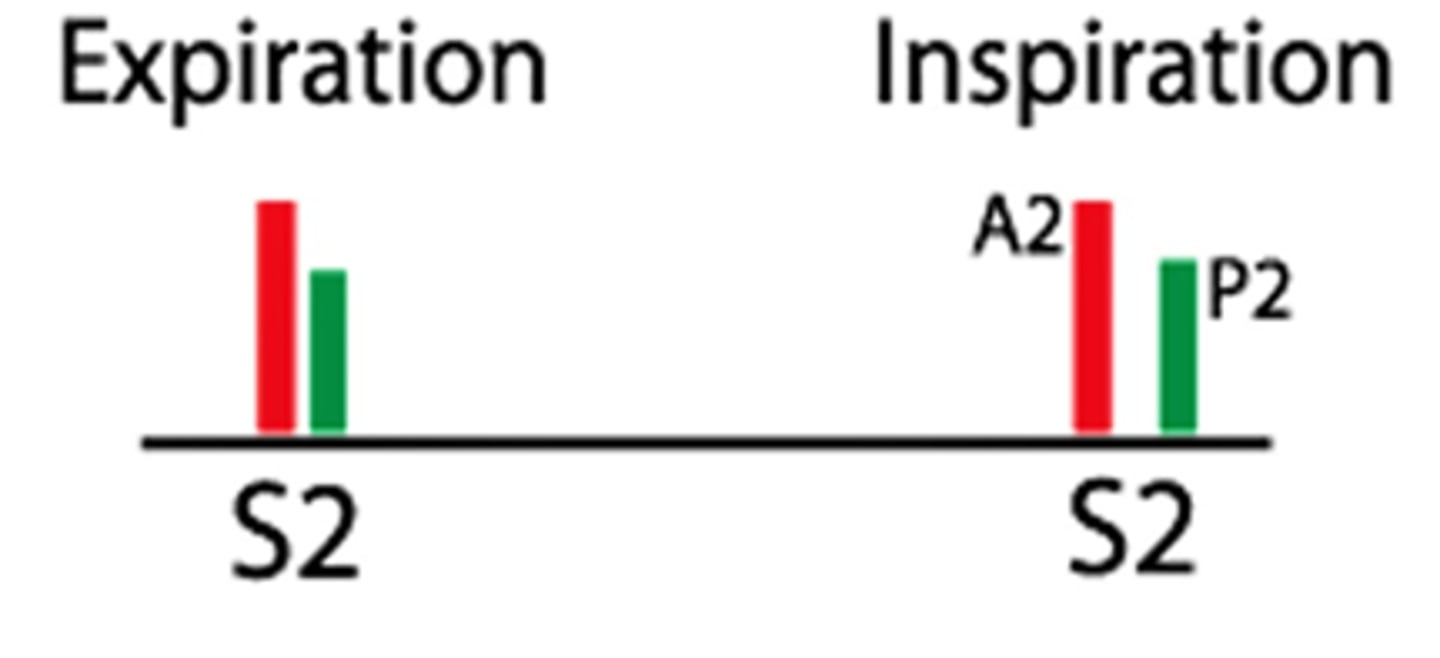
pathologic/fixed S2 split
NOT normal, persistent separation between the closure of the aortic valve and pulmonary valve regardless of breathing
pathologic/fixed S2 split in expiration and inspiration
splitting sound during expiration
splitting sound during inspiration
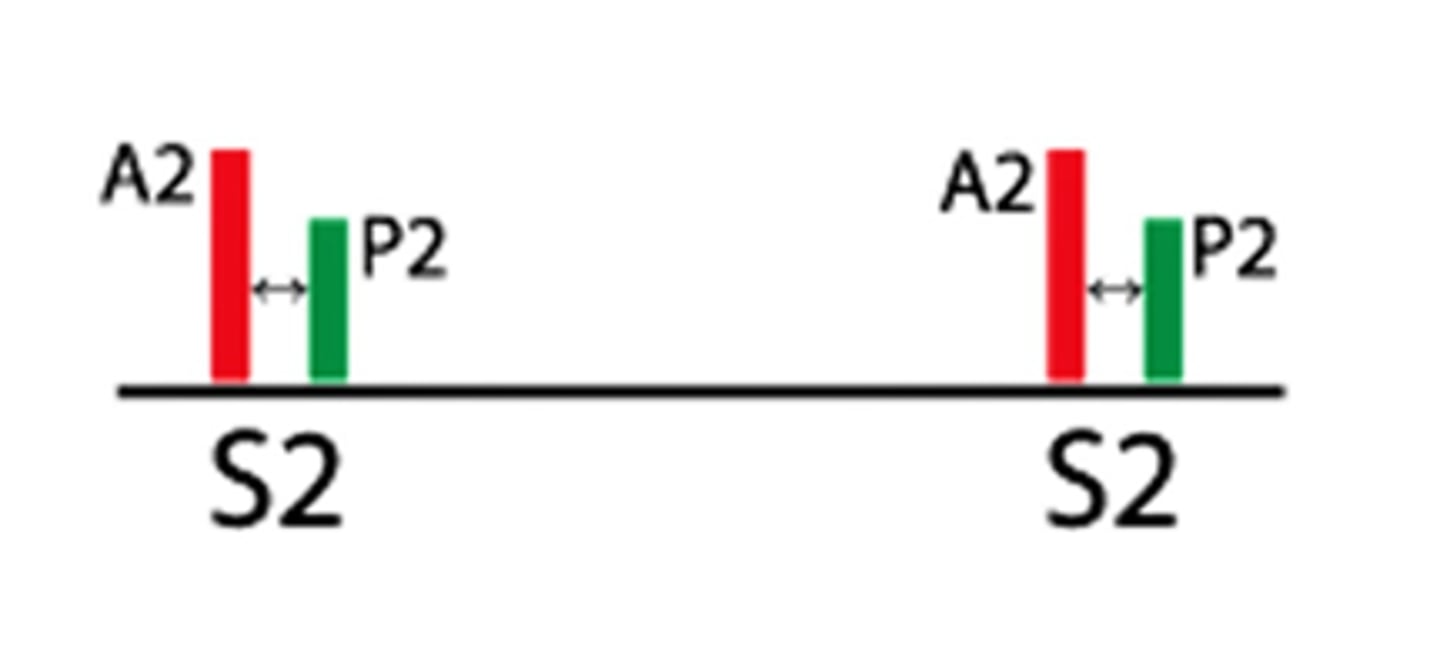
what could be some causes for a pathologic/fixed S2 split?
