APES Lessons 4 - 6 Practice Quizzes
1/157
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
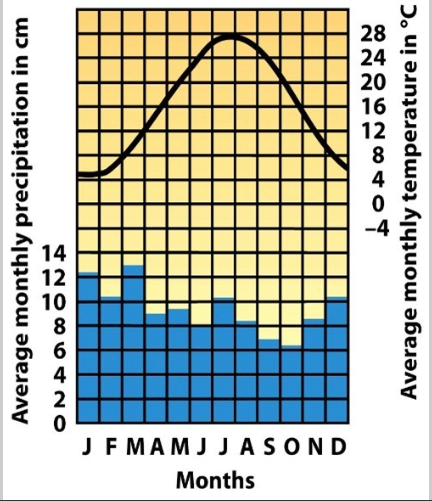
What biome is shown in the picture?
Temperate Rainforest
Taiga Boreal Forest
Deciduous Temperate Seasonal Rainforest
Tropical Rainforest
Deciduous Temperate Seasonal Rainforest
Trees: Maple, Oak, Elm, Hickory
Soil: nutrient rich - lots of humus from degrading leaves
Temps: 5°C - 28°C (41°F - 82°F)
Precipitation in ALL seasons (snow + rain)
East Coast U.S., Vermont, Canada, Russia Japan
What ecosystem service is the following:
Many varieties of species and various populations of animals and plants are able to live in forests, increasing the genetic diversity in the area
Provisioning Services
Regulating Services
Cultural Services
Supporting Services
Supporting Services
Ecosystems themselves couldn’t be sustained without the consistency of underlying natural processes, such as photosynthesis, nutrient cycling, the creation of soils, and the water cycle. These processes allow the Earth to sustain basic life forms, let alone whole ecosystems and people. Without supporting services, provisional, regulating, and cultural services wouldn’t exist.
Habitats for species, photosynthesis, maintenance of genetic diversity, soil formation, nutrient cycling, water cycle
The concept protecting the inner core of a preserve by establishing 2 buffer zones in which local people can extract resources sustainably without harming the inner core:
maximum sustainable land
land trust
multiple use land
sustainable forest management
biosphere reserve
biosphere reserve
What biome is shown in the picture?
Taiga Boreal Forest
Tropical Rainforest
Temperate Rainforest
Deciduous Temperate Seasonal Rainforest
Temperate Rainforest
Pine trees (conifers) + some broad leaved trees
Acidic soil - from pine trees
Little humus in soil - few leaved trees
Temp: 2°C to 18°C (36°F - 64°F)
Precipitation 20 cm high during winter, moderate during spring, 3cm in summer
Alaska, Oregon, Washington, New Zealand
Which of the following best achieves the goal of providing wood products for humans while preserving biodiversity?
Clear-cutting of large areas of old-growth forest
Selective cutting of large areas of old-growth forest
Using prescribed burns in large areas of old-growth forest
Planting large tree plantations in abandoned farm fields
Selective cutting of large areas of old-growth forest
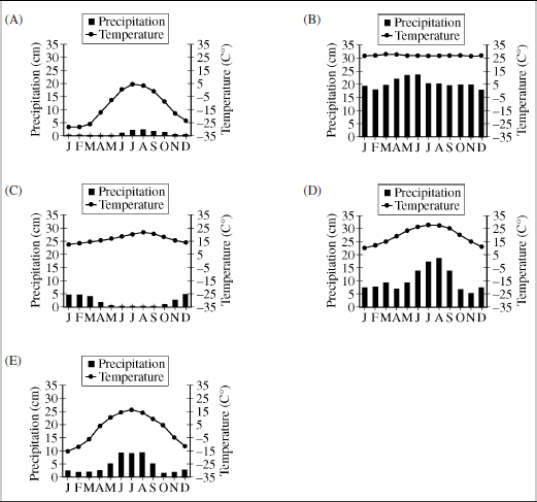
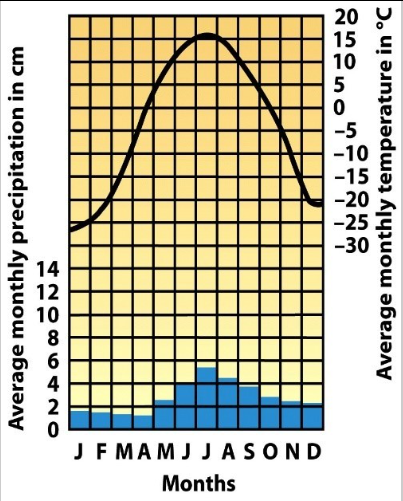
Which biome is characterized by the highest diversity of tree species, various broad leaved plants and epiphytes?
