Lab Practical - Experimental Plant Sciences - Dr Hammer - Wayne State College
0.0(0)Studied by 5 people
Card Sorting
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:57 PM on 2/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
1
New cards
Bryophytes
2
New cards
Does polytricum have mechanisms to regulate gasses?
no
3
New cards
Do bryophytes have vascular tissue?
no
4
New cards
Genetic state of the leafy plant?
haploid
5
New cards
Genetic state of the seta/sporangium?
Diploid
6
New cards
What structure was found where the base of the seta now occurs?
Archegonia
7
New cards
Function of the sporangium?
location where the spores are made and stored before meiosis
8
New cards
Function of the seta?
connects capsule to foot so that it may receive nutrients and raises capsule for better dispersal of seeds
9
New cards
Function of spores?
give rise to gametophyte/ long distance dispersal
10
New cards
Genetic state of mature spores?
haploid
11
New cards
Function of the operculum?
cap of the capsule, removed when spores mature
12
New cards
What is the genetic state of the operculum?
Diploid
13
New cards
Alternation of Generations
Some plants can alternate between haploid and diploid generations
14
New cards
What nuclear division is involved in the development of a sporophyte plant from a zygote?
mitosis
15
New cards
What type of nuclear division is involved in the development of spores?
meiosis
16
New cards
What is a zygote?
diploid cell
17
New cards
When does a zygote form?
after fertilization
18
New cards
What develops from an embryo in the bryophytes?
sporophyte
19
New cards
When the antheridia and archegonia are found on the same plant it is...
monoecious
20
New cards
When the antheridia and archegonia are NOT found on the same plant it is...
dioecious
21
New cards
What micro-climate conditions are required for fertilization? Why?
water so the sperm can travel
22
New cards
What micro-climate conditions is optimum for spore release? Why?
dry conditions to increase distance in seed dispersal
23
New cards
What type of environment does the typical bryophyte grow in?
damp/moist areas
24
New cards
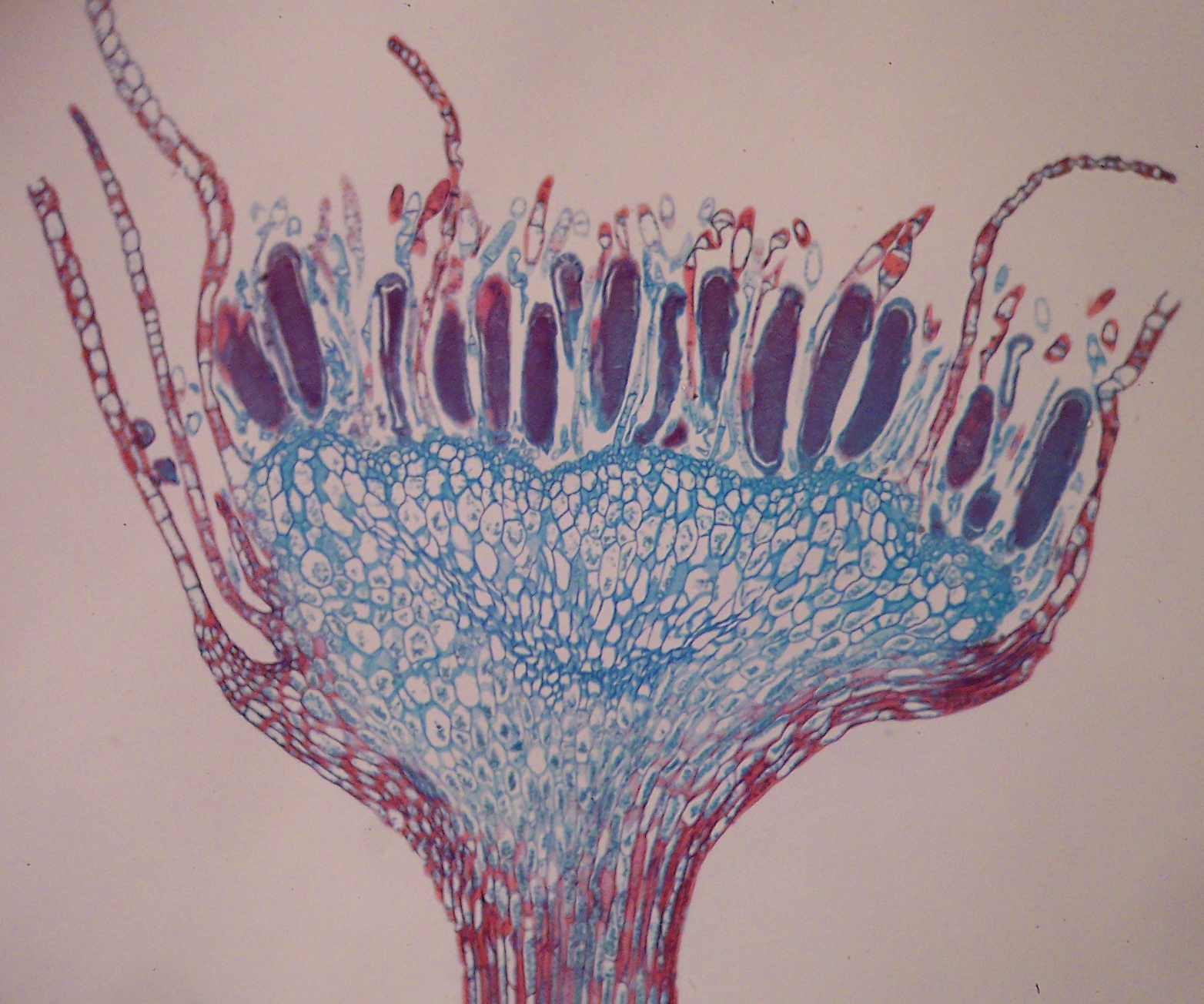
This is an archegonia/antheridia?
Antheridia
25
New cards
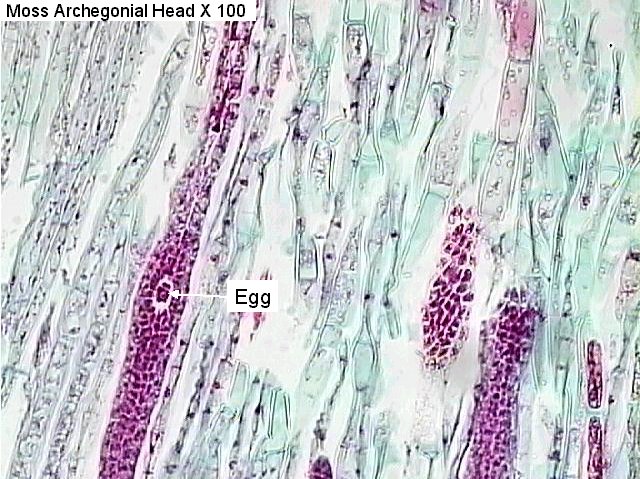
This is an archegonia/antheridia?
