Heart Physiology
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Atrioventricular (AV) valves
prevent blood backflow into the atria when ventricles contract
located between: atria and venticles
Two types of AV valves
Tricuspid valve
Bicuspid (mitral) valve
Tricuspid valve
allows blood to flow from the right atrium into the right ventricle
located between: right atrium and right ventricle
Bicuspid (mitral) valve
allows blood flow from the left atrium and the left ventricle
located between: left atrium and left ventricle
In the cardiac cycle, during diastole, AV valves
open, allowing blood to fill the ventricles
In the cardiac cycle, during systole , AV valves
close, preventing back flow into the atria
Chordae tendineae
attatch AV valve flaps to papillary muscles
Papillary muscles
contract to tighten chordae tendineae, preventing valve eversion (flipping inside out like an unmbrella)
Chordae tendineae and papillary muscles are only found in
AV valves
How do the chordae tendineae and papillary muscles work together?
Chordae tendineae attach AV valve flaps to papillary muscles.
Papillary muscles contract, tightening chordae tendineae to prevent eversion (flipping inside out like an umbrella).
This anchors the AV valves, ensuring one-way blood flow and preventing backflow
Semilunar (SL) valves
control blood flow preventing backflow into the heart
between the ventricles and arteries
Two types of SL valves
Pulmonary valve
Aortic valve
Pulmonary valve
sends deoxygenated blood to the lungs
located between: right ventricle and pulmonary artery
Aortic valve
sends oxygenated blood to the body
located between: left ventricle and aorta
In the cardiac cycle, during diastole, SL valves
close, preventing back flow into the ventricles
In the cardiac cycle, during systole, SL valves
open, allowing blood to the ejected from the ventricles
Blood flow through the heart
“Very Red Turtles - Run Past Peaceful Lakes - Passing Little Boats - Long Adventures Await”
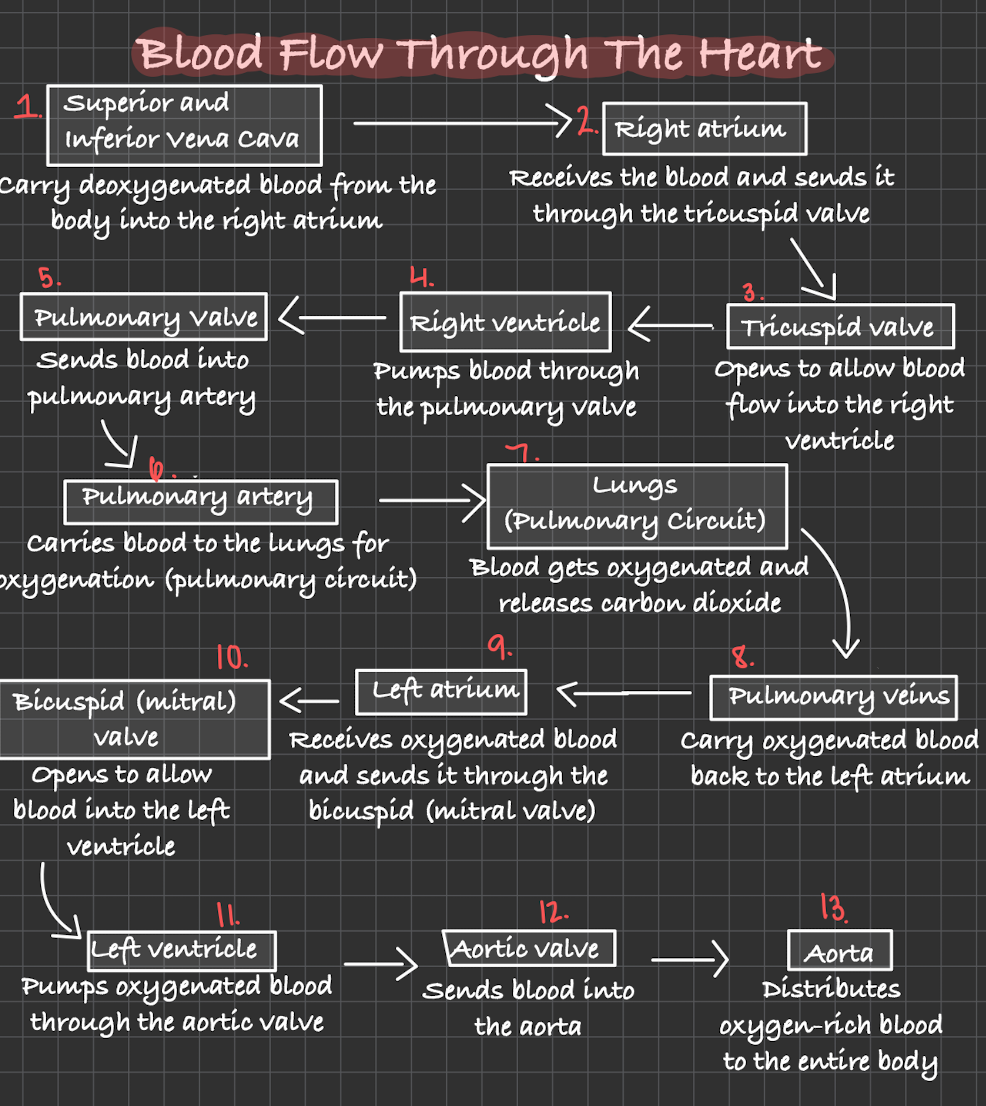
The vena cava and the pulmonary veins do not have
valves where they enter the atria
Both ventricles contract together to
push blood into the pulmonary artery and aorta
Both atria contract together to
push blood into the ventricles
Heart is in systole when
ventricle contract
Heart is in diastole when
ventricles relax
The “bump or “lub” sound is caused by
AV valves closing at the beginning of ventricular systole
The “dump or dub” sound is caused by
SL valves closing at the beginning of ventricular diastole
What are the phases of the cardiac cycle?
Mid-to-late Diastole (Heart Filling)
Ventricular Systole (Pumping)
Early Diastole (Relaxation)
Step 1 of Cardiac Cycle: Ventricular Filling (Mid-to-Late Diastole)
AV Valves open
Blood flows from atria to ventricles
Step 2 of Cardiac Cycle: Atrial Contraction (Mid-to-Late Diastole)
Atria contract, pushing remaining blood into ventricles
Step 3 of Cardiac Cycle: Isovolumetric Contraction (Ventricle Systole)
Ventricles contract but all valves are closed initially
Pressure builds up
Step 4 of Cardiac Cycle: Ventricular Ejection (Ventricle Systole)
SL valves open
blood is pumped into the pulmonary artery (right side) and aorta (left side)
Step 5 of Cardiac Cycle: Isovolumetric Relaxation (Early Diastole)
ventricles relax
SL Valves close (prevents backflow)