Pharmacokinetics Metabolism and Excretion - 2
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
The drug metabolising capacity of the body, especially the liver, is subject to?
Fluctuations in Activity
Environmental factors (drugs, natural products and chemicals) can modify the?
The Basal Rate of Drug Metabolizing Enzymes
Many compounds can increase the enzyme activity of the ……. When administered…..?
Cytochrome P450 monoxidase system
When Administered Quickly
Enzyme induction is an?
Adaptive increase in enzyme metabolising capacity (dynamic)
as a result of repeated or prolonged exposure to an inducing agent over several days
Enzyme induction effects are generally….?
Reversible
Enzyme induction is one of the causes of?
Drug Interactions
Drugs can act as inducing?
Inducing Agents
and can increase the activity of Cytochrome P450 enzymes when administered repeatedly
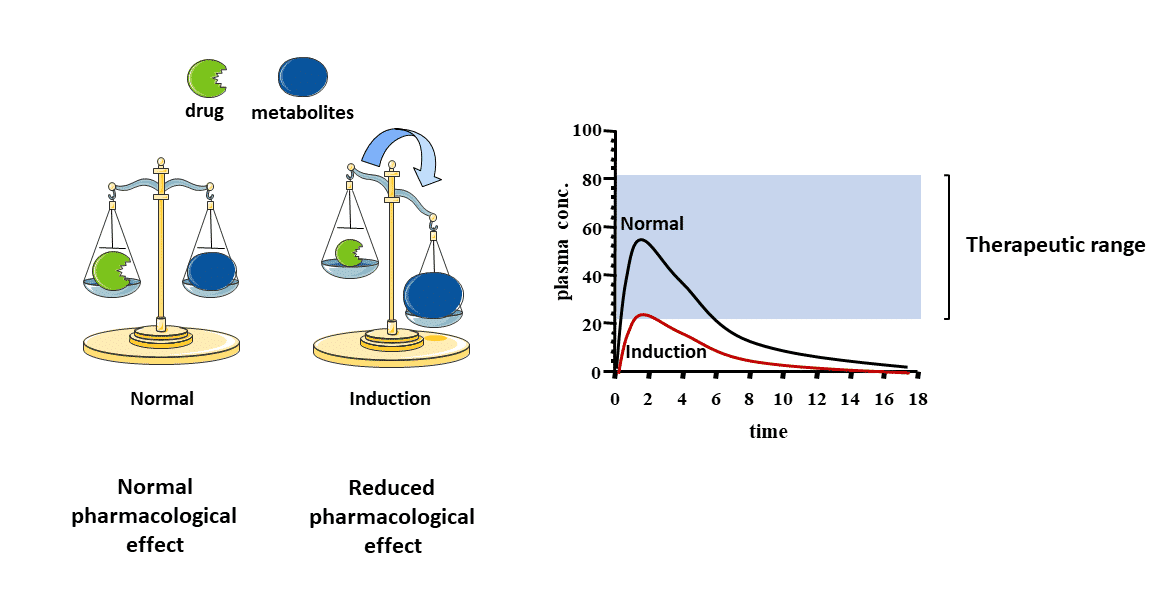
Enzyme induction increases metabolism of all?
Substrates of Enzymes
Enzyme induction increases metabolism of all substrates of the enzyme. As a result, drugs that are substrates for the induced enzyme?
Will be metabolized faster
Reduced Drug Action
Loss of Efficacy
Following enzyme induction, drugs will be?
Metabolized faster
Increased Drug Clearance
reduced drug plasma levels
shorter drug action.