valve dysfunction, heart problem
paradoxical S2 split
NOT normal, closure of the aortic valve occurs after the closure of the pulmonary valve
paradoxical S2 split in expiration and inspiration
Splitting sound during expiration
One sound during inspiration
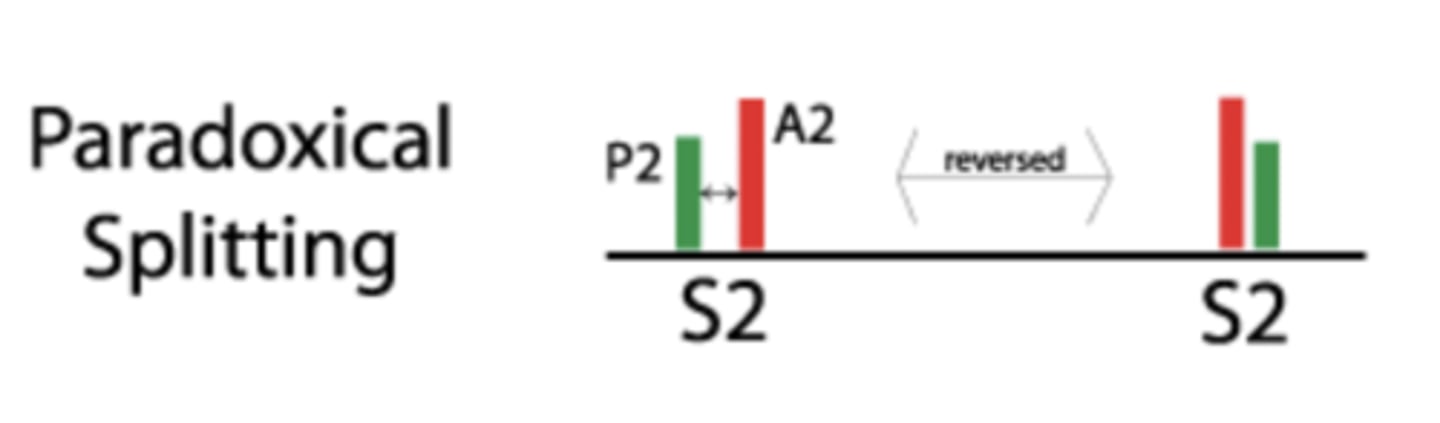
A2 closure of aortic valve
softer or louder
where is it heard?
louder
heard though precordium
P2 closure of pulmonic valve
softer or louder
where is it heard?
softer
heard 2nd and 3rd left interspace, close to sternum
split S1 also varies with inspiration/expiration t/f
false
1 multiple choice option
M1 closure of the mitral valve
softer or louder
where is it heard?
louder
heard throughout the precordium
T1 closure of the tricuspid valve
softer or louder
where is it heard?
softer
heard at the left lower sternal border
what parts of the heart are involved in the conduction system?
sinus node, AV node, bundle of HIS, right and left bundle branches, purkinje fiber
sinus node
right atria, dictates the HR
AV node
junction of atria and ventricles, coordinates timing of heart beats
bundle of HIS
in septum, conducts electrical impulses
right and left bundle branches
transmits impulses from Bundle of HIS to ventricles
purkinje fibers
inner ventricle walls, essential for rapid and coordinated ventricular contraction
what are the steps of the conduction system?
