Physics HL (Waves and SHM)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Term
Definition
SHM
Oscillatory motion about equilibrium with a restoring force proportional to displacement.
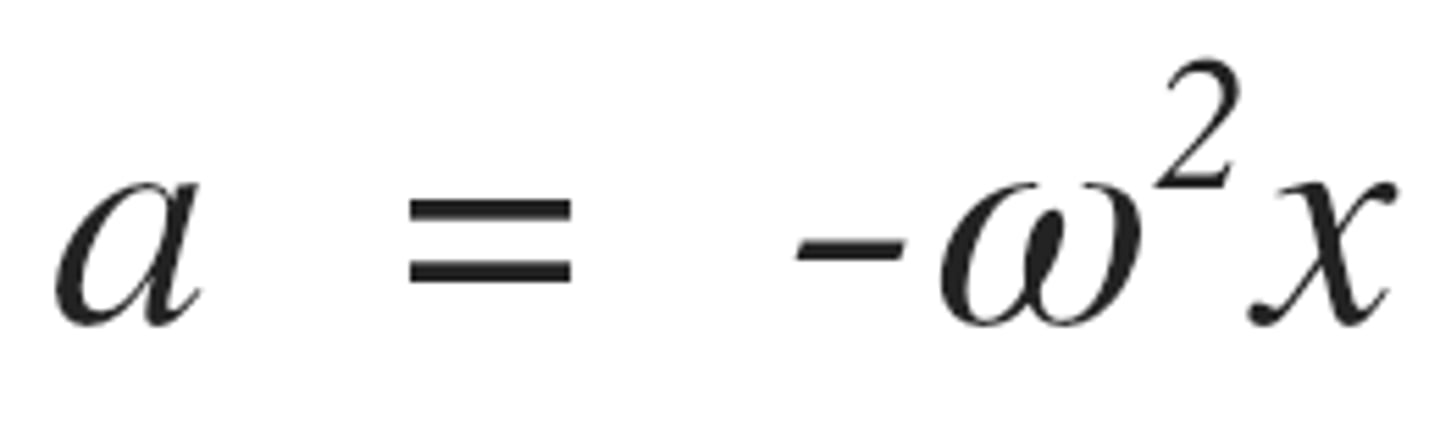
Equilibrium
The point where the net force on an object is zero.
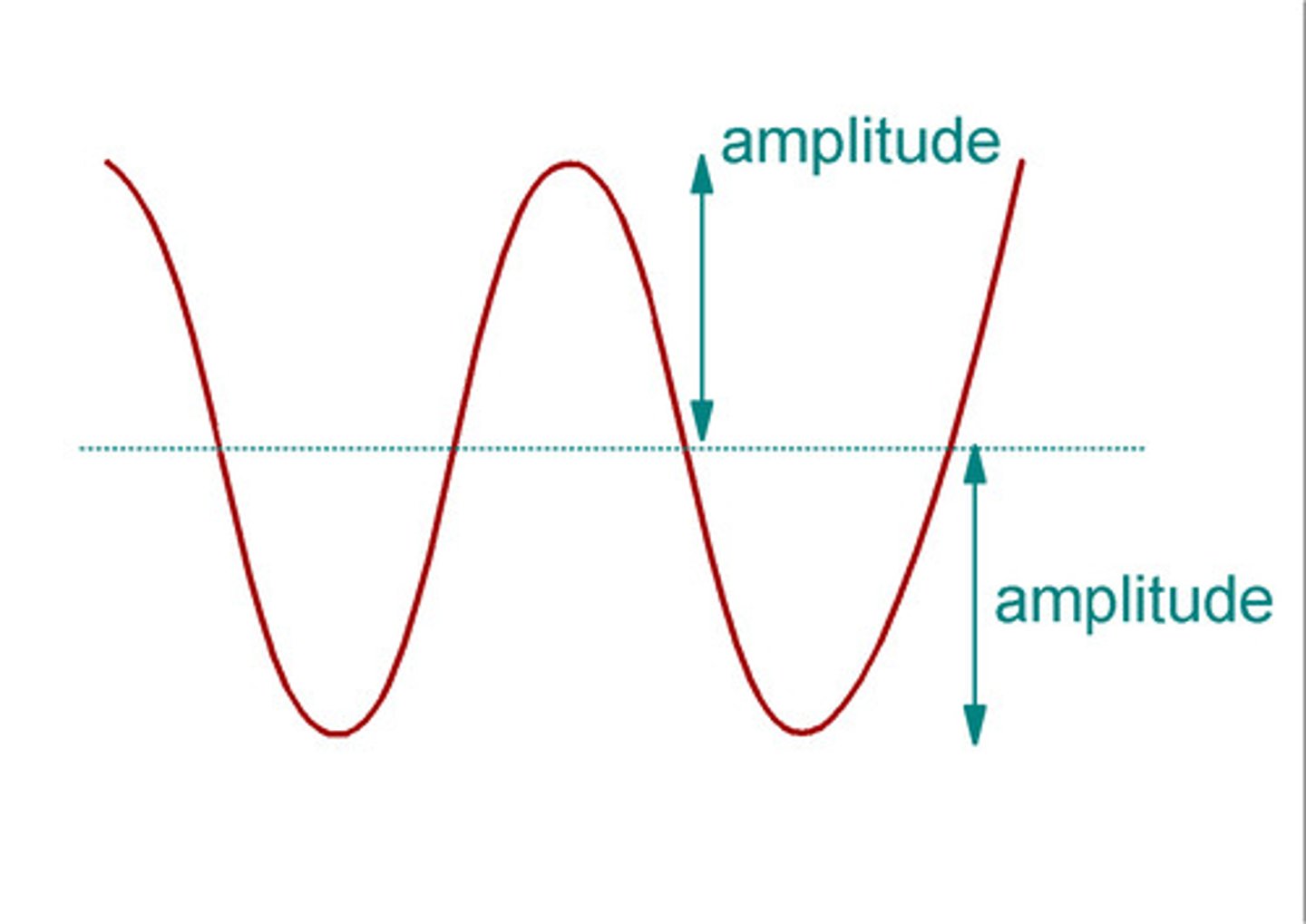
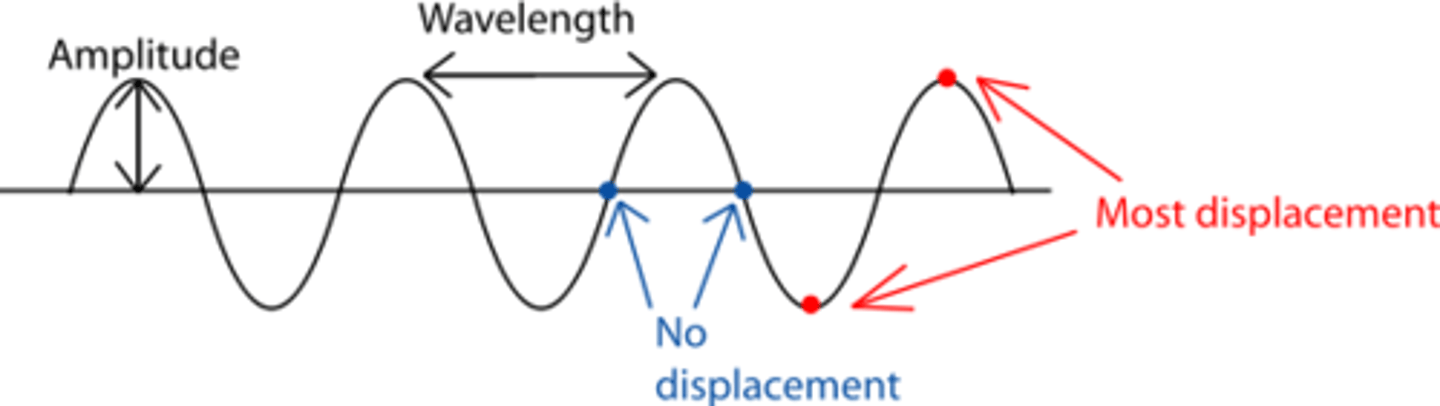
Amplitude
The maximum displacement from the equilibrium position.
Frequency
Number of complete oscillations per second (measured in hertz, Hz).
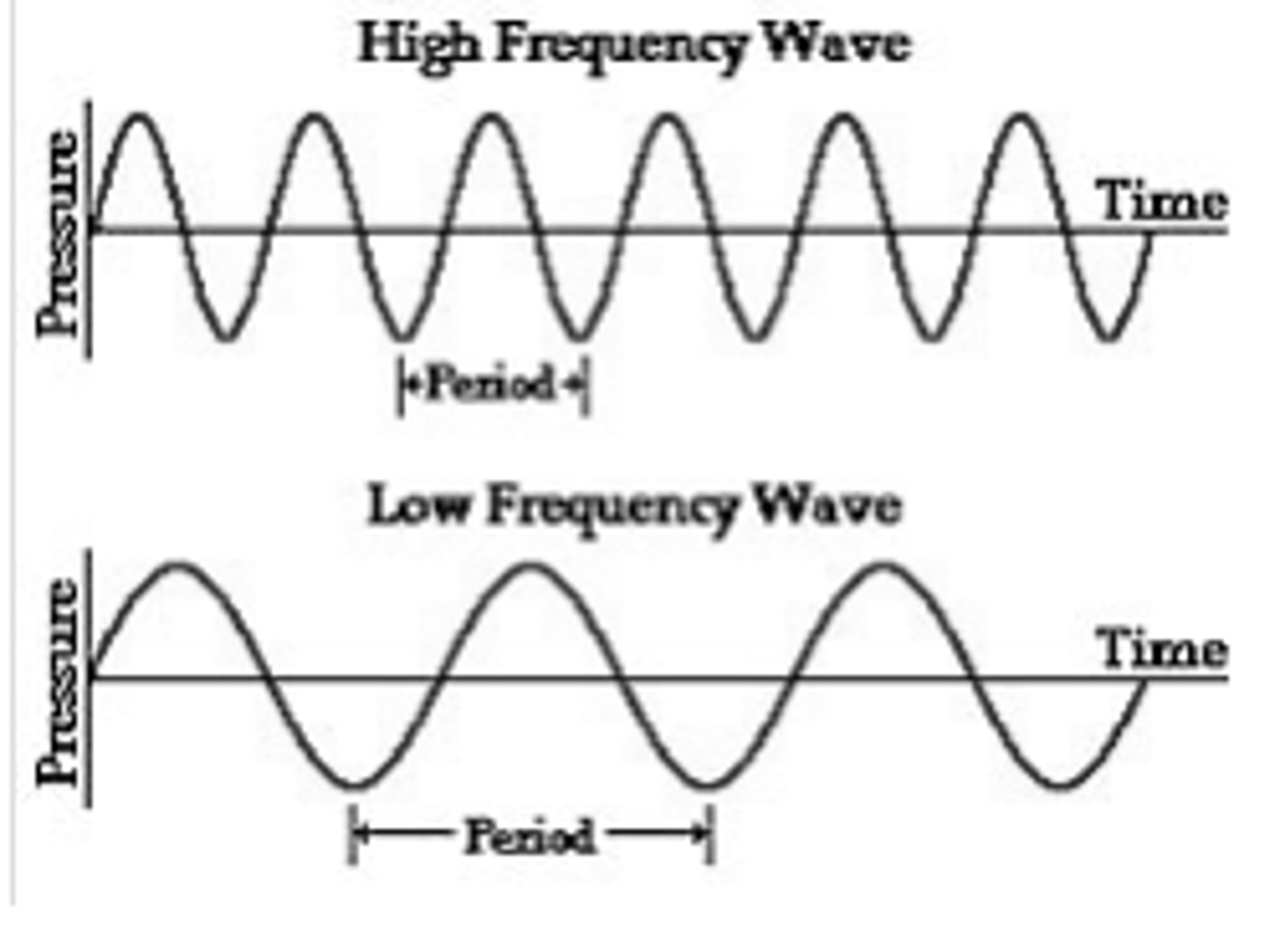
Period (T)
Time taken for one complete cycle of oscillation; T = 1/f.