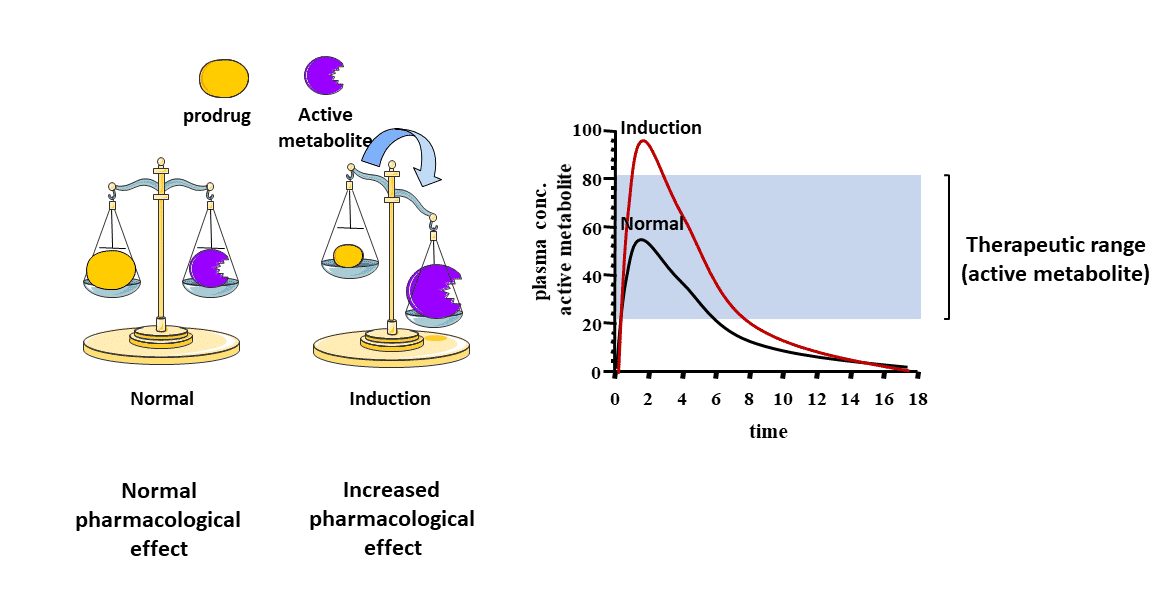
After Enzyme Induction Prodrugs will be metabolised faster too and form more?
Active Metabolize
Thus providing Longer drug action and increased efficacy.
Carbamazepine, an inducer of?
Hepatic microsomal enzymes
Carbamazepine can accelerate ?
the metabolism of the other drugs
such as oral contraceptives, warfarin and corticosteroids,
leading to loss of therapeutic efficacy.
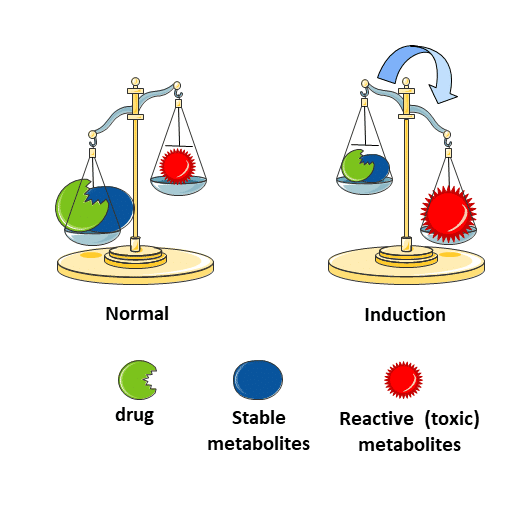
Enzyme induction can also increase drug toxicity in cases where metabolites formed by?
Phase 1 Reactions are More toxic than the parent compound
The susceptibility to paracetamol-induced liver toxicity is increased in?
People who consume Alcohol regularly
Regular alcohol consumption induces the….?
cytochrome P450 enzyme
responsible for the formation of the reactive (toxic) metabolite of
paracetamol ,
N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine
Drug metabolism can be affected by compounds that inhibit?
P450 Enzyme Activity.
Enzyme inhibition generally has a?
Prompt onset,
Within hours
Enzyme inhibition can occur by competition of?
2 or more drugs for the same binding site.