Archegonia
26
New cards
Seedless Vascular
27
New cards
Fiddleheads, fronds, and rhizomes are...
diploid
28
New cards
sori are clusters of...
sporangia
29
New cards
what is the function of the annulus?
serves in spore dispersal
30
New cards
When acetone is placed on the sporangium what happens? Why?
annulus opens up and spores are dispersed; the acetone creates artificial dry conditions drying out the annulus triggering spore dispersal
31
New cards
Is a mature spore haploid or diploid
haploid
32
New cards
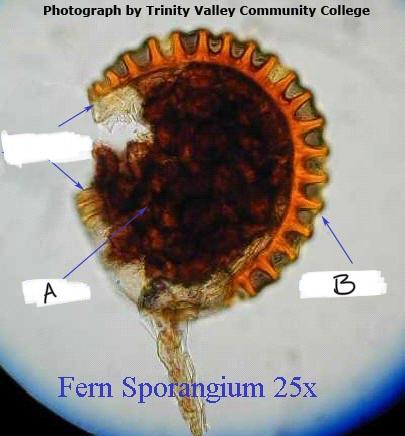
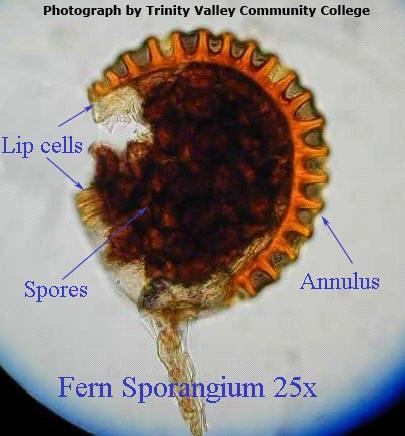
Name these structures; A. and B.
A .spores, B. annulus
33
New cards
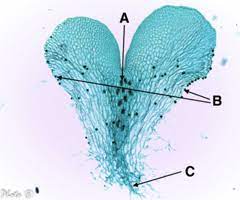
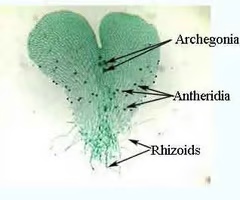
Know the location of archegonia, antheridia, and rhizoids
34
New cards
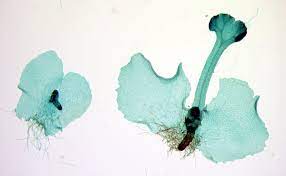
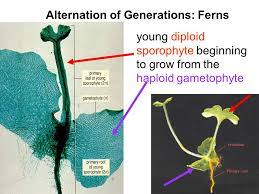
Know the location and genetic state of the sporophyte and gametophyte
Gametophyte \= haploid; sporophyte \= diploid
35
New cards
In what part of the whisk fern does photosynthesis occur?
aerial stems
36
New cards
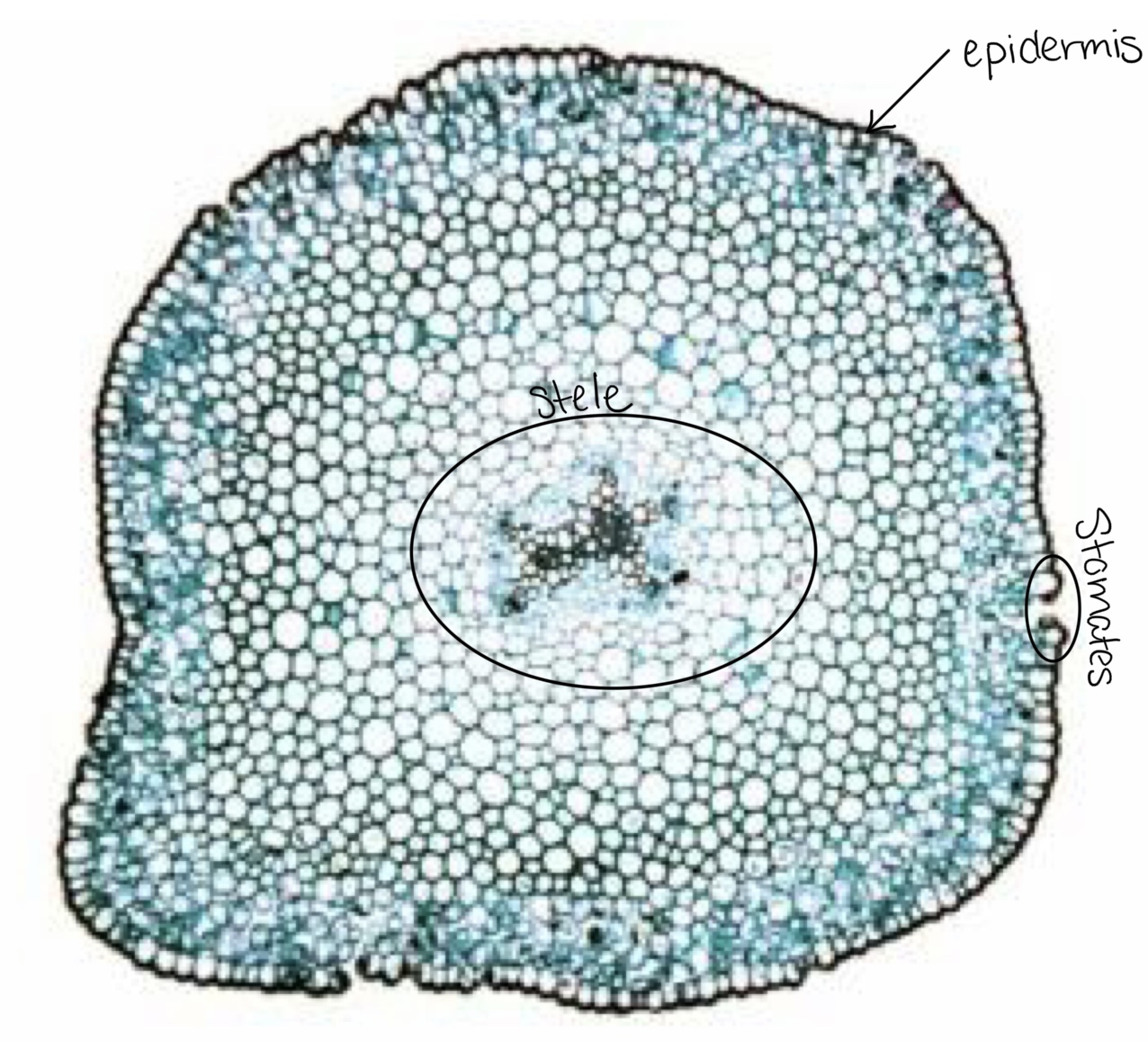
What is the stele? Why would we expect if in plants from this lab?
vascular tissue in fern stems; these plants are vascular plants
37
New cards
What waxy structure is on the outer surface of the epidermis?
cuticle
38
New cards
What is the function of the cuticle?