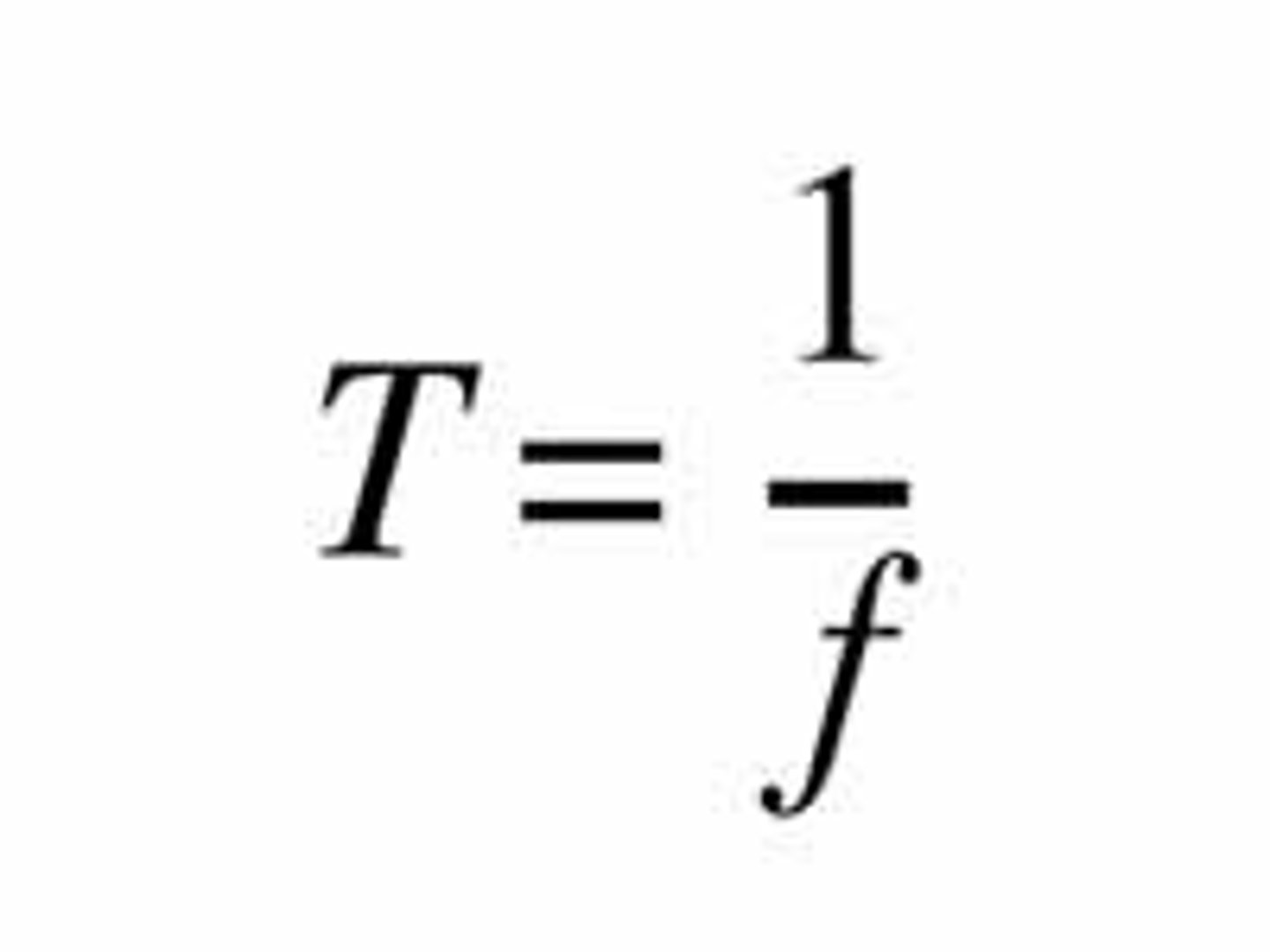
Angular frequency (ω)
Rate of phase change in radians per second; ω = 2πf.
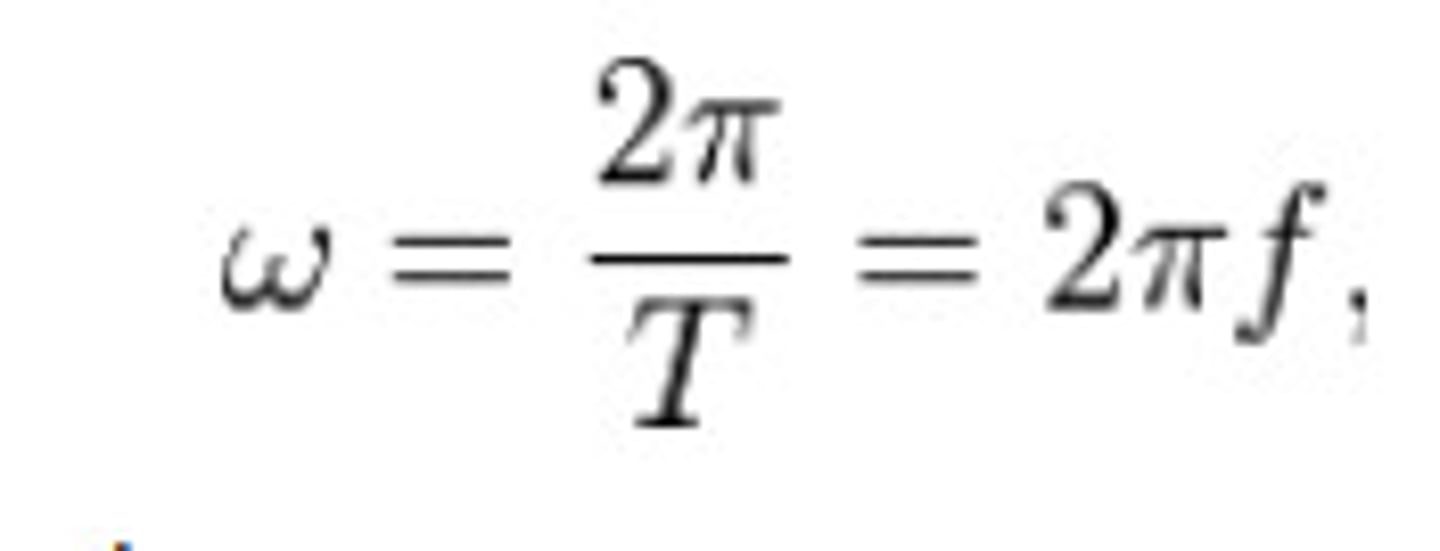
Displacement (x)
The distance and direction from equilibrium.
Restoring force
A force that acts to bring an object back toward equilibrium.
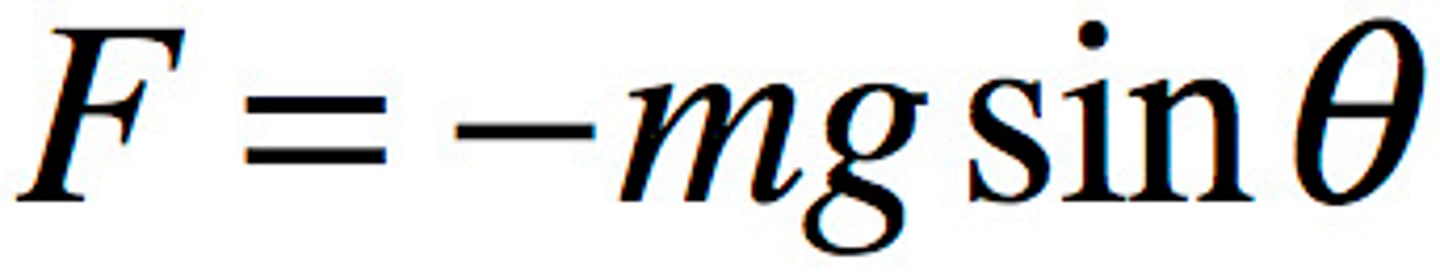
Phase angle
The position of the object in its cycle, measured in radians.
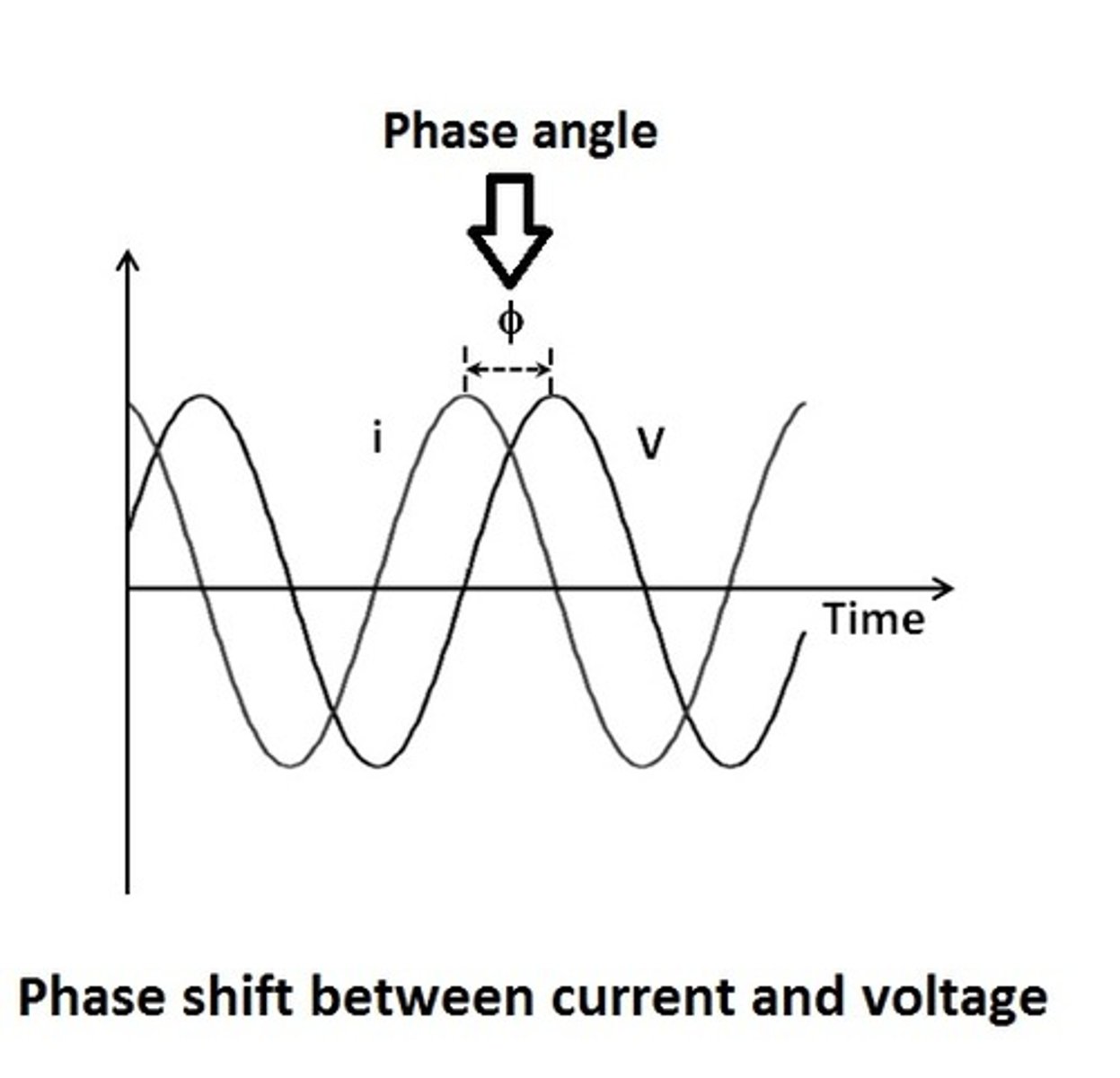
Energy in SHM
Kinetic and potential energy trade off; total energy is constant in an ideal system.
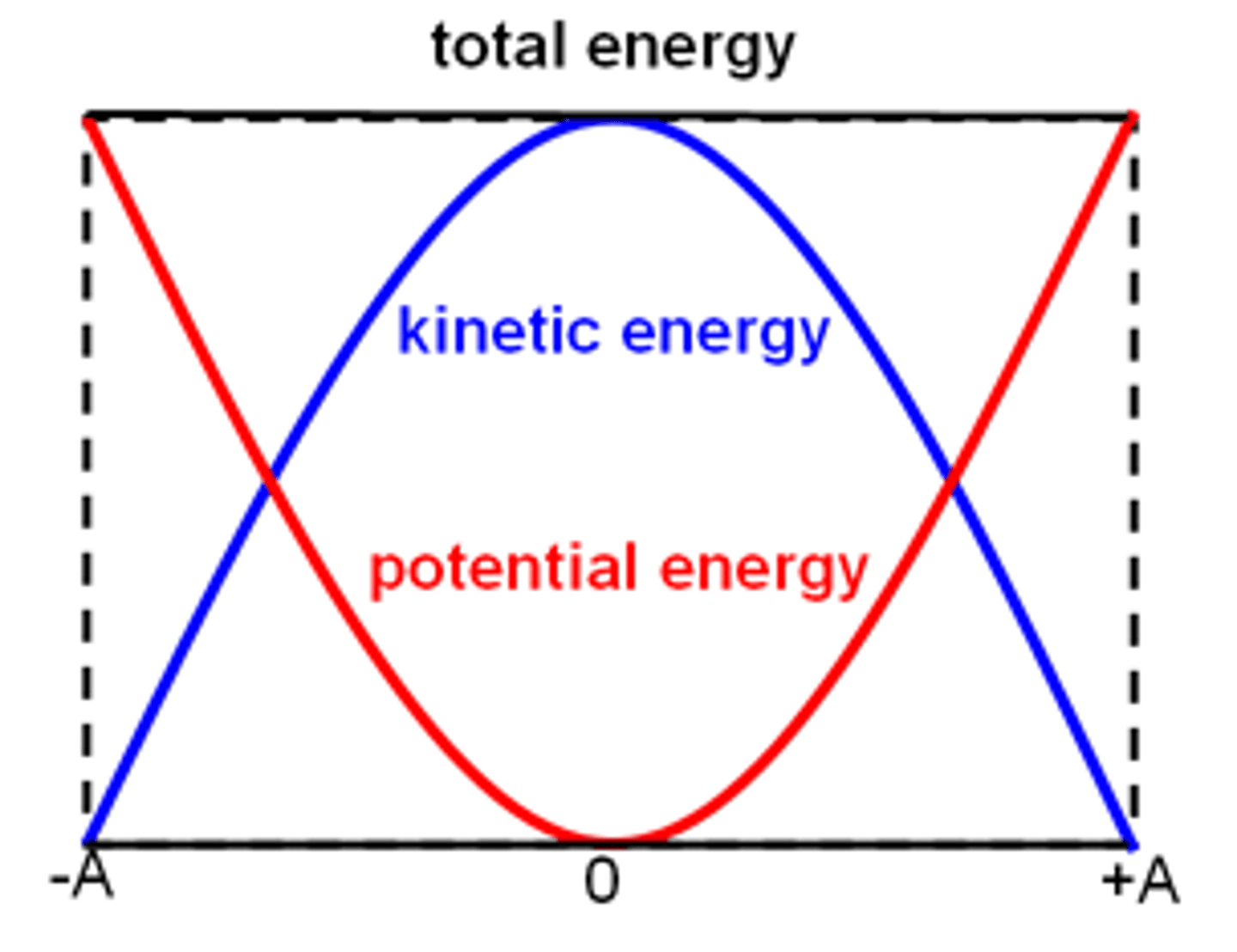
Transverse wave
A wave where the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of travel (e.g., light).
