Aquatic Ecology - 2 Content Study Guide
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What are the 2 classifications of waters? Describe their zonation
Lentic habitats: standing waters (lakes, ponds) (vertical zonation)
Lotic habitats: running waters (streams, rivers) (horizontal donation)
How do lakes change as they increase in age (and productivity)?
Go from oligotrophic lake (sparse fish population)
to mesotrophic lake (diverse, increasing fish population)
to eutrophic lake (dense, less diverse fish population)
dystrophic lake: acid, low nutrients, low plankton diversity, poor fishery
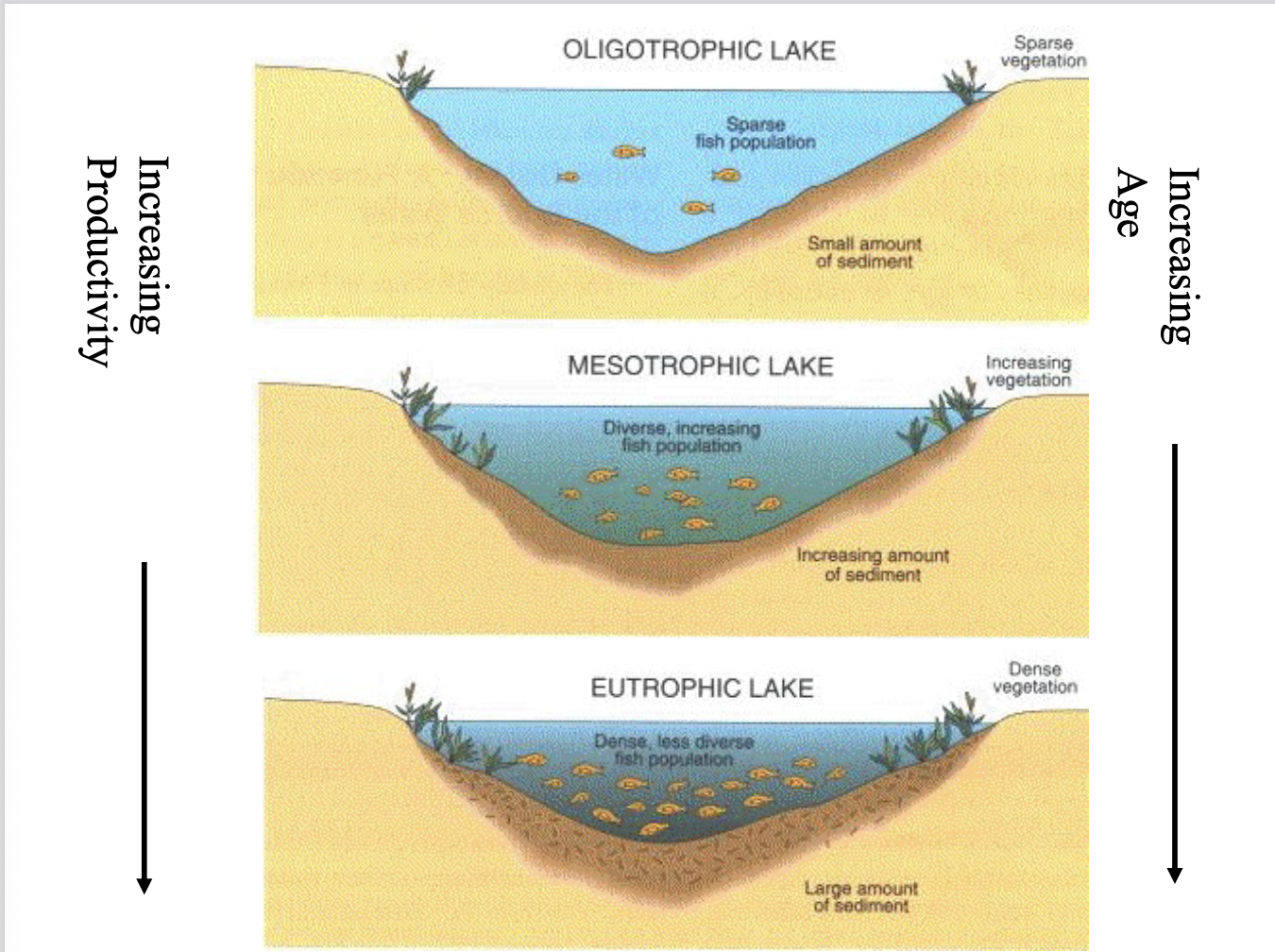
Describe differences between the 4 types of lakes: (including strength of fishery)
Oligotrophic: clear water, low productivity, very desirable fishery of large game fish
Mesotrophic: increased production, accumulated organic matter, occasional algae blood, good fishery
Eutrophic: very productive, may experience oxygen depletion, rough fish common
dystrophic lake: acid, low nutrients, low plankton diversity (as not enough calcium to support bone structure, acid prevents mineral balancing), poor fishery
Describe the thermocline during stratification in a dimiiclic lake over the course of the year
Early summer thermocline at the top, middle in late summer, bottom in fall. Fall turnover happens. in winter ice floats but warmer water is just below it and colder water is at the bottom. then spring turnover happens.
