Kines. Assignments (Final Study Guide)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
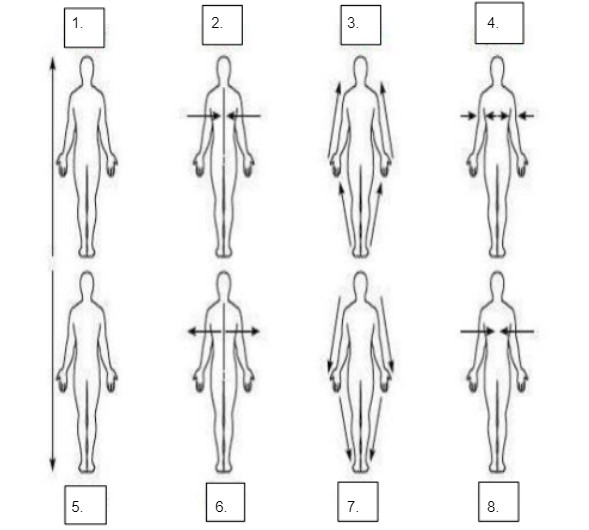
Superior
Medial
Proximal
Superficial
Inferior
Lateral
Distal
Deep
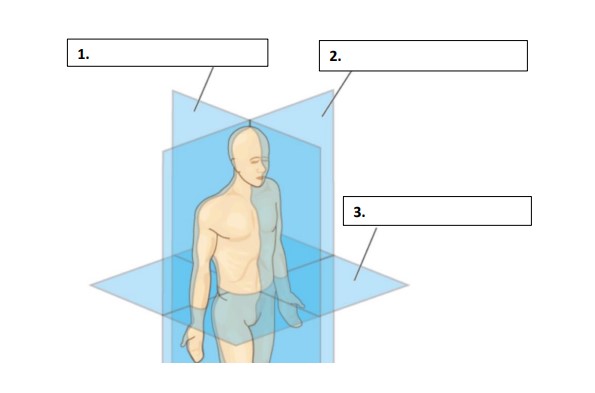
Sagittal
Frontal
Transverse
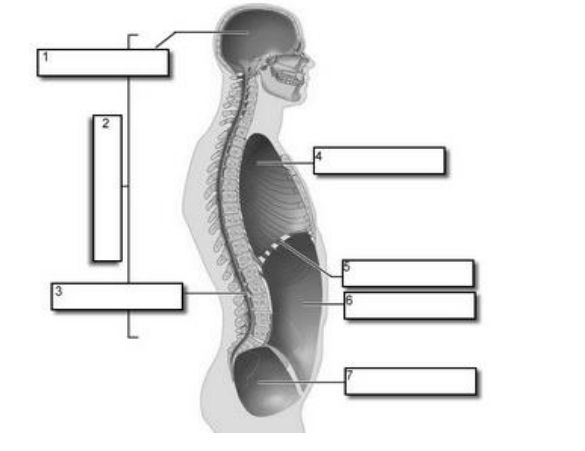
Cranial cavity
Dorsal cavity
Spinal cavity
Thoracic cavity
Diaphragm
Abdominal cavity
Pelvic cavity
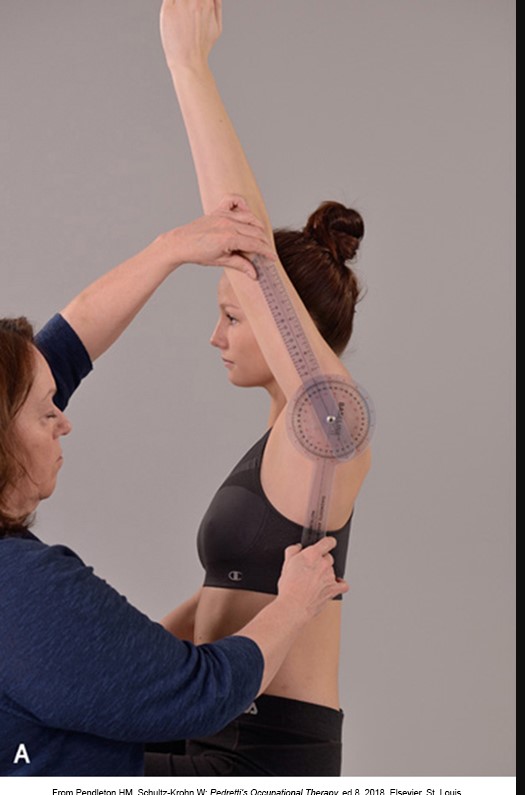

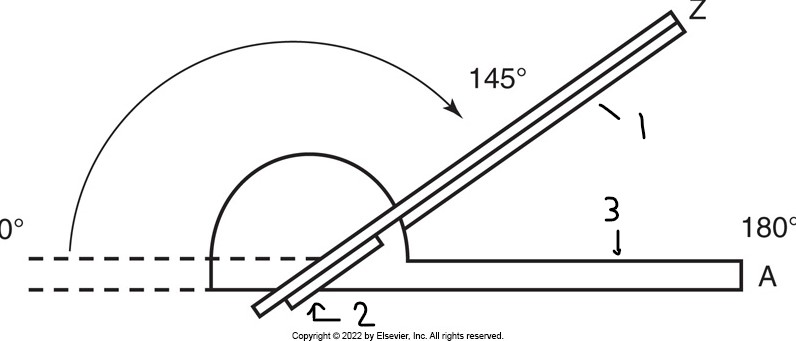
The following image demonstrates a measurement of which motion and approximately what ROM?
Shoulder flexion; 0-160 degrees
The following tool is called?
Goniometer
Moveable arm
Fulcrum axis
Stationary arm
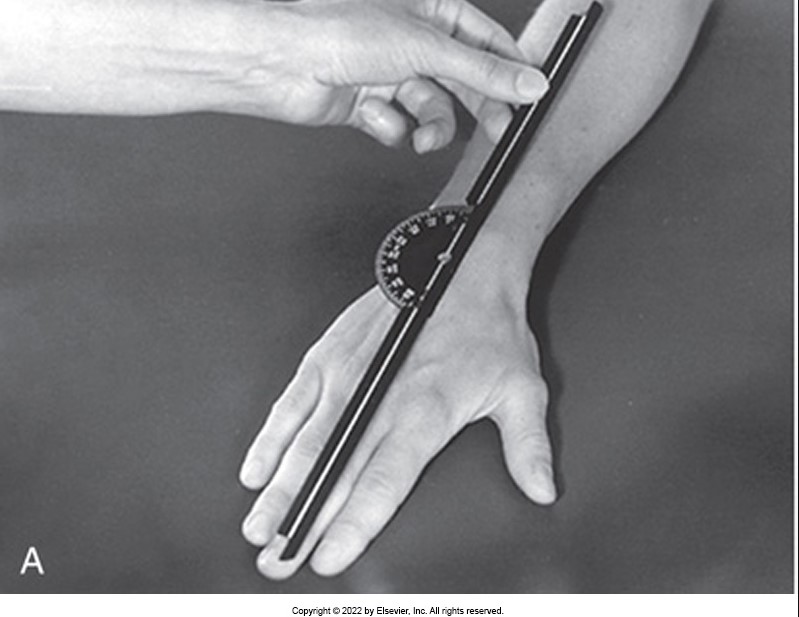
The following image shows a goniometer positioned to measure wrist _________________.
deviation
MMT can be used accurately with patient who have spasticity caused by upper motor neuron disorders.
False

Zero/None
Trace
Poor
Fair
Good
Normal
Types of force:
Traction/distraction - joint surfaces are pulled apart
Shear force - joint surfaces are parallel and in opposite direction of each other
Approximation, compression force - joint surfaces are pushed close together
Joint surface positions
Open-packed position - Incongruent joint surfaces
Closed-pack position - Congruent joint surfaces
Degrees of Freedom
One DOF - hinge & pivot joints
Two DOF - condyloid & saddle joint
Three DOF - ball and socket joint
Stability is increased by:
Increasing the BOS and lowering the COM
What is the effect of moving the line of gravity (LOG) to the edge of the base of support (BOS)?