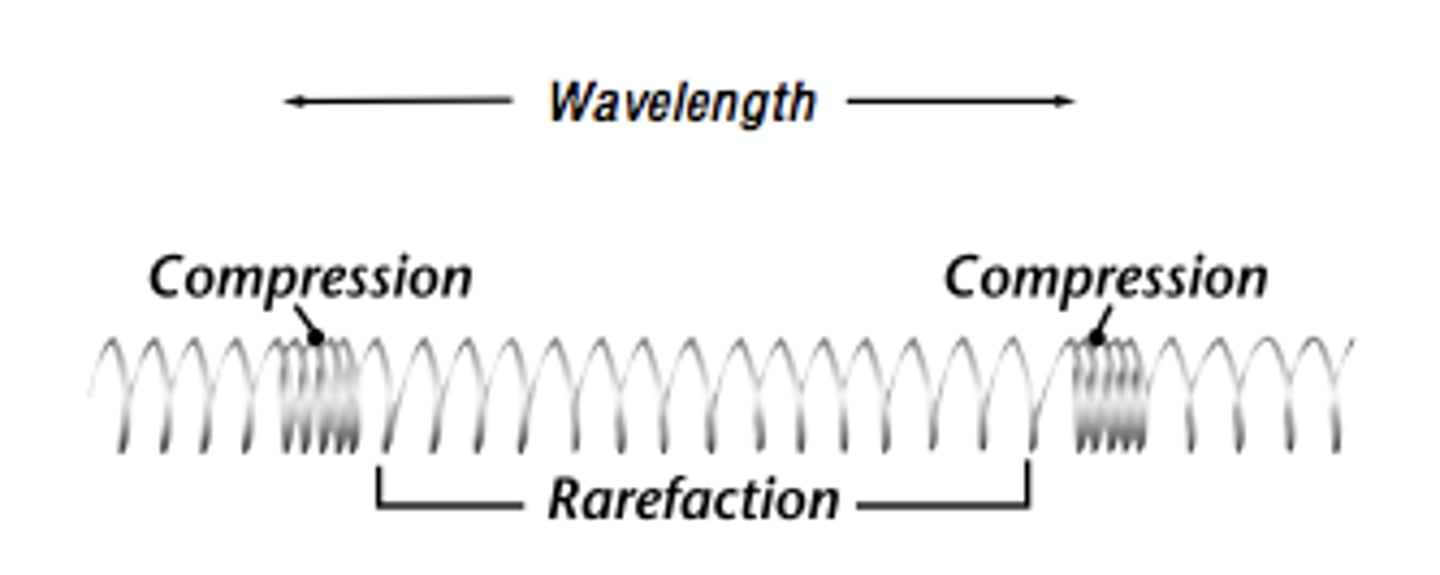
Longitudinal wave
A wave where the oscillation is parallel to the direction of travel (e.g., sound).
Mechanical wave
A wave that requires a medium to travel through (e.g., sound).
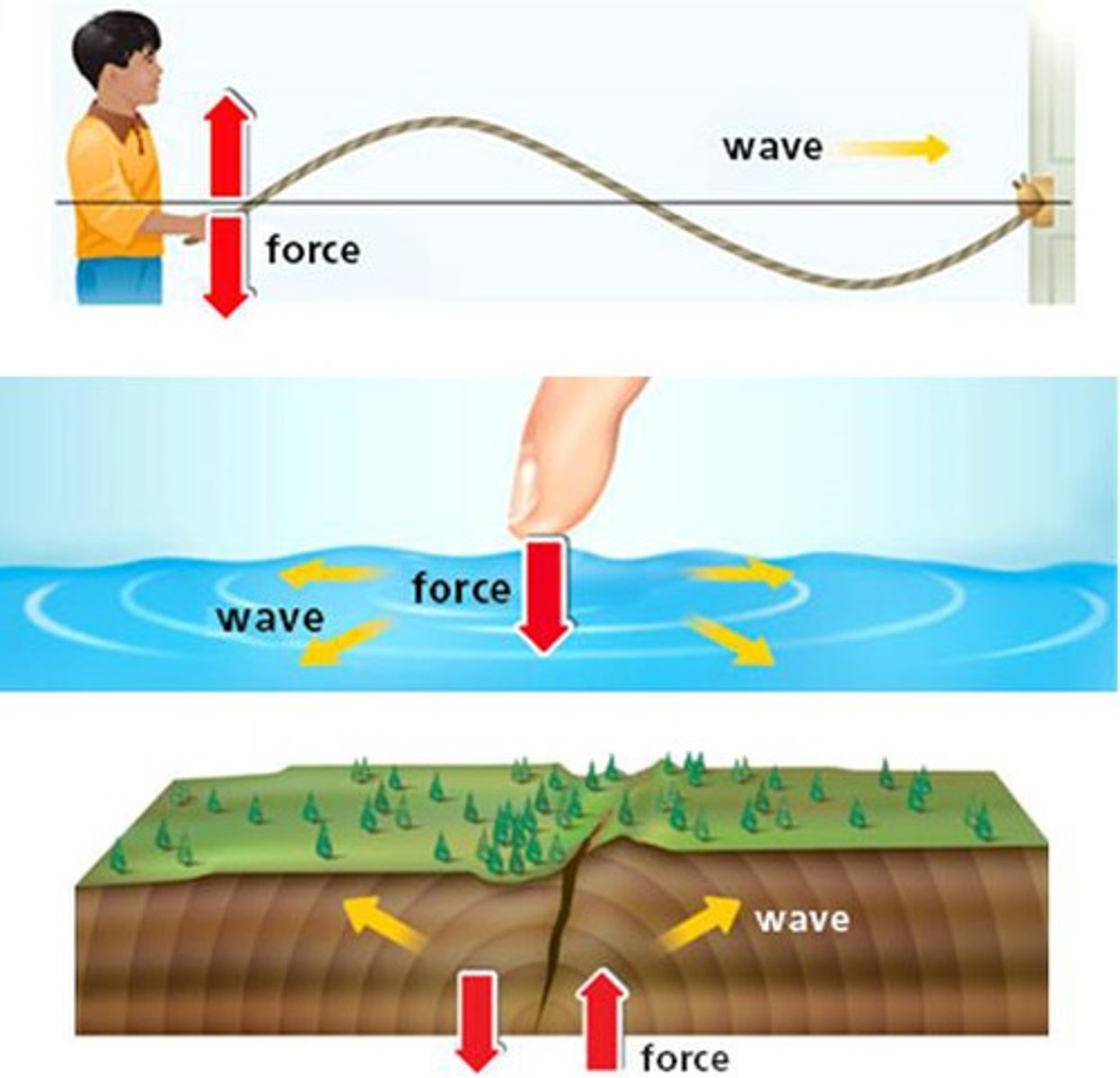
Electromagnetic wave
A wave that does not require a medium (e.g., light).
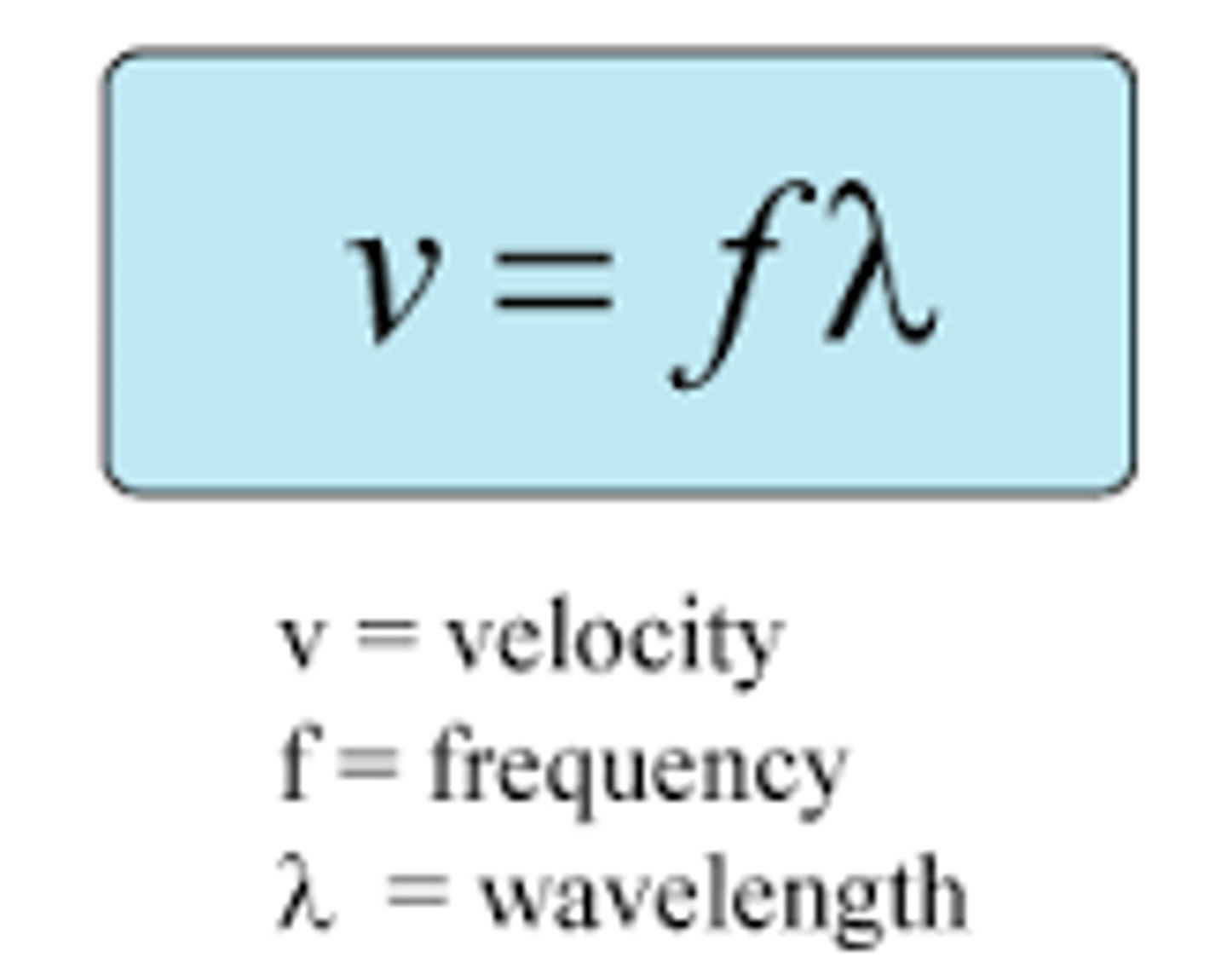
Wave speed (v)
Speed at which the wave propagates; v = fλ.