GRAPH A
GRAPH B
GRAPH C
GRAPH D
GRAPH E
GRAPH B
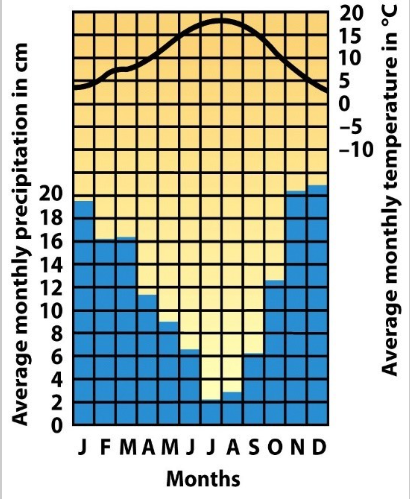
What biome is shown in the picture?
Temperate Rainforest
Taiga Boreal Forest
Tropical Rainforest
Deciduous Temperate Seasonal Rainforest
Tropical Rainforest
Trees: Broad leaf plants (canopy) + Epiphytes - plants that grow on rocks + other plants
Soil: Acidic from H+ (Hydrogen ions) forming when plants decompose
Little nutrients in soil because so many plants take up nutrients
Temp: Hot, 26°C (79°F), WET - 44 cm rain in a month
U.S., America, Asia
What term describes a population of new species formed due to the physical geographic separation?
habitat corridor speciation
bottleneck speciation
endemic speciation
allopatric speciation
habitat fragmentation speciation
allopatric speciation
AKA geographic isolation
Which letter of the biomes have the most humus in soil
Temperate Rainforest
Deciduous Temperate Seasonal Rainforest
Tropical Rainforest
Taiga Boreal Forest
Deciduous Temperate Seasonal Rainforest
humus: organic, dark material remaining after decomposition by microorganisms
What ecosystem service is the following:
Nutrient cycling takes place in forests decomposing dead leaves and turning it into humus
Provisioning Services
Regulating Services
Cultural Services
Supporting Services
Supporting Services
Ecosystems themselves couldn’t be sustained without the consistency of underlying natural processes, such as photosynthesis, nutrient cycling, the creation of soils, and the water cycle. These processes allow the Earth to sustain basic life forms, let alone whole ecosystems and people. Without supporting services, provisional, regulating, and cultural services wouldn’t exist.
Habitats for species, photosynthesis, maintenance of genetic diversity, soil formation, nutrient cycling, water cycle
What ecosystem service is the following:
Forests release oxygen (via photosynthesis).
Provisioning Services
Regulating Services
Cultural Services
Supporting Services
Regulating Services
A regulating service is the benefit provided by ecosystem processes that moderate natural phenomena. All these processes work together to make ecosystems clean, sustainable, functional, and resilient to change. Regulating services are the services that ecosystems provide by acting as regulators, e.g., regulating the quality of air and soil or by promoting flood and disease control.
Local climate and air quality, erosion prevention and soil fertility, carbon sequestration and storage, pollination, moderation of extreme events, biological control, water-water treatment, water flow
What is the biome located in Oregon, Washington, UK, South Australia and has coniferous trees (pine trees) like Douglas Fir and Spruce Trees?