Where does the thermocline happen?
Change in tempature is greater than 1C per M depth
What are the 3 layers of thermal stratification?
epilimnion (warm)
Metalimion
hypolimion (cold)
What are dimictic and polymictic lakes?
Dimicic lakes turnover x2 per year (spring, fall)
bigger + deeper lakes will turn over later into the fall
Polymicitic: water turns over often (like when the wind blows)
Why are there not a lot of plankton in dystrophic lakes?
There is not enough calcium in dystrophic lakes to support plankton bone structures. The acidic-ness of the lake is also due to the lake of mineral balancing.
What physical factors affect fish distribution?
temperature
turbidity (water purity)
What are the zones of a lake?
littoral zone
edge of a lake
submergent vegetation
rooted plants (production from rooted plants and attached algae), light penetration to bottom, zone of production
Ex. walleye
Limnetic zone
upper zone of the lake
considerable light penetration
above thermocline, photic zone, phytoplankton production, zooplankton primary consumers, schooling baitfish (alewife, shiners), zone of production
Profundal zone
lower zone of the lake
moderate light penetration
below photic zone, below compensation depth, zone of consumption, oxygen depletion
Ex. lake trout, brown trout, smelt, lake whitefish
Benthic zone
bottom of the lake (mud)
ex. white sucker, brown bullhead, sculpins
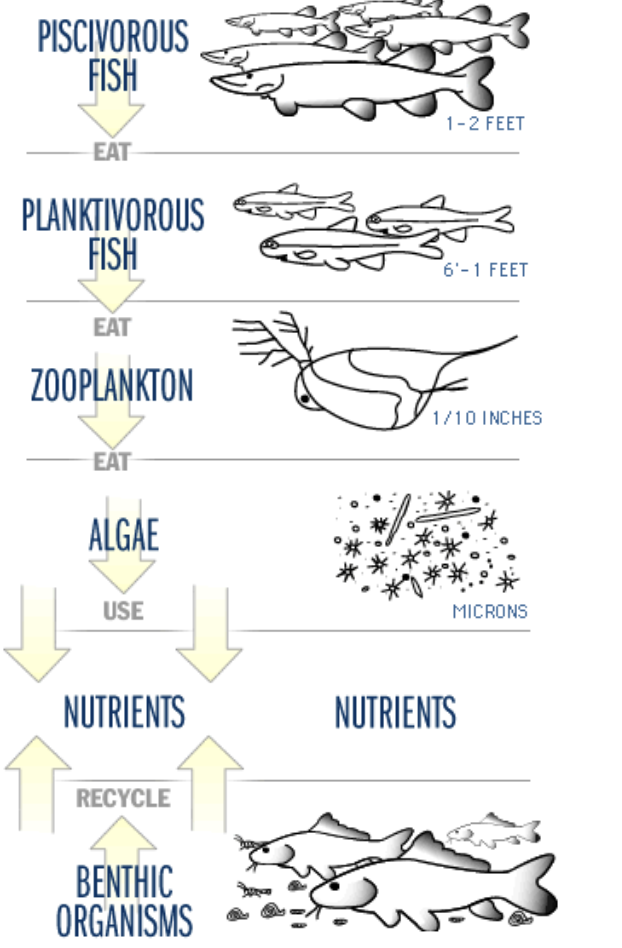
What is the nutrient/element cycle in lakes?
elements flow from abiotic to biotic to abiotic
element cycles are balanced (however recent technology and practices disrupt them
piscivorous fish eat planktivorous fish which eat zooplankton which eat algae which use nutrients from recycled benthic organisms
What percent of energy from food becomes work or biomass?