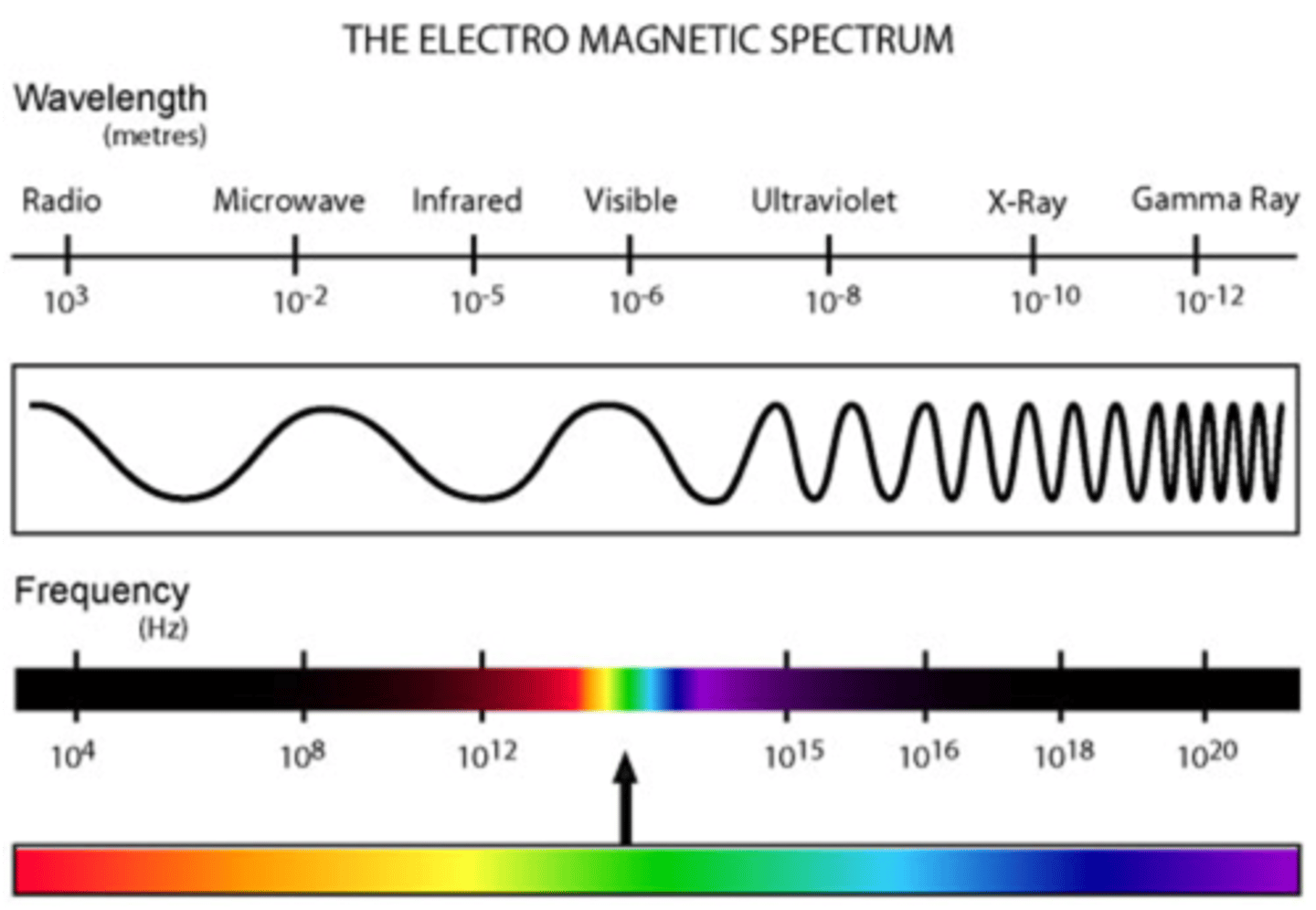
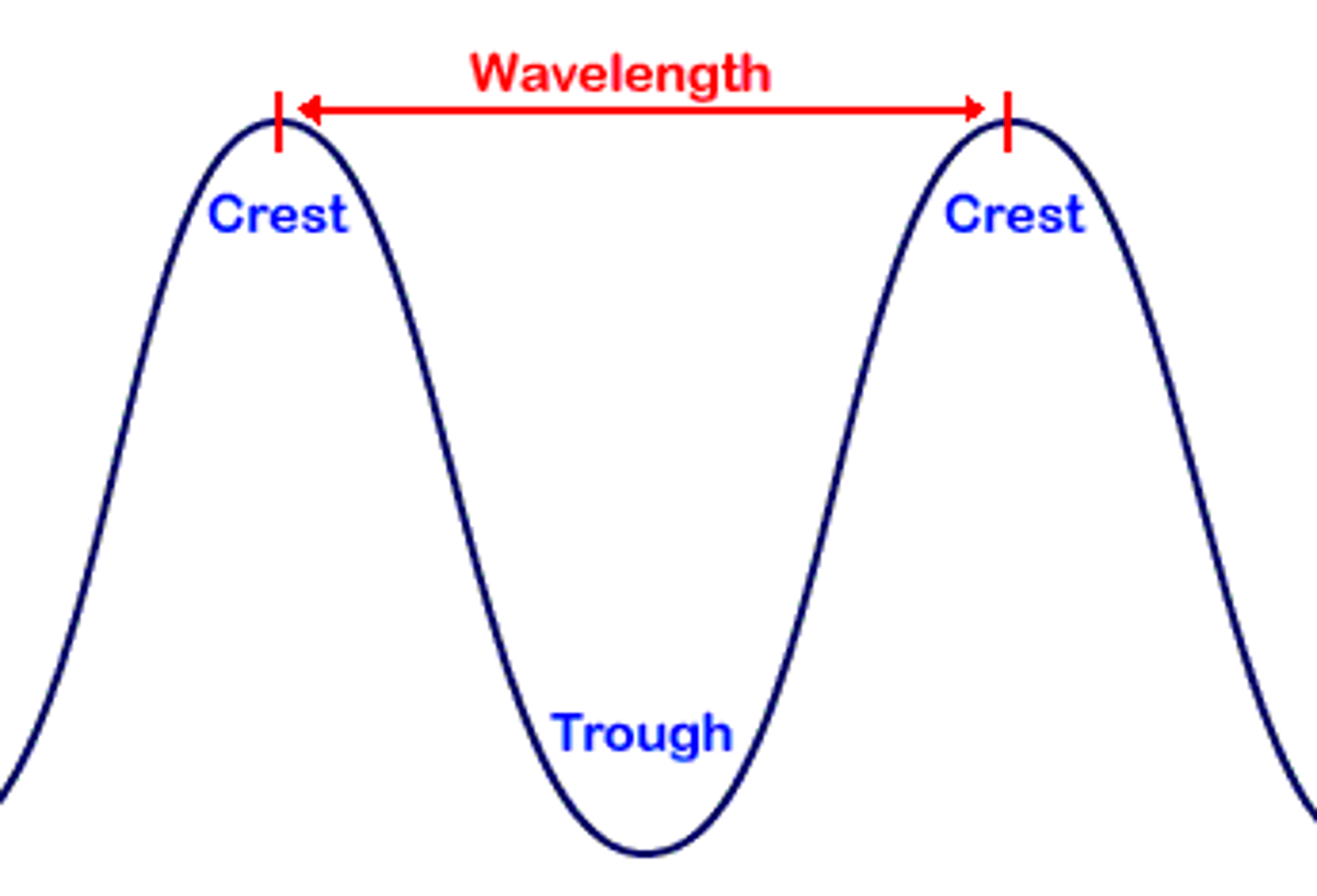
Wavelength (λ)
The distance between two successive points in phase on a wave.
Wavefront
A line connecting points of equal phase in a wave.
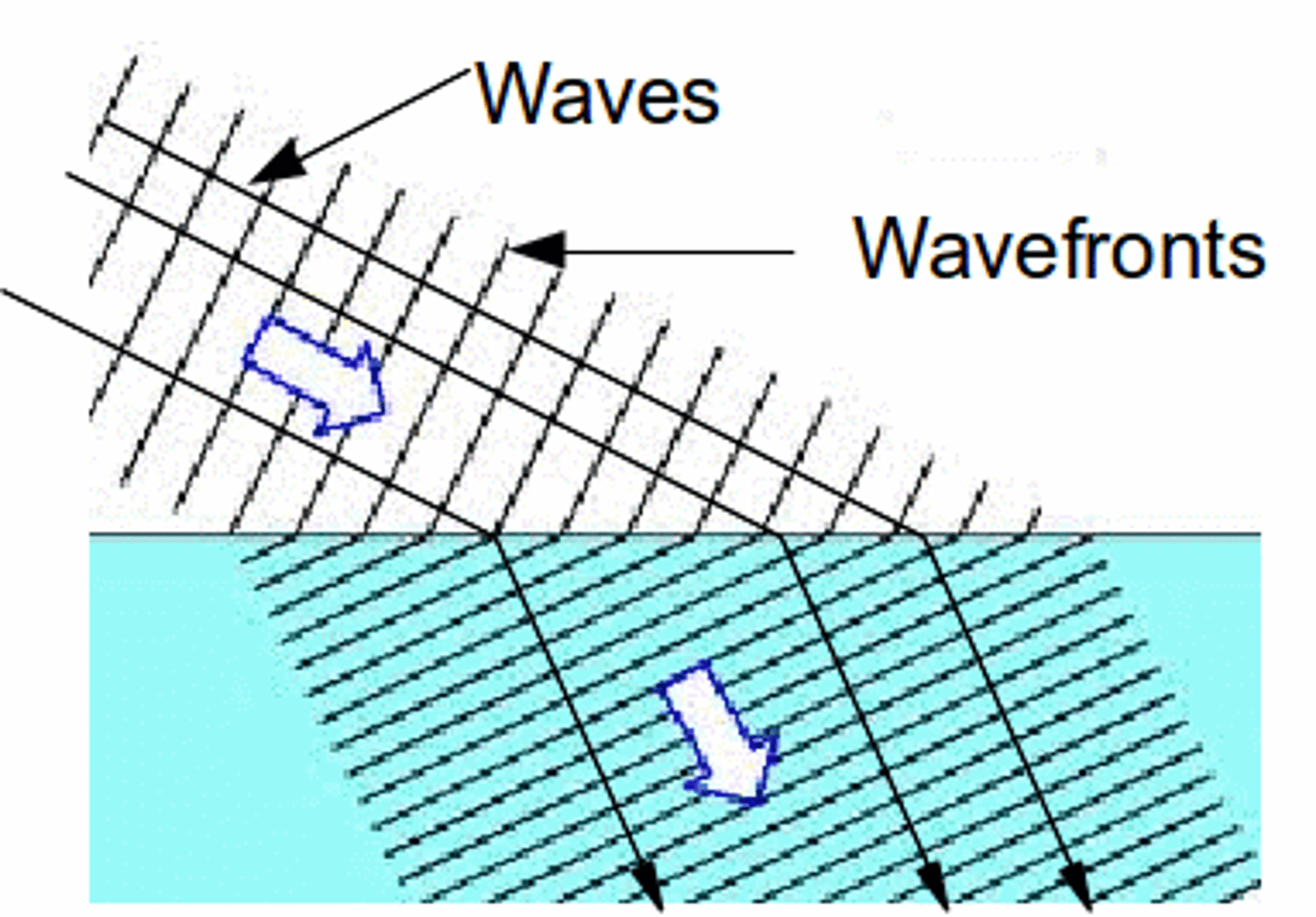
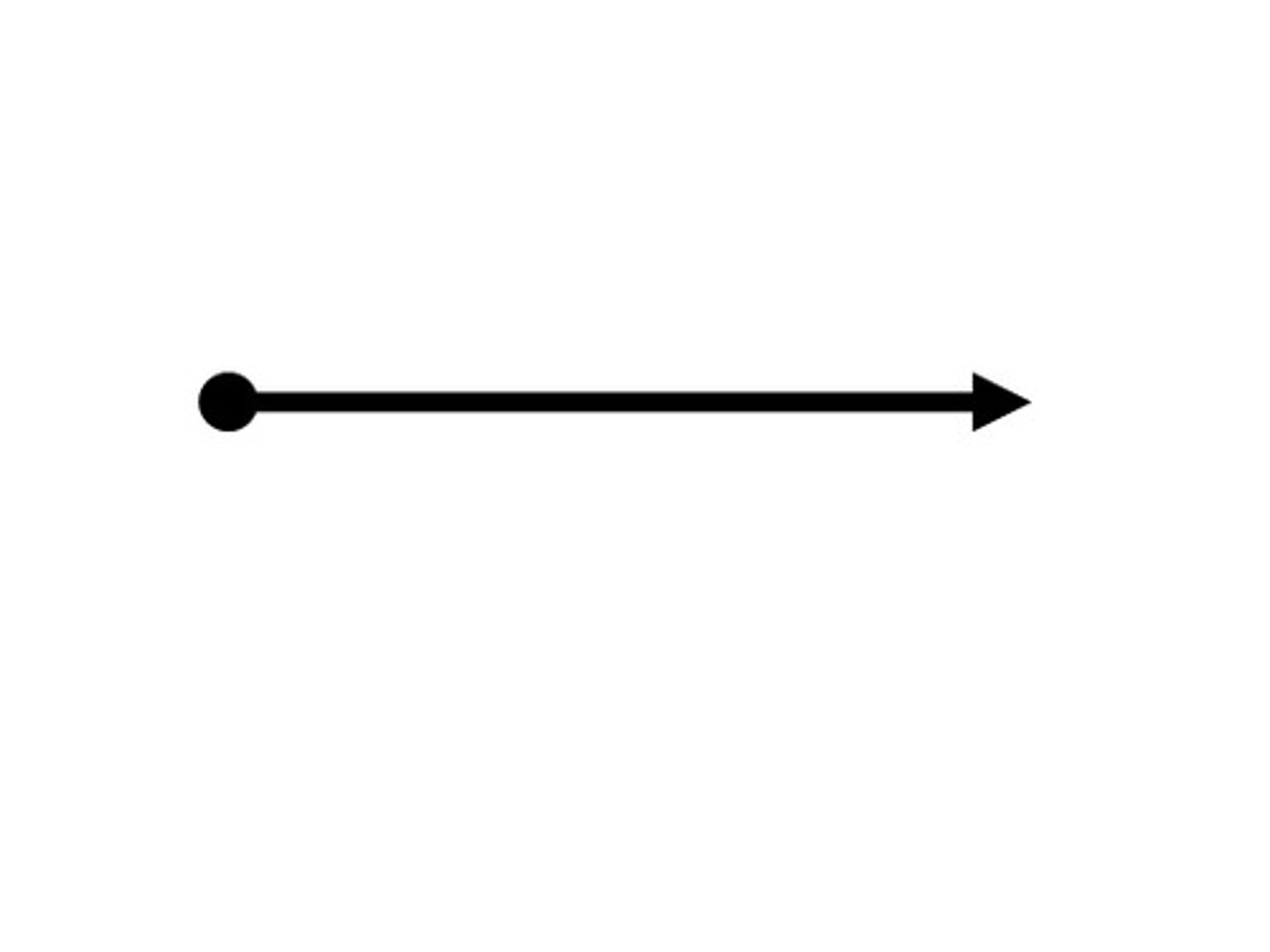
Ray
A line that shows the direction of wave travel.
