VHS Honors Biology Unit #4 (Photosynthesis) Review
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Define adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
an organic molecule that acts as the main energy source for cell processes
What is ATP composed of?
ATP is made of a sugar called ribose, a nitrogen-containing compound called adenine, and 3 phosphate molecules
How is energy released from ATP?
Energy is released from ATP during hydrolysis, which breaks covalent bonds between the phosphates.
Which molecule contains the medium amount of energy (ADP, AMP, or ATP)?
ADP
What is a redox reaction?
It is a reaction in which electrons are transferred between atoms.
Define oxidation.
a reactant loses one or more electrons becoming more positive in charge.
Define reduction.
a reactant gains one or more electrons becoming more negative in charge
In the photosynthesis equation, what is oxidized? What is it oxidized into?
water; oxygen
In the photosynthesis equation, what is reduced? What is it reduced into?
carbon dioxide; glucose
Where do almost all organisms get their energy?
the sun
Define autotroph.
an organism that uses energy from sunlight (or from chemical bonds in inorganic substances) to make organic compounds.
Which groups of organisms are autotrophs?
plants, some algae/protists, and some bacteria
What is a heterotroph?
organisms that must get energy from food
Which groups of organisms are heterotrophs?
animals, fungi, and some protists
What is the (simplified) equation for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H2O ----> C6H12O6 + 6O2
What is the (simplified) equation for cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 ----> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
How is photosynthesis related to cellular respiration?
The ending products of photosynthesis (glucose and oxygen) are the starting products of cellular respiration.
How is cellular respiration related to photosynthesis?
The ending products of cellular respiration (carbon dioxide and water) are the starting products of photosynthesis.
What are the two stages of photosynthesis?
the light reactions and the Calvin cycle
What is the function of a chloroplast?
to perform photosynthesis in eukaryotes
Which organisms have chloroplasts?
all plants and some algae
What are thylakoids?
a. flattened sacs inside second membrane of a chloroplast
b. the thylakoid membrane is where the light reactions occur
What are grand?
stacks of thylakoids
What is stroma?
a. the liquid inside a chloroplast that surrounds the grana
b. the location where the Calvin cycle occurs
c. where the chloroplasts DNA and ribosomes are located
What is chlorophyll?
a type of pigment located in the membrane of the thylakoids
Which pigment is directly involved in the light reactions?
chlorophyll a
What is chlorophyll b?
an accessory (extra) pigment that absorbs more blue light and less red light than chlorophyll a
What color of the rainbow does chlorophyll a absorb best?
blue light
What color of the rainbow does chlorophyll a absorb second best?
red light
What are carotenoids?
yellow, orange, and brown pigments that absorb different wavelengths of light
What is a photosystem?
a cluster of chlorophyll and other pigment molecules that harvest light energy
Name the photosystems.
a. photosystem I
b. photosystem II
Where are the photosystems located?
in the thylakoid membranes
Describe step 1 of the light reactions.
1. Energy from the sun (light) is absorbed by a chlorophyll molecule.
2. That energy is passed from one chlorophyll molecule to another until it reaches the double chlorophyll molecule.
3. That energy is given to one electron in the double chlorophyll molecule.
Describe step 2 of the light reactions.
1. The energized electron absorbs the energy from the sun and is moved to a higher energy level (the electron gets all hyper).
Is the double chlorophyll molecule oxidized or reduced?
oxidized
Is the primary electron acceptor oxidized or reduced?
reduced
Describe step 3 of the light reactions.
1. The excited electron leaves photosystem II and enters the electron transport chain (ETC).
2. As the electron passes down the ETC, it loses energy.
3. The electron enters the double chlorophyll molecule of photosystem I.
electron transport chain (ETC)
1. a series of proteins located between photosystem II and photosystem I, allowing the passage of electrons between the two photosystems
2. the electron loses its energy (that came from light)
What happens the the energy given up by the electrons as they move through the ETC?
it is used to move the H+ from the stroma into the thylakoid
Describe step 4 of the light reactions.
1. light is absorbed in Photosystem I (this occurs at the same time that light is absorbed in Photosystem II)
2. The light energy is transferred an electron in the double chlorophyll molecule.
3. That electron moves to a higher energy level (the electron gets all hyper), leaves photosystem I, and enters an ETC.
4. NADP+ is an electron acceptor ("taxi") and it accepts electrons from photosystem I, reducing it into NADPH (it also picks up a hydrogen ion).
NADP+ + 2 electrons + 1 hydrogen ion = NADPH
What happens to NADPH after is picks up 2 electrons and 1 hydrogen ion?