1. SA node fires
2. Excitation spreads through atrial myocardium
3. AV node fires
4. Excitation spreads down AV bundle
5. Purkinje fibers distribute excitation through ventricular myocardium
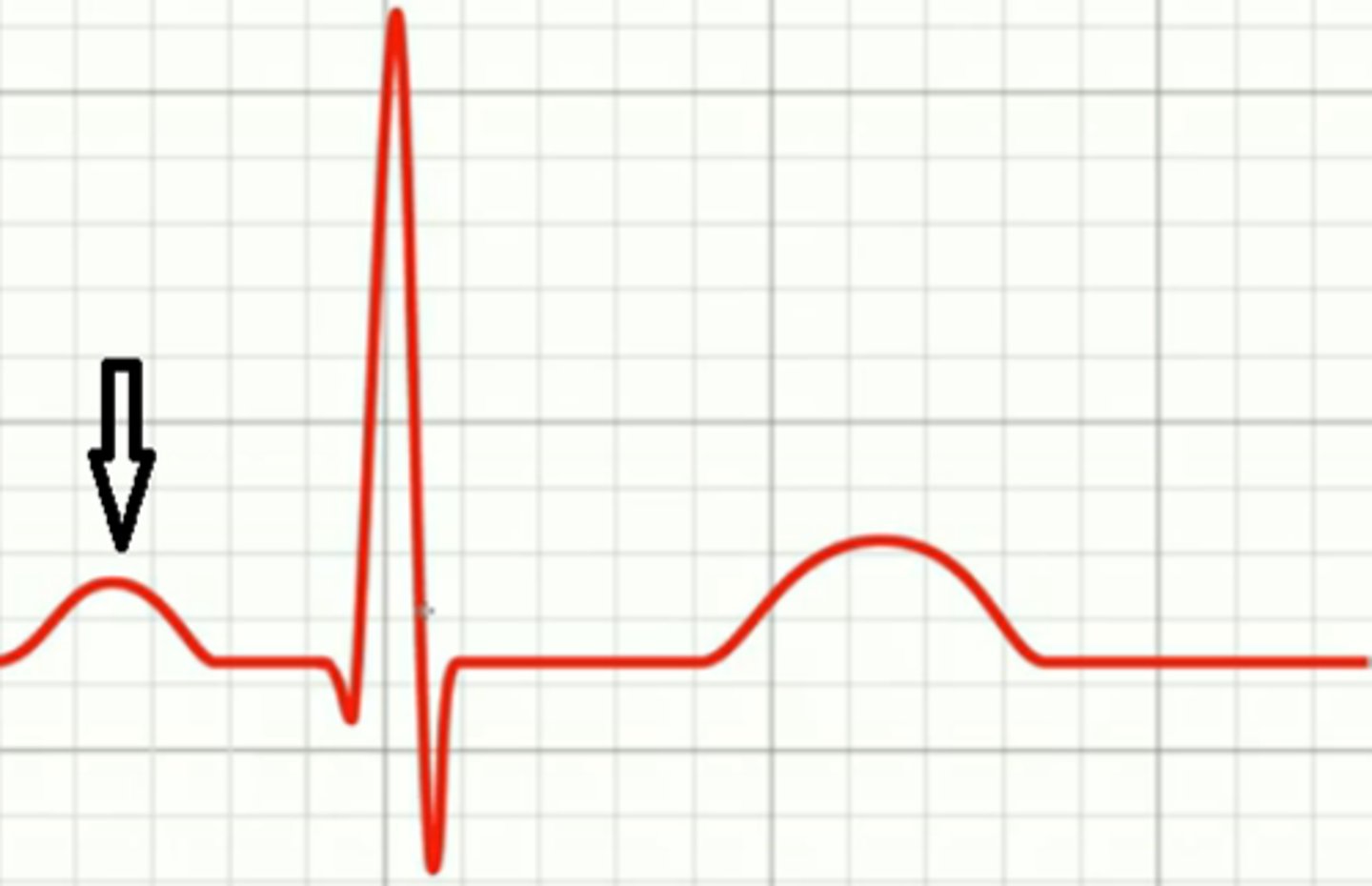
P wave
atrial depolarization
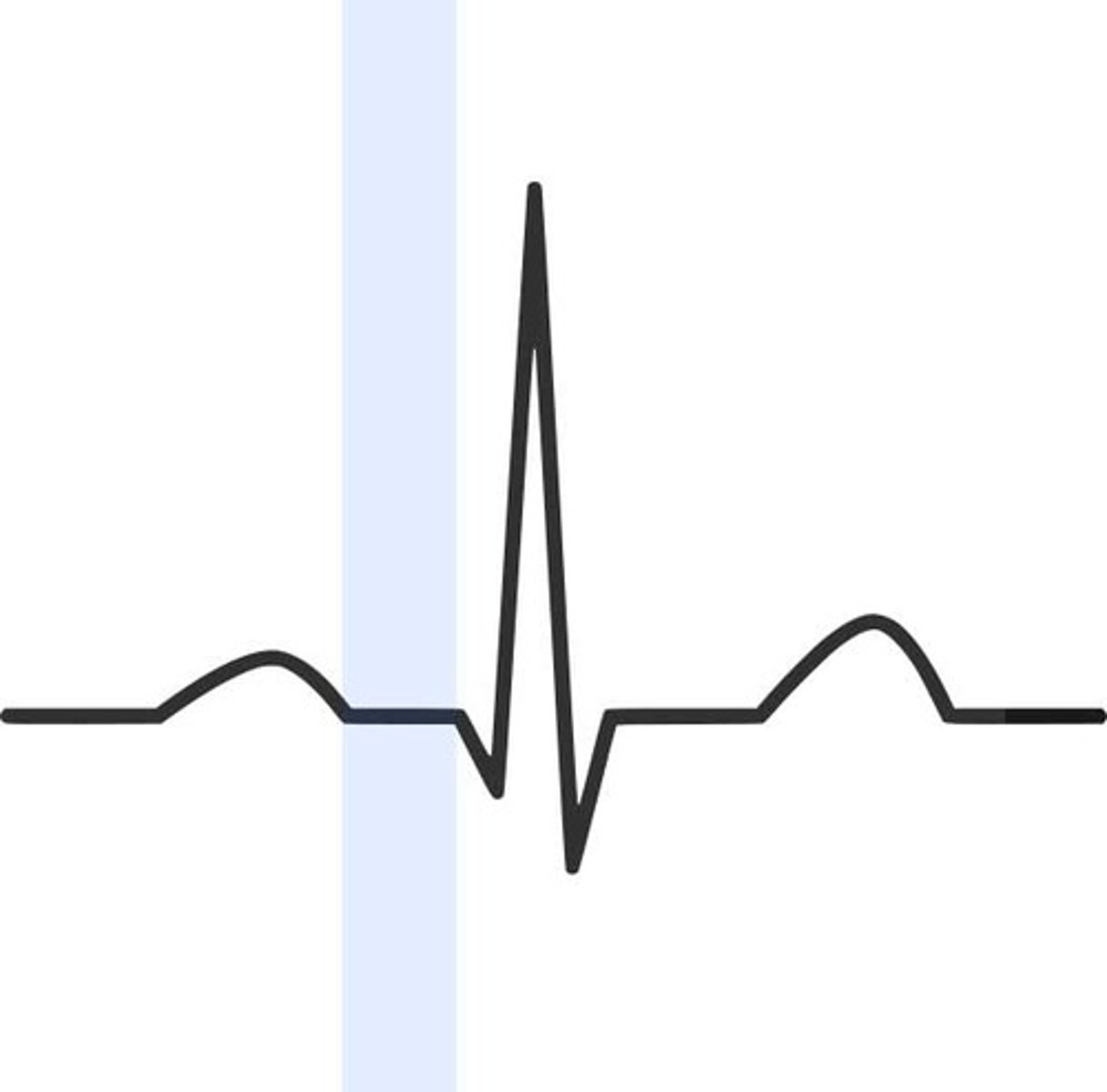
PR segment
delay at AV node
