Quiz 2 - chapters 2 (p2) CHEMISTRY HALF
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
Organic molecules are _ based
Carbon
Organic molecules are produced by _
Living things
Carbon is _
Covalent
Carbon can participate in up to _ covalent bonds
4
______ allow formation of large molecules with other atoms
Organic molecules
Carbon covalent bonds can form what 3 chains/structures?
Straight, branched, ring
A chain of carbons with hydrogens bound is called the _
Carbon skeleton
What does the bonding of carbon and hydrogen with other elements form?
Functional groups
What has most of the chemical and physical properties of a particular organic molecule?
Functional groups
Small organic molecules can be formed into _
Macromolecules
Macromolecules are made by dehydration synthesis of ____ into ______
Monomers, polymers
Bonding occurs by removing ___ from one molecule, ___ from the other, and _ is formed
H+, OH-, water
Linkage of multiple monomers forms _
Polymers
What are the 3 types of water based solutions?
Solution, colloid, suspension
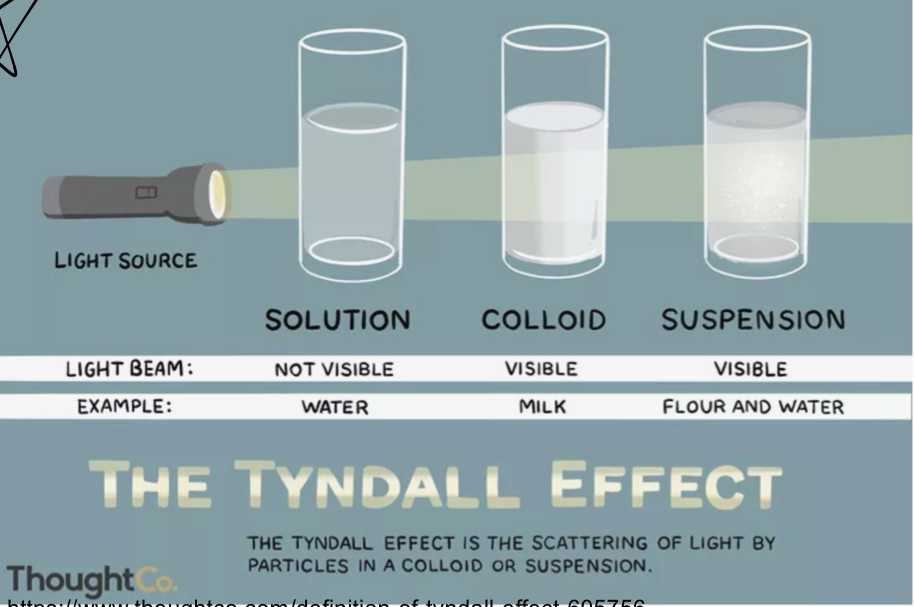
What is a solution?
Uniform mixture
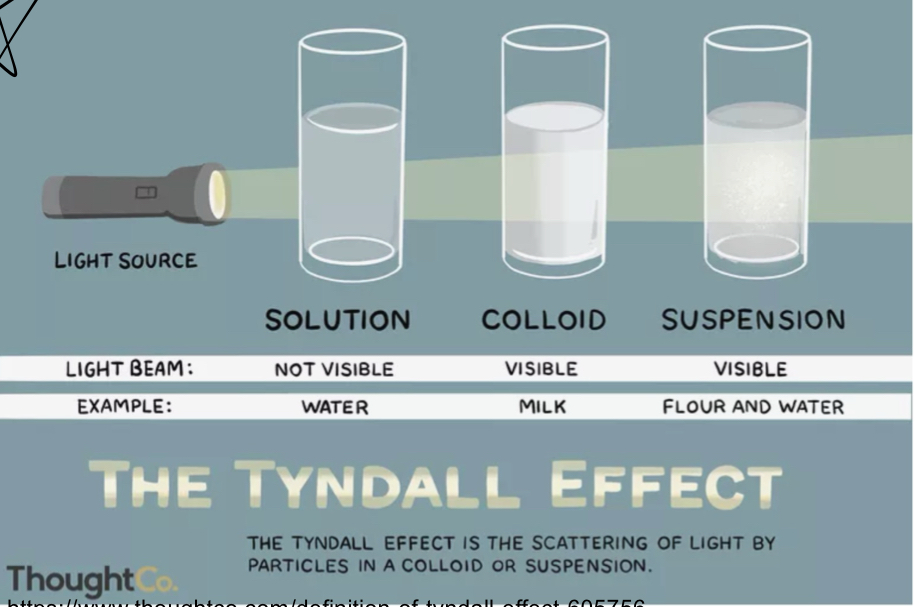
What is a colloid?