Temperate Rainforest
Deciduous Temperate Seasonal Rainforest
Tropical Rainforest
Taiga Boreal Forest
Temperate Rainforest
What ecosystem service is the following:
Forests improve the quality of soil and water by filtering sediments and other pollutants from the water in the soil before it reaches a water source
Provisioning Services
Regulating Services
Cultural Services
Supporting Services
Regulating Services
A regulating service is the benefit provided by ecosystem processes that moderate natural phenomena. All these processes work together to make ecosystems clean, sustainable, functional, and resilient to change. Regulating services are the services that ecosystems provide by acting as regulators, e.g., regulating the quality of air and soil or by promoting flood and disease control.
Local climate and air quality, erosion prevention and soil fertility, carbon sequestration and storage, pollination, moderation of extreme events, biological control, water-water treatment, water flow
Which of the following is a commercially used method for harvesting trees and is most likely to lead to a fragmented landscape with serious impacts on biodiversity?
Selective cutting
Clear-cutting
Shelter-wood cutting
Strip cutting
Snag cutting
Clear-cutting
What is the debate over whether it is better to make reserves large in size and few in number or many in number but small in size
Biosphere
Land Trust
SLOSS
Edge effects
Habitat corridors
SLOSS
Single Large reserves Or Several Small reserves
Large mammals need a single large reserve for hunting + mating
Insects/birds not affected by several small reserves (able to fly)
What ecosystem service is the following:
Forests provide habitats for many species. Trees are used for food, shelter, and sites for reproduction. Many animals also use trees for resting, nesting and for places from which to hunt or capture prey. When the trees mature, animals are able to enjoy fruits and foraging opportunities.
Provisioning Services
Regulating Services
Cultural Services
Supporting Services
Supporting Services
Ecosystems themselves couldn’t be sustained without the consistency of underlying natural processes, such as photosynthesis, nutrient cycling, the creation of soils, and the water cycle. These processes allow the Earth to sustain basic life forms, let alone whole ecosystems and people. Without supporting services, provisional, regulating, and cultural services wouldn’t exist.
Habitats for species, photosynthesis, maintenance of genetic diversity, soil formation, nutrient cycling, water cycle
What ecosystem service is the following:
Students are able to explore forests and learn about species interactions
Provisioning Services
Regulating Services
Cultural Services
Supporting Services
Cultural Services
A cultural service is a non-material benefit that contributes to the development and cultural advancement of people, including how ecosystems play a role in local, national, and global cultures; the building of knowledge and the spreading of ideas; creativity born from interactions with nature (music, art, architecture); and reaction such as hiking, horseback riding, swimming, skiing, hunting, and so on.
Recreation and mental and physical health, ecotourism, aesthetic appreciation and inspiration for culture, art and design, spiritual experience and sense of place
Which plant is a pioneer species in secondary succession?
Hickory Trees
Grasses
Oak Trees
Epiphytes
Lichen
Grasses
pioneer species: 1st plant to grow back in an area
grasses (die and leave nutrients) → shrubs → small trees → oak hickory trees (late successional trees)
Which an advantage of habitat corridors?
Decrease inbreeding
Facilitates movement of invasive species
Facilitates movement of fires
Facilitates movement of pathogens
Increases competition
Decrease inbreeding
What is not true about snags?
Insects that decay the snag are food for other wildlife
Animals make homes in snags
Snags accelerate erosion
Snags add nutrients to the soil increasing the health of the soil
Snags accelerate erosion
What ecosystem service is the following:
Forests have aesthetic value (hiking, camping, photography, tourism, etc.).
Provisioning Services
Regulating Services
Cultural Services
Supporting Services
Cultural Services
A cultural service is a non-material benefit that contributes to the development and cultural advancement of people, including how ecosystems play a role in local, national, and global cultures; the building of knowledge and the spreading of ideas; creativity born from interactions with nature (music, art, architecture); and reaction such as hiking, horseback riding, swimming, skiing, hunting, and so on.
Recreation and mental and physical health, ecotourism, aesthetic appreciation and inspiration for culture, art and design, spiritual experience and sense of place
Which of the following would be the best way to mitigate deforestation?
Grow more diverse timber products to increase economic value in an area.
