[FUNACC] Chapter 2 | ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLES AND REPORTING STANDARDS
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Accounting
measures and communicates the economic activities of organizations. Used by businesses, governments, universities, airports, airlines. All organizations need similar financial information to make decisions. Enables evaluation of profitability, liquidity, and solvency
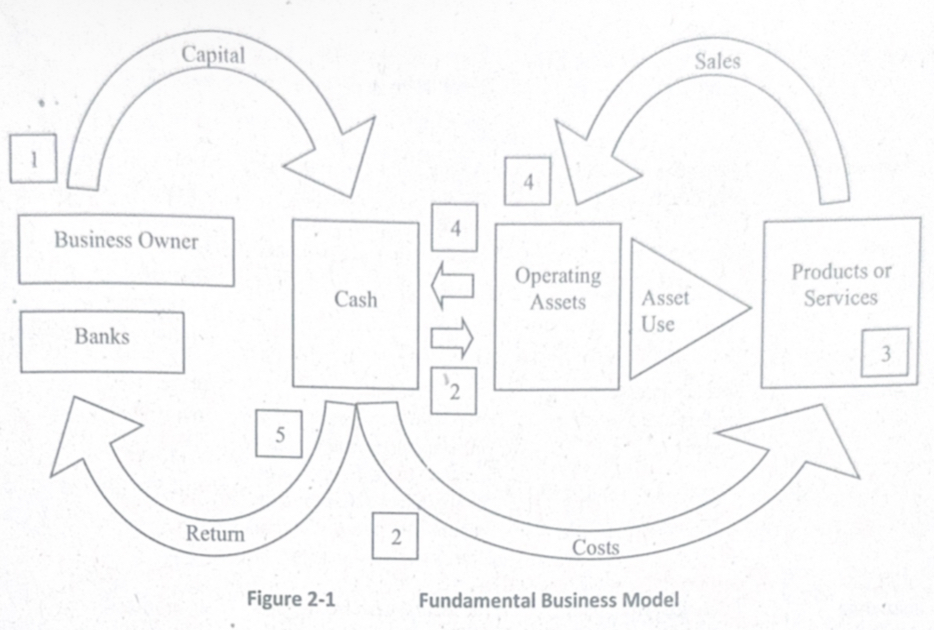
Airline Application:
Investors provide funds → purchase aircraft
Airline uses assets (planes, crew, fuel)
Flights operate (service)
Tickets sold → revenue collected
Revenue returns as cash → reinvested in operations
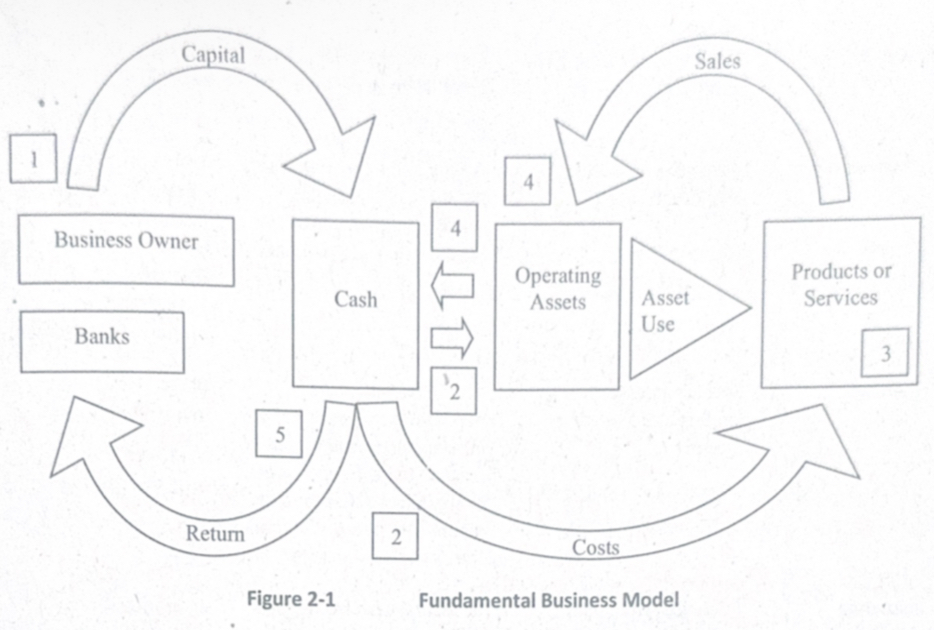
Fundamental Business Model
Airline Application:
Investors provide funds → purchase aircraft
Airline uses assets (planes, crew, fuel)
Flights operate (service)
Tickets sold → revenue collected
Revenue returns as cash → reinvested in operations
Service
[Types of business according to activity]
provides services (e.g., airlines, airports)
Ex: Philippine Airlines, CAAP, MROs
Trading
[Types of business according to activity]
buys and sells goods (e.g., aviation parts suppliers)
Ex: Fuel distributors, in-flight product suppliers
Manufacturing
[Types of business according to activity]
converts raw materials into products (e.g., Airbus, Boeing)
Ex: Aircraft, engine, avionics manufacturers
Sole Proprietorship
[FORMS OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS]
owned by one person
Ex: Small drone photography business
Partnership
[FORMS OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS]
owned by two or more person
Ex: Two pilots running an aviation consultancy
Corporation
[FORMS OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS]
separate legal entity owned by shareholders
Ex: PAL, Cebu Pacific, AirAsia, Clark Airport Corp
RA 9501
Under _________ and updated laws:
Micro: up to ₱3M assets
Small: ₱3M–₱15M assets
Medium: ₱15M–₱100M assets
Micro
Under RA 9501 and updated laws: up to ₱3M assets
Small
Under RA 9501 and updated laws: ₱3M–₱15M assets
Medium
Under RA 9501 and updated laws: ₱15M–₱100M assets
MSMEs IN AVIATION
Common examples:
Small travel agencies
Aviation training centers
Catering and ground support micro businesses
Airport terminal concessionaires
Aviation component sellers
OPERATING
FINANCING
INVESTING