prevent water loss through the leaves
39
New cards
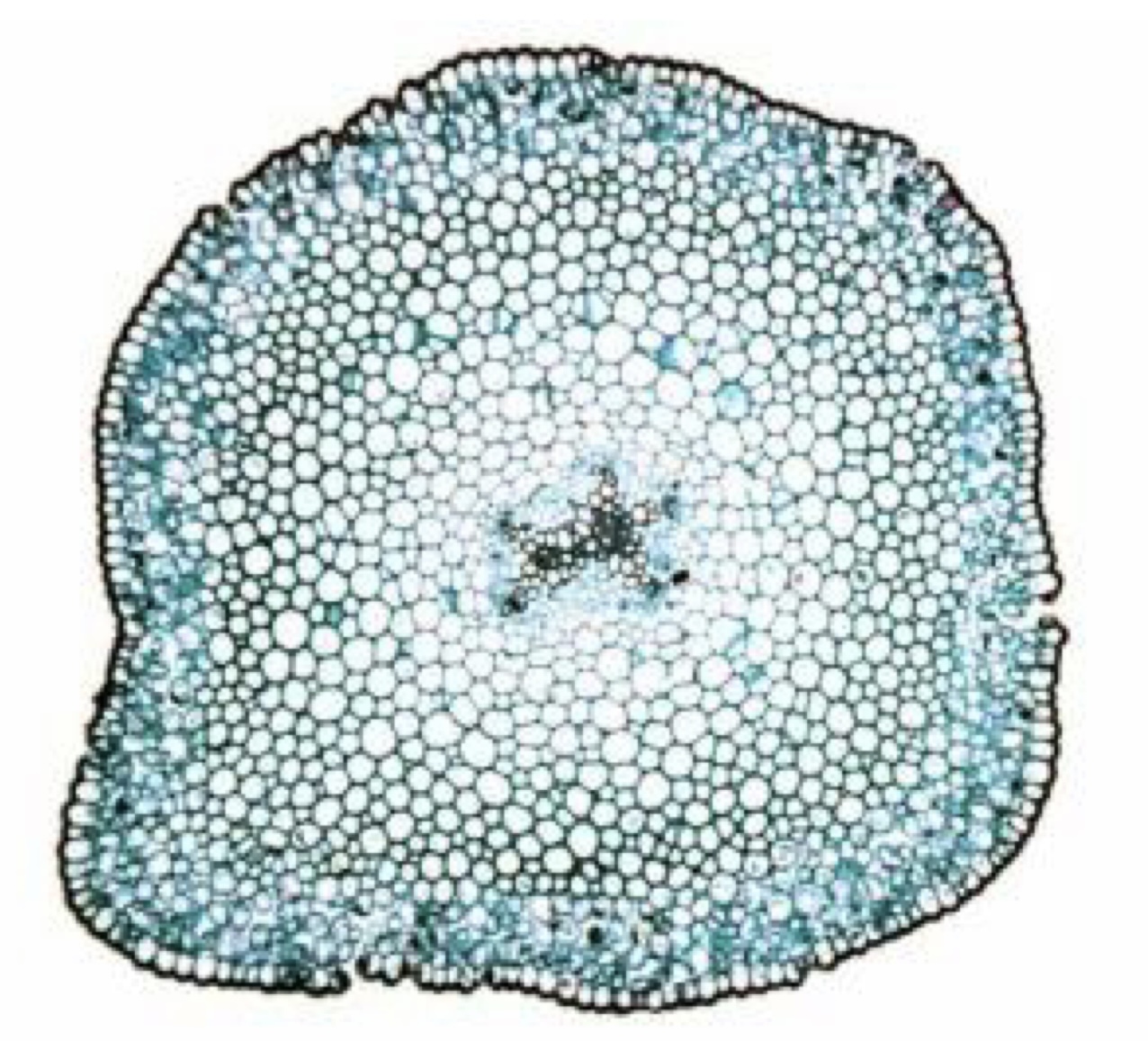
Know the location of the stele, epidermis, and stomates
40
New cards
Why are horsetails also called scouring rush?
stems are rough and durable
41
New cards
Why are the archegonia and antheridia of the fern are on the lower surface of the prothallus?
protection from dessication
42
New cards
Why are vascular plants larger than nonvascular plants?
they have a vascular system
43
New cards
What two characteristics of seedless vascular plants allow them to survive in dryer habitats?
cuticles and stomates
44
New cards
How are the life cycles of a fern and a moss similar? How are they different?
they both have alteration of generations; gametophytes wither away after fertilization creating an independent sporophyte
45
New cards
What weather conditions facilitate spore dispersal in seedless vascular plants?
wind and dry conditions
46
New cards
Gymnosperms
47
New cards
What kind of conditions are pines adapted to?
dry conditions
48
New cards
Why would a pine need to be adapted to dry conditions?
allows them to live in frozen conditions during winter
49
New cards
What is located on the side of the pollen? What is their function?
wings, serve in spore dispersal
50
New cards
How many seeds are generally produced on each cone scale?
2 seeds
51
New cards
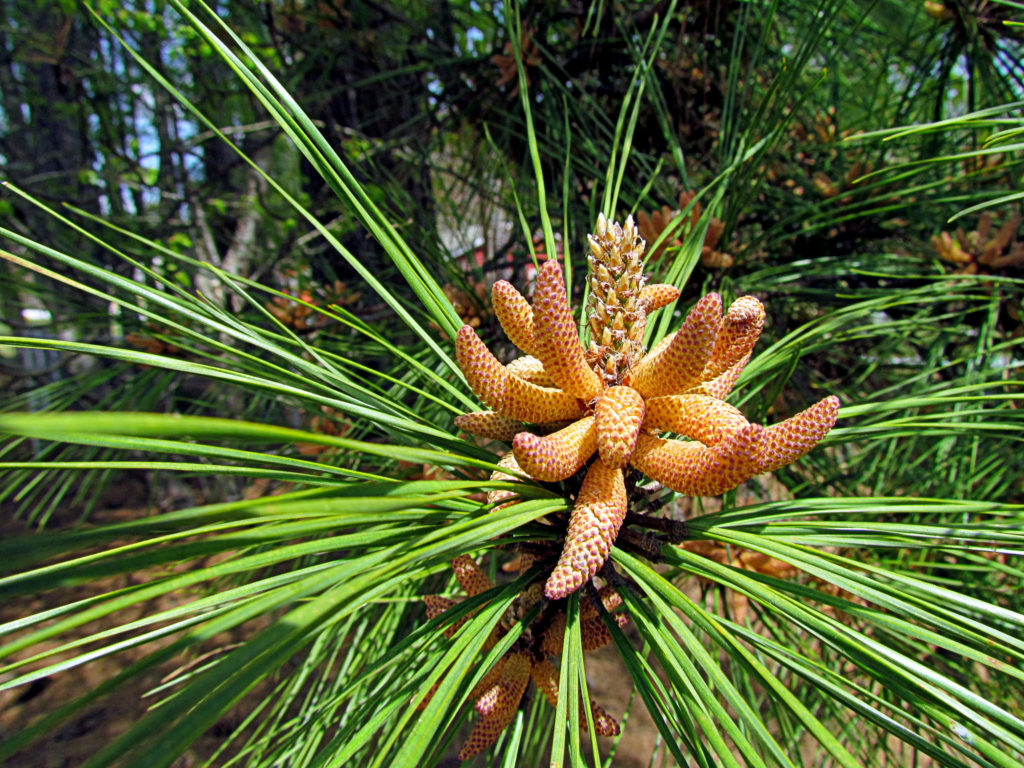

This is a male or female cone?
male
52
New cards

This is a male or female cone?