Stimulate intensive agricultural production of native vegetation close to villages.
Employ clear cutting harvest techniques that are more sustainable.
Replant and protect trees in areas that have been previously cleared.
Replant and protect trees in areas that have been previously cleared.
What term describes when a large area of land is divided into sections from logging, agricultural land, roads, and urban development creating smaller, scattered and isolated patches?
Habitat Corridor
Transitional Area
Multiple Use Land
Habitat Fragmentation
Bottle Neck Effect
Habitat Fragmentation
habitat corridor: strip of land that connects 2 areas allowing animals to cross
bottleneck effect: reduction in genetic diversity in a populated area caused by reduction of population size
less mates (less alleles) → offspring have more mutations + more susceptibility to disease
Forests that are intact and have not been logged or seriously disturbed by human activities or natural disasters are known as
Endemic Forests
Old Growth Forests
Biosphere Reserve Forests
Canopy Forests
Land Trust Forests
Old Growth Forests
old growth forests: trees between 120-800 years old
forests have never been logged; “intact”
trees have varying heights - which allows light to enter - reaches forest floor for seedlings to grow
high biodiversity
Endemic Species: unique to one area
Land Trust: organization that purchases land to protect it
Which are true about Secondary Succession? (multiple choice)
occurs in an area where soil is present
occurs in an area where rocks, but no soil is present
is slower than primary succession
occurs after logging takes place
occurs in an area where soil is present, occurs after logging takes place
secondary succession: after logging or fires
plants regrow when soil is present
growth is faster than primary succession (where rocks have to break down into soil)
What is the biome located in Maine, Canada, Russia and has coniferous trees (pine trees)
Temperate Rainforest
Deciduous Temperate Seasonal Rainforest
Tropical Rainforest
Taiga Boreal Forest
Taiga Boreal Forest
What is the disadvantage of selective cutting?
Cleared land could be invaded by aggressive plant species, causing changes to forest composition.
Requires special methods (helicopters) to extract single trees.
Results in habitat fragmentation
Reduces crowding of trees
Removes diseased trees
Requires special methods (helicopters) to extract single trees.
Which of the following statements best describes clear-cutting forests with the most unsustainable method to harvest timber?
All but the healthiest trees are removed from a forest.
The highest-value trees are selectively removed from a forest.
All of the shade-intolerant trees in a small section of a forest are cut down.
All of the trees in a forest are cut down and removed in one operation.
All of the trees in a forest are cut down and removed in one operation.
Which an advantage of tree plantations?
Reduces pressure from forests
Increased likelihood of soil erosion when all trees cut at once
Biodiversity decreased
Prone to disease- could wipe out crop of monoculture trees
Depletes soil of nutrients
Reduces pressure from forests
What ecosystem service is the following:
Forests provide wood (e.g., construction material, paper)
Provisioning Services
Regulating Services
Cultural Services
Supporting Services
Provisioning Services
A provision service is any type of benefit to people that can be extracted from nature. Along with food, other types of provisioning services include drinking water, timber, wood fuel, natural gas, oils, plants that can be made in clothes and other materials, and medicinal benefits.
Food, raw materials, fresh water, medical resources
In a typical forest ecosystem, dead trees and fallen trees are most important because of their role in which of the following?
Providing a valuable source of timber
Providing habitats for wildlife
Contributing to soil erosion
Increasing water runoff
Removing carbon dioxide from the air
Providing habitats for wildlife
A managed tract with uniformly aged trees of one or two genetically uniform species that are harvested by clear-cutting as soon as they become commercially valuable is known as
second growth forest
tree plantation
strip cutting plantation
clear cutting plantation
deflected plantation
tree plantation
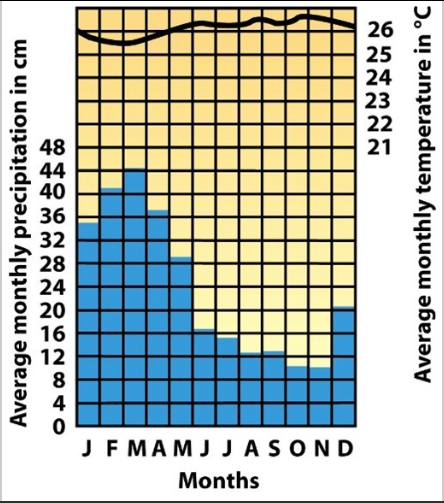
What biome is shown in the picture?