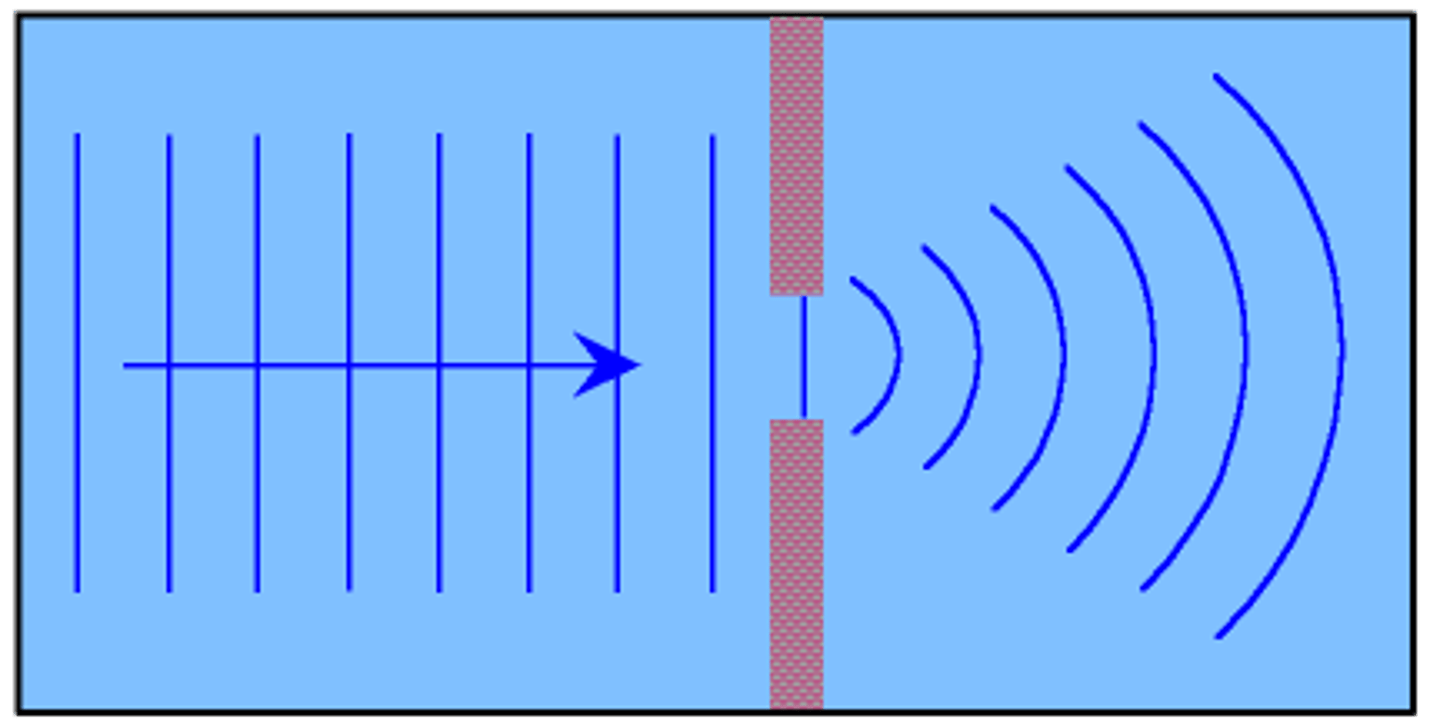
Diffraction
The bending of waves around obstacles or through slits.
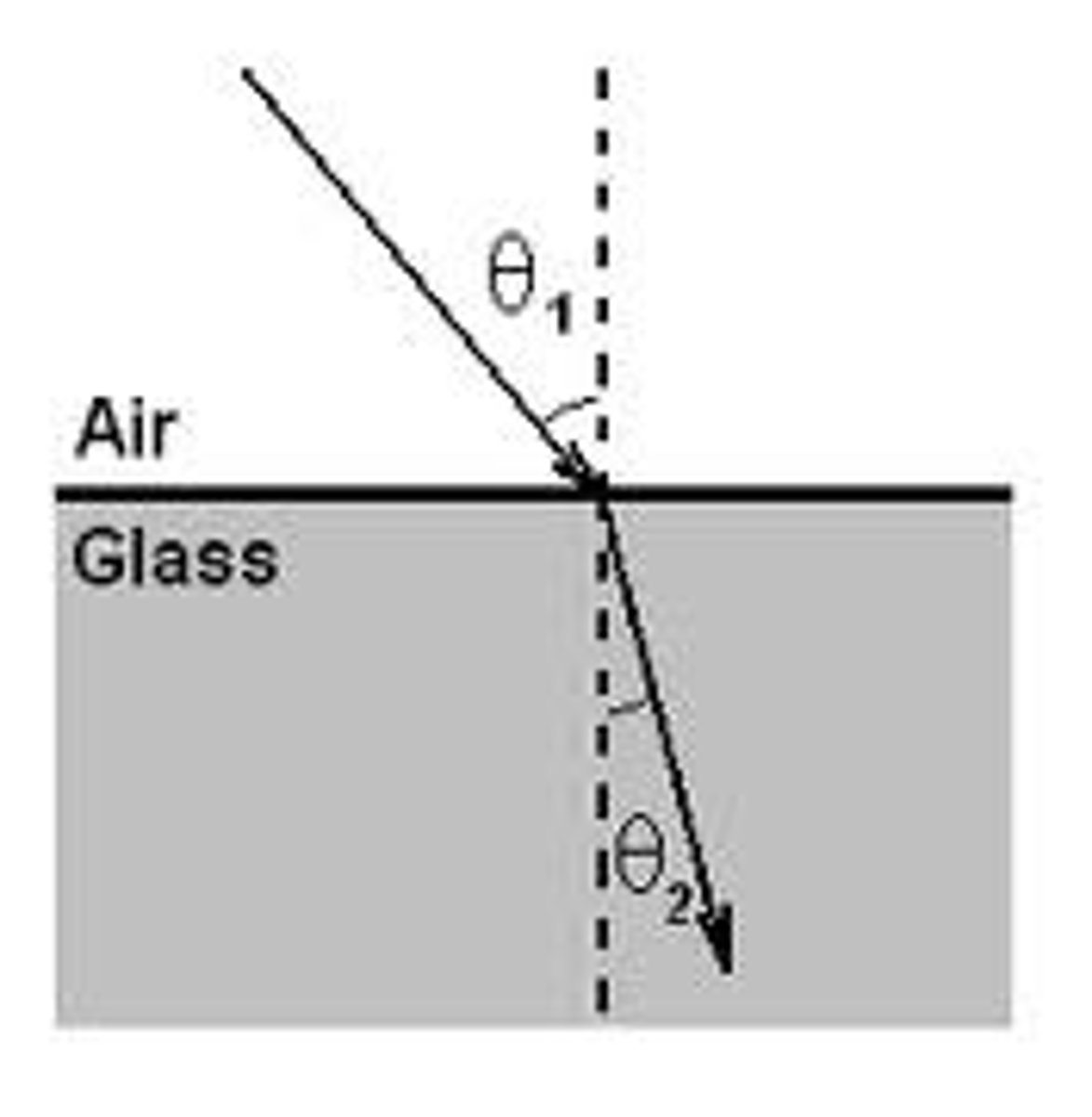
Refraction
The change in direction of a wave as it passes from one medium to another.
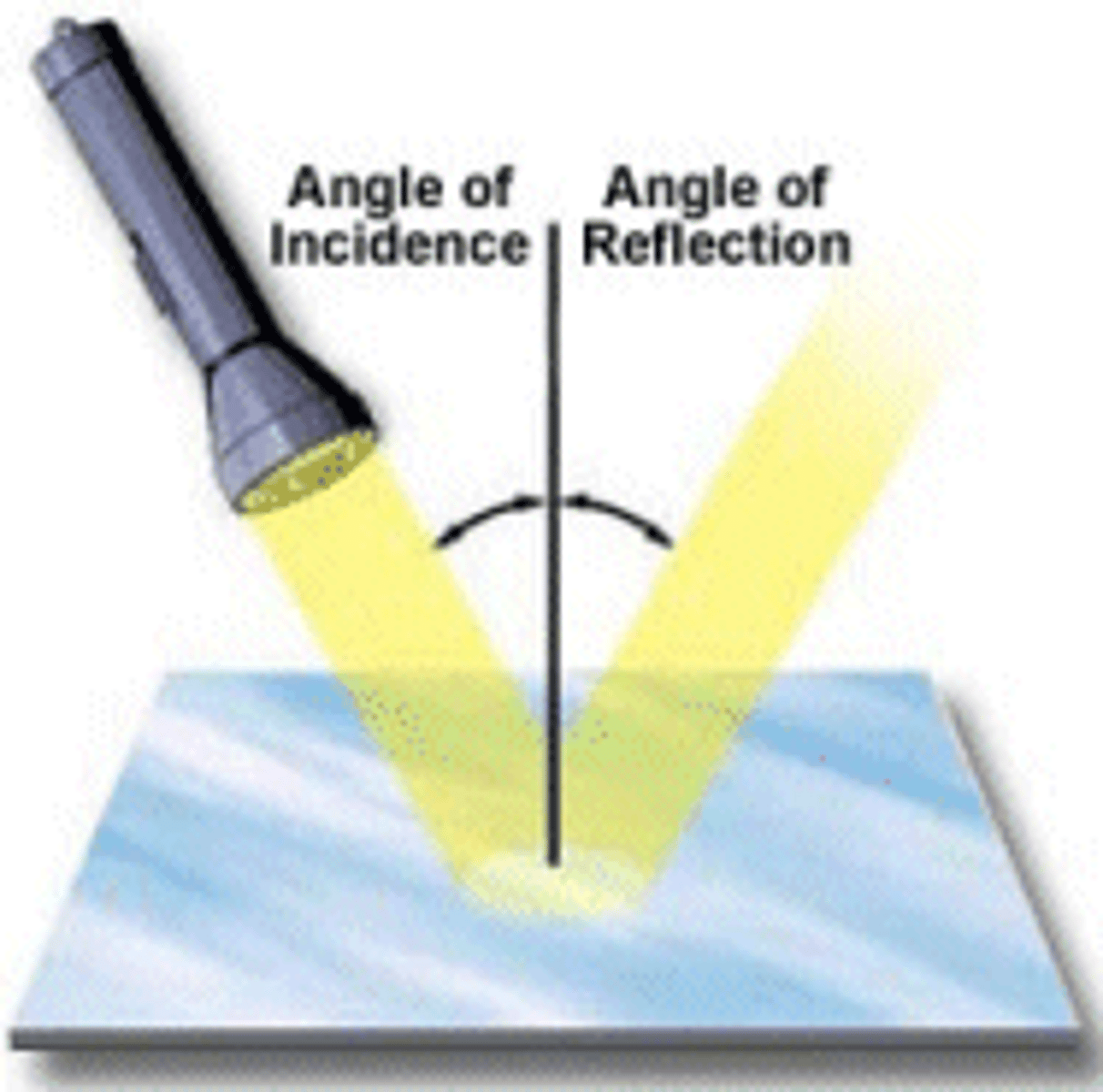
Reflection
The bouncing back of a wave when it hits a boundary.