contains proteins / large solutes
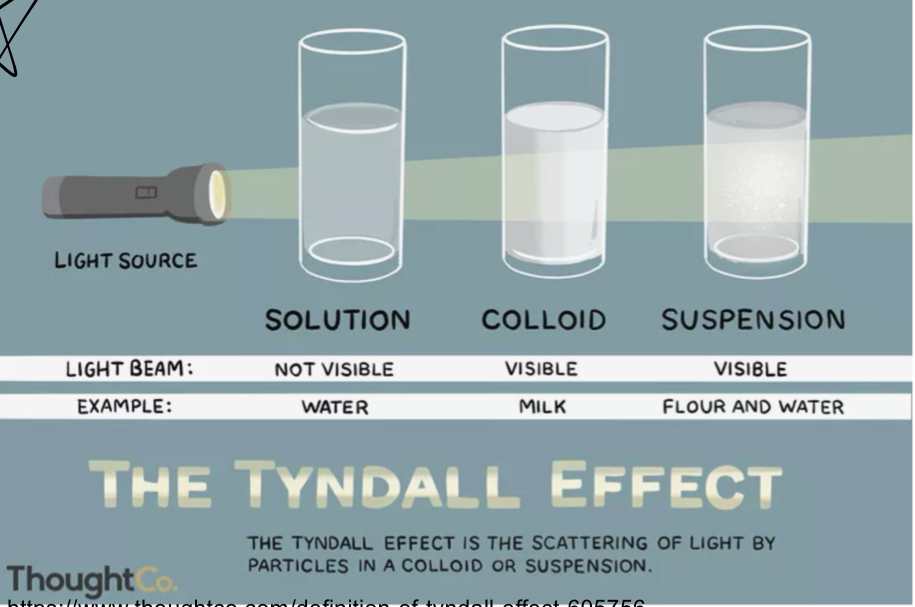
What is a suspension solution?
has large particles that settle out
Carbohydrates are _ +_
Sugars, starches
Carbohydrates are composed of __ in a __ ratio in monomer form
C:H:O, 1:2:1
Carbohydrates are used for ___, ___, ___
Energy, RNA/DNA, amino acids
A monosaccharide is a ___, ex: _____
Simple sugar, glucose
What is the most important human fuel?
Glucose
An _____ has same formula, shape
isomer
A disaccharide is 2 covalently bonded _______. ex: ______
Monosaccharides, sucrose
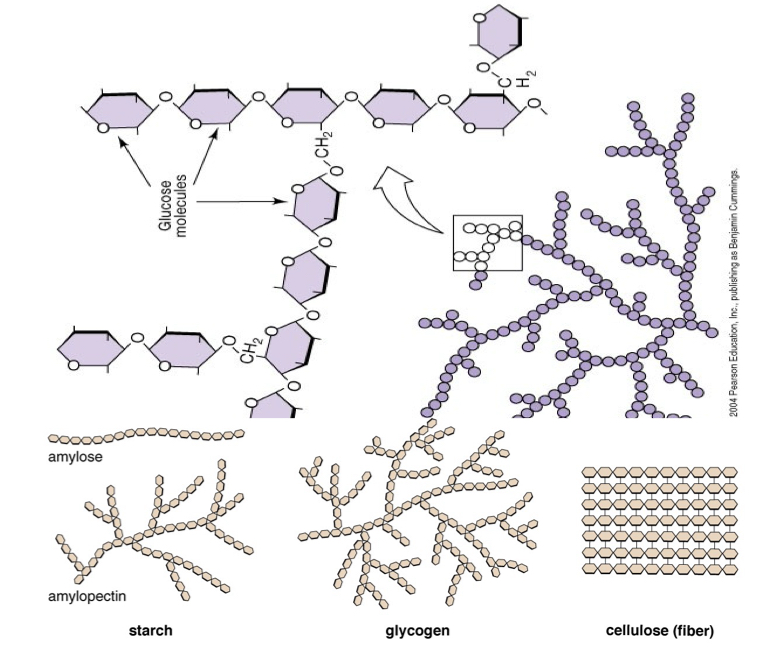
A polysaccharide is 3 or more covalently bonded _____. ex: ______
Monosaccharides, glycogen
Lipids are ____, _____, _____
Fats, oils, waxes
Lipids are polar or nonpolar?