Decreased stability
When resistance is between the axis and the force, which class of lever is created?
Second
Spasticity is caused the complex nerve circuits that control and ______ reflexes
Stretch
Bobert is 67 years old. He sustained a L CVA. You'd like to prime him for neuroplastic derived activities. He does have a cardiac condition but the physician has cleared him for aerobic activity within 60-70% of his max HR. What is 60% of his max heart rate?
91.8
220 - age = 153
.60 × 153 = 91.8
Weakness in the ______________ muscle causes scapular winging:
Serratus anterior
Force couple
Force couple is two or more things applying force in opposite directions resulting in clockwise or counterclockwise rotation.
Physical rehabilitation occurs in the following sequence
control pain/edema
improve ROM/extensibility
improve strength
improve proprioception/balance
improve endurance/plyometrics
return to baseline or above baseline function
Primary curves
thoracic and sacral curves (during fetal development)
Secondary curves
cervical and lumbar curves (developed after delivery)
Postural sway
slight movements/rocking anteriorly and posteriorly due to the movements happening at the ankles
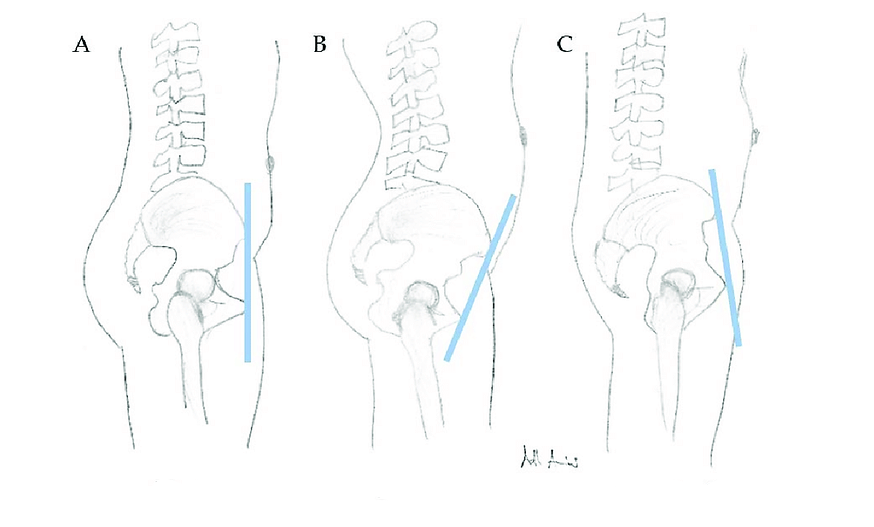
A. neutral
B. anterior
C. posterior
Pelvic tilt examples
Anterior: in supine, a person has an excessive lumbar lordosis; person in third trimester of pregnancy
Posterior: person has documented tight hamstrings; utilizing w/c for mobility
On a Berg Balance Scale, an individual at high risk to fall would score a ____________ (higher/lower) overall score.
lower
On a Timed Up & Go (TUG) Test, an individual who demonstrates a time of ______ seconds is a low risk of falling.
less than 12
Vitals should be monitored _____________, ________________, and ____________ after exercise.
before, during, right after
MET level
less than 3.0 METs - light intensity activity
3.0-6.0 METs - moderate intensity activity
>6.0 METs - vigorous intensity activity
50-63% HRmax - light intensity activity
64-76% HRmax - moderate intensity activity
77-93% HRmax - vigorous intensity activity
RPE (rating of perceived exertion)
<5/10 RPE - light intensity activity
5-6/10 RPE - moderate intensity activity
greater than or equal to 7/10 RPE - vigorous intensity activity