Taiga Boreal Forest
Temperate Rainforest
Deciduous Temperate Seasonal Rainforest
Tropical Rainforest
Taiga Boreal Forest
Pine trees (conifers)
Acidic soil due to pine needles
Little humus due to lack of leaves
Cold temp: -20°C to 15°C
Little precipitation: 1 to 5 cm
Alaska, Canada, Russia
Which biome does not have acidic soil?
Temperate Rainforest
Deciduous Temperate Seasonal Rainforest
Tropical Rainforest
Taiga Boreal Forest
Deciduous Temperate Seasonal Rainforest
Soil: nutrient rich - lost of humus from decaying leaves
What ecosystem service is the following:
Forests influence the local microclimate affecting humans (change in temperature, shade, UV, wind breaks).
Provisioning Services
Regulating Services
Cultural Services
Supporting Services
Regulating Services
A regulating service is the benefit provided by ecosystem processes that moderate natural phenomena. All these processes work together to make ecosystems clean, sustainable, functional, and resilient to change. Regulating services are the services that ecosystems provide by acting as regulators, e.g., regulating the quality of air and soil or by promoting flood and disease control.
Local climate and air quality, erosion prevention and soil fertility, carbon sequestration and storage, pollination, moderation of extreme events, biological control, water-water treatment, water flow
What forests form a single canopy layer of trees that are generally the same age after the original trees have been removed by human activities
Endemic Forests
Old Growth Forests
Biosphere Reserve Forests
Second Growth Forests
Land Trust Forests
Second Growth Forests
What ecosystem service is the following:
Forests provide food products for human consumption (nuts, fungi- mushrooms, deer).
Provisioning Services
Regulating Services
Cultural Services
Supporting Services
Provisioning Services
A provision service is any type of benefit to people that can be extracted from nature. Along with food, other types of provisioning services include drinking water, timber, wood fuel, natural gas, oils, plants that can be made in clothes and other materials, and medicinal benefits.
Food, raw materials, fresh water, medical resources
What ecosystem service is the following:
Forests provide habitat for many species. Trees are used for food, shelter, and sites for reproduction. Many animals also use trees for resting, nesting and for places from which to hunt or capture prey. When the trees mature, animals are able to enjoy fruits and foraging opportunities.
Provisioning Services
Regulating Services
Cultural Services
Supporting Services
Supporting Services
Ecosystems themselves couldn’t be sustained without the consistency of underlying natural processes, such as photosynthesis, nutrient cycling, the creation of soils, and the water cycle. These processes allow the Earth to sustain basic life forms, let alone whole ecosystems and people. Without supporting services, provisional, regulating, and cultural services wouldn’t exist.
Habitats for species, photosynthesis, maintenance of genetic diversity, soil formation, nutrient cycling, water cycle
Which best describes Second Growth Forests?
are important because they are biologically diverse and are often home to endemic and rare species.
are only dead trees in a forest
single canopy layer of trees that are generally the same age after the original trees have been removed by human activities.
a place where plants are grown for display to the public and often for scientific studies
are intact forests that have not been logged or seriously disturbed by human activities or natural disasters
single canopy layer of trees that are generally the same age after the original trees have been removed by human activities.
trees regrow at same rate, form single layer canopy → decreased light to forest floor + less seedlings
Which forest harvesting technique is will bring in the greatest profit?
Shelterbelt
Ecologically sustainable forestry
Selective cutting
Shelter tree
Clear-cutting
Clear-cutting
The term used to describe when local or regional organizations purchase land to protect it, is known as
maximum sustainable land
land trust
multiple use land
sustainable forest management
biosphere reserve
land trust
Which of the following is the logging method that clear cuts a section of trees along the contour (edge) of the land, with the corridor narrow enough to allow natural regeneration within a few years ?
