Chemistry Unit 7 Test
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
self-ionization of water
in a sample of water, a small number of water molecules dissociate
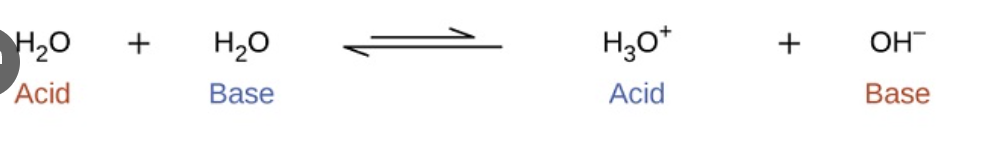
ion-product constant for water
Kw = [H3O+] [OH−]=1.0 × 10−14
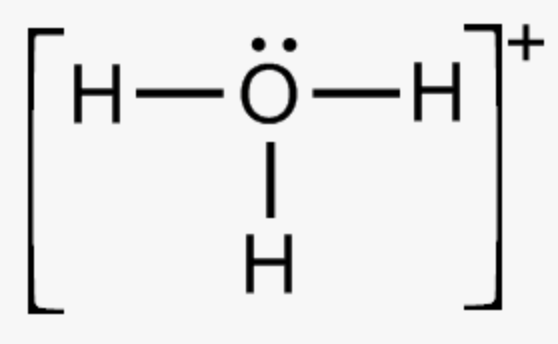
hydronium ion
H3O+
neutral solution
[H+]=[OH−], pH=7
acidic solution
[H+]>[OH−], pH<7
basic solution
[H+]<[OH−], pH>7
acid (Arrhenius definition)
dissociates to produce H+ in a solution

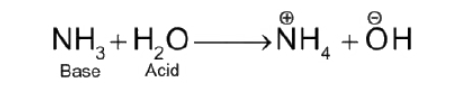
acid (Brønsted-Lowry definition)
H+ donor

base (Arrhenius definition)
dissociates to produce OH− in a solution

base (Brønsted-Lowry definition)
H+ reciever
pH
concentration of H+ in a solution
conjugate acid-base pair
present when weak acids + bases are in equilibrium
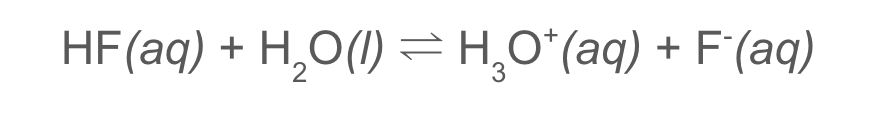
pH (calculation from strong acid concentration)
pH=-log[H+]
pH (calculation from strong base concentration)
pOH-=-log[OH-]
strong acid
dissociates completely to give H+ (HCl)
strong base
dissociates completely to give OH- (OH)
weak acid/weak base
does not dissociate completely
neutralization reaction
acid+base → salt+ water
titration
experimental technique in which a neutralization reaction is performed gradually, often to determine the concentration of an unknown solution
indicator
gives a visible sign of pH; example of chemical equilibrium
end point (titration)
pale pink solution; when the titrant and analyst are in perfect stoichiometry
titration calculation
MAVA=MBVB
buffer(by property)
solution resists changes in pH when a small amt of acid or base is added
buffer(by composition)
weak acid +salt of conj base