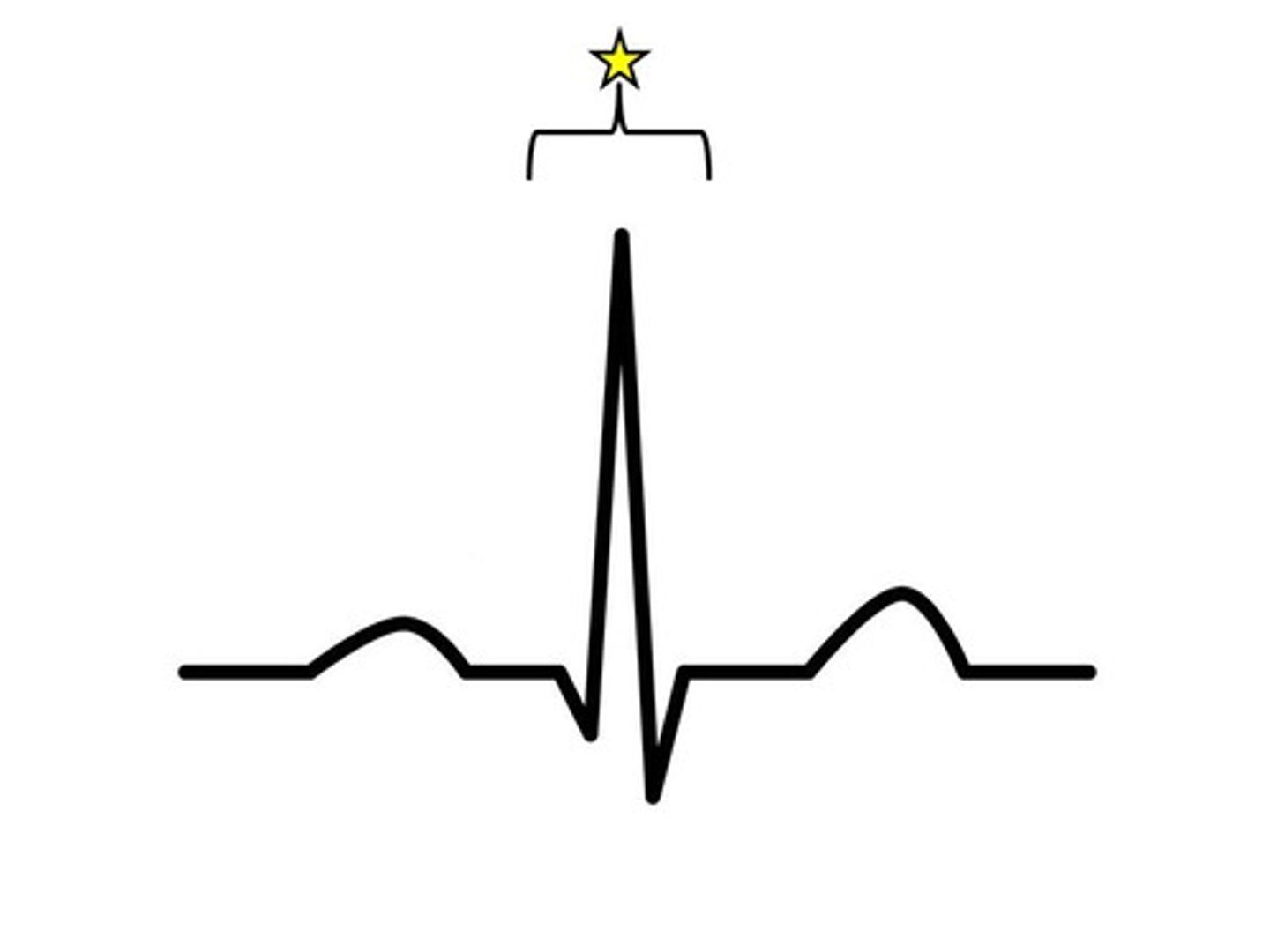
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization
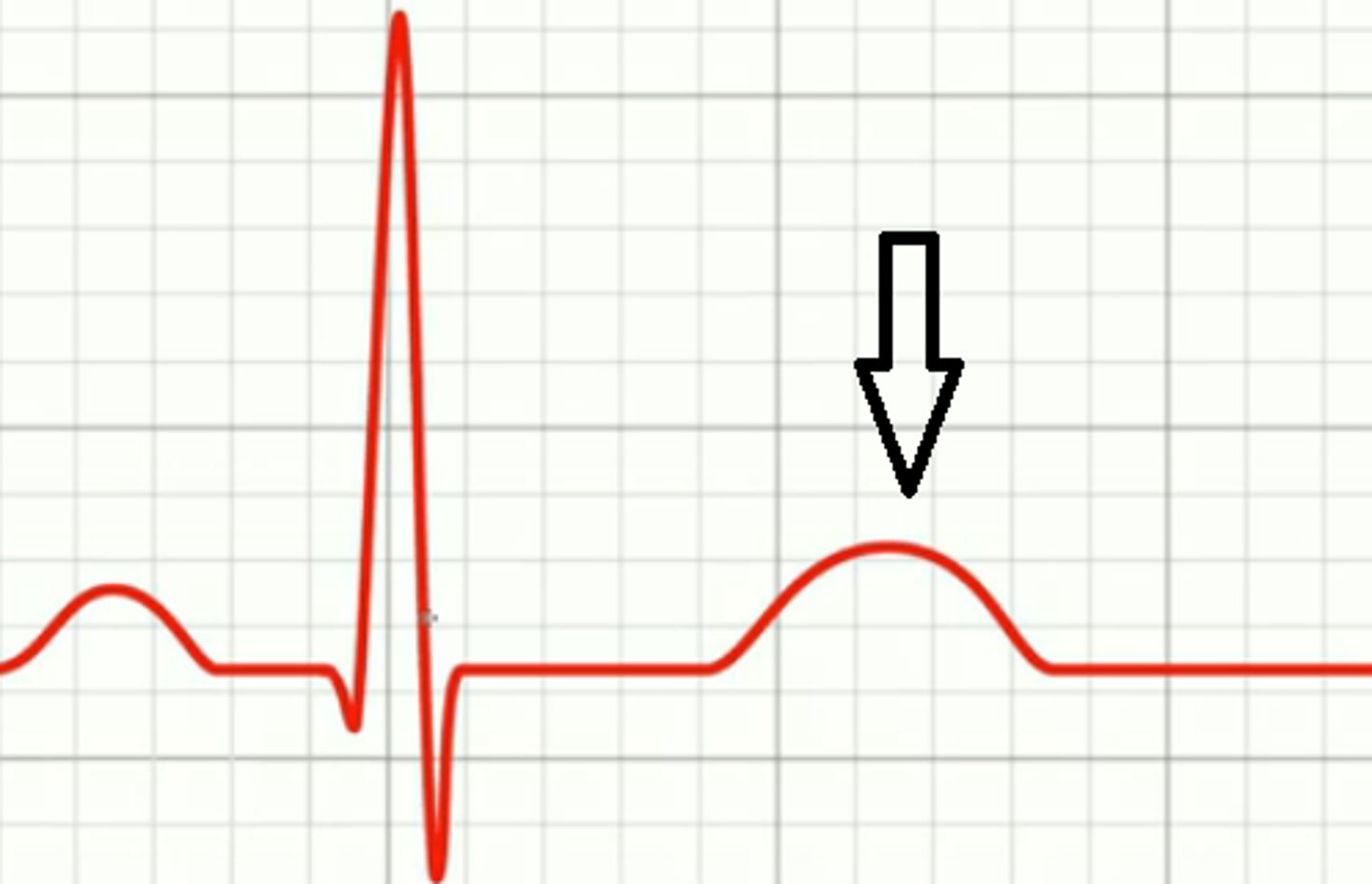
T wave
ventricular repolarization
isoelectric line
no electrical activity
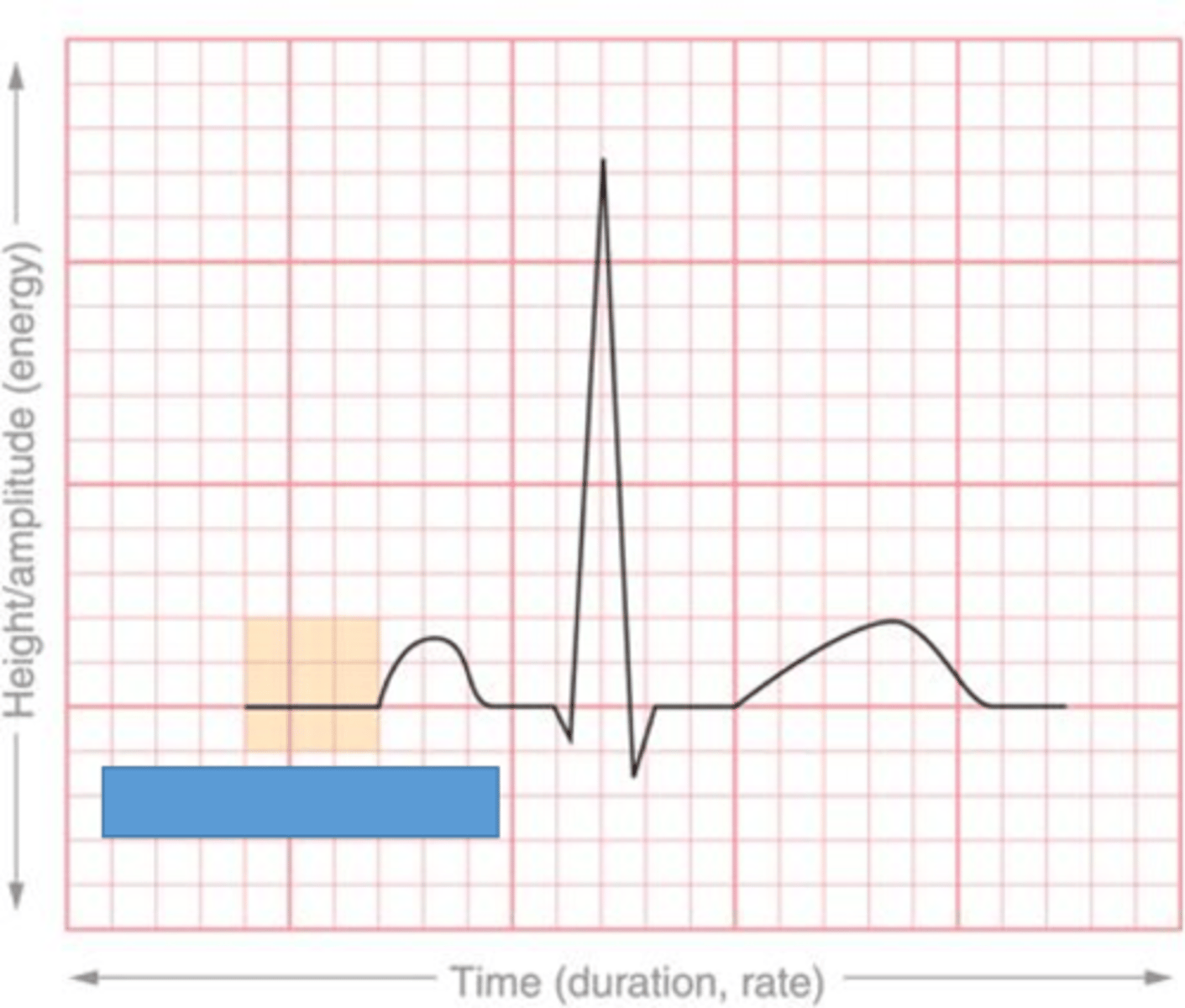
what part of the heart contracts and sends blood flow to systemic circulation?
left ventricle
the pressure wave that moves throughout the arterial system is the _______
pulse
what is the highest pressure pulse?
carotid
describe the pressure within the arterial system
peak in systole (contracting)
trough in diastole (relaxing)
what is pulse pressure?
difference between systolic and diastolic pressure
what can affect blood pressure?
LV stroke volume
Compliance of aorta and large arteries
Peripheral vascular resistance
Blood volume
what do jugular veins provide information about?
right heart pressures
what vein provides the most information?
right internal jugular
what does an increased JVP indicate?
heart failure, pulmonary hypertension
what does an decreased JVP indicate?