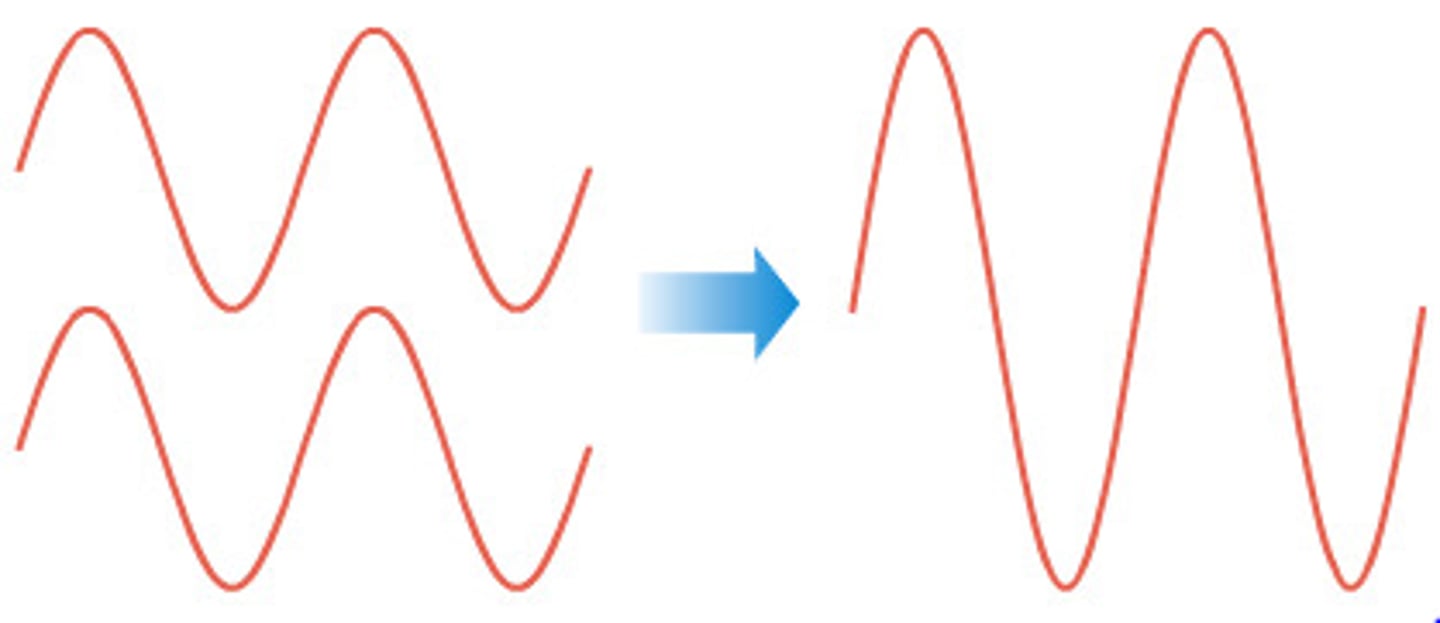
Superposition
When two or more waves overlap and combine.
Interference
The result of superposition: constructive (amplitude increases) or destructive (amplitude decreases).
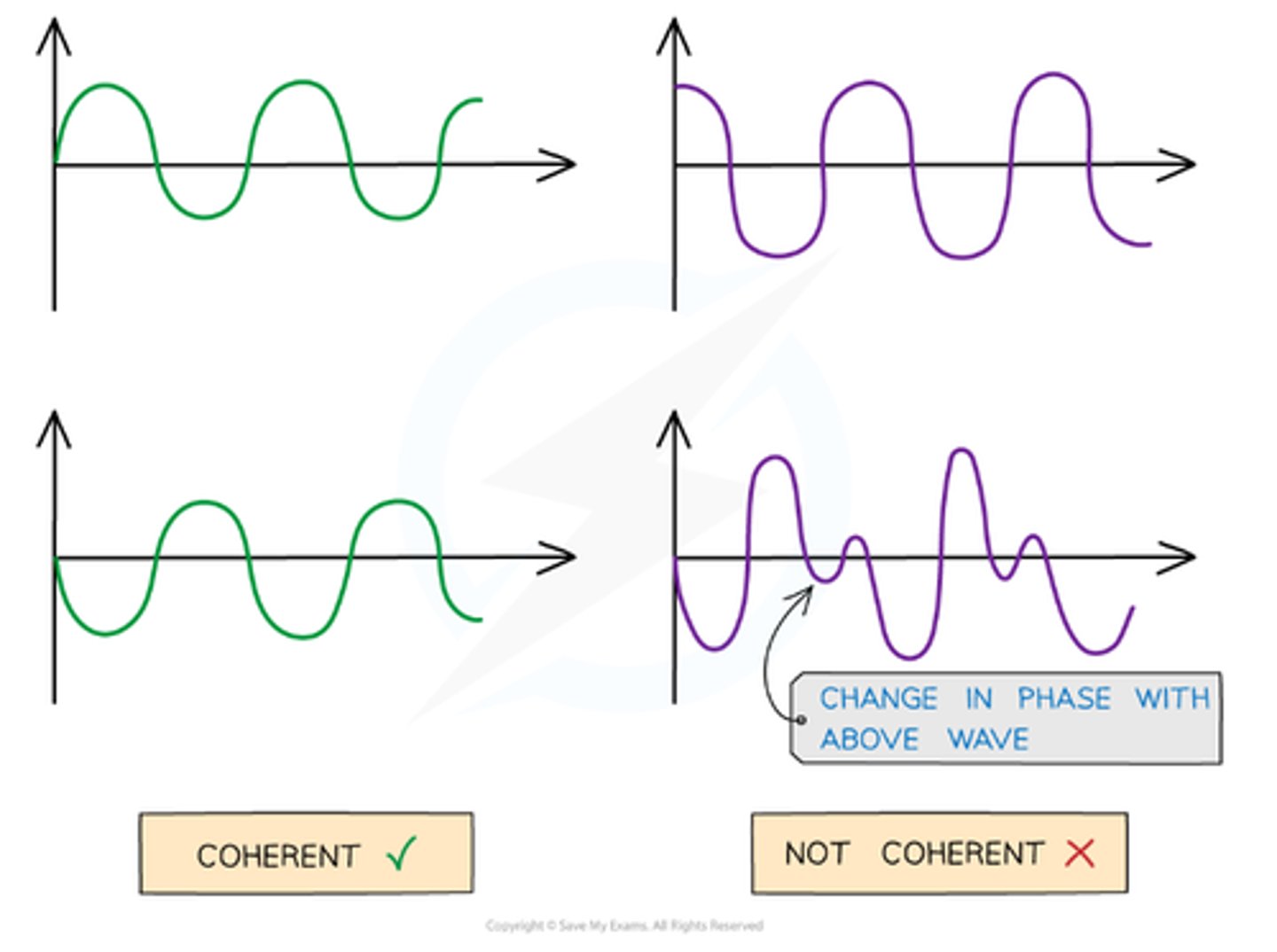
Coherence
Waves with constant phase difference; necessary for clear interference patterns.
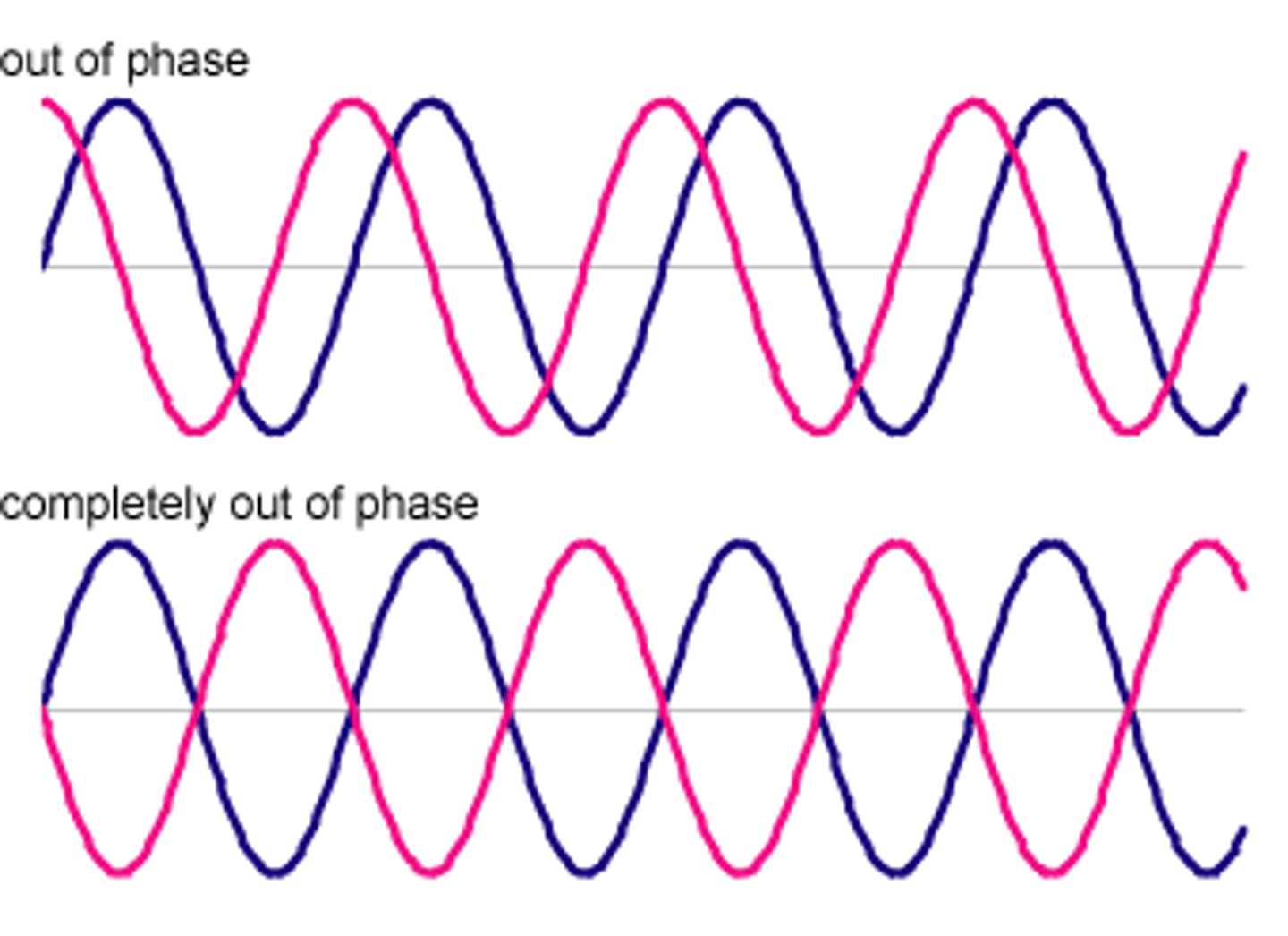
Phase
The fraction of a wave cycle that has passed relative to a reference point.
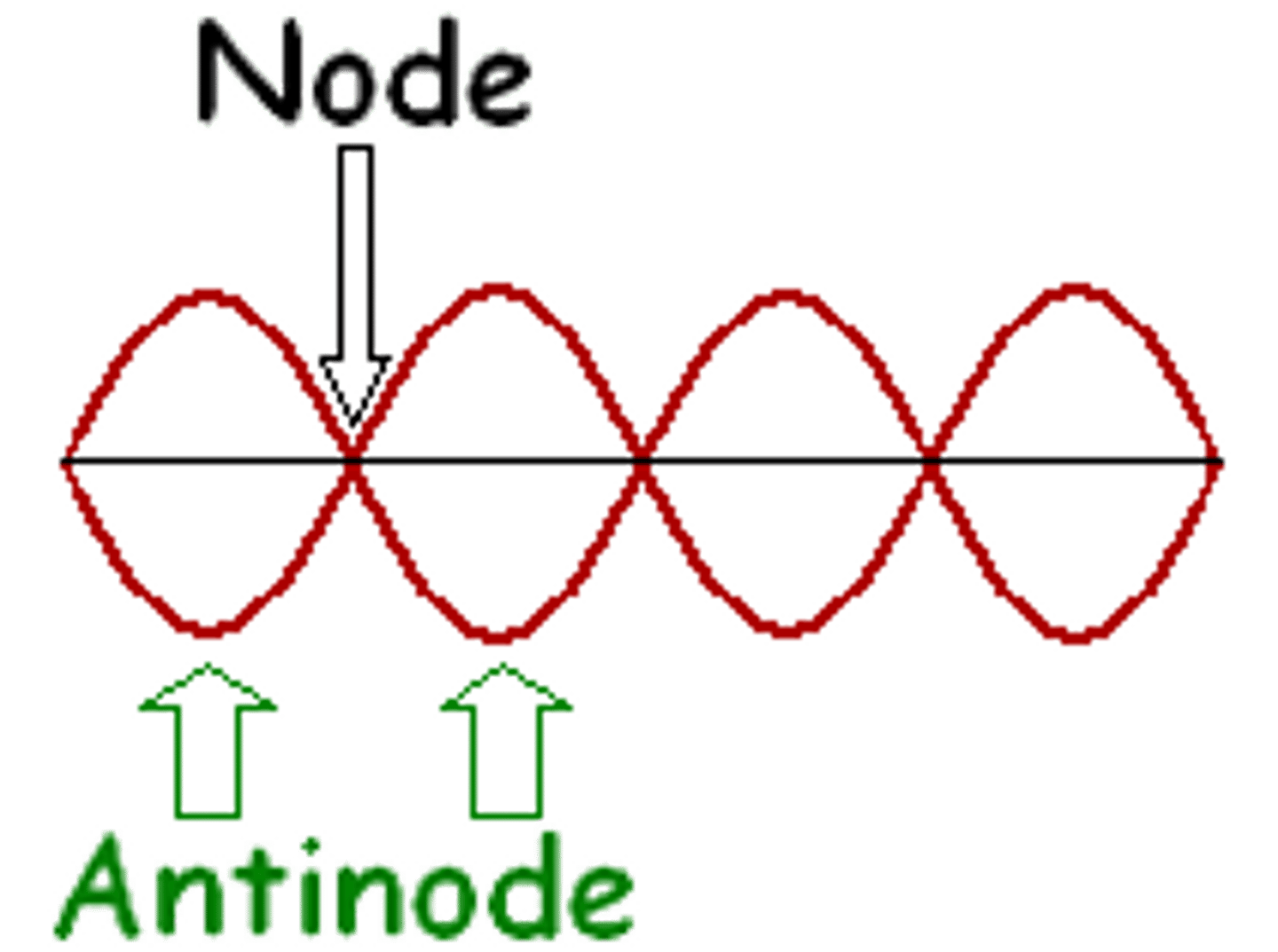
Nodes
Points of zero displacement in a standing wave.