ACTIVITIES OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS (3)
Operating Activities
[ACTIVITIES OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS]
Day-to-day operations
(e.g., ticket sales, fuel purchases, crew salaries)
Investing Activities
[ACTIVITIES OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS]
Buying/disposing long-term assets
(e.g., aircraft acquisition, hangar construction)
Financing Activities
[ACTIVITIES OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS]
Obtaining funds from creditors/owners (e.g., bank loans for aircraft, bond issuance)
Accounting
Purpose of ________ is to:
Produce useful financial information
Support decision-making
Assess profitability, liquidity, and solvency
Assist management and external users
Identifying
Recording
Classifying
Summarizing
Interpreting
PHASES OF ACCOUNTING (5)
INTERNAL USERS
[USERS OF ACCOUNTING]
Managers
Employees
Owners
Board of Directors
EXTERNAL USERS
[USERS OF ACCOUNTING]
Investors
Lenders
Suppliers
Gov’t agencies
Public
CAAP
[USERS IN AVIATION]
regulatory compliance
Airlines
[USERS IN AVIATION]
route profitability
Lessors
[USERS IN AVIATION]
evaluating aircraft lease payments
Investors
[USERS IN AVIATION]
profitability and long term viability
Banks
[USERS IN AVIATION]
loan decisions
Entity Concept
Business is separate from its owners
Periodicity
Business life is divided in to periods such as months or years
Stable Monetary Unit
The company is using a stable/single currency.
Objectivity
They use reliable evidence not opinions. (Ex: receipt)
Revenue Recognition
We record revenue when it is earned when necessarily when the cash is received
FINANCIAL REPORTING
To provide information useful for decision-making
HELP USERS ASSESS:
Economic resources of the entity
Claims against the entity
Changes in resources and claim
FINANCIAL REPORTING
________ SHOULD HELP USERS EVALUATE:
Buying/selling/holding decisions
Providing resources to the entity
Assessing management’s stewardship
Predicting future cash flow
Assets
Liabilities
Equity
Income
Expenses
ELEMENTS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (5)
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FUNDAMENTAL:
Relevance
Faithful Representation
ENHANCING:
Comparability
Verifiability
Timeliness
Understandabilit
GOING CONCERN ASSUMPTION
This assumption states that the business will continue to operate indefinitely