3.4.4 - oligopoly
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
characteristics of an oligopoly:
barriers to entry/exit
concentration ratio
interdependence of firms
product differentiation
barriers to entry/exit - start-up costs and sunk costs
concentration ratio - high but shared (eg. 5-firm concentration ratio = 5 biggest companies combined share of the market)
interdependence - high bc firms study each other’s behaviour
differentiation - products highly differentiated
collusive v non collusive behaviour
COLLUSIVE: firms cooperate to fix prices (raise them usually) + restrict output
NON-COLLUSIVE: firms actively compete for market share
6 reasons for collusion
few firms/competitors —> easy to understand each other’s actions, or collaborate
similar costs —> all firms have experienced economies of scale
similar revenue —> little incentive to decrease bc everyone will so its same market share but less profit
high barriers to entry —> no new entrants to disrupt
ineffective regulation —> little consequence for their actions
brand loyalty —> less benefits to competition because ppl just won’t switch brands
net effect of collusion
group of firms end up acting like a monopoly in the market
two types of collusion
overt - firms explicitly agree to limit competition or raise prices
tacit - firms avoid formal agreements but closely monitor each other (usually follow lead of largest firm)
most restrictive form of collusion
cartel —> group of firms providing the same products join together to limit output and raise prices (effectively acts as a monopoly)
example: OPEC (oil producing exporting countries)
this is illegal in most countries
how does overt collusion happen
price fixing - firms agree a price higher than equilibrium
output quotas - limit supply = price increases
monopsony power - agree to pay suppliers the same price = drive down supply chain prices
consequences of overt collusion
higher prices for consumers
less output in the market
poor quality products/customer service
less investment in innovation
most common form of tacit collusion
price leadership/price matching:
firms price match to the largest firm
difficult for regulators to prove that collusion has happened
consequences and benefits of tacit collusion
both similar to overt
what is game theory
a mathematical framework used by firms to ensure optimal decisions are made when there is a high level of interdependence
3 elements of a game
players (firms)
strategies
payoffs (outcomes)
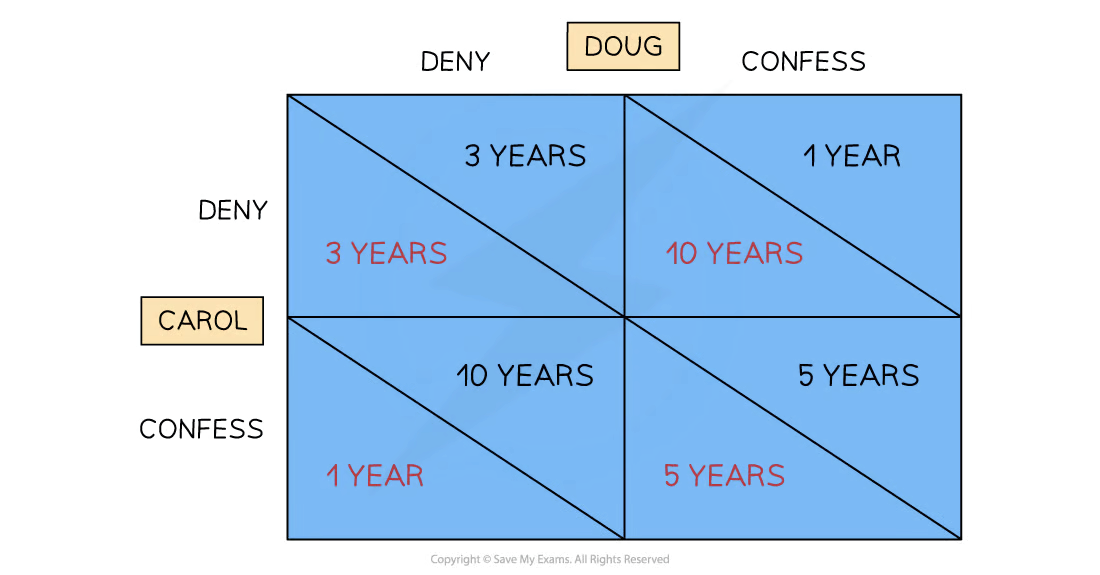
show a payoff matrix for the prisoners dillemma
players = carol + doug
strategies = deny + confess
payoffs inside boxes (red carol, black doug)
how do firms use game theory
making decisions about…
…prices
…advertising
…investment
…product bundling
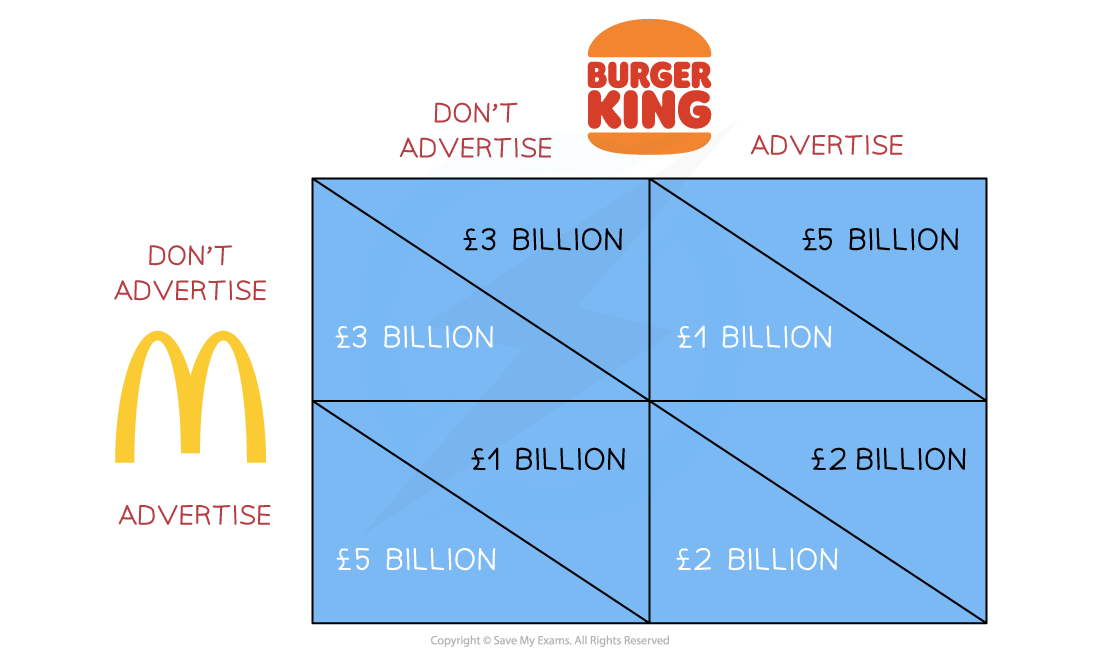
show a payoff matrix for two firms deciding whether or not to advertise
.
3 types of price competition in an oligopoly market
PRICE WARS —> firms repeatedly lower prices to undercut each other to gain market share
PREDATORY PRICING —> lowering prices to drive out a new competitor
LIMIT PRICING —> firms set a limit on how high a price can go in an industry
price wars - when does it usually happen
when…
…there’s a low level of non-price competition
…firms find it difficult to collude
predatory pricing - how does it work, and how is it viewed
prices lowered below costs of production
prices raised once the competitor leaves the market
usually illegal since it’s anticompetitive
limit pricing - how does it work
low prices = reduced profit = disincentive to join
higher barriers to entry = higher limit price since its already a disincentive
4 examples of non price competition
rewards schemes
celebrity sponsorship
branding/packaging
after-sales service/warranties