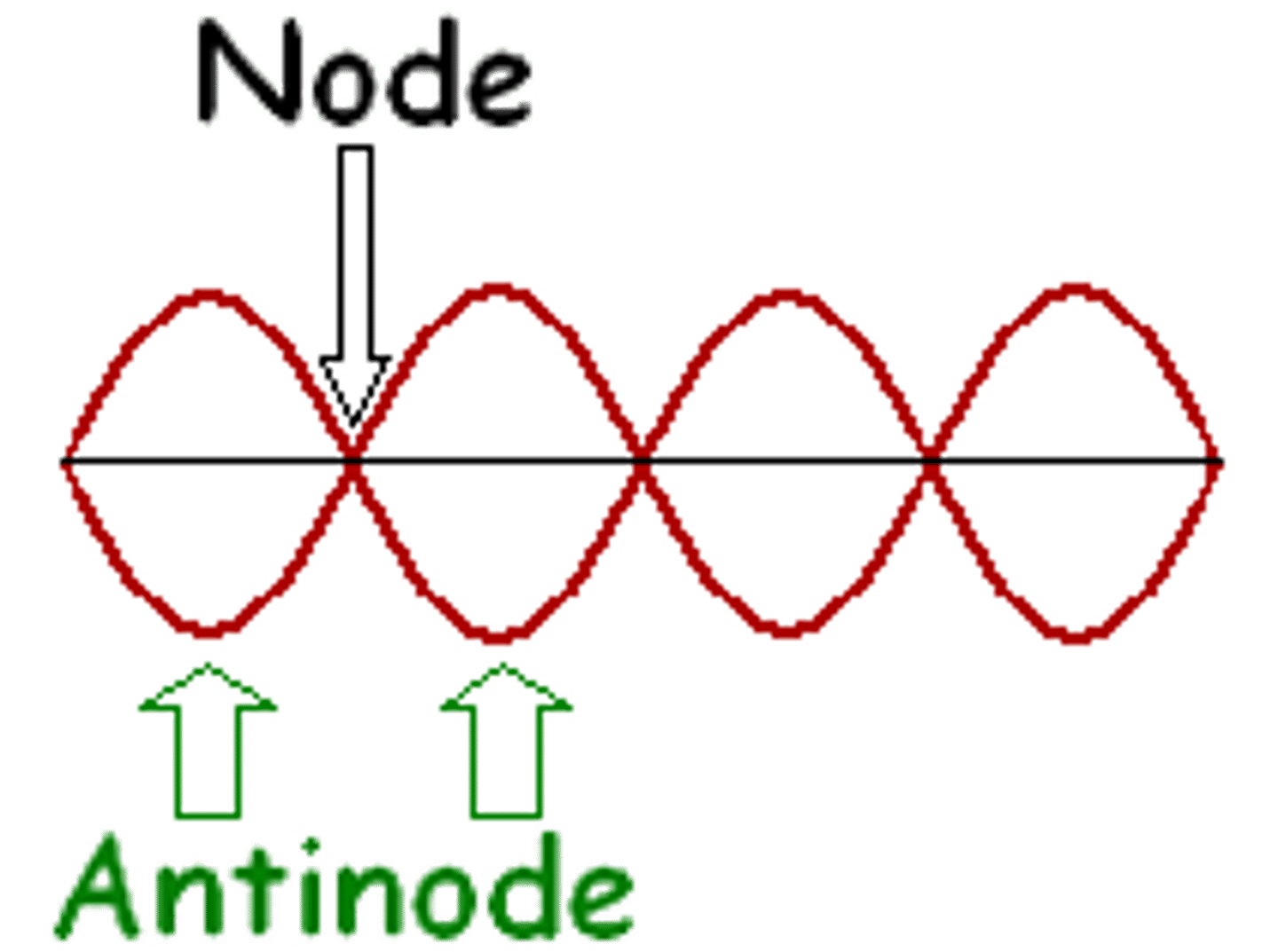
Antinodes
Points of maximum displacement in a standing wave.
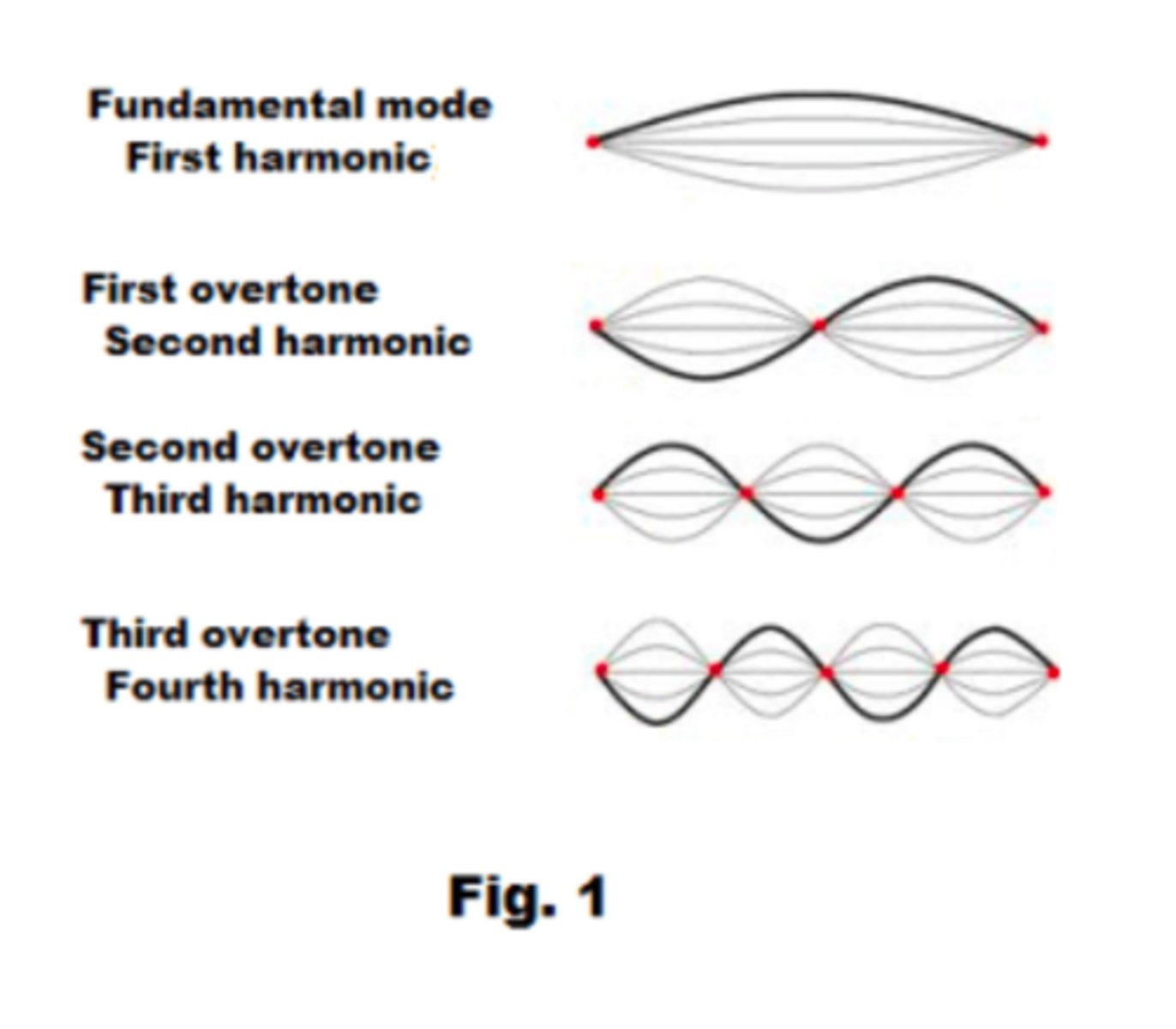
Harmonics
The natural vibration modes of a system, dependent on length and boundary conditions.
Resonance
Large amplitude response when driving frequency matches natural frequency.
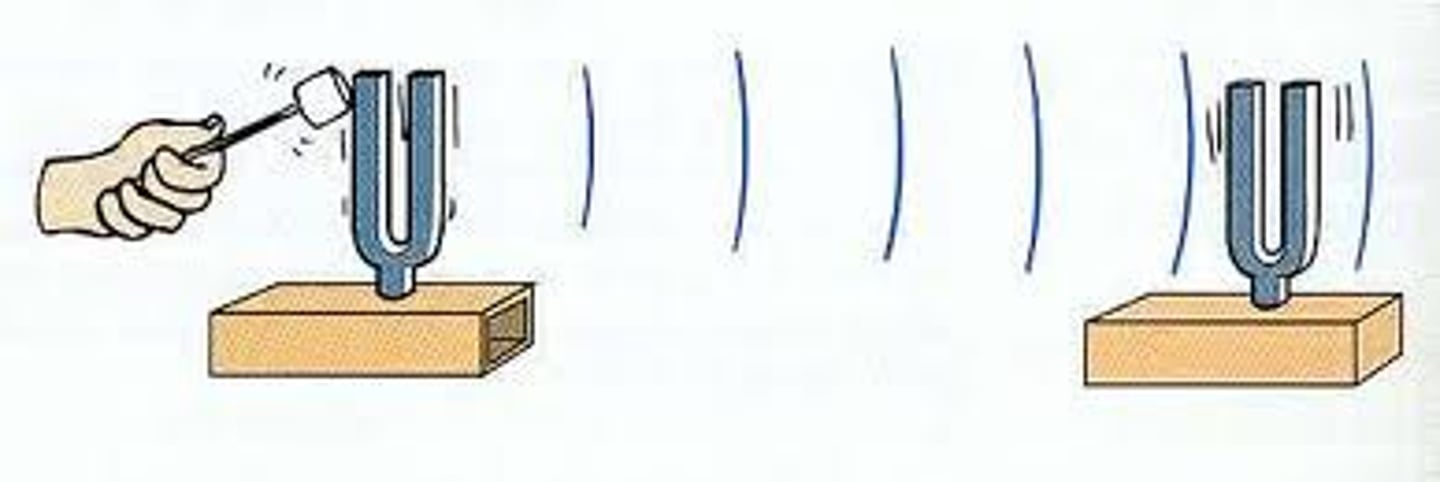
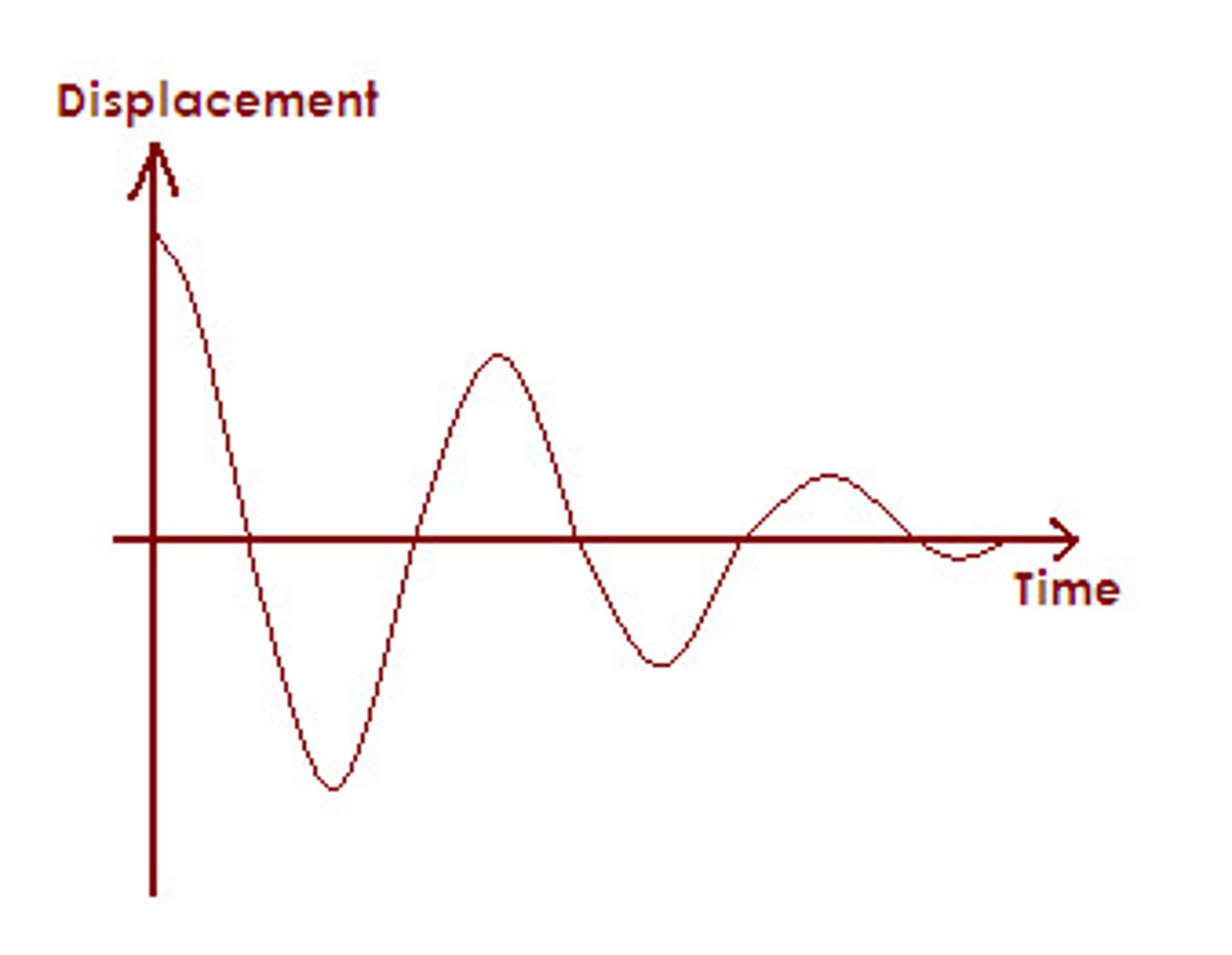
Damping
Energy loss in oscillations over time (light, critical, heavy).