female
53
New cards
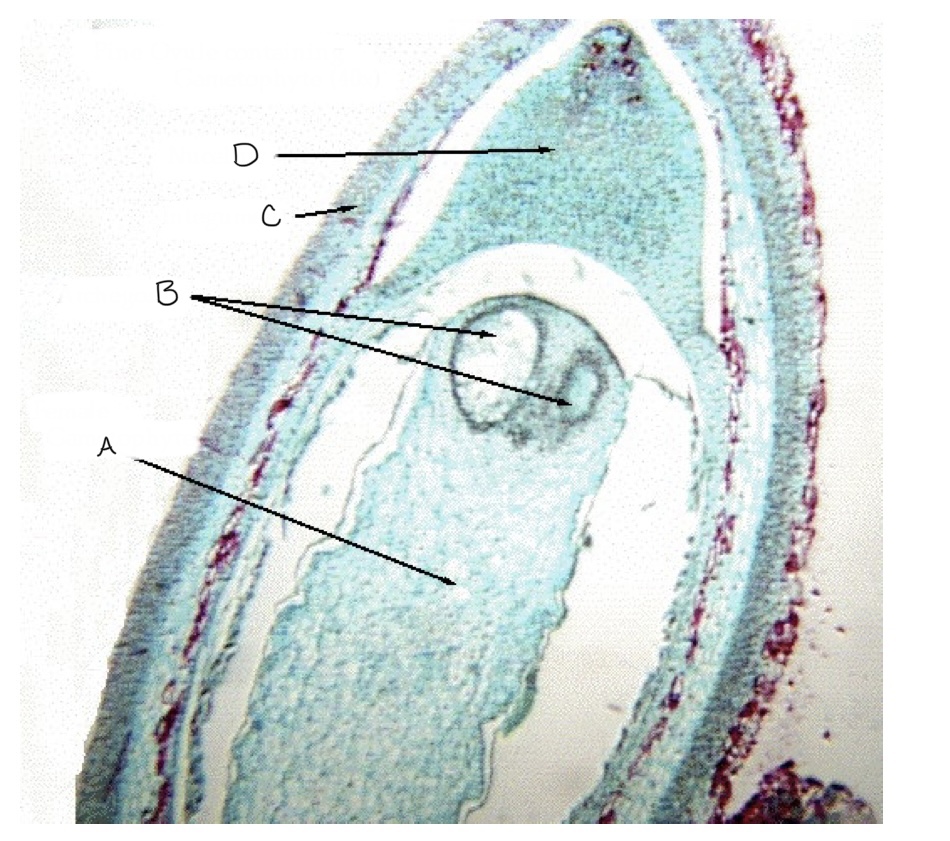
know the name and genetic state of A. B. C. D.
A) megagametophyte - haploid, B) egg (before fertilization megaspore) - haploid, C) integument - diploid, D) nucleus - haploid
54
New cards
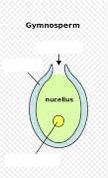
Be able to identify the micropyle
opening opposite of the archegonia
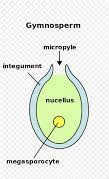
55
New cards
What does the integument develop into in a pinyon seed? What is its genetic state?
seed coat; diploid
56
New cards
What does the megagametophyte develop into in a pinyon seed? What is its genetic state?
developing tissue for the egg; haploid
57
New cards
What does the egg develop into in a pinyon seed? What is its genetic state?
sporophyte; diploid
58
New cards
How is the energy stored in megagametophytes?
as lipids
59
New cards
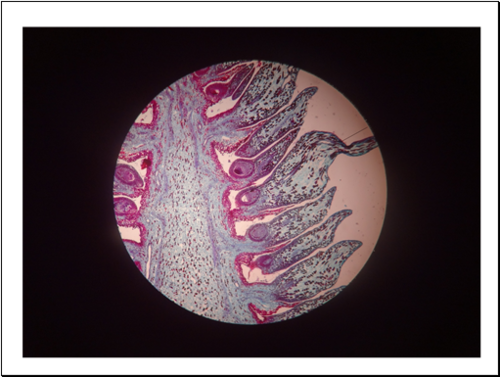
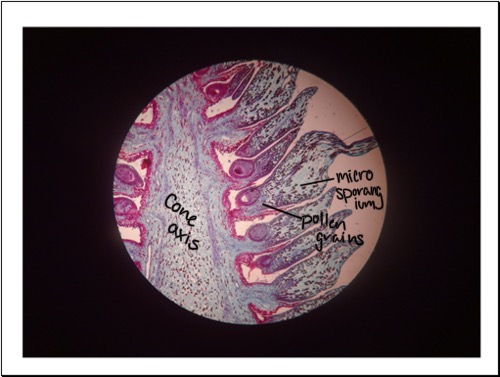
Be able to identify the microsporangium, cone axis, and pollen grains
\
60
New cards
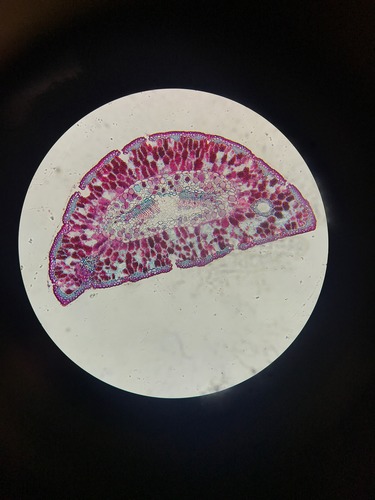
Be able to label the phloem, xylem, epidermis, cuticle, resin ducts, and mesophyll
\
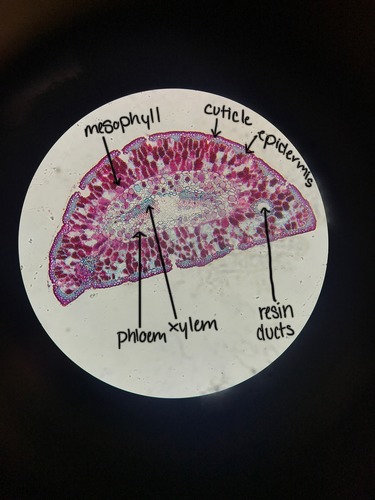
61
New cards
What kind of xylem cells make up pine wood?
tracheid cells
62
New cards
How does an angiosperm wood differ from the gymnosperm wood?
angiosperms have tracheid cells and vessel elements; gymnosperms ONLY have tracheid cells
63
New cards
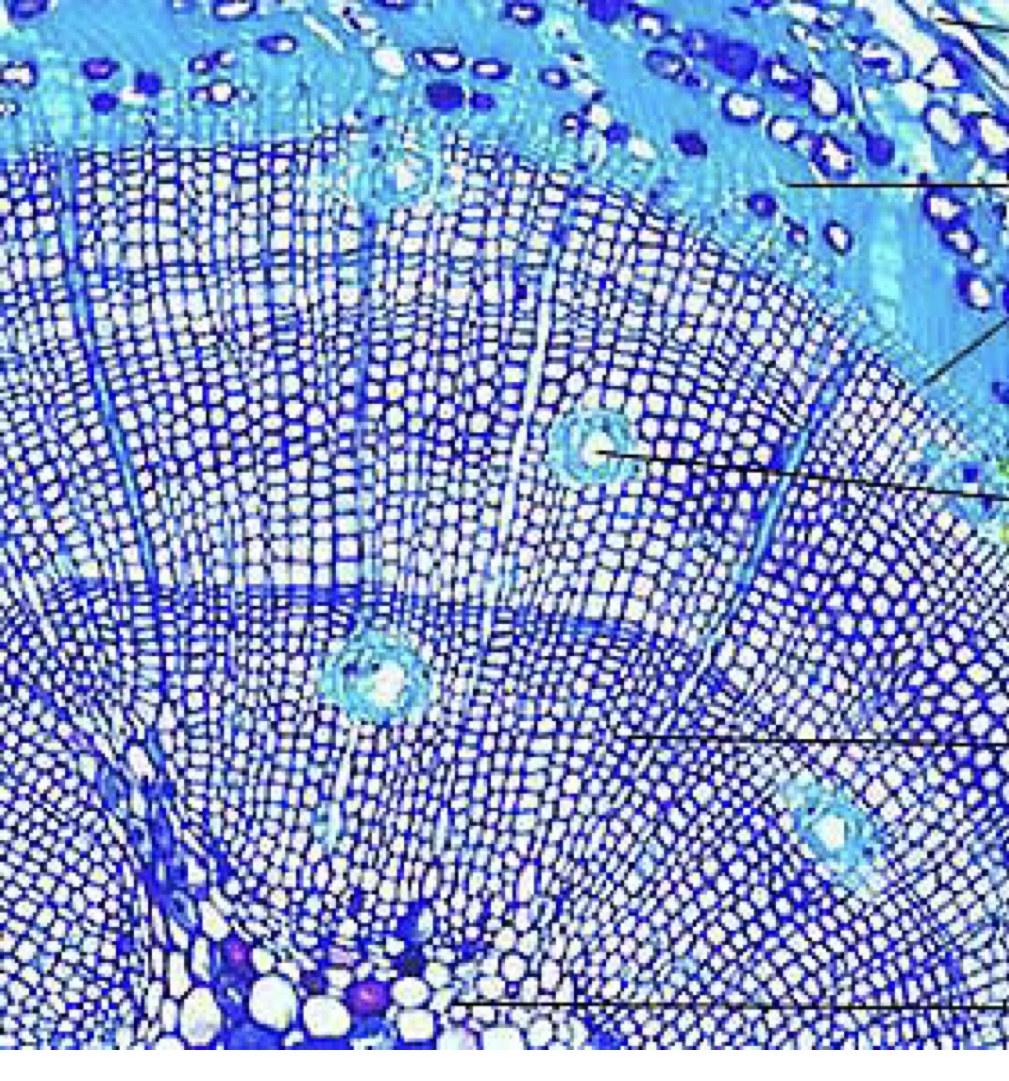

Be able to tell the age of a plant, based on the number of rings. How old is this plant?