Selective cutting
Clear-cutting
Shelter-wood cutting
Strip cutting
Snag cutting
Strip cutting
What is the biome located in East Coast, Japan, Russia and has Maple, Oak and Hickory trees?
Temperate Rainforest
Deciduous Temperate Seasonal Rainforest
Tropical Rainforest
Taiga Boreal Forest
Deciduous Temperate Seasonal Rainforest
Advantages of what logging method is .... Reduces damage to environment/habitats, reduces crowding of trees, causes less erosion, encourages the growth of younger trees, maintains the age distribution of the original forest, and can be sustainable.
prescribed cutting
selective cutting
secondary cutting
clear cutting
strip cutting
selective cutting
What is the biome located in South America, Asia, West Africa and has a canopy of broad leaved trees
Temperate Rainforest
Deciduous Temperate Seasonal Rainforest
Tropical Rainforest
Taiga Boreal Forest
Tropical Rainforest
A negative effect of smelting is
crown fires
air pollution
nutrient reduction in soil
acid mine drainage
landslides
Air pollution
What valuable mineral is mined from a Bauxite Ore?
Aluminum
Lead
Silicon
Uranium
Iron
Aluminum
The ______Law of thermodynamics describes how heat is lost when electricity is generated from coal.
2nd
1st
3rd
4th
2nd
DDT is considered both (multiple choice)
muscle soluble and builds up in your muscle tissue
water soluble and dissolves in your fat tissue
biomagnifying
water soluble and is excreted through urination and perspiration
fat soluble and builds up in your fat tissue
muscle soluble and builds up in your muscle tissue, fat soluble and builds up in your fat tissue
Swamps consisting of trees, ferns and moss have formed which fossil fuel? ________________
Oil
Coal
Natural gas
Nuclear
Coal
Placer Mining takes place
on the tops of mountains
on the hill side
in a river
underground
on flat land
in a river
The process of extracting and separating gold in remote regions often results in environmental contamination with which of the following?
Ozone
Cyanide
Sulfuric Acid
Asbestos
Selenium
Cyanide
What is a concern with contour mining?
Landslides
Methane explosion
Coal dust explosion
CO/CO2 = suffocation
Black lung disease
Landslides
What valuable mineral is mined from a Hematite Ore?
Aluminum
Lead
Silicon
Uranium
Iron
Iron
___________________ coal isn’t really coal, is partially decaying organic matter.
peat
anthracite
bituminous
lignite
peat
The Madrid Protocol prohibits mineral exploration for 50 years in
Antarctica
Hawaii
Alaska
Spain
Tropical Rainforests
Antarctica
How can methane explosions be prevented?
lead cutting tools
sprinkling mercury on methane
silicon chips in cutting tools
limestone sprinkled on methane
water sprayed from cutting tool
water sprayed from cutting tool
The type of mining on hilly or mountainous terrain when sections are cut out of the side of a hill is called
contour mining
open pit mining
subsurface mining
mountain top mining
strip mining
contour mining
Piles of overburden produced when materials are removed by mining is called
slag
tailings
heap
gangue
spoil
spoil
What process is described: Some toxic compounds pose special risks to humans and other organisms high on the food chain because as they prey on lower trophic levels the toxins move up.
Synergism
Compound contamination
Biomagnification
Threshold effect
Carcinogenesis
Biomagnification
In a lake, a fish consumes a toxin and over its lifetime it gets takes in more and more toxin in its tissue. This is an example of
Bio-Synergism
Bio-Overshoot
Biomagnification
Biopartioning
Bioaccumulation
Bioaccumulation
The gangue removed as impurities that is separated from the metal in an ore are called
tailings
overburden
slag
gangue
spoils
tailings
What type of mining is described: Type of mining used where the terrain is flat. An earthmover strips away the overburden, and a power shovel digs a cut to remove the mineral deposit. After removal of the mineral, the trench is filled with overburden, and a new cut is made parallel to the previous one.