blood loss, dehydration, ↓ blood volume
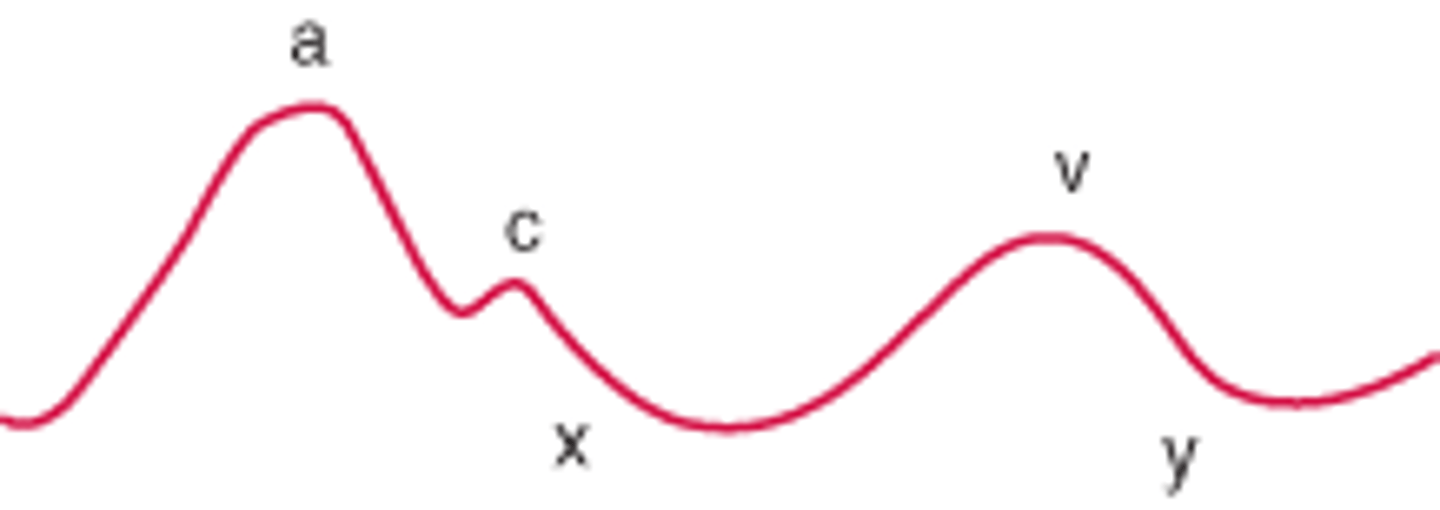
a wave
peak, right atrial pressure rises due to atrial contraction
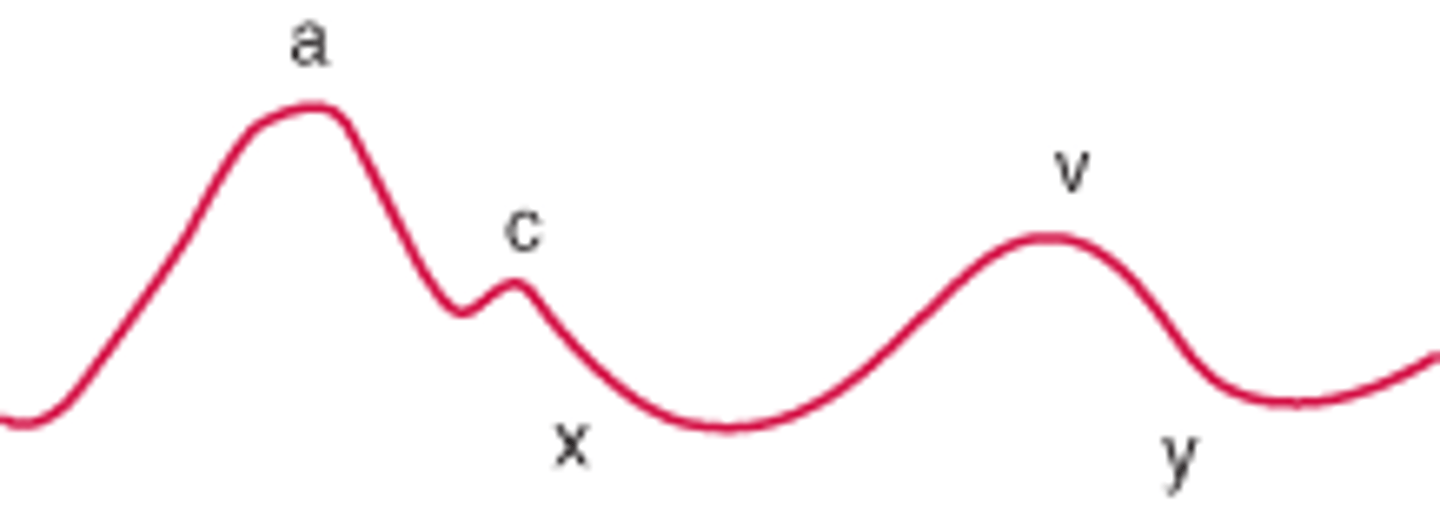
x wave
trough, right atrial pressure falls due to relaxation and atrial filling
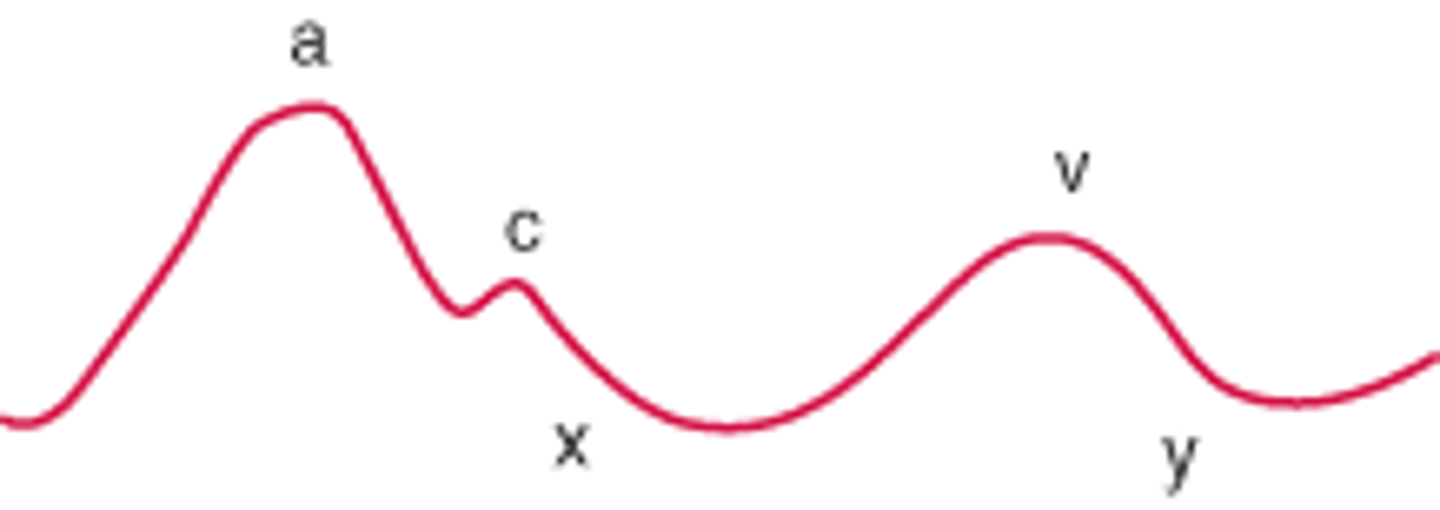
v wave
second peak, right atrial pressure rises due to inflow from the vena cava during systole
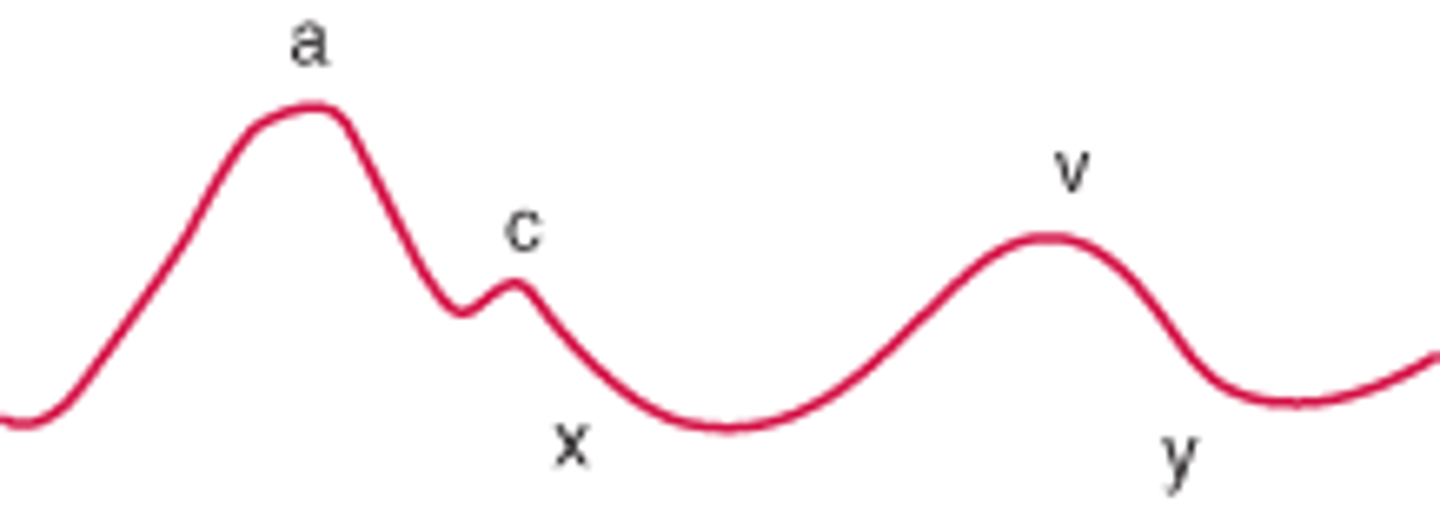
y wave
second trough, right atrial pressure falls as the RA passively empties to RV
Cardiac ROS
Chest pain
Palpitations
Shortness of breath
Edema
History of heart disease
Cardiac testing
Rick factors for CAD
History of a murmur
History of rheumatic fever (more common years ago)
Family history of CAD
what kind of questions do you need to be asking for a patient with chest pain?
Onset
Location
Duration
Pattern
Triggers
Quality
Radiation
Aggravating factors
Alleviating factors
Associated symptoms
Previous occurrence
Pain
what are pain questions you should ask your patients?
Pain scale (0-10)
Quality
Radiation
what kind of questions do you need to be asking for a patient with palpitations?
Onset
Location
Duration
Pattern
Triggers
Aggravating factors
Alleviating factors
Associated symptoms
Previous occurrence
what kind of questions do you need to be asking for a patient with shortness of breath?
Onset
Duration
Pattern
Triggers
Aggravating factors
Alleviating factors
Associated symptoms
Previous occurrence
dyspnea
uncomfortable awareness of breathing inappropriate to the level of exertion
orthopnea
dyspnea with lying down that improves with sitting up
paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
sudden dyspnea and orthopnea that awakens a patient from sleep
what kind of questions do you need to be asking for a patient with edema?
Onset
Location
Duration
Triggers
Aggravating factors
Alleviating factors
Associated symptoms
Previous occurrence
what additional characteristics should you consider with a patient that has edema?
pitting or not pitting
associated weight gain
temporal relation