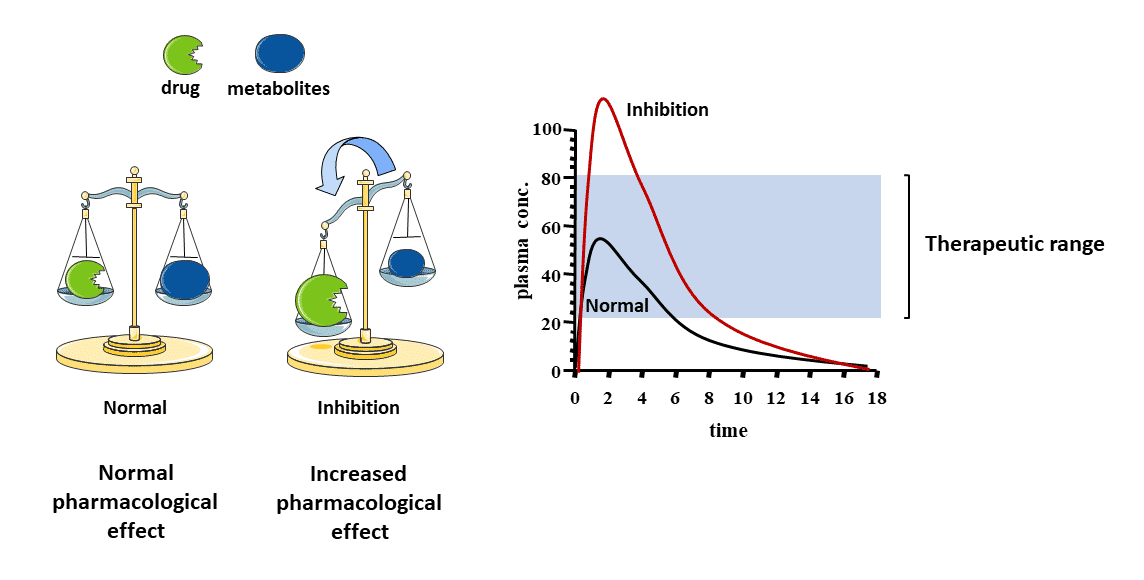
Enzyme Inhibition decreases metabolism of drug substrates by the…. and results in….?
the enzyme and results in
reduced drug clearance,
elevated drug plasma levels and prolonged drug action.
drug plasma levels to rise above the upper limit of the therapeutic range, which may result in an?
Augmented Biological Response
and Adverse Effects
drugs that are substrates for the inhibited enzyme will be metabolised slower and will have?
Metabolized Slower
Elevated drug plasma levels
Prolonged Drug Action
Following Enzyme Inhibition, Prodrugs will be?
Metabolised Slower
Produce Less active Metabolites
prodrugs will have an decreased drug action and efficacy following enzyme
Enzyme inhibition can be protective if the metabolite is?
More toxic than the parent compound.
Methanol and ethylene glycol are metabolised to reactive (toxic) products by the enzyme?
alcohol dehydrogenase
In general, drugs are metabolized more slowly in?
Neonatal and Elderly Humans
Why are Drugs metabolized more slowly in babies?
This is due to slower Phase 1 and 2 reactions in the first two weeks after birth
Why are Drugs metabolized more slowly in Elderly?
fall-off in liver metabolism of drugs in the elderly
there are higher rates of oxidation of oestrogens and benzodiazepines in?
Women compared to Men
Pharmacogenetic variations contribute to the individual response to?
Drugs and could cause unwanted or adverse drug reactions or toxicity.
In poor metabolisers, drugs will be?
Metabolized more slowly.
Their drug plasma levels will be elevated and there will be an increase in drug action and efficacy
poor metabolizers, prodrugs will be?
Metabolized slower
Produce less active Metabolites.
Succinylcholine (suxamethonium) is a?
Rapid Acting Muscle Relaxant.
Usually lasts 2-6 Minutes
The kidneys are the most significant site?
For Excretion
While lipophilic drugs are filtered just as?
hydrophilic drugs
hydrophilic compounds will remain in the?
Filtrate
he kidneys receive approximately one-…?
1/5 of Cardiac Output
the normal rate of plasma filtration in the glomeruli is?
125 mL per minute.
The glomerular filtration rate declines with?
Normal Aging
usually beginning around the age of 30 at a rate of 8% per decade
Other routes of drug elimination include excretion into the?
Bile (For Larger Compounds).
and via the lungs (for volatile compounds).
About 5% of alcohol is excreted by?
Exhalation