contour mining
open pit mining
subsurface mining
mountain top mining
strip mining
strip mining
What type of surface mining causes rock and dirt to fall into valleys and rivers below it?
contour mining
open pit mining
subsurface mining
mountain top mining
strip mining
mountain top mining
What type of surface mining causes water, air and noise pollution?
contour mining
open pit mining
subsurface mining
mountain top mining
strip mining
mountain top mining
How can coal dust explosions be prevented?
lead
mercury
silicon
limestone
water
limestone
____________________ coal has low sulfur and low energy.
anthracite
bituminous
lignite
peat
lignite
A chemical that is water soluble and is excreted through urination and perspiration is
lead
DDT
caffeine
Mercury
caffeine
The device that sprays water with a base on contaminated air removing sulfur dioxide and other acids is called a(n) _______________________________.
Bag house filter
Electrostatic precipitator
Wet scrubber
Cyclone separator
Wet scrubber
What is done to prevent coal dust explosions in subsurface mining?
limestone sprinkled on coal dust
water sprayed on machinery
coal dust sprinkled on machinery
canary birds detect coal dust levels
drainage of mines of acidic water
limestone sprinkled on coal dust
Waste or undesired material in an ore attached to the mineral/metal
overburden
tailings
heap
gangue
spoil
gangue
What type of mining used where the terrain is flat. An earthmover strips away the overburden, and a power shovel digs a cut to remove the mineral deposit?
contour mining
open pit mining
subsurface mining
mountain top mining
area strip mining
area strip mining
What type of mining is described: Extraction of a metal ore or fuel resource such as coal from a 100 m deep underground deposit
contour mining
open pit mining
subsurface mining
mountain top mining
strip mining
subsurface mining
A cost that is not included in the purchase price of the product or service is considered a
marginal cost
Kuznet’s cost
externality
full cost pricing
depletion cost
externality
Which of the following best describes acid mine drainage?
Reclamation of mines by removing excess water
When water rinses out toxic materials out of a mine carrying sulfuric acid to nearby streams and groundwater
The use of acids to leach minerals from rocks to increase smelting efficiency
Increased water pollution from acid rain entering copper mines
Acid production by anaerobic bacteria in coal mines
When water rinses out toxic materials out of a mine carrying sulfuric acid to nearby streams and groundwater
Which type of mining causes habitat fragmentation due to the high wall formed that prohibits animals from crossing?
contour mining
open pit mining
subsurface mining
mountain top mining
strip mining
contour mining
What valuable mineral is mined from a Galena Ore?
Aluminum
Lead
Silicon
Uranium
Iron
Lead
The stony waste matter separated from metals during the smelting or refining of ore is called
slag
tailings
overburden
gangue
spoil
slag
____________________ coal is the best because it has low sulfur and high energy.
anthracite
bituminous
lignite
peat
anthracite
What valuable mineral is mined from a Pitchblend Ore
Aluminum
Lead
Silicon
Uranium
Iron
Uranium
Illness in which coal miners' lungs become coated with coal dust, causing a chronic condition in which breathing becomes difficult and painful.
BLACK LUNG DISEASE
COAL LUNG DISEASE
METHANE LUNG DISEASE
MINING LUNG DISEASE
SUB-SURFACE MINING LUNG DISEASE
BLACK LUNG DISEASE
The process in which a desired metal is separated from the other elements in an ore using high temps is called
ore leaching
smelting
acid mine drainage
contour mining
heap leaching
smelting
What type of mining is described: Removing vertical and horizontal ores by digging them out of the earth's surface and leaving a hole.
contour mining
open pit mining
subsurface mining
mountain top mining
strip mining
open pit mining
Why does AMD turn river water a red/orange color?