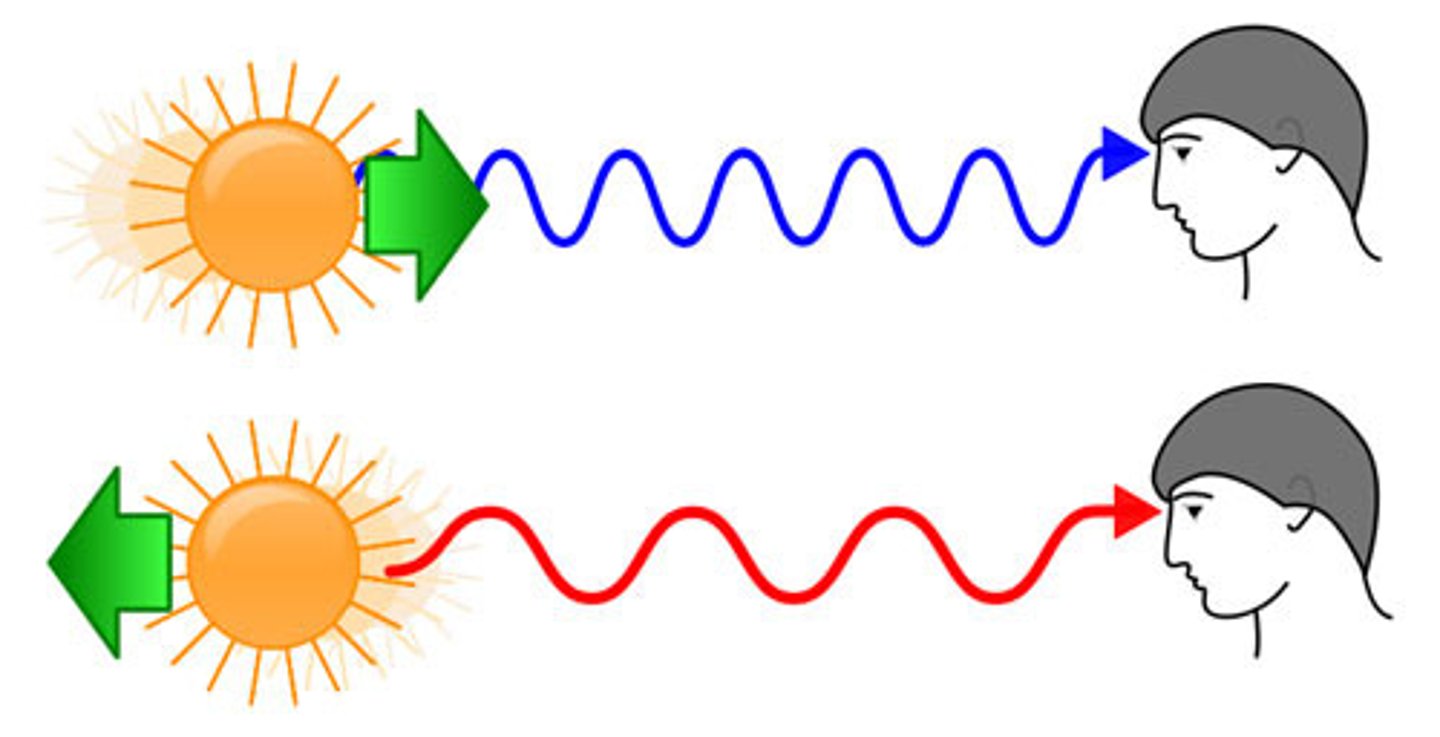
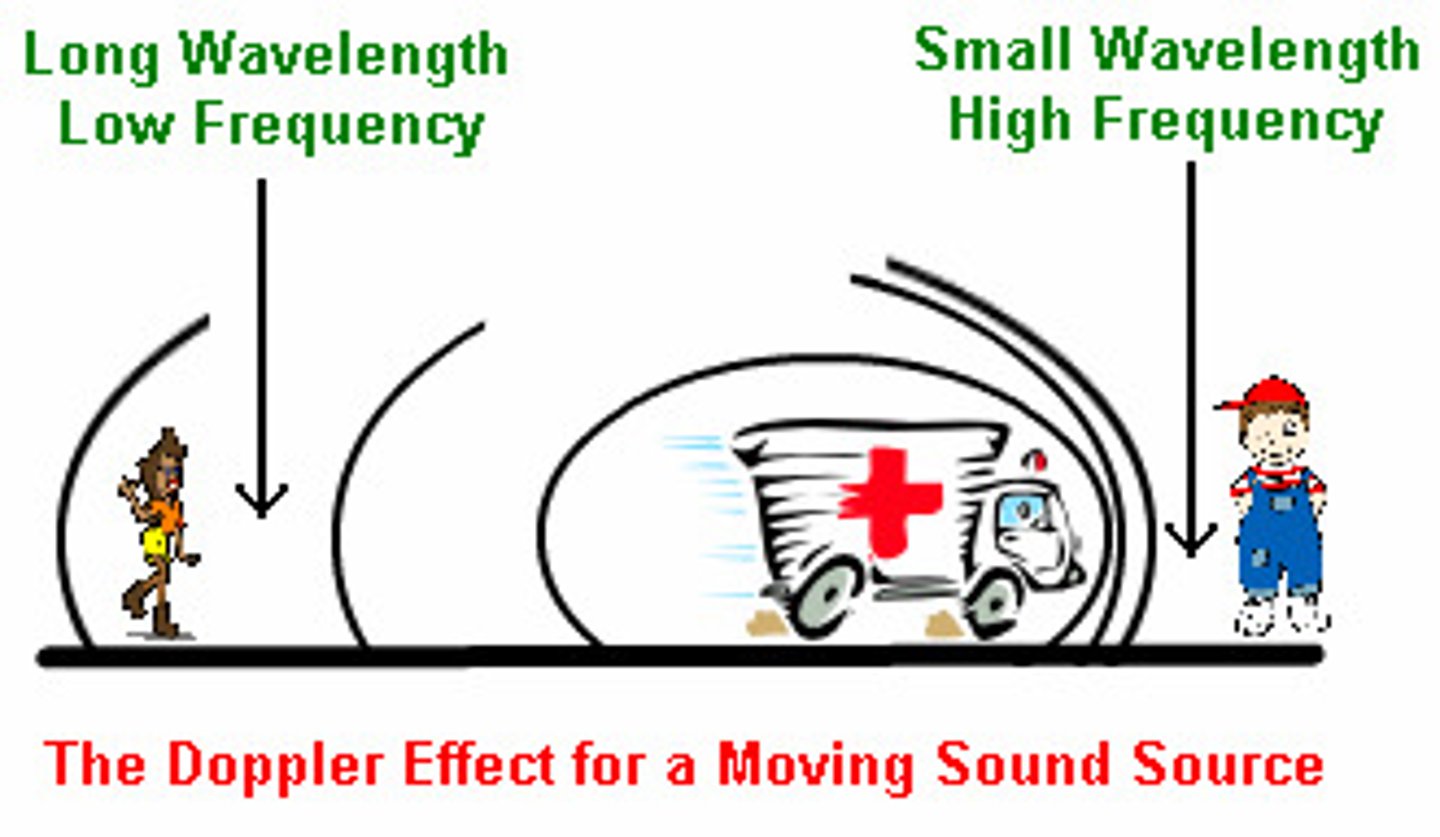
Doppler shift
The change in observed frequency due to motion of the source or observer.
Redshift
A decrease in observed frequency when the source is moving away.
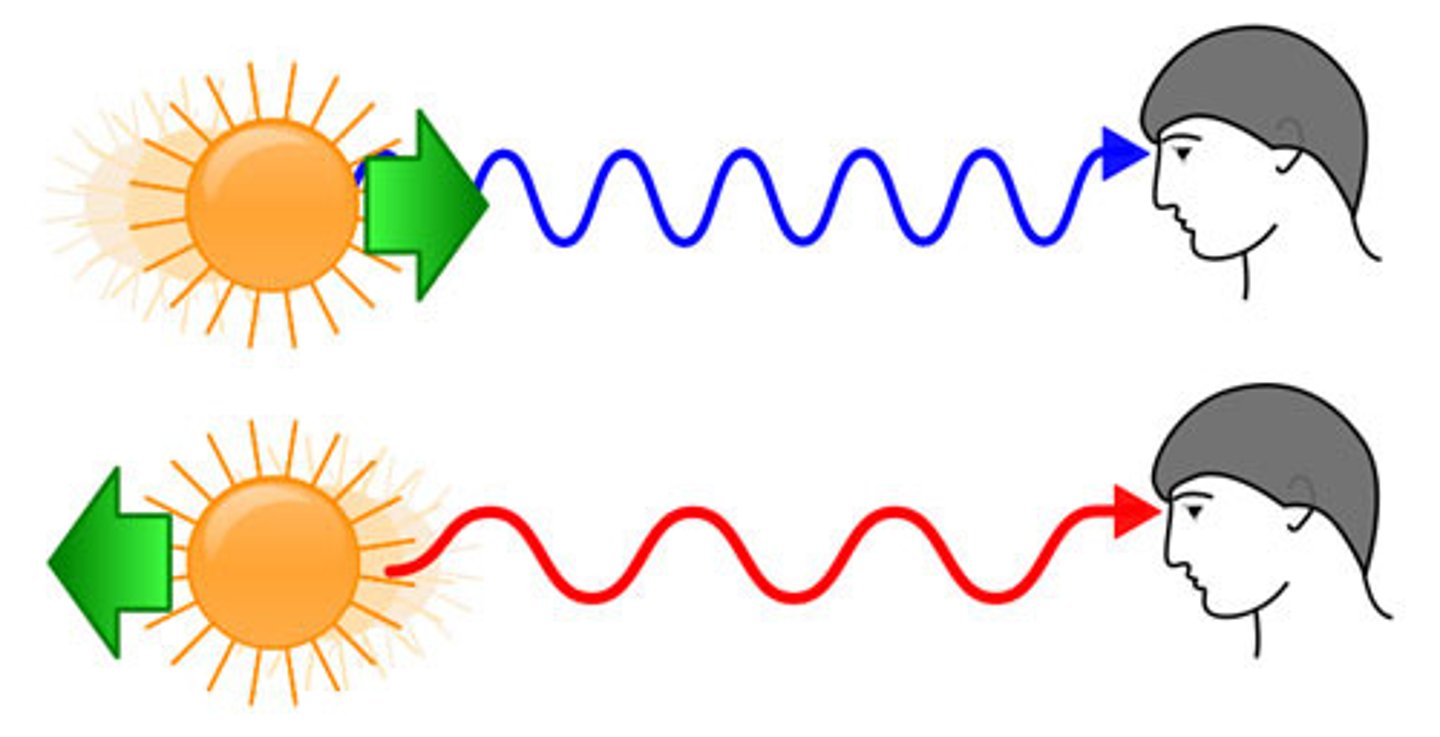
Blueshift
An increase in observed frequency when the source is moving closer.