Nonpolar
Simple lipids are composed of _____
CHO
What are the functions of a lipid? (hint there are 3)
Energy storage , make cell membranes, cell communication
Fatty acids are made from a _____ chain with ______ group
Hydrocarbon, carboxyl
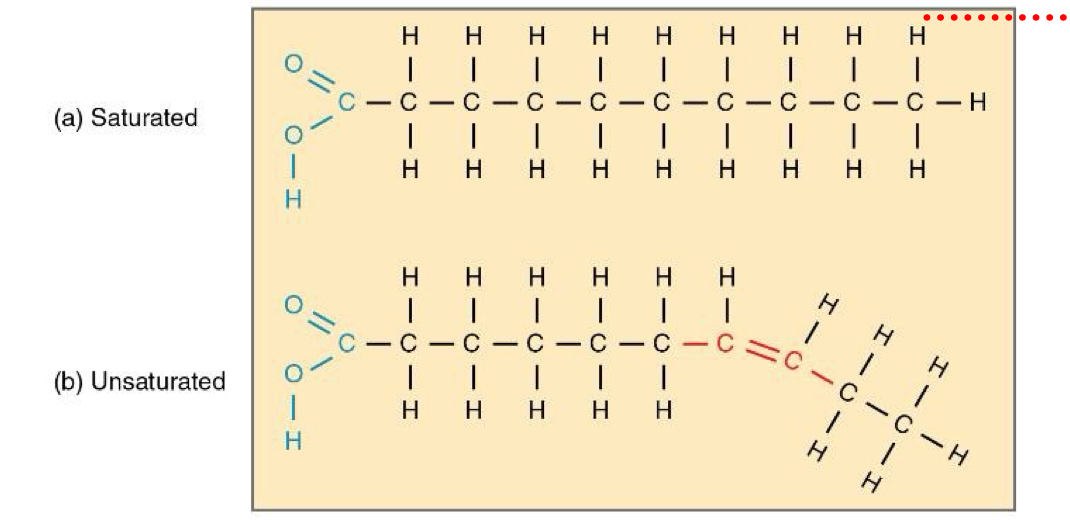
A fatty acid chain that has all single covalent bonds on the c's is _
Saturated
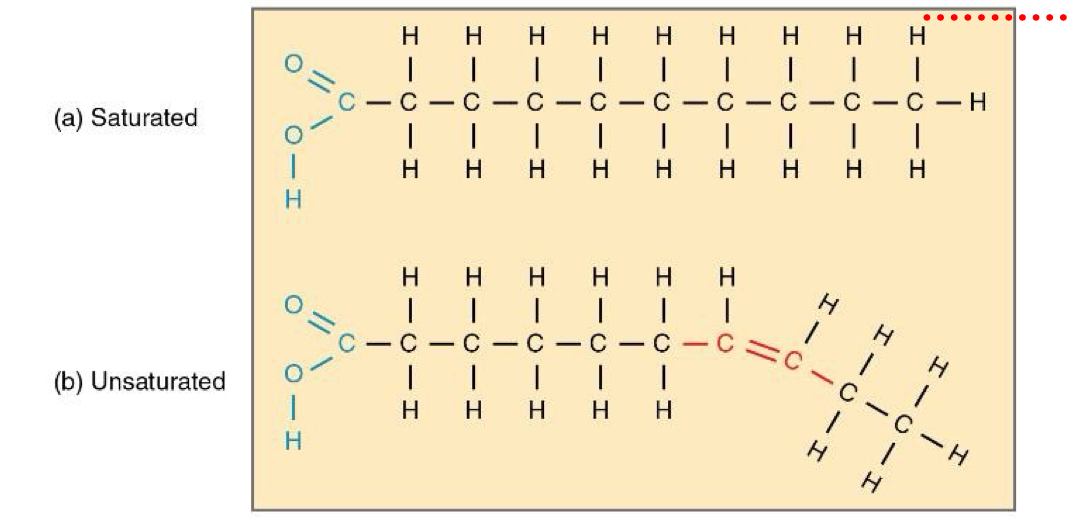
A fatty acid chain that has one or more double covalent bonds between Cs is -
Unsaturated
______ are derived from arachidonic acid which is a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid
Eicosanoids
What is the function of a eicosanoid?
Cellular communication
What are the 2 types of eicosanoids?
