The Pleural Membranes, Their Reflections & Recesses & The Mediastinum
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What are the main structures associated with the cranial mediastinum?
NOTE: is cranial to the heart, heart usually not seen here
Associated with T2
Thymus found in the ventral part of the cranial mediastinum
Cranial vena cava
Branches of aorta
oesophagus - left
trachea
Lungs
Pleural cavity
Thoracic Duct

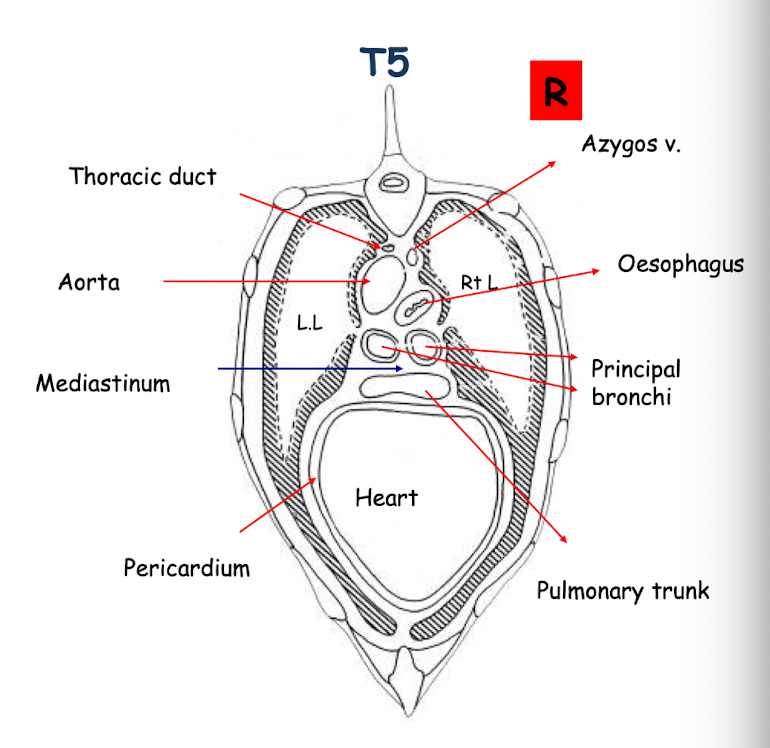
What are the main structures associated with the middle mediastinum?
Associated with T5
The heart within the pericardium (comprises largest part of the mediastinum)
Lungs
Mediastinum
Principle bronchi
Oesophagus
Aorta
Thoracic Duct
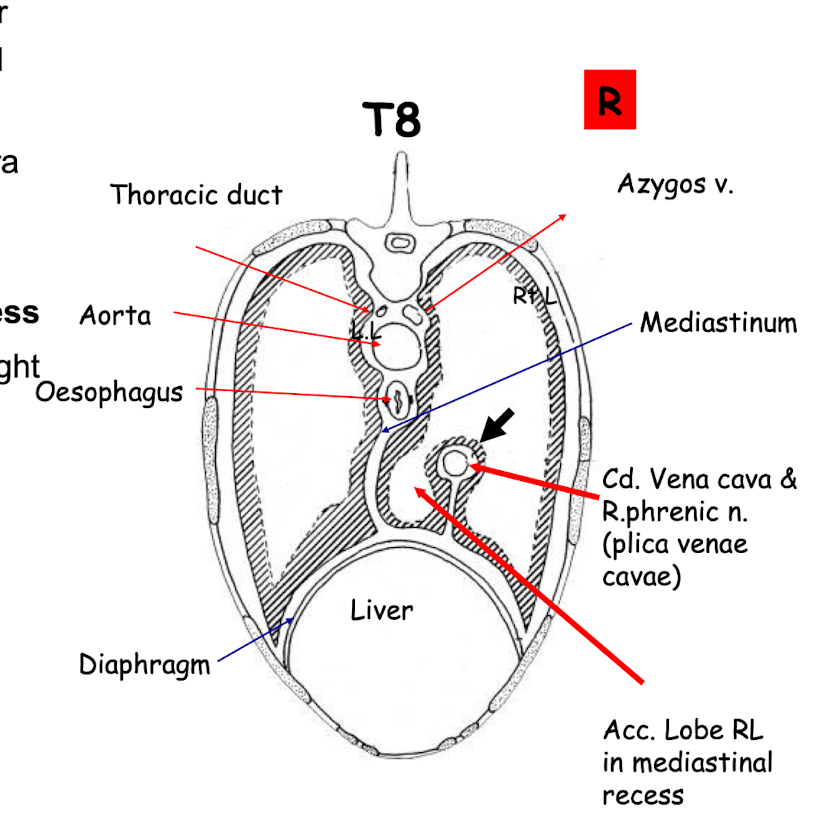
What are the main structures associated with the caudal mediastinum?