It takes its "passengers" (2 electrons and 1 hydrogen ion) to the Calvin cycle.
How do the electrons get replaced in photosystem I?
Electrons from chlorophyll a molecules in Photosystem II replace the electrons that leave chlorophyll a molecules in Photosystem I.
How do the electrons get replaced in photosystem II?
The replacement electrons for Photosystem II are from water molecules.
During photosynthesis, what happens to the oxygen in water molecules?
The oxygen in water is a waste and not used during photosynthesis.
What is chemiosmosis?
The process in which the movement of H+ down their concentration gradient across the thylakoid membrane is coupled to the production of ATP.
When does chemiosmosis occur during photosynthesis?
during the light reactions
Where does the chloroplast get H+ in order to perform chemiosmosis?
1. the breakdown of water produces H+
2. the energy produced by the first ETC (between Photosystems II and I) is used to actively pump H+ from the stroma inside the thylakoid
What purpose do the H+ serve during the light reactions?
1. the H+ diffuse through ATP synthase, which phosphorylates ADP into ATP
2. the H+ are picks dup by NADP+ and transported to the Calvin cycle where they will be added to 3-PGA and convert it into G3P
Name 4 things proceeded/created during the light reactions.
1. ATP
2. electrons (carried by NADPH)
3. hydrogen ions (carried by NADPH)
4. oxygen
Which three things are produced during the light reactions and used during the Calvin cycle?
1. ATP
2. electrons (carried by NADPH)
3. hydrogen ions (carried by NADPH)
What waste product is produced during the light reactions?
oxygen
What does water contribute to the light reactions?
1. It replaces electrons from photosystem II (and ultimately from photosystem I).
2. It supplies H+ to make sure that chemiosmosis occurs.
3. It supplies H+, some of which will be taken by HNADP to the Calvin cycle to help make G3P (glucose).
During what part of photosynthesis is light required?
the light reactions
What is carbon fixation?
the bonding of CO2 to an organic compound
When does carbon fixation occur during photosynthesis?
1. during the Calvin cycle
2. it occurs when CO2 is bonded to RuBP.
What enzyme performs carbon fixation during photosynthesis>?
rubisco
Where does the Calvin cycle occur?
in the stroma of a chloroplast
Describe step 1 of the Calvin cycle.
1. an enzyme called rubisco bonds CO2 to RuBP
2. RuBP is converted into 3-PGA
Describe step 2 of the Calvin cycle.
1. NADPH (electrons and H+) (from the light reactions) and ATP (from the light reactions) are combined with 3-PGA to produce G3P
Describe step 3 of the Calvin cycle.
about 20% of the G3P is used to make organic compounds
Describe step 4 of the Calvin cycle.
about 80% of the G3P is converted back into RuBP so that the Calvin cycle may continue
What is a C3 plant?
1. plants that fix carbon exclusively through the Calvin cycle
2. they do NOT store CO2 is other molecules (like C4 plants and CAM plants).
What does the plant do with glucose?
1. Some glucose is used to perform cellular respiration (produce energy, or ATP).
b. Most glucose is NOT immediately used and is stored as starch.
c. Some glucose is also used to make cellulose (cell wall of plant cells).
d. Some glucose is used to make other organic molecules, like proteins, lipids, or nucleic acids.
What are stomata?
1. Stomata are small pores usually located on the bottom of leaves from which plants lose water when they are open.
2. Stomata are responsible for allowing CO2 into the plant and O2 out of the plant during photosynthesis.
What gases pass through stomata for photosynthesis?
1. Carbon dioxide moves into the plant through stomata.
2. Oxygen moves out of the plant through stomata.
3. Water also moves out of the plant through stomata.
What happens to the gases levels when stomata are closed?
CO2 levels decrease and O2 levels increase inside the plant.
What is a C4 plant?
A plant that keeps its stomata partially closed during the hottest part of the day so that it doesn't;t lose as much water.
How many cells do C4 plants use to perform photosynthesis?
a. 2 cells
b. a smaller cell (mesophyll cell) to absorb (let in) CO2 and a special enzyme fixes the CO2 into a four-carbon compound
c. a larger cell (bundle sheath cell) to perform the Calvin cycle
Name two C4 plants.
1. corn
2. sugar cane,
Name two CAM plants.