Leukotrienes and prostaglandins
Leckotrienes are used by cells to _
Signal injury
Prostaglandins are used for cell-to-cell ____ to coordinate events
Signaling
glycerides are ____ and ____
Glycerol, fatty acids
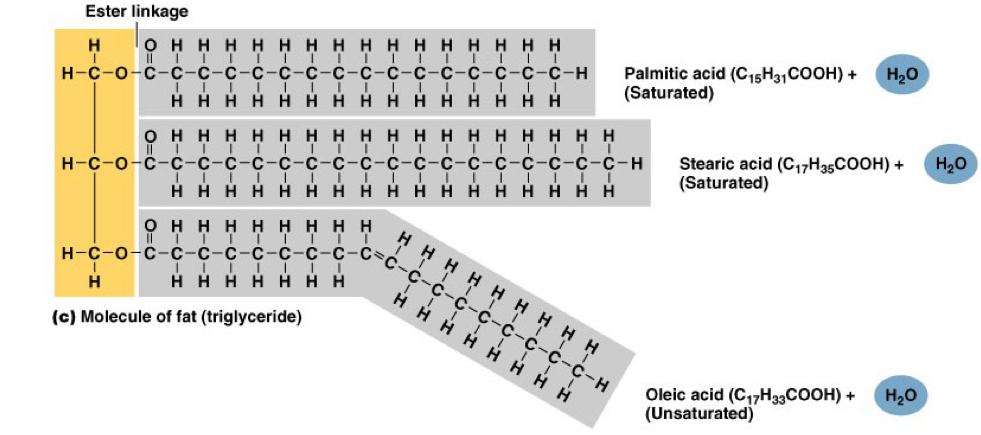
_____ make up fat deposits that are important for Energy storage, insulation, mechanical protection
Triglycerides
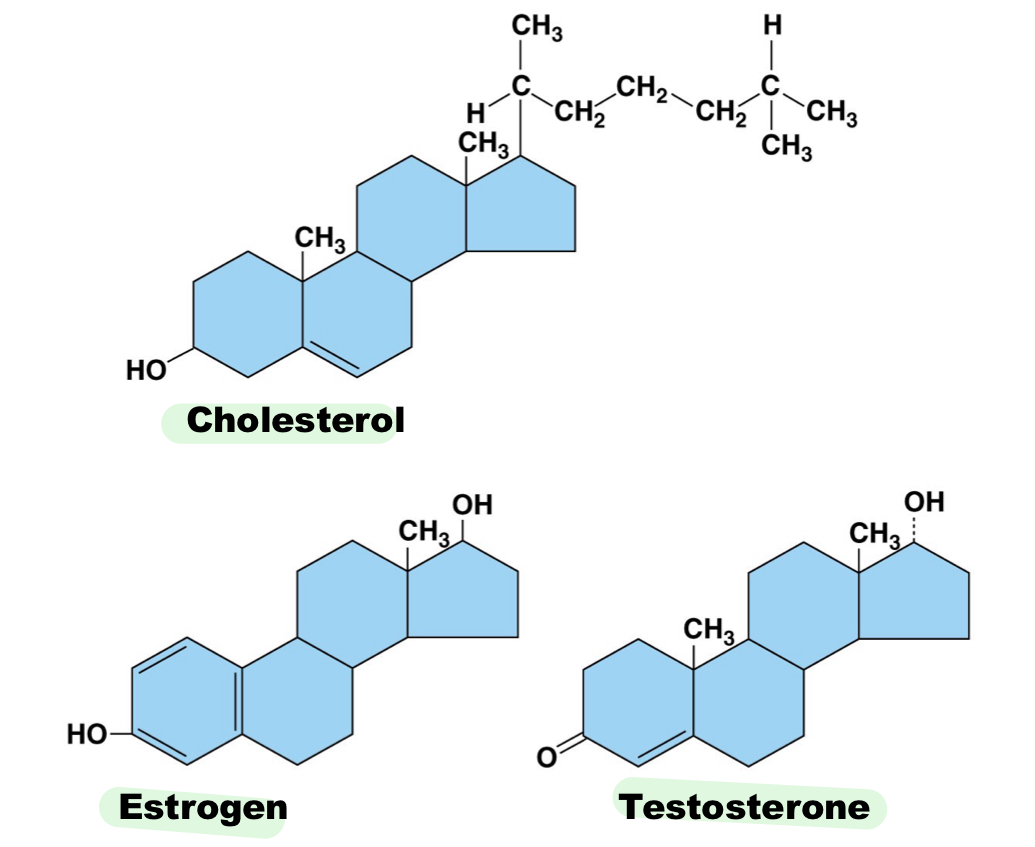
Steroids structures involve ____ carbon rings. ex: ___
4, cholesterol
Diglyceride + phosphate group + nonlipid group = _____
Phospholipid
diglyceride + carbohydrate = ______
glycolipid
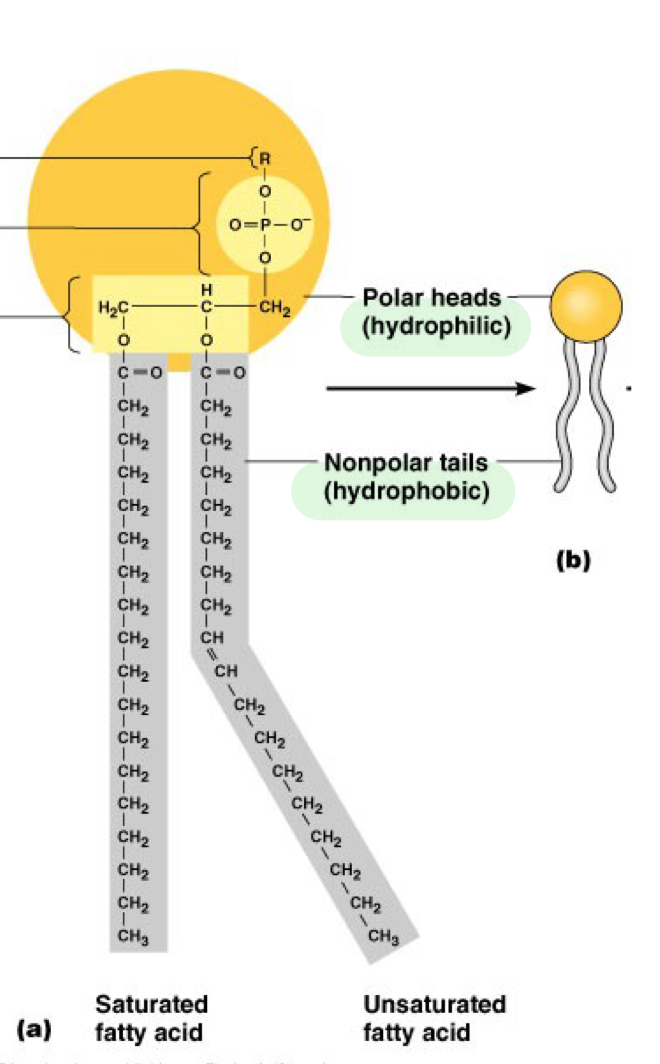
Hydrophilic head _____ with water
mixes
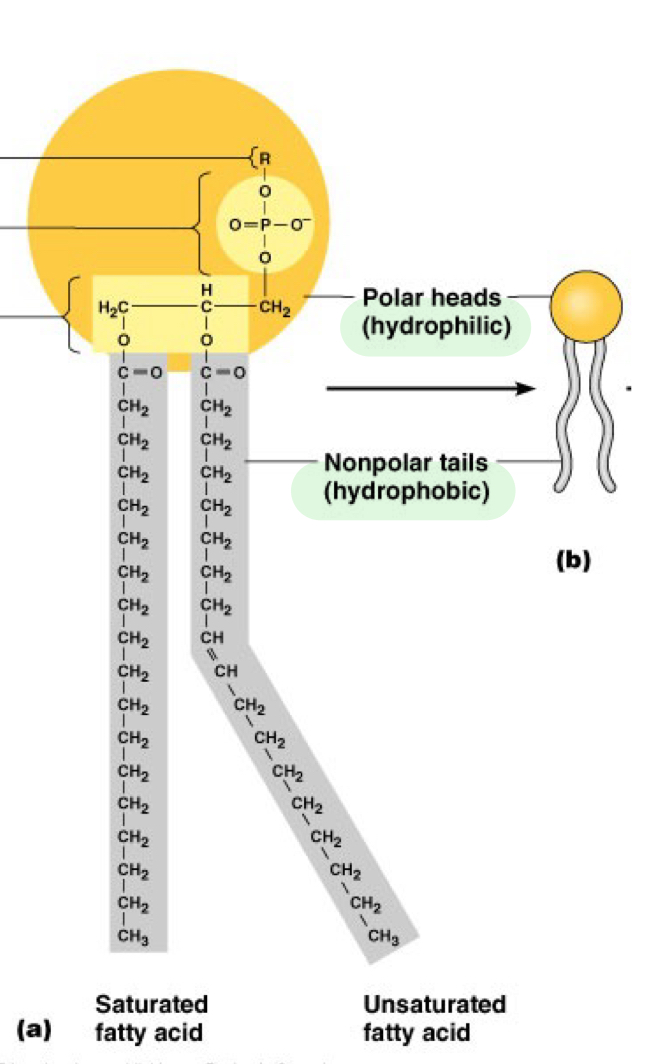
Hydrophobic tail _ water
Avoids
Hydrophilic =
Polar
Hydrophobic =
Nonpolar
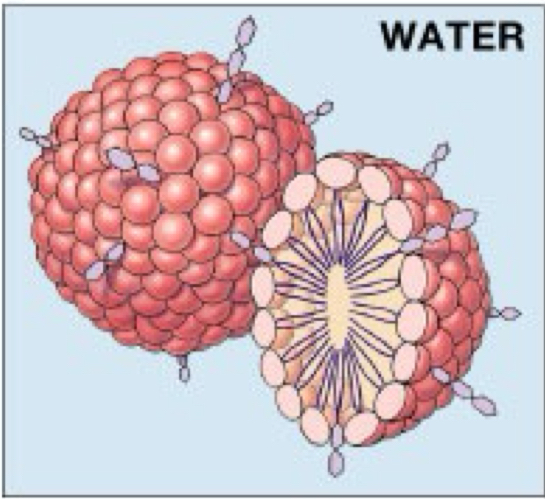
A _____ is a sphere formed with hydrophilic heads oriented out and hydrophobic tails pointed in
micelle
What is the most abundant organic molecule in cells?
Proteins
What elements are proteins composed of?
CHON
proteins are essential for cell ____ and _____
structure, function
what are proteins that support called?
structural proteins
proteins are formed from ____
amino acids
amino acids are the building blocks of ______
monomers
what are proteins that enable movement in muscle called?
contractile proteins
where are the transport proteins located?
in blood
_______ regulate pH of body fluids
buffer proteins