Associated with T8
• Plica venae cavae-parietal pleura of right sac is reflected over the caudal vena cava (arrow) the plica venae cavae is a loose fold of pleura that surrounds and covers the caudal vena cava AND plus right phrenic nerve as it passes through the thoracic cavity to the diaphragm. Is part of the mediastinal pleura.
Forms the Mediastinal recess
The accessory lobe of the right lung sits in this recess
Aorta
Oesophagus
Lungs
Thoracic duct
Caudal vena
Summarize the divisions of the mediastinum.
Summarize the organs and structures within the mediastinum.
Summarize structures outside of the mediastinum.

The lungs inflate during inspiration into what spaces?
These space are called pleural recesses, formed by reflections of the visceral pleura
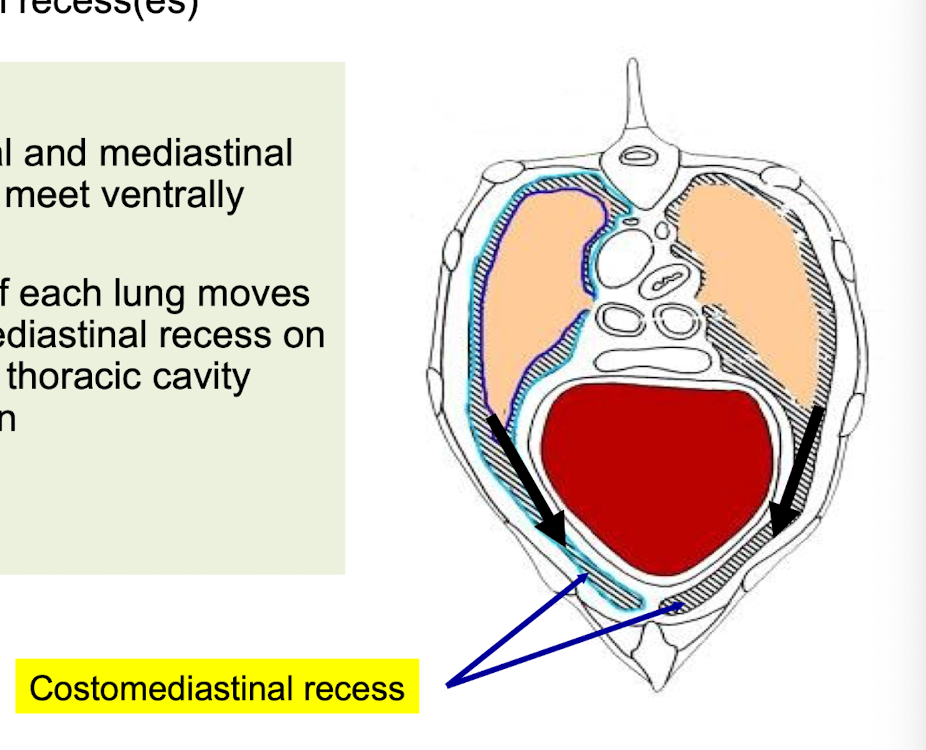
Describe the costo-mediastinal recesses.