3 years
64
New cards
When functioning are xylem cells are... (dead or alive)
dead
65
New cards
What type of cells are present in angiosperms that are absent in gymnosperms?
vessel elements
66
New cards
What structure is present in gymnosperms that is absent in angiosperms?
resin ducts
67
New cards
What does gymnosperm mean?
"naked seed"
68
New cards
How does pollination in gymnosperms differ from that of angiosperms?
gymnosperms rely ONLY on the wind; angiosperms use both wind and animals for pollination
69
New cards
What is an ovule?
contains the egg
70
New cards
Monoecious and Dioecious mean?
dioecious - male and female structures are on different plants
monoecious - both male and female structures are on the same plant
monoecious - both male and female structures are on the same plant
71
New cards
How is pine POLLEN dispersed? What evidence suggests this?
wind; pollen grains have wings
72
New cards
How are pine SEEDS dispersed? What evidence suggests this?
wind; seeds have wings
73
New cards
Why does the dispersal of pinyon seeds differ from pine seeds? How are pinyon seeds dispersed?
pinyon seeds don't have wings, pine seeds do; pinyon seeds rely on animals for dispersal
74
New cards
What causes growth rings in a tree?
Transition from early-wood to late-wood
75
New cards
Primary growth - a) direction of growth b) what meristem
.a) elongations/upward growth b) apical meristem.
76
New cards
How does secondary growth differ from primary growth...based on a) direction of growth and b) the meristems responsible?
Secondary growth - a) girth addition/outward growth b) lateral meristem
77
New cards
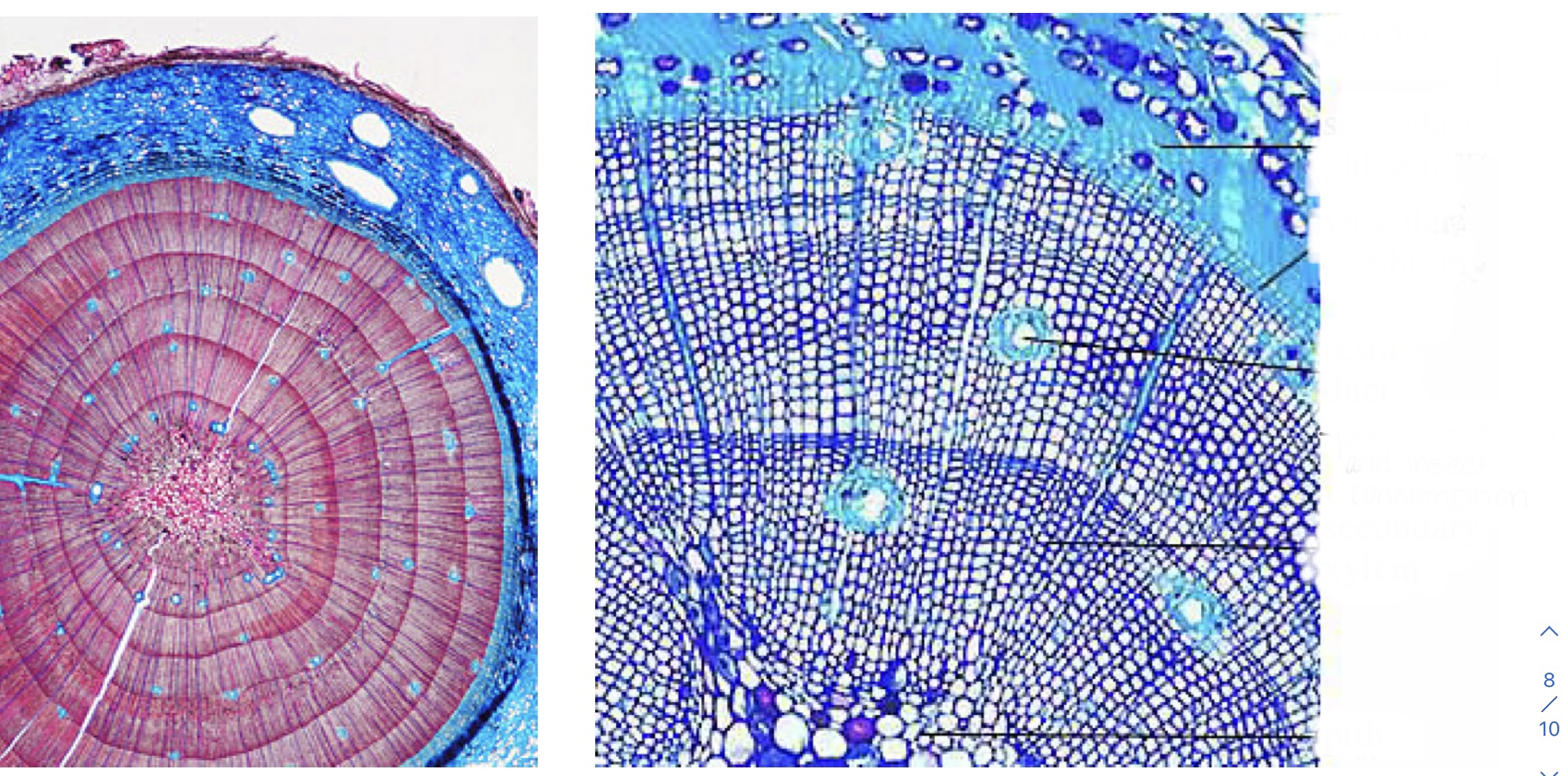
Identify the pith, annual rings, secondary xylem, early-wood, late-wood, rays, vascular cambium, secondary phloem, and cork. (Pinus stem)
\
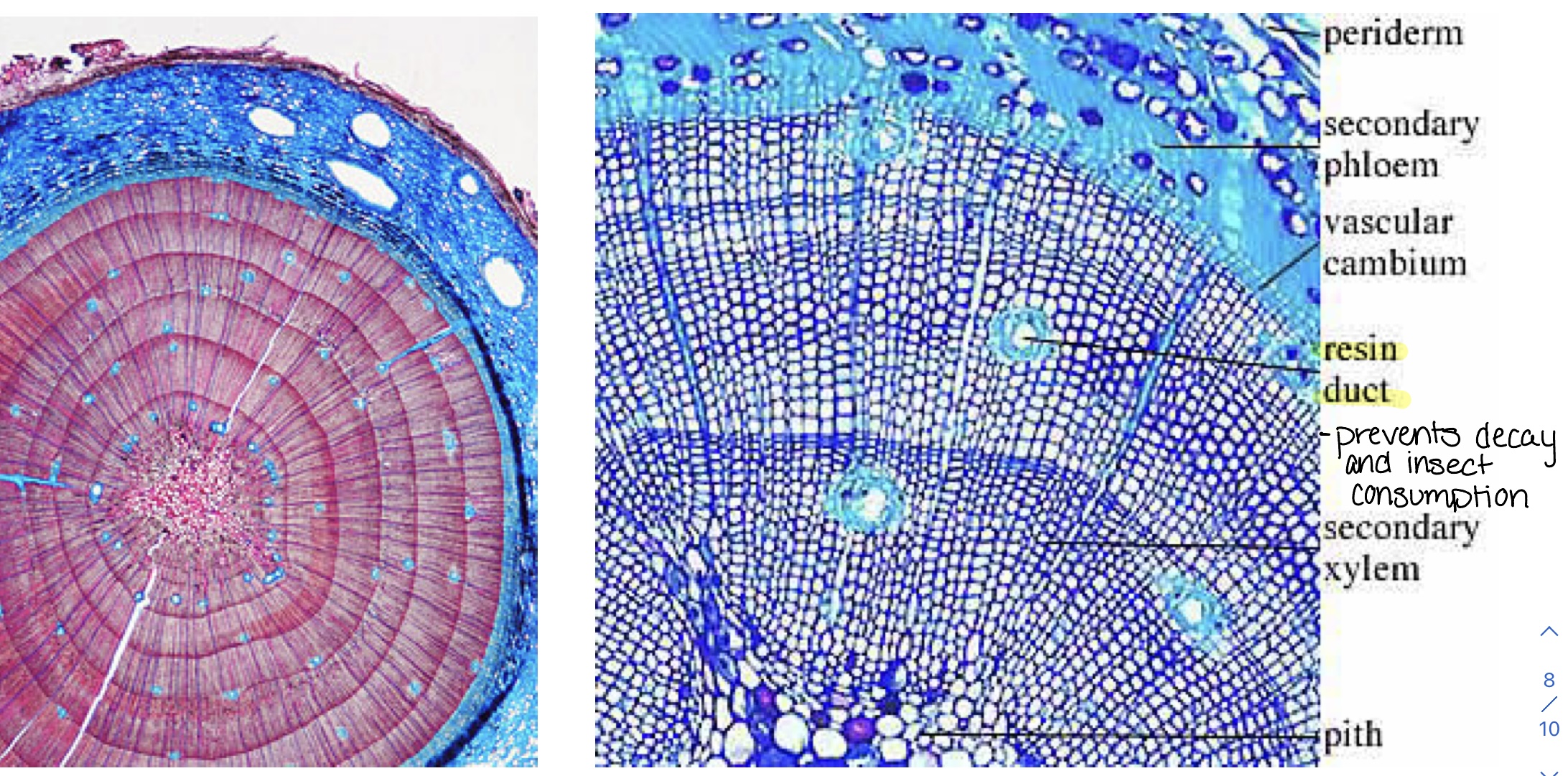
78
New cards
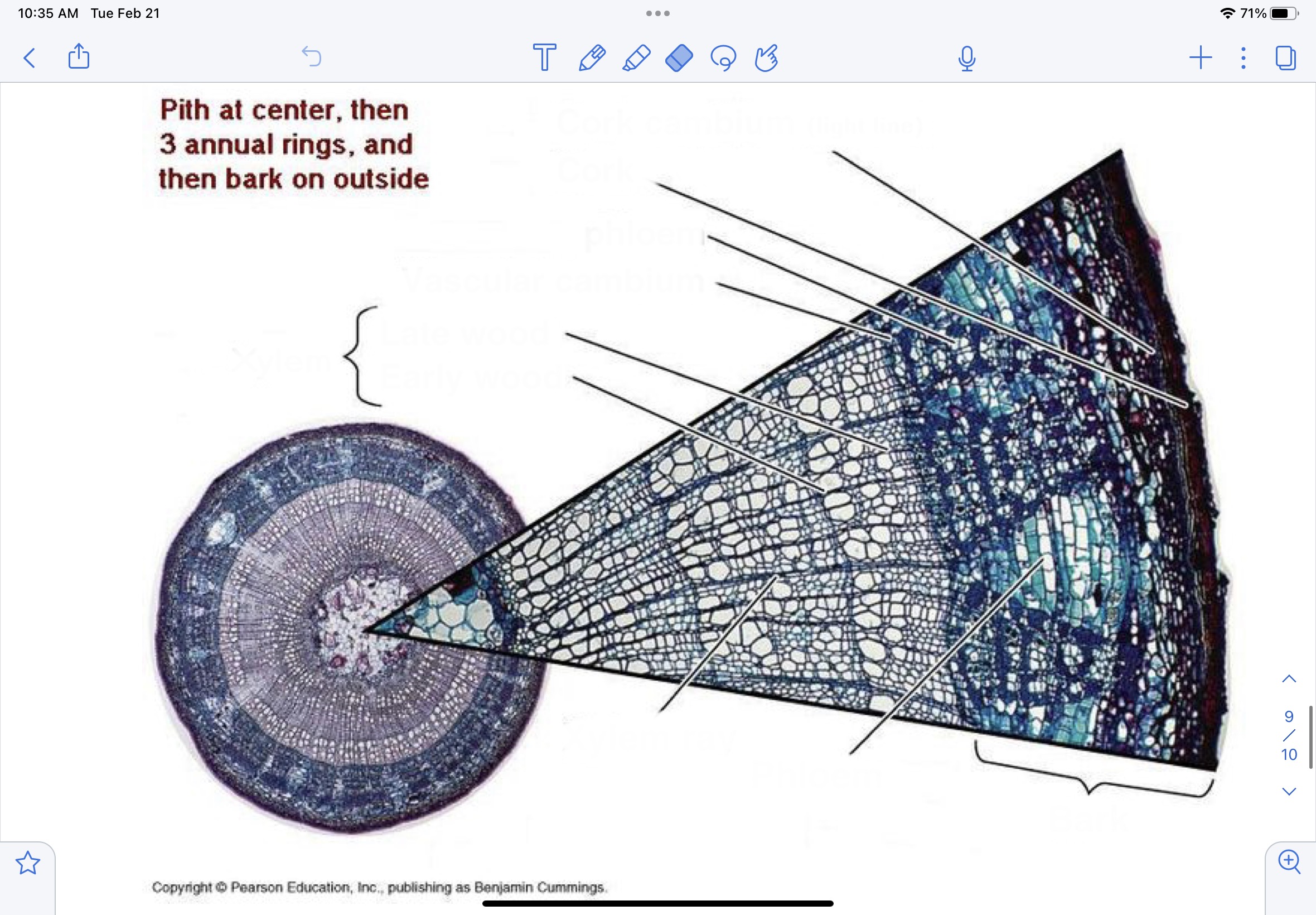
Identify the pith, annual rings, secondary xylem, early-wood, late-wood, rays, vascular cambium, secondary phloem, and cork. (basswood stem)
\
79
New cards
In a botanical sense, what is a pollen grain?
male reproductive organ
80
New cards
Angiosperms
81
New cards
Location of the stem where the leaf attaches is the…
Node
82
New cards

This is an example of what kind of leaf arrangement?