what are the proteins that coordinate and control called?
hormones
_______ help with keratin in skin, antibodies, clotting
defense proteins
_______ enable metabolic activity and regulation
enzymes
______ are formed from long strings of peptide bonded amino acids
proteins
a chain of peptide bonded amino acids = ____
polypeptide
_____ fold into proteins
polypeptides
what are the 2 characteristics of a proteins primary structure ?
linear, unique sequence
what are the 3 characteristics of a proteins secondary structure ?
twisting / folding, can create alpha helix or beta sheet, H bonds
what are the 2 characteristics of a proteins tertiary structure ?
global folding, interactions in R groups
if a protein consists of one single polypeptide it will be complete at which stage
tertiary
what are the characteristics of a proteins quaternary structure ?
fusion of multiple polypeptides
_______ results in the native conformation which is a functional protein
proper folding and fusion
what are the 2 possible shapes of a completed protein?
globular, fibrous
what are the 3 characteristics of a globular protein?
compact, round, soluble
what are the 2 characteristics of a fibrous protein?
strands, non-soluble
what is protein denaturing?
loss of shape and function
what are the most abundant proteins in the body?
enzymes
enzymes act as a biological ____ used for metabolism
catalyst
enzymes speed up reactions by _____
lowering activation energy
what is enzyme specificity?
substrate must fit specific enzymes active site
adding more substrate will ____ reaction rate until saturation
increase
at saturation the active site is always ___ and reactions cannot progress
full
what can turn an enzyme on or off?
cofactor
cofactors provide short term control over _____
reaction rates
what is a cofactor?
activates enzyme
a coenzyme is a non-protein organic molecule that acts as a ____
cofactor
proper active site shape depends on correctly folded ____
protein enzyme
metabolism is _____
essential for life
a ________ protein is a protein bound to other organic molecules
conjugated
what is a glycoprotein?
small carb + large protein
what is a proteoglycan?
large polysaccharide + polypeptide
nucleic acids are composed of what 5 elements?
CHONP
what do nucleic acids do?
store and process info
what are the 2 types of nucleic acid?
DNA, RNA
what does DNA do
store info
what does RNA do
protein synthesis
nucleic acids are composed of _____
nucleotides
what are the 3 parts of a nucleotide?
pentose sugar, phosphate group, nitrogen base
what are the 2 types of nitrogenous bases?
purines, pyrimidines
what do purines (single ring) contain?
adenine, guanine
what do pyrimidines (double ring) contain?
cytosine, thymine, uracil
what is the shape of RNA?
single strand, linear
what are the bases of RNA?
AUGC
what does mRNA do?
messenger