Metals are soluble in acidic water and then oxidize
Sulfur reacts with the soil
Smelting releases sulfur into the water
The toxins are fat soluble and builds up in the tissue of fish
Metals are soluble in acidic water and then oxidize
What are remediation options for Acid Mine Drainage? (multiple choice)
Use Plants in the process of Phytoremediation to remove heavy metals from the contaminated soil
Add a base- Limestone, Calcium Carbonate, Sodium Hydroxide to neutralize the acids
Add sulfur to neutralize the metals
Add more water to dilute the acids
Add Sulfate Reducing Bacteria to remove the acid conditions from the water
Use Plants in the process of Phytoremediation to remove heavy metals from the contaminated soil, Add a base- Limestone, Calcium Carbonate, Sodium Hydroxide to neutralize the acids, Add more water to dilute the acids, Add Sulfate Reducing Bacteria to remove the acid conditions from the water
When coal is used to generate electricity it also creates heat that can warm up nearby buildings, this is called ________________________.
Cogeneration
Biomass
Franking
By heat
Cogeneration
When Mercury enters a lake, it is converted to Methyl Mercury by
fish
bacteria
a reaction with acids
soil on the bottom of the lake
worms
bacteria
The layer of soil, rock and vegetation above a mineral deposit is known as
tailings
overburden
slag
gangue
spoils
overburden
Which is not a step to reclaim a mining area?
REMOVE SLAG FROM THE MINING AREA
ADD TOPSOIL (NUTRIENTS)
RESHAPE LAND
FILL HOLE WITH SEDIMENT
PLANT NATIVE PLANTS SO NATIVE ANIMALS RETURN
REMOVE SLAG FROM THE MINING AREA
Caffiene is considered
muscle soluble and builds up in your muscle tissue
water soluble and dissolves in your fat tissue
biomagnifying
water soluble and is excreted through urination and perspiration
fat soluble and builds up in your fat tissue
water soluble and is excreted through urination and perspiration
Coal is burned and heats up water in the _________________. Steam turns a ______________that is connected to the shaft of the______________________which turns and produces electricity.
furnace, boiler, turbine
Boiler, generator, turbine
boiler, turbine, generator
Wet scrubber, generator, turbine
boiler, turbine, generator
Which of the following pollutants poses a health risk to humans who eat large quantities of marine fish such as swordfish and tuna?
Radon
Mercury
Lead
Copper
Iron
Mercury
Which of the following is an environmental problem associated with abandoned coal mines?
Acid drainage due to leaching of spoil heaps by rainwater
Air pollution caused by smog from ozone formation
Alkaline solutions that pollute streams
Released nutrients that cause eutrophication into streams
Thermal pollution of streams in the area
Acid drainage due to leaching of spoil heaps by rainwater
Which of the following is the best description of bioaccumulation?
The uptake of essential nutrients by plant roots
The absorption of a substance by an organism at a rate greater than the rate of elimination
The transfer of persistent pollutants like PCBs from one generation to the next
A process that occurs exclusively in marine ecosystems
A high mortality rate in organisms that have been exposed to a toxin
The absorption of a substance by an organism at a rate greater than the rate of elimination
Minamata disease is a neurological disease cause by severe poisoning of what chemical?
DDT
Uranium
Mercury
Carbon Monoxide
Lead
Mercury
The legislation that mandates that land should be minimally disturbed during the mining process and reclaimed after mining is completed is called the
Mining Law of 1872
Madrid Protocol
General Surface Mining Act
Surface Mining Act
Surface Mining Control and Reclamation Act
Surface Mining Control and Reclamation Act
____________________ coal has high sulfur and high energy.
anthracite
bituminous
peat
lignite
bituminous
One device called a(n)_____________________ that removes particulates from contaminated air uses charged plates.
Cyclone separator
Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP)
Wet scrubber
Bag house filter
Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP)
What is a negative effect of Acid Mine Drainage?
Blocks sunlight, preventing photosynthesis, killing plants, decreasing oxygen and food for animals
Fish eggs & frog eggs develop quicker and population overshoots the carrying capacity
Plant tissues produce high levels of chlorophyll
Bacteria break down sulfur
Blocks sunlight, preventing photosynthesis, killing plants, decreasing oxygen and food for animals
What valuable mineral is mined from a Quartz Ore?
Aluminum
Lead
Silicon
Uranium
Iron
Silicon