Opposite arrangement
83
New cards

This is an example of what kind of leaf arrangement?
Alternate arrangement
84
New cards
An axillary bud is found where?
Where the leaf attaches to the stern
85
New cards
What is the name of the location between two nodes?
Internode
86
New cards
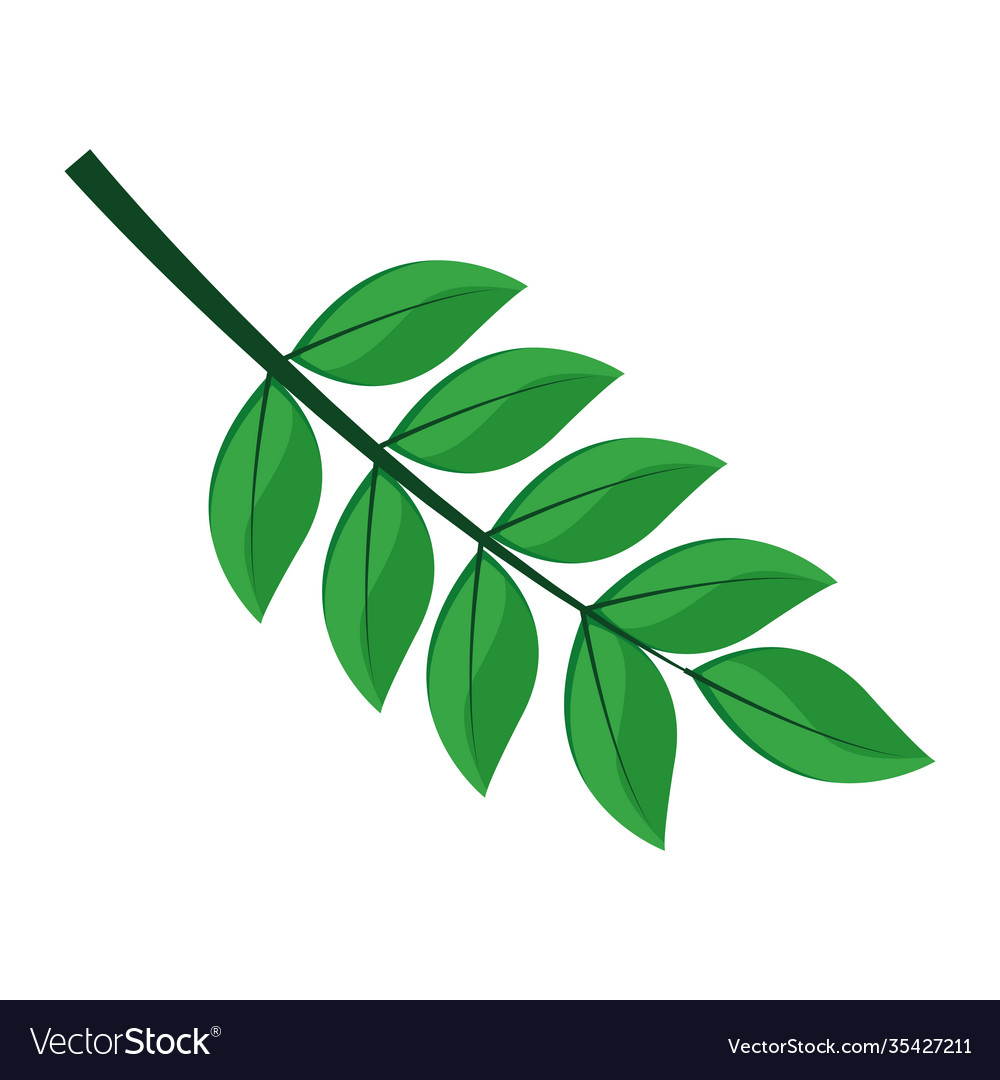

Is this leaf pinnate or palmate? Simple or complex?
Pinnate complex
87
New cards

Is this leaf pinnate or palmate? Simple or complex?
Palmate complex
88
New cards
What is the function of axillary buds?
Produce new shoots to promote growth
89
New cards
What is the function of lenticles?
Support stem water evaporation/gas exchange
90
New cards
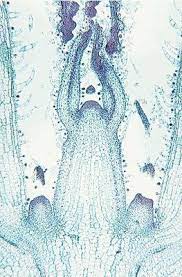
Be able to locate… apical meristem, leaf primordium, bud primordium, epidermis, parenchyma, and vascular tissue
axillary buds are where bud primordium are located, green stained cells \= parenchyma
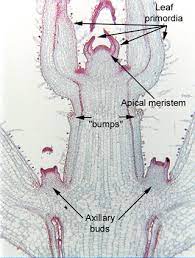
91
New cards
Why does the apical meristem and the bud primordium have a darker red stain than the other tissue?
Have more visible nuclei due to high levels of division because these parts are actively growing tissue
92
New cards
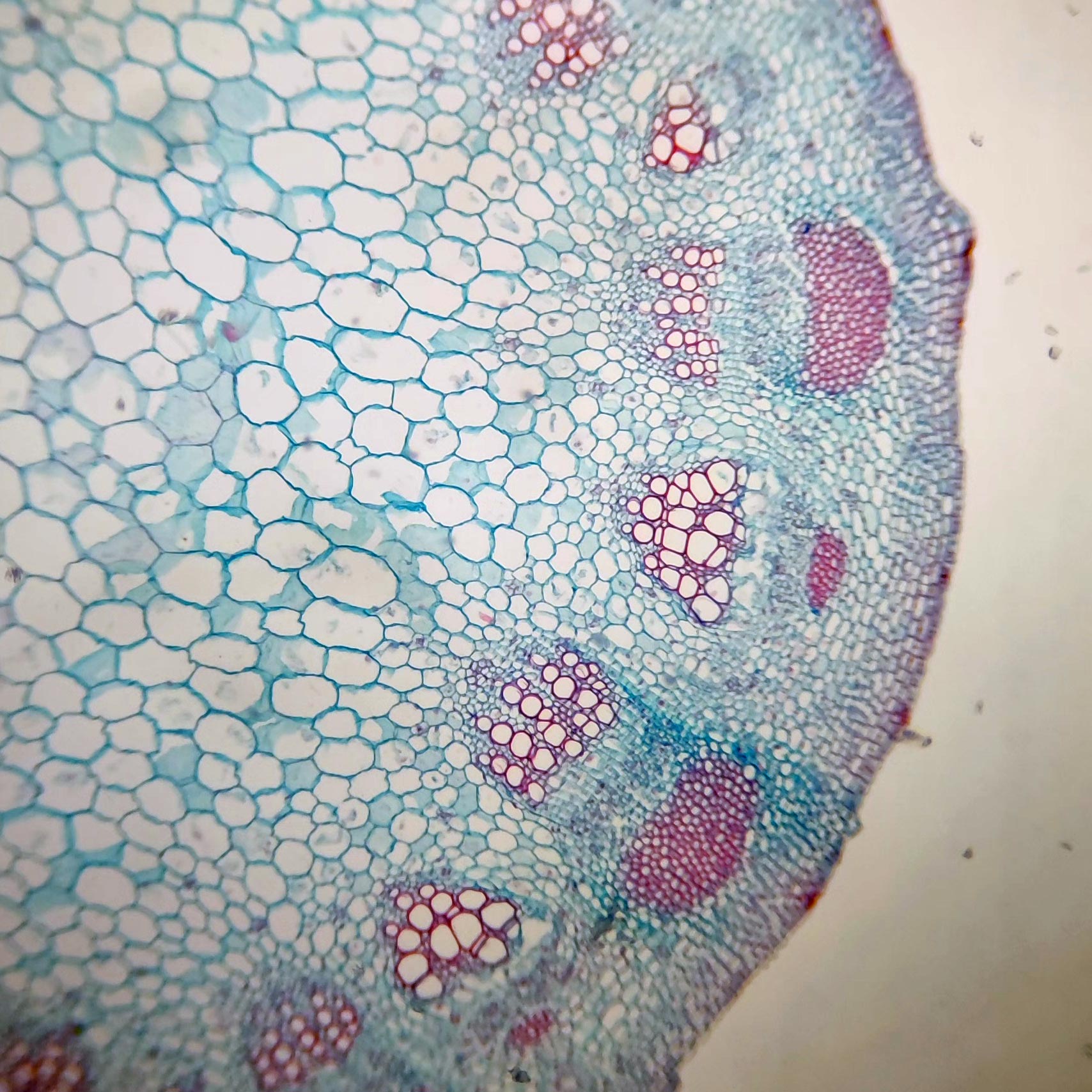