• Where the costal and mediastinal (parietal) pleura meet ventrally
• Ventral border of each lung moves into the costomediastinal recess on each side of the thoracic cavity during inspiration
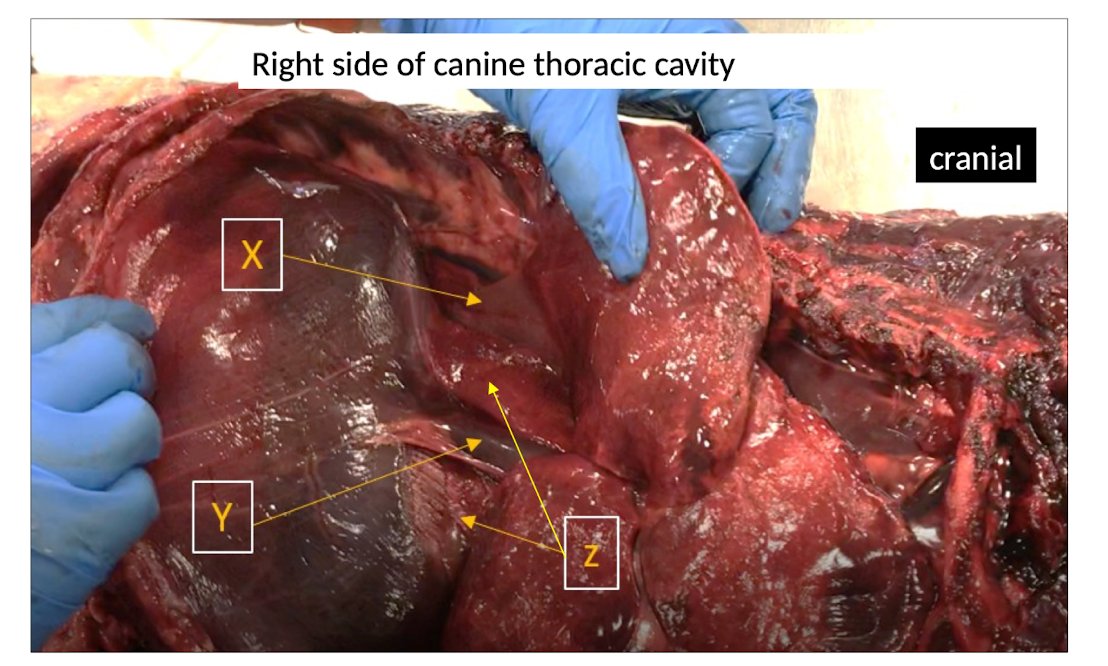
Describe the mediastinal recess.
Z = Mediastinal recess- recess formed between the plica vena cave and caudal mediastinal pleura; right accessory lobe of lung (X) extends into this recess during inspiration (Y = Cd. vena cava and L .Phrenic n. within Plica Vena Cavae)
What are the main features of the pulmonary ligament?
• Reflection of the visceral pleura at the medial surface of each lung
• Attaches the caudal lobe of each lung to the diaphragm
• Obvious and long in carnivores and pigs, but short in the ox and horse.
Describe the plural cupula.
• Right Plural cupula- formed where the costal pleura reflects to form the mediastinal pleura.
• Projects beyond first rib
• The apex of each lung moves into this space during inspiration, cranial part of thorax
• Vulnerable to trauma
Describe the costo-diaphragmatic recess.
• Reflection of Costal pleura onto diaphragmatic pleura (blue shaded area)
• Basal border of lung moves in and out of this recess, caudal aspect of lung
• Costodiaphragmatic line of pleural feflection - most caudal extent of this recess
What is the anatomical location of the costo-diaphragmatic line of pleural reflection?
• Runs approx. from the 8 costochondral junction to the proximal end of the last rib (drawn in a line)
• Marks the boundary between the pleural cavity (cranio-dorsal) and the peritoneal cavity (caudo-ventral).
Marks where the diaphragm attaches in the thoracic cavity
How does the costo-diaphragmatic line of pleural reflection appear in the canine, equine and bovine?
• In the canine and equine the line closely follows the curve of the costal arch but is about a hands breadth more craniodorsal.
• In the bovine, the line is relatively steep and straight, making it a reliable landmark for surgical and diagnostic procedures.
• Important for thoracocentesis: entry into the pleural cavity must be made cranio-dorsal to this line to avoid penetrating the peritoneal cavity.
What is defined as the minimum area for auscultation and percussion of the lungs?
How does it change in the diseased state?
• 'Minimum Area' is the benchmark in normal animal
• Defined as the area of contact between the lung and the thoracic wall at the end of expiration
• In diseased state the 'Minimum area' changes
- Decreases if lung partially collapsed e.g pneumothorax or pleural effusion
- Increases if the lung becomes enlarged e.g alveolar emphysema