10%
How do trophic levels work in aquatic systems?
usually at least 5 steps:
sun —> phytoplankton —> zooplankton —> smelt —→ salmon —→ man
in order for us to gain 1lb from eating salmon the lake needs to produce 5 tons of phytoplankton (assuming 10 fold loss of energy at each level
Define biomass and standing crop biomass
Biomass: weight of organic matter per unit area, usually refers to organisms, population or community
Standing crop biomass: weight of living material at a given place at a given time
Define production and primary production
production: energy (biomass) storage per unit time
primary production: energy (biomass) stored by plants per unit time. Depends of availability of nutrients and limitations on the physical/chemical environment
Define growth
Growth results from the accumulation of biomass
Define herbivorous food chain and detrital food chain
Herbivrous food chain: living plants —> herbivores (primary consumers) —> carnivores (secondary consumer) —> carnivore —→ top carnivore
Detrital food chain: plant material —> detritivore (primary consumer) —> carnivore (secondary consumer eats animals) —> carnivore —> top carnivore
What is the primary energy source in most aquatic ecosystems?
Typically light (but can also be chemical energy)
most aquatic ecosystems capture 13% of the light available. Can store 19% of available light energy under optimal conditions
what is the lowest level of ecological colonization?
organism
What are the abiotic components of an ecosystem? What are the biotic components?
Abiotic:
physical (temp, light, water, depth, current, etc.).
Chemical (ph, oxygen, alkalinity, hardness, etc.
Biotic:
populations of plants, animals, microorganisms that form the communities of the ecosystem
Does warm or cold water have more oxygen?
cold water
Why are fish distributed differently in lakes?
physical properties of water, temp, watershed characteristics and water chemistry
biological factors: predation, food availability, habitat preferences
How does oxygen get into the water?
diffusion from atmospheric
**cannot happen if there is ice on top (neither air nor sunlight can get in
this is why ponds in NY need to be 8-10 ft deep minimum for there to be enough oxygen storage for the winter
photosynthetic activity
storage (limited)
Define stratification
Stratification is layered water temps
What drives fall and spring turnover?
Fall turnover: density driven
Spring turnover: not density driven
Which is more dense? salt or fresh water?
salt water is more dense than freshwater
What is a chemocline?
Chemocline is perminatly stratified, never touches the atmosphere
What is a meromictic lake?
What is a anthropogenic miromicic lake?
laeyers of both fresh and salt water (from hitting salt mines in ground, tidal waves, etc.
permanently stratified
Antropogenic mirocmictic lake: human caused (ex. by salting the roads)
How does light and temperature affect veritical zonation?
a lake may look blue as that is the last wave length to get back to you, as that wavelength goes the deepest
What is the photoic and aphonic zone? What is in the middle?
Photoic zone: production zone
compensation depth (repiration + photosynthesis even out)
Aphotic zone: needs to get its resources imported from above
What is the neuston? Why is it important?
Top 6” of water (most productive: has energy, light, nutrients, diffusion from atmosphere, etc.)
How does leaf size change as you get deeper into the littoral zone?
The deeper you get, the smaller the leaves as plants cannot do photosynthesis
What are the top down and bottom up watershed management practices?
Bottom up: restricting nutrients by controlling the water shed (farm run off, etc.)
Top down: manage the nutrients in the system (plankton, forage fish —> deciding where you want the nutrients)
What are piviscorous fish?
Fish that eat other fish
What does plankton antenna tell us about their lifestyle?
Short antenna: less open water
Long antenna: open water (over 2/3 of their body)
What predation style does clear water use?
Top down
What is the primary energy source for aquatic ecosystems?
The sun (then thermovent)
What is biochemical cycling?
How nutrients move back and forth with the biological and physical world
What is aqua shade?
Aqua shade is a chemical that makes ponds look blue/green, which can shade it to control their environment
What does seishe mean?
thermocline rocks back and forth on a node (this can be caused by prolong wind as wind puts density on the water)