Be able to locate… parenchyma, vascular bundle, primary xylem, primary phloem, sclerenchyma(bundle cap), collenchyma, and epidermis
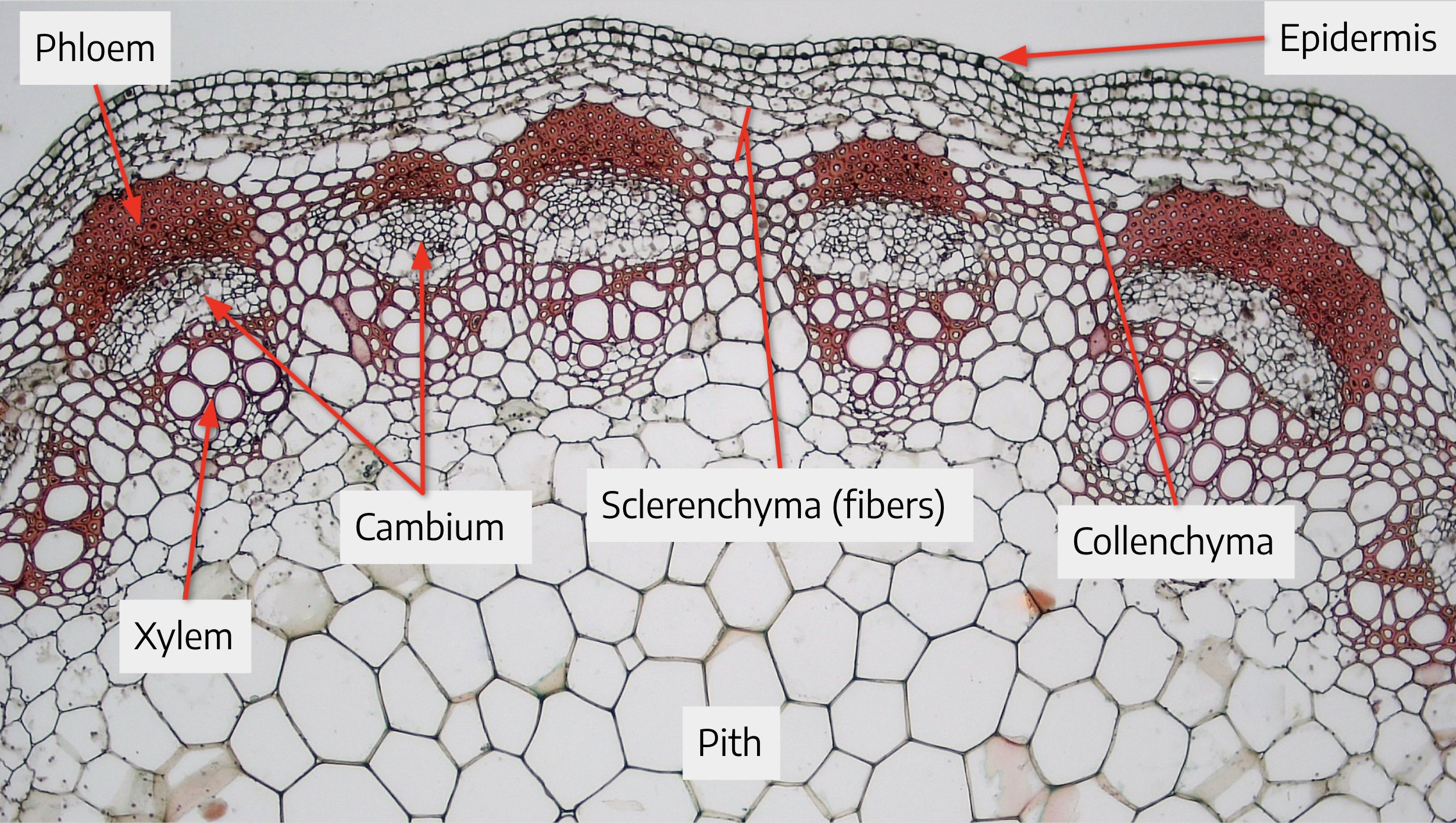
93
New cards
Describe the vascular bundle arrangements in a dicot stem x.s?
uniform ring
94
New cards
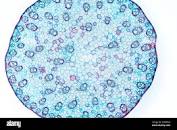
Be able to locate… vascular bundles, primary xylem, primary phloem, sclerenchyma, parenchyma, and epidermis
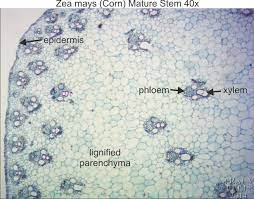
95
New cards
How does the distribution of vascular bundles differ in monocots and dicots?
vascular bundles are arranged on the outer layer of dicots in ring formation, monocots vascular bundles a placed sporadically around
96
New cards
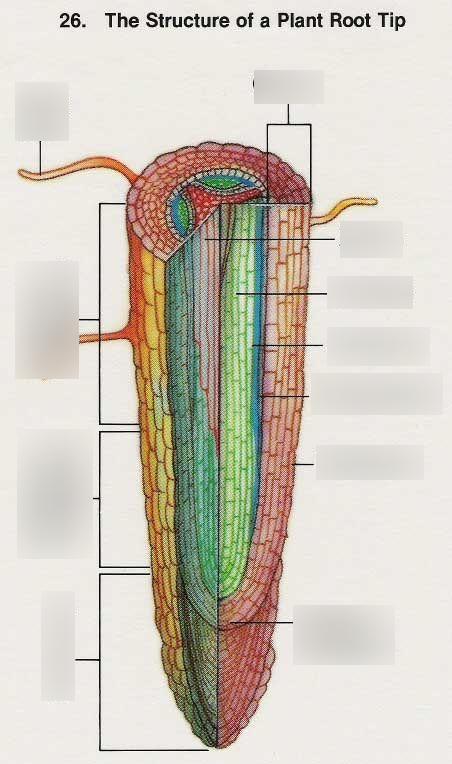
Be able to locate… root cap, apical meristem, zone of cell division, zone of elongation, zone of cell maturation, and root hairs

97
New cards
In which zone do you see the most mitosis?
zone of cell division
98
New cards
In which zone do you see the root hairs developing?
zone of maturation
99
New cards
Are root hairs separate cells or extensions of the epidermal cells?
extensions
100
New cards
How do the locations of the root and shoot apical meristems differ?
root \= found in root cap; underground shoot \= found in apical meristem; above ground (no cap)