1. cacti
2. pineapple
Describe CAM plants.
plants that open their stomata at night when it's cooler and close them during the day when it's hotter
What do CAM plants do at night?
they take in CO2 and fix it into a variety of organic compounds
What do CAM plants do during the day?
the CO2 is released from these compounds and enters the Calvin cycle
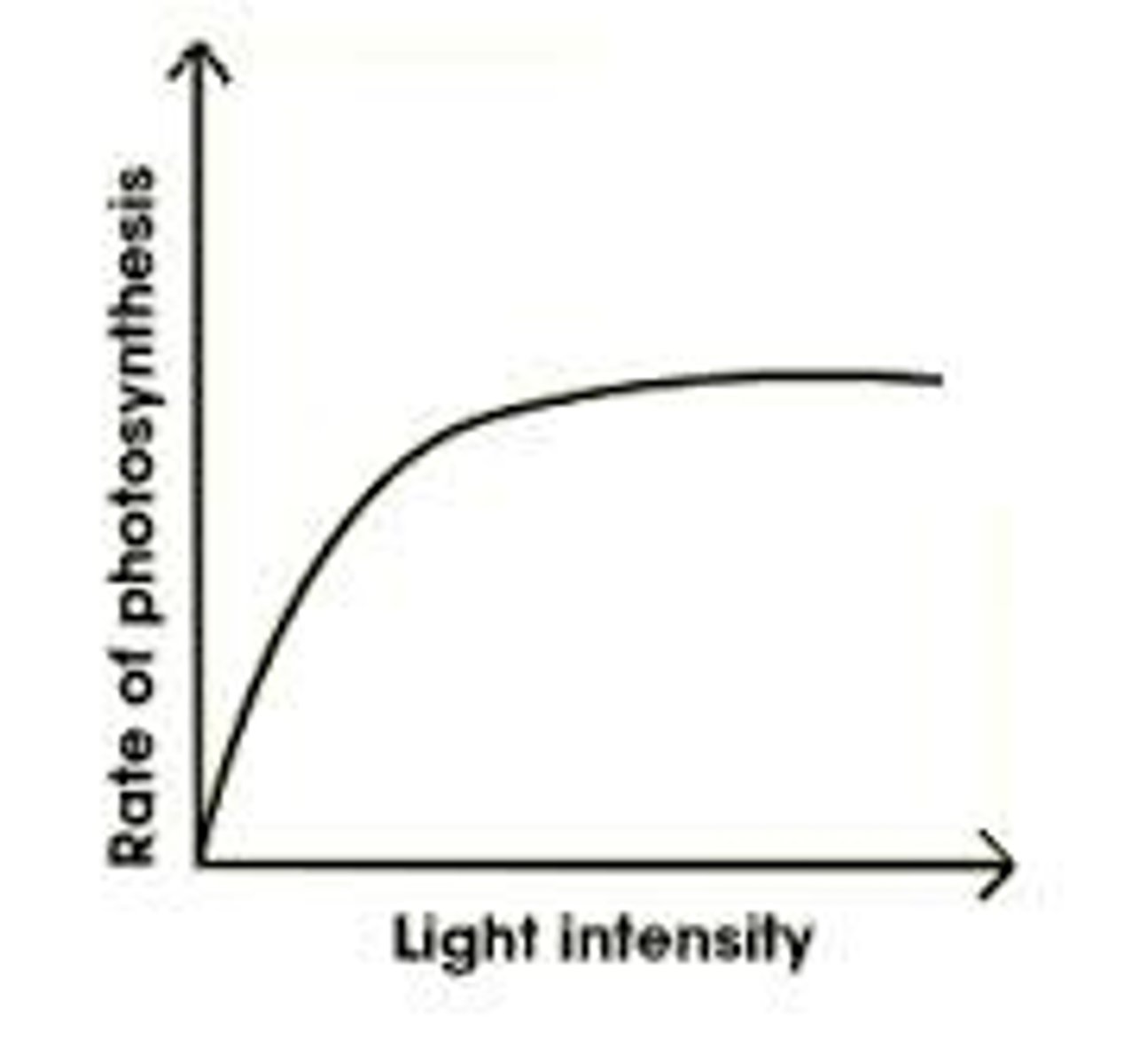
Describe how light intensity affects photosynthesis.
the rate of photosynthesis increases with light intensity and then levels off at the peak
Describe how carbon dioxide levels affects photosynthesis.
the rate of photosynthesis increases with carbon dioxide levels and then levels off at a peak
Describe how temperature affects photosynthesis.
the rate of photosynthesis increases until the temperature reaches its optimal and then begins to decrease as the enzymes are denatured at high temperatures
In order for autotrophs to make glucose (C6H12O6) they need to get carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). Where do they get their carbon?
carbon dioxide
In order for autotrophs to make glucose (C6H12O6) they need to get carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). Where do they get their oxygen?
carbon dioxide
In order for autotrophs to make glucose (C6H12O6) they need to get carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). Where do they get their hydrogen?
water